- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up

ManagementSkills →
No results found in working knowledge.
- Were any results found in one of the other content buckets on the left?
- Try removing some search filters.
- Use different search filters.
50 Best Finance Dissertation Topics For Research Students
Link Copied
Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter
Share on LinkedIn

Finance Dissertation Made Easier!
Embarking on your dissertation adventure? Look no further! Choosing the right finance dissertation topics is like laying the foundation for your research journey in Finance, and we're here to light up your path. In this blog, we're diving deep into why dissertation topics in finance matter so much. We've got some golden writing tips to share with you! We're also unveiling the secret recipe for structuring a stellar finance dissertation and exploring intriguing topics across various finance sub-fields. Whether you're captivated by cryptocurrency, risk management strategies, or exploring the wonders of Internet banking, microfinance, retail and commercial banking - our buffet of Finance dissertation topics will surely set your research spirit on fire!
What is a Finance Dissertation?
Finance dissertations are academic papers that delve into specific finance topics chosen by students, covering areas such as stock markets, banking, risk management, and healthcare finance. These dissertations require extensive research to create a compelling report and contribute to the student's confidence and satisfaction in the field of Finance. Now, let's understand why these dissertations are so important and why choosing the right Finance dissertation topics is crucial!
Why Are Finance Dissertation Topics Important?
Choosing the dissertation topics for Finance students is essential as it will influence the course of your research. It determines the direction and scope of your study. You must make sure that the Finance dissertation topics you choose are relevant to your field of interest, or you may end up finding it more challenging to write. Here are a few reasons why finance thesis topics are important:
1. Relevance
Opting for relevant finance thesis topics ensures that your research contributes to the existing body of knowledge and addresses contemporary issues in the field of Finance. Choosing a dissertation topic in Finance that is relevant to the industry can make a meaningful impact and advance understanding in your chosen area.
2. Personal Interest
Selecting Finance dissertation topics that align with your interests and career goals is vital. When genuinely passionate about your research area, you are more likely to stay motivated during the dissertation process. Your interest will drive you to explore the subject thoroughly and produce high-quality work.
3. Future Opportunities
Well-chosen Finance dissertation topics can open doors to various future opportunities. It can enhance your employability by showcasing your expertise in a specific finance area. It may lead to potential research collaborations and invitations to conferences in your field of interest.
4. Academic Supervision
Your choice of topics for dissertation in Finance also influences the availability of academic supervisors with expertise in your chosen area. Selecting a well-defined research area increases the likelihood of finding a supervisor to guide you effectively throughout the dissertation. Their knowledge and guidance will greatly contribute to the success of your research.
Writing Tips for Finance Dissertation
A lot of planning, formatting, and structuring goes into writing a dissertation. It starts with deciding on topics for a dissertation in Finance and conducting tons of research, deciding on methods, and so on. However, you can navigate the process more effectively with proper planning and organisation. Below are some tips to assist you along the way, and here is a blog on the 10 tips on writing a dissertation that can give you more information, should you need it!
1. Select a Manageable Topic
Choosing Finance research topics within the given timeframe and resources is important. Select a research area that interests you and aligns with your career goals. It will help you stay inspired throughout the dissertation process.
2. Conduct a Thorough Literature Review
A comprehensive literature review forms the backbone of your research. After choosing the Finance dissertation topics, dive deep into academic papers, books, and industry reports, gaining a solid understanding of your chosen area to identify research gaps and establish the significance of your study.
3. Define Clear Research Objectives
Clearly define your dissertation's research questions and objectives. It will provide a clear direction for your research and guide your data collection, analysis, and overall structure. Ensure your objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
4. Collect and Analyse Data
Depending on your research methodology and your Finance dissertation topics, collect and analyze relevant data to support your findings. It may involve conducting surveys, interviews, experiments, and analyzing existing datasets. Choose appropriate statistical techniques and qualitative methods to derive meaningful insights from your data.
5. Structure and Organization
Pay attention to the structure and organization of your dissertation. Follow a logical progression of chapters and sections, ensuring that each chapter contributes to the overall coherence of your study. Use headings, subheadings, and clear signposts to guide the reader through your work.
6. Proofread and Edit
Once you have completed the writing process, take the time to proofread and edit your dissertation carefully. Check for clarity, coherence, and proper grammar. Ensure that your arguments are well-supported, and eliminate any inconsistencies or repetitions. Pay attention to formatting, citation styles, and consistency in referencing throughout your dissertation.
Don't let student accommodation hassles derail your finance research.
Book through amber today!
Finance Dissertation Topics
Now that you know what a finance dissertation is and why they are important, it's time to have a look at some of the best Finance dissertation topics. For your convenience, we have segregated these topics into categories, including cryptocurrency, risk management, internet banking, and so many more. So, let's dive right in and explore the best Finance dissertation topics:
Dissertation topics in Finance related to Cryptocurrency
1. The Impact of Regulatory Frameworks on the Volatility and Liquidity of Cryptocurrencies.
2. Exploring the Factors Influencing Cryptocurrency Adoption: A Comparative Study.
3. Assessing the Efficiency and Market Integration of Cryptocurrency Exchanges.
4. An Analysis of the Relationship between Cryptocurrency Prices and Macroeconomic Factors.
5. The Role of Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) in Financing Startups: Opportunities and Challenges.
Dissertation topics in Finance related to Risk Management
1. The Effectiveness of Different Risk Management Strategies in Mitigating Financial Risks in Banking Institutions.
2. The Role of Derivatives in Hedging Financial Risks: A Comparative Study.
3. Analyzing the Impact of Risk Management Practices on Firm Performance: A Case Study of a Specific Industry.
4. The Use of Stress Testing in Evaluating Systemic Risk: Lessons from the Global Financial Crisis.
5. Assessing the Relationship between Corporate Governance and Risk Management in Financial Institutions.
Dissertation topics in Finance related to Internet Banking
1. Customer Adoption of Internet Banking: An Empirical Study on Factors Influencing Usage.
Enhancing Security in Internet Banking: Exploring Biometric Authentication Technologies.
2. The Impact of Mobile Banking Applications on Customer Engagement and Satisfaction.
3. Evaluating the Efficiency and Effectiveness of Internet Banking Services in Emerging Markets.
4. The Role of Social Media in Shaping Customer Perception and Adoption of Internet Banking.
Dissertation topics in Finance related to Microfinance
1. The Impact of Microfinance on Poverty Alleviation: A Comparative Study of Different Models.
2. Exploring the Role of Microfinance in Empowering Women Entrepreneurs.
3. Assessing the Financial Sustainability of Microfinance Institutions in Developing Countries.
4. The Effectiveness of Microfinance in Promoting Rural Development: Evidence from a Specific Region.
5. Analyzing the Relationship between Microfinance and Entrepreneurial Success: A Longitudinal Study.
Dissertation topics in Finance related to Retail and Commercial Banking
1. The Impact of Digital Transformation on Retail and Commercial Banking: A Case Study of a Specific Bank.
2. Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty in Retail Banking: An Analysis of Service Quality Dimensions.
3. Analyzing the Relationship between Bank Branch Expansion and Financial Performance.
4. The Role of Fintech Startups in Disrupting Retail and Commercial Banking: Opportunities and Challenges.
5. Assessing the Impact of Mergers and Acquisitions on the Performance of Retail and Commercial Banks.
Dissertation topics in Finance related to Alternative Investment
1. The Performance and Risk Characteristics of Hedge Funds: A Comparative Analysis.
2. Exploring the Role of Private Equity in Financing and Growing Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises.
3. Analyzing the Relationship between Real Estate Investments and Portfolio Diversification.
4. The Potential of Impact Investing: Evaluating the Social and Financial Returns.
5. Assessing the Risk-Return Tradeoff in Cryptocurrency Investments: A Comparative Study.
Dissertation topics in Finance related to International Affairs
1. The Impact of Exchange Rate Volatility on International Trade: A Case Study of a Specific Industry.
2. Analyzing the Effectiveness of Capital Controls in Managing Financial Crises: Comparative Study of Different Countries.
3. The Role of International Financial Institutions in Promoting Economic Development in Developing Countries.
4. Evaluating the Implications of Trade Wars on Global Financial Markets.
5. Assessing the Role of Central Banks in Managing Financial Stability in a Globalized Economy.
Dissertation topics in Finance related to Sustainable Finance
1. The impact of sustainable investing on financial performance.
2. The role of green bonds in financing climate change mitigation and adaptation.
3. The development of carbon markets.
4. The use of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in investment decision-making.
5. The challenges and opportunities of sustainable Finance in emerging markets.
Dissertation topics in Finance related to Investment Banking
1. The valuation of distressed assets.
2. The pricing of derivatives.
3. The risk management of financial institutions.
4. The regulation of investment banks.
5. The impact of technology on the investment banking industry.
Dissertation topics in Finance related to Actuarial Science
1. The development of new actuarial models for pricing insurance products.
2. The use of big data in actuarial analysis.
3. The impact of climate change on insurance risk.
4. The design of pension plans that are sustainable in the long term.
5. The use of actuarial science to manage risk in other industries, such as healthcare and Finance.
Tips To Find Good Finance Dissertation Topics
Embarking on a financial dissertation journey requires careful consideration of various factors. Your choice of topic in finance research topics is pivotal, as it sets the stage for the entire research process. Finding a good financial dissertation topic is essential to blend your interests with the current trends in the financial landscape. We suggest the following tips that can help you pick the perfect dissertation topic:
1. Identify your interests and strengths
2. Check for current relevance
3. Feedback from your superiors
4. Finalise the research methods
5. Gather the data
6. Work on the outline of your dissertation
7. Make a draft and proofread it
In this blog, we have discussed the importance of finance thesis topics and provided valuable writing tips and tips for finding the right topic, too. We have also presented a list of topics within various subfields of Finance. With this, we hope you have great ideas for finance dissertations. Good luck with your finance research journey!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do i research for my dissertation project topics in finance, what is the best topic for dissertation topics for mba finance, what is the hardest finance topic, how do i choose the right topic for my dissertation in finance, where can i find a dissertation topic in finance.
