How to Develop a Successful Marketing Mix Strategy [+ Templates]
Updated: July 28, 2021
Published: July 02, 2020
One of the first things you're taught in your Introduction to Marketing class is that marketing can be best explained using the marketing mix – also known as the four Ps.

They are – and say 'em with me because if you took that class, you know these four words by heart:
![market mix in business plan → Free Resource: 4 Marketing Mix Templates [Access Now]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/c79f682e-61ec-4234-80b3-0b1f3833ee30.png)
However, once you're in your first marketing internship or job, you learn that marketing entails so much more than can be simplified in a four-section marketing mix matrix.
Still, there's an undeniable benefit of marketing teams organizing their work into the marketing mix framework.
When you stray too far away from the four P's, it can be easy to lose focus on your purpose as a marketer.
Marketing truly is about teams and individuals working together to promote a product in the right place at the right price point. Efforts beyond this scope are essential, but they do all stem off of this foundation of the marketing mix.
Here, we're going to dive into what a marketing mix is and how to develop a successful marketing mix strategy for your own company.

What is a marketing mix?
The marketing mix refers to the actions a company takes to market its product(s) and/or service(s). Typically, it acts as a framework for breaking down the four key components of marketing — product, price, place, and promotion.
The marketing mix helps companies organize their marketing initiatives by task and department for more process-driven and impactful marketing campaigns.
This framework has roots dating back to the 1940s and has been evolving ever since. While some elements have been added or tweaked over the years – most notably for the modern digital age – the core elements of the marketing mix (i.e. the four P's) have remained consistent for decades.
Featured Resource: Marketing Mix Templates

