The 8 Parts of Speech in English Grammar


Table of Contents
Introduction, what are parts of speech, a list of 8 parts of speech.
A. Action Verbs : Action verbs denote physical or mental actions and are the most common type of verbs. These verbs can be conjugated in simple and continuous tenses
C. Linking Verbs: Linking verbs connect the subject of a sentence to a subject complement, which describes or identifies the subject.
READ MOR ABOUT VERBS
Prepositions
Conjunctions, interjections, analyzing sentence structure (parts of speech) .
- My Storyboards
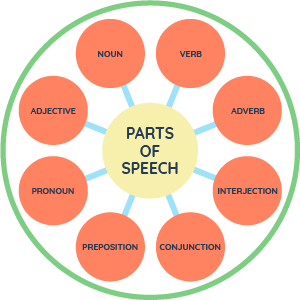
8 Parts of Speech
Parts of speech are an important aspect of the language taught in English Language Arts and English as a New Language classrooms. Not only do the parts of speech help in formulating correct sentences, they also help the reader to understand what is taking place. As a staple of clear communication and analysis, mastery of the parts of speech is essential for students. The eight parts of speech chart on the right is a great visual for displaying the 8 categories of words that are included.
Teachers use a variety of different approaches to engage students in their parts of speech lesson plans. One popular idea for a "bodily kinesthetic" activity for parts of speech is to conduct a scavenger hunt to have students identify the 8 different parts of speech existing around the classroom. There is also the classic lesson on parts of speech that instructs students to diagram and label sentences provided by the teacher.
A parts of speech writing activity could begin with students first writing about a simple topic like what they are going to do after school. After they have their sentences down, they could work individually or with a partner to label each of the 8 parts of speech. Another fun part of speech activity is to have students play "Grammar Bingo". They can fill in a bingo card that includes all 8 parts of speech!
These are all effective activities for part of speech where students can see the language in action or on paper and identify these important grammatical elements. However, the reality is that this particular part of language learning and development can be boring and dry for students. Teachers can liven up their parts of speech lesson plans for elementary, middle and high school students with Storyboard That!
Storyboard That can help teachers use more creative ways to teach parts of speech!
The 8 Parts of Speech Lessons Help You
- Understand clearly what is being said in a sentence.
- Know how and when to use words correctly.
- Reflect more accurately on the English language.
What are the Parts of Speech?
| Part of Speech | Definition | Example Words |
|---|---|---|
| a person, place, thing, or idea | pen, dog, work, music, town, London, teacher, John | |
| action or state of being | (to) be, have, do, like, work, sing, can, must | |
| a quality of a noun | some, good, big, red, interesting | |
| describes or modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb | quickly, silently, well, badly, very, really | |
| stands in for a noun | I, you, he, she, we, they, your | |
| links a noun to another word | to, at, after, on, before, around, over, of, in, for, with, throughout, from, beneath | |
| joins words, clauses, and sentences | and, but, when, or, however, although, nevertheless, therefore, yet, so | |
| short exclamation, sometimes inserted into a sentence | oh, ouch, hi, well |
Do You Know Each Part of Speech?
| ANSWER (Part of Speech) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| That hurts! | How are you? | I don't know. | |
| I like dogs I like cats. | I like cats dogs. | I like dogs, I don't like cats. | |
| Tara is smart. is going to college three years early. | George wants paper back. | Rashad wants a book, so goes to the library. | |
| Facebook.com a website. | I Facebook.com. | I my Facebook every day. | |
| This is my . | He lives in my . | We live in . | |
| We went school Monday. | Please look the bed | The book is a boy who gets lost the woods. | |
| My dog is . | I like dogs. | My German Shepherd is than your Chihuahua. | |
| My dog eats . | When he is hungry, he eats . | I get out of bed . | |
8 Parts of Speech Activity
The parts of speech activity below shows how you can use the Storyboard That Creator to make storyboards depicting the different parts of speech, in this case three different verbs. Teachers can quickly create a parts of speech lesson plan using the "create an assignment" wizard where they can input directions and even a template to help students get started. The template could include the titles of the parts of speech for students to depict such as:

8 Parts of Speech Lesson Plans
In reading and writing, it is important to make clear for your audience who or what is most important in a sentence, what is happening, and other important details that enhance the information being conveyed. Using the Storyboard Creator in your parts of speech lesson allows students to make visual depictions of the parts of speech and help them remember these important pieces of writing!
Some General Elementary School Parts of Speech Activity Ideas
- Use Storyboard That’s parts of speech template to create your own storyboard using the 8 parts of speech.
- Provide students with a sentence that has certain underlined or highlighted words by replacing "EXAMPLE SENTENCE".
Note: If you're not a Storyboard That user yet, sign up for a free trial .
- Have students make a visualization of the sentences on the storyboard.
- While creating the storyboards, students will make sure to point out which part of speech they are illustrating by drawing attention to the word using an arrow or other indicator.
- Lesson Extension: Have students come up with their own sentences and use storyboards to depict them!
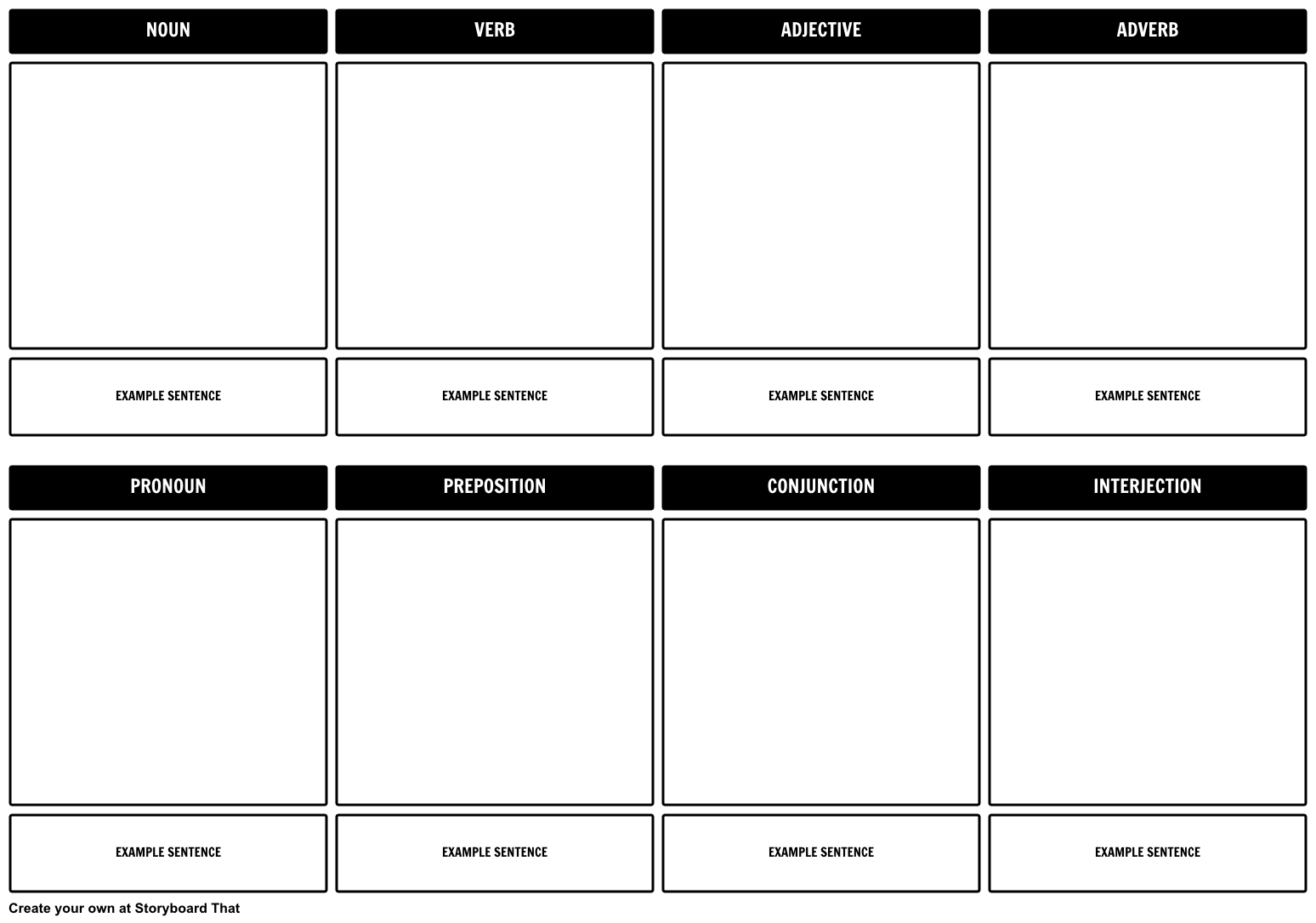
Example Project for the 8 Parts of Speech

More Parts of Speech Project Ideas
- Make a storyboard that describes and illustrates the most common prepositions.
- Make a T-chart that illustrates examples of action verbs and nonaction verbs.
- Choose at least one prepositional phrase and make a storyboard to illustrate it.
- Make a storyboard that illustrates adjectives that express emotion. Teachers can either give students a list so that students all have the same words, or have students choose their own.
- Research and define the many different speech definitions such as: independent clauses, complex sentences, main verbs, and so much more!
- A fun adverbs project idea is to have students answer a prompt in the storyboard such as the one below. The teacher can include the prompt in the template and have the students write and illustrate their answer using as many other adverbs as they can! To modify this assignment, the template could include the description box on the bottom where students can write more full sentences showing their understanding of how to use adverbs. This project could also be modified to be an activity for any of the 8 parts of speech.
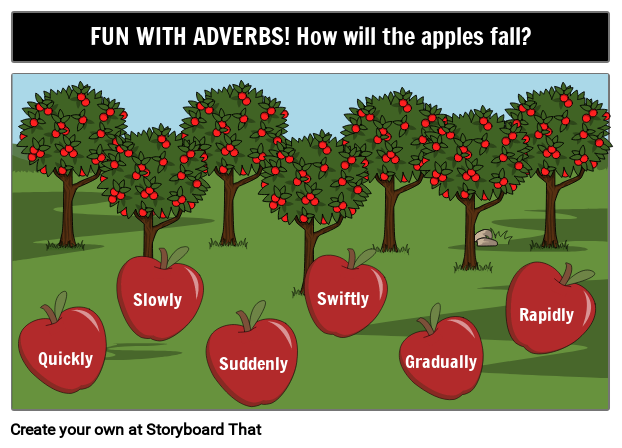
Related Activities

How to Teach Parts of Speech with Games and Activities
Choose games and activities.
Select games and activities that are engaging and appropriate for the age and skill level of your students. Examples of games and activities that teach parts of speech include Mad Libs, Charades, Parts of Speech Bingo, Parts of Speech Jeopardy, and Word Sorts.
Define Parts of Speech
Before starting the games and activities, make sure your students understand the basics of parts of speech. Define and provide examples of the main parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
Model Parts of Speech Use
Model the use of different parts of speech to ensure that students understand how they function in language. Use sentences or examples from the games or activities you have chosen to illustrate the different parts of speech.
Play Games and Activities
Play the games and activities with your students, making sure to explain the rules and provide any necessary guidance. Encourage active participation and engagement from all students, and provide support or additional practice for students who may need it.
Reinforce Learning
After playing the games and activities, reinforce learning by reviewing the parts of speech used and how they function in language. Ask students to explain how they used different parts of speech in the games and activities and provide feedback or corrections as needed.
Create Your Own Games and Activities
Encourage students to create their own games and activities that incorporate parts of speech. This can help them solidify their understanding of the concepts and provide opportunities for peer teaching and learning.
Assess Understanding
Finally, assess students' understanding of parts of speech through quizzes, writing assignments, or other assessments. Make sure that your assessments reflect the skills and knowledge you want students to acquire, such as identifying parts of speech and using them correctly in context. Use the results of your assessments to guide further instruction and support for students who may need it.
Frequently Asked Questions about 8 Parts of Speech
What is included in a parts of speech chart.
The 8 parts of speech to include in a parts of speech chart are:
- Noun : Nouns are a person, place, thing, or idea
- Verb : Verbs are actions or states of being
- Adjective : Adjectives describe nouns
- Adverb : Adverbs describe a verb, adjective or another adverb
- Pronoun : Pronouns stand in for a noun
- Preposition : Prepositions link a noun to another word
- Conjunction : Conjunctions join words, clauses, and sentences
- Interjection : Interjections are short exclamations
What are some parts of speech activities to do with students?
There are many 8 parts of speech lesson plans that incorporate the storyboard Creator that will help students visualize and be able to demonstrate their understanding. Some parts of speech activities using the Storyboard That Creator are:
- Create a visual part of speech diagram of a sentence using a storyboard! Many teachers instruct students to diagram parts of speech in their sentences by underlining or circling different parts of speech. However, by illustrating what is occurring in the sentence and how those parts of speech are related, students are more apt to retain the information.
- Create a list of all of the different parts of speech with illustrations and definitions.
- Make a quiz for a fellow classmate!
How can teachers create parts of speech lesson plans in Storyboard That?
Creating assignments in Storyboard That is as easy as 1-2-3! The easiest way to create a lesson is to copy one of our awesome premade lesson plans and customize it how you see fit. To create a lesson from scratch, simply follow the “create an assignment” steps.
What is the difference between proper nouns and common nouns?
The difference between a proper noun and a common noun is that a common noun refers to general things, such as a mountain, river, or lake. A proper noun, however, refers to a specific noun, such as Mt. Everest, Nile River, or Lake Michigan.
Try 1 Month For
30 Day Money Back Guarantee New Customers Only Full Price After Introductory Offer
Learn more about our Department, School, and District packages
- 30 Day Money Back Guarantee
- New Customers Only
- Full Price After Introductory Offer
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Parts of speech
The 8 Parts of Speech | Chart, Definition & Examples