Your ideal student home & a flight ticket awaits
Follow us on :

Related Posts
.webp)
The Best 17 Best Study Apps For Students To Download In 2024

10 Most Common Challenges Of Studying Abroad In 2024

Top 10 Essential Google Sheet Tips to Boost Your Productivity

Planning to Study Abroad ?

Your ideal student accommodation is a few steps away! Please fill in your details below so we can find you a new home!
We have got your response

amber © 2024. All rights reserved.
4.8/5 on Trustpilot
Rated as "Excellent" • 4800+ Reviews by students
Rated as "Excellent" • 4800+ Reviews by Students
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Research: Negotiating Is Unlikely to Jeopardize Your Job Offer
- Einav Hart,
- Julia Bear,
- Zhiying (Bella) Ren

A series of seven studies found that candidates have more power than they assume.
Job seekers worry about negotiating an offer for many reasons, including the worst-case scenario that the offer will be rescinded. Across a series of seven studies, researchers found that these fears are consistently exaggerated: Candidates think they are much more likely to jeopardize a deal than managers report they are. This fear can lead candidates to avoid negotiating altogether. The authors explore two reasons driving this fear and offer research-backed advice on how anxious candidates can approach job negotiations.
Imagine that you just received a job offer for a position you are excited about. Now what? You might consider negotiating for a higher salary, job flexibility, or other benefits , but you’re apprehensive. You can’t help thinking: What if I don’t get what I ask for? Or, in the worst-case scenario, what if the hiring manager decides to withdraw the offer?
- Einav Hart is an assistant professor of management at George Mason University’s Costello College of Business, and a visiting scholar at the Wharton School. Her research interests include conflict management, negotiations, and organizational behavior.
- Julia Bear is a professor of organizational behavior at the College of Business at Stony Brook University (SUNY). Her research interests include the influence of gender on negotiation, as well as understanding gender gaps in organizations more broadly.
- Zhiying (Bella) Ren is a doctoral student at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania. Her research focuses on conversational dynamics in organizations and negotiations.
Partner Center
Bridging private equity’s value creation gap
For the past 40 years or so, private equity (PE) buyout managers largely invested capital in an environment of declining interest rates and escalating asset prices. During that period, they were able to rely on financial leverage, enhanced tax and debt structures, and increasing valuations on high-quality assets to generate outsize returns for investors and create value.
Times have changed , however. Since 2020, the cost of debt has increased and liquidity in debt markets is harder to access given current interest rates, asset valuations, and typical bank borrowing standards. Fund performance has suffered as a result: PE buyout entry multiples declined from 11.9 to 11.0 times EBITDA through the first nine months of 2023. 1 2024 Global Private Markets Review , McKinsey, March 2024.
Even as debt markets begin to bounce back, a new macroeconomic reality is setting in—one that requires more than just financial acumen to drive returns. Buyout managers now need to focus on operational value creation strategies for revenue growth, as well as margin expansion to offset compression of multiples and to deliver desired returns to investors.
Based on our years of research and experience working with a range of private-capital firms across the globe, we have identified two key principles to maximize operational value creation.
First, buyout managers should invest with operational value creation at the forefront . This means that in addition to strategic diligence, they should conduct operational diligence for new assets. Their focus should be on developing a rigorous, bespoke, and integrated approach to assessing top-line and operational efficiency. During the underwriting process, managers can also identify actions that could expand and improve EBITDA margins and growth rates during the holding period, identify the costs involved in this transformation, and create rough timelines to track the assets’ performance. And if they acquire the asset, the manager should: 1) clearly establish the value creation objectives before deal signing, 2) emphasize operational and top-line improvements after closing, and 3) pursue continual improvements in ways of working with portfolio companies. Meanwhile, for existing assets, the manager should ensure that the level of oversight and monitoring is closely aligned with the health of each asset.
Second, everyone should understand and have a hand in improving operations . Within the PE firm, the operating group and deal teams should work together to enable and hold portfolio companies accountable for the execution of the value creation plan. This begins with an explicit focus on “linking talent to value”—ensuring leaders with the right combination of skills and experience are in place and empowered to deliver the plan, improve internal processes, and build organizational capabilities.
In our experience, getting these two principles right can significantly improve PE fund performance. Our initial analysis of more than 100 PE funds with vintages after 2020 indicates that general partners that focus on creating value through asset operations achieve a higher internal rate of return—up to two to three percentage points higher, on average—compared with peers.
The case for operational efficiency
The ongoing macroeconomic uncertainty has made it difficult for buyout managers to achieve historical levels of returns in the PE buyout industry using old ways of value creation. 2 Overall, roughly two-thirds of the total return for buyout deals that were entered in 2010 or later, and exited 2021 or before, can be attributed to market multiple expansion and leverage. See 2024 Global Private Markets Review . And it’s not going to get any easier anytime soon, for two reasons.
Higher-for-longer rates will trigger financing issues
The US Federal Reserve projects that the federal funds rate will remain around 4.5 percent through 2024, then potentially drop to about 3.0 percent by the end of 2026. 3 “Summary of economic projections,” Federal Reserve Board, December 13, 2023. Yet, even if rates decline by 200 basis points over the next two years, they will still be higher than they were over the past four years when PE buyout deals were underwritten.
This could create issues with recapitalization or floating interest rate resets for a portfolio company’s standing debt. Consider that the average borrower takes a leveraged loan at an interest coverage ratio of about three times EBIDTA (or 3x). 4 The interest coverage ratio is an indicator of a borrower’s ability to service debt, or potential default risk. With rising interest expenses and additional profitability headwinds, these coverage ratios could quickly fall below 2x and get close to or trip covenant triggers around 1x. In 2023, for example, the average leveraged loan in the healthcare and software industries was already at less than a 2x interest coverage ratio. 5 James Gelfer and Stephanie Rader, “What’s the worst that could happen? Default and recovery rates in private credit,” Goldman Sachs, April 20, 2023. To avoid a covenant breach, or (if needed) increasing recapitalization capital available without equity paydown, managers will need to rely on operational efficiency to increase EBITDA.
Valuations are mismatched
If interest rates remain high, the most recent vintage of PE assets is likely to face valuation mismatches at exit, or extended hold periods until value can be realized. Moreover, valuation of PE assets has remained high relative to their public-market equivalents, partly a result of the natural lag in how these assets are marked to market. As the CEO of Harvard University’s endowment explained in Harvard’s 2023 annual report, it will likely take more time for private valuations to fully reflect market conditions due to the continued slowdown in exits and financing rounds. 6 Message from the CEO of Harvard Management Company, September 2023.
Adapting PE’s value creation approach
Operational efficiency isn’t a new concept in the PE world. We’ve previously written about the strategic shift among firms, increasingly notable since 2018, moving from the historical “buy smart and hold” approach to one of “acquire, align on strategy, and improve operating performance.”
However, the role of operations in creating more value is no longer just a source of competitive advantage but a competitive necessity for managers. Let’s take a closer look at the two principles that can create operational efficiency.
Invest with operational value creation at the forefront
PE fund managers can improve the profitability and exit valuations of assets by having operations-related conversations up front.
Assessing new assets. Prior to acquiring an asset, PE managers typically conduct financial and strategic diligence to refine their understanding of a given market and the asset’s position in that market. They should also undertake operational diligence—if they are not already doing so—to develop a holistic view of the asset to inform their value creation agenda.
Operational diligence involves the detailed assessment of an asset’s operations, including identification of opportunities to improve margins or accelerate organic growth. A well-executed operational-diligence process can reveal or confirm which types of initiatives could generate top-line and efficiency-driven value, the estimated cash flow improvements these initiatives could generate, the approximate timing of any cash flow improvements, and the potential costs of such initiatives.
The results of an operational-diligence process can be advantageous in other ways, too. Managers can use the findings to create a compelling value creation plan, or a detailed memo summarizing the near-term improvement opportunities available in the current profit-and-loss statement, as well as potential opportunities for expansion into adjacencies or new markets. After this step is done, they should determine, in collaboration with their operating-group colleagues, whether they have the appropriate leaders in place to successfully implement the value creation plan.
These results can also help managers resolve any potential issues up front, prior to deal signing, which in turn could increase the likelihood of receiving investment committee approval for the acquisition. Managers also can share the diligence findings with co-investors and financiers to help boost their confidence in the investment and the associated value creation thesis.