Need a way to visualize your marketing mix to share it with your employees or investors? Use these four marketing mix templates to organize your initiatives and activities by the right section. Click here to download them now .
Marketing Mix Elements
When perfected and synchronized, the core elements of a marketing mix provide a well-rounded approach to marketing strategy.
Product refers to what your business is selling – product(s), service(s), or both. The bulk of the work in this element is typically done by product marketers or managers.
Nailing the product element of the marketing mix means doing extensive research and development, understanding the need for the product, developing a product launch plan and timeline, and educating customers and employees – especially salespeople – on the product's purpose.
Price refers to the price point at which you'll sell your product(s)/service(s) to consumers. Arriving on this dollar amount requires consideration of multiple pricing strategies, analysis of similarly priced products in your market, and insights from consumers through surveys and focus groups.
Price speaks to positioning in the market, the speed at which you want to penetrate your market, and your company's revenue goals and profit margin.
In the marketing mix, place refers to where your product or service will be sold. For tangible products, this will include physical locations such as your own store, or a retailer where your product will be resold.
It can also include the other methods where your products can be purchased, like online or over the phone.
4. Promotion
Promotional activities are those that make your target market aware and excited about what you're selling.
While this does include paid initiatives like commercials and advertising, promotion also entails organic initiatives like word-of-mouth marketing, content marketing, and public relations.
Other Elements
While the marketing mix can often be simplified down to the 4 P's, the expansion of the scope of marketing in recent years has resulted in more P's added to the list.
For example, Smart Insights includes the following elements in its marketing mix definition:
- Process , or the large internal initiatives taken to support a product launch, such as including salespeople in goal setting.
- People , which can refer to your buyer, market, and target audience, or your internal team responsible for a launch.
- Partners , or who you'll be working with outside of your company, such as distributors or co-marketing partners.
Some of the other P's can include:
- Payment , or how transactions will be held and processed.
- Physical evidence, or anything tangible pertaining to your product or service, like any materials needed to complete your service or deliver your product.
- Packaging , or anything pertaining to the physicality of your product, like how it looks or how it's packaged.
These other marketing mix elements should be utilized as you see fit for your projects. However, every good marketing mix should rely on a thorough exploration of those first 4 Ps.
Marketing Mix Templates
Fill out the form to get your templates, marketing mix examples from real businesses.
Fintech companies are everywhere, but how many of them focus on organic and non-GMO agriculture?
As sustainable agriculture becomes more top of mind, brands like Mercaris help support agriculture companies looking to stay ahead in the market. Beyond delivering a service, the company identified a niche and launched a business with few direct competitors.
They offer a monthly subscription-based service that arms agricultural companies with the market intelligence needed to compete in the space. This includes detailed reports on food production, commodity prices, and market shifts.
Not long after Airbnb launched, users filed complaints of racism from their hosts and expressed reluctance to use the platform's services. The company implemented measures to appease these concerns. However, it brought attention to an important issue.
It's this uncertainty that allowed Noirbnb to enter the market. The brand tapped into people of color's desire to feel safe and welcomed in their temporary home while traveling – then, they used it as their unique selling position (USP).
The brand even plays on Airbnb's name – which is now a household one – to indicate that they offer a similar service that's been adapted to cater to travelers of color.
Warby Parker
This online retailer of prescription eyeglasses and sunglasses is known for its stylish yet affordable glasses. Warby Parker 's pricing, which starts at $95, undercuts many of its competitors, making it a popular go-to for consumers.
The brand's pricing strategy is based on public perception. In interviews, the founders revealed that originally, they were going to price their frames as low as $45. However, after considering how low prices for items like glasses can be perceived as low quality, they doubled the price to settle at a number that was still competitive.
A brand's pricing strategy can have an important role in how it's perceived in the market. So, it's important to consider what that perception is and if it's the one you want to put out there.
When Canva entered the market, it was every small business owner's dream. You could design any marketing material you wanted for FREE, what more could you ask for?
Eventually, the brand introduced premium versions of its platform. Catering to businesses ranging from small to enterprise-level, they added features like high-quality stock visuals, social media publishing tools, marketing campaign management, and large cloud storage.
Hu , short for "Get Back to Human," is a dessert company that specializes in making organic, paleo chocolate bars free of the junk ingredients we find in big-name products.
The brand has made its products available from multiple major retailers, including Walmart, Target, and Whole Foods. They also have a virtual storefront on Amazon. If stock ever runs out there, you can always purchase their products through their website.
Hu has made its product accessible through multiple channels, maximizing its earning potential while expanding its brand awareness.
The Lip Bar
Vegan beauty brand The Lip Bar leverages influencers and celebrities to promote its products and increase its brand awareness. Recently, the brand partnered with beauty influencer Raye Boyce to announce its expansion into Walmart stores and its nine latest products.
The Lip Bar places women of color at the center of its products and collaborating with a Black influencer known for her love of lipsticks is in perfect alignment with the brand's identity.
Beyond a robust social media presence, the company also has a blog on its website with content that appeals to audiences across the buyer's journey.
Avant-Garde Vegan
Some brands launch a product then promote, while others promote then launch.
Avant-Garde Vegan , an online brand created by UK-based chef Gaz Oakley, grew his business on social media – namely YouTube. Oakley gained popularity posting recipes for healthy, vegan dishes and soon became a go-to resource for new and established vegan consumers.
Eventually, Oakley released his first product, a cookbook. Now the brand sells both cookbooks as well as merchandise.
The reason why this strategy works particularly well is that it focuses on adding value instead of selling. Oakley gained his audience's trust and loyalty through consistent and quality posts on social media.
Once he introduced a product, many of his followers were ready to make a purchase. It's a long-term strategy that can have a big payoff if executed well.
How to Develop a Marketing Mix Strategy
Because the marketing mix incorporates elements from across your department – and even your company – it's imperative to establish a marketing mix strategy for each product you launch, or for your company as a whole. For a fully fleshed-out marketing mix, follow these steps.
1. Engage in market research and product development.
The success of your marketing work is first and foremost contingent on your product. Make sure it's well developed and your team can speak to its benefits and the story behind it.
Best practices in this step include:
- Engaging in market research to understand your buyers' needs.
- Speaking to your current customers to uncover their pain points and see which needs to address in your current product or service line.
- Monitoring industry trends to identify a potential demand in your market.
- Examining the competition.
- Collaborating with your product team during product development to ensure it meets your buyer personas' needs.
- Having your product tested by current customers to see how they're using the product or service and if it's actually solving for their problems.
Taking these actions ensures you're making every effort to understand and solve for your customer, providing a solid foundation for your product to launch successfully.
Featured Tool: Market Research Kit . To make your R&D more impactful, use these free market research templates so you can better understand your customers and competitors.
2. Determine your pricing model.
A lot goes into choosing a price point – so much so that we wrote an entire guide to pricing strategies .
Luckily, you'll be able to refer to much of the work done in the previous section. Thanks to your understanding of your market through research, you'll have answered most of the necessary questions in this section. You'll also need to take your costs into account so you can maximize unit sales and profit.
During this stage, make sure you do the following.
- Speak to customers (or refer to previously completed market research) to determine the ideal selling price.
- Work with the product team to ensure the product can be developed in a cost-effective manner that would ensure profitability at your target price point.
- Meet with financial experts to determine aggressive yet realistic sales forecasts to contribute to the company's bottom line.
- Collaborate with your sales team to determine discounting strategies.
- Determine how you'll adjust price and revenue forecasts when selling through resellers.
Lastly, don't forget to factor in the perceived value by the customer. Even if your product or service doesn't cost a significant amount to make, you'll be able to mark up your product more if you face little competition and provide an irreplaceable benefit to your customers.
Featured Tool: Pricing Strategy Calculator . If you need help selecting your pricing model, use this template to compare different pricing strategies and see which will yield your company the most profit and revenue based on your forecasts.
3. Choose your distribution channels.
The "place" part of the marketing mix answers where your product will be sold. Keep in mind, this can be any combination of your store, a distributor's store, or online. You'll want to address the following points before moving onto the promotion stage:
- Determine if your product will fare best in your physical location, a store of another retailer, on your website, on another company's website, or some combination of these locations.
- Think about geographic location – make sure your supply meets regional demand, and plan for whether or not what you're selling will be available in a certain city, a state, the country, or worldwide.
- Come to an agreement with retailers and resellers on margins, markups, and manufacturer suggested retail prices (MSRP).
- Figure out how many salespeople will be needed to ensure you meet your goals.
- Set goals for retail, third-party sellers, since you may be sharing shelf space or search results with a competitor or two.
4. Select your promotion tactics.
Finally, it's time to promote your product. While this is probably the element most associated with marketing, it's crucial that this element be completed last, because you need the foundation of product, price, and place before determining promotion tactics.
Think about it – shouldn't you know what you're promoting, why you're promoting it, and where it's available before actually promoting it? It's tempting to jump right to this step, but your promotion will be much better off if it's done after everything else in the marketing mix.
Once you do have that understanding, consider the following promotional channels and choose the one(s) that makes the most sense for your product, its buyers, and its price point:
- Content marketing efforts, such as blogging, content creation, and building a website.
- Public relations and working with affiliates and/or influencers.
- Social media marketing – both organic and paid – on channels such as LinkedIn, Facebook, and Instagram.
- Search engine ads on sites like Google and Bing.
- Ads to air on video streaming sites like YouTube, or on TV.
- Event marketing, including attending industry events or hosting your own event.
- Customer marketing and utilizing referrals.
- And more – There are countless promotional ideas you can use to spread the word on your product, service, or business.
Featured Tool: Marketing Plan Template . If your promotional tactics are multi-faceted enough, consider documenting your plans in this customizable template.
Every company's marketing mix is different, placing emphasis on certain factors over others.
Some businesses use their marketing mix for a single product, while others adopt a company-wide marketing mix. However, good marketing mixes should tie in all the elements without neglecting one.
All elements of the marketing mix are important, so don't be quick to overlook any of them, and find ways for different elements of the mix to overlap and share goals.
With so many activities happening to support a single initiative, it's helpful to organize everything in a single template for easy reference. Here are a few examples of marketing mix templates your marketing department can use, in addition to when they might make sense to reference.
1. Simple Marketing Mix Template
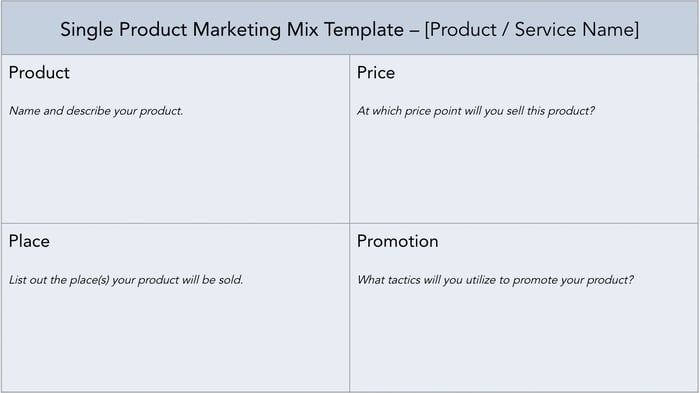
Download this Template
This template is a great starter for organizing a marketing mix. It's ideal for one product and for the marketing mix's maker to get an understanding of all the elements involved in the marketing of a product.
2. Company Marketing Mix Template
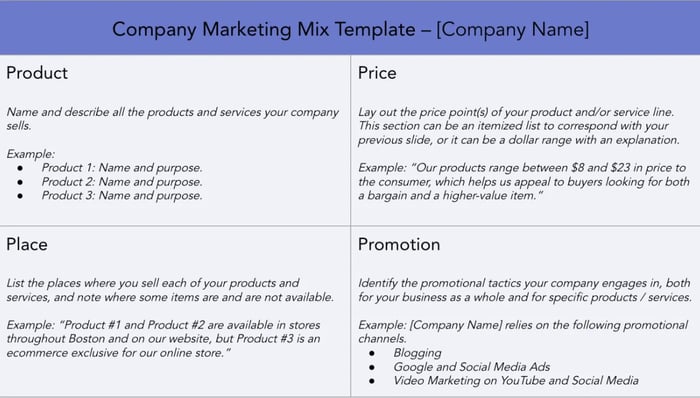
For a marketing mix that applies company-wide, this template is a perfect fit. You can outline the initiatives that apply to most or all of the products and/or services in your suite.
3. Structured Marketing Mix Template
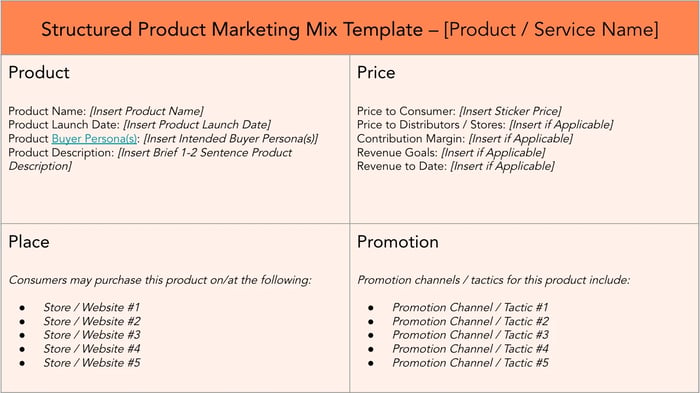
For when you need to get right to the point with a more organized, actionable visualization, use this structured, bulleted template for quick reference and clarification.
4. Production Marketing Mix Template
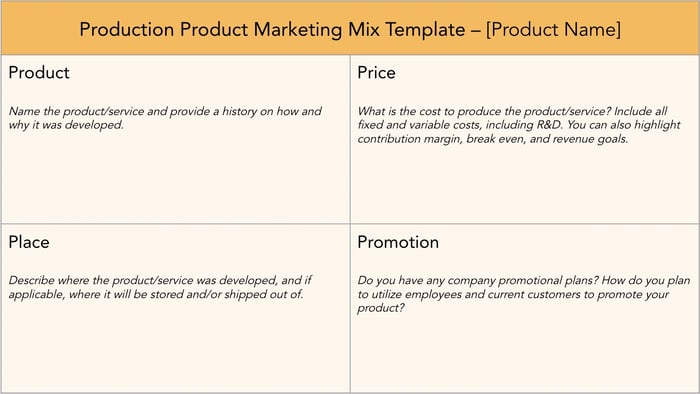
Finally, a production marketing mix template is best utilized for internal reference. This template answers questions on the go-to-market efforts for products and services that you're selling.
Mix It All Together
Whether you're a student just learning to understand everything that marketing entails or a CMO hoping to clearly convey the work that your team is doing to your fellow employees, the marketing mix framework is an essential tool to help you get the job done.
Don't forget – if you need to organize your marketing initiatives into a central location, try using HubSpot's Marketing Mix Templates to document your activities in one place.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