A part of speech (also called a word class ) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and interjections . Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles .
Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on how they are used. For example, “laugh” can be a noun (e.g., “I like your laugh”) or a verb (e.g., “don’t laugh”).
Table of contents
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Other parts of speech
Interesting language articles, frequently asked questions.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, concept, place, or thing. Nouns can act as the subject of a sentence (i.e., the person or thing performing the action) or as the object of a verb (i.e., the person or thing affected by the action).
There are numerous types of nouns, including common nouns (used to refer to nonspecific people, concepts, places, or things), proper nouns (used to refer to specific people, concepts, places, or things), and collective nouns (used to refer to a group of people or things).
Ella lives in France .
Other types of nouns include countable and uncountable nouns , concrete nouns , abstract nouns , and gerunds .
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Pronouns typically refer back to an antecedent (a previously mentioned noun) and must demonstrate correct pronoun-antecedent agreement . Like nouns, pronouns can refer to people, places, concepts, and things.
There are numerous types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (used in place of the proper name of a person), demonstrative pronouns (used to refer to specific things and indicate their relative position), and interrogative pronouns (used to introduce questions about things, people, and ownership).
That is a horrible painting!
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., “jump”), occurrence (e.g., “become”), or state of being (e.g., “exist”). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
Verbs can change form depending on subject (e.g., first person singular), tense (e.g., simple past), mood (e.g., interrogative), and voice (e.g., passive voice ).
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding“-ed” to the end of the word (or “-d” if the word already ends in “e”). Irregular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participles are formed in some other way.
“I’ve already checked twice.”
“I heard that you used to sing .”
Other types of verbs include auxiliary verbs , linking verbs , modal verbs , and phrasal verbs .
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive , appearing before a noun (e.g., “a red hat”), or predicative , appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like “to be” (e.g., “the hat is red ”).
Adjectives can also have a comparative function. Comparative adjectives compare two or more things. Superlative adjectives describe something as having the most or least of a specific characteristic.
Other types of adjectives include coordinate adjectives , participial adjectives , and denominal adjectives .
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding “-ly” to the end of an adjective (e.g., “slow” becomes “slowly”), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
There are numerous types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner (used to describe how something occurs), adverbs of degree (used to indicate extent or degree), and adverbs of place (used to describe the location of an action or event).
Talia writes quite quickly.
Other types of adverbs include adverbs of frequency , adverbs of purpose , focusing adverbs , and adverbial phrases .
A preposition is a word (e.g., “at”) or phrase (e.g., “on top of”) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time , place , and direction .
I left the cup on the kitchen counter.
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
The main types of conjunctions are coordinating conjunctions (used to connect items that are grammatically equal), subordinating conjunctions (used to introduce a dependent clause), and correlative conjunctions (used in pairs to join grammatically equal parts of a sentence).
You can choose what movie we watch because I chose the last time.
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of interjections include volitive interjections (used to make a demand or request), emotive interjections (used to express a feeling or reaction), cognitive interjections (used to indicate thoughts), and greetings and parting words (used at the beginning and end of a conversation).
Ouch ! I hurt my arm.
I’m, um , not sure.
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
- Determiners
A determiner is a word that describes a noun by indicating quantity, possession, or relative position.
Common types of determiners include demonstrative determiners (used to indicate the relative position of a noun), possessive determiners (used to describe ownership), and quantifiers (used to indicate the quantity of a noun).
My brother is selling his old car.
Other types of determiners include distributive determiners , determiners of difference , and numbers .
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general.
- The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., “the door,” “the energy,” “the mountains”).
- The indefinite articles a and an refer to general or unspecific nouns. The indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns (e.g., “a poster,” “an engine”).
There’s a concert this weekend.
If you want to know more about nouns , pronouns , verbs , and other parts of speech, make sure to check out some of our language articles with explanations and examples.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Proper nouns
- Collective nouns
- Personal pronouns
- Uncountable and countable nouns
- Verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Types of verbs
- Active vs passive voice
- Subject-verb agreement
A is an indefinite article (along with an ). While articles can be classed as their own part of speech, they’re also considered a type of determiner .
The indefinite articles are used to introduce nonspecific countable nouns (e.g., “a dog,” “an island”).
In is primarily classed as a preposition, but it can be classed as various other parts of speech, depending on how it is used:
- Preposition (e.g., “ in the field”)
- Noun (e.g., “I have an in with that company”)
- Adjective (e.g., “Tim is part of the in crowd”)
- Adverb (e.g., “Will you be in this evening?”)
As a part of speech, and is classed as a conjunction . Specifically, it’s a coordinating conjunction .
And can be used to connect grammatically equal parts of a sentence, such as two nouns (e.g., “a cup and plate”), or two adjectives (e.g., “strong and smart”). And can also be used to connect phrases and clauses.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, what is a collective noun | examples & definition.
- What Is an Adjective? | Definition, Types & Examples
- Using Conjunctions | Definition, Rules & Examples
More interesting articles
- Definite and Indefinite Articles | When to Use "The", "A" or "An"
- Ending a Sentence with a Preposition | Examples & Tips
- What Are Prepositions? | List, Examples & How to Use
- What Is a Determiner? | Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Interjection? | Examples, Definition & Types
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Log In 0 The website uses cookies for functionality and the collection of anonymised analytics data. We do not set cookies for marketing or advertising purposes. By using our website, you agree to our use of cookies and our privacy policy . We're sorry, but you cannot use our site without agreeing to our cookie usage and privacy policy . You can change your mind and continue to use our site by clicking the button below. This confirms that you accept our cookie usage and privacy policy.
Free English Lessons
Parts of speech in english – video.
Download PDF

In this lesson, you can learn about parts of speech in English.
How many parts of speech are there in english can you name them, and explain what they do, understanding parts of speech —nouns, verbs, adjectives, and so on—can help you to understand english sentence structure and how english grammar works., in this class, you’ll learn the basic information about parts of speech, you’ll see some ways that parts of speech can be more complicated than you might expect, and you’ll have several chances to practice, quiz: parts of speech in english.
Now test your understanding of the different parts of speech by trying this quiz. There are 20 questions, which get harder as you go through it!
When you have finished, click ‘View Questions’ to see all the correct answers and read the explanations. There are links to further study resources in the explanations.
Quiz Summary
0 of 20 Questions completed
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 20 Questions answered correctly
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), ( 0 )
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0 , ( 0 ) 0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0 )
| Average score | |
| Your score |
- Not categorized 0%
Well done! You’ve finished!
That’s an excellent score and this quiz is extremely difficult! Congratulations!
A perfect score on an incredibly difficult quiz! Congratulations!
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
1 . Question
For the first five questions, answer true or false.
True or false: a word can be different parts of speech depending on its function and meaning in the sentence.
Review part three of the lesson if you need help with this one.
2 . Question
True or false: a noun can be a word or a phrase.
3 . Question
True or false: if a word can be a noun, it can only be a noun.
4 . Question
True or false: when analysing parts of speech, you don’t need to think about what the sentence means.
5 . Question
True or false: articles (‘the’, ‘a’), demonstratives (‘this’, ‘that’), quantifiers (‘some’, ‘few’) and possessive adjectives (‘your’, ‘their’) are all determiners.
Remember that determiners specify the noun you’re referring to. Do all these words do this?
6 . Question
For the next five questions, choose the part of speech described.
What part of speech can be an action or a state?
- Interjections
- Conjunctions
‘Run’ is an action and ‘understand’ is a state.
7 . Question
What part of speech can describe verbs, adjectives, adverbs or whole sentences?
- Prepositions
8 . Question
What part of speech represents or replaces nouns?
9 . Question
What part of speech expresses an emotion or can be used to react to something?
10 . Question
Which part of speech doesn’t indicate something about a noun?
- Determiners
11 . Question
For the next five questions, match the words in the sentence with the parts of speech.
“He slept badly.”
Sort elements
12 . Question
Match the words in the sentence with the parts of speech.
“She has bought a second-hand car.”
- noun phrase
This time, you’re not analysing each word but the function of word groups and phrases in the sentence.
13 . Question
“Um, can you stop making so much noise, please?”
- ‘um’ and ‘please’
- 'can' and 'stop'
- 'you'
- 'making so much noise'
14 . Question
“Is this your bag or mine?”
- conjunction
- (possessive) pronoun
15 . Question
“Hey! Give his new watch back to him.”
- interjection
- preposition
16 . Question
For the last five questions, tick all the words that are correct.
Which words can be nouns?
You need to choose three answers.
17 . Question
Which words can be adverbs?
Only one word here is not an adverb.
18 . Question
Which words can be determiners?
This time there are two correct answers.
19 . Question
Which words can be more than one part of speech?
Two answers are correct; one of the others doesn’t even exist!
20 . Question
Which words are conjunctions?
- nevertheless
This is a deliberately difficult question to end with! A conjunction must be followed by a noun (or noun phrase) and then a verb, with no commas.
So, first question: how many parts of speech are there?
Well, we did a Google search, and many of the top results said ‘eight’. So there must be eight parts of speech in English.
Wrong! There are nine.
So, what are they?
1. Guide to Parts of Speech in English
Number one: nouns. Nouns can be things, animals, or people, like doctor, pencil, tree or cat.
Nouns can also be ideas or abstract things, like idea, happiness, time or money.

Number two: verbs. Verbs can be actions, like do, run, fly or win.
Verbs can also describe states, like be, love, believe or understand.
Number three: adjectives. Adjectives describe nouns. For example: red, big, metal, or beautiful.
Number four: adverbs . Adverbs can describe verbs, meaning they describe how someone does something. For example, quickly, loudly, angrily or well.
Adverbs can also describe adjectives, other adverbs, or even whole sentences. For example, very is an adverb which can describe an adjective— very slow —or another adverb— very slowly.
Unfortunately or sometimes are adverbs which can be used to add information to a whole sentence.
For example:
- Unfortunately, they missed the train and were late to their own wedding!
- Sometimes, I wish I’d made different choices in life.
So, adverbs are a little more complicated. Here’s a good way to remember it: adjectives and adverbs both describe other words. They are both used to add information to something else.
Adjectives describe nouns, and adverbs describe everything else: verbs, adjectives, adverbs and whole sentences.
Number five: pronouns.
Pronouns replace or represent nouns. For example, I, you, she or they are pronouns which represent different people.
You use pronouns to avoid repeating the same word, or to refer to something when it’s obvious what you mean.
- How was the weather there?
There is a pronoun which refers to a place. If you’ve already mentioned the place you’re talking about, you don’t need to say it again.
Another example:
- Give me two, please.
Two is a pronoun which refers to a quantity of something which has already been mentioned. The person you’re talking to already knows what you’re talking about.
Number six: prepositions.
Prepositions usually go before a noun or noun phrase. What’s their job?
Prepositions can do two basic things: first, they can add an idea of time, place, or movement to a noun. For example:
- on Wednesday
- in the corner
- towards the door
Secondly, prepositions can connect other words to a noun, or a pronoun.
For example, think about the verb depend on. The preposition on connects the verb depend to the object of the verb. For example:
- It depends on the cost.
Usually, the noun or noun phrase goes after the preposition.
However, sometimes the preposition can link to a noun (or pronoun) earlier in the sentence. For example:
- What does it depend on?
Here, on links to the pronoun what.
Number seven: conjunctions.
Conjunctions connect two things. A conjunction can connect two words:
- I like cake and ice-cream.
A conjunction can connect two phrases:
- Do you want to go now or wait till this afternoon?
You can also use a conjunction to connect two clauses:
- Although I’ve been trying to learn for years, I’m still really bad at drawing.
Number eight: determiners
Determiners go before a noun. They include words like a, the, this or that, which help to specify which noun you’re talking about.
Words like my, your, his, her, etc. are also determiners. They specify which noun you’re talking about by saying who something belongs to.
Determiners can also tell you how many of something there are. Look at three examples:
- ten bananas
- some people
- both of my brothers
The words ten, some and both are determiners.
Number nine: interjections
Interjections are different, because they aren’t normally part of a sentence.
Interjections are words or phrases which show how you feel. For example:

So, now you know about the nine parts of speech in English.
2. Practice with Parts of Speech in English
Let’s practice! Look at three sentences. Each sentence has five words.
- They told me about it.
- Look in the big cupboard.
- Put it there, but carefully.
Can you identify which part of speech each word is? Pause the video and think about your answers.
How did you do? Could you identify the parts of speech correctly?
Let’s look at one more.
- I’m staying in this evening.
What part of speech are these words? Think about it.
So, I is a pronoun, am is a verb, and staying is also a verb.
What about in? Did you say it’s a preposition?
It’s not a preposition; it’s an adverb.
How does this work? We had the word in in one of the sentences you saw before, and it was a preposition.
So, what’s going on?
3. The Same Word Can be More than One Part of Speech
Some words can only be one thing.
For example, the words independence or hair can only be nouns.
Believe and destroy can only be verbs.
However, many words can be more than one part of speech.
There are two things happening here.
First, a word can be two different things, which have the same written form and the same pronunciation.
Think about the word win. Is it a noun or a verb?
It can be both.
- I’m sure they’ll win the game this weekend.
- We’ll be hoping for a win in the big game this weekend.
Many words are like this. Another example: red can be an adjective or a noun.
- What do you think about this red for the kitchen?
- I like that red top she was wearing.
This is very common: very often, a word with one written form can be two (or more) different parts of speech.
We told you there are two things happening here; what’s the other?
Sometimes, a word can be different parts of speech depending on its function in the sentence.
Look at two sentences:
- I have a few photos of my grandparents.
- Sure, you can have a few.
Here’s a question: what part of speech is few in these sentences?
In the first sentence, few is a determiner; in the second, it’s a pronoun.
Can you explain why this is?
Think about what few does in these two sentences.
In the first sentence, few adds a quantity to the noun photos. It tells us how many photos you have. This makes it a determiner.
In the second sentence, few replaces a noun. You don’t know which noun it replaces, but in context, you would understand what the person meant.
Maybe it was ‘a few biscuits’, or ‘a few pieces of paper.’
We don’t know! But, you do know that few replaces a noun, which makes it a pronoun.
Another example is the sentence we saw before:
Prepositions go with nouns, and connect nouns to other words in the sentence. In here doesn’t go with a noun, so it can’t be a preposition.
Learn more with this Oxford Online English lesson on adverbs – to, in, at .
In here means ‘at home’, and it adds information to the verb stay. What kind of words add information to verbs?
Adverbs! So, in is an adverb.
Wait a minute, did we ever finish explaining what parts of speech are in this sentence?
You’re right! We didn’t. Let’s do it now. You need to say what parts of speech the words this evening are.
Can you do it?
Maybe you said that this is a determiner, and evening is a noun. That’s technically correct, but it’s not the best answer.
The best answer is that this evening is an adverb.
How do you explain that?
4. Compound Parts of Speech in English
Until now, you’ve seen single words, and how single words can be nouns, verbs, etc.
However, when you’re thinking about parts of speech, you can’t just think about single words. Phrases can also be nouns, verbs, adjectives, and so on.
Let’s do an example:
- Add a small spoonful of brown sugar, then turn the heat down and stir the mixture gently.
Think about the first part of this sentence: add a small spoonful of brown sugar.
What parts of speech do we have here?
Of course, you can go through it word by word. You can say, add is a verb, a is a determiner, small is an adjective and so on.
But, is that the most useful way of looking at it?
It makes more sense to see this as a verb— add —and a noun— a small spoonful of brown sugar.
The noun is made up of several parts of speech: determiners, adjectives, prepositions and nouns, but together they have one meaning. These words refer to one thing.
You can analyse a sentence in several different layers. So, you can see a small spoonful of brown sugar as six individual words, or one noun phrase.
You could also see it as three parts: a determiner— a small spoonful —a preposition— of —and a noun— brown sugar.
Confused? We understand! You want to know the answer. You want to know which way is ‘correct’.
There isn’t one ‘correct’ way to see this. There are different perspectives.
A better question is: which perspective makes more sense?
In this sentence, a small spoonful of brown sugar refers to one thing in the world. So it makes sense to think of it as one part of speech in the sentence.
What about the second part of the sentence? How would you analyse the parts of speech?
As you saw before, there isn’t one right answer, but here’s a suggestion.
The sentence contains a conjunction— then —and then two verb phrases linked with the conjunction and.
This makes sense because the sentence is telling you to do two things: turn the heat down and stir the mixture gently.
So, it makes sense to see turn the heat down as one part of speech, because it’s telling you do to one thing.
Let’s put these ideas together.
First, when you think about parts of speech, you can’t just memorise information. You have to look at each sentence individually, and think about what each word is doing.
Secondly, always think about what the sentence means in the real world. Sentences aren’t abstract things; they refer to real people, real things and real actions.
There is always more than one way to analyse the parts of speech in a sentence: choose the way that makes sense based on what the sentence is telling you about real life!
Let’s do a more challenging practice exercise so you can see these ideas in action.
5. More Challenging Practice with English Parts of Speech
Look at three sentences:
- Amazing! It’s way better than I ever thought it would be.
- She was an amazing clinician , who came up with many innovative ways to treat patients.
- I don’t believe it!
How would you analyse the parts of speech in these sentences? Think about the ideas we talked about in the last section. Does it make sense to break the sentences into individual words, or is it better to group words into phrases?
Pause the video and think about your ideas.
You can pause the video again to look at these in more detail.
Notice how the same word can be different parts of speech in different sentences. For example, amazing is an interjection in one sentence, and an adjective in another.
Notice also the different layers of analysis. For example, look at the phrase many innovative ways. You can see this as one noun phrase, or as a determiner plus a noun phrase, or as three individual parts: a determiner, an adjective and a noun.
Which is correct? They all are! Choose the perspective which makes more sense to you.
Thanks for watching!
We Offer Video Licensing and Production
Use our videos in your own materials or corporate training, videos edited to your specifications, scripts written to reflect your training needs, bulk pricing available.
Interested?
More English Lessons
English grammar lessons.