It is crucial that managers have in-depth familiarity with company operations, since operational diligence is not just an analytical-sizing exercise. If they perform operational diligence well, they can ensure that the full value creation strategy and performance improvement opportunities are embedded in the annual operating plan and the longer-term three- to five-year plan of the portfolio company’s management team.
Assessing existing assets. When it comes to existing assets, a fundamental question for PE managers is how to continue to improve performance throughout the deal life cycle. Particularly in the current macroeconomic and geopolitical environment, where uncertainty reigns, managers should focus more—and more often—on directly monitoring assets and intervening when required. They can complement this monitoring with routine touchpoints with the CEO, CFO, and chief transformation officer (CTO) of individual assets to get updates on critical initiatives driving the value creation plan, along with ensuring their operating group has full access to each portfolio company’s financials. Few PE managers currently provide this level of transparency into their assets’ performance.
To effectively monitor existing assets, managers can use key performance indicators (KPIs) directly linked to the fund’s investment thesis. For instance, if the fund’s investment thesis is centered on the availability of inventory, they may rigorously track forecasts of supply and demand and order volumes. This way, they can identify and address issues with inventory early on. Some managers pull information directly from the enterprise resource planning systems in their portfolio companies to get full visibility into operations. Others have set up specific “transformation management offices” to support performance improvements in key assets and improve transparency on key initiatives.
We’ve seen managers adopt various approaches with assets that are on track to meet return hurdles. They have frequent discussions with the portfolio company’s management team, perform quarterly credit checks on key suppliers and customers to ensure stability of their extended operations, and do a detailed review of the portfolio company’s operations and financial performance two to three years into the hold period. Managers can therefore confirm whether the management team is delivering on their value creation plans and also identify any new opportunities associated with the well-performing assets.
If existing assets are underperforming or distressed, managers’ prompt interventions to improve operations in the near term, and improve revenue over the medium term, can determine whether they should continue to own the asset or reduce their equity position through a bankruptcy proceeding. One manager implemented a cash management program to monitor and improve the cash flow for an underperforming retail asset of a portfolio company. The approach helped the portfolio company overcome a peak cash flow crisis period, avoid tripping liquidity covenants in an asset-backed loan, and get the time needed for the asset’s long-term performance to improve.
Reassess internal operations and governance
In addition to operational improvements, managers should also assess their own operations and consider shifting to an operating model that encourages increased engagement between their team and the portfolio companies. They should cultivate a stable of trusted, experienced executives within the operating group. They should empower these executives to be equal collaborators with the deal team in determining the value available in the asset to be underwritten, developing an appropriate value creation strategy, and overseeing performance of the portfolio company’s management.
Shift to a ‘just right’ operating model for operating partners. The operating model through which buyout managers engage with portfolio companies should be “just right”—that is, aligned with the fund’s overall strategy, how the fund is structured, and who sets the strategic vision for each individual portfolio company.
There are two types of engagement operating models—consultative and directive. When choosing an operating model, firms should align their hiring and internal capabilities to support their operating norms, how they add value to their portfolio companies, and the desired relationship with the management team (exhibit).
Take the example of a traditional buyout manager that acquires good companies with good management teams. In such a case, the portfolio company’s management team is likely to already have a strategic vision for the asset. These managers may therefore choose a more consultative engagement approach (for instance, providing advice and support to the portfolio company for any board-related issues or other challenges).
For value- or operations-focused funds, the manager may have higher ownership in the strategic vision for the asset, so their initial goal should be to develop a management team that can deliver on a specific investment thesis. In this case, the support required by the portfolio company could be less specialized (for example, the manager helps in hiring the right talent for key functional areas), and more integrative, to ensure a successful end-to-end transformation for the asset. As such, a more directive or oversight-focused engagement operating model may be preferred.
Successful execution of these engagement models requires the operating group to have the right talent mix and experience levels. If the manager implements a “generalist” coverage model, for example, where the focus is on monitoring and overseeing portfolio companies, the operating group will need people with the ability (and experience) to support the management in end-to-end transformations. However, a different type of skill set is required if the manager chooses a “specialist” coverage model, where the focus is on providing functional guidance and expertise (leaving transformations to the portfolio company’s management teams). Larger and more mature operating groups frequently use a mix of both talent pools.
Empower the operating group. In the past, many buyout managers did not have operating teams, so they relied on the management teams in the portfolio companies to fully identify and implement the value creation plan while running the asset’s day-to-day operations. Over time, many top PE funds began to establish internal operating groups to provide strategic direction, coaching, and support to their portfolio companies. The operating groups, however, tended to take a back seat to deal teams, largely because legacy mindsets and governance structures placed responsibility for the performance of an asset on the deal team. In our view, while the deal team needs to remain responsible and accountable for the deal, certain tasks can be delegated to the operating group.
Some managers give their operating group members seats on portfolio company boards, hiring authority for key executives, and even decision-making rights on certain value creation strategies within the portfolio. For optimal performance, these operating groups should have leaders with prior C-suite responsibility or commensurate accountability within the PE fund and experience executing cross-functional mandates and company transformations. Certain funds with a core commitment to portfolio value creation include the leader of the operating group on the investment committee. Less-experienced members of the operating group can have consultative arrangements or peer-to-peer relationships with key portfolio company leaders.
Since the main KPIs for operating teams are financial, it is critical that their leaders understand a buyout asset’s business model, financing, and general market dynamics. The operating group should also be involved in the deal during the diligence phase, and participate in the development of the value creation thesis as well as the underwriting process. Upon deal close, the operating team should be as empowered as the deal team to serve as stewards of the asset and resolve issues concerning company operations.
Some funds also are hiring CTOs for their portfolio companies to steer them through large transformations. Similar to the CTO in any organization , they help the organization align on a common vision, translate strategy into concrete initiatives for better performance, and create a system of continuous improvement and growth for the employees. However, when deployed by the PE fund, the CTO also often serves as a bridge between the PE fund and the portfolio company and can serve as a plug-and-play executive to fill short-term gaps in the portfolio company management team. In many instances, the CTO is given signatory, and occasionally broader, functional responsibilities. In addition, their personal incentives can be aligned with the fund’s desired outcomes. For example, funds may tie an element of the CTO’s overall compensation to EBITDA improvement or the success of the transformation.
Bring best-of-breed capabilities to portfolio companies. Buyout managers can bring a range of compelling capabilities to their portfolio companies, especially to smaller and midmarket companies and their internal operating teams. Our conversations with industry stakeholders revealed that buyout managers’ skills can be particularly useful in the following three areas:
- Procurement. Portfolio companies can draw on a buyout manager’s long-established procurement processes, team, and negotiating support. For instance, managers often have prenegotiated rates with suppliers or group purchasing arrangements that portfolio companies can leverage to minimize their own procurement costs and reduce third-party spending.
- Executive talent. They can also capitalize on the diverse and robust network of top talent that buyout managers have likely cultivated over time, including homegrown leaders and ones found through executive search firms (both within and outside the PE industry).
- Partners. Similarly, they can work with the buyout manager’s roster of external experts, business partners, suppliers, and advisers to find the best solutions to their emerging business challenges (for instance, gaining access to offshore resources during a carve-out transaction).
Ongoing macroeconomic uncertainty is creating unprecedented times in the PE buyout industry. Managers should use this as an opportunity to redouble their efforts on creating operational improvements in their existing portfolio, as well as new assets. It won’t be easy to adapt and evolve value creation processes and practices, but managers that succeed have an opportunity to close the gap between the current state of value creation and historical returns and outperform their peers.
Jose Luis Blanco is a senior partner in McKinsey’s New York office, where Matthew Maloney is a partner; William Bundy is a partner in the Washington, DC, office; and Jason Phillips is a senior partner in the London office.
The authors wish to thank Louis Dufau and Bill Leigh for their contributions to this article.
This article was edited by Arshiya Khullar, an editor in McKinsey’s Gurugram office.

Explore a career with us
Related articles.

McKinsey Global Private Markets Review 2024: Private markets in a slower era

CEO alpha: A new approach to generating private equity outperformance

Private equity operating groups and the pursuit of ‘portfolio alpha’
- Open access
- Published: 09 May 2024
Evaluation of integrated community case management of the common childhood illness program in Gondar city, northwest Ethiopia: a case study evaluation design
- Mekides Geta 1 ,
- Geta Asrade Alemayehu 2 ,
- Wubshet Debebe Negash 2 ,
- Tadele Biresaw Belachew 2 ,
- Chalie Tadie Tsehay 2 &
- Getachew Teshale 2
BMC Pediatrics volume 24 , Article number: 310 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
103 Accesses
Metrics details
Integrated Community Case Management (ICCM) of common childhood illness is one of the global initiatives to reduce mortality among under-five children by two-thirds. It is also implemented in Ethiopia to improve community access and coverage of health services. However, as per our best knowledge the implementation status of integrated community case management in the study area is not well evaluated. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the implementation status of the integrated community case management program in Gondar City, Northwest Ethiopia.
A single case study design with mixed methods was employed to evaluate the process of integrated community case management for common childhood illness in Gondar town from March 17 to April 17, 2022. The availability, compliance, and acceptability dimensions of the program implementation were evaluated using 49 indicators. In this evaluation, 484 mothers or caregivers participated in exit interviews; 230 records were reviewed, 21 key informants were interviewed; and 42 observations were included. To identify the predictor variables associated with acceptability, we used a multivariable logistic regression analysis. Statistically significant variables were identified based on the adjusted odds ratio (AOR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) and p-value. The qualitative data was recorded, transcribed, and translated into English, and thematic analysis was carried out.