Marketing Agencies We Admired in 2023
![market mix in business plan Marketing Budget: How Much Should Your Team Spend in 2024? [By Industry]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how%20to%20spend%20your%20marketing%20budget_featured.webp)
Marketing Budget: How Much Should Your Team Spend in 2024? [By Industry]

12 Best Free (& Private) Email Accounts & Service Providers for 2024
![market mix in business plan How to Delete Your Instagram [Easy Guide]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/delete-instagram.png)
How to Delete Your Instagram [Easy Guide]

The Best Free Business Budget Templates
![market mix in business plan Millennials vs. Gen Z: Why Marketers Need to Know the Difference [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/millenials%20vs%20gen%20z%20what%20marketers%20need%20to%20know%20when%20trying%20to%20reach%20each%20generation.jpg)
Millennials vs. Gen Z: Why Marketers Need to Know the Difference [New Data]
![market mix in business plan How Marketing Leaders are Navigating Recession [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how%20marketing%20leaders%20are%20navigating%20recession.webp)
How Marketing Leaders are Navigating Recession [New Data]

The 11 Best Ways to Send Large Files
![market mix in business plan 3 Ways Marketers are Already Navigating Potential Recession [Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-marketers-are-navigating-recession.jpg)
3 Ways Marketers are Already Navigating Potential Recession [Data]
![market mix in business plan How to Edit a PDF [Easy Guide]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/280_How-to-Edit-PDF.png)
How to Edit a PDF [Easy Guide]
Organize your product, price, place, and promotion initiatives in a simple, single template.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