- Facebook 153
- Odnoklassniki icon Odnoklassniki 0
- VKontakte 0
- Pinterest 0
- LinkedIn 29

Parts of Speech: The Ultimate Guide for Students and Teachers
This article is part of the ultimate guide to language for teachers and students. Click the buttons below to view these.
What are Parts of Speech ?
Just as a skilled bricklayer must get to grips with the trowel, brick hammer, tape measure, and spirit level, the student-writer must develop a thorough understanding of the tools of their trade too.
In English, words can be categorized according to their common syntactic function in a sentence, i.e. the job they perform.
We call these different categories Parts of Speech . Understanding the various parts of speech and how they work has several compelling benefits for our students.
Without first acquiring a firm grasp of the various parts of speech, students will struggle to fully comprehend how language works. This is essential not only for the development of their reading comprehension but their writing skills too.

Parts of speech are the core building blocks of grammar . To understand how a language works at a sentence and a whole-text level, we must first master parts of speech.
In English, we can identify eight of these individual parts of speech, and these will provide the focus for our Complete Guide to Parts of Speech .
THE EIGHT PARTS OF SPEECH (Click to jump to each section)
A complete unit on teaching figurative language.

FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE is like “SPECIAL EFFECTS FOR AUTHORS.” It is a powerful tool to create VIVID IMAGERY through words. This HUGE UNIT guides you through completely understanding FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE .
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (26 Reviews)

Often the first word a child speaks will be a noun, for example, Mum , Dad , cow , dog , etc.
Nouns are naming words, and, as most school kids can recite, they are the names of people, places, and things . But, what isn’t as widely understood by many of our students is that nouns can be further classified into more specific categories.
These categories are:
Common Nouns
Proper nouns, concrete nouns, abstract nouns, collective nouns, countable nouns, uncountable nouns.
All nouns can be classified as either common or proper .
Common nouns are the general names of people, places, and things. They are groups or classes on their own, rather than specific types of people, places, or things such as we find in proper nouns.
Common nouns can be further classified as abstract or concrete – more on this shortly!
Some examples of common nouns include:
People: teacher, author, engineer, artist, singer.
Places: country, city, town, house, garden.
Things: language, trophy, magazine, movie, book.
Proper nouns are the specific names for people, places, and things. Unlike common nouns, which are always lowercase, proper nouns are capitalized. This makes them easy to identify in a text.
Where possible, using proper nouns in place of common nouns helps bring precision to a student’s writing.
Some examples of proper nouns include:
People: Mrs Casey, J.K. Rowling, Nikola Tesla, Pablo Picasso, Billie Eilish.
Places: Australia, San Francisco, Llandovery, The White House, Gardens of Versailles.
Things: Bulgarian, The World Cup, Rolling Stone, The Lion King, The Hunger Games.
Nouns Teaching Activity: Common vs Proper Nouns
- Provide students with books suitable for their current reading level.
- Instruct students to go through a page or two and identify all the nouns.
- Ask students to sort these nouns into two lists according to whether they are common nouns or proper nouns.
As mentioned, all common and proper nouns can be further classified as either concrete or abstract .
A concrete noun is any noun that can be experienced through one of the five senses. In other words, if you can see, smell, hear, taste, or touch it, then it’s a concrete noun.
Some examples of concrete nouns include:
Abstract nouns refer to those things that can’t be experienced or identified through the five senses.
They are not physical things we can perceive but intangible concepts and ideas, qualities and states.
Some examples of abstract nouns include:
Nouns Teaching Activity: Concrete Vs. Abstract Nouns
- Provide students with a book suitable for their current reading level.
- Instruct students to go through a page or two and identify all the nouns (the lists from Practice Activity #1 may be suitable).
- This time, ask students to sort these nouns into two lists according to whether they are concrete or abstract nouns.
A collective noun is the name of a group of people or things. That is, a collective noun always refers to more than one of something.
Some examples of collective nouns include:
People: a board of directors, a team of football players, a cast of actors, a band of musicians, a class of students.
Places: a range of mountains, a suite of rooms, a union of states, a chain of islands.
Things: a bale of hay, a constellation of stars, a bag of sweets, a school of fish, a flock of seagulls.
Countable nouns are nouns that refer to things that can be counted. They come in two flavors: singular and plural .
In their singular form, countable nouns are often preceded by the article, e.g. a , an , or the .
In their plural form, countable nouns are often preceded by a number. They can also be used in conjunction with quantifiers such as a few and many .
Some examples of countable nouns include:
COUNTABLE NOUNS EXAMPLES
| a driver | two drivers |
| the house | the houses |
| an apple | a few apples |
| dog | dogs |
Also known as mass nouns, uncountable nouns are, as their name suggests, impossible to count. Abstract ideas such as bravery and compassion are uncountable, as are things like liquid and bread .
These types of nouns are always treated in the singular and usually do not have a plural form.
They can stand alone or be used in conjunction with words and phrases such as any , some , a little , a lot of , and much .
Some examples of uncountable nouns include:
UNCOUNTABLE NOUNS EXAMPLES
| Advice |
| Money |
| Baggage |
| Danger |
| Warmth |
| Milk |
Nouns Teaching Activity: How many can you list ?
- Organize students into small groups to work collaboratively.
- Challenge students to list as many countable and uncountable nouns as they can in ten minutes.
- To make things more challenging, stipulate that there must be an uncountable noun and a countable noun to gain a point.
- The winning group is the one that scores the most points.

Without a verb, there is no sentence! Verbs are the words we use to represent both internal and external actions or states of being. Without a verb, nothing happens.

There are many different types of verbs. Here, we will look at five important verb forms organised according to the jobs they perform:
Dynamic Verbs
Stative verbs, transitive verbs, intransitive verbs, auxiliary verbs.
Each verb can be classified as being either an action or a stative verb.
Dynamic or action verbs describe the physical activity performed by the subject of a sentence. This type of verb is usually the first we learn as children.
For example, run , hit , throw , hide , eat , sleep , watch , write , etc. are all dynamic verbs, as is any action performed by the body.
Let’s see a few examples in sentences:
- I jogged around the track three times.
- She will dance as if her life depends on it.
- She took a candy from the bag, unwrapped it, and popped it into her mouth.
If a verb doesn’t describe a physical activity, then it is a stative verb.
Stative verbs refer to states of being, conditions, or mental processes. Generally, we can classify stative verbs into four types:
- Emotions/Thoughts
Some examples of stative verbs include:
Senses: hurt, see, smell, taste, hear, etc.
Emotions: love, doubt, desire, remember, believe, etc.
Being: be, have, require, involve, contain, etc.
Possession: want, include, own, have, belong, etc.
Here are some stative verbs at work in sentences:
- That is one thing we can agree on.
- I remember my first day at school like it was yesterday.
- The university requires students to score at least 80%.
- She has only three remaining.
Sometimes verbs can fit into more than one category, e.g., be , have , look , see , e.g.,
- She looks beautiful. (Stative)
- I look through the telescope. (Dynamic)
Each action or stative verb can also be further classified as transitive or intransitive .
A transitive verb takes a direct object after it. The object is the noun, noun phrase, or pronoun that has something done to it by the subject of the sentence.
We see this in the most straightforward English sentences, i.e., the Subject-Verb-Object or SVO sentence.
Here are two examples to illustrate. Note: the subject of each sentence is underlined, and the transitive verbs are in bold.
- The teacher answered the student’s questions.
- She studies languages at university.
- My friend loves cabbage.
Most sentences in English employ transitive verbs.
An intransitive verb does not take a direct object after it. It is important to note that only nouns, noun phrases, and pronouns can be classed as direct objects.
Here are some examples of intransitive verbs – notice how none of these sentences has direct objects after their verbs.
- Jane’s health improved .
- The car ran smoothly.
- The school opens at 9 o’clock.
Auxiliary verbs, also known as ‘helping’ verbs, work with other verbs to affect the meaning of a sentence. They do this by combining with a main verb to alter the sentence’s tense, mood, or voice.
Auxiliary verbs will frequently use not in the negative.
There are relatively few auxiliary verbs in English. Here is a list of the main ones:
- be (am, are, is, was, were, being)
- do (did, does, doing)
- have (had, has, having)
Here are some examples of auxiliary verbs (in bold) in action alongside a main verb (underlined).
She is working as hard as she can.
- You must not eat dinner until after five o’clock.
- The parents may come to the graduation ceremony.
The Subject-Auxiliary Inversion Test
To test whether or not a verb is an auxiliary verb, you can use the Subject-Auxiliary Inversion Test .
- Take the sentence, e.g:
- Now, invert the subject and the suspected auxiliary verb to see if it creates a question.
Is she working as hard as she can?
- Can it take ‘not’ in the negative form?
She is not working as hard as she can.
- If the answer to both of these questions is yes, you have an auxiliary verb. If not, you have a full verb.
Verbs Teaching Activity: Identify the Verbs
- Instruct students to go through an appropriate text length (e.g., paragraph, page, etc.) and compile a list of verbs.
- In groups, students should then discuss and categorize each verb according to whether they think they are dynamic or stative, transitive or intransitive, and/or auxiliary verbs.
The job of an adjective is to modify a noun or a pronoun. It does this by describing, quantifying, or identifying the noun or pronoun. Adjectives help to make writing more interesting and specific. Usually, the adjective is placed before the word it modifies.

As with other parts of speech, not all adjectives are the same. There are many different types of adjectives and, in this article, we will look at:
Descriptive Adjectives
- Degrees of Adjectives
Quantitative Adjectives
Demonstrative adjectives, possessive adjectives, interrogative adjectives, proper adjectives.
Descriptive adjectives are what most students think of first when asked what an adjective is. Descriptive adjectives tell us something about the quality of the noun or pronoun in question. For this reason, they are sometimes referred to as qualitative adjectives .
Some examples of this type of adjective include:
- hard-working
In sentences, they look like this:
- The pumpkin was enormous .
- It was an impressive feat of athleticism I ever saw.
- Undoubtedly, this was an exquisite vase.
- She faced some tough competition.
Degrees of Adjectives
Descriptive adjectives have three degrees to express varying degrees of intensity and to compare one thing to another. These degrees are referred to as positive , comparative , and superlative .
The positive degree is the regular form of the descriptive adjective when no comparison is being made, e.g., strong .
The comparative degree is used to compare two people, places, or things, e.g., stronger .
There are several ways to form the comparative, methods include:
- Adding more or less before the adjective
- Adding -er to the end of one syllable adjectives
- For two-syllable adjectives ending in y , change the y to an i and add -er to the end.
The superlative degree is typically used when comparing three or more things to denote the upper or lowermost limit of a quality, e.g., strongest .
There are several ways to form the superlative, including:
- Adding most or least before the adjective
- Adding -est to the end of one syllable adjectives
- For two-syllable adjectives ending in y , change the y to an i and add -est to the end.
There are also some irregular adjectives of degree that follow no discernible pattern that must be learned off by students, e.g., good – better – best .
Let’s take a look at these degrees of adjectives in their different forms.
| beautiful | more beautiful | most beautiful |
| delicious | less delicious | least delicious |
| near | nearer | nearest |
| happy | happier | happiest |
| bad | worse | worst |
Let’s take a quick look at some sample sentences:
- It was a beautiful example of kindness.
Comparative
- The red is nice, but the green is prettier .
Superlative
- This mango is the most delicious fruit I have ever tastiest.
Quantitive adjectives provide information about how many or how much of the noun or pronoun.
Some quantitive adjectives include:
- She only ate half of her sandwich.
- This is my first time here.
- I would like three slices, please.
- There isn’t a single good reason to go.
- There aren’t many places like it.
- It’s too much of a good thing.
- I gave her a whole box of them.
A demonstrative adjective identifies or emphasizes a noun’s place in time or space. The most common demonstrative adjectives are this , that , these , and those .
Here are some examples of demonstrative adjectives in use:
- This boat is mine.
- That car belongs to her.
- These shoes clash with my dress.
- Those people are from Canada.
Possessive adjectives show ownership, and they are sometimes confused with possessive pronouns.
The most common possessive adjectives are my , your , his , her , our , and their .
Students need to be careful not to confuse these with possessive pronouns such as mine , yours , his (same in both contexts), hers , ours , and theirs .
Here are some examples of possessive adjectives in sentences:
- My favorite food is sushi.
- I would like to read your book when you have finished it.
- I believe her car is the red one.
- This is their way of doing things.
- Our work here is done.
Interrogative adjectives ask questions, and, in common with many types of adjectives, they are always followed by a noun. Basically, these are the question words we use to start questions. Be careful however, interrogative adjectives modify nouns. If the word after the question word is a verb, then you have an interrogative adverb on hand.
Some examples of interrogative adjectives include what , which , and whose .
Let’s take a look at these in action:
- What drink would you like?
- Which car should we take?
- Whose shoes are these?
Please note: Whose can also fit into the possessive adjective category too.
We can think of proper adjectives as the adjective form of proper nouns – remember those? They were the specific names of people, places, and things and need to be capitalized.
Let’s take the proper noun for the place America . If we wanted to make an adjective out of this proper noun to describe something, say, a car we would get ‘ American car’.
Let’s take a look at another few examples:
- Joe enjoyed his cup of Ethiopian coffee.
- My favorite plays are Shakespearean tragedies.
- No doubt about it, Fender guitars are some of the best in the world.
- The Mona Lisa is a fine example of Renaissance art.
Though it may come as a surprise to some, articles are also adjectives as, like all adjectives, they modify nouns. Articles help us determine a noun’s specification.
For example, ‘a’ and ‘an’ are used in front of an unspecific noun, while ‘the’ is used when referring to a specific noun.
Let’s see some articles as adjectives in action!
- You will find an apple inside the cupboard.
- This is a car.
- The recipe is a family secret.
Adjectives Teaching Activity: Types of Adjective Tally
- Choose a suitable book and assign an appropriate number of pages or length of a chapter for students to work with.
- Students work their way through each page, tallying up the number of each type of adjective they can identify using a table like the one below:
| Descriptive | |
| Comparative | |
| Superlative | |
| Quantitative | |
| Demonstrative | |
| Possessive | |
| Interrogative | |
| Proper | |
| Articles |
- Note how degrees of adjective has been split into comparative and superlative. The positive forms will take care of in the descriptive category.
- You may wish to adapt this table to exclude the easier categories to identify, such as articles and demonstrative, for example.