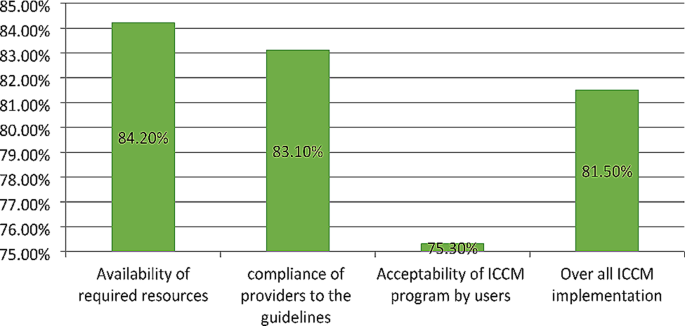
The overall implementation of integrated community case management was 81.5%, of which availability (84.2%), compliance (83.1%), and acceptability (75.3%) contributed. Some drugs and medical equipment, like Cotrimoxazole, vitamin K, a timer, and a resuscitation bag, were stocked out. Health care providers complained that lack of refreshment training and continuous supportive supervision was the common challenges that led to a skill gap for effective program delivery. Educational status (primary AOR = 0.27, 95% CI:0.11–0.52), secondary AOR = 0.16, 95% CI:0.07–0.39), and college and above AOR = 0.08, 95% CI:0.07–0.39), prescribed drug availability (AOR = 2.17, 95% CI:1.14–4.10), travel time to the to the ICCM site (AOR = 3.8, 95% CI:1.99–7.35), and waiting time (AOR = 2.80, 95% CI:1.16–6.79) were factors associated with the acceptability of the program by caregivers.
Conclusion and recommendation
The overall implementation status of the integrated community case management program was judged as good. However, there were gaps observed in the assessment, classification, and treatment of diseases. Educational status, availability of the prescribed drugs, waiting time and travel time to integrated community case management sites were factors associated with the program acceptability. Continuous supportive supervision for health facilities, refreshment training for HEW’s to maximize compliance, construction clean water sources for HPs, and conducting longitudinal studies for the future are the forwarded recommendation.
Peer Review reports
Integrated Community Case Management (ICCM) is a critical public health strategy for expanding the coverage of quality child care services [ 1 , 2 ]. It mainly concentrated on curative care and also on the diagnosis, treatment, and referral of children who are ill with infectious diseases [ 3 , 4 ].
Based on the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) recommendations, Ethiopia adopted and implemented a national policy supporting community-based treatment of common childhood illnesses like pneumonia, Diarrhea, uncomplicated malnutrition, malaria and other febrile illness and Amhara region was one the piloted regions in late 2010 [ 5 ]. The Ethiopian primary healthcare units, established at district levels include primary hospitals, health centers (HCs), and health posts (HPs). The HPs are run by Health Extension Workers (HEWs), and they have function of monitoring health programs and disease occurrence, providing health education, essential primary care services, and timely referrals to HCs [ 6 , 7 ]. The Health Extension Program (HEP) uses task shifting and community ownership to provide essential health services at the first level using the health development army and a network of woman volunteers. These groups are organized to promote health and prevent diseases through community participation and empowerment by identifying the salient local bottlenecks which hinder vital maternal, neonatal, and child health service utilization [ 8 , 9 ].
One of the key steps to enhance the clinical case of health extension staff is to encourage better growth and development among under-five children by health extension. Healthy family and neighborhood practices are also encouraged [ 10 , 11 ]. The program also combines immunization, community-based feeding, vitamin A and de-worming with multiple preventive measures [ 12 , 13 ]. Now a days rapidly scaling up of ICCM approach to efficiently manage the most common causes of morbidity and mortality of children under the age of five in an integrated manner at the community level is required [ 14 , 15 ].
Over 5.3 million children are died at a global level in 2018 and most causes (75%) are preventable or treatable diseases such as pneumonia, malaria and diarrhea [ 16 ]. About 99% of the global burden of mortality and morbidity of under-five children which exists in developing countries are due to common childhood diseases such as pneumonia, diarrhea, malaria and malnutrition [ 17 ].
In 2013, the mortality rate of under-five children in Sub-Saharan Africa decreased to 86 deaths per 1000 live birth and estimated to be 25 per 1000live births by 2030. However, it is a huge figure and the trends are not sufficient to reach the target [ 18 ]. About half of global under-five deaths occurred in sub-Saharan Africa. And from the top 26 nations burdened with 80% of the world’s under-five deaths, 19 are in sub-Saharan Africa [ 19 ].
To alleviate the burden, the Ethiopian government tries to deliver basic child care services at the community level by trained health extension workers. The program improves the health of the children not only in Ethiopia but also in some African nations. Despite its proven benefits, the program implementation had several challenges, in particular, non-adherence to the national guidelines among health care workers [ 20 ]. Addressing those challenges could further improve the program performance. Present treatment levels in sub-Saharan Africa are unacceptably poor; only 39% of children receive proper diarrhea treatment, 13% of children with suspected pneumonia receive antibiotics, 13% of children with fever receive a finger/heel stick to screen for malaria [ 21 ].
To improve the program performance, program gaps should be identified through scientific evaluations and stakeholder involvement. This evaluation not only identify gaps but also forward recommendations for the observed gaps. Furthermore, the implementation status of ICCM of common childhood illnesses has not been evaluated in the study area yet. Therefore, this work aimed to evaluate the implementation status of integrated community case management program implementation in Gondar town, northwest Ethiopia. The findings may be used by policy makers, healthcare providers, funders and researchers.
Method and material
Evaluation design and settings.
A single-case study design with concurrent mixed-methods evaluation was conducted in Gondar city, northwest Ethiopia, from March 17 to April 17, 2022. The evaluability assessment was done from December 15–30, 2021. Both qualitative and quantitative data were collected concurrently, analyzed separately, and integrated at the result interpretation phase.
The evaluation area, Gondar City, is located in northwest Ethiopia, 740 km from Addis Ababa, the capital city of the country. It has six sub-cities and thirty-six kebeles (25 urban and 11 rural). In 2019, the estimated total population of the town was 338,646, and 58,519 (17.3%) were under-five children. In the town there are eight public health centers and 14 health posts serving the population. All health posts provide ICCM service for more than 70,852 populations.
Evaluation approach and dimensions
Program stakeholders.
The evaluation followed a formative participatory approach by engaging the potential stakeholders in the program. Prior to the development of the proposal, an extensive discussion was held with the Gondar City Health Department to identify other key stakeholders in the program. Service providers at each health facility (HCs and HPs), caretakers of sick children, the Gondar City Health Office (GCHO), the Amhara Regional Health Bureau (ARHB), the Minister of Health (MoH), and NGOs (IFHP and Save the Children) were considered key stakeholders. During the Evaluability Assessment (EA), the stakeholders were involved in the development of evaluation questions, objectives, indicators, and judgment criteria of the evaluation.
Evaluation dimensions
The availability and acceptability dimensions from the access framework [ 22 ] and compliance dimension from the fidelity framework [ 23 ] were used to evaluate the implementation of ICCM.
Population and samplings
All under-five children and their caregivers attended at the HPs; program implementers (health extension workers, healthcare providers, healthcare managers, PHCU focal persons, MCH coordinators, and other stakeholders); and ICCM records and registries in the health posts of Gondar city administration were included in the evaluation. For quantitative data, the required sample size was proportionally allocated for each health post based on the number of cases served in the recent one month. But the qualitative sample size was determined by data saturation, and the samples were selected purposefully.
The data sources and sample size for the compliance dimension were all administrative records/reports and ICCM registration books (230 documents) in all health posts registered from December 1, 2021, to February 30, 2022 (three months retrospectively) included in the evaluation. The registries were assessed starting from the most recent registration number until the required sample size was obtained for each health post.
The sample size to measure the mothers’/caregivers’ acceptability towards ICCM was calculated by taking prevalence of caregivers’ satisfaction on ICCM program p = 74% from previously similar study [ 24 ] and considering standard error 4% at 95% CI and 10% non- responses, which gave 508. Except those who were seriously ill, all caregivers attending the ICCM sites during data collection were selected and interviewed consecutively.
The availability of required supplies, materials and human resources for the program were assessed in all 14HPs. The data collectors observed the health posts and collected required data by using a resources inventory checklist.
A total of 70 non-participatory patient-provider interactions were also observed. The observations were conducted per each health post and for health posts which have more than one health extension workers one of them were selected randomly. The observation findings were used to triangulate the findings obtained through other data collection techniques. Since people may act accordingly to the standards when they know they are observed for their activities, we discarded the first two observations from analysis. It is one of the strategies to minimize the Hawthorne effect of the study. Finally a total of 42 (3 in each HPs) observations were included in the analysis.
Twenty one key informants (14 HEWs, 3 PHCU focal person, 3 health center heads and one MCH coordinator) were interviewed. These key informants were selected since they are assumed to be best teachers in the program. Besides originally developed key informant interview questions, the data collectors probed them to get more detail and clear information.
