

How To Cite a Research Paper: MLA, APA, and Chicago Style
- Posted on January 25, 2022
When you’re writing a research paper, you’ll use a variety of sources to find information. You might find that you end up using other people’s research papers as sources of information for your own work. You need to know how to cite a research paper properly.
Using text citations tells readers where you got your information, and help build a sense of trust, allowing the reader to feel confident that you haven’t falsified the information. You have to prove that you’ve done the research and found data to back up the claims you’re making.
Writing a paper without giving credit to people whose work you’re using is plagiarism. Unless you’re citing a direct quote you want to change the language enough, by putting the quote in your own words, so it sounds like original content. Quetext’s plagiarism checker helps you search for similar content across the web so you can turn in a completely original paper.
Whether you’re submitting a research paper to school or for publication in a peer-reviewed journal, you’re required to cite your sources. Editors often reread the work of writers and researchers to ensure the information is factual. A teacher or professor will definitely check that your sources are accurate, so using tools like Quetext will help avoid unintentional plagiarism errors or wrongfully cited information.
Why Text Citations are Important
If you don’t have sources to back up your research, others might accuse you of spreading false information or plagiarism. Any journal publishing papers should verify what they’re printing, but ultimately, as the author, the buck stops with you.
In general, it’s a kindness to cite your sources. The people who created them did a lot of work, so it’s wrong to claim ownership of their ideas and information. But it’s also an ethical issue that can have major repercussions.
There have been cases where researchers make up information or falsify their sources and must face the consequences. People depend on factual information and don’t react well when they realize you lied to them or falsely paraphrase information.
That’s why it’s common knowledge to write a well-researched paper with text citations. If anyone claims your information is incorrect, you can point them to the source where you found the data. This doesn’t guarantee that the information you cited is correct, but you’ll be able to provide readers with a source of where you gathered your information.
When you’re citing other people’s research papers, make sure the source is legitimate. You should only use peer-reviewed journals so you know the article has gone through edits and fact-checking. Something identified as a research paper that is only on a blog or message board isn’t always a reliable source.
Many students like to use Wikipedia because there’s so much information available from one source. However, Wikipedia allows users to edit the information. What you read in a specific entry might not be true. It’s best to scroll down to the works cited and go to the original source yourself. If you can’t find a reliable, original source for the information, you shouldn’t use it.
Using the Various Citation Styles
The information used in any citation is basically the same across each style guide. The formatting and order of some elements may vary, so it’s important to know the difference between Modern Language Association (MLA), American Psychological Association (APA), and Chicago Styles.
The style you use depends on what type of writing you’re doing. All will use these basic elements in some form or another:
Source name
Volume and edition
Publication date
Page numbers
Publisher name
City and country of the publisher
URL and DOI for web pages and digital sources
The date you accessed the material
In addition to a reference list at the end of your work, you’ll also use in-text citations. Whenever you reference an idea or data that isn’t yours, you cite it. Each style has different types of in-text citations as well. Read on to find out about each citation format.
You’ll likely use the MLA citation guide if you’re writing papers in the humanities, such as for language arts, literary criticism, cultural studies, and more. The current edition of the MLA Handbook is the ninth because the style constantly evolves. As new technology creates new potential sources, MLA adds information to help students and researchers cite everything correctly.
The MLA Handbook has instructions on how to cite song lyrics, social media posts, and digital images, along with all of the standard research outlets. The book also gives detailed information on how to cite a research paper.
The MLA Handbook includes information about how to format your reference page. Use a 12-pt standard font like Times New Roman, so the text in italics is clearly different from the regular font. Center the title, Works Cited, at the top of the page. Your last name and page number are in the top right corner, and the reference page always comes at the end of your document.
Alphabetize citations according to the last name of the author. Left-align the citations and double-space them with no extra lines between each entry. When a citation goes beyond a single line, use a hanging indent to format it correctly. This lets the reader know it’s still the same citation continuing on.
Now that you know the basic format for the Works Cited page read on to find out how to cite a research paper for inclusion on this list.
Citing a Research Paper in MLA Style
When you’re citing a research paper in MLA style, you start with the author’s full name, putting the last name of the author first, followed by the title of the research paper in quotation marks. Next comes the the title of the journal that published the paper in italics, followed by the volume number, issue number, and date of publication.
You’ll also include the page number since the paper is in a journal with many pages. If you found the source online, include the digital object identifier or DOI. The DOI is a way to give a document a permanent web address so people reading your work can easily find the source.
MLA format also asks you to include the date you accessed online materials. Doing so gives your reader more information about when you read the research if it changed since that date. Here is an example of a research paper citation in MLA style:
Writer, Maria. “My Research Paper.” Research Journal, vol 3, no. 4, 2020, pp. 7-9. doi:12.34/mfs.12.34. Accessed 13 March 2021.
If the work wasn’t published online, you could stop your citation after the page numbers.
Sometimes you might find research papers that aren’t published in a scholarly journal. You can still use those in your work, but the MLA citation will look different. You’ll still put the last name of the author first, but instead of putting the title of the research paper in quotation marks, you’ll put it in italics.
Here is an example of an unpublished research paper citation in MLA style:
Writer, Maria. My Research Paper. 2020, http://websiteused.com . Accessed 13 March 2021.
These two examples show you how to document the source on your Works Cited page. In-text citations look different.
In-Text Citations for a Research Paper in MLA Style
When you’re working with the MLA format, an in-text reference requires a parenthetical citation.
If you refer to someone else’s research in a sentence, either with a direct quote or by paraphrasing, you need to give that author credit. At the end of the sentence where you use the information, you’ll put the author’s information in parenthesis and then put the sentence’s ending punctuation.
You use the author’s last name and the page number where you found the information for in-text citations. Then anyone reading your work can go to your Works Cited page, find the entry by the author’s last name, and access the document themselves. The page number directs them to where you got the specific information, so they don’t have to read the whole paper to find it. Here is an example of an in-text citation in MLA style:
Over 80% of the city’s garbage ended up in the ocean (Writer, 8).
You might mention the author’s name in your sentence. In that case, the parenthetical citation only needs to have the page numbers for reference. Here is an example:
According to Maria Writer, over 80% of the city’s garbage went into the ocean (8).
Researchers in the social science field, like sociology, anthropology, and psychology, use the APA style in their work. Like the MLA Handbook, the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association has gone through changes over the years. It’s currently on the 7th edition.
In addition to helping you understand how to cite research, the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association has information about how to format your paper to include tables, figures, and headings that often accompany scientific journal articles.
The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association also tells you how to format your reference page. In MLA style, this is the Works Cited page. For APA style, it’s either the Reference List or Reference Page.
This page uses the same font style as the rest of the paper but starts on its own page with a number in the top right corner. The title of the page is bold and centered at the top and should simply read “References.”
List citations in alphabetical order by author’s last name regardless of the type of source. Each citation is double-spaced and has a hanging indent if it goes beyond one line.
Now that you understand how to properly format your APA reference page, learn how to cite a research paper to include on the list.
Citing a Research Paper in APA Style
When you use a research paper in your work, you need to include it on your APA references page at the end of your document.
An APA citation includes the same information as the MLA format but in a different order. The citation starts with the author’s last name but only uses their first initial. Then comes the year of publication in parenthesis.
The paper’s title follows, then the title of the journal in italics. You also include the journal volume, issue number, and page numbers. As with MLA citations, include a DOI if you found the research paper online. Here is an example of a published research paper cited in APA format:
Writer, M. (2020). My Research Paper. Research Journal, 3(4), 7-9. doi:12.34/mfs.12.34
If the paper isn’t published in a journal, you can still use it in your work with a proper citation. Here is an example:
Writer, M. (2020). My Research Paper [PDF]. Retrieved from http://websiteused.com
In-Text Citations for a Research Paper in APA Style
In-text citations in the APA format differ from MLA style. You still put it in parenthesis, but you include different information. For APA parentheticals, include the author’s last name and the paper’s year of publication. This method applies when you’re summarizing or paraphrasing the author’s idea. Here is an example of an in-text citation for a research paper in APA style:
Over 80% of the city’s garbage went into the ocean (Writer, 2020).
If you’re using a direct quote from the work you need to include the page number so the reader can find the quotation. Here is an example:
Maria Writer said, “Over 80% of the city’s garbage is going into the ocean” (2020, p. 8).
Chicago Style
Chicago Style got its name from the University of Chicago, where the style originated. Writers use this format for works in the field of history, but you can also use it for the sciences, social sciences, and humanities.
MLA style has a Works Cited page, APA has References, and Chicago Style differs because it includes a Bibliography. The page comes at the end of your work with a page number in the top right corner. The title, “Bibliography,” is bold and centered at the top.
You will single-space your citations, but you’ll add an extra line between each entry. As with the other reference pages, you’ll left-align the work and use a hanging indent when a citation continues onto a second line.
Having an overview of how to format the bibliography will help you understand the citation styles for a research paper.
Citing a Research Paper in Chicago Style
Citations in Chicago Style are a mix of MLA and APA formats. It’s easiest to follow this template:
Writer, Maria. 2020. “My Research Paper.” Research Journal 3 (4): 7-9. doi:12.34/mfs.12.34.
As with other styles, you can reference an unpublished research paper as a document. Here is an example:
Writer, Maria. 2020. My Research Paper. PDF. http://websiteused.com .
In both instances, if there are multiple authors for a paper, list the rest of the authors in normal format. For example:
Author, Alan, Stanley Sample, and Maria Writer. 2020. “My Research Paper.” Research Journal 3 (4): 7-9. doi:12.34/mfs.12.34.
In-Text Citations for a Research Paper in Chicago Style
An in-text citation in Chicago Style is much simpler than both MLA and APA formats. You only need to include the last name of the author and year of publication in parenthesis with no comma in between them. For example:
Almost 80% of the city’s garbage goes into the ocean (Writer 2020).
You’ll include the page number for specificity if you’re quoting the author. Here’s an example:
Maria Writer said, “Over 80% of the city’s garbage is going into the ocean” (2020, 8).
You can also use endnotes in Chicago Style. A citation refers the reader to your source, but an endnote includes a bit of an explanation of why you used it. The information included in an endnote would disrupt the flow of your paper, but it’s still something you want the reader to know.
Make Text Citations Easy
Knowing when you need to cite a source helps you manage your research. Anytime you find information that you’re going to paraphrase, summarize, or quote in your work, you need to cite the source. The full citation will go on your reference page, but you’ll need an in-text citation where you use the information in your paper.
When you’re stating something that is common knowledge , there’s no need to make a citation. Common knowledge is something that your reader would believe without needing proof. You can check if something is common knowledge by searching for it and finding it mentioned, without a citation, in at least five sources.
Once you learn the basics about citing a research paper in MLA, APA, and Chicago Styles, you’ll feel more confident in your work. The important thing is to pay attention to small details, like capitalization, italics and the use of abbreviations. But there’s no need to do it all on your own—Quetext has a citation assistant waiting to help. Give Quetext citation generator a try on your next project.
Sign Up for Quetext Today!
Click below to find a pricing plan that fits your needs.
You May Also Like

A Safer Learning Environment: The Impact of AI Detection on School Security
- Posted on May 17, 2024

Rethinking Academic Integrity Policies in the AI Era
- Posted on May 10, 2024 May 10, 2024

Jargon Phrases to Avoid in Business Writing
- Posted on May 3, 2024 May 3, 2024

Comparing Two Documents for Plagiarism: Everything You Need to Know
- Posted on April 26, 2024 April 26, 2024

Mastering Tone in Email Communication: A Guide to Professional Correspondence
- Posted on April 17, 2024

Mastering End-of-Sentence Punctuation: Periods, Question Marks, Exclamation Points, and More
- Posted on April 12, 2024

Mastering the Basics: Understanding the 4 Types of Sentences
- Posted on April 5, 2024

Can You Go to Jail for Plagiarism?
- Posted on March 22, 2024 March 22, 2024
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Erin Wright Writing
Writing-Related Software Tutorials
How to Insert Citations in Microsoft Word (Step-by-Step)
By Erin Wright
Managing citations for research papers, theses, dissertations, and other nonfiction works can be overwhelming. However, you can ease the process by learning how to insert citations in Microsoft Word using the software’s citation and bibliography tools.
This tutorial covers six topics:
- How to select a citation style
- How to insert citations for new sources
- How to insert citations for existing sources
- How to edit sources
- How to use citation placeholders
- How to insert bibliographies, reference lists, or works cited lists
Important Note: At the time this tutorial was published, Microsoft Word did not offer the most up-to-date formatting for several of our primary style guides , including APA, Chicago, MLA, and Turabian. Therefore, I encourage you to review the available styles before using the citation and bibliography tools. We will cover the steps to customize citation and bibliography styles in a separate tutorial.
This tutorial is also available as a YouTube video showing all the steps in real time.
Watch more than 200 other writing-related software tutorials on my YouTube channel .
The images below are from Word in Microsoft 365. The steps are the same in Word 2021, Word 2019, and Word 2016. However, your interface may look slightly different in those older versions of the software.
How to Select a Citation Style in Microsoft Word
- Select the References tab in the ribbon.

- Select your citation style from the Style menu in the Citations & Bibliography group.

How to Insert Citations for New Sources in Microsoft Word
- Place your cursor where you want to insert the citation.

- Select the References tab in the ribbon (see figure 1).
- Select the Insert Citation button in the Citations & Bibliography group.

- Select Add New Source from the drop-down menu.

- Select the source type from the Type of Source menu in the Create Source dialog box.

- Enter the source information into the bibliography fields.

- (Optional Step) Select Show All Bibliography Fields if you need to add additional information.

- (Optional Step) Enter the source information into the additional fields.

- Select the OK button.

Your citation should appear in your text.

How to Insert Citations for Existing Sources in Microsoft Word
Once you enter a source, as shown in the section above, you can create additional citations for that source without reentering the information.
- Place your cursor where you want to insert the citation (see figure 3).
- Select the Insert Citation button in the Citations & Bibliography group (see figure 4).
- Select the source from the drop-down menu.

Your citation should appear in your text (see figure 11).
How to Edit Sources in Microsoft Word
When you edit an existing source, you will also edit any existing citations for that source in your current document.
- Select the Manage Sources button in the Citations & Bibliography group.

- Select the source you want to edit in the Master List or the Current List in the Source Manager dialog box.

Pro Tip: The Master List is stored in your computer and is accessible in all your documents. The Current List is part of your current file and is only accessible in that file. By default, Word stores new sources in the Master List and the Current List.
- Select the Edit button.

- Enter your edits in the Edit Source dialog box. (Select Show All Bibliography Fields , if necessary.)

- Select Yes or No in the alert box stating that you will be updating the source in both the Master List and the Current List. (Strongly consider selecting Yes to update both lists if you plan to cite this source in future documents.)

- Select the Close button in the Source Manager dialog box.

How to Use Citation Placeholders in Microsoft Word
You can use placeholders if your source information is not available.
- Place your cursor where you want to insert the citation placeholder.
- Select Add New Placeholder from the drop-down menu.

- (Optional Step) Change the name of the placeholder in the Placeholder Name dialog box.

Pro Tip : You can use the same placeholder in the future by selecting it from the Insert Citation drop-down menu (see figure 12).
- When you are ready to replace the placeholder with a source, complete the steps in How to Edit Sources above.
How to Insert Bibliographies, Reference Lists, or Works Cited Lists in Microsoft Word
These steps will only work if you inserted your sources using Word’s citation and bibliography tools.
- Place your cursor where you want to insert the bibliography, reference list, or works cited list.
- Select the Bibliography button in the Citations & Bibliography group.

- Select Bibliography , References , or Works Cited from the drop-down menu.