Traditionally, adverbs are defined as those words that modify verbs, but they do so much more than that. They can be used not only to describe how verbs are performed but also to modify adjectives, other adverbs, clauses, prepositions, or entire sentences.
With such a broad range of tasks at the feet of the humble adverb, it would be impossible to cover every possibility in this article alone. However, there are five main types of adverbs our students should familiarize themselves with. These are:
Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of time, adverbs of frequency, adverbs of place, adverbs of degree.
Adverbs of manner describe how or the way in which something happens or is done. This type of adverb is often the first type taught to students. Many of these end with -ly . Some common examples include happily , quickly , sadly , slowly , and fast .
Here are a few taster sentences employing adverbs of manner:
- She cooks Chinese food well .
- The children played happily together.
- The students worked diligently on their projects.
- Her mother taught her to cross the road carefully .
- The date went badly .
Adverbs of time indicate when something happens. Common adverbs of time include before , now , then , after , already , immediately , and soon .
Here are some sentences employing adverbs of time:
- I go to school early on Wednesdays.
- She would like to finish her studies eventually .
- Recently , Sarah moved to Bulgaria.
- I have already finished my homework.
- They have been missing training lately .
While adverbs of time deal with when something happens, adverbs of frequency are concerned with how often something happens. Common adverbs of frequency include always , frequently , sometimes , seldom , and never .
Here’s what they look like in sentences:
- Harry usually goes to bed around ten.
- Rachel rarely eats breakfast in the morning.
- Often , I’ll go home straight after school.
- I occasionally have ketchup on my pizza.
- She seldom goes out with her friends.
Adverbs of place, as the name suggests, describe where something happens or where it is. They can refer to position, distance, or direction. Some common adverbs of place include above , below , beside , inside , and anywhere .
Check out some examples in the sentences below:
- Underneath the bridge, there lived a troll.
- There were pizzerias everywhere in the city.
- We walked around the park in the pouring rain.
- If the door is open, then go inside .
- When I am older, I would like to live nearby .
Adverbs of degree express the degree to which or how much of something is done. They can also be used to describe levels of intensity. Some common adverbs of degree include barely , little , lots , completely , and entirely .
Here are some adverbs of degree at work in sentences:
- I hardly noticed her when she walked into the room.
- The little girl had almost finished her homework.
- The job was completely finished.
- I was so delighted to hear the good news.
- Jack was totally delighted to see Diane after all these years.
Adverb Teaching Activity: The Adverb Generator
- Give students a worksheet containing a table divided into five columns. Each column bears a heading of one of the different types of adverbs ( manner , time , frequency , place , degree ).
- Challenge each group to generate as many different examples of each adverb type and record these in the table.
- The winning group is the one with the most adverbs. As a bonus, or tiebreaker, task the students to make sentences with some of the adverbs.

Pronouns are used in place of a specific noun used earlier in a sentence. They are helpful when the writer wants to avoid repetitive use of a particular noun such as a name. For example, in the following sentences, the pronoun she is used to stand for the girl’s name Mary after it is used in the first sentence.
Mary loved traveling. She had been to France, Thailand, and Taiwan already, but her favorite place in the world was Australia. She had never seen an animal quite as curious-looking as the duck-billed platypus.
We also see her used in place of Mary’s in the above passage. There are many different pronouns and, in this article, we’ll take a look at:
Subject Pronouns
Object pronouns, possessive pronouns, reflexive pronouns, intensive pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, interrogative pronouns.
Subject pronouns are the type of pronoun most of us think of when we hear the term pronoun . They operate as the subject of a verb in a sentence. They are also known as personal pronouns.
The subject pronouns are:
Here are a few examples of subject pronouns doing what they do best:
- Sarah and I went to the movies last Thursday night.
- That is my pet dog. It is an Irish Wolfhound.
- My friends are coming over tonight, they will be here at seven.
- We won’t all fit into the same car.
- You have done a fantastic job with your grammar homework!
Object pronouns operate as the object of a verb, or a preposition, in a sentence. They act in the same way as object nouns but are used when it is clear what the object is.
The object pronouns are:
Here are a few examples of object pronouns in sentences:
- I told you , this is a great opportunity for you .
- Give her some more time, please.
- I told her I did not want to do it .
- That is for us .
- Catherine is the girl whom I mentioned in my letter.
Possessive pronouns indicate ownership of a noun. For example, in the sentence:
These books are mine .
The word mine stands for my books . It’s important to note that while possessive pronouns look similar to possessive adjectives, their function in a sentence is different.
The possessive pronouns are:
Let’s take a look at how these are used in sentences:
- Yours is the yellow jacket.
- I hope this ticket is mine .
- The train that leaves at midnight is theirs .
- Ours is the first house on the right.
- She is the person whose opinion I value most.
- I believe that is his .
Reflexive pronouns are used in instances where the object and the subject are the same. For example, in the sentence, she did it herself , the words she and herself refer to the same person.
The reflexive pronoun forms are:
Here are a few more examples of reflexive pronouns at work:
- I told myself that numerous times.
- He got himself a new computer with his wages.
- We will go there ourselves .
- You must do it yourself .
- The only thing to fear is fear itself .
This type of pronoun can be used to indicate emphasis. For example, when we write, I spoke to the manager herself , the point is made that we talked to the person in charge and not someone lower down the hierarchy.
Similar to the reflexive pronouns above, we can easily differentiate between reflexive and intensive pronouns by asking if the pronoun is essential to the sentence’s meaning. If it isn’t, then it is used solely for emphasis, and therefore, it’s an intensive rather than a reflexive pronoun.
Often confused with demonstrative adjectives, demonstrative pronouns can stand alone in a sentence.
When this , that , these , and those are used as demonstrative adjectives they come before the noun they modify. When these same words are used as demonstrative pronouns, they replace a noun rather than modify it.
Here are some examples of demonstrative pronouns in sentences:
- This is delicious.
- That is the most beautiful thing I have ever seen.
- These are not mine.
- Those belong to the driver.
Interrogative pronouns are used to form questions. They are the typical question words that come at the start of questions, with a question mark coming at the end. The interrogative pronouns are:
Putting them into sentences looks like this:
- What is the name of your best friend?
- Which of these is your favourite?
- Who goes to the market with you?
- Whom do you think will win?
- Whose is that?
Pronoun Teaching Activity: Pronoun Review Table
- Provide students with a review table like the one below to revise the various pronoun forms.
- They can use this table to help them produce independent sentences.
- Once students have had a chance to familiarize themselves thoroughly with each of the different types of pronouns, provide the students with the headings and ask them to complete a table from memory.
| | ||||||
| I | me | my | myself | myself | this | what |
| you | you | your | yourself | yourself | that | which |
| he | him | his | himself | himself | these | who |
| she | her | her | herself | herself | those | whom |
| it | it | its | itself | itself | whose | |
| we | us | our | ourselves | ourselves | ||
| you | you | your | yourselves | yourselves | ||
| they | them | their | themselves | themselves |
Prepositions

Prepositions provide extra information showing the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another part of a sentence. These are usually short words that come directly before nouns or pronouns, e.g., in , at , on , etc.
There are, of course, many different types of prepositions, each relating to particular types of information. In this article, we will look at:
Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of place, prepositions of movement, prepositions of manner, prepositions of measure.
- Preposition of Agency
- Preposition of Possession
- Preposition of Source
Phrasal Prepositions
It’s worth noting that several prepositional words make an appearance in several different categories of prepositions.
Prepositions of time indicate when something happens. Common prepositions of time include after , at , before , during , in , on .
Let’s see some of these at work:
- I have been here since Thursday.
- My daughter was born on the first of September.
- He went overseas during the war.
- Before you go, can you pay the bill, please?
- We will go out after work.
Sometimes students have difficulty knowing when to use in , on , or at . These little words are often confused. The table below provides helpful guidance to help students use the right preposition in the right context.
| Centuries YearsSeasonsMonthsTime of day | ||
| DaysDatesSpecific holidays | ||
| Some time of day exceptionsFestivals |
The prepositions of place, in , at , on , will be instantly recognisable as they also double as prepositions of time. Again, students can sometimes struggle a little to select the correct one for the situation they are describing. Some guidelines can be helpful.
- If something is contained or confined inside, we use in .
- If something is placed upon a surface, we use on .
- If something is located at a specific point, we use at .
A few example sentences will assist in illustrating these:
- He is in the house.
- I saw it in a magazine.
- In France, we saw many great works of art.
- Put it on the table.
- We sailed on the river.
- Hang that picture on the wall, please.
- We arrived at the airport just after 1 pm.
- I saw her at university.
- The boy stood at the window.
Usually used with verbs of motion, prepositions of movement indicate movement from one place to another. The most commonly used preposition of movement is to .
Some other prepositions of movement include:
Here’s how they look in some sample sentences:
- The ball rolled across the table towards me.
- We looked up into the sky.
- The children ran past the shop on their way home.
- Jackie ran down the road to greet her friend.
- She walked confidently through the curtains and out onto the stage.
Preposition of manner shows us how something is done or how it happens. The most common of these are by , in , like , on , with .
Let’s take a look at how they work in sentences:
- We went to school by bus.
- During the holidays, they traveled across the Rockies on foot.
- Janet went to the airport in a taxi.
- She played soccer like a professional.
- I greeted her with a smile.
Prepositions of measure are used to indicate quantities and specific units of measurement. The two most common of these are by and of .
Check out these sample sentences:
- I’m afraid we only sell that fabric by the meter.
- I will pay you by the hour.
- She only ate half of the ice cream. I ate the other half.
- A kilogram of apples is the same weight as a kilogram of feathers.
Prepositions of Agency
These prepositions indicate the causal relationship between a noun or pronoun and an action. They show the cause of something happening. The most commonly used prepositions of agency are by and with .
Here are some examples of their use in sentences:
- The Harry Potter series was written by J.K. Rowling.
- This bowl was made by a skilled craftsman.
- His heart was filled with love.
- The glass was filled with water.
Prepositions of Possession
Prepositions of possessions indicate who or what something belongs to. The most common of these are of , to , and with .
Let’s take a look:
- He is the husband of my cousin.
- He is a friend of the mayor.
- This once belonged to my grandmother.
- All these lands belong to the Ministry.
- The man with the hat is waiting outside.
- The boy with the big feet tripped and fell.
Prepositions of Source
Prepositions of source indicate where something comes from or its origins. The two most common prepositions of source are from and by . There is some crossover here with prepositions of agency.
Here are some examples:
- He comes from New Zealand.
- These oranges are from our own orchard.
- I was warmed by the heat of the fire.
- She was hugged by her husband.
- The yoghurt is of Bulgarian origin.
Phrasal prepositions are also known as compound prepositions. These are phrases of two or more words that function in the same way as prepositions. That is, they join nouns or pronouns to the rest of the sentence.
Some common phrasal prepositions are:
- According to
- For a change
- In addition to
- In spite of
- Rather than
- With the exception of
Students should be careful of overusing phrasal prepositions as some of them can seem clichéd. Frequently, it’s best to say things in as few words as is necessary.
Preposition Teaching Activity: Pr eposition Sort
- Print out a selection of the different types of prepositions on pieces of paper.
- Organize students into smaller working groups and provide each group with a set of prepositions.
- Using the headings above as categories, challenge students to sort the prepositions into the correct groups. Note that some prepositions will comfortably fit into more than one group.
- The winning group is the one to sort all prepositions correctly first.
- As an extension exercise, students can select a preposition from each category and write a sample sentence for it.
ConjunctionS

Conjunctions are used to connect words, phrases, and clauses. There are three main types of conjunction that are used to join different parts of sentences. These are:
- Coordinating
- Subordinating
- Correlative
Coordinating Conjunctions
These conjunctions are used to join sentence components that are equal such as two words, two phrases, or two clauses. In English, there are seven of these that can be memorized using the mnemonic FANBOYS:
Here are a few example sentences employing coordinating conjunctions:
- As a writer, he needed only a pen and paper.
- I would describe him as strong but lazy.
- Either we go now or not at all.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions are used to introduce dependent clauses in sentences. Basically, dependent clauses are parts of sentences that cannot stand as complete sentences on their own.
Some of the most common subordinate conjunctions are:
Let’s take a look at some example sentences:
- I will complete it by Tuesday if I have time.
- Although she likes it, she won’t buy it.
- Jack will give it to you after he finds it.
Correlative Conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions are like shoes; they come in pairs. They work together to make sentences work. Some come correlative conjunctions are:
- either / or
- neither / nor
- Not only / but also
Let’s see how some of these work together:
- If I were you, I would get either the green one or the yellow one.
- John wants neither pity nor help.
- I don’t know whether you prefer horror or romantic movies.
Conjunction Teaching Activity: Conjunction Challenge
- Organize students into Talking Pairs .
- Partner A gives Partner B an example of a conjunction.
- Partner B must state which type of conjunction it is, e.g. coordinating, subordinating, or correlative.
- Partner B must then compose a sentence that uses the conjunction correctly and tell it to Partner A.
- Partners then swap roles.
InterjectionS

Interjections focus on feelings and are generally grammatically unrelated to the rest of the sentence or sentences around them. They convey thoughts and feelings and are common in our speech. They are often followed by exclamation marks in writing. Interjections include expressions such as:
- Eww! That is so gross!
- Oh , I don’t know. I’ve never used one before.
- That’s very… err …generous of you, I suppose.
- Wow! That is fantastic news!
- Uh-Oh! I don’t have any more left.
Interjection Teaching Activity: Create a scenario
- Once students clearly understand what interjections are, brainstorm as a class as many as possible.
- Write a master list of interjections on the whiteboard.
- Partner A suggests an interjection word or phrase to Partner B.
- Partner B must create a fictional scenario where this interjection would be used appropriately.
With a good grasp of the fundamentals of parts of speech, your students will now be equipped to do a deeper dive into the wild waters of English grammar.
To learn more about the twists and turns of English grammar, check out our comprehensive article on English grammar here.
DOWNLOAD THESE 9 FREE CLASSROOM PARTS OF SPEECH POSTERS