Variables and measurement
The availability of resources, including trained healthcare workers, was examined using 17 indicators, with weighted score of 35%. Compliance was used to assess HEWs’ adherence to the ICCM treatment guidelines by observing patient-provider interactions and conducting document reviews. We used 18 indicators and a weighted value of 40%.
Mothers’ /caregivers’/ acceptance of ICCM service was examined using 14 indicators and had a weighted score of 25%. The indicators were developed with a five-point Likert scale (1: strongly disagree, 2: disagree, 3: neutral, 4: agree and 5: strongly agree). The cut off point for this categorization was calculated using the demarcation threshold formula: ( \(\frac{\text{t}\text{o}\text{t}\text{a}\text{l}\, \text{h}\text{i}\text{g}\text{h}\text{e}\text{s}\text{t}\, \text{s}\text{c}\text{o}\text{r}\text{e}-\,\text{t}\text{o}\text{t}\text{a}\text{l}\, \text{l}\text{o}\text{w}\text{e}\text{s}\text{t} \,\text{s}\text{c}\text{o}\text{r}\text{e}}{2}) +total lowest score\) ( 25 – 27 ). Those mothers/caregivers/ who scored above cut point (42) were considered as “satisfied”, otherwise “dissatisfied”. The indicators were adapted from the national ICCM and IMNCI implementation guideline and other related evaluations with the participation of stakeholders. Indicator weight was given by the stakeholders during EA. Indicators score was calculated using the formula \(\left(achieved \,in \%=\frac{indicator \,score \,x \,100}{indicator\, weight} \right)\) [ 26 , 28 ].
The independent variables for the acceptability dimension were socio-demographic and economic variables (age, educational status, marital status, occupation of caregiver, family size, income level, and mode of transport), availability of prescribed drugs, waiting time, travel time to ICCM site, home to home visit, consultation time, appointment, and source of information.
The overall implementation of ICCM was measured by using 49 indicators over the three dimensions: availability (17 indicators), compliance (18 indicators) and acceptability (14 indicators).
Program logic model
Based on the constructed program logic model and trained health care providers, mothers/caregivers received health information and counseling on child feeding; children were assessed, classified, and treated for disease, received follow-up; they were checked for vitamin A; and deworming and immunization status were the expected outputs of the program activities. Improved knowledge of HEWs on ICCM, increased health-seeking behavior, improved quality of health services, increased utilization of services, improved data quality and information use, and improved child health conditions are considered outcomes of the program. Reduction of under-five morbidity and mortality and improving quality of life in the society are the distant outcomes or impacts of the program (Fig. 1 ).
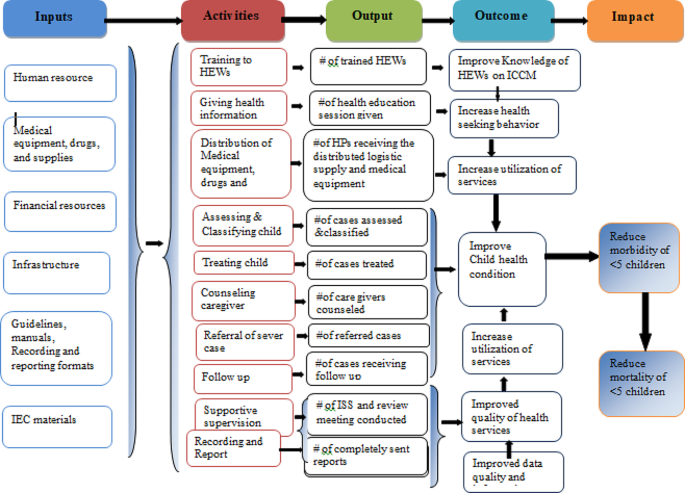
Integrated community case management of childhood illness program logic model in Gondar City in 2022
Data collection tools and procedure
Resource inventory and data extraction checklists were adapted from standard ICCM tool and check lists [ 29 ]. A structured interviewer administered questionnaire was adapted by referring different literatures [ 30 , 31 ] to measure the acceptability of ICCM. The key informant interview (KII) guide was also developed to explore the views of KIs. The interview questionnaire and guide were initially developed in English and translated into the local language (Amharic) and finally back to English to ensure consistency. All the interviews were done in the local language, Amharic.
Five trained clinical nurses and one BSC nurse were recruited from Gondar zuria and Wegera district as data collectors and supervisors, respectively. Two days training on the overall purpose of the evaluation and basic data collection procedures were provided prior to data collection. Then, both quantitative and qualitative data were gathered at the same time. The quantitative data were gathered from program documentation, charts of ICCM program visitors and, exit interview. Interviews with 21 KIIs and non-participatory observations of patient-provider interactions were used to acquire qualitative data. Key informant interviews were conducted to investigate the gaps and best practices in the implementation of the ICCM program.
A pretest was conducted to 26 mothers/caregivers/ at Maksegnit health post and appropriate modifications were made based on the pretest results. The data collectors were supervised and principal evaluator examined the completeness and consistency of the data on a daily basis.
Data management and analysis
For analysis, quantitative data were entered into epi-data version 4.6 and exported to Stata 14 software for analysis. Narration and tabular statistics were used to present descriptive statistics. Based on established judgment criteria, the total program implementation was examined and interpreted as a mix of the availability, compliance, and acceptability dimensions. To investigate the factors associated with ICCM acceptance, a binary logistic regression analysis was performed. During bivariable analysis, variables with p-values less than 0.25 were included in multivariable analysis. Finally, variables having a p-value less than 0.05 and an adjusted odds ratio (AOR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) were judged statistically significant. Qualitative data were collected recorded, transcribed into Amharic, then translated into English and finally coded and thematically analyzed.
Judgment matrix analysis
The weighted values of availability, compliance, and acceptability dimensions were 35, 40, and 25 based on the stakeholder and investigator agreement on each indicator, respectively. The judgment parameters for each dimension and the overall implementation of the program were categorized as poor (< 60%), fair (60–74.9%), good (75-84.9%), and very good (85–100%).
Availability of resources
A total of 26 HEWs were assigned within the fourteen health posts, and 72.7% of them were trained on ICCM to manage common childhood illnesses in under-five children. However, the training was given before four years, and they didn’t get even refreshment training about ICCM. The KII responses also supported that the shortage of HEWs at the HPs was the problem in implementing the program properly.
I am the only HEW in this health post and I have not been trained on ICCM program. So, this may compromise the quality of service and client satisfaction.(25 years old HEW with two years’ experience)
All observed health posts had ICCM registration books, monthly report and referral formats, functional thermometer, weighting scale and MUAC tape meter. However, timer and resuscitation bag was not available in all HPs. Most of the key informant finding showed that, in all HPs there was no shortage of guideline, registration book and recording tool; however, there was no OTP card in some health posts.
“Guideline, ICCM registration book for 2–59 months of age, and other different recording and reporting formats and booklet charts are available since September/2016. However, OTP card is not available in most HPs.”. (A 30 years male health center director)
Only one-fifth (21%) of HPs had a clean water source for drinking and washing of equipment. Most of Key-informant interview findings showed that the availability of infrastructures like water was not available in most HPs. Poor linkage between HPs, HCs, town health department, and local Kebele administer were the reason for unavailability.
Since there is no water for hand washing, or drinking, we obligated to bring water from our home for daily consumptions. This increases the burden for us in our daily activity. (35 years old HEW)
Most medicines, such as anti-malaria drugs with RDT, Quartem, Albendazole, Amoxicillin, vitamin A capsules, ORS, and gloves, were available in all the health posts. Drugs like zinc, paracetamol, TTC eye ointment, and folic acid were available in some HPs. However, cotrimoxazole and vitamin K capsules were stocked-out in all health posts for the last six months. The key informant also revealed that: “Vitamin K was not available starting from the beginning of this program and Cotrimoxazole was not available for the past one year and they told us they would avail it soon but still not availed. Some essential ICCM drugs like anti malaria drugs, De-worming, Amoxicillin, vitamin A capsules, ORS and medical supplies were also not available in HCs regularly.”(28 years’ Female PHCU focal)
The overall availability of resources for ICCM implementation was 84.2% which was good based on our presetting judgment parameter (Table 1 ).
Health extension worker’s compliance
From the 42 patient-provider interactions, we found that 85.7%, 71.4%, 76.2%, and 95.2% of the children were checked for body temperature, weight, general danger signs, and immunization status respectively. Out of total (42) observation, 33(78.6%) of sick children were classified for their nutritional status. During observation time 29 (69.1%) of caregivers were counseled by HEWs on food, fluid and when to return back and 35 (83.3%) of children were appointed for next follow-up visit. Key informant interviews also affirmed that;
“Most of our health extension workers were trained on ICCM program guidelines but still there are problems on assessment classification and treatment of disease based on guidelines and standards this is mainly due to lack refreshment training on the program and lack of continuous supportive supervision from the respective body.” (27years’ Male health center head)
From 10 clients classified as having severe pneumonia cases, all of them were referred to a health center (with pre-referral treatment), and from those 57 pneumonia cases, 50 (87.7%) were treated at the HP with amoxicillin or cotrimoxazole. All children with severe diarrhea, very severe disease, and severe complicated malnutrition cases were referred to health centers with a pre-referral treatment for severe dehydration, very severe febrile disease, and severe complicated malnutrition, respectively. From those with some dehydration and no dehydration cases, (82.4%) and (86.8%) were treated at the HPs for some dehydration (ORS; plan B) and for no dehydration (ORS; plan A), respectively. Moreover, zinc sulfate was prescribed for 63 (90%) of under-five children with some dehydration or no dehydration. From 26 malaria cases and 32 severe uncomplicated malnutrition and moderate acute malnutrition cases, 20 (76.9%) and 25 (78.1%) were treated at the HPs, respectively. Of the total reviewed documents, 56 (93.3%), 66 (94.3%), 38 (84.4%), and 25 (78.1%) of them were given a follow-up date for pneumonia, diarrhea, malaria, and malnutrition, respectively.