Your bibliography, reference list, or works cited list should appear in your document.
Related Resources
How to Create Hanging Indents in Microsoft Word
How to Insert Footnotes and Endnotes in Microsoft Word
How to Convert Individual Footnotes to Endnotes in Microsoft Word (and Individual Endnotes to Footnotes)
How to Create a Cover Page in Microsoft Word (Built-In and Custom)
How to Add Citations and a Bibliography in Google Docs
Updated May 21, 2023
- Microsoft Word Tutorials
- Adobe Acrobat Tutorials
- PowerPoint Tutorials
- Writing Tips
- Editing Tips
- Writing-Related Resources
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / How to Cite Sources
How to Cite Sources
Here is a complete list for how to cite sources. Most of these guides present citation guidance and examples in MLA, APA, and Chicago.
If you’re looking for general information on MLA or APA citations , the EasyBib Writing Center was designed for you! It has articles on what’s needed in an MLA in-text citation , how to format an APA paper, what an MLA annotated bibliography is, making an MLA works cited page, and much more!
MLA Format Citation Examples
The Modern Language Association created the MLA Style, currently in its 9th edition, to provide researchers with guidelines for writing and documenting scholarly borrowings. Most often used in the humanities, MLA style (or MLA format ) has been adopted and used by numerous other disciplines, in multiple parts of the world.
MLA provides standard rules to follow so that most research papers are formatted in a similar manner. This makes it easier for readers to comprehend the information. The MLA in-text citation guidelines, MLA works cited standards, and MLA annotated bibliography instructions provide scholars with the information they need to properly cite sources in their research papers, articles, and assignments.
- Book Chapter
- Conference Paper
- Documentary
- Encyclopedia
- Google Images
- Kindle Book
- Memorial Inscription
- Museum Exhibit
- Painting or Artwork
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Sheet Music
- Thesis or Dissertation
- YouTube Video
APA Format Citation Examples
The American Psychological Association created the APA citation style in 1929 as a way to help psychologists, anthropologists, and even business managers establish one common way to cite sources and present content.
APA is used when citing sources for academic articles such as journals, and is intended to help readers better comprehend content, and to avoid language bias wherever possible. The APA style (or APA format ) is now in its 7th edition, and provides citation style guides for virtually any type of resource.
Chicago Style Citation Examples
The Chicago/Turabian style of citing sources is generally used when citing sources for humanities papers, and is best known for its requirement that writers place bibliographic citations at the bottom of a page (in Chicago-format footnotes ) or at the end of a paper (endnotes).
The Turabian and Chicago citation styles are almost identical, but the Turabian style is geared towards student published papers such as theses and dissertations, while the Chicago style provides guidelines for all types of publications. This is why you’ll commonly see Chicago style and Turabian style presented together. The Chicago Manual of Style is currently in its 17th edition, and Turabian’s A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations is in its 8th edition.
Citing Specific Sources or Events
- Declaration of Independence
- Gettysburg Address
- Martin Luther King Jr. Speech
- President Obama’s Farewell Address
- President Trump’s Inauguration Speech
- White House Press Briefing
Additional FAQs
- Citing Archived Contributors
- Citing a Blog
- Citing a Book Chapter
- Citing a Source in a Foreign Language
- Citing an Image
- Citing a Song
- Citing Special Contributors
- Citing a Translated Article
- Citing a Tweet
6 Interesting Citation Facts
The world of citations may seem cut and dry, but there’s more to them than just specific capitalization rules, MLA in-text citations , and other formatting specifications. Citations have been helping researches document their sources for hundreds of years, and are a great way to learn more about a particular subject area.
Ever wonder what sets all the different styles apart, or how they came to be in the first place? Read on for some interesting facts about citations!
1. There are Over 7,000 Different Citation Styles
You may be familiar with MLA and APA citation styles, but there are actually thousands of citation styles used for all different academic disciplines all across the world. Deciding which one to use can be difficult, so be sure to ask you instructor which one you should be using for your next paper.
2. Some Citation Styles are Named After People
While a majority of citation styles are named for the specific organizations that publish them (i.e. APA is published by the American Psychological Association, and MLA format is named for the Modern Language Association), some are actually named after individuals. The most well-known example of this is perhaps Turabian style, named for Kate L. Turabian, an American educator and writer. She developed this style as a condensed version of the Chicago Manual of Style in order to present a more concise set of rules to students.
3. There are Some Really Specific and Uniquely Named Citation Styles
How specific can citation styles get? The answer is very. For example, the “Flavour and Fragrance Journal” style is based on a bimonthly, peer-reviewed scientific journal published since 1985 by John Wiley & Sons. It publishes original research articles, reviews and special reports on all aspects of flavor and fragrance. Another example is “Nordic Pulp and Paper Research,” a style used by an international scientific magazine covering science and technology for the areas of wood or bio-mass constituents.
4. More citations were created on EasyBib.com in the first quarter of 2018 than there are people in California.
The US Census Bureau estimates that approximately 39.5 million people live in the state of California. Meanwhile, about 43 million citations were made on EasyBib from January to March of 2018. That’s a lot of citations.
5. “Citations” is a Word With a Long History
The word “citations” can be traced back literally thousands of years to the Latin word “citare” meaning “to summon, urge, call; put in sudden motion, call forward; rouse, excite.” The word then took on its more modern meaning and relevance to writing papers in the 1600s, where it became known as the “act of citing or quoting a passage from a book, etc.”
6. Citation Styles are Always Changing
The concept of citations always stays the same. It is a means of preventing plagiarism and demonstrating where you relied on outside sources. The specific style rules, however, can and do change regularly. For example, in 2018 alone, 46 new citation styles were introduced , and 106 updates were made to exiting styles. At EasyBib, we are always on the lookout for ways to improve our styles and opportunities to add new ones to our list.
Why Citations Matter
Here are the ways accurate citations can help your students achieve academic success, and how you can answer the dreaded question, “why should I cite my sources?”
They Give Credit to the Right People
Citing their sources makes sure that the reader can differentiate the student’s original thoughts from those of other researchers. Not only does this make sure that the sources they use receive proper credit for their work, it ensures that the student receives deserved recognition for their unique contributions to the topic. Whether the student is citing in MLA format , APA format , or any other style, citations serve as a natural way to place a student’s work in the broader context of the subject area, and serve as an easy way to gauge their commitment to the project.
They Provide Hard Evidence of Ideas
Having many citations from a wide variety of sources related to their idea means that the student is working on a well-researched and respected subject. Citing sources that back up their claim creates room for fact-checking and further research . And, if they can cite a few sources that have the converse opinion or idea, and then demonstrate to the reader why they believe that that viewpoint is wrong by again citing credible sources, the student is well on their way to winning over the reader and cementing their point of view.
They Promote Originality and Prevent Plagiarism
The point of research projects is not to regurgitate information that can already be found elsewhere. We have Google for that! What the student’s project should aim to do is promote an original idea or a spin on an existing idea, and use reliable sources to promote that idea. Copying or directly referencing a source without proper citation can lead to not only a poor grade, but accusations of academic dishonesty. By citing their sources regularly and accurately, students can easily avoid the trap of plagiarism , and promote further research on their topic.
They Create Better Researchers
By researching sources to back up and promote their ideas, students are becoming better researchers without even knowing it! Each time a new source is read or researched, the student is becoming more engaged with the project and is developing a deeper understanding of the subject area. Proper citations demonstrate a breadth of the student’s reading and dedication to the project itself. By creating citations, students are compelled to make connections between their sources and discern research patterns. Each time they complete this process, they are helping themselves become better researchers and writers overall.
When is the Right Time to Start Making Citations?
Make in-text/parenthetical citations as you need them.
As you are writing your paper, be sure to include references within the text that correspond with references in a works cited or bibliography. These are usually called in-text citations or parenthetical citations in MLA and APA formats. The most effective time to complete these is directly after you have made your reference to another source. For instance, after writing the line from Charles Dickens’ A Tale of Two Cities : “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times…,” you would include a citation like this (depending on your chosen citation style):
(Dickens 11).
This signals to the reader that you have referenced an outside source. What’s great about this system is that the in-text citations serve as a natural list for all of the citations you have made in your paper, which will make completing the works cited page a whole lot easier. After you are done writing, all that will be left for you to do is scan your paper for these references, and then build a works cited page that includes a citation for each one.
Need help creating an MLA works cited page ? Try the MLA format generator on EasyBib.com! We also have a guide on how to format an APA reference page .
2. Understand the General Formatting Rules of Your Citation Style Before You Start Writing
While reading up on paper formatting may not sound exciting, being aware of how your paper should look early on in the paper writing process is super important. Citation styles can dictate more than just the appearance of the citations themselves, but rather can impact the layout of your paper as a whole, with specific guidelines concerning margin width, title treatment, and even font size and spacing. Knowing how to organize your paper before you start writing will ensure that you do not receive a low grade for something as trivial as forgetting a hanging indent.
Don’t know where to start? Here’s a formatting guide on APA format .
3. Double-check All of Your Outside Sources for Relevance and Trustworthiness First
Collecting outside sources that support your research and specific topic is a critical step in writing an effective paper. But before you run to the library and grab the first 20 books you can lay your hands on, keep in mind that selecting a source to include in your paper should not be taken lightly. Before you proceed with using it to backup your ideas, run a quick Internet search for it and see if other scholars in your field have written about it as well. Check to see if there are book reviews about it or peer accolades. If you spot something that seems off to you, you may want to consider leaving it out of your work. Doing this before your start making citations can save you a ton of time in the long run.
Finished with your paper? It may be time to run it through a grammar and plagiarism checker , like the one offered by EasyBib Plus. If you’re just looking to brush up on the basics, our grammar guides are ready anytime you are.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Citation Basics
Harvard Referencing
Plagiarism Basics
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
- TutorHome |
- IntranetHome |
- Contact the OU Contact the OU Contact the OU |
- Accessibility Accessibility
- StudentHome
- Help Centre
You are here
Help and support.
- Referencing and plagiarism
Quick guide to Harvard referencing (Cite Them Right)
- Accessibility statement: Library

Print this page
There are different versions of the Harvard referencing style. This guide is a quick introduction to the commonly-used Cite Them Right version. You will find further guidance available through the OU Library on the Cite Them Right Database .
For help and support with referencing and the full Cite Them Right guide, have a look at the Library’s page on referencing and plagiarism . If you need guidance referencing OU module material you can check out which sections of Cite Them Right are recommended when referencing physical and online module material .
This guide does not apply to OU Law undergraduate students . If you are studying a module beginning with W1xx, W2xx or W3xx, you should refer to the Quick guide to Cite Them Right referencing for Law modules .
Table of contents
In-text citations and full references.
- Secondary referencing
- Page numbers
- Citing multiple sources published in the same year by the same author
Full reference examples
Referencing consists of two elements:
- in-text citations, which are inserted in the body of your text and are included in the word count. An in-text citation gives the author(s) and publication date of a source you are referring to. If the publication date is not given, the phrase 'no date' is used instead of a date. If using direct quotations or you refer to a specific section in the source you also need the page number/s if available, or paragraph number for web pages.
- full references, which are given in alphabetical order in reference list at the end of your work and are not included in the word count. Full references give full bibliographical information for all the sources you have referred to in the body of your text.
To see a reference list and intext citations check out this example assignment on Cite Them Right .
Difference between reference list and bibliography
a reference list only includes sources you have referred to in the body of your text
a bibliography includes sources you have referred to in the body of your text AND sources that were part of your background reading that you did not use in your assignment
Back to top
Examples of in-text citations
You need to include an in-text citation wherever you quote or paraphrase from a source. An in-text citation consists of the last name of the author(s), the year of publication, and a page number if relevant. There are a number of ways of incorporating in-text citations into your work - some examples are provided below. Alternatively you can see examples of setting out in-text citations in Cite Them Right .
Note: When referencing a chapter of an edited book, your in-text citation should give the author(s) of the chapter.
Online module materials
(Includes written online module activities, audio-visual material such as online tutorials, recordings or videos).
When referencing material from module websites, the date of publication is the year you started studying the module.
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication/presentation) 'Title of item'. Module code: Module title . Available at: URL of VLE (Accessed: date).
OR, if there is no named author:
The Open University (Year of publication/presentation) 'Title of item'. Module code: Module title . Available at: URL of VLE (Accessed: date).
Rietdorf, K. and Bootman, M. (2022) 'Topic 3: Rare diseases'. S290: Investigating human health and disease . Available at: https://learn2.open.ac.uk/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=1967195 (Accessed: 24 January 2023).
The Open University (2022) ‘3.1 The purposes of childhood and youth research’. EK313: Issues in research with children and young people . Available at: https://learn2.open.ac.uk/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=1949633§ion=1.3 (Accessed: 24 January 2023).
You can also use this template to reference videos and audio that are hosted on your module website:
The Open University (2022) ‘Video 2.7 An example of a Frith-Happé animation’. SK298: Brain, mind and mental health . Available at: https://learn2.open.ac.uk/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=2013014§ion=4.9.6 (Accessed: 22 November 2022).
The Open University (2022) ‘Audio 2 Interview with Richard Sorabji (Part 2)’. A113: Revolutions . Available at: https://learn2.open.ac.uk/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=1960941§ion=5.6 (Accessed: 22 November 2022).
Note: if a complete journal article has been uploaded to a module website, or if you have seen an article referred to on the website and then accessed the original version, reference the original journal article, and do not mention the module materials. If only an extract from an article is included in your module materials that you want to reference, you should use secondary referencing, with the module materials as the 'cited in' source, as described above.
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of message', Title of discussion board , in Module code: Module title . Available at: URL of VLE (Accessed: date).
Fitzpatrick, M. (2022) ‘A215 - presentation of TMAs', Tutor group discussion & Workbook activities , in A215: Creative writing . Available at: https://learn2.open.ac.uk/mod/forumng/discuss.php?d=4209566 (Accessed: 24 January 2022).
Note: When an ebook looks like a printed book, with publication details and pagination, reference as a printed book.
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) Title . Edition if later than first. Place of publication: publisher. Series and volume number if relevant.
For ebooks that do not contain print publication details
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) Title of book . Available at: DOI or URL (Accessed: date).
Example with one author:
Bell, J. (2014) Doing your research project . Maidenhead: Open University Press.
Adams, D. (1979) The hitchhiker's guide to the galaxy . Available at: http://www.amazon.co.uk/kindle-ebooks (Accessed: 23 June 2021).
Example with two or three authors:
Goddard, J. and Barrett, S. (2015) The health needs of young people leaving care . Norwich: University of East Anglia, School of Social Work and Psychosocial Studies.
Example with four or more authors:
Young, H.D. et al. (2015) Sears and Zemansky's university physics . San Francisco, CA: Addison-Wesley.
Note: You can choose one or other method to reference four or more authors (unless your School requires you to name all authors in your reference list) and your approach should be consistent.
Note: Books that have an editor, or editors, where each chapter is written by a different author or authors.
Surname of chapter author, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of chapter or section', in Initial. Surname of book editor (ed.) Title of book . Place of publication: publisher, Page reference.
Franklin, A.W. (2012) 'Management of the problem', in S.M. Smith (ed.) The maltreatment of children . Lancaster: MTP, pp. 83–95.
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of article', Title of Journal , volume number (issue number), page reference.
If accessed online:
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of article', Title of Journal , volume number (issue number), page reference. Available at: DOI or URL (if required) (Accessed: date).
Shirazi, T. (2010) 'Successful teaching placements in secondary schools: achieving QTS practical handbooks', European Journal of Teacher Education , 33(3), pp. 323–326.
Shirazi, T. (2010) 'Successful teaching placements in secondary schools: achieving QTS practical handbooks', European Journal of Teacher Education , 33(3), pp. 323–326. Available at: https://libezproxy.open.ac.uk/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/log... (Accessed: 27 January 2023).
Barke, M. and Mowl, G. (2016) 'Málaga – a failed resort of the early twentieth century?', Journal of Tourism History , 2(3), pp. 187–212. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1080/1755182X.2010.523145
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of article', Title of Newspaper , Day and month, Page reference.
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of article', Title of Newspaper , Day and month, Page reference if available. Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
Mansell, W. and Bloom, A. (2012) ‘£10,000 carrot to tempt physics experts’, The Guardian , 20 June, p. 5.
Roberts, D. and Ackerman, S. (2013) 'US draft resolution allows Obama 90 days for military action against Syria', The Guardian , 4 September. Available at: http://www.theguardian.com/world/2013/sep/04/syria-strikes-draft-resolut... (Accessed: 9 September 2015).
Surname, Initial. (Year that the site was published/last updated) Title of web page . Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
Organisation (Year that the page was last updated) Title of web page . Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
Robinson, J. (2007) Social variation across the UK . Available at: https://www.bl.uk/british-accents-and-dialects/articles/social-variation... (Accessed: 21 November 2021).
The British Psychological Society (2018) Code of Ethics and Conduct . Available at: https://www.bps.org.uk/news-and-policy/bps-code-ethics-and-conduct (Accessed: 22 March 2019).
Note: Cite Them Right Online offers guidance for referencing webpages that do not include authors' names and dates. However, be extra vigilant about the suitability of such webpages.
Surname, Initial. (Year) Title of photograph . Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
Kitton, J. (2013) Golden sunset . Available at: https://www.jameskittophotography.co.uk/photo_8692150.html (Accessed: 21 November 2021).
stanitsa_dance (2021) Cossack dance ensemble . Available at: https://www.instagram.com/p/COI_slphWJ_/ (Accessed: 13 June 2023).
Note: If no title can be found then replace it with a short description.
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Getting started with the online library
- Disabled user support
- Finding resources for your assignment
- Finding ejournals and articles
- Access eresources using Google Scholar
- Help with online resources
- Finding and using books and theses
- Finding information on your research topic
- Canllaw Cyflym i Gyfeirnodi Harvard (Cite Them Right)
- Quick guide to Cite Them Right referencing for Law modules
- The Classical Studies guide to referencing
- Bibliographic management
- What if I cannot find the reference type I need in my referencing guide?
- I have found a web page with no author, date or publisher - how do I reference it?
- Identifying a source
- Training and skills
- Study materials
- Using other libraries and SCONUL Access
- Borrowing at the Walton Hall Library
- OU Glossary
- Contacting the helpdesk
Smarter searching with library databases
Wednesday, 24 July, 2024 - 19:30
Learn how to access library databases, take advantage of the functionality they offer, and devise a proper search technique.

Library Helpdesk
Chat to a Librarian - Available 24/7
Other ways to contact the Library Helpdesk
The Open University
- Study with us
- Supported distance learning
- Funding your studies
- International students
- Global reputation
- Apprenticeships
- Develop your workforce
- News & media
- Contact the OU
Undergraduate
- Arts and Humanities
- Art History
- Business and Management
- Combined Studies
- Computing and IT
- Counselling
- Creative Writing
- Criminology
- Early Years
- Electronic Engineering
- Engineering
- Environment
- Film and Media
- Health and Social Care
- Health and Wellbeing
- Health Sciences
- International Studies
- Mathematics
- Mental Health
- Nursing and Healthcare
- Religious Studies
- Social Sciences
- Social Work
- Software Engineering
- Sport and Fitness
Postgraduate
- Postgraduate study
- Research degrees
- Masters in Art History (MA)
- Masters in Computing (MSc)
- Masters in Creative Writing (MA)
- Masters degree in Education
- Masters in Engineering (MSc)
- Masters in English Literature (MA)
- Masters in History (MA)
- Master of Laws (LLM)
- Masters in Mathematics (MSc)
- Masters in Psychology (MSc)
- A to Z of Masters degrees
- Accessibility statement
- Conditions of use
- Privacy policy
- Cookie policy
- Manage cookie preferences
- Modern slavery act (pdf 149kb)
Follow us on Social media
- Student Policies and Regulations
- Student Charter
- System Status
- Contact the OU Contact the OU
- Modern Slavery Act (pdf 149kb)
© . . .
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to content