What Is Marketing Mix And Why It Matters In Business
The marketing mix is a term to describe the multi-faceted approach to a complete and effective marketing plan. Traditionally, this plan included the four Ps of marketing : price, product, promotion, and place. But the exact makeup of a marketing mix has undergone various changes in response to new technologies and ways of thinking. Additions to the four Ps include physical evidence, people, process, and even politics.
Table of Contents
Understanding marketing mix
While many understand marketing as “putting the right product in the right place, at the right price, at the right time,” few know how to implement this in practice.
Identifying the individual elements of a marketing mix and then creating robust plans for each allows a business to market accordingly.
It also allows a business to market to its strengths while minimizing or eliminating its weaknesses.
At the very least, a marketing mix should include the four Ps of marketing :
This can include a tangible good or an intangible service.
Businesses must understand their product or service in the context of the problem that it aims to solve.
If the product does not seem to address any problem, then the potential profitability of the product should be re-analyzed.
The target audience, or those who will buy the product, must also be identified.
Price has a direct impact on how well a product will sell and is linked to the perceived value of the product in the mind of a consumer.
In other words, price is not related to what the business thinks the product is worth.
Thus, it is important to know what the consumer values and price it accordingly.
To a lesser extent, price may also be influenced by rival products and value chain costs.
Promotion includes all marketing communication strategies, such as advertising, sales promotions, and public relations.
Irrespective of the channel, communication must be a good fit for the product, price, and target audience.
Place describes the physical location in which a customer can use, access, or purchase the end product.
Determining where buyers look for a product or service may seem simplistic, but it has implications for marketing and product development.
For example, place determines which distribution methods are most suitable.
It also dictates whether a product needs a sales team or whether it should be taken to a trade fair to be sampled and advertised.
Other elements of an effective marketing mix
Conventional marketing mixes are product-centric, but services and other intangible goods are also commonplace for many businesses.
People, process, and physical evidence are three more Ps that these businesses should implement.
People refers to the staff who are directly and indirectly involved in marketing the brand.
Employing the best people for the job is crucial since people shape the direction of the brand and therefore the goals and values of the business.
Process covers the interface between business and consumer, otherwise known as customer service.
Process is important because customers often give feedback on their service, which enables a business to improve its systems across the board.
Effective processes should make purchasing pleasing and simple while simultaneously increasing brand equity.
- Physical evidence
Physical evidence describes anything that consumers see when interacting with a brand. Physical evidence can take the form of packaging, branding, and even the physical layout and design of retail spaces and shop fronts.
Physical evidence also extends to how staff dress and interact with customers and the possible impact that this has on sales.
Principles of the Marketing Mix:
- Alignment: The elements of the marketing mix should be aligned with the overall marketing and business objectives.
- Customer-Centric: The marketing mix should be designed with a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences.
- Adaptation: It may need to be adjusted over time to respond to changes in the market, competition, and consumer behavior.
- Integration: The elements of the marketing mix should work harmoniously to create a consistent and compelling marketing strategy .
Advantages of the Marketing Mix:
- Strategic Planning: It provides a structured framework for developing marketing strategies.
- Customization: The marketing mix allows businesses to tailor their approach to specific target markets.
- Market Expansion: It facilitates entry into new markets and the launch of new products or services.
- Competitive Advantage: Effective use of the marketing mix can create a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Challenges of the Marketing Mix:
- Complexity: Balancing and optimizing the four elements can be complex, especially in dynamic markets.
- Changing Consumer Behavior: Consumer preferences and behaviors may evolve, requiring adjustments to the marketing mix.
- Resource Allocation: Effective use of the marketing mix often involves resource allocation decisions.
- Global Considerations: In the case of international markets, cultural and regulatory differences may impact the marketing mix.
When to Use the Marketing Mix:
- Product Development: During product development, the marketing mix helps define the product’s features and positioning.
- Market Entry: When entering new markets or launching new products, it guides market entry strategies.
- Competitive Response: In response to changing competitive dynamics, businesses can adjust their marketing mix to maintain or gain market share.
- Strategic Planning: The marketing mix is a central component of strategic planning for businesses of all sizes.
What to Expect from Using the Marketing Mix:
- Market Responsiveness: Effective use of the marketing mix can lead to improved responsiveness to market demands.
- Customer Engagement: It enhances customer engagement by delivering products and services that meet their needs.
- Revenue Growth: A well-implemented marketing mix can contribute to revenue growth and market expansion.
- Brand Building: The marketing mix plays a significant role in building and strengthening brand identity.
Long-Term Impact of the Marketing Mix:
- Sustainable Growth: Businesses that consistently adapt and optimize their marketing mix are better positioned for sustainable growth.
- Competitive Edge: A strong marketing mix can provide a sustained competitive advantage.
- Brand Equity: Over time, the marketing mix contributes to the development of brand equity and customer loyalty.
- Innovation Culture: A focus on the marketing mix fosters a culture of innovation in product development and marketing strategies.
Key highlights
- Marketing mix refers to a suite of actions that a business uses to promote its products or services in the market.
- Marketing mix should as a minimum have strategies devised for product, price, promotion, and place.
- Service-oriented businesses should adopt a broader marketing mix, otherwise known as the seven Ps of marketing.
What is marketing mix modeling and why it matters to understand how to balance your marketing mix?
Marketing mix modeling (MMM) is a statistical method for evaluating marketing campaign effectiveness.
The method quantifies the impact of multiple marketing inputs on market share or sales which then determines how much to spend on each.
Understanding marketing mix modeling
Marketing mix modeling uses statistical analysis to analyze the past and future impact of different marketing tactics on sales or profit.
The approach is based on the popular 4 Ps marketing mix theory.
In essence, the purpose of MMM is to measure the past performance of a campaign and improve future marketing return on investment (MROI).
Conclusions drawn from the statistical analysis then determine how resources can be better allocated across various tactics, products, segments, and markets.
Marketing mix modeling utilizes the multi-linear regression (MLR) statistical technique to assess the relationship between dependent and independent variables.
The dependent variable is normally market share or sales, while the independent variable could be price, distribution, or ad spend for different channels.
The four phases of marketing mix modeling
Each MMM project has four distinct phases that we have explained in detail below.
Phase 1: Data collection and integrity
In the first phase, the business collects data on the products to be analyzed, the desired timeframe, and the markets to be modeled.
The sales performance metric should also be quantified at this point.
Will it be volume, units, sales, or some other metric?
Brand margin rates and marketing spend should also be determined so that the MROI can be calculated later on.
MMM also requires the business to use data that will yield the best results. In other words:
- Has the best available data been incorporated?
- Is the data consistent over the entire life cycle?
- Are there multiple years of data to account for factors such as seasonality?
Before moving to the next phase, key project stakeholders should also hold a review session to ensure data integrity.
In some cases, data will have to be aggregated or cleansed before moving forward.
Phase 2: Modeling
In the second phase, brand managers must collaborate with their internal analytics staff to discuss statistical details, specifications, and methods.
We noted earlier that a multi-linear regression is commonly used, but other methods such as time-series regression are also used.
Ultimately, the method chosen will depend on the organization’s goals, data quality, and in some cases the entity providing the statistical analysis on behalf of the client.
Phase 3: Model-based business measures
Once the statistical analysis has been performed, it will produce output data that measures how each tactic impacts sales.
The data must also answer or address the overarching purpose of the project, with many organizations choosing to frame project purpose as questions such as:
- What is the best marketing plan to maximize future net profits with respect to the current and future budget?
- For a particular demographic, what are the most efficient or effective marketing tactics?
- What is the impact of advertising on consumer price sensitivity?
- Which competitor advertising campaign is having the most negative impact on sales?
Most MMM projects will also feature a pie chart showing the decomposition of sales where sales volume is broken down according to each tactic.
These charts separate two types of tactics:
- Core tactics – or those not controlled by the marketing team such as seasonality, distribution, weather, and competitive trade. Core tactics can also encompass the sales that would occur in the total absence of any promotional effort.
- Incremental tactics – or those that are controlled by the marketing team.
Once a decomposition of sales has been performed, the organization can calculate three important metrics:
- Effectiveness – which is determined by dividing the number of incremental sales by each marketing effort.
- Efficiency – where incremental sales are divided by the expenditure of each tactic. This is normally the total media spend, and
- Marketing return on investment – the MROI can be calculated by dividing the gross profit of each tactic by its total spend.
Phase 4: Optimization and simulation
In the final phase, MMM outputs are transformed into inputs for future marketing campaigns.
Simulations help the organization model the impact of a new tactic before it is used in a real-world scenario.
They also enable teams to determine the best combination of tactics that will enable them to achieve campaign goals.
Marketing mix modeling examples
In the past few decades, marketing mix modeling has been adopted by several Fortune 500 companies such as Kraft, The Coca-Cola Company, Pepsi, AT&T, and Proctor & Gamble.
While there has been particular interest from consumer packaged goods (CPG) companies, others now use MMM because of the increased prevalence of companies providing these specialist services.
Indeed, marketing mix modeling is popular in the retail and pharmaceutical industries because firms like Nielsen can provide syndicated data on stores, product categories, geographic markets, and distribution channels .
What’s more, the increased availability of time-series data has also seen MMM incorporated into industries such as telecommunications, financial services, hospitality, and automotive.