Supportive supervision and performance review meetings were conducted only in 10 (71.4%) HPs, but all (100%) HPs sent timely reports to the next supervisory body.
Most of the key informants’ interview findings showed that supportive supervision was not conducted regularly and for all HPs.
I had mentored and supervised by supportive supervision teams who came to our health post at different times from health center, town health office and zonal health department. I received this integrated supervision from town health office irregularly, but every month from catchment health center and last integrated supportive supervision from HC was on January. The problem is the supervision was conducted for all programs.(32 years’ old and nine years experienced female HEW)
Moreover, the result showed that there was poor compliance of HEWs for the program mainly due to weak supportive supervision system of managerial and technical health workers. It was also supported by key informants as:
We conducted supportive supervision and performance review meeting at different time, but still there was not regular and not addressed all HPs. In addition to this the supervision and review meeting was conducted as integration of ICCM program with other services. The other problem is that most of the time we didn’t used checklist during supportive supervision. (Mid 30 years old male HC director)
Based on our observation and ICCM document review, 83.1% of the HEWs were complied with the ICCM guidelines and judged as fair (Table 2 ).
Acceptability of ICCM program
Sociodemographic and obstetric characteristics of participants.
A total of 484 study participants responded to the interviewer-administered questionnaire with a response rate of 95.3%. The mean age of study participants was 30.7 (SD ± 5.5) years. Of the total caregivers, the majority (38.6%) were categorized under the age group of 26–30 years. Among the total respondents, 89.3% were married, and regarding religion, the majorities (84.5%) were Orthodox Christian followers. Regarding educational status, over half of caregivers (52.1%) were illiterate (unable to read or write). Nearly two-thirds of the caregivers (62.6%) were housewives (Table 3 ).
All the caregivers came to the health post on foot, and most of them 418 (86.4%) arrived within one hour. The majority of 452 (93.4%) caregivers responded that the waiting time to get the service was less than 30 min. Caregivers who got the prescribed drugs at the health post were 409 (84.5%). Most of the respondents, 429 (88.6%) and 438 (90.5%), received counseling services on providing extra fluid and feeding for their sick child and were given a follow-up date.
Most 298 (61.6%) of the caregivers were satisfied with the convenience of the working hours of HPs, and more than three-fourths (80.8%) were satisfied with the counseling services they received. Most of the respondents, 366 (75.6%), were satisfied with the appropriateness of waiting time and 431 (89%) with the appropriateness of consultation time. The majority (448 (92.6%) of caregivers were satisfied with the way of communicating with HEWs, and 269 (55.6%) were satisfied with the knowledge and competence of HEWs. Nearly half of the caregivers (240, or 49.6%) were satisfied with the availability of drugs at health posts.
The overall acceptability of the ICCM program was 75.3%, which was judged as good. A low proportion of acceptability was measured on the cleanliness of the health posts, the appropriateness of the waiting area, and the competence and knowledge of the HEWs. On the other hand, high proportion of acceptability was measured on appropriateness of waiting time, way of communication with HEWs, and the availability of drugs (Table 4 ).
Factors associated with acceptability of ICCM program
In the final multivariable logistic regression analysis, educational status of caregivers, availability of prescribed drugs, time to arrive, and waiting time were factors significantly associated with the satisfaction of caregivers with the ICCM program.
Accordingly, the odds of caregivers with primary education, secondary education, and college and above were 73% (AOR = 0.27, 95% CI: 0.11–0.52), 84% (AOR = 0.16, 95% CI: 0.07–0.39), and 92% (AOR = 0.08, 95% CI: 0.07–0.40) less likely to accept the program as compared to mothers or caregivers who were not able to read and write, respectively. The odds of caregivers or mothers who received prescribed drugs were 2.17 times more likely to accept the program as compared to their counters (AOR = 2.17, 95% CI: 1.14–4.10). The odds of caregivers or mothers who waited for services for less than 30 min were 2.8 times more likely to accept the program as compared to those who waited for more than 30 min (AOR = 2.80, 95% CI: 1.16–6.79). Moreover, the odds of caregivers/mothers who traveled an hour or less for service were 3.8 times more likely to accept the ICCM program as compared to their counters (AOR = 3.82, 95% CI:1.99–7.35) (Table 5 ).
Overall ICCM program implementation and judgment
The implementation of the ICCM program in Gondar city administration was measured in terms of availability (84.2%), compliance (83.1%), and acceptability (75.3%) dimensions. In the availability dimension, amoxicillin, antimalarial drugs, albendazole, Vit. A, and ORS were available in all health posts, but only six HPs had Ready-to-Use Therapeutic Feedings, three HPs had ORT Corners, and none of the HPs had functional timers. In all health posts, the health extension workers asked the chief to complain, correctly assessed for pneumonia, diarrhea, malaria, and malnutrition, and sent reports based on the national schedule. However, only 70% of caretakers counseled about food, fluids, and when to return, 66% and 76% of the sick children were checked for anemia and other danger signs, respectively. The acceptability level of the program by caretakers and caretakers’/mothers’ educational status, waiting time to get the service and travel time ICCM sites were the factors affecting its acceptability. The overall ICCM program in Gondar city administration was 81.5% and judged as good (Fig. 2 ).
Overall ICCM program implementation and the evaluation dimensions in Gondar city administration, 2022
The implementation status of ICCM was judged by using three dimensions including availability, compliance and acceptability of the program. The judgment cut of points was determined during evaluability assessment (EA) along with the stakeholders. As a result, we found that the overall implementation status of ICCM program was good as per the presetting judgment parameter. Availability of resources for the program implementation, compliance of HEWs to the treatment guideline and acceptability of the program services by users were also judged as good as per the judgment parameter.
This evaluation showed that most medications, equipment and recording and reporting materials available. This finding was comparable with the standard ICCM treatment guide line [ 10 ]. On the other hand trained health care providers, some medications like Zink, Paracetamol and TTC eye ointment, folic acid and syringes were not found in some HPs. However the finding was higher than the study conducted in SNNPR on selected health posts [ 33 ] and a study conducted in Soro district, southern Ethiopia [ 24 ]. The possible reason might be due to low interruption of drugs at town health office or regional health department stores, regular supplies of essential drugs and good supply management and distribution of drug from health centers to health post.
The result of this evaluation showed that only one fourth of health posts had functional ORT Corner which was lower compared to the study conducted in SNNPR [ 34 ]. This might be due poor coverage of functional pipe water in the kebeles and the installation was not set at the beginning of health post construction as reported from one of ICCM program coordinator.
Compliance of HEWs to the treatment guidelines in this evaluation was higher than the study done in southern Ethiopia (65.6%) [ 24 ]. This might be due to availability of essential drugs educational level of HEWs and good utilization of ICCM guideline and chart booklet by HEWs. The observations showed most of the sick children were assessed for danger sign, weight, and temperature respectively. This finding is lower than the study conducted in Rwanda [ 35 ]. This difference might be due to lack of refreshment training and regular supportive supervision for HEWs. This also higher compared to the study done in three regions of Ethiopia indicates that 88%, 92% and 93% of children classified as per standard for Pneumonia, diarrhea and malaria respectively [ 36 ]. The reason for this difference may be due to the presence of medical equipment and supplies including RDT kit for malaria, and good educational level of HEWs.
Moreover most HPs received supportive supervision and performance review meeting was conducted and all of them send reports timely to next level. The finding of this evaluation was lower than the study conducted on implementation evaluation of ICCM program southern Ethiopia [ 24 ] and study done in three regions of Ethiopia (Amhara, Tigray and SNNPR) [ 37 ]. This difference might be due sample size variation.
The overall acceptability of the ICCM program was less than the presetting judgment parameter but slightly higher compared to the study in southern Ethiopia [ 24 ]. This might be due to presence of essential drugs for treating children, reasonable waiting and counseling time provided by HEWs, and smooth communication between HEWs and caregivers. In contrast, this was lower than similar studies conducted in Wakiso district, Uganda [ 38 ]. The reason for this might be due to contextual difference between the two countries, inappropriate waiting area to receive the service and poor cleanness of the HPs in our study area. Low acceptability of caregivers to ICCM service was observed in the appropriateness of waiting area, availability of drugs, cleanness of health post, and competence of HEWs while high level of caregiver’s acceptability was consultation time, counseling service they received, communication with HEWs, treatment given for their sick children and interest to return back for ICCM service.