- Home – AI for Research

How to Cite Research Papers: A Step-by-Step Guide
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on how to cite research papers.
Properly citing sources is crucial in academic and professional writing to give credit to the original authors and avoid plagiarism. In this step-by-step guide, we will explore the importance of citations, different citation styles such as. APA ,. MLA , and. Chicago , and provide practical examples to help you master the art of citing research papers effectively. Whether you are a student, researcher, or writer, understanding how to cite sources correctly is a valuable skill that enhances the credibility of your work. By the end of this guide, you will have the knowledge and tools to create accurate and consistent citations for your research papers. Let’s dive into the world of academic integrity and learn how to acknowledge the contributions of other scholars through proper citation practices.
Popular Citation Styles and Their Characteristics
When it comes to academic writing, proper citation is crucial to give credit to the original sources and to avoid plagiarism. Different disciplines and institutions may follow specific citation styles. Here are some of the most popular citation styles and their characteristics:.
- Developed by the American Psychological Association, APA Style is commonly used in social sciences. It features in-text citations with an author-date format and a reference list at the end of the document. APA Style also provides guidelines for formatting papers, citing sources, and creating a reference page.
- MLA Style:.
- The Modern Language Association created MLA Style, which is often used in humanities disciplines. MLA uses parenthetical citations in the text and includes a Works Cited page. In addition to citation rules, MLA Style covers various aspects of academic writing, such as paper formatting, headings, and abbreviations.
- Chicago/Turabian Style:.
- Chicago Style has two variations: Notes and Bibliography and Author-Date. It is widely used in history and some social science disciplines. Turabian Style, based on Chicago Style, is a simpler version often used by students. Chicago/Turabian Style provides detailed guidelines for citing different types of sources, creating footnotes or endnotes, and formatting the bibliography.
- IEEE Style:.
- The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) developed this style for technical fields like engineering and computer science. IEEE uses numbered citations in square brackets and includes a reference list with full bibliographic details. Apart from citation rules, IEEE Style addresses aspects like equations, tables, and figures in technical documents.
Each citation style has its own rules for formatting citations, references, and bibliographies. Writers should pay attention to details such as punctuation, capitalization, and italics when applying a specific style. Understanding the nuances of each citation style is essential for researchers, students, and academics to communicate their ideas effectively and ethically in scholarly writing.
Additional Information:
Harvard Style
- The Harvard referencing style is widely used in the UK and Australia. It utilizes an author-date system for in-text citations and a bibliography at the end of the document. Harvard Style emphasizes the importance of providing detailed information about all sources cited, including page numbers for direct quotes.
- Vancouver Style:.
- Commonly used in biomedical sciences, the Vancouver Style uses a numerical citation system. In-text citations are indicated by numbers in square brackets, and a numbered reference list is included at the end of the document. Vancouver Style is known for its simplicity and ease of use in scientific writing.
- AMA Style:.
- The American Medical Association Style is predominantly used in medical and biological sciences. AMA Style features numbered citations in superscript in the text and a corresponding numbered reference list. This style also includes specific guidelines for citing medical literature, clinical studies, and online resources.
- Bluebook Style:.
- Primarily used in legal writing, the Bluebook Style provides rules for citing legal documents, court cases, statutes, and other legal sources. Bluebook citations include abbreviations for legal terms and specific formatting requirements for legal citations.
By familiarizing themselves with various citation styles, writers can adapt their writing to meet the standards of different disciplines and publications. Choosing the appropriate citation style enhances the credibility and professionalism of academic and research papers.
Guidelines for Citing Research Papers
When citing research papers, it is essential to follow specific guidelines to give proper credit to the original authors and sources. Here are some key points to consider:.
- Formatting Author Names and Titles: When citing research papers, ensure that you accurately format the author names and titles. Follow the required citation style guide, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to correctly present this information. Include the author’s full name when possible, and if there are multiple authors, list them in the order they appear on the paper.
- Incorporating Citations in the Body of the Paper: Integrate citations smoothly within the body of your paper to support your arguments or provide evidence for your statements. Make sure to include the author’s name and the publication year when citing within the text. Additionally, consider using signal phrases to introduce citations effectively, such as ‘According to’ or ‘As stated by.’ This helps seamlessly integrate the citation into your writing.
- Creating a Reference Section: At the end of your research paper, compile a reference section listing all the sources you cited in your paper. Organize the references alphabetically by the author’s last name or by the title if no author is provided. Include all the necessary publication details for each source, such as the title of the work, the name(s) of the author(s), the publication date, and the source (e.g., journal, book, website).
- Avoiding Plagiarism: Plagiarism is a serious academic offense that can have severe consequences. Always properly cite the sources you use in your research paper to avoid plagiarism. If you directly quote a source, use quotation marks and provide the page number in your citation. Paraphrased information also requires citation to give credit to the original author.
- Using Citation Management Tools: Consider using citation management tools like Zotero, EndNote, or Mendeley to organize your references and generate citations automatically. These tools can save you time and ensure accuracy in your citations and reference list.
By following these comprehensive guidelines for citing research papers, you not only demonstrate academic integrity but also contribute to the scholarly conversation in your field. Proper citation practices help build a foundation of knowledge and acknowledge the work of others, fostering a culture of respect and collaboration in academia.
Avoiding Plagiarism and Ethical Considerations
Plagiarism is a serious offense in the academic and professional world, and it can have severe consequences. To maintain academic integrity and uphold ethical standards, it is crucial to understand the importance of citing resources properly. When writing any form of content, whether it’s an essay, research paper, article, or even a blog post, it is essential to give credit to the original sources.
Importance of Citing Resources to Avoid Plagiarism:
- Acknowledgment of Intellectual Property: Citing sources gives credit to the original creators of ideas, research, or work. It acknowledges their intellectual property rights and contributions.
- Building Credibility: Proper citations add credibility to your own work by showing that your arguments and ideas are supported by reputable sources.
- Avoiding Plagiarism Allegations: By citing sources correctly, you demonstrate that you have done your research and are not trying to pass off someone else’s work as your own.
When and How to Properly Cite Sources:
- Direct Quotes: Whenever you directly quote a source, use quotation marks and provide a citation indicating the source.
- Paraphrasing: When you paraphrase someone else’s ideas or work, even if you are not using their exact words, you still need to cite the original source.
- Common Knowledge: Information that is considered common knowledge does not require citation. However, if in doubt, it is better to provide a reference.
- Citation Styles: Different academic disciplines use specific citation styles such as APA, MLA, Chicago, or Harvard. Make sure to follow the appropriate style guide for your field.
Additional Considerations:
- Self-Plagiarism: It is also important to note that self-plagiarism, which involves reusing your own previously published work without proper citation, is considered unethical in many academic settings. Always cite your own work if you are incorporating it into a new piece.
- Online Sources: With the proliferation of online content, it is crucial to properly cite digital sources, including websites, online articles, and social media posts. Be sure to include URLs and access dates when referencing online material.
- Plagiarism Detection Tools: Utilize plagiarism detection software to check your work before submission. These tools can help identify unintentional instances of plagiarism and ensure that your writing is original.
By understanding the importance of citing resources and following ethical guidelines, you can avoid plagiarism and contribute to a culture of academic honesty and integrity.
Mastering the art of citing research papers is a fundamental skill for any academic or researcher. By following a step-by-step guide, individuals can ensure that they give proper credit to the original authors and sources, thereby upholding academic integrity. Additionally, learning how to write a scientific abstract is equally crucial, as it serves as a concise summary of the research study. The webpage at Avidnote offers valuable insights and tips on crafting effective scientific abstracts, which can greatly benefit PhD students and researchers. By honing these skills through practice and repetition, individuals can enhance their academic writing abilities and effectively communicate their research findings to a broader audience. Visit the provided link to delve deeper into the art of writing a compelling scientific abstract.
Privacy Overview
Adding {{itemName}} to cart
Added {{itemName}} to cart
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 11. Citing Sources
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A citation is a formal reference to a published or unpublished source that you consulted and obtained information from while writing your research paper. It refers to a source of information that supports a factual statement, proposition, argument, or assertion or any quoted text obtained from a book, article, web site, or any other type of material . In-text citations are embedded within the body of your paper and use a shorthand notation style that refers to a complete description of the item at the end of the paper. Materials cited at the end of a paper may be listed under the heading References, Sources, Works Cited, or Bibliography. Rules on how to properly cite a source depends on the writing style manual your professor wants you to use for the class [e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago, Turabian, etc.]. Note that some disciplines have their own citation rules [e.g., law].
Citations: Overview. OASIS Writing Center, Walden University; Research and Citation. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Citing Sources. University Writing Center, Texas A&M University.
Reasons for Citing Your Sources
Reasons for Citing Sources in Your Research Paper
English scientist, Sir Isaac Newton, once wrote, "If I have seen further, it is by standing on the shoulders of giants.”* Citations support learning how to "see further" through processes of intellectual discovery, critical thinking, and applying a deliberate method of navigating through the scholarly landscape by tracking how cited works are propagated by scholars over time and the subsequent ways this leads to the devarication of new knowledge.
Listed below are specific reasons why citing sources is an important part of doing good research.
- Shows the reader where to find more information . Citations help readers expand their understanding and knowledge about the issues being investigated. One of the most effective strategies for locating authoritative, relevant sources about a research problem is to review materials cited in studies published by other authors. In this way, the sources you cite help the reader identify where to go to examine the topic in more depth and detail.
- Increases your credibility as an author . Citations to the words, ideas, and arguments of scholars demonstrates that you have conducted a thorough review of the literature and, therefore, you are reporting your research results or proposing recommended courses of action from an informed and critically engaged perspective. Your citations offer evidence that you effectively contemplated, evaluated, and synthesized sources of information in relation to your conceptualization of the research problem.
- Illustrates the non-linear and contested nature of knowledge creation . The sources you cite show the reader how you characterized the dynamics of prior knowledge creation relevant to the research problem and how you managed to effectively identify the contested relationships between problems and solutions proposed among scholars. Citations don't just list materials used in your study, they tell a story about how prior knowledge-making emerged from a constant state of creation, renewal, and transformation.
- Reinforces your arguments . Sources cited in your paper provide the evidence that readers need to determine that you properly addressed the “So What?” question. This refers to whether you considered the relevance and significance of the research problem, its implications applied to creating new knowledge, and its importance for improving practice. In this way, citations draw attention to and support the legitimacy and originality of your own ideas.
- Demonstrates that you "listened" to relevant conversations among scholars before joining in . Your citations tell the reader where you developed an understanding of the debates among scholars. They show how you educated yourself about ongoing conversations taking place within relevant communities of researchers before inserting your own ideas and arguments. In peer-reviewed scholarship, most of these conversations emerge within books, research reports, journal articles, and other cited works.
- Delineates alternative approaches to explaining the research problem . If you disagree with prior research assumptions or you believe that a topic has been understudied or you find that there is a gap in how scholars have understood a problem, your citations serve as the source materials from which to analyze and present an alternative viewpoint or to assert that a different course of action should be pursued. In short, the materials you cite serve as the means by which to argue persuasively against long-standing assumptions propagated in prior studies.
- Helps the reader understand contextual aspects of your research . Cited sources help readers understand the specific circumstances, conditions, and settings of the problem being investigated and, by extension, how your arguments can be fully understood and assessed. Citations place your line of reasoning within a specific contextualized framework based on how others have studied the problem and how you interpreted their findings in support of your overall research objectives.
- Frames the development of concepts and ideas within the literature . No topic in the social and behavioral sciences rests in isolation from research that has taken place in the past. Your citations help the reader understand the growth and transformation of the theoretical assumptions, key concepts, and systematic inquiries that emerged prior to your engagement with the research problem.
- Underscores what sources were most important to you . Your citations represent a set of choices made about what you determined to be the most important sources for understanding the topic. They not only list what you discovered, but why it matters and how the materials you chose to cite fit within the broader context of your research design and arguments. As part of an overall assessment of the study’s validity and reliability , the choices you make also helps the reader determine what research may have been excluded.
- Provides evidence of interdisciplinary thinking . An important principle of good research is to extend your review of the literature beyond the predominant disciplinary space where scholars have examined a topic. Citations provide evidence that you have integrated epistemological arguments, observations, and/or the methodological strategies from other disciplines into your paper, thereby demonstrating that you understand the complex, interconnected nature of contemporary research problems.
- Supports critical thinking and independent learning . Evaluating the authenticity, reliability, validity, and originality of prior research is an act of interpretation and introspective reasoning applied to assessing whether a source of information will contribute to understanding the problem in ways that are persuasive and align with your overall research objectives. Reviewing and citing prior studies represents a deliberate act of critically scrutinizing each source as part of your overall assessment of how scholars have confronted the research problem.
- Honors the achievements of others . As Susan Blum recently noted,** citations not only identify sources used, they acknowledge the achievements of scholars within the larger network of research about the topic. Citing sources is a normative act of professionalism within academe and a way to highlight and recognize the work of scholars who likely do not obtain any tangible benefits or monetary value from their research endeavors.
*Vernon. Jamie L. "On the Shoulder of Giants." American Scientist 105 (July-August 2017): 194.
**Blum, Susan D. "In Defense of the Morality of Citation.” Inside Higher Ed , January 29, 2024.
Aksnes, Dag W., Liv Langfeldt, and Paul Wouters. "Citations, Citation Indicators, and Research Quality: An Overview of Basic Concepts and Theories." Sage Open 9 (January-March 2019): https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244019829575; Blum, Susan Debra. My Word!: Plagiarism and College Culture . Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 2009; Bretag, Tracey., editor. Handbook of Academic Integrity . Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2020; Ballenger, Bruce P. The Curious Researcher: A Guide to Writing Research Papers . 7th edition. Boston, MA: Pearson, 2012; D'Angelo, Barbara J. "Using Source Analysis to Promote Critical Thinking." Research Strategies 18 (Winter 2001): 303-309; Mauer, Barry and John Venecek. “Scholarship as Conversation.” Strategies for Conducting Literary Research, University of Central Florida, 2021; Why Cite? Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning, Yale University; Citing Information. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Harvard Guide to Using Sources. Harvard College Writing Program. Harvard University; Newton, Philip. "Academic Integrity: A Quantitative Study of Confidence and Understanding in Students at the Start of Their Higher Education." Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education 41 (2016): 482-497; Referencing More Effectively. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra; Using Sources. Yale College Writing Center. Yale University; Vosburgh, Richard M. "Closing the Academic-practitioner Gap: Research Must Answer the “SO WHAT” Question." H uman Resource Management Review 32 (March 2022): 100633; When and Why to Cite Sources. Information Literacy Playlists, SUNY, Albany Libraries.
Structure and Writing Style
Referencing your sources means systematically showing what information or ideas you acquired from another author’s work, and identifying where that information come from . You must cite research in order to do research, but at the same time, you must delineate what are your original thoughts and ideas and what are the thoughts and ideas of others. Citations help achieve this. Procedures used to cite sources vary among different fields of study. If not outlined in your course syllabus or writing assignment, always speak with your professor about what writing style for citing sources should be used for the class because it is important to fully understand the citation style to be used in your paper, and to apply it consistently. If your professor defers and tells you to "choose whatever you want, just be consistent," then choose the citation style you are most familiar with or that is appropriate to your major [e.g., use Chicago style if its a history class; use APA if its an education course; use MLA if it is literature or a general writing course].
GENERAL GUIDELINES
1. Are there any reasons I should avoid referencing other people's work? No. If placed in the proper context, r eferencing other people's research is never an indication that your work is substandard or lacks originality. In fact, the opposite is true. If you write your paper without adequate references to previous studies, you are signaling to the reader that you are not familiar with the literature on the topic, thereby, undermining the validity of your study and your credibility as a researcher. Including references in academic writing is one of the most important ways to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of how the research problem has been addressed. It is the intellectual packaging around which you present your thoughts and ideas to the reader.
2. What should I do if I find out that my great idea has already been studied by another researcher? It can be frustrating to come up with what you believe is a great topic only to find that it's already been thoroughly studied. However, do not become frustrated by this. You can acknowledge the prior research by writing in the text of your paper [see also Smith, 2002], then citing the complete source in your list of references. Use the discovery of prior studies as an opportunity to demonstrate the significance of the problem being investigated and, if applicable, as a means of delineating your analysis from those of others [e.g., the prior study is ten years old and doesn't take into account new variables]. Strategies for responding to prior research can include: stating how your study updates previous understandings about the topic, offering a new or different perspective, applying a different or innovative method of data gathering, and/or describing a new set of insights, guidelines, recommendations, best practices, or working solutions.
3. What should I do if I want to use an adapted version of someone else's work? You still must cite the original work. For example, maybe you are using a table of statistics from a journal article published in 1996 by author Smith, but you have altered or added new data to it. Reference the revised chart, such as, [adapted from Smith, 1996], then cite the complete source in your list of references. You can also use other terms in order to specify the exact relationship between the original source and the version you have presented, such as, "based on data from Smith [1996]...," or "summarized from Smith [1996]...." Citing the original source helps the reader locate where the information was first presented and under what context it was used as well as to evaluate how effectively you applied it to your own research.
4. What should I do if several authors have published very similar information or ideas? You can indicate that the idea or information can be found in the works of others by stating something similar to the following example: "Though many scholars have applied rational choice theory to understanding economic relations among nations [Smith, 1989; Jones, 1991; Johnson, 1994; Anderson, 2003], little attention has been given to applying the theory to examining the influence of non-governmental organizations in a globalized economy." If you only reference one author or only the most recent study, then your readers may assume that only one author has published on this topic, or more likely, they will conclude that you have not conducted a thorough literature review. Referencing all relevant authors of prior studies gives your readers a clear idea of the breadth of analysis you conducted in preparing to study the research problem. If there has been a significant number of prior studies on the topic, describe the most comprehensive and recent works because they will presumably discuss and reference the older studies. However, note in your review of the literature that there has been significant scholarship devoted to the topic so the reader knows that you are aware of the numerous prior studies.
5. What if I find exactly what I want to say in the writing of another researcher? In the social sciences, the rationale in duplicating prior research is generally governed by the passage of time, changing circumstances or conditions, or the emergence of variables that necessitate a new investigation . If someone else has recently conducted a thorough investigation of precisely the same research problem that you intend to study, then you likely will have to revise your topic, or at the very least, review this literature to identify something new to say about the problem. However, if it is someone else's particularly succinct expression, but it fits perfectly with what you are trying to say, then you can quote from the author directly, referencing the source. Identifying an author who has made the exact same point that you want to make can be an opportunity to add legitimacy to, as well as reinforce the significance of, the research problem you are investigating. The key is to build on that idea in new and innovative ways. If you are not sure how to do this, consult with a librarian .
6. Should I cite a source even if it was published long ago? Any source used in writing your paper should be cited, regardless of when it was written. However, in building a case for understanding prior research about your topic, it is generally true that you should focus on citing more recently published studies because they presumably have built upon the research of older studies. When referencing prior studies, use the research problem as your guide when considering what to cite. If a study from forty years ago investigated the same topic, it probably should be examined and considered in your list of references because the research may have been foundational or groundbreaking at the time, even if its findings are no longer relevant to current conditions or reflect current thinking [one way to determine if a study is foundational or groundbreaking is to examine how often it has been cited in recent studies using the "Cited by" feature of Google Scholar ]. However, if an older study only relates to the research problem tangentially or it has not been cited in recent studies, then it may be more appropriate to list it under further readings .
7. Can I cite unusual and non-scholarly sources in my research paper? The majority of the citations in a research paper should be to scholarly [a.k.a., academic; peer-reviewed] studies that rely on an objective and logical analysis of the research problem based on empirical evidence that reliably supports your arguments. However, any type of source can be considered valid if it brings relevant understanding and clarity to the topic. This can include, for example, non-textual elements such as photographs, maps, or illustrations. A source can include materials from special or archival collections, such as, personal papers, manuscripts, business memorandums, the official records of an organization, or digitized collections. Citations can also be to unusual items, such as, an audio recording, a transcript from a television show, a unique set of data, or a social media post. The challenge is knowing how to properly cite unusual and non-scholarly sources because they often do not fit within standard citation rules like books or journal articles. Given this, consult with a librarian if you are unsure how to cite a source.
NOTE : In any academic writing, you are required to identify which ideas, facts, thoughts, concepts, or declarative statements are yours and which are derived from the research of others. The only exception to this rule is information that is considered to be a commonly known fact [e.g., "George Washington was the first president of the United States"] or a statement that is self-evident [e.g., "Australia is a country in the Global South"]. Appreciate, however, that any "commonly known fact" or self-evidencing statement is culturally constructed and shaped by specific social and aesthetical biases . If you have any doubt about whether or not a fact is considered to be widely understood knowledge, provide a supporting citation, or, ask your professor for clarification about whether the statement should be cited.
Ballenger, Bruce P. The Curious Researcher: A Guide to Writing Research Papers . 7th edition. Boston, MA: Pearson, 2012; Blum, Susan Debra. My Word!: Plagiarism and College Culture . Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 2009; Bretag, Tracey., editor. Handbook of Academic Integrity . Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2020; Carlock, Janine. Developing Information Literacy Skills: A Guide to Finding, Evaluating, and Citing Sources . Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2020; Harvard Guide to Using Sources. Harvard College Writing Program. Harvard University; How to Cite Other Sources in Your Paper. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Lunsford, Andrea A. and Robert Connors; The St. Martin's Handbook . New York: St. Martin's Press, 1989; Mills, Elizabeth Shown. Evidence Explained: Citing History Sources from Artifacts to Cyberspace . 3rd edition. Baltimore, MD: Genealogical Publishing Company, 2015; Research and Citation Resources. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Why Cite? Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning, Yale Univeraity.
Other Citation Research Guides
The following USC Libraries research guide can help you properly cite sources in your research paper:
- Citation Guide
The following USC Libraries research guide offers basic information on using images and media in research:
Listed below are particularly well-done and comprehensive websites that provide specific examples of how to cite sources under different style guidelines.
- Purdue University Online Writing Lab
- Southern Cross University Harvard Referencing Style
- University of Wisconsin Writing Center
This is a useful guide concerning how to properly cite images in your research paper.
- Colgate Visual Resources Library, Citing Images
This guide provides good information on the act of citation analysis, whereby you count the number of times a published work is cited by other works in order to measure the impact of a publication or author.
Measuring Your Impact: Impact Factor, Citation Analysis, and other Metrics: Citation Analysis [Sandy De Groote, University of Illinois, Chicago]
Automatic Citation Generators
The links below lead to systems where you can type in your information and have a citation compiled for you. Note that these systems are not foolproof so it is important that you verify that the citation is correct and check your spelling, capitalization, etc. However, they can be useful in creating basic types of citations, particularly for online sources.
- BibMe -- APA, MLA, Chicago, and Turabian styles
- DocsCite -- for citing government publications in APA or MLA formats
- EasyBib -- APA, MLA, and Chicago styles
- Son of Citation Machine -- APA, MLA, Chicago, and Turabian styles
NOTE: Many companies that create the research databases the USC Libraries subscribe to, such as ProQuest , include built-in citation generators that help take the guesswork out of how to properly cite a work. When available, you should always utilize these features because they not only generate a citation to the source [e.g., a journal article], but include information about where you accessed the source [e.g., the database].
- << Previous: Writing Concisely
- Next: Avoiding Plagiarism >>
- Last Updated: May 22, 2024 12:03 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Cite a Research Paper in APA
Last Updated: October 19, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by wikiHow Staff . Our trained team of editors and researchers validate articles for accuracy and comprehensiveness. wikiHow's Content Management Team carefully monitors the work from our editorial staff to ensure that each article is backed by trusted research and meets our high quality standards. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 160,357 times. Learn more...
If you’re citing a research article or paper in APA style, you’ll need to use a specific citation format that varies depending on the source. Assess whether your source is an article or report published in an academic journal or book, or whether it is an unpublished research paper, such as a print-only thesis or dissertation. Either way, your in-text citations will need to include information about the author (if available) and the date when your source was published or written.
Sample Citations

Writing an In-Text Citation

- For example, you may write, “Gardener (2008) notes, ‘There are several factors to consider about lobsters’ (p. 199).”

- For example, you may write, “‘There are several factors to consider about lobsters’ (Gardner, 2008, p. 199).” Or, “The paper claims, ‘The fallen angel trope is common in religious and non-religious texts’ (Meek & Hill, 2015, p.13-14).”
- For articles with 3-5 authors, write out the names of all the authors the first time you cite the source. For example: (Hammett, Wooster, Smith, & Charles, 1928). In subsequent citations, write only the first author’s name, followed by et al.: (Hammett et al., 1928).
- If there are 6 or more authors for the paper, include the last name of the first author listed and then write "et al." to indicate that there are more than 5 authors.
- For example, you may write, "'This is a quote' (Minaj et al., 1997, p. 45)."

- For example, you may write, “‘The risk of cervical cancer in women is rising’ (American Cancer Society, 2012, p. 2).”

- For example, you may write, “‘Shakespeare may have been a woman’ (“Radical English Literature,” 2004, p. 45).” Or, “The paper notes, ‘There is a boom in Virgin Mary imagery’ (“Art History in Italy,” 2011, p. 32).”

- For example, you may write, “‘There are several factors to consider about lobsters’ (Gardner, 2008, p. 199).” Or, “The paper claims, ‘The fallen angel trope is common in religious and non-religious texts’ (“Iconography in Italian Frescos,” 2015, p.13-14).”