However, in these industries, it is acknowledged that marketing mix modeling is still in its infancy and will require further standardization to be effective.
MMM case study for Facebook advertisers
Facebook (now Meta) is one of several modern platforms that offer a family of services and apps that have dynamic and nuanced advertising needs.
Since consumer preferences are in a constant state of flux, this makes it difficult for brands to assess the impact of Facebook advertising compared to traditional channels such as television and print.
A standard marketing mix modeling project assesses data from two or three years. But for online social platforms, data over this time span may become outdated.
To counteract this tendency, Facebook recommends advertisers analyze data over a 6 to 12-month period.
They should then adjust their methods to account for the statistical power that is sacrificed when analyzing a shorter time frame.
Professional services company Accenture ran multiple MMM analyses in 2021 for disruptor brands requiring a reliable and cost-effective system to optimize their promotional efforts and produce actionable and granular results.
How was this achieved?
Tailored data was first sourced from Facebook, Instagram, and Audience Network, which considered standard engagement metrics such as clicks but also paid impressions.
Data were then integrated with machine learning techniques such as the Bayesian belief network to analyze potential synergies between multiple channels.
This involved analyzing the relationship between six independent variables (video, display, Facebook app, organic search, Instagram, and paid search) and their dependent online and offline channels.
The results of the analysis showed how various marketing channels could drive impacts across other channels. A few of the more significant results are listed below:
- Drivers of paid search – paid search (78%), offline drivers (10.9%), and organic search (5.5%).
- Drivers of Facebook app – Facebook app (87.6%), offline drivers (7.4%), and display (4.0%).
- Drivers of Instagram – Instagram direct (87.9%), video (6.0%), and Facebook app (3.7%).
In summary, Accenture found that disruptor brands that focus their resources on social, organic search, and offline channels could better impact paid search and, ultimately, increase their web traffic.
Key highlights on marketing mix modeling
- Marketing mix modeling uses statistical analysis to analyze the past and future impact of different marketing tactics on sales or profit. The approach is based on the popular 4 Ps marketing mix theory.
- Each marketing mix modeling project should have four distinct phases: data collection and integrity, modeling, model-based business measures, and optimization and simulation.
- MMM is popular among consumer packaged goods companies such as Kraft, The Coca-Cola Company, Pepsi. It is also useful for brands advertising on social media platforms such as Facebook where markets and consumer behavior are more dynamic.
Amazon marketing mix case study
How does Amazon balance product, price, promotion, and place to create and sustain its competitive advantage?
Let’s delve into Amazon’s marketing mix below.
Amazon offers a diverse selection of products to maintain its status as the foremost company in online retail.
These products support the company’s mission and vision and, thanks to continued expansion, can now be found in industries such as cloud infrastructure, database services, content production, artificial intelligence, gaming, and pharmaceuticals.
Amazon’s core product remains its eCommerce platform where the company sells private-label and third-party items to consumers across categories such as consumer electronics, art, home appliances, sports and outdoors, car accessories, jewelry, and home improvement.
Through its highly successful Amazon Prime membership program, the company offered free expedited delivery and discounted priority and residential express delivery.
Prime members also receive access to exclusive discounts and Amazon’s video, music, and e-book platforms.
Amazon primarily uses market-oriented pricing to attract customers to its eCommerce platform.
Prices for the company’s private label Amazon Basics range are based on similar products sold by competitors.
As a retailer with a near-global presence, Amazon also uses the price discrimination strategy to vary prices for identical products according to region.
For example, the price of a Samsung television in Spain may be different to the price offered to consumers in the USA.
This enables the company to adjust prices based on local market conditions, consumer preferences, and perceived product value.
More generally speaking, Amazon uses technology to set and adjust prices based on the time of day, season, and competitor activity.
It also cleverly prices its Prime membership option to attract customers who want to take advantage of deals and discounts.
In addition to marketing to broader audiences, Amazon also markets to individuals by analyzing their shopping habits and purchase behavior.
Using this information, it strives to turn one-time visitors or buyers into repeat, high-value, long-term customers.
To attract repeat purchasers, the company frequently promotes its fast delivery.
Amazon promotes is various products and services with ads on other websites, newspapers, billboards, television, and social media.
The Amazon Affiliate Program – one of the largest in the world – is also a vital promotional channel for the company with around 1.235 million affiliate sites advertising or reviewing products on the Amazon website.
Amazon is primarily an online business that reaches customers on Amazon.com and its various region-specific derivatives.
However, the company does operate in the real world to some extent. Its acquisition of Whole Foods Market in 2017 allowed it to establish a bricks-and-mortar supermarket presence.
Amazon also operates several Amazon Fresh and Amazon Go stores, with the latter a chain of convenience outlets without cashiers where consumers pay for goods using an app.
In August 2021, Amazon announced it would open several new physical retail stores to extend its reach across electronics, home goods, and clothes.
Many see this move as a way for the company to own as much of the retail industry as possible.
Case Studies
- Product: High-quality smartphones, laptops, and wearables with sleek designs.
- Price: Premium pricing strategy for a perception of exclusivity.
- Place: Apple Stores, authorized retailers, and online store.
- Promotion: Creative advertising campaigns and product launches.
- Product: A menu of burgers, fries, and beverages.
- Price: Value meals, combo pricing, and occasional promotions.
- Place: A network of drive-thru outlets, dine-in restaurants, and delivery services.
- Promotion: Television ads, social media campaigns, and Happy Meal toys.
- Product: A range of vehicles from compact cars to SUVs and hybrids.
- Price: Competitive pricing with options for customization.
- Place: Dealerships, showrooms, and online configurators.
- Promotion: Television and digital advertising, sponsorships, and test drive events.
- Product: Trendy clothing and accessories for men, women, and children.
- Price: Competitive pricing with seasonal sales and discounts.
- Place: Brick-and-mortar stores in prime locations and an online store.
- Promotion: Seasonal fashion shows, social media marketing, and email newsletters.
- Product: A range of banking services including checking accounts, savings accounts, loans, and credit cards.
- Price: Fee structures, interest rates, and introductory offers.
- Place: Physical branches, ATMs, and online banking platforms.
- Promotion: Advertising financial products, referral programs, and online tutorials.
- Product: Various types of accommodations from luxury resorts to budget-friendly hotels.
- Price: Room rates, loyalty programs, and seasonal discounts.
- Place: Hotel locations, booking websites, and travel agencies.
- Promotion: Online advertising, partnerships with travel websites, and loyalty rewards.
- Product: Software suites for productivity, collaboration, and communication.
- Price: Subscription-based pricing models and one-time purchases.
- Place: Online stores, authorized retailers, and corporate licensing.
- Promotion: Product demos, webinars, and advertising tailored to specific business needs.
- Product: A wide range of beverages including carbonated soft drinks, juices, and bottled water.
- Price: Various pricing strategies, including premium pricing for specialty products.
- Place: Distribution through supermarkets, convenience stores, and vending machines.
- Promotion: Extensive advertising campaigns, sponsorships, and product placements.
- Product: Comprehensive medical services, research, and patient care.
- Price: Transparent pricing for medical procedures and insurance coverage.
- Place: Hospitals, clinics, telehealth platforms, and partnerships.
- Promotion: Healthcare seminars, educational content, and patient testimonials.
- Product: An extensive online marketplace offering a wide range of products.
- Price: Competitive pricing, discounts, and subscription services (e.g., Amazon Prime).
- Place: Online platform accessible worldwide.
- Promotion: Personalized recommendations, customer reviews, and Prime Day sales events.
Key Highlights:
- The marketing mix encompasses a comprehensive strategy for effective marketing planning.
- Traditionally, it consisted of the four Ps: Product, Price, Promotion, and Place.
- Additional elements have been introduced, including Physical Evidence, People, Process, and even Politics.
- A well-rounded marketing mix involves creating plans for each element to address strengths and weaknesses.
- It ensures that marketing efforts align with the target audience and the problem the product or service solves.
- Product: Tangible goods or intangible services that address specific problems and target audiences.
- Price: Directly affects sales and is linked to perceived value in the consumer’s mind.
- Promotion: Includes marketing communication strategies like advertising, sales promotions, and public relations.
- Place: Refers to the physical location where customers can access or purchase the product.
- People: Refers to staff involved in marketing the brand, influencing its direction and values.
- Process: Encompasses customer service and ensures effective interactions and purchasing experiences.
- Physical Evidence: Anything consumers see when interacting with the brand, including packaging, branding, and more.
- Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) is a statistical method to evaluate marketing campaign effectiveness.
- It quantifies the impact of various marketing inputs on market share or sales to optimize resource allocation.
- MMM involves four phases: data collection and integrity, modeling, model-based business measures, and optimization and simulation.
- Facebook used MMM to analyze its advertising impact compared to traditional channels.
- Analyzing 6-12 months of data, Facebook adjusted methods to account for the dynamic nature of social media.
- Accenture ran MMM analyses, integrating data from Facebook and other channels to optimize promotional efforts.
- Product: Amazon offers a wide range of products and services, including eCommerce, cloud infrastructure, content production, and more.
- Price: Utilizes market-oriented pricing and price discrimination based on regions and market conditions.
- Promotion: Targets individuals by analyzing shopping habits and uses ads, promotions, and affiliate programs.
- Place: Primarily operates online but also has physical retail presence, such as Whole Foods and Amazon Fresh stores.
What are the 4 types of marketing mix?
The four main elements of the marketing mix are:
What is 7 P's marketing mix?
The 7 P’s marketing mix is an extension of the traditional marketing mix. In a 4 Ps marketing mix, you get Product, Price, Promotion, and Place. In a 7 Ps marketing mix variation, you get three other elements:
Why is marketing mix important?
A marketing mix is critical as it enables companies to structure an effective marketing strategy by understanding the main channels that can be leveraged to build a viable business.
In some instances, some channels will be more critical in a marketing mix strategy .
Over time, it will be critical to balance out various channels as part of the marketing mix to build a solid business model.
Visual Marketing Glossary
Account-Based Marketing