PARTS OF SPEECH TUTORIAL VIDEOS

MORE ARTICLES RELATED TO PARTS OF SPEECH

English EFL
Introduction to grammar
Parts of Speech
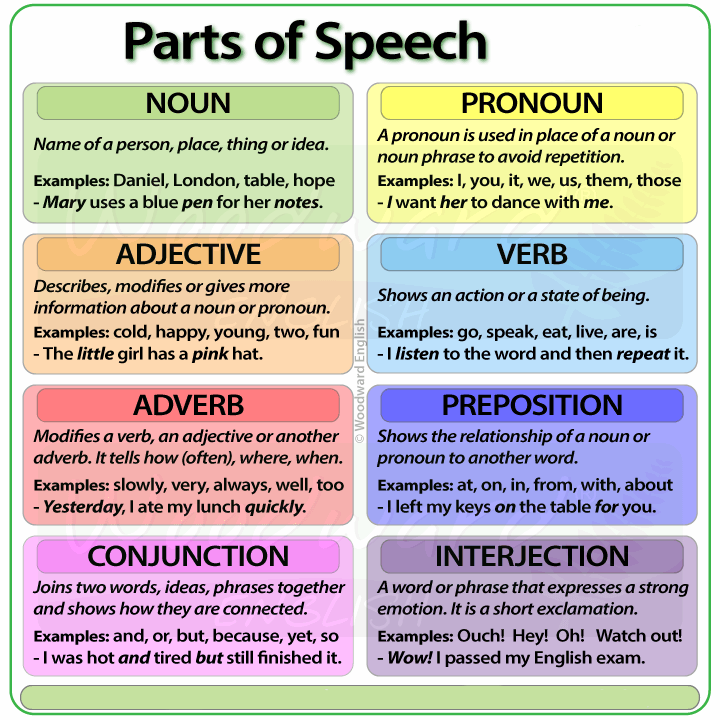
The parts of speech explain how a word is used in a sentence.
There are eight main parts of speech (also known as word classes): nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections .
Most parts of speech can be divided into sub-classes. Prepositions can be divided into prepositions of time, prepositions of place etc. Nouns can be divided into proper nouns, common nouns, concrete nouns etc.
It is important to know that a word can sometimes be in more than one part of speech. For example with the word increase .
Increase can be a verb e.g. Prices increased and increase can also be a noun e.g. There was an increase in the number of followers.
A list of parts of speech in English grammar include the following:
A verb is used to show an action or a state of being
go, write, exist, be
A noun is a word used to refer to people, animals, objects, substances, states, events, ideas and feelings. A noun functions as a subject or object of a verb and can be modified by an adjective.
John, lion, table, freedom, love ...
3. Adjective
Adjectives are used to describe or specify a noun or pronoun
good, beautiful, nice, my ...
An adverb is used to modify a verb, adjective and other adverbs.
completely, never, there ...
A pronoun is used in the place of a noun or phrase.
I, you, he, she, it ...
6. Preposition
Prepositions are used before nouns to form a phrase that shows where, when, how and why
in, above, to, for, at ...
7. Conjunction
Conjunctions join clauses or sentences or words
and, but, when ...
8. Interjection
Interjections are used to show surprise or emotion.
oh!, Good Lord
Examples of parts of speech
Here are some examples of parts of speech: My ( adjective ) friend ( noun ) speaks ( verb ) English ( noun ) fluently ( adverb ). Oh! ( interjection ) I ( pronoun ) went ( verb ) to ( preposition ) school ( noun ) and ( conjunction ) I ( pronoun ) met ( verb ) Fred ( noun ).
Course Curriculum
- Basic English Grammar Components 20 mins
- Auxiliary Verbs 30 mins
- Articles 20 mins
- Parts of Speech 20 mins
Lesson Plan
Parts of speech: breaking down sentences, view aligned standards, learning objectives.
Students will be able to identify nouns, verbs, adjectives, and pronouns in a sentence. Students will be able to write sentences that consist of nouns, verbs, adjectives, and pronouns.
Introduction

- Ask your students the meaning of the following parts of speech: noun, verb, adjective, and pronoun.
- Explain to your students that a noun is a person, place, animal, or thing. Tell your students that a verb is an action. Remind them that a pronoun is a word that is used instead of a noun. Define an adjective as a word that describes a noun.
- Ask your students to come up with an example for each part of speech. Write down the examples that your students come up with on the board.
Related Guided Lesson


Parts of Speech
What is a Part of Speech?
We can categorize English words into 9 basic types called "parts of speech" or "word classes". It's quite important to recognize parts of speech. This helps you to analyze sentences and understand them. It also helps you to construct good sentences.
Parts of Speech Table
Parts of speech examples.
- Parts of Speech Quiz
This is a summary of the 9 parts of speech*. You can find more detail if you click on each part of speech.
| part of speech | function or "job" | example words | example sentences |
|---|---|---|---|
| action or state | (to) be, have, do, like, work, sing, can, must | EnglishClub a website. I EnglishClub. | |
| thing or person | pen, dog, work, music, town, London, teacher, John | This is my . He lives in my . We live in . | |
| describes a noun | good, big, red, well, interesting | My dogs are . I like dogs. | |
| limits or "determines" a noun | a/an, the, 2, some, many | I have dogs and rabbits. | |
| describes a verb, adjective or adverb | quickly, silently, well, badly, very, really | My dog eats . When he is hungry, he eats quickly. | |
| replaces a noun | I, you, he, she, some | Tara is Indian. is beautiful. | |
| links a noun to another word | to, at, after, on, but | We went school Monday. | |
| joins clauses or sentences or words | and, but, when | I like dogs I like cats. I like cats dogs. I like dogs I don't like cats. | |
| short exclamation, sometimes inserted into a sentence | oh!, ouch!, hi!, well | ! That hurts! ! How are you? , I don't know. |
- lexical Verbs ( work, like, run )
- auxiliary Verbs ( be, have, must )
- Determiners may be treated as adjectives, instead of being a separate part of speech.
Here are some examples of sentences made with different English parts of speech:
| verb |
|---|
| Stop! |
| noun | verb |
|---|---|
| John | works. |
| noun | verb | verb |
|---|---|---|
| John | is | working. |
| pronoun | verb | noun |
|---|---|---|
| She | loves | animals. |
| noun | verb | noun | adverb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tara | speaks | English | well. |
| noun | verb | adjective | noun |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tara | speaks | good | English. |
| pronoun | verb | preposition | determiner | noun | adverb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| She | ran | to | the | station | quickly. |
| pron. | verb | adj. | noun | conjunction | pron. | verb | pron. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| She | likes | big | snakes | but | I | hate | them. |
Here is a sentence that contains every part of speech:
| interjection | pron. | conj. | det. | adj. | noun | verb | prep. | noun | adverb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Well, | she | and | my | young | John | walk | to | school | slowly. |
Words with More Than One Job
Many words in English can have more than one job, or be more than one part of speech. For example, "work" can be a verb and a noun; "but" can be a conjunction and a preposition; "well" can be an adjective, an adverb and an interjection. In addition, many nouns can act as adjectives.
To analyze the part of speech, ask yourself: "What job is this word doing in this sentence?"
In the table below you can see a few examples. Of course, there are more, even for some of the words in the table. In fact, if you look in a good dictionary you will see that the word " but " has six jobs to do:
- verb, noun, adverb, pronoun, preposition and conjunction!
| word | part of speech | example |
|---|---|---|
| work | noun | My is easy. |
| verb | I in London. | |
| but | conjunction | John came Mary didn't come. |
| preposition | Everyone came Mary. | |
| well | adjective | Are you ? |
| adverb | She speaks . | |
| interjection | ! That's expensive! | |
| afternoon | noun | We ate in the . |
| noun acting as adjective | We had tea. |
People often ask
FAQ: frequently asked parts of speech questions

Parts of Speech
What are the parts of speech, a formal definition.
Table of Contents
The Part of Speech Is Determined by the Word's Function
Are there 8 or 9 parts of speech, the nine parts of speech, (1) adjective, (3) conjunction, (4) determiner, (5) interjection, (7) preposition, (8) pronoun, why the parts of speech are important, video lesson.

- You need to dig a well . (noun)
- You look well . (adjective)
- You dance well . (adverb)
- Well , I agree. (interjection)
- My eyes will well up. (verb)
- red, happy, enormous
- Ask the boy in the red jumper.
- I live in a happy place.
- I caught a fish this morning! I mean an enormous one.
- happily, loosely, often
- They skipped happily to the counter.
- Tie the knot loosely so they can escape.
- I often walk to work.
- It is an intriguingly magic setting.
- He plays the piano extremely well.
- and, or, but
- it is a large and important city.
- Shall we run to the hills or hide in the bushes?
- I know you are lying, but I cannot prove it.
- my, those, two, many
- My dog is fine with those cats.
- There are two dogs but many cats.
- ouch, oops, eek
- Ouch , that hurt.
- Oops , it's broken.
- Eek! A mouse just ran past my foot!
- leader, town, apple
- Take me to your leader .
- I will see you in town later.
- An apple fell on his head .
- in, near, on, with
- Sarah is hiding in the box.
- I live near the train station.
- Put your hands on your head.
- She yelled with enthusiasm.
- she, we, they, that
- Joanne is smart. She is also funny.
- Our team has studied the evidence. We know the truth.
- Jack and Jill went up the hill, but they never returned.
- That is clever!
- work, be, write, exist
- Tony works down the pit now. He was unemployed.
- I will write a song for you.
- I think aliens exist .
Are you a visual learner? Do you prefer video to text? Here is a list of all our grammar videos .
Video for Each Part of Speech
The Most Important Writing Issues
The top issue related to adjectives.
| Don't write... | Do write... |
|---|---|
| very happy boy | delighted boy |
| very angry | livid |
| extremely posh hotel | luxurious hotel |
| really serious look | stern look |
The Top Issue Related to Adverbs
- Extremely annoyed, she stared menacingly at her rival.
- Infuriated, she glared at her rival.
The Top Issue Related to Conjunctions
- Burger, Fries, and a shake
- Fish, chips and peas
The Top Issue Related to Determiners
The Top Issue Related to Interjections
The top issue related to nouns, the top issue related to prepositions, the top issue related to pronouns, the top issue related to verbs.
| Unnatural (Overusing Nouns) | Natural (Using a Verb) |
|---|---|
| They are in agreement that he was in violation of several regulations. | They agree he violated several regulations. |
| She will be in attendance to present a demonstration of how the weather will have an effect on our process. | She will attend to demonstrate how the weather will affect our process. |
- Crack the parts of speech to help with learning a foreign language or to take your writing to the next level.

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
You might also like...

Was something wrong with this page?

Use #gm to find us quicker .