- For example, you may write, “‘There are several factors to consider about lobsters’ (Gardner, 2008, p. 199).” Or, “The paper claims, ‘The fallen angel trope is common in religious and non-religious texts’ (“Iconography in Italian Frescos,” 2015, p.145-146).”

- For example, you may write, “‘The effects of food deprivation are long-term’ (Mett, 2005, para. 18).”
Creating a Reference List Citation for a Published Source
- Material on websites is also considered “published,” even if it’s not peer-reviewed or associated with a formal publishing company.
- While academic dissertations or theses that are print-only are considered unpublished, these types of documents are considered published if they’re included in an online database (such as ProQuest) or incorporated into an institutional repository.

- For example, you may write, “Gardner, L. M.” Or, “Meek, P. Q., Kendrick, L. H., & Hill, R. W.”
- If there is no author, you can list the name of the organization that published the research paper. For example, you may write, “American Cancer Society” or “The Reading Room.”
- Formally published documents that don’t list an author or that have a corporate author are typically reports or white papers .

- For example, you may write, “Gardner, L. M. (2008).” Or, “American Cancer Society. (2015).”

- For example, you may write, “Gardner, L. M. (2008). Crustaceans: Research and data.” Or, “American Cancer Society. (2015). Cervical cancer rates in women ages 20-45.”

- For example, for a journal article, you may write, “Gardner, L. M. (2008). Crustaceans: Research and data. Modern Journal of Malacostracan Research, 25, 150-305.”
- For a book chapter, you could write: “Wooster, B. W. (1937). A comparative study of modern Dutch cow creamers. In T. E. Travers (Ed.), A Detailed History of Tea Serviceware (pp. 127-155). London: Wimble Press."

- For example, you may write, “Kotb, M. A., Kamal, A. M., Aldossary, N. M., & Bedewi, M. A. (2019). Effect of vitamin D replacement on depression in multiple sclerosis patients. Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders, 29, 111-117. Retrieved from PubMed, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30708308.
- If you’re citing a paper or article that was published online but did not come from an academic journal or database, provide information about the author (if known), the date of publication (if available), and the website where you found the article. For example: “Hill, M. (n.d.). Egypt in the Ptolemaic Period. Retrieved from https://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/ptol/hd_ptol.htm”
Citing Unpublished Sources in Your Reference List

- Print-only dissertations or theses.
- Articles or book chapters that are in press or have been recently prepared or submitted for publication.
- Papers that have been rejected for publication or were never intended for publication (such as student research papers or unpublished conference papers).

- If the paper is currently being prepared for publication, include the author’s name, the year when the current draft was completed, and the title of the article in italics, followed by “Manuscript in preparation.” For example: Wooster, B. W. (1932). What the well-dressed man is wearing. Manuscript in preparation.
- If the paper has been submitted for publication, format the citation the same way as if it were in preparation, but instead follow the title with “Manuscript submitted for publication.” For example: Wooster, B. W. (1932). What the well-dressed man is wearing. Manuscript submitted for publication.
- If the paper has been accepted for publication but is not yet published, replace the date with “in press.” Do not italicize the paper title, but do include the title of the periodical or book in which it will be published and italicize that. For example: Wooster, B. W. (in press). What the well-dressed man is wearing. Milady’s Boudoir.

- If the paper was written for a conference but never published, your citation should look like this: Riker, W. T. (2019, March). Traditional methods for the preparation of spiny lobe-fish. Paper presented at the 325th Annual Intergalactic Culinary Conference, San Francisco, CA.
- For an unpublished paper written by a student for a class, include details about the institution where the paper was written. For example: Crusher, B. H. (2019). A typology of Cardassian skin diseases. Unpublished manuscript, Department of External Medicine, Starfleet Academy, San Francisco, CA.

- For example, you may write, “Pendlebottom, R. H. (2011). Iconography in Italian Frescos (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). New York University, New York, United States.”
Community Q&A
- If you want certain information to stand out in the research paper, then you can consider using a block quote. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libraryguides.vu.edu.au/apa-referencing/7JournalArticles
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_author_authors.html
- ↑ https://bowvalleycollege.libguides.com/c.php?g=714519&p=5093747
- ↑ https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/apaquickguide/intext
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://libguides.southernct.edu/c.php?g=7125&p=34582#1951239
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_electronic_sources.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_articles_in_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_books.html
- ↑ https://morlingcollege.libguides.com/apareferencing/unpublished-or-informally-published-work
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/general_apa_faqs.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_other_print_sources.html
About This Article

To cite a research paper in-text in APA, name the author in the text to introduce the quote and put the publication date for the text in parentheses. At the end of your quote, put the page number in parentheses. If you don’t mention the author in your prose, include them in the citation. Start the citation, which should come at the end of the quote, by listing the author’s last name, the year of publication, and the page number. Make sure to put all of this information in parentheses. If there’s no author, use the name of the organization that published the paper or the first few words from the title. To learn how to cite published and unpublished sources in your reference list, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Referencing
A Quick Guide to Referencing | Cite Your Sources Correctly
Referencing means acknowledging the sources you have used in your writing. Including references helps you support your claims and ensures that you avoid plagiarism .
There are many referencing styles, but they usually consist of two things:
- A citation wherever you refer to a source in your text.
- A reference list or bibliography at the end listing full details of all your sources.
The most common method of referencing in UK universities is Harvard style , which uses author-date citations in the text. Our free Harvard Reference Generator automatically creates accurate references in this style.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Referencing styles, citing your sources with in-text citations, creating your reference list or bibliography, harvard referencing examples, frequently asked questions about referencing.
Each referencing style has different rules for presenting source information. For in-text citations, some use footnotes or endnotes , while others include the author’s surname and date of publication in brackets in the text.
The reference list or bibliography is presented differently in each style, with different rules for things like capitalisation, italics, and quotation marks in references.
Your university will usually tell you which referencing style to use; they may even have their own unique style. Always follow your university’s guidelines, and ask your tutor if you are unsure. The most common styles are summarised below.
Harvard referencing, the most commonly used style at UK universities, uses author–date in-text citations corresponding to an alphabetical bibliography or reference list at the end.
Harvard Referencing Guide
Vancouver referencing, used in biomedicine and other sciences, uses reference numbers in the text corresponding to a numbered reference list at the end.
Vancouver Referencing Guide
APA referencing, used in the social and behavioural sciences, uses author–date in-text citations corresponding to an alphabetical reference list at the end.
APA Referencing Guide APA Reference Generator
MHRA referencing, used in the humanities, uses footnotes in the text with source information, in addition to an alphabetised bibliography at the end.
MHRA Referencing Guide
OSCOLA referencing, used in law, uses footnotes in the text with source information, and an alphabetical bibliography at the end in longer texts.
OSCOLA Referencing Guide
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
In-text citations should be used whenever you quote, paraphrase, or refer to information from a source (e.g. a book, article, image, website, or video).
Quoting and paraphrasing
Quoting is when you directly copy some text from a source and enclose it in quotation marks to indicate that it is not your own writing.
Paraphrasing is when you rephrase the original source into your own words. In this case, you don’t use quotation marks, but you still need to include a citation.
In most referencing styles, page numbers are included when you’re quoting or paraphrasing a particular passage. If you are referring to the text as a whole, no page number is needed.
In-text citations
In-text citations are quick references to your sources. In Harvard referencing, you use the author’s surname and the date of publication in brackets.
Up to three authors are included in a Harvard in-text citation. If the source has more than three authors, include the first author followed by ‘ et al. ‘
The point of these citations is to direct your reader to the alphabetised reference list, where you give full information about each source. For example, to find the source cited above, the reader would look under ‘J’ in your reference list to find the title and publication details of the source.
Placement of in-text citations
In-text citations should be placed directly after the quotation or information they refer to, usually before a comma or full stop. If a sentence is supported by multiple sources, you can combine them in one set of brackets, separated by a semicolon.
If you mention the author’s name in the text already, you don’t include it in the citation, and you can place the citation immediately after the name.
- Another researcher warns that the results of this method are ‘inconsistent’ (Singh, 2018, p. 13) .
- Previous research has frequently illustrated the pitfalls of this method (Singh, 2018; Jones, 2016) .
- Singh (2018, p. 13) warns that the results of this method are ‘inconsistent’.
The terms ‘bibliography’ and ‘reference list’ are sometimes used interchangeably. Both refer to a list that contains full information on all the sources cited in your text. Sometimes ‘bibliography’ is used to mean a more extensive list, also containing sources that you consulted but did not cite in the text.
A reference list or bibliography is usually mandatory, since in-text citations typically don’t provide full source information. For styles that already include full source information in footnotes (e.g. OSCOLA and Chicago Style ), the bibliography is optional, although your university may still require you to include one.
Format of the reference list
Reference lists are usually alphabetised by authors’ last names. Each entry in the list appears on a new line, and a hanging indent is applied if an entry extends onto multiple lines.

Different source information is included for different source types. Each style provides detailed guidelines for exactly what information should be included and how it should be presented.
Below are some examples of reference list entries for common source types in Harvard style.
- Chapter of a book
- Journal article
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Your university should tell you which referencing style to follow. If you’re unsure, check with a supervisor. Commonly used styles include:
- Harvard referencing , the most commonly used style in UK universities.
- MHRA , used in humanities subjects.
- APA , used in the social sciences.
- Vancouver , used in biomedicine.
- OSCOLA , used in law.
Your university may have its own referencing style guide.
If you are allowed to choose which style to follow, we recommend Harvard referencing, as it is a straightforward and widely used style.
References should be included in your text whenever you use words, ideas, or information from a source. A source can be anything from a book or journal article to a website or YouTube video.
If you don’t acknowledge your sources, you can get in trouble for plagiarism .
To avoid plagiarism , always include a reference when you use words, ideas or information from a source. This shows that you are not trying to pass the work of others off as your own.
You must also properly quote or paraphrase the source. If you’re not sure whether you’ve done this correctly, you can use the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker to find and correct any mistakes.
Harvard referencing uses an author–date system. Sources are cited by the author’s last name and the publication year in brackets. Each Harvard in-text citation corresponds to an entry in the alphabetised reference list at the end of the paper.
Vancouver referencing uses a numerical system. Sources are cited by a number in parentheses or superscript. Each number corresponds to a full reference at the end of the paper.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- A Quick Guide to Harvard Referencing | Citation Examples
- APA Referencing (7th Ed.) Quick Guide | In-text Citations & References
How to Avoid Plagiarism | Tips on Citing Sources
More interesting articles.
- A Quick Guide to OSCOLA Referencing | Rules & Examples
- Harvard In-Text Citation | A Complete Guide & Examples
- Harvard Referencing for Journal Articles | Templates & Examples
- Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples
- MHRA Referencing | A Quick Guide & Citation Examples
- Reference a Website in Harvard Style | Templates & Examples
- Referencing Books in Harvard Style | Templates & Examples
- Vancouver Referencing | A Quick Guide & Reference Examples
Scribbr APA Citation Checker
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!


Add citations in a Word document
In Word, you can easily add citations when writing a document where you need to cite your sources, such as a research paper. Citations can be added in various formats, including APA , Chicago-style , GOST, IEEE, ISO 690, and MLA . Afterwards, you can create a bibliography of the sources you used to write your paper.
To add a citation to your document, you first add the source that you used.
Add a new citation and source to a document
On the References tab, in the Citations & Bibliography group, click the arrow next to Style and click the style that you want to use for the citation and source. For example, social sciences documents usually use the MLA or APA styles for citations and sources.
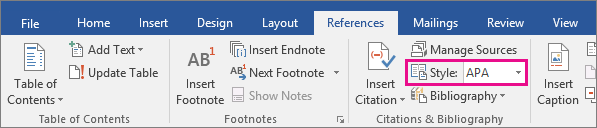
Click at the end of the sentence or phrase that you want to cite.
On the Reference tab, click Insert Citation and then do one of the following:
To add the source information, click Add New Source , and then, in the Create Source dialog box, click the arrow next to Type of Source , and select the type of source you want to use (for example, a book section or a website).
To add a placeholder, so that you can create a citation and fill in the source information later, click Add New Placeholder . A question mark appears next to placeholder sources in Source Manager.
If you chose to add a source, enter the details for the source. To add more information about a source, click the Show All Bibliography Fields check box.
Click OK when finished. The source is added as a citation at the place you selected in your document.
When you've completed these steps, the citation is added to the list of available citations. The next time you quote this reference, you don't have to type it all out again. You just add the citation to your document . After you've added a source, you may find you need to make changes to it at a later time. To do this, see Edit a source .
If you've added a placeholder and want to replace it with citation information, see Edit a source .
If you choose a GOST or ISO 690 style for your sources and a citation is not unique, append an alphabetic character to the year. For example, a citation would appear as [Pasteur, 1848a].
If you choose ISO 690-Numerical Reference and your citations still don't appear consecutively, you must click the ISO 690 style again, and then press ENTER to correctly order the citations.
Add citations to your document
Click at the end of the sentence or phrase that you want to cite, and then on the References tab, in the Citations & Bibliography group, click Insert Citations .
From the list of citations under Insert Citation , select the citation you want to use.
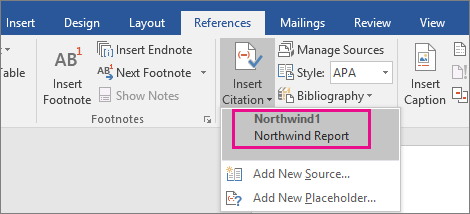
Find a source
The list of sources that you use can become quite long. At times, you might need to search for a source that you cited in another document.
On the References tab, in the Citations & Bibliography group, click Manage Sources .
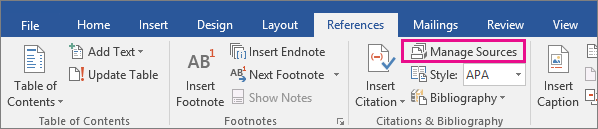
If you open a new document that does not yet contain citations, all of the sources that you used in previous documents appear under Master List .
If you open a document that includes citations, the sources for those citations appear under Current List . All the sources that you have cited, either in previous documents or in the current document, appear under Master List .
To find a specific source, do one of the following:
In the sorting box, sort by author, title, citation tag name, or year, and then look for the source that you want in the resulting list.
In the Search box, type the title or author for the source that you want to find. The list dynamically narrows to match your search term.
Note: You can click the Browse button in Source Manager to select another master list from which you can import new sources into your document. For example, you might connect to a file on a shared server, on a research colleague's computer or server, or on a Web site that is hosted by a university or research institution.

Edit a source
In the Source Manager dialog box, under Master List or Current List , select the source you want to edit, and then click Edit .
Note: To edit a placeholder to add citation information, select the placeholder from Current List and click Edit .
In the Edit Source dialog box, make the changes you want and click OK .