AARRR Funnel

Affinity Marketing

Ambush Marketing

Affiliate Marketing

Bullseye Framework

- Brand Building

Brand Dilution

Brand Essence Wheel

- Brand Equity

Brand Positioning

Business Storytelling

Content Marketing

Customer Lifetime Value

- Customer Segmentation

Developer Marketing

Digital Marketing Channels

Field Marketing

Funnel Marketing

Go-To-Market Strategy

Greenwashing

Grassroots Marketing

Growth Marketing

Guerrilla Marketing

Hunger Marketing

Integrated Communication

Inbound Marketing

Integrated Marketing

Marketing Mix

Marketing Myopia

Marketing Personas

Meme Marketing

Microtargeting

Multi-Channel Marketing

Multi-Level Marketing

Net Promoter Score

Neuromarketing

Newsjacking

Niche Marketing

Push vs. Pull Marketing

Real-Time Marketing

Relationship Marketing

Reverse Marketing

Remarketing

Sensory Marketing

Services Marketing

Sustainable Marketing

Word-of-Mouth Marketing

360 Marketing

- Market Segmentation
- Brand Awareness
- Types of Business Models You Need to Know
- Business Strategy: Definition, Examples, And Case Studies
- Marketing Strategy: Definition, Types, And Examples
- Platform Business Models In A Nutshell
- Network Effects In A Nutshell
- Gross Margin In A Nutshell
More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- 70+ Business Models
- Airbnb Business Model
- Amazon Business Model
- Apple Business Model
- Google Business Model
- Facebook [Meta] Business Model
- Microsoft Business Model
- Netflix Business Model
- Uber Business Model
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
The 4 Ps of Marketing: What They Are and How to Use Them
Learn what the 4 Ps are and how they can help you in your next marketing endeavor.
![market mix in business plan [Featured image] A man holding a tablet stands in front of a whiteboard where the 4 Ps of marketing are listed in green marker.](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/18UCaz3VIpE9UA9ptFeNLL/02bcc9fa499f0fc5adf775bc377b0b0c/GettyImages-934865812.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
The four Ps are a “marketing mix” comprised of four key elements—product, price, place, and promotion—used when marketing a product or service. Typically, successful marketers and businesses consider the four Ps when creating marketing plans and strategies to effectively market to their target audience.
Although there are many other “marketing mixes,” the four Ps are the most common and foundational to creating a successful marketing strategy . In this article, you will learn more about their purpose, history and find a detailed breakdown of the four Ps.
What are the 4Ps of marketing? (Marketing mix explained)
The four Ps are product, price, place, and promotion. They are an example of a “marketing mix,” or the combined tools and methodologies used by marketers to achieve their marketing objectives.
The 4 Ps were first formally conceptualized in 1960 by E. Jerome McCarthy in the highly influential text, Basic Marketing, A Managerial Approach [ 1 ]. There, McCarthy noted that while the text of the book was “similar to that found in the traditional texts, the approach is not.”
McCarthy’s novel approach was influenced by the still-recent “marketing mix” concept, which Harvard Business School professor Neil. H. Borden popularized in the 1950s. In fact, Borden himself had been influenced by a 1948 study written by James Culliton, in which the author equated business executives to “artists” or “mixer[s] of ingredients” [ 2 ]. Rather than using the same approach for every situation, then, Culliton and Borden recognized that successful executives instead mixed different methods depending on variable market forces.
McCarthy streamlined this concept into the four Ps—product, place, price, and promotion—to help marketers design plans that fit the dynamic social and political realities of their time and target market . In effect, the purpose of the four Ps remains the same today as when McCarthy first published his book: “developing the ‘right’ product and making it available at the ‘right’ place with the ‘right’ promotion and at the ‘right’ price, to satisfy target consumers and still meet the objectives of the business” [ 3 ].
The four Ps
The four Ps form a dynamic relationship with one another. Rather than one taking priority over the other, each is considered equally important in crafting a strategic marketing plan.
The product is the good or service being marketed to the target audience.
Generally, successful products fill a need not currently being met in the marketplace or provide a novel customer experience that creates demand. For example, the original iPhone filled a need in the market for a simplified device that paired a phone with an iPod, and the chia pet provided a humorous experience for consumers that was utterly unique.
As you are working on your product, it is essential to consider potential customers in your target audience and their unique needs. Some questions to consider when working on a product include:
What is your product?
What does your product do? Does the product meet an unfilled need or provide a novel experience?
Who is your product’s target audience?
How is your product different from what others offer?
Read more: Competitive Product: Definition + How to Analyze One
Price is the cost of a product or service.
When marketing a product or service, it is important to pick a price that is simultaneously accessible to the target market and meets business goals. Different pricing models can have a significant impact on the overall success of a product. For example, if you price your product too high for your targeted audience, then very few of them will likely purchase it. Similarly, if you price your product too low, then some might pass it up simply because they are concerned it might be of inferior quality and cut into your potential profit margins.
To identify a successful price, you will want to thoroughly understand your target audience and their willingness to pay for your product. Some questions you might ask yourself as you are considering your product’s price include:
What is the price range of your product’s competitors?
What is the price range of your target audience?
What price is too high for your audience? What price is too low?
What price best fits your target market?
Read more: What Is a Pricing Strategy? + How To Chose One for Your Business
Place is where you sell your product and the distribution channels you use to get it to your customer.
Much like price, finding the right place to market and sell your product is a key factor in reaching your target audience. If you put your product in a place that your target customer doesn’t visit—whether on or offline— then you will likely not meet your sales target. The right place, meanwhile, can help you connect with your target audience and set you up for success.
For example, imagine you are selling an athletic shoe you designed. Your target market is athletes in their early twenties to late thirties, so you decide to market your product in sports publications and sell it at specialty athletics stores. By focusing on sports stores over shoe stores in general, you are targeting your efforts to a specific place that best fits your marketing mix.
To decide the best place to market and sell your product, you should consider researching the physical places or digital channels that your target audience shops and consumes information. Some questions to consider include:
Where will you sell your product?
Where does your target audience shop?
What distribution channels are best to reach your target market?
Read more: What Is a Marketing Channel? 6 Types to Prioritize in 2023
Promotion is how you advertise your product or service. Through promotional activities, you will get the word out about your product with an effective marketing campaign that resonates with your target audience.
There are many different ways to promote your product. Some traditional methods include word of mouth, print advertisements, and television commercials. In the digital age, though, you can create online marketing campaigns to promote your product, using such channels as content marketing , email marketing , display ads , and social media marketing .
Some questions to consider as you are working on your product promotion include:
What is the best time to reach your target audience?
What marketing channels are most effective for your target audience?
What marketing messages would most resonate with your target audience?
What advertising approaches are most persuasive to your target audience?
Other marketing mixes
The four Ps aren’t the only marketing mix used today. Some other modern marketing mixes include the five Ps, the seven Ps, and the 5 Cs. Although each of these reflects certain aspects of the four Ps, they also each possess some unique elements that alter their emphasis on the marketing process.
The five Ps
The five Ps are product, price, place, promotion, and people .
Today, many marketers use the five Ps over the four Ps because it centers the experiences of customers and staff in the marketing process. Typical considerations include how a customer behaves, their experience with the product, and their overall satisfaction with the business.
The seven Ps
The seven Ps are product, price, place, promotion, people, processes , and physical evidence .
The seven Ps are a further elaboration of the five Ps, adding considerations of the processes that define the customer experience and the physical evidence that the target market needs to see to become customers. While processes might involve the specific customer service processes that define a product, physical evidence can be websites or store displays that help the target market imagine themselves using the product.
The five Cs
The five Cs are customer, company, competition, collaborators, and climate.
In some respects, the five Cs reflect many of the same concerns of the four and five Ps, but with added emphasis on external factors, such as possible outside collaborations and competitive research.
Furthermore, while “climate” refers to the social, political, and economic context surrounding the market, “customer” refers to the target market and customer experience. “Company,” meanwhile, refers to the place of the company and their available resources in the marketing process.
How to use the 4 Ps of marketing
Now that you know the 4Ps and other marketing mixes, here is a quick refresher on your main objectives for your marketing strategy:
Communicate the benefits that the product offers potential customers.
Demonstrate how the product's value matches the price.
Place the product where your target audience is most likely to encounter it.
Promote the product in ways that resonate with your target audience.
Build your marketing skills on Coursera
Develop or strengthen your marketing skills with any of these top-rated products on Coursera:
Want to keep learning about the 4 Ps? Define your Ps with Marketing Mix Implementation from IE Business School, which covers brand and product management, pricing strategy, and more.
Just getting started in marketing? Build the skills you need for an entry-level role with the Meta Social Media Marketing or Marketing Analytics Professional Certificates on Coursera.
Ready to take on the world of digital marketing? Learn internet marketing strategies in less than six months with the Google Digital Marketing & E-commerce Professional Certificate .
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
What is the most important out of the 4 ps .
All of the 4 Ps—product, price, place, and promotion—are important components of your marketing strategy. They work most effectively when marketers use them in conjunction with one another. You may find yourself focusing on one or another at different phases of business development. For example, you might focus on product and price at earlier stages, while place and promotion might become priorities at a later stage when you’re preparing to introduce the product to the market.
Are the 4 Ps of marketing still useful?
Although the 4 Ps of marketing has been around since the 1960s, the concept is still considered useful, even as marketing rapidly evolves and becomes increasingly digitized. You can think of the 4 Ps as comprising the foundation to developing effective marketing strategies. At the same time, it’s a good idea to use some of the other models—the 5 Ps (product, price, place, promotion, and people) or the 5 Cs (customer, company, competition, collaborators, and climate)—to build a more thorough approach to marketing.
Article sources
Oxford Reference. “ E Jerome McCarthy , https://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/oi/authority.20110803100143321.” Accessed July 10, 2023.
Guillaum Nicaise. “ The Concept of the Marketing Mix , http://www.guillaumenicaise.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/Borden-1984_The-concept-of-marketing-mix.pdf.” Accessed July 10, 2023.
HathiTrust. “ Basic Marketing: a managerial approach , https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=inu.30000041584743&view=1up&seq=1.” Accessed July 10, 2023.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.
Marketing Mix Examples: The Building Block of a Successful Brand
Learn about marketing mix and its examples through advertising campaigns of various leading brands..
- overview#goto" data-overview-topic-param="what">What is marketing mix?
- overview#goto" data-overview-topic-param="origination">Origination of the 4P's
- overview#goto" data-overview-topic-param="important">Why is marketing mix important?
- overview#goto" data-overview-topic-param="examples">Examples of marketing mix
- overview#goto" data-overview-topic-param="7">7P's of marketing mix
- overview#goto" data-overview-topic-param="why">Why is it important?
- overview#goto" data-overview-topic-param="write">Best practices to write marketing mix