Caregivers who achieved primary, secondary, and college and above were more likely accept the program services than those who were illiterate. This may more educated mothers know about their child health condition and expect quality service from healthcare providers which is more likely reduce the acceptability of the service. The finding is congruent with a study done on implementation evaluation of ICCM program in southern Ethiopia [ 24 ]. However, inconsistent with a study conducted in wakiso district in Uganda [ 38 ]. The possible reason for this might be due to contextual differences between the two countries. The ICCM program acceptability was high in caregivers who received all prescribed drugs than those did not. Caregivers those waited less than 30 min for service were more accepted ICCM services compared to those more than 30 minutes’ waiting time. This finding is similar compared with the study conducted on implementation evaluation of ICCM program in southern Ethiopia [ 24 ]. In contrary, the result was incongruent with a survey result conducted by Ethiopian public health institute in all regions and two administrative cities of Ethiopia [ 39 ]. This variation might be due to smaller sample size in our study the previous one. Moreover, caregivers who traveled to HPs less than 60 min were more likely accepted the program than who traveled more and the finding was similar with the study finding in Jimma zone [ 40 ].
Strengths and limitations
This evaluation used three evaluation dimensions, mixed method and different data sources that would enhance the reliability and credibility of the findings. However, the study might have limitations like social desirability bias, recall bias and Hawthorne effect.
The implementation of the ICCM program in Gondar city administration was measured in terms of availability (84.2%), compliance (83.1%), and acceptability (75.3%) dimensions. In the availability dimension, amoxicillin, antimalarial drugs, albendazole, Vit. A, and ORS were available in all health posts, but only six HPs had Ready-to-Use Therapeutic Feedings, three HPs had ORT Corners, and none of the HPs had functional timers.
This evaluation assessed the implementation status of the ICCM program, focusing mainly on availability, compliance, and acceptability dimensions. The overall implementation status of the program was judged as good. The availability dimension is compromised due to stock-outs of chloroquine syrup, cotrimoxazole, and vitamin K and the inaccessibility of clean water supply in some health posts. Educational statuses of caregivers, availability of prescribed drugs at the HPs, time to arrive to HPs, and waiting time to receive the service were the factors associated with the acceptability of the ICCM program.
Therefore, continuous supportive supervision for health facilities, and refreshment training for HEW’s to maximize compliance are recommended. Materials and supplies shall be delivered directly to the health centers or health posts to solve the transportation problem. HEWs shall document the assessment findings and the services provided using the registration format to identify their gaps, limitations, and better performances. The health facilities and local administrations should construct clean water sources for health facilities. Furthermore, we recommend for future researchers and program evaluators to conduct longitudinal studies to know the causal relationship of the program interventions and the outcomes.
Data availability
Data will be available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
Ethiopian Demographic and Health Survey
Health Center/Health Facility
Health Extension Program
Health Extension Workers
Health Post
Health Sector Development Plan
Integrated Community Case Management of Common Childhood Illnesses
Information Communication and Education
Integrated Family Health Program
Integrated Management of Neonatal and Childhood Illness
Integrated Supportive Supervision
Maternal and Child Health
Mid Upper Arm Circumference
Non-Government Organization
Oral Rehydration Salts
Outpatient Therapeutic program
Primary health care unit
Rapid Diagnostics Test
Ready to Use Therapeutic Foods
Sever Acute Malnutrition
South Nation Nationalities People Region
United Nations International Child Emergency Fund
World Health Organization
Brenner JL, Barigye C, Maling S, Kabakyenga J, Nettel-Aguirre A, Buchner D, et al. Where there is no doctor: can volunteer community health workers in rural Uganda provide integrated community case management? Afr Health Sci. 2017;17(1):237–46.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mubiru D, Byabasheija R, Bwanika JB, Meier JE, Magumba G, Kaggwa FM, et al. Evaluation of integrated community case management in eight districts of Central Uganda. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(8):e0134767.
Samuel S, Arba A. Utilization of integrated community case management service and associated factors among mothers/caregivers who have sick eligible children in southern Ethiopia. Risk Manage Healthc Policy. 2021;14:431.
Article Google Scholar
Kavle JA, Pacqué M, Dalglish S, Mbombeshayi E, Anzolo J, Mirindi J, et al. Strengthening nutrition services within integrated community case management (iCCM) of childhood illnesses in the Democratic Republic of Congo: evidence to guide implementation. Matern Child Nutr. 2019;15:e12725.
Miller NP, Amouzou A, Tafesse M, Hazel E, Legesse H, Degefie T, et al. Integrated community case management of childhood illness in Ethiopia: implementation strength and quality of care. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014;91(2):424.
WHO. Annual report 2016: Partnership and policy engagement. World Health Organization, 2017.
Banteyerga H. Ethiopia’s health extension program: improving health through community involvement. MEDICC Rev. 2011;13:46–9.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Wang H, Tesfaye R, Ramana NV, Chekagn G. CT. Ethiopia health extension program: an institutionalized community approach for universal health coverage. The World Bank; 2016.
Donnelly J. Ethiopia gears up for more major health reforms. Lancet. 2011;377(9781):1907–8.
Legesse H, Degefie T, Hiluf M, Sime K, Tesfaye C, Abebe H, et al. National scale-up of integrated community case management in rural Ethiopia: implementation and early lessons learned. Ethiop Med J. 2014;52(Suppl 3):15–26.
Google Scholar
Miller NP, Amouzou A, Hazel E, Legesse H, Degefie T, Tafesse M et al. Assessment of the impact of quality improvement interventions on the quality of sick child care provided by Health Extension workers in Ethiopia. J Global Health. 2016;6(2).
Oliver K, Young M, Oliphant N, Diaz T, Kim JJNYU. Review of systematic challenges to the scale-up of integrated community case management. Emerging lessons & recommendations from the catalytic initiative (CI/IHSS); 2012.
FMoH E. Health Sector Transformation Plan 2015: https://www.slideshare.net . Accessed 12 Jan 2022.
McGorman L, Marsh DR, Guenther T, Gilroy K, Barat LM, Hammamy D, et al. A health systems approach to integrated community case management of childhood illness: methods and tools. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 2012;87(5 Suppl):69.
Young M, Wolfheim C, Marsh DR, Hammamy D. World Health Organization/United Nations Children’s Fund joint statement on integrated community case management: an equity-focused strategy to improve access to essential treatment services for children. The American journal of tropical medicine and hygiene. 2012;87(5 Suppl):6.
Ezbakhe F, Pérez-Foguet A. Child mortality levels and trends. Demographic Research.2020;43:1263-96.
UNICEF, Ending child deaths from pneumonia and diarrhoea. 2016 report: Available at https://data.unicef.org. accessed 13 Jan 2022.
UNITED NATIONS, The Millinium Development Goals Report 2015: Available at https://www.un.org.Accessed 12 Jan 2022
Bent W, Beyene W, Adamu A. Factors Affecting Implementation of Integrated Community Case Management Of Childhood Illness In South West Shoa Zone, Central Ethiopia 2015.
Abdosh B. The quality of hospital services in eastern Ethiopia: Patient’s perspective.The Ethiopian Journal of Health Development. 2006;20(3).
Young M, Wolfheim C, Marsh DR, Hammamy DJTAjotm, hygiene. World Health Organization/United Nations Children’s Fund joint statement on integrated community case management: an equity-focused strategy to improve access to essential treatment services for children.2012;87(5_Suppl):6–10.
Obrist B, Iteba N, Lengeler C, Makemba A, Mshana C, Nathan R, et al. Access to health care in contexts of livelihood insecurity: a framework for analysis and action.PLoS medicine. 2007;4(10):e308.
Carroll C, Patterson M, Wood S, Booth A, Rick J, Balain S. A conceptual framework for implementation fidelity. Implementation science. 2007;2(1):1–9.
Dunalo S, Tadesse B, Abraham G. Implementation Evaluation of Integrated Community Case Management of Common Childhood Illness (ICCM) Program in Soro Woreda, Hadiya Zone Southern Ethiopia 2017 2017.
Asefa G, Atnafu A, Dellie E, Gebremedhin T, Aschalew AY, Tsehay CT. Health System Responsiveness for HIV/AIDS Treatment and Care Services in Shewarobit, North Shewa Zone, Ethiopia. Patient preference and adherence. 2021;15:581.
Gebremedhin T, Daka DW, Alemayehu YK, Yitbarek K, Debie A. Process evaluation of the community-based newborn care program implementation in Geze Gofa district,south Ethiopia: a case study evaluation design. BMC pregnancy and childbirth. 2019;19(1):1–13.
Pitaloka DS, Rizal A. Patient’s satisfaction in antenatal clinic hospital Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia. Jurnal Kesihatan Masyarakat (Malaysia). 2006;12(1):1–10.
Teshale G, Debie A, Dellie E, Gebremedhin T. Evaluation of the outpatient therapeutic program for severe acute malnourished children aged 6–59 months implementation in Dehana District, Northern Ethiopia: a mixed-methods evaluation. BMC pediatrics. 2022;22(1):1–13.
Mason E. WHO’s strategy on Integrated Management of Childhood Illness. Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 2006;84(8):595.
Shaw B, Amouzou A, Miller NP, Tafesse M, Bryce J, Surkan PJ. Access to integrated community case management of childhood illnesses services in rural Ethiopia: a qualitative study of the perspectives and experiences of caregivers. Health policy and planning.2016;31(5):656 – 66.
Organization WH. Annual report 2016: Partnership and policy engagement. World Health Organization, 2017.