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
- Privacy Policy

Home » How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and Examples
How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Paper Citation
Research paper citation refers to the act of acknowledging and referencing a previously published work in a scholarly or academic paper . When citing sources, researchers provide information that allows readers to locate the original source, validate the claims or arguments made in the paper, and give credit to the original author(s) for their work.
The citation may include the author’s name, title of the publication, year of publication, publisher, and other relevant details that allow readers to trace the source of the information. Proper citation is a crucial component of academic writing, as it helps to ensure accuracy, credibility, and transparency in research.
How to Cite Research Paper
There are several formats that are used to cite a research paper. Follow the guide for the Citation of a Research Paper:
Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Year of Publication.
Example : Smith, John. The History of the World. Penguin Press, 2010.
Journal Article
Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Year of Publication, pp. Page Numbers.
Example : Johnson, Emma. “The Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture.” Environmental Science Journal, vol. 10, no. 2, 2019, pp. 45-59.
Research Paper
Last Name, First Name. “Title of Paper.” Conference Name, Location, Date of Conference.
Example : Garcia, Maria. “The Importance of Early Childhood Education.” International Conference on Education, Paris, 5-7 June 2018.
Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Webpage.” Website Title, Publisher, Date of Publication, URL.
Example : Smith, John. “The Benefits of Exercise.” Healthline, Healthline Media, 1 March 2022, https://www.healthline.com/health/benefits-of-exercise.
News Article
Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Name of Newspaper, Date of Publication, URL.
Example : Robinson, Sarah. “Biden Announces New Climate Change Policies.” The New York Times, 22 Jan. 2021, https://www.nytimes.com/2021/01/22/climate/biden-climate-change-policies.html.
Author, A. A. (Year of publication). Title of book. Publisher.
Example: Smith, J. (2010). The History of the World. Penguin Press.
Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (Year of publication). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), page range.
Example: Johnson, E., Smith, K., & Lee, M. (2019). The Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture. Environmental Science Journal, 10(2), 45-59.
Author, A. A. (Year of publication). Title of paper. In Editor First Initial. Last Name (Ed.), Title of Conference Proceedings (page numbers). Publisher.
Example: Garcia, M. (2018). The Importance of Early Childhood Education. In J. Smith (Ed.), Proceedings from the International Conference on Education (pp. 60-75). Springer.
Author, A. A. (Year, Month Day of publication). Title of webpage. Website name. URL
Example: Smith, J. (2022, March 1). The Benefits of Exercise. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/benefits-of-exercise
Author, A. A. (Year, Month Day of publication). Title of article. Newspaper name. URL.
Example: Robinson, S. (2021, January 22). Biden Announces New Climate Change Policies. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/01/22/climate/biden-climate-change-policies.html
Chicago/Turabian style
Please note that there are two main variations of the Chicago style: the author-date system and the notes and bibliography system. I will provide examples for both systems below.
Author-Date system:
- In-text citation: (Author Last Name Year, Page Number)
- Reference list: Author Last Name, First Name. Year. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher.
- In-text citation: (Smith 2005, 28)
- Reference list: Smith, John. 2005. The History of America. New York: Penguin Press.
Notes and Bibliography system:
- Footnote/Endnote citation: Author First Name Last Name, Title of Book (Place of publication: Publisher, Year), Page Number.
- Bibliography citation: Author Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher, Year.
- Footnote/Endnote citation: John Smith, The History of America (New York: Penguin Press, 2005), 28.
- Bibliography citation: Smith, John. The History of America. New York: Penguin Press, 2005.
JOURNAL ARTICLES:
- Reference list: Author Last Name, First Name. Year. “Article Title.” Journal Title Volume Number (Issue Number): Page Range.
- In-text citation: (Johnson 2010, 45)
- Reference list: Johnson, Mary. 2010. “The Impact of Social Media on Society.” Journal of Communication 60(2): 39-56.
- Footnote/Endnote citation: Author First Name Last Name, “Article Title,” Journal Title Volume Number, Issue Number (Year): Page Range.
- Bibliography citation: Author Last Name, First Name. “Article Title.” Journal Title Volume Number, Issue Number (Year): Page Range.
- Footnote/Endnote citation: Mary Johnson, “The Impact of Social Media on Society,” Journal of Communication 60, no. 2 (2010): 39-56.
- Bibliography citation: Johnson, Mary. “The Impact of Social Media on Society.” Journal of Communication 60, no. 2 (2010): 39-56.
RESEARCH PAPERS:
- Reference list: Author Last Name, First Name. Year. “Title of Paper.” Conference Proceedings Title, Location, Date. Publisher, Page Range.
- In-text citation: (Jones 2015, 12)
- Reference list: Jones, David. 2015. “The Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture.” Proceedings of the International Conference on Climate Change, Paris, France, June 1-3, 2015. Springer, 10-20.
- Footnote/Endnote citation: Author First Name Last Name, “Title of Paper,” Conference Proceedings Title, Location, Date (Place of publication: Publisher, Year), Page Range.
- Bibliography citation: Author Last Name, First Name. “Title of Paper.” Conference Proceedings Title, Location, Date. Place of publication: Publisher, Year.
- Footnote/Endnote citation: David Jones, “The Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture,” Proceedings of the International Conference on Climate Change, Paris, France, June 1-3, 2015 (New York: Springer, 10-20).
- Bibliography citation: Jones, David. “The Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture.” Proceedings of the International Conference on Climate Change, Paris, France, June 1-3, 2015. New York: Springer, 10-20.
- In-text citation: (Author Last Name Year)
- Reference list: Author Last Name, First Name. Year. “Title of Webpage.” Website Name. URL.
- In-text citation: (Smith 2018)
- Reference list: Smith, John. 2018. “The Importance of Recycling.” Environmental News Network. https://www.enn.com/articles/54374-the-importance-of-recycling.
- Footnote/Endnote citation: Author First Name Last Name, “Title of Webpage,” Website Name, URL (accessed Date).
- Bibliography citation: Author Last Name, First Name. “Title of Webpage.” Website Name. URL (accessed Date).
- Footnote/Endnote citation: John Smith, “The Importance of Recycling,” Environmental News Network, https://www.enn.com/articles/54374-the-importance-of-recycling (accessed April 8, 2023).
- Bibliography citation: Smith, John. “The Importance of Recycling.” Environmental News Network. https://www.enn.com/articles/54374-the-importance-of-recycling (accessed April 8, 2023).
NEWS ARTICLES:
- Reference list: Author Last Name, First Name. Year. “Title of Article.” Name of Newspaper, Month Day.
- In-text citation: (Johnson 2022)
- Reference list: Johnson, Mary. 2022. “New Study Finds Link Between Coffee and Longevity.” The New York Times, January 15.
- Footnote/Endnote citation: Author First Name Last Name, “Title of Article,” Name of Newspaper (City), Month Day, Year.
- Bibliography citation: Author Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Name of Newspaper (City), Month Day, Year.
- Footnote/Endnote citation: Mary Johnson, “New Study Finds Link Between Coffee and Longevity,” The New York Times (New York), January 15, 2022.
- Bibliography citation: Johnson, Mary. “New Study Finds Link Between Coffee and Longevity.” The New York Times (New York), January 15, 2022.
Harvard referencing style
Format: Author’s Last name, First initial. (Year of publication). Title of book. Publisher.
Example: Smith, J. (2008). The Art of War. Random House.
Journal article:
Format: Author’s Last name, First initial. (Year of publication). Title of article. Title of journal, volume number(issue number), page range.
Example: Brown, M. (2012). The impact of social media on business communication. Harvard Business Review, 90(12), 85-92.
Research paper:
Format: Author’s Last name, First initial. (Year of publication). Title of paper. In Editor’s First initial. Last name (Ed.), Title of book (page range). Publisher.
Example: Johnson, R. (2015). The effects of climate change on agriculture. In S. Lee (Ed.), Climate Change and Sustainable Development (pp. 45-62). Springer.
Format: Author’s Last name, First initial. (Year, Month Day of publication). Title of page. Website name. URL.
Example: Smith, J. (2017, May 23). The history of the internet. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/topic/history-of-the-internet
News article:
Format: Author’s Last name, First initial. (Year, Month Day of publication). Title of article. Title of newspaper, page number (if applicable).
Example: Thompson, E. (2022, January 5). New study finds coffee may lower risk of dementia. The New York Times, A1.
IEEE Format
Author(s). (Year of Publication). Title of Book. Publisher.
Smith, J. K. (2015). The Power of Habit: Why We Do What We Do in Life and Business. Random House.
Journal Article:
Author(s). (Year of Publication). Title of Article. Title of Journal, Volume Number (Issue Number), page numbers.
Johnson, T. J., & Kaye, B. K. (2016). Interactivity and the Future of Journalism. Journalism Studies, 17(2), 228-246.
Author(s). (Year of Publication). Title of Paper. Paper presented at Conference Name, Location.
Jones, L. K., & Brown, M. A. (2018). The Role of Social Media in Political Campaigns. Paper presented at the 2018 International Conference on Social Media and Society, Copenhagen, Denmark.
- Website: Author(s) or Organization Name. (Year of Publication or Last Update). Title of Webpage. Website Name. URL.
Example: National Aeronautics and Space Administration. (2019, August 29). NASA’s Mission to Mars. NASA. https://www.nasa.gov/topics/journeytomars/index.html
- News Article: Author(s). (Year of Publication). Title of Article. Name of News Source. URL.
Example: Johnson, M. (2022, February 16). Climate Change: Is it Too Late to Save the Planet? CNN. https://www.cnn.com/2022/02/16/world/climate-change-planet-scn/index.html
Vancouver Style
In-text citation: Use superscript numbers to cite sources in the text, e.g., “The study conducted by Smith and Johnson^1 found that…”.
Reference list citation: Format: Author(s). Title of book. Edition if any. Place of publication: Publisher; Year of publication.
Example: Smith J, Johnson L. Introduction to Molecular Biology. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley-Blackwell; 2015.
In-text citation: Use superscript numbers to cite sources in the text, e.g., “Several studies have reported that^1,2,3…”.
Reference list citation: Format: Author(s). Title of article. Abbreviated name of journal. Year of publication; Volume number (Issue number): Page range.
Example: Jones S, Patel K, Smith J. The effects of exercise on cardiovascular health. J Cardiol. 2018; 25(2): 78-84.
In-text citation: Use superscript numbers to cite sources in the text, e.g., “Previous research has shown that^1,2,3…”.
Reference list citation: Format: Author(s). Title of paper. In: Editor(s). Title of the conference proceedings. Place of publication: Publisher; Year of publication. Page range.
Example: Johnson L, Smith J. The role of stem cells in tissue regeneration. In: Patel S, ed. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Regenerative Medicine. London: Academic Press; 2016. p. 68-73.
In-text citation: Use superscript numbers to cite sources in the text, e.g., “According to the World Health Organization^1…”.
Reference list citation: Format: Author(s). Title of webpage. Name of website. URL [Accessed Date].
Example: World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) advice for the public. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease/novel-coronavirus-2019/advice-for-public [Accessed 3 March 2023].
In-text citation: Use superscript numbers to cite sources in the text, e.g., “According to the New York Times^1…”.
Reference list citation: Format: Author(s). Title of article. Name of newspaper. Year Month Day; Section (if any): Page number.
Example: Jones S. Study shows that sleep is essential for good health. The New York Times. 2022 Jan 12; Health: A8.
Author(s). Title of Book. Edition Number (if it is not the first edition). Publisher: Place of publication, Year of publication.
Example: Smith, J. Chemistry of Natural Products. 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 2015.
Journal articles:
Author(s). Article Title. Journal Name Year, Volume, Inclusive Pagination.
Example: Garcia, A. M.; Jones, B. A.; Smith, J. R. Selective Synthesis of Alkenes from Alkynes via Catalytic Hydrogenation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 10754-10759.
Research papers:
Author(s). Title of Paper. Journal Name Year, Volume, Inclusive Pagination.
Example: Brown, H. D.; Jackson, C. D.; Patel, S. D. A New Approach to Photovoltaic Solar Cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2018, 26, 134-142.
Author(s) (if available). Title of Webpage. Name of Website. URL (accessed Month Day, Year).
Example: National Institutes of Health. Heart Disease and Stroke. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/heart-disease-and-stroke (accessed April 7, 2023).
News articles:
Author(s). Title of Article. Name of News Publication. Date of Publication. URL (accessed Month Day, Year).
Example: Friedman, T. L. The World is Flat. New York Times. April 7, 2023. https://www.nytimes.com/2023/04/07/opinion/world-flat-globalization.html (accessed April 7, 2023).
In AMA Style Format, the citation for a book should include the following information, in this order:
- Title of book (in italics)
- Edition (if applicable)
- Place of publication
- Year of publication
Lodish H, Berk A, Zipursky SL, et al. Molecular Cell Biology. 4th ed. New York, NY: W. H. Freeman; 2000.
In AMA Style Format, the citation for a journal article should include the following information, in this order:
- Title of article
- Abbreviated title of journal (in italics)
- Year of publication; volume number(issue number):page numbers.
Chen H, Huang Y, Li Y, et al. Effects of mindfulness-based stress reduction on depression in adolescents and young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(6):e207081. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.7081
In AMA Style Format, the citation for a research paper should include the following information, in this order:
- Title of paper
- Name of journal or conference proceeding (in italics)
- Volume number(issue number):page numbers.
Bredenoord AL, Kroes HY, Cuppen E, Parker M, van Delden JJ. Disclosure of individual genetic data to research participants: the debate reconsidered. Trends Genet. 2011;27(2):41-47. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2010.11.004
In AMA Style Format, the citation for a website should include the following information, in this order:
- Title of web page or article
- Name of website (in italics)
- Date of publication or last update (if available)
- URL (website address)
- Date of access (month day, year)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. How to protect yourself and others. CDC. Published February 11, 2022. Accessed February 14, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html
In AMA Style Format, the citation for a news article should include the following information, in this order:
- Name of newspaper or news website (in italics)
- Date of publication
Gorman J. Scientists use stem cells from frogs to build first living robots. The New York Times. January 13, 2020. Accessed January 14, 2020. https://www.nytimes.com/2020/01/13/science/living-robots-xenobots.html
Bluebook Format
One author: Daniel J. Solove, The Future of Reputation: Gossip, Rumor, and Privacy on the Internet (Yale University Press 2007).
Two or more authors: Martha Nussbaum and Saul Levmore, eds., The Offensive Internet: Speech, Privacy, and Reputation (Harvard University Press 2010).
Journal article
One author: Daniel J. Solove, “A Taxonomy of Privacy,” University of Pennsylvania Law Review 154, no. 3 (January 2006): 477-560.
Two or more authors: Ethan Katsh and Andrea Schneider, “The Emergence of Online Dispute Resolution,” Journal of Dispute Resolution 2003, no. 1 (2003): 7-19.
One author: Daniel J. Solove, “A Taxonomy of Privacy,” GWU Law School Public Law Research Paper No. 113, 2005.
Two or more authors: Ethan Katsh and Andrea Schneider, “The Emergence of Online Dispute Resolution,” Cyberlaw Research Paper Series Paper No. 00-5, 2000.
WebsiteElectronic Frontier Foundation, “Surveillance Self-Defense,” accessed April 8, 2023, https://ssd.eff.org/.
News article
One author: Mark Sherman, “Court Deals Major Blow to Net Neutrality Rules,” ABC News, January 14, 2014, https://abcnews.go.com/Politics/wireStory/court-deals-major-blow-net-neutrality-rules-21586820.
Two or more authors: Siobhan Hughes and Brent Kendall, “AT&T Wins Approval to Buy Time Warner,” Wall Street Journal, June 12, 2018, https://www.wsj.com/articles/at-t-wins-approval-to-buy-time-warner-1528847249.
In-Text Citation: (Author’s last name Year of Publication: Page Number)
Example: (Smith 2010: 35)
Reference List Citation: Author’s last name First Initial. Title of Book. Edition. Place of publication: Publisher; Year of publication.
Example: Smith J. Biology: A Textbook. 2nd ed. New York: Oxford University Press; 2010.
Example: (Johnson 2014: 27)
Reference List Citation: Author’s last name First Initial. Title of Article. Abbreviated Title of Journal. Year of publication;Volume(Issue):Page Numbers.
Example: Johnson S. The role of dopamine in addiction. J Neurosci. 2014;34(8): 2262-2272.
Example: (Brown 2018: 10)
Reference List Citation: Author’s last name First Initial. Title of Paper. Paper presented at: Name of Conference; Date of Conference; Place of Conference.
Example: Brown R. The impact of social media on mental health. Paper presented at: Annual Meeting of the American Psychological Association; August 2018; San Francisco, CA.
Example: (World Health Organization 2020: para. 2)
Reference List Citation: Author’s last name First Initial. Title of Webpage. Name of Website. URL. Published date. Accessed date.
Example: World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. WHO website. https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-coronavirus-2019. Updated August 17, 2020. Accessed September 5, 2021.
Example: (Smith 2019: para. 5)
Reference List Citation: Author’s last name First Initial. Title of Article. Title of Newspaper or Magazine. Year of publication; Month Day:Page Numbers.
Example: Smith K. New study finds link between exercise and mental health. The New York Times. 2019;May 20: A6.
Purpose of Research Paper Citation
The purpose of citing sources in a research paper is to give credit to the original authors and acknowledge their contribution to your work. By citing sources, you are also demonstrating the validity and reliability of your research by showing that you have consulted credible and authoritative sources. Citations help readers to locate the original sources that you have referenced and to verify the accuracy and credibility of your research. Additionally, citing sources is important for avoiding plagiarism, which is the act of presenting someone else’s work as your own. Proper citation also shows that you have conducted a thorough literature review and have used the existing research to inform your own work. Overall, citing sources is an essential aspect of academic writing and is necessary for building credibility, demonstrating research skills, and avoiding plagiarism.
Advantages of Research Paper Citation
There are several advantages of research paper citation, including:
- Giving credit: By citing the works of other researchers in your field, you are acknowledging their contribution and giving credit where it is due.
- Strengthening your argument: Citing relevant and reliable sources in your research paper can strengthen your argument and increase its credibility. It shows that you have done your due diligence and considered various perspectives before drawing your conclusions.
- Demonstrating familiarity with the literature : By citing various sources, you are demonstrating your familiarity with the existing literature in your field. This is important as it shows that you are well-informed about the topic and have done a thorough review of the available research.
- Providing a roadmap for further research: By citing relevant sources, you are providing a roadmap for further research on the topic. This can be helpful for future researchers who are interested in exploring the same or related issues.
- Building your own reputation: By citing the works of established researchers in your field, you can build your own reputation as a knowledgeable and informed scholar. This can be particularly helpful if you are early in your career and looking to establish yourself as an expert in your field.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and...

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
In-Text Citations: The Basics

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here .
Reference citations in text are covered on pages 261-268 of the Publication Manual. What follows are some general guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay.
Note: On pages 117-118, the Publication Manual suggests that authors of research papers should use the past tense or present perfect tense for signal phrases that occur in the literature review and procedure descriptions (for example, Jones (1998) found or Jones (1998) has found ...). Contexts other than traditionally-structured research writing may permit the simple present tense (for example, Jones (1998) finds ).
APA Citation Basics
When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
If you are referring to an idea from another work but NOT directly quoting the material, or making reference to an entire book, article or other work, you only have to make reference to the author and year of publication and not the page number in your in-text reference.
On the other hand, if you are directly quoting or borrowing from another work, you should include the page number at the end of the parenthetical citation. Use the abbreviation “p.” (for one page) or “pp.” (for multiple pages) before listing the page number(s). Use an en dash for page ranges. For example, you might write (Jones, 1998, p. 199) or (Jones, 1998, pp. 199–201). This information is reiterated below.
Regardless of how they are referenced, all sources that are cited in the text must appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
In-text citation capitalization, quotes, and italics/underlining
- Always capitalize proper nouns, including author names and initials: D. Jones.
- If you refer to the title of a source within your paper, capitalize all words that are four letters long or greater within the title of a source: Permanence and Change . Exceptions apply to short words that are verbs, nouns, pronouns, adjectives, and adverbs: Writing New Media , There Is Nothing Left to Lose .
( Note: in your References list, only the first word of a title will be capitalized: Writing new media .)
- When capitalizing titles, capitalize both words in a hyphenated compound word: Natural-Born Cyborgs .
- Capitalize the first word after a dash or colon: "Defining Film Rhetoric: The Case of Hitchcock's Vertigo ."
- If the title of the work is italicized in your reference list, italicize it and use title case capitalization in the text: The Closing of the American Mind ; The Wizard of Oz ; Friends .
- If the title of the work is not italicized in your reference list, use double quotation marks and title case capitalization (even though the reference list uses sentence case): "Multimedia Narration: Constructing Possible Worlds;" "The One Where Chandler Can't Cry."
Short quotations
If you are directly quoting from a work, you will need to include the author, year of publication, and page number for the reference (preceded by "p." for a single page and “pp.” for a span of multiple pages, with the page numbers separated by an en dash).
You can introduce the quotation with a signal phrase that includes the author's last name followed by the date of publication in parentheses.
If you do not include the author’s name in the text of the sentence, place the author's last name, the year of publication, and the page number in parentheses after the quotation.
Long quotations
Place direct quotations that are 40 words or longer in a free-standing block of typewritten lines and omit quotation marks. Start the quotation on a new line, indented 1/2 inch from the left margin, i.e., in the same place you would begin a new paragraph. Type the entire quotation on the new margin, and indent the first line of any subsequent paragraph within the quotation 1/2 inch from the new margin. Maintain double-spacing throughout, but do not add an extra blank line before or after it. The parenthetical citation should come after the closing punctuation mark.
Because block quotation formatting is difficult for us to replicate in the OWL's content management system, we have simply provided a screenshot of a generic example below.

Formatting example for block quotations in APA 7 style.
Quotations from sources without pages
Direct quotations from sources that do not contain pages should not reference a page number. Instead, you may reference another logical identifying element: a paragraph, a chapter number, a section number, a table number, or something else. Older works (like religious texts) can also incorporate special location identifiers like verse numbers. In short: pick a substitute for page numbers that makes sense for your source.
Summary or paraphrase
If you are paraphrasing an idea from another work, you only have to make reference to the author and year of publication in your in-text reference and may omit the page numbers. APA guidelines, however, do encourage including a page range for a summary or paraphrase when it will help the reader find the information in a longer work.
- Deutschland
- United Kingdom

- Journal Proofreading
- Dissertation Proofreading
- Scientific Editing
- PhD Thesis Editing
PhD Thesis Proofreading
- Master’s Proofreading
- Bachelor’s Proofreading
- Book Proofreading
Manuscript Proofreading
- Scientific Proofeading
- Report Proofreading
- Research Proofreading
- Conference Proofreading
- Grant Proofreading
Medical Proofreading
- Bioscience Proofreading
- Biomedical Proofreading
- Nursing Papers
- Psychology Proofreading
- Economics Proofreading
- Philosophy Proofreading
- Sociology Proofreading
- Chemistry Proofreading
- Material Science
- Planetary Science
- Physical Sciences
- Biosciences
- Veterinary Science
- Pharmaceutical Science
- Plant Science
- How It Works
Select Page
How To Write References for Academic & Scientific Research Papers
Posted by rene | Jun 26, 2021 | Advice on Constructing Academic References & Bibliographies | 0 |