Marketing mix can make or break a product’s success. We have put together the best marketing mix examples of leading brands for your understanding and a guide to help you craft an effective marketing mix strategy for your brand.
What is Marketing Mix?
Let's start with the Marketing mix definition before moving on to the guide.
A marketing mix is a blend of business strategies brought into execution that make up the overall marketing strategy for a product.
Typically, marketing mix collectively includes the 4 Ps of marketing: product, price, place, and promotion.
With dynamic changes in the business environment, these four Ps were further expanded into the 7 P's of marketing mix to include: people, process, and physical evidence.
The intersection of these factors leads to the formation of a distinct marketing strategy that is tailored for a brand. Having a marketing mix that is compatible with your brand values is crucial for the success of a company.

Origination of the 4 P's of Marketing Mix
Prof. James Culliton was the first one to mention the marketing mix in the late 1940s. Later his colleague, Neil Broden published an article - The concept of the marketing mix .
Jerome McCarthy first introduced the concept of the 4 P's of marketing mix in his book “Basic marketing: A managerial approach”.

Why is Marketing Mix important?
Imagine if Tiffany diamonds were sold in Walmart.
Or McDonald’s was located in remote locations.
Or Red Bull was advertised on a kid’s Television channel.
Or an artist was the brand ambassador of Nike.
This would have gone terribly wrong, and these brands might not even be in the market today.
The slightest angle change in a marketing mix can tremendously impact the market you are targeting. Every element must be selected carefully after rigorous market research and analysis.
A right marketing mix ensures you are -
creating a product that solves a problem
selling it at the correct price
promoting it to your target customers
distributing it at a place easily accessible by the consumers
All these factors need to work in tandem to ensure the creation of a well-oiled marketing engine.
Is Marketing Mix rigid in nature?
The marketing mix isn’t set in stone. It ebbs and flows in alignment with the dynamic changes in the business environment and company growth. Often a company might test various combinations of the marketing mix elements to settle on marketing tactics that give the highest returns.
With that let’s dive into the world of marketing mix with marketing examples from leading brands around the world to give you a practical understanding.

4 P's of Marketing Mix with Examples
A marketing plan must be based on thorough market research and analysis of the many factors of marketing. A marketing design without a solid blueprint is like aiming in the dark, you’ll never hit the target. Understanding the 4 P’s of marketing is crucial for devising a marketing scheme that hits home.
Here are the 4 P's of marketing mix with examples.
Product Marketing Mix
Product is at the core of all marketing strategies. The product attributes don’t only refer to tangible goods but also intangible service products and ideas. It is what a company has to offer to its customers.
A great product is at the center of a brand’s success. Noteworthy marketing tactics can get the product in front of the target customers and get them to try it once, but after that, the product is on its own. The product must have the potential to survive and thrive in the market.
The product must solve customers’ problems efficiently, and better than others in the market, otherwise, customers won’t buy it. The question is, what’s in it for them?
Product marketing refers to product benefits, market research, product features, design, quality, technology, and warranties.
To develop a product mix, a marketing manager takes into consideration the following questions:
Who is your target market?
What are their pain points or problems?
What quality product are they looking for?
What is your competitor’s offering?
How can you gain a competitive advantage over them?
How large is the target market?
What pain point are you solving?
Which product features and benefits solve that problem?
Apart from the above checklist, feedback from the customers about what they like or dislike about the product is taken further to mold the product to suit their needs.
This will help you craft customer-centric marketing instead of product-centric.
Product Marketing Mix Example
Apple 's unique selling proposition is its product marketing mix by producing products with innovative features, advanced technology, and sleek design. From their iconic iPhones to their ingenious MacBooks, Apple’s products are the perfect combination of form and function. Apple’s product mix includes more than just hardware. Their services and add-ons make their products irresistible. Customers have access to the world of entertainment and convenience with iTunes, iCloud, and Apple Music.
Apple treats its customers like a kind by providing a simple user interface, exceptional support, and warranty claims. Apple is a legendary marketing example everyone must take notes from.
Source: Apple Website

Source: Unsplash
Price Marketing Mix
Price is the money paid by the customers to own, access, or avail of your product. Pricing strategies must be profitable to the company. Prices are determined based on the cost incurred, the expected profit margin, and how much the customers are willing to pay.
Does your product solve a problem better than others, is it sold for an appropriate price, and is it worth the price? Based on your business strategy, product prices can be luxury, premium, or bargain price.
Price marketing mix elements include pricing strategy, payment terms, credit policy, discount, allowances, and payment mode.
To develop a pricing strategy, the marketing manager first determines:
The income range of their target consumer
Brand’s value perception by the customer
How much are they willing to pay?
How much do their competitors charge?
Do you want to adopt a luxury, bargain, or premium pricing strategy?
How will your price portray your brand?
Premium prices give the impression that the brand must be superior. The right price is the one that meets your profit margins and keeps more customers happy, a win-win situation.
Price Marketing Mix Examples
Coca-Cola uses a competitive pricing strategy for penetrative marketing. It is a pricing expert such that it matches the competitor’s prices head-on combined with a value-based pricing approach to push discounts for stimulating higher sales. The business is adaptable and it also changes its prices to meet local laws and market conditions.

Another example is Walmart which uses Everyday Low Prices (EDLP) pricing strategy that entails selling products at a low price to attract more customers, higher sales volume, and increase profits. Walmart does this by buying products in massive quantities from all over the world and use economies of scale to sell products at high discount rates depending on the demand.

Source: Walmart Website

Source: Tech Crunch
Place Marketing Mix
The third P, Place refers to the chain through which the products go from manufacturer to customer. This chain is determined based on who is the target audience, where will you find them, and how will you reach your product to them.
The quicker the goods travel from production to point of sale, the higher customer satisfaction.
Place mix determines the distribution channels and place where the product will be sold like online/eCommerce stores, physical locations like retail, wholesale, convenience stores, brand owned outlets. It is significant to research where your customers will be looking for your product and how to best serve them.
Place marketing mix elements include warehouse, transport, distribution channel, inventory control, and areas covered.
To determine the place marketing mix strategy, marketing managers find the answers to the following questions:
Where will your customers find your product?
Where will you sell your products?
Will they be available in eCommerce stores, retail stores, or brand store chains?
A well-optimized distribution channel is even more important for retail businesses. You can read our marketing mix case studies on Costco , Pepsi , or Airbnb to get more perspective on how they manage their distribution.
Place Marketing Mix Examples
McDonald’s has more than 36,000 franchises and company-owned outlets all across the globe. It also has drive-ins, online ordering through its app, and food delivery partners. Consumers can either dine at the restaurant itself or get a takeaway at their convenience. McDonald’s is located in easily accessible locations providing its customers serving tasty food quickly at low prices.