Berhanu D, Avan B. Community Based Newborn Care Baseline Survey Report Ethiopia,October 2014.
Save the children, Enhancing Ethiopia’s Health Extension Package in the Southern Nations and Nationalities People’s Region (SNNPR) Shebedino and Lanfero Woredas report.Hawassa;. 2012: Avalable at https://ethiopia.savethechildren.net
Kolbe AR, Muggah R, Hutson RA, James L, Puccio M, Trzcinski E, et al. Assessing Needs After the Quake: Preliminary Findings from a Randomized Survey of Port-au-Prince Households. University of Michigan/Small Arms Survey: Available at https://deepbluelibumichedu PDF. 2010.
Teferi E, Teno D, Ali I, Alemu H, Bulto T. Quality and use of IMNCI services at health center under-five clinics after introduction of integrated community-based case management (ICCM) in three regions of Ethiopia. Ethiopian Medical Journal. 2014;52(Suppl 3):91 – 8.
Last 10 Km project, Integrated Community Case Management (iCCM) Survey report in Amhara, SNNP, and Tigray Regions, 2017: Avaialable at https://l10k.jsi.com
Tumuhamye N, Rutebemberwa E, Kwesiga D, Bagonza J, Mukose A. Client satisfaction with integrated community case management program in Wakiso District, Uganda, October 2012: A cross sectional survey. Health scrip org. 2013;2013.
EPHI. Ethiopia service provision assessment plus survey 2014 report: available at http://repository.iifphc.org
Gintamo B. EY, Assefa Y. Implementation Evaluation of IMNCI Program at Public Health Centers of Soro District, Hadiya Zone, Southern Ethiopia,. 2017: Available at https://repository.ju.edu.et
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to University of Gondar and Gondar town health office for its welcoming approaches. We would also like to thank all of the study participants of this evaluation for their information and commitment. Our appreciation also goes to the data collectors and supervisors for their unreserved contribution.
No funding is secured for this evaluation study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Metema District Health office, Gondar, Ethiopia
Mekides Geta
Department of Health Systems and Policy, Institute of Public Health, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Gondar, P.O. Box 196, Gondar, Ethiopia
Geta Asrade Alemayehu, Wubshet Debebe Negash, Tadele Biresaw Belachew, Chalie Tadie Tsehay & Getachew Teshale
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the preparation of the manuscript. M.G. conceived and designed the evaluation and performed the analysis then T.B.B., W.D.N., G.A.A., C.T.T. and G.T. revised the analysis. G.T. prepared the manuscript and all the authors revised and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Getachew Teshale .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethical approval was obtained from Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Institute of Public Health, College of Medicine and Health sciences, University of Gondar (Ref No/IPH/1482/2013). Informed consent was obtained from all subjects and/or their legal guardian(s).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All authors declared that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Geta, M., Alemayehu, G.A., Negash, W.D. et al. Evaluation of integrated community case management of the common childhood illness program in Gondar city, northwest Ethiopia: a case study evaluation design. BMC Pediatr 24 , 310 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-024-04785-0
Download citation
Received : 20 February 2024
Accepted : 22 April 2024
Published : 09 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-024-04785-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Integrated community case management
BMC Pediatrics
ISSN: 1471-2431
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
strategies of hiring managers to hire employees for organizational fit, the case study. design was the appropriate design for exploring the research question. Reviewing previous research studies that utilize the case study design aided with. solidifying the reasoning for using this method within this research study.
Although case studies have been discussed extensively in the literature, little has been written about the specific steps one may use to conduct case study research effectively (Gagnon, 2010; Hancock & Algozzine, 2016).Baskarada (2014) also emphasized the need to have a succinct guideline that can be practically followed as it is actually tough to execute a case study well in practice.
The purpose of case study research is twofold: (1) to provide descriptive information and (2) to suggest theoretical relevance. Rich description enables an in-depth or sharpened understanding of the case. It is unique given one characteristic: case studies draw from more than one data source. Case studies are inherently multimodal or mixed ...
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Abstract. This working paper reports on a major Harvard Business School project designed to enhance MBA and practicing executives in case learning. The work is built on the foundation of HBS field cases employing the monomyth "hero's journey" classic story structure along with the creation of associated fictional case characters designed ...
communication, involvement, strong leadership and understanding the change context. This. Dissertation sought to establish factors affecting change management using a sin gle case study of. an NGO ...
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Change Management. New research on change management from Harvard Business School faculty on issues including how to plan for opportunities, how to effect change in the workplace, and case studies on how business leaders managed the economic crisis. Page 1 of 66 Results →. 12 Dec 2023.
by Aaron Chatterji, Solene Delecourt, Sharique Hasan, and Rembrand Koning. This study of 100 high-growth startups in India finds that founder-executives can learn how to improve their management style from their peers at other firms. These interfirm network connections between founders may help explain why some companies are well managed and ...
Fifty four percent of raw case users came from outside the U.S.. The Yale School of Management (SOM) case study directory pages received over 160K page views from 177 countries with approximately a third originating in India followed by the U.S. and the Philippines. Twenty-six of the cases in the list are raw cases.
Bachelor Thesis 19 April 2022 . Abstract ... The Role of Middle Level Managers in Strategic Change and Decision-Making in a company: A Case Study of Swappie. Number of Pages: 33 pages + 3 appendices Date: 19 April 2022 Degree: Metropolia Business School ... In order to understand the importance of middle managers, case study on Swappie's RMA
A key aim of this study was to undcrstandthc role managers play in the support and success of Employee Assistance Programmes (EAP} within the context of well-being. Through the approach of a case study with 13 participants within an identified organisation, the research study investigated the perceptions of managers, well-being subject matter ...
My hypothesis is that successful female leaders adopt a transformational leadership. style and have a high level of emotional intelligence, as compared to unsuccessful leaders who. will adopt more of a transactional style of leadership and have a lower level of emotional. intelligence. 4.
multiple case study was to explore challenges faced by this population. Avruch's theory of culture, the Human needs theory by Burton, and the cross-cultural adaptation theory by Kim were the conceptual frameworks for this study. Participants included 15 project managers or senior leaders of multicultural software development teams in Nigeria and
Title of study The importance of strategic management, Case study of H&M Type of project Thesis Date 27.4.2011 Pages 59+12 Supervisor(s) of study 1st Antti Iire 2nd Anneli Juutilainen Executive organization H&M in Kuopio,Finland Abstract Hennes & Mauritz (H&M) is a 100 billion Sweden company, engaged in designing and
PSD acts as human resource manager to the management and. development of high -performing, dynamic, effective, efficient, and fair human resources to establish. an outstanding and people -oriented ...
The thesis will look into two different project management case studies: the Bilbao Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao Spain, and the San Roque Power Facility on the Lower Agnos River in the Philippines. The objective of the thesis is to analyze two case studies from a project management perspective in order to make an evaluation
The project management case studies listed below place the students in the position of the project manager, sponsor, and other stakeholders. Students develop problem solving skills by critically analyzing the various scenarios. The case studies are broken down to allow for easy integration with the various lecture topics of PM-1.
A thesis submitted to the Faculty of Liberty University By Jessica Windsor In partial fulfillment of The requirements for the degree of Master of Public Administration Disaster Management March 2021 . Emergency Management: A Case Study of Special Needs Populations and Disaster Preparedness By Jessica Windsor Liberty University APPROVED BY: Dr ...
Stress Management - A Case Study. Dr. Radhika Kapur. Abstract. Stress is considered to be an integral part of ones life; stress can be any kind of worry, anxiety, hassle, trauma, tension, pain ...
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Division of Construction Management. Chalmers University of Technology SE-412 96 Göteborg Sweden Telephone: + 46 (0)31-772 1000. Sweden 2011. Risk Management Practices in a Construction Project - a case study. Master of Science Thesis in the Master's Programme.
Dissertation topics in Finance related to Retail and Commercial Banking. 1. The Impact of Digital Transformation on Retail and Commercial Banking: A Case Study of a Specific Bank. 2. Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty in Retail Banking: An Analysis of Service Quality Dimensions. 3.
This research study was designed to learn from social work case managers practicing in the field of social work in urban northeast Ohio. The utilization of the Maslach Burnout Inventory-Human Services Survey (MBI-HSS) can indicate social work case managers who are at risk for burnout (Quinn-Lee et al., 2014).
Summary. Job seekers worry about negotiating an offer for many reasons, including the worst-case scenario that the offer will be rescinded. Across a series of seven studies, researchers found that ...
For the past 40 years or so, private equity (PE) buyout managers largely invested capital in an environment of declining interest rates and escalating asset prices. During that period, they were able to rely on financial leverage, enhanced tax and debt structures, and increasing valuations on high-quality assets to generate outsize returns for investors and create value.
Integrated Community Case Management (ICCM) of common childhood illness is one of the global initiatives to reduce mortality among under-five children by two-thirds. It is also implemented in Ethiopia to improve community access and coverage of health services. However, as per our best knowledge the implementation status of integrated community case management in the study area is not well ...
However, enhancing community flood resilience presents numerous obstacles and potential downsides. To address such a challenge, this dissertation investigates the interactions among natural, built environment, and actor systems using a case study of flooding in Jakarta, Indonesia, focusing on the Ciliwung river watershed.