How To Write References for Academic and Scientific Research Papers Writing accurate & appropriate references is an essential aspect of preparing a research paper for successful publication, examination or any other kind of serious dissemination or evaluation. This article explains exactly how to write perfect references in two widely used scholarly styles: the parenthetical author–date system recommended by the American Psychological Association (APA) & the sequential numerical or Vancouver system frequently used in the sciences. The post also includes several clear examples of in-text citations & complete bibliographical references formatted in both styles.
Neither of these documentation styles is inherently complex, though each does have its characteristic pitfalls, and the utmost accuracy is essential when using either. Accusations of plagiarism or misrepresentation of the work of other scholars can be the unpleasant result if authors are not absolutely correct and scrupulously thorough in providing citations and references when they should to acknowledge the research of others. In addition, publication attempts can prove unsuccessful and grades lower than expected if instructions and guidelines for references are not observed with precision and consistency. The discussion and examples offered below outline exactly how to provide scholarly references for articles and books in one version of an author–date documentation style – APA – and one of a numerical style – Vancouver – but do be aware that various versions of these two basic styles exist, so consulting the guidelines, instructions or manual specific to the research paper you are writing is always imperative before finalising formats for in-text citations and complete references.
Writing APA Author–Date References for a Research Paper Writing an accurate and appropriate APA author–date reference is a two-stage process involving 1) the creation of an in-text citation in the main body of the paper and 2) the addition of a complete bibliographical entry about the source in a list of references at the end of the paper.
1. The in-text citation should contain the last name of the author (or last names of the authors if there is more than one) who wrote the article, book or other document followed by the document’s date of publication. This information most frequently appears in parentheses immediately after the statement related to the paper, as in this example: • A recent study of the text presents a similar argument (Wilson & Bond, 2016).
Alternatively, the names of the authors or the date of publication can be integrated into the main text, with the remaining information presented in parentheses: • Wilson and Bond present a similar argument in their recent study of the text (2016). • A 2016 examination of the text presents a similar argument (Wilson & Bond). Rewording of the main text is obviously necessary, but the only difference (beyond arrangement) in the citation information itself is that the word ‘and’ is used between the author names in the main text, whereas an ampersand (&) is used between those names when they appear in parentheses. The parentheses can sometimes be eliminated altogether by writing both author names and publication date in the main text: • Wilson and Bond’s 2016 study of the text presents a similar argument.
Dissertation Proofreading Services
Page numbers can be used for referring to specific information in particular parts of a publication, but they are usually only required in APA style for direct quotations when a passage or other part of a published document is reproduced word for word in a new research paper. In such cases, the page number is separated from the publication date by a comma and preceded by the abbreviation ‘p.’ for ‘page’: • As Wilson and Bond explain, ‘the political reading of the text, even the most personal of its episodes, seems universal until the book falls into a woman’s hands’ (2016, p.88).
When two or more sources are cited in the same set of parentheses, semicolons are used to separate the sources: • Both studies consider the poem in relation to urban culture (Samuel & Watson, 2013; Wilson & Bond, 2016). The normal arrangement when multiple sources are cited in a single set of parentheses is to observe alphabetical order according to the author names, as I have done above (with ‘Samuel’ preceding ‘Wilson’). Notice that the in-text citation takes the same form whether the source cited is a book or an article, with ‘Samuel & Watson’ referring here to a monograph and ‘Wilson & Bond’ to a journal article.
2. Every source cited in the text of an academic or scientific research paper using APA style should also be included in a list that is entitled ‘References’ and presented at the end of the paper. An APA list of references should be arranged alphabetically based on author names, and all the bibliographical information required for readers to find each source must be provided in a specific format. The author names for a publication come first and are inverted, with the last name of the first author of each document opening the bibliographical entry. Author names are followed by the date of publication (in parentheses), with these two pieces of information serving readers by connecting the complete reference to the in-text citation. It is therefore vital that the last names of authors and the publication dates provided in both places are checked against each other for errors and inconsistencies and then carefully corrected to agree with precision.
For the complete reference to a journal article, the title of the article follows the date of publication. The name and volume number of the journal come next, both of them in italic font, though do be aware that special fonts may not be displayed in this post. The pages on which the article can be found come next, and if there is a doi or url for an online version of the paper, that should be the last item in the entry, which would take this form: • Wilson, S., & Bond, F. (2016). Political and personal readings of the earliest zone poem. Urban Poetry, 12, 72–94. doi:00.0000/00000000000000
For the complete reference to a book, the information, and thus the format, is a little different. The title of the book follows the publication date and appears in italic font, with the place of publication and publisher’s name completing the reference: • Samuel, H., & Watson, M. (2013). Political poetry and modern urbanity. London: Big City Press.
Journal Article Editing Services
Writing Sequential Numerical References for a Research Paper The same two-step process is necessary when writing the sequential numerical references used for Vancouver style documentation, but in-text citations are notably simpler, a different arrangement is used for the list of references and a somewhat different format is required for the complete bibliographical entries included in the list.
1. For a numerical in-text citation, a single Arabic numeral is all that is required. Each source is assigned a number when it is first cited, so the sources used in a research paper are numbered sequentially according to the order of first citation, with each source retaining throughout the paper the number it was originally assigned. The first source cited would therefore be reference 1, the second reference 2 and so on. The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) recommends placing these reference numbers in parentheses, with a citation taking this form: • A recent study of the text presents a similar argument (1).
As is the case with author–date citations, information about sources can also be added in the main text: • Wilson and Bond present a similar argument in their recent study of the text (1). • A 2016 examination of the text presents a similar argument (1). • Wilson and Bond’s 2016 study of the text presents a similar argument (1). Unlike author–date citations, however, this additional information in the text does not negate the need for the reference number, which is always required.
If you need to cite a specific page of a document to point readers to a particular piece of information or indicate the location of a quoted passage, the page number should be added after the reference number, usually with a comma to separate it from the reference number and a preceding ‘p.’ to avoid confusion: • As Wilson and Bond explain, ‘the political reading of the text, even the most personal of its episodes, seems universal until the book falls into a woman’s hands’ (1, p.88). When two or more sources are cited at the same time, commas are generally used to separate the reference numbers, usually without intervening spaces: • Several studies have taken this approach to the text (1,2,5–8).
2. The reference list for sequential numerical citations is arranged, not surprisingly, by the numerical sequence of the citations. This means that the first source cited in a research paper (reference 1) is also the first source listed in the References section of the paper, the second is the second source in the list and so on. The following two sample references follow ICMJE guidelines and would serve as the opening entries in a numerical list of references: • 1. Wilson S, Bond F. Political and personal readings of the earliest zone poem. Urban Poetry. 2016;12:72–94. doi:00.0000/00000000000000. • 2. Samuel H, Watson M. Political Poetry and Modern Urbanity. London: Big City Press; 2013.
As these examples show, the information required for a complete reference varies according to the nature of the source cited, just as it does with author–date references. In addition, the names of journals (but not books) are often abbreviated when preparing numerical references. It is essential, however, that the correct or standard abbreviation for each journal be used when shortening journal titles, which can easily be confused in their abbreviated forms, so a little research may be necessary to determine the right abbreviation. Use of the complete journal title is recommended when there is any doubt or there is no standard abbreviation.
A cautionary note is in order when writing sequential numerical references. Adding or deleting sources from a numerical list of references that has been arranged according to the order in which sources are first cited can necessitate changes in subsequent list entries as well as in the in-text citations, and the same is the case with any changes to those in-text citations. The reason is simple: if, for example, you remove reference 3 from the text or list, what was reference 4 becomes reference 3, what was reference 5 becomes reference 4 and so on. If you add that removed reference back in elsewhere more alterations will ensue. It is therefore wise to check and finalise the order of the reference list very carefully indeed after all the in-text citations are in their final places, and to ensure that the assigned reference numbers agree with the utmost accuracy between in-text citations and the list of references.
Why Our Editing and Proofreading Services? At Proof-Reading-Service.com we offer the highest quality journal article editing , phd thesis editing and proofreading services via our large and extremely dedicated team of academic and scientific professionals. All of our proofreaders and editors are native speakers of English who have earned their own postgraduate degrees, and their areas of specialisation cover such a wide range of disciplines that we are able to help our international clientele with research editing to improve and perfect all kinds of academic manuscripts for successful publication. Many of the carefully trained members of our expert editing and proofreading team work predominantly on articles intended for publication in scholarly journals, applying painstaking journal editing standards to ensure that the references and formatting used in each paper are in conformity with the journal’s instructions for authors and to correct any grammar, spelling, punctuation or simple typing errors. In this way, we enable our clients to report their research in the clear and accurate ways required to impress acquisitions editors and achieve publication.
Our scientific editing services for the authors of a wide variety of scientific journal papers are especially popular, but we also offer manuscript editing services and have the experience and expertise to proofread and edit manuscripts in all scholarly disciplines, as well as beyond them. We have team members who specialise in medical editing services , and some of our experts dedicate their time exclusively to PhD proofreading and master’s proofreading , offering research students the opportunity to improve their use of formatting and language through the most exacting PhD thesis editing and dissertation proofreading practices. Whether you are preparing a conference paper for presentation, polishing a progress report to share with colleagues, or facing the daunting task of editing and perfecting any kind of scholarly document for publication, a qualified member of our professional team can provide invaluable assistance and give you greater confidence in your written work.
If you are in the process of preparing an article for an academic or scientific journal, or planning one for the near future, you may well be interested in a new book, Guide to Journal Publication , which is available on our Tips and Advice on Publishing Research in Journals website.
Academic Proofreading Services
Journal article proofreading.
Journal article proofreading services
PhD thesis proofreading services
Scientific Proofreading
Scientific proofreading services
Medical proofreading services
Academic Proofreading
Academic proofreading services
Manuscript proofreading services
Summary How To Write References for Academic & Scientific Research Papers
How To Write References for Academic & Scientific Research Papers
Related posts.