Create a QR code for this, or any, page.
mailing list
grammar forum
teachers' zone
Confirmatory test.
This test is printable and sendable
expand to full page
show as slides
download as .doc
print as handout
send as homework
display QR code
ESL Activities
ESL Games, Activities, Lesson Plans, Jobs & More
in Listening · Reading · Speaking · Writing
ESL Parts of Speech Activities, Worksheets & Lesson Plans
In English, there are 8 parts of speech: adjectives, adverbs, nouns, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections. In this article, you’ll find parts of speech activities and games, along with worksheets and lesson plans.
Why is it important for ESL students to understand part of speech? It’s so that students can work towards more complex language and sentence structure. As teachers, it’s very important to provide opportunities to practice these things through memorable activities, games, and worksheets. The goal is that students will understand the meaning of words, word function and also how to use these grammatically within a sentence.
ESL parts of speech
ESL Parts of Speech
We’ve broken down some of the parts of speech into small subsections. For example, nouns or verbs are a big category and things like modal verbs or phrasal verbs are quite different things. You’ll find these interesting and engaging ESL activity ideas useful for beginner to advanced students. You may also find this one useful: List of Categories .
Adjectives describe nouns and are key for rich, varied English usage. They are also one of the most common parts of speech that even beginners will need to know. Check out some of the top game, activity, worksheet and lesson plan ideas:
ESL Adjective Activities
Also be sure to check out this simple comparative adjective quiz for students:
Please enable JavaScript
Adjectives of Feeling and Emotion
Adjectives are an important part of speech for ESL and can be used to describe a lot of things, but these ones focus on feelings. Check out these parts of speech games and activities:
Feeling and Emotion Adjective Activities
In English, adverbs serve an important function int hat they describe or modify a verb, as well as certain other parts of speech. Check out some of the best activities for this:
Adverb Activities and Games .
Adverbs of Frequency
Adverbs are an important part of speech in English and one of the most common uses of them is with frequency. Basically, expressions with, “How often” fall into this category.
Adverbs of Frequency ESL Activities
- Amazon Kindle Edition
- Bolen, Jackie (Author)
- English (Publication Language)
- 87 Pages - 10/24/2019 (Publication Date)
Although not specifically a part of speech, articles are key because they combine with nouns and are a key part of correct sentence structure.
Articles ESL Activities and Games
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
Comparatives and superlatives adjectives—an example is big, bigger, biggest. They are a very common English part of speech and our English learners need to master them early on. Here are some ideas for your lesson plans:
ESL Comparative and Superlative Adjective Games
Compound Nouns
Nouns are the most common English part of speech and within that category, you’ll see a ton of compound nouns. They’re basically two words that are joined together to have a possibly separate meaning from those two original words. For example snowstorm or water skiing.
ESL Compound Noun Activities
Conjunctions and Transitions
We use conjunctions and transitions all the time in English to make writing especially easier to read. They show the relationship between sentences and parts within a sentence.
Conjunction Transition Activities
You may also want to check out this sequence words list.
Countable and Uncountable Nouns
Check out these countable and uncountable noun activities that will help students figure out the difference between these two noun categories. They’ll also learn how to use them correctly in a sentence with a quantifier.
Countable and Uncountable Noun ESL Activities
Future Verb Forms
Talking about the future is a key part of mastering the English language. However, there are a few different ways to do that and it can be a little bit tricky for students to know when to use which one. Check out some of the best ideas here:
Future Verbs Forms ESL Activities
- 57 Pages - 10/26/2015 (Publication Date)
Imperatives
We use imperatives when we want to give a command, order or direction. Listen to a conversation between a teacher and student or child and parents and you’ll notice that the utterances are filled with them! Find out more:
ESL Imperative Activities and Games .
Indefinite Pronouns
We use an indefinite pronoun as a way to refer to something, but not to any specific person, amount or thing. Some common examples are nobody, somebody, everything, etc. We use them all the time in the English language which is why it’s vital to work on them with our students. Here are some ideas:
Indefinite Pronouns Activities .
Irregular Verbs
Unfortunately, English is filled with irregular verbs that don’t have the typical “ed” ending in the past tense (more ideas here: past continuous games and past tense ESL ). Students have to memorize them—there’s just no way around it. However, you can help your students become more proficient at this ESL part of speech by trying out some of the following:
ESL Irregular Verb Games.
Linking Verbs
A linking verb in English is also known as an auxiliary or helping verb. There are several functions, but they mainly serve to extend the meaning of the main verb. Check out some of the best ideas here:
Linking Verb Games .
Modal Verbs
Modals are words like can, might, should, etc. and they are important ESL part of speech. They can be used to express things like permission, ability, obligation, possibility, and more. Here are some of the top recommendations:
Modal Verb Activities and Games.
Passive Voice Activities
The passive voice is used in some very specific situations in English. For example, when the person doing the action isn’t important (She counted out the change for me) or when it’s obvious who the agent is (I was instructed to be friendlier to customers).
Passive Voice ESL Games and Activities
Past Tense Verb Activities
Verbs are a vital ESL part of speech. However, in the past tense, irregular verbs make this a little bit tricky for our students sometimes. Check out these ideas here:
Past Tense ESL Activities and Worksheets
Phrasal Verbs
One common verb type in English is a phrasal verb. This is where a verb is combined with an adverb or preposition and the resulting combination has a different meaning. For example: back off, call back, etc. They are a very common part of speech in English and something that our students need to master.
Phrasal Verb ESL Activities
- 108 Pages - 08/26/2021 (Publication Date)
Possessive Adjectives and Pronouns
Both pronoun and adjective parts of speech can be used to express ownership of something. Here are some of the best ideas for helping students with possessives:
ESL Possessives Activities and Games
A prefix is some letters at the beginning of a word that changes its meaning in some way. It could negate it, make it opposite or express a manner or time. Here are some recommendations:
Prefix Games
Prepositions
If you’re looking for activities, games, worksheets and lesson plans specifically for prepositions of place (in, on, at, etc.), then you’ll want to check out the following resource:
ESL Prepositions of Place
Present Perfect Verbs
The present perfect is a key verb tense for students to master. Verbs are a major part of speech in English and this is a commonly used tense.
Present Perfect ESL Games
Present Continuous
We use the present continuous to talk about things that are currently happening and will probably continue into the future. Have a look here:
Activities for present continuous .
Quantifiers
Any, some, much, many are all examples of quantifiers in English that deal with how much of something. Students need to master quantifier expressions in order to become proficient in English. Here are some recommendations for student-centred, fun activities to work on them:
ESL Quantifier Activities
Reflexive Pronouns
There are nine reflexive pronouns in English which are words that end in “self” or “selves.” For example, myself or themselves. They’re used when the subject and object of a sentence are the same.
Check out these recommendations:
Reflexive Pronouns Games .
- 146 Pages - 06/18/2020 (Publication Date)
Singular and Plural Nouns
English nouns are found in both singular and plural forms. It’s often one of the first concepts that beginners learn when they’re just getting started out with English.
Here are some of the best activities for teaching this important concept:
ESL Singular and Plural Nouns
Subject and Object Pronoun Activities
Subject and Object pronouns are an important part of speech that students need to master in order to become proficient in English. These student-centred ESL activities and worksheets will help students do that!
Subject-Object Pronoun ESL Games
Subject-Verb Agreement
Unfortunately for English learners, the verb form changes with the subject. It’s often a mistake that even more advanced learners can make when they’re not actively thinking about it. That’s why it’s key to provide opportunities for our students for lots of practice.
English Subject Verb Agreement Activities and Worksheets
Suffixes are letters that are added onto the end of base words to change the meaning or part of speech. For example, ed added onto the end of a verb makes it into the past tense. Or, ing plus a verb makes it into a continuous form. The good news is that there are specific rules for how suffixes function.
Suffix Games and Activities
Verb Activities
There are plenty of subcategories of verbs to consider when thinking about ESL parts of speech. However, if you want some general games and activities that focus on them, here is your best resource.
ESL Verb Activities
- 122 Pages - 02/23/2020 (Publication Date)
Verbs: Present Perfect For and Since
Verbs are a key part of ESL parts of speech and the present perfect is a vital thing for our students to master if they want to become proficient in English. It can be a little bit tricky because of the verb changes in this tense. Check out our recommendations here for mastering the present perfect with for and since:
ESL Present Perfect Activities
WH Question Games and Activities
Okay, so “WH” questions aren’t exactly a part of speech in English! However, they are certainly important in English and something that students need to master. You’ll certainly want to spend some time working on them with your students. All the details here:
ESL WH Questions Games and Activities
English part of speech activities
Yes/No Questions
Yes/no questions are one of the first grammar concepts that beginners learn. For example:
- Do you like ice cream?
- Are you 10 years old?
Find out some of the best ideas for teaching them here:
Yes/No Question Games .
What are some Common Language Teaching Methods?
There are various approaches and methods for teaching language, ranging from grammar-translation to the communicative language approach to task-based learning. Have a look here for all the details:
Methods and Approaches in Language Teaching .
Parts of Speech ESL Activities
If you’re looking for some ESL parts of speech activities and games, here are a few of the best options:
- Odd one out
- Fill in the blank activities
- Word categories
- Videos in the ESL classroom
- Use a reading lesson plan
- 3 things writing activity
- Word association
More Ideas for Teaching English
- 211 Pages - 12/22/2022 (Publication Date) - Independently published (Publisher)
If you want to brush up on English teaching methodology and practice, then you’ll definitely want to check out this book. I put my 20 years of classroom experience into a single book—the result is a very practical, helpful guide to teaching ESL/EFL.
Pick up a copy of the book today, and get ready for better English classes tomorrow:
ESL Parts of Speech FAQs
There are a number of common questions that people have about English parts of speech, along with activities and games to practice them. Here are some of the most popular ones.
What are the 10 parts of speech?
In English, there are 10 main parts of speech. They include the following:
- prepositions
- conjunctions
- interjections
- articles/determiners
What are the four main parts of speech?
In English, the four main parts of speech are nouns, verbs, adverbs, and adjectives.
How do you teach parts of speech?
Teaching parts of speech can be quite a difficult task if done together. That’s why most ESL textbooks and English teachers teach small parts of them in sequence. For example, a lesson on the simple past, then one on pronouns, usage of articles, then adjectives, etc. Once students are more advanced, lessons focused on identifying the various parts of speech in a sentence can be a useful exercise.
How do you identify a noun?
In English, a noun is considered to be a person, place, thing or idea. It can be found in various parts of the sentence and can be the subject, object, indirect object, complement, object complement, appositive, or adjective.
What is basic English grammar?
Basic English grammar involves the following word order in a sentence: subject, verb, object. There are other parts of speech used at various points including adjectives, adverbs, articles, etc to form more complex sentences.
How to teach parts of speech in a fun way?
It’s possible to teach parts of speech in a fun way by using various ESL games and activities. Some of the best ones include Bingo, running dictation, charades, mixed up sentences, dictation activities, videos, songs, chants, and more.
ESL Parts of Speech Worksheets
If you’re looking for some parts of speech ESL worksheets, check out some of the top options:
ISL Collective
English for Everyone
English Worksheets
Parts of speech ESL worksheets
Have your say about these ESL Parts of Speech
Do you have any recommendations for resources to help our students with parts of speech ESL? Leave a comment below and let us know. We’d love to hear from you.
Also be sure to give this article a share on Facebook, Pinterest, or Twitter. It’ll help other busy teachers, like yourself find this useful teaching resource.
Last update on 2022-07-17 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API
About Jackie
Jackie Bolen has been teaching English for more than 15 years to students in South Korea and Canada. She's taught all ages, levels and kinds of TEFL classes. She holds an MA degree, along with the Celta and Delta English teaching certifications.
Jackie is the author of more than 60 books for English teachers and English learners, including Business English Vocabulary Builder and 39 No-Prep/Low-Prep ESL Speaking Activities for Teenagers and Adults . She loves to share her ESL games, activities, teaching tips, and more with other teachers throughout the world.
You can find her on social media at: YouTube Facebook Pinterest TikTok LinkedIn Instagram
Top Selling ESL Activity Book
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
More ESL Activities and Games
Line up game for esl/efl classes | line up game questions, simple debate topics: easy topics to debate for all ages, esl classroom management tips and tricks | teaching esl, esl shopping activities, games, worksheets, lesson plans and more, about, contact, privacy policy.
Best-selling author and English teacher Jackie Bolen has been talking ESL activities and games since 2015. The goal is to bring you the best ideas, lesson plans, and activity recommendations for your TEFL classes.
Get in touch: About + Contact
Privacy Policy and Terms of Use
Email: [email protected]
Address: 2436 Kelly Ave, Port Coquitlam, Canada

- All Lessons
- business english
- comprehension
- culture & tips
- expressions
- pronunciation
Basic English: The 8 Parts of Speech
Test your understanding of this English lesson
48 comments.
Many thanks dear teacher I caught very well these parts of speech
Thank you very much for this lesson, It was really helpful.
Thanks Gill.
Thank you so much.
1o/1o Thanks Mrs.Jill for this short review of the different parts of speech This class really helps us to identify all these parts of speech when we look at a sentence
Thanks you Gill for a valuable lesson which refreched my memmory and add new information.
Thank you Miss Jill! This lesson is really going to help me to help my nieces to study English…
Good Morning,Teacher I am thankful to you for basic parts of speech learning
it’s good
Well done!!
thanks teacher
i got 9/10. thanks for this useful lesson
Sorry I am not good in English 🥺
Thanks teacher
Need to learn more and more
Nice explanation. Thanks!!!
Thanks very much
I’m from Bangladesh, i want to improve my english skills
I really enjoyed it thanks madam
Wows….i really enjoyed the lesion. okey…i like this sound…okey….after each sentences. thankyou very . nice class
thanks teacher!
Thank you! this was really helpful. It helped improve my English.
thats nice thanks
Thank you Gill
i can not see youtube
Our videos are on YouTube, so if you are viewing the site from China, the videos will be blocked. However, you can also watch some of our videos on Bilibili .
tankyou so much
Thank you teacher,lol
thanks teacher for your help
Some mistakes need to see this again
8 out of 10 again;)
Thanks so much!
Thanks a lot mem
Thank you so much
thank you teacher
thank’s
Thank you. 9/10
Good lesson and thank you.
Nice lesson, Thank you!
about engVid
Learn English for free with 2074 video lessons by experienced teachers. Classes cover English grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation, IELTS, TOEFL, and more. Join millions of English learners worldwide who are improving every day with engVid.
- 2-Intermediate
- Privacy Policy
© 2024 LearnVid Inc.
8 Parts of speech with Examples PDF | Detailed Lesson
What are the 8 parts of speech? Parts of speech are a very important part of English grammar. For an ESL student learning parts of speech is a must thing to do. It will help in building the initial concepts. It is the building block of English grammar.
Here is the quick list of 8 Parts of Speech :
Conjunction
Interjection, preposition, parts of speech with examples.
“It is the name of a certain place, thing, or a person. Like Daniel, English or a lion, etc.”
There are further two major types of nouns Common nouns and Proper nouns.
- Common noun : The name of a commonplace, non-specific person or a thing is known as a common noun like chair, book, city, etc.
- Proper noun : The name of a special place, person, or thing is known as a proper noun like Allama Muhammad Iqbal, Lahore, etc.
For Example, An old woman brought me a very long dress from a tailor , and then she quickly disappeared.
Here is the examples list of nouns:
| Beard | Ice | Raincoat |
| Boy | Iron | River |
| Australia | Honey | Potato |
| Beach | Hydrogen | Rainbow |
| Advertisement | Grass | Parrot |
| Afternoon | Greece | Pencil |
| Belgium | Insurance | Restaurant |
| Branch | Island | Rocket |
| Banana | Hospital | Quill |
| Apple | Helmet | Plastic |
| Actor | Gold | Painting |
| Airport | Guitar | Piano |
| Ambulance | Hair | Pillow |
| Balloon | Horse | Queen |
| Answer | Helicopter | Planet |
| Bed | Insect | Refrigerator |
| Battery | House | Rain |
| Army | Holiday | Portugal |
| Breakfast | Jackal | Room |
| Animal | Hamburger | Pizza |
“A word that is used at the place of a noun is known as a pronoun such as he, she and it, etc”
Basically, the pronoun is a word that is usually substituted for a noun. Pronouns are further defined by their type such as
- A personal pronoun refers to a specific person or a thing he, she, it, etc. Parts of speech
- Reflexive pronouns are used to emphasise another noun or a pronoun myself, himself, etc.
- Possessive pronouns indicate ownership of his, her, its, etc.
Here is the Examples List of Pronouns:
| whomsoever | whose | everything |
| you | whichsoever | your |
| he | where | nobody |
| whom so | this | thee |
| somewhat | whatever | wherein |
| whereof | any | ourself |
| whosever | them | whosoever |
| wherefrom | him | yourselves |
| its | theirself | naught |
| something | such | both |
| somebody | enough | mine |
| I | herself | neither |
| everyone | whatnot | anybody |
| whom | several | our |
| one | there | it |
| whosesoever | themselves | anyone |
| wherever | no one | whomever |
| whereto | whether | itself |
| that | some | nothing |
“A word which qualifies or modifies a noun or pronoun is known as an adjective such as sweet, pretty, hot, etc.”
- It can also specify the size, quality, and a number of things.
For Example , An old woman brought me a very long dress from a tailor, and then she quickly disappeared.
Here is the Examples List of Adjectives:
| capricious | unable | talented |
| womanly | elfin | decorous |
| well-to-do | bland | quack |
| kind | nebulous | light |
| hot | abject | harsh |
| screeching | curved | wise |
| tan | disgusted | absent |
| savory | deep | nonsensical |
| vengeful | gleaming | brave |
| exasperated | tame | parsimonious |
| humdrum | glossy | telling |
| meaty | holistic | gray |
| adventurous | prickly | medical |
| ablaze | square | longing |
| lonely | smooth | wistful |
| utter | limping | goofy |
| adamant | lowly | windy |
| brash | breezy | acrid |
| keen | loutish | chivalrous |
“It describes or modifies a verb, an adjective or another adverb, but never a noun such as gently, quickly, etc.”
- They are usually used to answer the question of when, where, how. They usually end with the word –ly.
For Example, An old woman brought me a very long dress from a tailor, and then she quickly disappeared.
Here is the Examples List of Adverbs:
| Shyly | Tensely | Violently |
| Generously | Gently | Gladly |
| Rapidly | Rudely | Selfishly |
| Calmly | Carefully | Cautiously |
| Eagerly | Easily | Elegantly |
| Madly | Politely | Poorly |
| Badly | Blindly | Carelessly |
| Beautifully | Boldly | Bravely |
| Faithfully | Frankly | Honestly |
| Joyously | Kindly | Neatly |
| Inadequately | Justly | Lazily |
| Perfectly | Powerfully | Anxiously |
| Well | Angrily | Awkwardly |
| Promptly | Quickly | Quietly |
| Cheerfully | Equally | Frantically |
| Obediently | Openly | Patiently |
“Conjunctions joins words, clauses or phrases and indicates the relationship between them, such as but, or so, yet are conjunctions.”
Here is the Examples List of Conjunction:
| until | how | since |
| just as | where | wherever |
| before | why | so that |
| as soon as | as far as | as though |
| by the time | in as much as | inasmuch |
| supposing | when | or not |
| since | because | whose |
| provided | provide that | if |
| as if | as long as | as much as |
| in order to | in order that | in case |
| lest | though | now that |
| whereas | where if | whether |
| even if | even | even though |
| than | till | whenever |
| whoever | unless | while |
| if then | if when | if only |
| now since | now when | now |
“A verb expresses the action of being, doing, or having.”
- There is a main verb in a sentence and sometimes one or more helping verbs. Such as ( she can sing. Here sing is the main verb and can be a helping verb)
For Example, An old woman brought me a very long dress from a tailor, and then she quickly disappeared .
Here is the Examples List of Verbs:
| Turn off | Turn on | Wait |
| Read | Ride | Sew |
| Talk | Think | Throw away |
| Climb | Close | Cook |
| Crawl | Cry | Cut |
| Ski | Sleep | Smell |
| Knit | Laugh | Listen |
| Bow | Buy | Clap |
| Dance | Dig | Dive |
| Dream | Drink | Eat |
| Shake | Sing | Sit down |
| Hug | Jump | Kiss |
| Wash | Watch TV | Win |
| Snore | Stack | Stand up |
| Open | Paint | Play |
| Fight | Fly | Give |
“Interjections are the words used to express emotions such as Oo! Woo! Etc.”
It is often followed by the sign of exclamation .
- Hurrah! We won the match.
Here is the Examples List of Interjections:
| bah | Basta | bastard |
| aargh | ach | a-choo |
| adieu | adios | affirmative |
| avast | avaunt | aw |
| aaargh | aagh | aah |
| ah | a-ha | ahem |
| ahh | alas | alleluia |
| batter up | begorrah | bejaysus |
| aoogah | ar | areet |
| ay | aye | bacaw |
| aloha | amen | aooga |
“A preposition is a word placed before a noun or pronoun to form a phrase modifying another word in the sentence such as by, with, on, etc”
- The book is on the table.
- He wrote a letter with the blue pen.
Here is the Examples List of Prepositions:
| Forward of | From | In |
| Among | Apart from | Astride |
| Close to | Far | Far from |
| Around | At | Before |
| By | Circa | During |
| Into | Minus | Near |
| Below | Beneath | Beside |
| Aboard | Above | Across |
| About | After | Ago |
| Following | For | From |
| Gone | In | On |
| At | Atop | Behind |
| Until/till | Up to | Up until |
| In between | In front of | Inside |
| Between | Beyond | By |
| Against | Alongside | Amid |
| Past | Prior to | Since |
You may like to read All tenses in English.
Infographics (Parts of Speech)