Online Guides for Using Chicago Manual of Style References
June 13, 2020

Helpful Tips on How To Find and Use the AMA Manual of Style
June 15, 2020

PhD Theses or Dissertations: Footnotes-Notes for Documentation
May 23, 2021

Adding a Bibliography and Supplementary Material
June 24, 2020
Recent Posts

Recent Reviews
- Responding to Peer Reviewer Comments: A Free Example Letter Score: 96%
- Example of a Quantitative Research Paper for Researchers Score: 95%
- How To Write the Findings Section of a Research Paper Score: 94%
- Free Sample Letters for Withdrawing a Manuscript from a Publisher Score: 98%
- Why Does Google Scholar Not Find My Research Paper? Score: 92%
- Advice & Discussions for Postgraduates on Writing Theses & Dissertations (81)
- Advice & Discussions on Preparing & Submitting Journal Articles for Publication (210)
- Advice on Constructing Academic References & Bibliographies (18)
- Advice on How To Deal Successfully with Journal Paper Rejection (5)
- Articles for Professional Proofreaders, Editors & Copyeditors (5)
- Communicating Successfully with Journal Editors about Your Paper (14)
- Help with Perfecting Grammar in Academic & Scientific Writing (71)
- Help with Writing and Responding to Peer Reviews of Journal Papers (9)
- Our 10 Most Popular PRS Blog Posts on Academic Writing and Publishing (3)
- Our Top 5 Blog Posts on Academic and Scientific Writing and Publishing (2)
- Using Abbreviations Effectively in Academic and Scientific Writing (8)
- Writing a Cover Letter To Submit a Research Paper for Publication (5)
- How to write a research paper
Last updated
11 January 2024
Reviewed by
With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience.
Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
By documenting your findings, you can inspire others and make a difference in your field. Here's how you can make your research paper unique and comprehensive.
- What is a research paper?
Research papers allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. These papers are usually lengthier and more detailed than typical essays, requiring deeper insight into the chosen topic.
To write a research paper, you must first choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to the field of study. Once you’ve selected your topic, gathering as many relevant resources as possible, including books, scholarly articles, credible websites, and other academic materials, is essential. You must then read and analyze these sources, summarizing their key points and identifying gaps in the current research.
You can formulate your ideas and opinions once you thoroughly understand the existing research. To get there might involve conducting original research, gathering data, or analyzing existing data sets. It could also involve presenting an original argument or interpretation of the existing research.
Writing a successful research paper involves presenting your findings clearly and engagingly, which might involve using charts, graphs, or other visual aids to present your data and using concise language to explain your findings. You must also ensure your paper adheres to relevant academic formatting guidelines, including proper citations and references.
Overall, writing a research paper requires a significant amount of time, effort, and attention to detail. However, it is also an enriching experience that allows you to delve deeply into a subject that interests you and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your chosen field.
- How long should a research paper be?
Research papers are deep dives into a topic. Therefore, they tend to be longer pieces of work than essays or opinion pieces.
However, a suitable length depends on the complexity of the topic and your level of expertise. For instance, are you a first-year college student or an experienced professional?
Also, remember that the best research papers provide valuable information for the benefit of others. Therefore, the quality of information matters most, not necessarily the length. Being concise is valuable.
Following these best practice steps will help keep your process simple and productive:
1. Gaining a deep understanding of any expectations
Before diving into your intended topic or beginning the research phase, take some time to orient yourself. Suppose there’s a specific topic assigned to you. In that case, it’s essential to deeply understand the question and organize your planning and approach in response. Pay attention to the key requirements and ensure you align your writing accordingly.
This preparation step entails
Deeply understanding the task or assignment
Being clear about the expected format and length
Familiarizing yourself with the citation and referencing requirements
Understanding any defined limits for your research contribution
Where applicable, speaking to your professor or research supervisor for further clarification
2. Choose your research topic
Select a research topic that aligns with both your interests and available resources. Ideally, focus on a field where you possess significant experience and analytical skills. In crafting your research paper, it's crucial to go beyond summarizing existing data and contribute fresh insights to the chosen area.
Consider narrowing your focus to a specific aspect of the topic. For example, if exploring the link between technology and mental health, delve into how social media use during the pandemic impacts the well-being of college students. Conducting interviews and surveys with students could provide firsthand data and unique perspectives, adding substantial value to the existing knowledge.
When finalizing your topic, adhere to legal and ethical norms in the relevant area (this ensures the integrity of your research, protects participants' rights, upholds intellectual property standards, and ensures transparency and accountability). Following these principles not only maintains the credibility of your work but also builds trust within your academic or professional community.
For instance, in writing about medical research, consider legal and ethical norms , including patient confidentiality laws and informed consent requirements. Similarly, if analyzing user data on social media platforms, be mindful of data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws governing personal information collection and use. Aligning with legal and ethical standards not only avoids potential issues but also underscores the responsible conduct of your research.
3. Gather preliminary research
Once you’ve landed on your topic, it’s time to explore it further. You’ll want to discover more about available resources and existing research relevant to your assignment at this stage.
This exploratory phase is vital as you may discover issues with your original idea or realize you have insufficient resources to explore the topic effectively. This key bit of groundwork allows you to redirect your research topic in a different, more feasible, or more relevant direction if necessary.
Spending ample time at this stage ensures you gather everything you need, learn as much as you can about the topic, and discover gaps where the topic has yet to be sufficiently covered, offering an opportunity to research it further.
4. Define your research question
To produce a well-structured and focused paper, it is imperative to formulate a clear and precise research question that will guide your work. Your research question must be informed by the existing literature and tailored to the scope and objectives of your project. By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers.
5. Write a thesis statement
A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction. It serves as an overall guide to summarize the overall intent of the research paper for you and anyone wanting to know more about the research.
A strong thesis statement is:
Concise and clear: Explain your case in simple sentences (avoid covering multiple ideas). It might help to think of this section as an elevator pitch.
Specific: Ensure that there is no ambiguity in your statement and that your summary covers the points argued in the paper.
Debatable: A thesis statement puts forward a specific argument––it is not merely a statement but a debatable point that can be analyzed and discussed.
Here are three thesis statement examples from different disciplines:
Psychology thesis example: "We're studying adults aged 25-40 to see if taking short breaks for mindfulness can help with stress. Our goal is to find practical ways to manage anxiety better."
Environmental science thesis example: "This research paper looks into how having more city parks might make the air cleaner and keep people healthier. I want to find out if more green spaces means breathing fewer carcinogens in big cities."
UX research thesis example: "This study focuses on improving mobile banking for older adults using ethnographic research, eye-tracking analysis, and interactive prototyping. We investigate the usefulness of eye-tracking analysis with older individuals, aiming to spark debate and offer fresh perspectives on UX design and digital inclusivity for the aging population."
6. Conduct in-depth research
A research paper doesn’t just include research that you’ve uncovered from other papers and studies but your fresh insights, too. You will seek to become an expert on your topic––understanding the nuances in the current leading theories. You will analyze existing research and add your thinking and discoveries. It's crucial to conduct well-designed research that is rigorous, robust, and based on reliable sources. Suppose a research paper lacks evidence or is biased. In that case, it won't benefit the academic community or the general public. Therefore, examining the topic thoroughly and furthering its understanding through high-quality research is essential. That usually means conducting new research. Depending on the area under investigation, you may conduct surveys, interviews, diary studies , or observational research to uncover new insights or bolster current claims.
7. Determine supporting evidence
Not every piece of research you’ve discovered will be relevant to your research paper. It’s important to categorize the most meaningful evidence to include alongside your discoveries. It's important to include evidence that doesn't support your claims to avoid exclusion bias and ensure a fair research paper.
8. Write a research paper outline
Before diving in and writing the whole paper, start with an outline. It will help you to see if more research is needed, and it will provide a framework by which to write a more compelling paper. Your supervisor may even request an outline to approve before beginning to write the first draft of the full paper. An outline will include your topic, thesis statement, key headings, short summaries of the research, and your arguments.
9. Write your first draft
Once you feel confident about your outline and sources, it’s time to write your first draft. While penning a long piece of content can be intimidating, if you’ve laid the groundwork, you will have a structure to help you move steadily through each section. To keep up motivation and inspiration, it’s often best to keep the pace quick. Stopping for long periods can interrupt your flow and make jumping back in harder than writing when things are fresh in your mind.
10. Cite your sources correctly
It's always a good practice to give credit where it's due, and the same goes for citing any works that have influenced your paper. Building your arguments on credible references adds value and authenticity to your research. In the formatting guidelines section, you’ll find an overview of different citation styles (MLA, CMOS, or APA), which will help you meet any publishing or academic requirements and strengthen your paper's credibility. It is essential to follow the guidelines provided by your school or the publication you are submitting to ensure the accuracy and relevance of your citations.
11. Ensure your work is original
It is crucial to ensure the originality of your paper, as plagiarism can lead to serious consequences. To avoid plagiarism, you should use proper paraphrasing and quoting techniques. Paraphrasing is rewriting a text in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Quoting involves directly citing the source. Giving credit to the original author or source is essential whenever you borrow their ideas or words. You can also use plagiarism detection tools such as Scribbr or Grammarly to check the originality of your paper. These tools compare your draft writing to a vast database of online sources. If you find any accidental plagiarism, you should correct it immediately by rephrasing or citing the source.
12. Revise, edit, and proofread
One of the essential qualities of excellent writers is their ability to understand the importance of editing and proofreading. Even though it's tempting to call it a day once you've finished your writing, editing your work can significantly improve its quality. It's natural to overlook the weaker areas when you've just finished writing a paper. Therefore, it's best to take a break of a day or two, or even up to a week, to refresh your mind. This way, you can return to your work with a new perspective. After some breathing room, you can spot any inconsistencies, spelling and grammar errors, typos, or missing citations and correct them.
- The best research paper format
The format of your research paper should align with the requirements set forth by your college, school, or target publication.
There is no one “best” format, per se. Depending on the stated requirements, you may need to include the following elements:
Title page: The title page of a research paper typically includes the title, author's name, and institutional affiliation and may include additional information such as a course name or instructor's name.
Table of contents: Include a table of contents to make it easy for readers to find specific sections of your paper.
Abstract: The abstract is a summary of the purpose of the paper.
Methods : In this section, describe the research methods used. This may include collecting data , conducting interviews, or doing field research .
Results: Summarize the conclusions you drew from your research in this section.
Discussion: In this section, discuss the implications of your research . Be sure to mention any significant limitations to your approach and suggest areas for further research.
Tables, charts, and illustrations: Use tables, charts, and illustrations to help convey your research findings and make them easier to understand.
Works cited or reference page: Include a works cited or reference page to give credit to the sources that you used to conduct your research.
Bibliography: Provide a list of all the sources you consulted while conducting your research.
Dedication and acknowledgments : Optionally, you may include a dedication and acknowledgments section to thank individuals who helped you with your research.
- General style and formatting guidelines
Formatting your research paper means you can submit it to your college, journal, or other publications in compliance with their criteria.
Research papers tend to follow the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), or Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) guidelines.
Here’s how each style guide is typically used:
Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS):
CMOS is a versatile style guide used for various types of writing. It's known for its flexibility and use in the humanities. CMOS provides guidelines for citations, formatting, and overall writing style. It allows for both footnotes and in-text citations, giving writers options based on their preferences or publication requirements.
American Psychological Association (APA):
APA is common in the social sciences. It’s hailed for its clarity and emphasis on precision. It has specific rules for citing sources, creating references, and formatting papers. APA style uses in-text citations with an accompanying reference list. It's designed to convey information efficiently and is widely used in academic and scientific writing.
Modern Language Association (MLA):
MLA is widely used in the humanities, especially literature and language studies. It emphasizes the author-page format for in-text citations and provides guidelines for creating a "Works Cited" page. MLA is known for its focus on the author's name and the literary works cited. It’s frequently used in disciplines that prioritize literary analysis and critical thinking.
To confirm you're using the latest style guide, check the official website or publisher's site for updates, consult academic resources, and verify the guide's publication date. Online platforms and educational resources may also provide summaries and alerts about any revisions or additions to the style guide.
Citing sources
When working on your research paper, it's important to cite the sources you used properly. Your citation style will guide you through this process. Generally, there are three parts to citing sources in your research paper:
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation.
Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
In-text citations include the author's surname and the date of the citation.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of each page of your research paper. They may also be summarized within a reference list at the end of the paper.
A reference list includes all of the research used within the paper at the end of the document. It should include the author, date, paper title, and publisher listed in the order that aligns with your citation style.
10 research paper writing tips:
Following some best practices is essential to writing a research paper that contributes to your field of study and creates a positive impact.
These tactics will help you structure your argument effectively and ensure your work benefits others:
Clear and precise language: Ensure your language is unambiguous. Use academic language appropriately, but keep it simple. Also, provide clear takeaways for your audience.
Effective idea separation: Organize the vast amount of information and sources in your paper with paragraphs and titles. Create easily digestible sections for your readers to navigate through.
Compelling intro: Craft an engaging introduction that captures your reader's interest. Hook your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
Thorough revision and editing: Take the time to review and edit your paper comprehensively. Use tools like Grammarly to detect and correct small, overlooked errors.
Thesis precision: Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your paper. Ensure that your thesis aligns with your research's overall purpose and contribution.
Logical flow of ideas: Maintain a logical progression throughout the paper. Use transitions effectively to connect different sections and maintain coherence.
Critical evaluation of sources: Evaluate and critically assess the relevance and reliability of your sources. Ensure that your research is based on credible and up-to-date information.
Thematic consistency: Maintain a consistent theme throughout the paper. Ensure that all sections contribute cohesively to the overall argument.
Relevant supporting evidence: Provide concise and relevant evidence to support your arguments. Avoid unnecessary details that may distract from the main points.
Embrace counterarguments: Acknowledge and address opposing views to strengthen your position. Show that you have considered alternative arguments in your field.
7 research tips
If you want your paper to not only be well-written but also contribute to the progress of human knowledge, consider these tips to take your paper to the next level:
Selecting the appropriate topic: The topic you select should align with your area of expertise, comply with the requirements of your project, and have sufficient resources for a comprehensive investigation.
Use academic databases: Academic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and JSTOR offer a wealth of research papers that can help you discover everything you need to know about your chosen topic.
Critically evaluate sources: It is important not to accept research findings at face value. Instead, it is crucial to critically analyze the information to avoid jumping to conclusions or overlooking important details. A well-written research paper requires a critical analysis with thorough reasoning to support claims.
Diversify your sources: Expand your research horizons by exploring a variety of sources beyond the standard databases. Utilize books, conference proceedings, and interviews to gather diverse perspectives and enrich your understanding of the topic.
Take detailed notes: Detailed note-taking is crucial during research and can help you form the outline and body of your paper.
Stay up on trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in your field by regularly checking for recent publications. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant journals, and attend conferences to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements.
Engage in peer review: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the rigor and validity of your research . Peer review helps identify potential weaknesses in your methodology and strengthens the overall credibility of your findings.
- The real-world impact of research papers
Writing a research paper is more than an academic or business exercise. The experience provides an opportunity to explore a subject in-depth, broaden one's understanding, and arrive at meaningful conclusions. With careful planning, dedication, and hard work, writing a research paper can be a fulfilling and enriching experience contributing to advancing knowledge.
How do I publish my research paper?
Many academics wish to publish their research papers. While challenging, your paper might get traction if it covers new and well-written information. To publish your research paper, find a target publication, thoroughly read their guidelines, format your paper accordingly, and send it to them per their instructions. You may need to include a cover letter, too. After submission, your paper may be peer-reviewed by experts to assess its legitimacy, quality, originality, and methodology. Following review, you will be informed by the publication whether they have accepted or rejected your paper.
What is a good opening sentence for a research paper?
Beginning your research paper with a compelling introduction can ensure readers are interested in going further. A relevant quote, a compelling statistic, or a bold argument can start the paper and hook your reader. Remember, though, that the most important aspect of a research paper is the quality of the information––not necessarily your ability to storytell, so ensure anything you write aligns with your goals.
Research paper vs. a research proposal—what’s the difference?
While some may confuse research papers and proposals, they are different documents.
A research proposal comes before a research paper. It is a detailed document that outlines an intended area of exploration. It includes the research topic, methodology, timeline, sources, and potential conclusions. Research proposals are often required when seeking approval to conduct research.
A research paper is a summary of research findings. A research paper follows a structured format to present those findings and construct an argument or conclusion.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
- 10 research paper
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
Citation Generator
Powered by chegg.
- Select style:
- Archive material
- Chapter of an edited book
- Conference proceedings
- Dictionary entry
- Dissertation
- DVD, video, or film
- E-book or PDF
- Edited book
- Encyclopedia article
- Government publication
- Music or recording
- Online image or video
- Presentation
- Press release
- Religious text
What Is Cite This For Me’s Citation Generator?
Cite This For Me’s open-access generator is an automated citation machine that turns any of your sources into citations in just a click. Using a citation generator helps students to integrate referencing into their research and writing routine; turning a time-consuming ordeal into a simple task.
A citation machine is essentially a works cited generator that accesses information from across the web, drawing the relevant information into a fully-formatted bibliography that clearly presents all of the sources that have contributed to your work.
If you don’t know how to cite correctly, or have a fast-approaching deadline, Cite This For Me’s accurate and intuitive citation machine will lend you the confidence to realise your full academic potential. In order to get a grade that reflects all your hard work, your citations must be accurate and complete. Using a citation maker to create your references not only saves you time but also ensures that you don’t lose valuable marks on your assignment.
Not sure how to format your citations, what citations are, or just want to find out more about Cite This For Me’s citation machine? This guide outlines everything you need to know to equip yourself with the know-how and confidence to research and cite a wide range of diverse sources in your work.
Why Do I Need To Cite?
Simply put, referencing is the citing of sources used in essays, articles, research, conferences etc. When another source contributes to your work, you have to give the original owner the appropriate credit. After all, you wouldn’t steal someone else’s possessions so why would you steal their ideas?
Any factual material or ideas you take from another source must be acknowledged in a reference, unless it is common knowledge (e.g. President Kennedy was killed in 1963). Failing to credit all of your sources, even when you’ve paraphrased or completely reworded the information, is plagiarism. Plagiarizing will result in disciplinary action, which can range from losing precious points on your assignment to expulsion from your university.
What’s more, attributing your research infuses credibility and authority into your work, both by supporting your own ideas and by demonstrating the breadth of your research. For many students, crediting sources can be a confusing and tedious process, but it’s a surefire way to improve the quality of your work so it’s essential to get it right. Luckily for you, using Cite This For Me’s citation machine makes creating accurate references easier than ever, leaving more time for you to excel in your studies.
In summary, the referencing process serves three main functions:
- To validate the statements and conclusions in your work by providing directions to other sound sources that support and verify them.
- To help your readers locate, read and check your sources, as well as establishing their contribution to your work.
- To give credit to the original author and hence avoid committing intellectual property theft (known as ‘plagiarism’ in academia).
How Do I Cite My Sources With The Cite This For Me Citation Machine?
Cite This For Me’s citation generator is the most accurate citation machine available, so whether you’re not sure how to format in-text citations or are looking for a foolproof solution to automate a fully-formatted works cited list, this citation machine will solve all of your referencing needs.
Referencing your source material doesn’t just prevent you from losing valuable marks for plagiarism, it also provides all of the information to help your reader find for themselves the book, article, or other item you are citing. The accessible interface of this citation builder makes it easy for you to identify the source you have used – simply enter its unique identifier into the citation machine search bar. If this information is not available you can search for the title or author instead, and then select from the search results that appear below the citation generator.
The good news is that by using tools such as Cite This For Me, which help you work smarter, you don’t need to limit your research to sources that are traditional to cite. In fact, there are no limits to what you can reference, whether it be a YouTube video, website or a tweet.
To use the works cited generator, simply:
- Select from APA, MLA, Chicago, ASA, IEEE and AMA * styles.
- Choose the type of source you would like to cite (e.g. website, book, journal, video).
- Enter the URL , DOI , ISBN , title, or other unique source information into the citation generator to find your source.
- Click the ‘Cite’ button on the citation machine.
- Copy your new reference from the citation generator into your bibliography or works cited list.
- Repeat for each source that has contributed to your work.
*If you require another referencing style for your paper, essay or other academic work, you can select from over 1,000 styles by creating a free Cite This For Me account.
Once you have created your Cite This For Me account you will be able to use the citation machine to generate multiple references and save them into a project. Use the highly-rated iOS or Android apps to create references in a flash with your smartphone camera, export your complete bibliography in one go, and much more.
What Will The Citation Machine Create For Me?
Cite This For Me’s citation maker will generate your reference in two parts; an in-text citation and a full reference to be copied straight into your work.
The citation machine will auto-generate the correct formatting for your works cited list or bibliography depending on your chosen style. For instance, if you select a parenthetical style on the citation machine it will generate an in-text citation in parentheses, along with a full reference to slot into your bibliography. Likewise, if the citation generator is set to a footnote style then it will create a fully-formatted reference for your reference page and bibliography, as well as a corresponding footnote to insert at the bottom of the page containing the relevant source.
Parenthetical referencing examples:
In-text example: A nation has been defined as an imagined community (Anderson, 2006).* Alternative format: Anderson (2006) defined a nation as an imagined community.
*The citation machine will create your references in the first style, but this should be edited if the author’s name already appears in the text.
Bibliography / Works Cited list example: Anderson, B. (2006). Imagined Communities. London: Verso.
Popular Citation Examples
- Citing archive material
- Citing artwork
- Citing an audiobook
- Citing the Bible
- Citing a blog
- Citing a book
- Citing a book chapter
- Citing a comic book
- Citing conference proceedings
- Citing a court case
- Citing a database
- Citing a dictionary entry
- Citing a dissertation
- Citing an eBook
- Citing an edited book
- Citing an email
- Citing an encyclopedia article
- Citing a government publication
- Citing an image
- Citing an interview
- Citing a journal article
- Citing legislation
- Citing a magazine
- Citing a meme
- Citing a mobile app
- Citing a movie
- Citing a newspaper
- Citing a pamphlet
- Citing a patent
- Citing a play
- Citing a podcast
- Citing a poem
- Citing a presentation
- Citing a press release
- Citing a pseudonym
- Citing a report
- Citing Shakespeare
- Citing social media
- Citing a song
- Citing software
- Citing a speech
- Citing translated book
- Citing a TV Show
- Citing a weather report
- Citing a website
- Citing Wikipedia article
- Citing a YouTube video
What Are Citation Styles?
A citation style is a set of rules that you, as an academic writer, must follow to ensure the quality and relevance of your work. There are thousands of styles that are used in different academic institutions around the world, but in the US the most common are APA, MLA and Chicago.
The style you need to use will depend on the preference of your professor, discipline or academic institution – so if you’re unsure which style you should be using, consult your department and follow their guidelines exactly, as this is what you’ll be evaluated on when it comes to grading.
Referencing isn’t just there to guard against plagiarism – presenting your research in a clear and consistent way eases the reader’s comprehension. Each style has a different set of rules for both page formatting and referencing. Be sure to adhere to formatting rules such as font type, font size and line spacing to ensure that your work is easily legible. Furthermore, if your work is published as part of an anthology or collected works, each entry will need to be presented in the same style to maintain uniformity throughout. It is important to make sure that you don’t jump from one style to another, so follow the rules carefully to ensure your reference page and bibliography are both accurate and complete.
If you need a hand with your referencing then why not try Cite This For Me’s citation builder? It’s the quickest and easiest way to reference any source, in any style. The citation generator above will create your references in MLA format style as standard, but this powerful citation machine can generate fully-formatted references in over 1,000 styles – including individual university variations of each style. So, whether your subject requires you to use the APA citation , or your professor has asked you to adopt the Chicago style citation so that your work includes numbered footnotes, we’re sure to have the style you need. Cite This For Me also offers a citation machine and helpful formatting guide for styles such as ASA , IEEE , AMA or Harvard . To access all of them, simply create your free Cite This For Me account and search for your specific style.
Popular Citation Styles
- ACS Referencing Generator
- AMA Citation Generator
- APA Citation Generator
- APSA Referencing Generator
- ASA Citation Generator
- Bluebook Citation Generator
- Chicago Style Citation Generator
- Harvard Referencing Generator
- IEEE Referencing Generator
- MHRA Referencing Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Nature Referencing Generator
- OSCOLA Referencing Generator
- Oxford Referencing Generator
- Turabian Citation Generator
- Vancouver Referencing Generator
- View all Citation Styles
How Do I Format A Works Cited List Or Bibliography?
Drawing on a wide range of sources greatly enhances the quality of your work, and reading above and beyond your recommended reading list – and then using these sources to support your own thesis – is an excellent way to impress your reader. A clearly presented works cited list or bibliography demonstrates the lengths you have gone to in researching your chosen topic.
Typically, a works cited list starts on a new page at the end of the main body of text and includes a complete list of the sources you have actually cited in your paper. This list should contain all the information needed for the reader to locate the original source of the information, quote or statistic that directly contributed to your work. On the other hand, a bibliography is a comprehensive list of all the material you may have consulted throughout your research and writing process. Both provide the necessary information for readers to retrieve and check the sources cited in your work.
Each style’s guidelines will define the terminology of ‘ works cited ’ and ‘ bibliography ’, as well as providing formatting guidelines for font, line spacing and page indentations. In addition, it will instruct you on how to order your works cited list or bibliography – this will usually be either alphabetical or chronological (meaning the order that these sources appear in your work). Before submitting your work, be sure to check that you have formatted your whole paper – including your reference page and bibliography – according to your style’s formatting guidelines.
Sounds complicated? Referencing has never been so easy; Cite This For Me’s citation machine will automatically generate fully-formatted references for your works cited page or bibliography in your chosen style.
How Do Citations Actually Work?
Although the citation generator will create your bibliography and works cited list for you in record time, it is still useful to understand how this system works behind the scenes. Understanding how a citation machine actually generates references will greatly increase the quality of your work.
As well as saving you time with its citation maker, Cite This For Me provides the learning resources to help you fully understand the citing process and the benefits of adopting great referencing standards.
The referencing process:
- Find a book, journal, website or other source that will contribute to your work.
- Save the quote, image, data or other information that you will use in your work.
- Save the source information that enables you to find it again (i.e. URL, ISBN, DOI etc.).
- Format the source information into a reference.
- Copy and paste the reference into the body of the text.
- Repeat for each source that contributes to your work.
- Export or copy and paste the fully-formatted reference into your bibliography.
Manage all your citations in one place
Create projects, add notes, cite directly from the browser and scan books’ barcodes with a mobile app.
Sign up to Cite This For Me – the ultimate citation management tool.
Paper Tiger? Chinese Science and Home Bias in Citations
We investigate the phenomenon of home bias in scientific citations, where researchers disproportionately cite work from their own country. We develop a benchmark for expected citations based on the relative size of countries, defining home bias as deviations from this norm. Our findings reveal that China exhibits the largest home bias across all major countries and in nearly all scientific fields studied. This stands in contrast to the pattern of home bias for China’s trade in goods and services, where China does not stand out from most industrialized countries. After adjusting citation counts for home bias, we demonstrate that China’s apparent rise in citation rankings is overstated. Our adjusted ranking places China fourth globally, behind the US, the UK, and Germany, tempering the perception of China’s scientific dominance.
All authors contributed equally. Address correspondence to [email protected]. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Bureau of Economic Research.
MARC RIS BibTeΧ
Download Citation Data
Working Groups
More from nber.
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .


How to Write a Research Paper
- Smodin Editorial Team
- Updated: May 17, 2024
Most students hate writing research papers. The process can often feel long, tedious, and sometimes outright boring. Nevertheless, these assignments are vital to a student’s academic journey. Want to learn how to write a research paper that captures the depth of the subject and maintains the reader’s interest? If so, this guide is for you.
Today, we’ll show you how to assemble a well-organized research paper to help you make the grade. You can transform any topic into a compelling research paper with a thoughtful approach to your research and a persuasive argument.
In this guide, we’ll provide seven simple but practical tips to help demystify the process and guide you on your way. We’ll also explain how AI tools can expedite the research and writing process so you can focus on critical thinking.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear roadmap for tackling these essays. You will also learn how to tackle them quickly and efficiently. With time and dedication, you’ll soon master the art of research paper writing.
Ready to get started?
What Is a Research Paper?
A research paper is a comprehensive essay that gives a detailed analysis, interpretation, or argument based on your own independent research. In higher-level academic settings, it goes beyond a simple summarization and includes a deep inquiry into the topic or topics.
The term “research paper” is a broad term that can be applied to many different forms of academic writing. The goal is to combine your thoughts with the findings from peer-reviewed scholarly literature.
By the time your essay is done, you should have provided your reader with a new perspective or challenged existing findings. This demonstrates your mastery of the subject and contributes to ongoing scholarly debates.
7 Tips for Writing a Research Paper
Often, getting started is the most challenging part of a research paper. While the process can seem daunting, breaking it down into manageable steps can make it easier to manage. The following are seven tips for getting your ideas out of your head and onto the page.
1. Understand Your Assignment
It may sound simple, but the first step in writing a successful research paper is to read the assignment. Sit down, take a few moments of your time, and go through the instructions so you fully understand your assignment.
Misinterpreting the assignment can not only lead to a significant waste of time but also affect your grade. No matter how patient your teacher or professor may be, ignoring basic instructions is often inexcusable.
If you read the instructions and are still confused, ask for clarification before you start writing. If that’s impossible, you can use tools like Smodin’s AI chat to help. Smodin can help highlight critical requirements that you may overlook.
This initial investment ensures that all your future efforts will be focused and efficient. Remember, thinking is just as important as actually writing the essay, and it can also pave the wave for a smoother writing process.
2. Gather Research Materials
Now comes the fun part: doing the research. As you gather research materials, always use credible sources, such as academic journals or peer-reviewed papers. Only use search engines that filter for accredited sources and academic databases so you can ensure your information is reliable.
To optimize your time, you must learn to master the art of skimming. If a source seems relevant and valuable, save it and review it later. The last thing you want to do is waste time on material that won’t make it into the final paper.
To speed up the process even more, consider using Smodin’s AI summarizer . This tool can help summarize large texts, highlighting key information relevant to your topic. By systematically gathering and filing research materials early in the writing process, you build a strong foundation for your thesis.
3. Write Your Thesis
Creating a solid thesis statement is the most important thing you can do to bring structure and focus to your research paper. Your thesis should express the main point of your argument in one or two simple sentences. Remember, when you create your thesis, you’re setting the tone and direction for the entire paper.
Of course, you can’t just pull a winning thesis out of thin air. Start by brainstorming potential thesis ideas based on your preliminary research. And don’t overthink things; sometimes, the most straightforward ideas are often the best.
You want a thesis that is specific enough to be manageable within the scope of your paper but broad enough to allow for a unique discussion. Your thesis should challenge existing expectations and provide the reader with fresh insight into the topic. Use your thesis to hook the reader in the opening paragraph and keep them engaged until the very last word.
4. Write Your Outline
An outline is an often overlooked but essential tool for organizing your thoughts and structuring your paper. Many students skip the outline because it feels like doing double work, but a strong outline will save you work in the long run.
Here’s how to effectively structure your outline.
- Introduction: List your thesis statement and outline the main questions your essay will answer.
- Literature Review: Outline the key literature you plan to discuss and explain how it will relate to your thesis.
- Methodology: Explain the research methods you will use to gather and analyze the information.
- Discussion: Plan how you will interpret the results and their implications for your thesis.
- Conclusion: Summarize the content above to elucidate your thesis fully.
To further streamline this process, consider using Smodin’s Research Writer. This tool offers a feature that allows you to generate and tweak an outline to your liking based on the initial input you provide. You can adjust this outline to fit your research findings better and ensure that your paper remains well-organized and focused.
5. Write a Rough Draft
Once your outline is in place, you can begin the writing process. Remember, when you write a rough draft, it isn’t meant to be perfect. Instead, use it as a working document where you can experiment with and rearrange your arguments and evidence.
Don’t worry too much about grammar, style, or syntax as you write your rough draft. Focus on getting your ideas down on paper and flush out your thesis arguments. You can always refine and rearrange the content the next time around.
Follow the basic structure of your outline but with the freedom to explore different ways of expressing your thoughts. Smodin’s Essay Writer offers a powerful solution for those struggling with starting or structuring their drafts.
After you approve the outline, Smodin can generate an essay based on your initial inputs. This feature can help you quickly create a comprehensive draft, which you can then review and refine. You can even use the power of AI to create multiple rough drafts from which to choose.
6. Add or Subtract Supporting Evidence
Once you have a rough draft, but before you start the final revision, it’s time to do a little cleanup. In this phase, you need to review all your supporting evidence. You want to ensure that there is nothing redundant and that you haven’t overlooked any crucial details.
Many students struggle to make the required word count for an essay and resort to padding their writing with redundant statements. Instead of adding unnecessary content, focus on expanding your analysis to provide deeper insights.
A good essay, regardless of the topic or format, needs to be streamlined. It should convey clear, convincing, relevant information supporting your thesis. If you find some information doesn’t do that, consider tweaking your sources.
Include a variety of sources, including studies, data, and quotes from scholars or other experts. Remember, you’re not just strengthening your argument but demonstrating the depth of your research.
If you want comprehensive feedback on your essay without going to a writing center or pestering your professor, use Smodin. The AI Chat can look at your draft and offer suggestions for improvement.
7. Revise, Cite, and Submit
The final stages of crafting a research paper involve revision, citation, and final review. You must ensure your paper is polished, professionally presented, and plagiarism-free. Of course, integrating Smodin’s AI tools can significantly streamline this process and enhance the quality of your final submission.
Start by using Smodin’s Rewriter tool. This AI-powered feature can help rephrase and refine your draft to improve overall readability. If a specific section of your essay just “doesn’t sound right,” the AI can suggest alternative sentence structures and word choices.
Proper citation is a must for all academic papers. Thankfully, thanks to Smodin’s Research Paper app, this once tedious process is easier than ever. The AI ensures all sources are accurately cited according to the required style guide (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
Plagiarism Checker:
All students need to realize that accidental plagiarism can happen. That’s why using a Plagiarism Checker to scan your essay before you submit it is always useful. Smodin’s Plagiarism Checker can highlight areas of concern so you can adjust accordingly.
Final Submission
After revising, rephrasing, and ensuring all citations are in order, use Smodin’s AI Content Detector to give your paper one last review. This tool can help you analyze your paper’s overall quality and readability so you can make any final tweaks or improvements.
Mastering Research Papers
Mastering the art of the research paper cannot be overstated, whether you’re in high school, college, or postgraduate studies. You can confidently prepare your research paper for submission by leveraging the AI tools listed above.
Research papers help refine your abilities to think critically and write persuasively. The skills you develop here will serve you well beyond the walls of the classroom. Communicating complex ideas clearly and effectively is one of the most powerful tools you can possess.
With the advancements of AI tools like Smodin , writing a research paper has become more accessible than ever before. These technologies streamline the process of organizing, writing, and revising your work. Write with confidence, knowing your best work is yet to come!
Things you buy through our links may earn Vox Media a commission.
- Why Scientific Fraud Is Suddenly Everywhere