Download this Lesson of Parts of Speech PDF File Below:
Download PDF
What are the 12 Parts of Speech?
Most of us believe that there are more than eight parts of speech, but keep in mind that in actuality there are only 8 parts of speech that are enough to explain and under the complete concept of English.
But some of us believe or think that they may be more than 8, yes there are more than 8, some say 9, and some 12. So let me give you the list of twelves.
Here are some commonly listed eleven parts of Speech:
- preposition
- conjunction
- interjection
Parts of Speech – Video lesson
Related Posts

16 Verb and its Types | Download Detailed Lesson
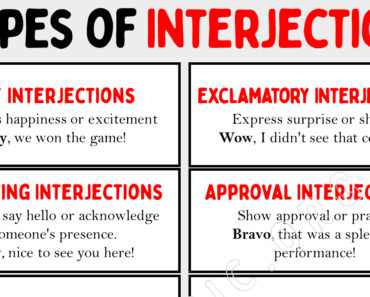
Types of Interjection Definition and Examples
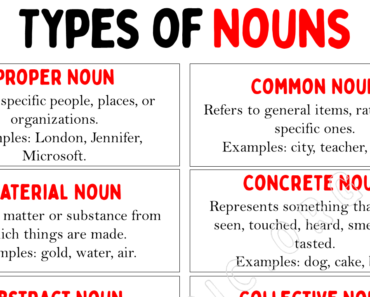
10 Types of Nouns in English Grammar

Learn 4 Different Types of Conjunction in Grammar

10 Different Types of Pronouns in English Grammar
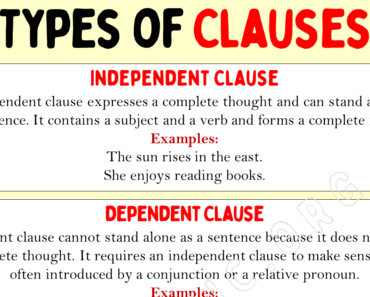
Clause and its Types
About the author.
Hi, I'm USMI, engdic.org's Author & Lifestyle Linguist. My decade-long journey in language and lifestyle curation fuels my passion for weaving words into everyday life. Join me in exploring the dynamic interplay between English and our diverse lifestyles. Dive into my latest insights, where language enriches every aspect of living.

Learning English: The 8 Parts of Speech and How to Use Them
When you begin learning the English language, you will probably start by studying the basics, like the 8 Parts of Speech and How to Use Them . In the English language, every single word in a sentence can be classified as a part of speech. The role a word plays in a sentence tells you what part of speech it belongs to and how to use it.
Now, the grammatical rules of English can get a bit confusing. We’re going to focus on the basics today and leave the more nuanced complexities for another time. So what are the 8 parts of speech, and how do you know which words are classified in each part?
What is a Part of Speech?
Parts of speech can be defined as categories of words that perform different roles or serve a similar grammatical purpose in a sentence. In the English language, the 8 basic parts of speech would be nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections . Each of the categories plays a different part in communicating meaning within a sentence. While these 8 parts of speech also have subcategories, we’re just going to focus on the basics today.
The 8 Parts of Speech with Examples
Nouns are a category of words that generally refer to people, living creatures, places, objects, ideas, and events. Again, this is a pretty simplistic definition, but we don’t want to get into the more abstract possibilities today.
Nouns can be classified into two main groups: common nouns and proper nouns . Common nouns are used to indicate a generic noun and don’t name specific items. They refer to things like people (the woman, the boy), living creatures (horse, tree), places (country, school), objects (book, car), ideas (culture, justice), states of being (integrity, beauty), and events (party, concert).
Proper nouns are more specific than common nouns. Names are considered proper nouns. For example, while “country” is a common noun, Mexico is a proper noun since it refers to a specific country. You’ll usually see the first letter of a proper noun capitalized, which can help give you clues when you’re learning to distinguish between common and proper nouns.
Examples of nouns used in sentences:
- He is my father . ( person )
- I have a pet and a plant . ( living creatures )
- This is my house . ( place )
- He drew a picture . ( object )
- She is full of excitement . ( idea )
- They are going to a party . ( event )
#2 | Pronouns
Pronouns are pretty simple. They are (generally short) words that can be substituted for either a noun or a noun phrase. We use them to make language less awkward by allowing us to refer to someone or something without having to repeat the noun over and over. For example, if I’m telling you about my cousin Javier, it would start to sound strange if I repeated his name too frequently. So instead, I’d use a pronoun, like he or him, to refer to Javier throughout the story.
There are a few different types of pronoun classes. The most commonly used pronouns are personal pronouns: she, her, he, him, I, me, you, it, we, us, they, and them . Then you have possessive pronouns that you would use to indicate ownership: my, your, its, his, her, our, their, and whose . Other examples of pronouns would include: t hese, those, who, what, which, and whose. While this list is not exhaustive, it’s a pretty good foundation for beginners learning English.
Examples of pronouns used in sentences:
- He is my father.
- I have a pet and a plant.
- This is my house.
- He drew a picture.
- She is full of excitement.
- They are going to her party.
You might hear verbs referred to as action words in early lessons. In sentences, verbs explain or describe what the subject of the sentence is doing or their state of being. To make a complete sentence, you must have both a subject and a verb. Some basic examples would include run, jump, speak, listen, and play . Sometimes verbs have helper words. It would be grammatically correct to say both “I can jump” and “I am jumping”, although they mean slightly different things.
English has a whole bunch of irregular verbs as well, which we won’t be diving into today. They are easier to pick up for native speakers as you can generally “hear” when they sound correct or not. It’s more difficult to explain why they are that way, even when we know they’re right or wrong. English is weird.
Examples of verbs used in sentences:
- He is my father. I am Luke.
- We listened to the teacher in class.
- He painted a picture for his mother.
- She ate cake at the party.
- They are going on vacation.
#4 | Adjectives
Adjectives add color and description to your sentences. We use adjectives to describe a noun or pronoun and give more detail by describing how they look, smell, feel, taste, sound, feel, and more . Adjectives often let us answer the questions of which one, what kind, or how many . Articles, short words that are often considered adjectives, would be words like a, an, and, and the .
Examples of adjectives used in sentences:
- My father enjoys fresh, green apples.
- I have a furry pet and a spiky plant.
- My house has a large yard.
- He drew a colorful picture.
- She is excited to watch the graceful dancers.
- They are going to a birthday party.
| Parts of Speech | Function | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Used to name people, places, animals, ideas, and things | Is this your ? I have a that likes to eat . | |
| Used as a substitute for a noun in a sentence | went to the store to buy a present for mom. Do know called earlier? | |
| Indicates an action or a state of being | They to class. The dog with the ball every day. | |
| Describes a noun or subject of the sentence | The classroom was and full of students. | |
| Modifies an adjective, verb, or another adverb | Did you come to buy a book? (Adverb of ) I did not go to the store . (Adverb of ) She reads books . (Adverb of ) Can you please come ? (Adverb of ) He was so tired that he could keep his eyes open. (Adverb of | |
| Shows the position/relation of an object or the subject in a sentence | The man searched the car for the cat that ran him. | |
| Joins words, phrases, and clauses | The students the teachers were ready the weekend. | |
| Expresses emotion or excitement |
#5 | Adverbs
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs in a sentence. Adverbs usually answer the questions how?, when?, where?, in what way?, and to what extent? There are five main types of adverbs: adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency . While adverbs commonly end in -ly, not all do. Some examples of adverbs are today, slowly, here, often, randomly, early, 8 a.m. etc .
Examples of adverbs used in sentences:
- Did you come here to buy a book? (Adverb of place )
- I did not go to the store today . (Adverb of time )
- Can you please come quickly ? (Adverb of manner )
- He was so tired that he could hardly keep his eyes open. (Adverb of degree )
- She reads books everyday . (Adverb of frequency )
#6 | Prepositions
Prepositions are pretty simple. They are words we use to link one part of the sentence to another and to show the position of the object or subject in a sentence. Prepositions convey things such as position, place, direction, movement, time, possession, comparison, and how an action is completed. Some examples of prepositions are under, above, in, out, besides, in front of, through, near, opposite, across from, etc.
Examples of prepositions used in sentences:
- My father found an apple underneath the tree.
- The boy ran through the yard looking around for his dog.
- The grocery store is across from the gas station.
- We need to get gas before we go to the concert.
- Because of the rain, she grabbed the umbrella next to the door.
#7 | Conjunctions
We’re almost done, hang in there! Let’s take a look at conjunctions. These are words we use to connect different parts of a sentence, clause, or phrase in English. Conjunctions are also used when making lists within sentences. Some of the most common conjunctions are for, and, but, nor, yet, so, and or , but there are many more out there!
Examples of conjunctions used in sentences:
- My father found an apple underneath the tree, so he ate it.
- The boy ran through the yard looking, and then he jumped over the fence.
- We went to the grocery store for cookies, and they were delicious!
- We need to get gas before we go to the concert, or we won’t make it.
- She grabbed the umbrella, her raincoat, and her boots.
#8 | Interjections
Woohoo! We’re almost done, and the last part of speech you need to learn about today is one of the easiest to identify. Interjections are words that are used to convey strong feelings or emotions, and they are often, but not always, followed by an exclamation mark. They’re usually at the beginning of a paragraph, but that’s not always the case. Some examples of interjections would be oh, wow, ugh, woohoo, yikes, alas, yippee, etc.
Examples of interjections used in sentences:
- Wow! That meal was delicious.
- Ouch! You stepped on my foot.
- Oh my! That is a beautiful dress.
- Ugh! We’re having sandwiches again?
- Woohoo! We won the game!
Feeling Overwhelmed? Excel English Institute Can Help You Learn English
That may seem like a lot to learn, especially when you’re just getting started. But don’t feel overwhelmed! These are the basic building blocks for the sentences in English, and they will begin to feel more natural as you continue to learn and practice.
If you want to improve any area of your English language skills, you might be interested in one of our English classes . We have new sessions starting every few weeks , and you can apply anytime !

- 1101 East Arapaho Rd Suite 150 Richardson, TX 75081 214-363-1700 2415 Avenue J Suite 100 Arlington, TX 76006 817-262-2667 > Admissions
- info@excelenglishinstitute.com
- Program Payment
All sales final. No refunds.

Excel English Institute is accredited by the Commission on English Language Program Accreditation for the period April 2024 through April 2033 and agrees to uphold the CEA Standards for English Language Programs and Institutions. CEA is recognized by the U.S. Secretary of Education as a nationally recognized accrediting agency for English language programs and institutions in the U.S. For further information about this accreditation, please contact CEA, 1001 N. Fairfax Street, Suite 630, Alexandria, VA 22314, (703) 665-3400, www.cea-accredit.org .

This school is authorized under Federal law to enroll nonimmigrant alien students.

How to File a Complaint

We're not available right now, but you can send us an email and we'll get back to you as soon as possible.