Junk science has been forcing a reckoning among scientific and medical researchers for the past year, leading to thousands of retracted papers. Last year, Stanford president Marc Tessier-Lavigne resigned amid reporting that some of his most high-profile work on Alzheimer’s disease was at best inaccurate. (A probe commissioned by the university’s board of trustees later exonerated him of manipulating the data).
But the problems around credible science appear to be getting worse. Last week, scientific publisher Wiley decided to shutter 19 scientific journals after retracting 11,300 sham papers. There is a large-scale industry of so-called “paper mills” that sell fictive research, sometimes written by artificial intelligence, to researchers who then publish it in peer-reviewed journals — which are sometimes edited by people who had been placed by those sham groups. Among the institutions exposing such practices is Retraction Watch, a 14-year-old organization co-founded by journalists Ivan Oransky and Adam Marcus. I spoke with Oransky about why there has been a surge in fake research and whether fraud accusations against the presidents of Harvard and Stanford are actually good for academia.
Give me a sense of how big a problem these paper mills are.
I’ll start by saying that paper mills are not the problem; they are a symptom of the actual problem. Adam Marcus, my co-founder, had broken a really big and frightening story about a painkiller involving scientific fraud , which led to dozens of retractions. That’s what got us interested in that. There were all these retractions, far more than we thought but far fewer than there are now. Now, they’re hiding in plain sight.
That was 2010. Certainly, AI has accelerated things, but we’ve known about paper mills for a long time. Everybody wanted to pretend all these problems didn’t exist. The problems in scientific literature are long-standing, and they’re an incentive problem. And the metrics that people use to measure research feed a business model — a ravenous sort of insatiable business model. Hindsight is always going to be 20/20, but a lot of people actually were predicting what we’re seeing now.
Regarding your comment that paper mills are symptoms of a larger problem, I read this story in Science and was struck by the drive for credentialing — which gets you better jobs, higher pay, and more prestige. In academia, there aren’t enough jobs; are the hurdles to these jobs impossibly high, especially for people who may be smart but are from China or India and may not have entry into an American or European university?
I actually would go one step higher. When you say there aren’t enough jobs, it’s because we’re training so many Ph.D.’s and convincing them all that the only way to remain a scientist is to stay in academia. It’s not, and that hasn’t been true for a long time. So there’s definitely a supply-and-demand problem, and people are going to compete.
You may recall the story about high-school students who were paying to get medical papers published in order to get into college. That’s the sort of level we’re at now. It’s just pervasive. People are looking only at metrics, not at actual papers. We’re so fixated on metrics because they determine funding for a university based on where it is in the rankings. So it comes from there and then it filters down. What do universities then want? Well, they want to attract people who are likely to publish papers. So how do you decide that? “Oh, you’ve already published some papers, great. We’re gonna bring you in.” And then when you’re there, you’ve got to publish even more.
You’re replacing actual findings and science and methodology and the process with what I would argue are incredibly misleading — even false — metrics. Paper mills are industrializing it. This is like the horse versus the steam engine.
So they’re Moneyballing it.
Absolutely. They’ve Moneyballed it with a caveat: Moneyball sort of worked. The paper mills have metricized it, which is not as sexy to say. If you were to isolate one factor, citations matter the most, and if you look at the ranking systems, it’s all right there. The Times Higher Education world-university rankings , U.S. News — look at whichever you want, and somewhere between like 30 percent and 60 percent of those rankings are based on citations. Citations are so easy to game. So people are setting up citation cartels: “Yes, we will get all of our other clients to cite you, and nobody will notice because we’re doing it in this algorithmic, mixed-up way.” Eventually, people do notice, but it’s the insistence on citations as the coin of the realm that all of this comes from.
Your work gets to the heart of researchers’ integrity. Do you feel like you’re a pariah in the scientific community?
I’m a volunteer. Adam is paid a very small amount. We use our funding to pay two reporters and then two people work on our database side. We approach these things journalistically; we don’t actually identify the problems ourselves. It’s very, very rare for us to do that. Even when it may appear that way on a superficial read — we’ve broken some stories recently about clear problems in literature — it’s always because a source showed us the way. Sometimes those sources want to be named, sometimes they don’t.
We’ve been doing this for 14 years. There are various ways to look at what the scientific community thinks of us. We’re publishing 100 posts a year about people committing bad behavior and only getting, on average, one cease-and-desist letter a year. We have never been sued, but we do carried defamation insurance. Our work is cited hundreds of times in the scientific literature. I definitely don’t feel like a pariah. Me saying I’m a pariah would be a little bit like, you know, someone whose alleged cancellation has promoted them to the top of Twitter.
People are unhappy that we have do what we do. If you talk to scientists, the things we’re exposing or others are exposing are well known to them. Because of the structures, the hierarchies, and the power differentials in science, it’s very difficult for them as insiders to blow the whistle. There’s a book out by Carl Elliott about whistleblowers , mostly in the sort of more clinical fields. That’s the vulnerable position. That’s where you end up being a pariah even though you should be considered a hero or heroine.
Are some fields better at policing their own research than others?
Yes. Going back to the origin story of Retraction Watch, Adam broke a story about this guy named Scott Reuben, who came from anesthesiology. We have a leaderboard of the people with the most retractions in the world, and at least three out of the top ten right now are anesthesiologists. That is a much higher percentage than one might expect. Some people may say, “Oh, does anesthesiology have a problem?” No, in fact, anesthesiology has been doing something about this arguably longer than any other field has.
What is it about anesthesiology that makes it so anesthesiologists are more willing to scrutinize the work in their own field?
It had a crisis earlier than others, and it’s small. Journal editors are generally considered pretty august personages, leaders in the field. They got together and it was like a collective action by the journal editors when they realized they had problems. I’m not saying anesthesiologists are better, but they’re a more tight-knit community, which I do think is important. The same thing happened in social psychology and in psychology writ large. There’s a higher number than you would expect of people on leaderboards in that field. So it’s a question of, When did they get there, and how did they react to it? There are fields that haven’t actually gotten there, even though it’s been a while. So maybe there are some sociologists who could tell you better than me why that might be the case.
That wasn’t the reason I expected. I thought you would say something along the lines of, well, it’s life or death and anesthesiologists don’t want to see people dying on the table.
If anything, sometimes when the stakes are higher, fields are more resistant.
There’s a guy named Ben Mol. Ben is an OB/GYN, and he is a force to be reckoned with. Fascinating character. He’s a pit bull, and he has found tons and tons of problems in the OB/GYN literature. I would characterize the leaders in that field now as still a bit more reluctant to engage with these issues than some of the other fields I mentioned.
Can you tell me how you go about authenticating real language from AI, especially in papers that can be hard to parse and are laden with jargon to begin with?
We rely on experts. We’re not really doing that ourselves. You don’t need to be an expert; you just need to know how to use Ctrl+F if you see certain phrases in a paper. And by the way, a lot of journals are perfectly fine with people using chat GPT and other kinds of AI. It’s just whether you disclose it or not. These are cases where they didn’t disclose it.
With the resignation of Stanford’s and Harvard’s presidents, do you worry about the way the general public has been using these tools?
The fact that they’re giving speeding tickets to certain groups of people doesn’t mean we’re not all speeding. It means they’re getting targeted in, I would argue, an unfair way. We’re in a great reckoning with Harvard’s Claudine Gay being the key example. Former Stanford president Marc Tessier-Lavigne is not an example of that. The targeting is a concern. And clearly, there are false positives. The flip side of this is that AI is being used to find these problems.
This interview has been edited for length and clarity. The story was updated to include that a probe found that Tessier-Lavigne didn’t manipulate data.
- just asking questions
Most Viewed Stories
- ‘How Many Politicians Curl Up With Their Wife on the Floor?’
- Rudy Giuliani Forgets to Mute His Microphone While Going to the Bathroom
- Deflation Never Happens, Except Right Now
- Why Does the New Kate Middleton Portrait Look Nothing Like Her?
- Chess Brat: Hans Niemann, One Year After the Cheating Scandal
- Who’s the Trump VP Pick? Latest Odds for Every Shortlist Candidate.
Editor’s Picks

Most Popular
- ‘How Many Politicians Curl Up With Their Wife on the Floor?’ By Dan Merica
- Rudy Giuliani Forgets to Mute His Microphone While Going to the Bathroom By Matt Stieb
- Why Scientific Fraud Is Suddenly Everywhere By Kevin T. Dugan
- Deflation Never Happens, Except Right Now By Kevin T. Dugan
- Why Does the New Kate Middleton Portrait Look Nothing Like Her? By Margaret Hartmann
- Chess Brat: Hans Niemann, One Year After the Cheating Scandal By Jen Wieczner
- Who’s the Trump VP Pick? Latest Odds for Every Shortlist Candidate. By Margaret Hartmann

What is your email?
This email will be used to sign into all New York sites. By submitting your email, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy and to receive email correspondence from us.
Sign In To Continue Reading
Create your free account.
Password must be at least 8 characters and contain:
- Lower case letters (a-z)
- Upper case letters (A-Z)
- Numbers (0-9)
- Special Characters (!@#$%^&*)
As part of your account, you’ll receive occasional updates and offers from New York , which you can opt out of anytime.
Physical Review Research
- Collections
- Editorial Team
- Accepted Paper
Limited data on infectious disease distribution exposes ambiguity in epidemic modeling choices
Phys. rev. research, laura di domenico, eugenio valdano, and vittoria colizza.
Traditional disease transmission models assume that the infectious period is exponentially distributed with a recovery rate fixed in time and across individuals. This assumption provides analytical and computational advantages, however it is often unrealistic when compared to empirical data. Current efforts in modeling non-exponentially distributed infectious periods are either limited to special cases or lead to unsolvable models. Also, the link between empirical data (the infectious period distribution) and the modeling needs (the definition of the corresponding recovery rates) lacks a clear understanding. Here we introduce a mapping of an arbitrary distribution of infectious periods into a distribution of recovery rates. Under the markovian assumption to ensure analytical tractability, we show that the same infectious period distribution at the population level can be reproduced by two modeling schemes –~that we call host-based and population-based~– depending on the individual response to the infection, and aggregated empirical data cannot easily discriminate the correct scheme. Besides being conceptually different, the two schemes also lead to different epidemic trajectories. Although sharing the same behavior close to the disease-free equilibrium, the host-based scheme deviates from the expected epidemic when reaching the endemic equilibrium of an SIS (susceptible-infectious-susceptible) transmission model, while the population-based scheme turns out to be equivalent to assuming a homogeneous recovery rate. We show this through analytical computations and stochastic epidemic simulations on a contact network, using both generative network models and empirical contact data. It is therefore possible to reproduce heterogeneous infectious periods in network-based transmission models, however the resulting prevalence is sensitive to the modeling choice for the interpretation of the empirically collected data on the length of the infectious period. In absence of higher resolution data, studies should acknowledge such deviations in the epidemic predictions.
Sign up to receive regular email alerts from Physical Review Research
- Forgot your username/password?
- Create an account
Article Lookup
Paste a citation or doi, enter a citation.
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Cryptography and Security
Title: gpt-4 jailbreaks itself with near-perfect success using self-explanation.
Abstract: Research on jailbreaking has been valuable for testing and understanding the safety and security issues of large language models (LLMs). In this paper, we introduce Iterative Refinement Induced Self-Jailbreak (IRIS), a novel approach that leverages the reflective capabilities of LLMs for jailbreaking with only black-box access. Unlike previous methods, IRIS simplifies the jailbreaking process by using a single model as both the attacker and target. This method first iteratively refines adversarial prompts through self-explanation, which is crucial for ensuring that even well-aligned LLMs obey adversarial instructions. IRIS then rates and enhances the output given the refined prompt to increase its harmfulness. We find IRIS achieves jailbreak success rates of 98% on GPT-4 and 92% on GPT-4 Turbo in under 7 queries. It significantly outperforms prior approaches in automatic, black-box and interpretable jailbreaking, while requiring substantially fewer queries, thereby establishing a new standard for interpretable jailbreaking methods.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

COMMENTS
The free Scribbr Citation Generator is the quickest way to cite sources in these styles. Simply enter the URL, DOI, or title, and we'll generate an accurate, correctly formatted citation. ... At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays, research papers, and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
The paper's title follows, then the title of the journal in italics. You also include the journal volume, issue number, and page numbers. As with MLA citations, include a DOI if you found the research paper online. Here is an example of a published research paper cited in APA format: Writer, M. (2020).
Place your cursor where you want to insert the citation. Figure 3. Cursor placed for citation insertion. Select the References tab in the ribbon (see figure 1). Select the Insert Citation button in the Citations & Bibliography group. Figure 4. Insert Citation button. Select Add New Source from the drop-down menu.
In this situation the original author and date should be stated first followed by 'as cited in' followed by the author and date of the secondary source. For example: Lorde (1980) as cited in Mitchell (2017) Or (Lorde, 1980, as cited in Mitchell, 2017) Back to top. 3. How to Cite Different Source Types.
If you want to cite a special issue of a journal rather than a regular article, the name (s) of the editor (s) and the title of the issue appear in place of the author's name and article title: APA format. Last name, Initials. (Ed. or Eds.). ( Year ). Title of issue [Special issue]. Journal Name, Volume ( Issue ).
The Chicago/Turabian style of citing sources is generally used when citing sources for humanities papers, and is best known for its requirement that writers place bibliographic citations at the bottom of a page (in Chicago-format footnotes) or at the end of a paper (endnotes). The Turabian and Chicago citation styles are almost identical, but ...
Here are some specifics of the APA citation format for a journal article: Write the title of the article in the sentence case (capitalize only the first word and proper nouns). Write the title of the journal in the title case and mention the volume number after adding a comma. Don't italicize the comma between the journal title and volume ...
Examples of in-text citations. You need to include an in-text citation wherever you quote or paraphrase from a source. An in-text citation consists of the last name of the author(s), the year of publication, and a page number if relevant. There are a number of ways of incorporating in-text citations into your work - some examples are provided ...
When you cite a source with up to three authors, cite all authors' names. For four or more authors, list only the first name, followed by ' et al. ': Number of authors. In-text citation example. 1 author. (Davis, 2019) 2 authors. (Davis and Barrett, 2019) 3 authors.
In this step-by-step guide, we will explore the importance of citations, different citation styles such as. APA ,. MLA , and. Chicago , and provide practical examples to help you master the art of citing research papers effectively. Whether you are a student, researcher, or writer, understanding how to cite sources correctly is a valuable skill ...
The majority of the citations in a research paper should be to scholarly [a.k.a., academic; peer-reviewed] studies that rely on an objective and logical analysis of the research problem based on empirical evidence that reliably supports your arguments. However, any type of source can be considered valid if it brings relevant understanding and ...
1. Name the author and the publication date in-text before a quote. To simplify the in-text citation, place the last name of the author in the text to introduce the quote and then the publication date for the text in parentheses. You can then leave the author's name and the publication date out of the quote itself. [1]
In-text citations are quick references to your sources. In Harvard referencing, you use the author's surname and the date of publication in brackets. Up to three authors are included in a Harvard in-text citation. If the source has more than three authors, include the first author followed by ' et al. '.
Click at the end of the sentence or phrase that you want to cite. On the Reference tab, click Insert Citation and then do one of the following: To add the source information, click Add New Source, and then, in the Create Source dialog box, click the arrow next to Type of Source, and select the type of source you want to use (for example, a book ...
Research paper: In-text citation: Use superscript numbers to cite sources in the text, e.g., "Previous research has shown that^1,2,3…". Reference list citation: Format: Author (s). Title of paper. In: Editor (s). Title of the conference proceedings. Place of publication: Publisher; Year of publication. Page range.
When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
An in-text citation can be included in one of two ways as shown below: 1. Put all the citation information at the end of the sentence: 2. Include author name as part of the sentence (if author name unavailable, include title of work): Each source cited in-text must also be listed on your Works Cited page. RefWorks includes a citation builder ...
For each author-date citation in the text, there must be a corresponding entry in the reference list under the same name and date. An author-date citation in running text or at the end of a block quotation consists of the last (family) name of the author, followed by the year of publication of the work in question.
There are two main kinds of titles. Firstly, titles can be the name of the standalone work like books and research papers. In this case, the title of the work should appear in the title element of the reference. Secondly, they can be a part of a bigger work, such as edited chapters, podcast episodes, and even songs.
All titles used in the reference section of a Chicago-style paper use title case. Here are the general guidelines of Chicago style citations: Book: First Name Last Name, Title of Book. State of Publication, Publisher, Year of Publication. Example: Simon Thompson, The Year of the Wolf. Texas, Preston and Buchanan, 1982.
Notice that the in-text citation takes the same form whether the source cited is a book or an article, with 'Samuel & Watson' referring here to a monograph and 'Wilson & Bond' to a journal article. 2. Every source cited in the text of an academic or scientific research paper using APA style should also be included in a list that is ...
Separate the names of multiple authors with commas. Before the last author's name, you should also insert an ampersand (&). A reference entry may contain up to 20 authors. If there are more than 20, list the first 19 authors, followed by an ellipsis (. . .) and the last author's name. Andreff, W., & Staudohar, P. D.
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation. Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
Enter the URL, DOI, ISBN, title, or other unique source information into the citation generator to find your source. Click the 'Cite' button on the citation machine. Copy your new reference from the citation generator into your bibliography or works cited list. Repeat for each source that has contributed to your work.
Chinese Science and Home Bias in Citations. Shumin Qiu, Claudia Steinwender & Pierre Azoulay. Working Paper 32468. DOI 10.3386/w32468. Issue Date May 2024. We investigate the phenomenon of home bias in scientific citations, where researchers disproportionately cite work from their own country. We develop a benchmark for expected citations based ...
You can adjust this outline to fit your research findings better and ensure that your paper remains well-organized and focused. 5. Write a Rough Draft. Once your outline is in place, you can begin the writing process. Remember, when you write a rough draft, it isn't meant to be perfect.
Retraction Watch co-founder Ivan Oransky talks about how academic metrics got Moneyballed, causing many research journals to fold.
Accepted Paper; Limited data on infectious disease distribution exposes ambiguity in epidemic modeling choices Phys. Rev. Research Laura Di Domenico, Eugenio Valdano, and Vittoria Colizza
Research on jailbreaking has been valuable for testing and understanding the safety and security issues of large language models (LLMs). In this paper, we introduce Iterative Refinement Induced Self-Jailbreak (IRIS), a novel approach that leverages the reflective capabilities of LLMs for jailbreaking with only black-box access. Unlike previous methods, IRIS simplifies the jailbreaking process ...