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
Lessons For English
8 Parts of Speech, Parts of Speech Exercises, Definition and Example Sentences
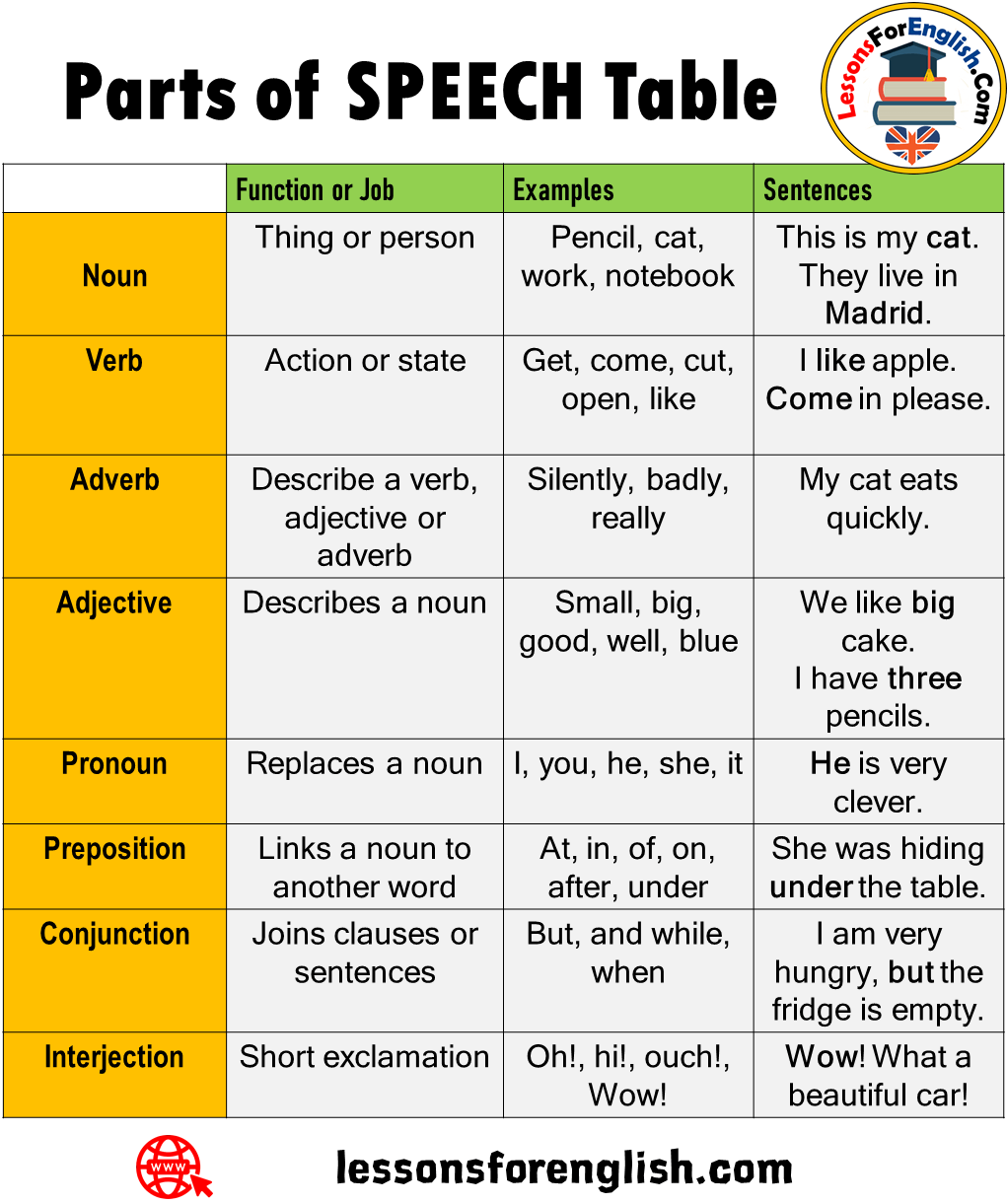
Table of Contents
Parts of Speech
If we consider a sentence in English as a wall, there should be bricks, to build it, right? These bricks are called parts of speech. Parts of speech are the functionally differentiated parts of a sentence. There are 8 parts of speech in English.
To use English better and understand it well you should know these 8 parts of speech. What are they? You will be learning throughout this page.
Nouns are the leader part of a sentence. They could be anything like a person, people, an object, a thing, a thought. The noun is the base of a sentence.
A noun can be an object, a subject of an action, or a statement. The bold written words of the sentences of the examples below are nouns.
- Bojack Horseman is a melancholic horse-man in the series.
- A pretty woman is walking down the street.
- Marcus Miller is one of the greatest bassists in the world. This guy is not breaking a leg. He is breaking the entire skeleton.
Pronouns are the words that are used to refer to a noun. They can be referring to multiple nouns. Also, pronouns mention the gender of the noun they refer to. For pronoun examples in bold:
- I was made for loving you baby.
- Have you heard anything about Jane? We haven’t seen her for a while.
- There was not any single memory from her ex-boyfriend. Probably, she demonized him to get over better.
Verbs are the part of speech that carry on the expression or action of the sentence. You express your ideas by verbs. In English, some words could be different forms in different tenses. Let’s find out the verbs in the following examples. The bold words are the verbs of sentences.
- You gave the love a bad name, she said . (The quotations don’t include verbs)
- When the wild wind blows , I will come home and hug
- Dark Tranquility is a metal band influenced by several genres such as heavy metal, melodic metal, and symphonic metal.
- I am the one who walks alone walking the dark road.
Adjectives are the part of speech that describes any noun of the sentence. You can find the following question. How is a noun?
- A pretty woman is walking towards the dog.
- The French Revolution was really bloody.
- When the wild wind blows, the red tree will be in danger.
- I have the higher ground Luke, he said.
Preposition
The role of a preposition in a sentence is to present the relations of the noun or pronoun between the other objects of the sentence. The relations can be in the framework of spatial or temporal or role.
- There was a rage against the machine.
- We were talking about
- Gather around my children.
Conjunction
Conjunction exists in a sentence to join two different sentences.
- I wasn’t hungry but I have eaten all the donuts
- Life continues and the band goes on.
Articles and Determiner
The main role of articles and determiners is to specify the thing is being used. You don’t say “a girl” when you describe your crush. You say “the girl”.
- A child should always be happy.
- The children in the backyard are playing.
Interjection
Interjections are one of the parts of speech. They carry out a high amount of emotions or reactions towards anything.
- Ooops , said Barney. I didn’t know she was your crush.
- D’oh! Bart is stealing my donuts, Marge.
- Yeah! I call this a triple shot.
Related Posts
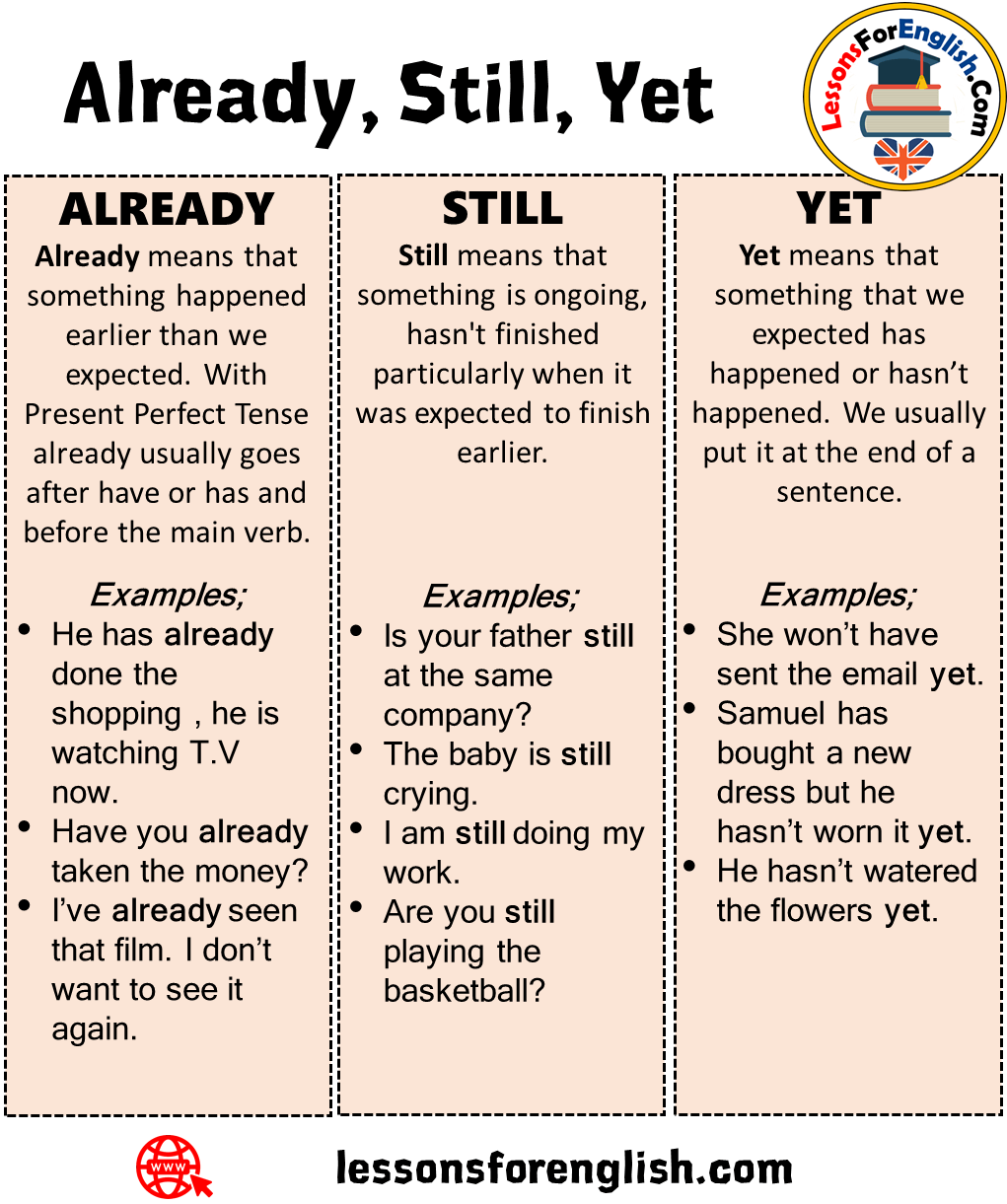
How to use Already, Still, Yet in English and Example Sentences

Uses This, That, These, Those in English, Definition and Example Sentences
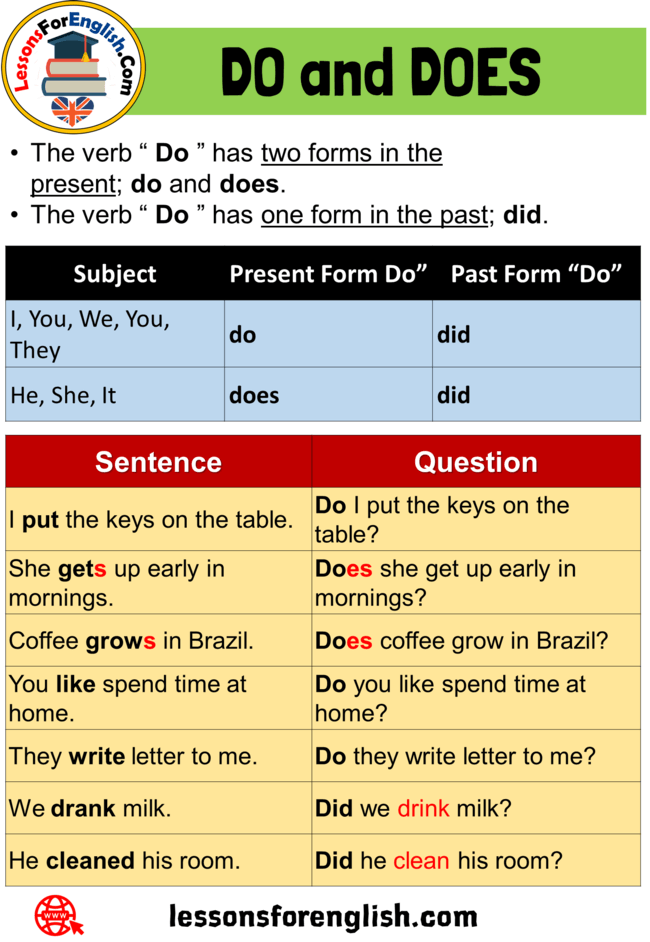
Uses DO and DOES, Definition and 7 Examples
About the author.
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In English, there are eight parts of speech: Verbs. Nouns. Adjectives. Adverbs. Pronouns. Interjection. Conjunction. Prepositions; Let's explore these parts of speech in more detail! A List of 8 Parts of Speech Verbs. Definition: Verbs express actions or states of being within a sentence. Examples: She goes to school every day. He writes a ...
Parts of speech are an important aspect of the language taught in English Language Arts and English as a New Language classrooms. Not only do the parts of speech help in formulating correct sentences, they also help the reader to understand what is taking place. ... 8 Parts of Speech Lesson Plans . In reading and writing, it is important to ...
Do you know the 8 parts of speech? Nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, conjunctions and prepositions? 📝 *GET THE FREE LESSON PDF* _here_ 👉🏼 https...
The eight parts of speech are nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Each part of speech is explained with examples below. Each part of speech ...
A part of speech (also called a word class) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence.Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing. The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs ...
True or false: a word can be different parts of speech depending on its function and meaning in the sentence. 1. 2. True or false: a noun can be a word or a phrase. 1. True. 2. False. True or false: if a word can be a noun, it can only be a noun.
Parts of Speech: The Ultimate Guide for Students and Teachers. By Shane Mac Donnchaidh September 11, 2021March 5, 2024 March 5, 2024. This article is part of the ultimate guide to language for teachers and students. Click the buttons below to view these.
Learn the eight parts of speech: 1) Noun, 2) Verb, 3) Pronoun, 4) Adjective, 5) Adverb, 6) Conjunction, 7) Preposition, and 8) Interjection. In this video, w...
The parts of speech explain how a word is used in a sentence. There are eight main parts of speech (also known as word classes): nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections. Most parts of speech can be divided into sub-classes.Prepositions can be divided into prepositions of time, prepositions of place etc. Nouns can be divided into proper nouns ...
Free online lessons and exercises on the eight parts of speech. These online English lessons teach students about all eight parts of speech including verbs, adjectives, nouns, adverbs, prepositions, pronouns, conjunctions, and interjections. These online exercises are sure to improve punctuation and writing. Come learn English online with English Maven!
Introduction. (10 minutes) Ask your students the meaning of the following parts of speech: noun, verb, adjective, and pronoun. Explain to your students that a noun is a person, place, animal, or thing. Tell your students that a verb is an action. Remind them that a pronoun is a word that is used instead of a noun.
* Some grammar sources traditionally categorize English into 8 parts of speech. Others say 10. At EnglishClub, we use the more recent categorization of 9 parts of speech. Examples of other categorizations are: Verbs may be treated as two different parts of speech:
The 9 parts of speech are adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, determiners, interjections, nouns, prepositions, pronouns, and verbs. (These are also known as "word classes.") A Formal Definition. A "part of speech" is a category to which a word is assigned in accordance with its syntactic functions. In English, the main parts of speech are noun ...
ESL Parts of Speech Activities, Worksheets & Lesson Plans. In English, there are 8 parts of speech: adjectives, adverbs, nouns, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections. In this article, you'll find parts of speech activities and games, along with worksheets and lesson plans. Why is it important for ESL students to understand ...
Learn the 8 basic parts of speech in English. Once you learn the parts of speech, it will be much easier for you to understand other grammar lessons as you progress in your English studies. In this class, I explain what each part of speech is, and will give you examples of each as well. ... Test your understanding of the English lesson by ...
What are the 8 parts of speech? Parts of speech are a very important part of English grammar. For an ESL student learning parts of speech is a must thing to do. It will help in building the initial concepts. It is the building block of English grammar. Here is the quick list of 8 Parts of Speech: Noun; Pronoun; Adjective; Adverb; Conjunction ...
A part of speech is simply the name given to a word based on the function it performs in a sentence. Learning parts of speech is necessary to understand the correct definition of a word and to speed up your study of English grammar.. You can think of parts of speech like job titles. Just as a person can be a soldier, a teacher or a baker, a word can be a noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb ...
Parts of speech can be defined as categories of words that perform different roles or serve a similar grammatical purpose in a sentence. In the English language, the 8 basic parts of speech would be nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.Each of the categories plays a different part in communicating meaning within a sentence.
Challenge students by using words, like 'but' and 'pretty' instead of the 8 parts of speech. As an exit slip, ask students to write the 8 parts of speech and give examples of each without using notes.
Nouns are the leader part of a sentence. They could be anything like a person, people, an object, a thing, a thought. The noun is the base of a sentence. A noun can be an object, a subject of an action, or a statement. The bold written words of the sentences of the examples below are nouns. Bojack Horseman is a melancholic horse-man in the series.
of words and then see how they can help us further understand the parts of. r a diagram of the parts of speech, see the final page of this handout.]Parts of SpeechTher. are eight forms of words in the English language, typically called the parts of speech. They are no. , adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interject.
The document outlines an English lesson plan about the eight parts of speech. It includes objectives, subject matter, procedures, and an evaluation. The lesson plan aims to teach students to identify and explain the eight parts of speech, and create sentences applying them. The procedures involve introducing each part of speech through examples, discussion, and an activity where students write ...
That was part of this deal we put together, this bipartisan deal. More fentanyl machines, were able to detect drugs, more numbers of agents, more numbers of all the people at the border.