Source: McDonald's blog
Tiffany & Co is a high-end luxury jewelry brand. It sells its signature Tiffany True only in its stores creating exclusivity and an elite user experience.

Source: Harpers Bazaar
Promotion Marketing Mix
Promotion defines the strategies to make your potential customers aware of your brand. Simply put, how to get the word out about your product to your potential customers. Promotion marketing mix advertises, differentiates your product in the target market, and convinces your ideal customers to buy your product.
Promotional mix elements in the digital age include television ads, publicity, sales promotion, digital marketing, social media ads, personal selling, direct marketing, public relations, print advertising, search engine marketing, and online marketing.
Questions marketing managers ask when devising a promotion marketing mix strategy:
Where do your customers hang out online & offline?
Where will you promote your product?
What promotion tactical marketing tools will you use?
One needs to perform a lot of trial and error in devising promotional channel strategies. You can read this book to know many possible growth channels - Traction by Gabriel Weinberg
Promotion Marketing Mix Example
Red Bull spends extensively on promotions to stay at the top of its consumer's mind. 'Red Bull gives you wings' tagline has made a home in people’s minds. It’s impossible to plainly say it without dragging out the wings in a high-pitched voice. Red Bull promotes itself as a high-energy drink for intense activity. Its promotion strategy includes creative ads, digital marketing, content marketing, and sponsorship of extreme sports events .
Nike’s target buyers are athletes and people seeking a sporty and healthy lifestyle. It collaborates with high-profile sportspersons to promote its product line and maintain its brand image of being a premium sportswear brand. Michael Jordan, Serena Williams, and Kobe Bryant are a few of Nike’s brand ambassadors. Managers must study Nike's marketing example to devise their promotion strategy.

Source: Footwear News

Source: WWD
The 4 Ps of marketing work in unison to create a brand’s marketing strategy. It’s like a four-legged chair. If one leg is of the wrong height or broken, the chair won’t stay upright.
As businesses became more dynamic, more elements were added to the 4 Ps of marketing to derive an effective marketing plan to meet today’s business needs.
What are the 7 P’s of Marketing Mix?
The 4 Ps were expanded into the 7 P's of marketing mix to keep up with the modern business environment. The additional P’s are Physical evidence, people, and process.
Let’s learn about each one of them with marketing examples.
Physical Evidence Marketing Mix
It is the look and feel of your product and brand. It includes exterior design, interior decor, ambiance, atmosphere, furnishing, packaging, employee appearance, and overall experience.
Physical Evidence Marketing Mix Example
Starbucks serves exquisite coffees in a soothing ambiance. It positions itself as a place where you can work, interact, or hang out in a peaceful atmosphere with utmost ease. The experience Starbucks offers is what makes users choose it over others.

Paperboat’s packaging is vibrant and colorful with unique shapes and sizes because its consumers are children. Kids are attracted to colorful things that catch their eye in an instant. This way Paperboat distinguishes itself in a sea of competitors.
Source: Elephant design
People Marketing Mix
People marketing mix refers to the people involved in the development, distribution, and selling of the product. Personnel is the backbone of a company because they represent the company in front of its consumers and leave an impression. Hiring the right people, and training them thoroughly to match the quality of your brand is crucial for a brand’s success. The people marketing mix includes employees, service providers, sales executives, delivery staff, and work culture.
People Marketing Mix Example
Taj is a world leader in hospitality. It keeps customer satisfaction at the forefront. They train their personnel, right from the front desk to managerial staff, rigorously to provide the best customer experience.

Source: Taj Hotels
Process marketing mix
The process consists of the direct and indirect activities involved in the manufacturing, delivery, and consumption of the product. It also includes customer feedback to solve any inconvenience and give consumers what they need. The efficiency of the process decides the performance of a product.
Process Marketing Mix Example
Starbucks holds customer feedback in high esteem to refine its product offering. Starbucks' “My Starbucks Idea” platform was in operation for nearly 10 years before being retired. It provided consumers with a better way to share their concerns and submit requests. The aim was to give consumers exactly what they want while building a relationship and a loyal customer base.
Source: Braineet

Marketing mix elements work in agreement with each other to formulate the right marketing design for a brand. You cannot focus on a single element and call it a day. If there are internal discrepancies between the elements then those must be eliminated to provide the best value to the customer.
Why should you care about Marketing Mix?
The marketing mixes work in unison aiding each other. They are interrelated like the tires of a car, driving the company forward.
A correct marketing mix ensures you target the right buyers, make them aware of your product, position yourself distinctly, and offer a product they want, at a price they are willing to pay, and at a place easily accessible to them.
Each element decides the strategy for other elements. For example, a luxury product with a premium price cannot be sold at indie shops that follow cost-sensitive pricing strategies.
Best Practices to write a Marketing Mix Strategy
Use these best practices to write an effective marketing mix strategy for your product:
Clear, measurable, time-specific and stretch goals for a marketing campaign improve marketing success rate as one works towards a defined outcome. Is your aim to attract more customers, get more sales, differentiate yourself from competitors, enhance brand image, or increase brand awareness?
Perform Market Research
Market research gives a direction and validation to your marketing mix as to whom you need to sell in the first place. It helps define a target audience, finalize product's features, get inspired from competition's promotion tactics, etc. The result is a customer-centric product stand that has a distinct unique selling proposition backed by research.
Incorporate customer feedback
Are your product's benefits truly aligning with your customer's expectations? What is the perceived value of your product in front of your potential customers ? Can you increase your product pricing? Should you invest in search engine marketing?
All such present and future product decisions can be made by actively taking customer feedback. You also get a clear data if your marketing mix work on your target audience as strategized.
Get started with your brand's marketing strategy today
The marketing mix is crucial to successfully market your product and achieve marketing goals. Effective marketing mix results in higher customer satisfaction, larger market share, increased sales, and finally soaring profit margins. Now that you have a clear understanding of the marketing mix, it’s time for you to devise a marketing mix plan for your product and achieve those banger sales and profit goals.
- popover#mouseOver mouseout->popover#mouseOut" data-popover-translate-x="-25%" , data-popover-translate-y="-220%"> Copy link
- bottom-bar#toggleTagsSection"> popover#mouseOver mouseout->popover#mouseOut" data-popover-translate-x="-25%" , data-popover-translate-y="-220%"> Copy Link
- bottom-bar#toggleTagsSection">

"Must read for every entrepreneur"

"The best part is it's written by real entrepreneurs"

"My favorite newsletter on the web"
You'll love these articles too!

Co-founder at Flexiple, buildd & Remote Tools ($3 million revenue, bootstrapped)
Breaking Down The Maruti Suzuki Marketing Strategy: How they became a brand that rules India's automobile market
Learn about Maruti Suzuki's iconic marketing strategy and advertising campaigns. Read how Maruti Suzuki's aces the 4Ps of marketing mix - Product, Price, Promotion & Placement.

Clinical Research | Data Analytics

Partner at Deloitte | Banking & Capital Markets | Cloud Strategy | FinOps Offering Leader | Board...

Co-founder & CEO at Flexiple ($3mn+ revenue, bootstrapped) & buildd.co | Helping Startup...
Swiggy Business Model: How the Company is Building a Brand That's Hard to Resist
Explore the innovative business strategies behind Swiggy's success, including the company's approach to building a strong brand and delivering unbeatable customer experiences. Learn how Swiggy is disrupting the food delivery industry and solidifying its place as a leader in the market.

Market Penetration Definition, Rate Calculation Examples and Strategies
Learn all you need to know about market penetration. Find the market penetration definition, how to calculate it, examples and strategies.

BE Mechatronics |

Hi! My name is Uche, a Nigerian and undergraduate degree student at Brigham Young University (...

The Marketing Mix: A Guide to Creating a Winning Strategy
In the world of marketing, the term “ Marketing Mix ” is a fundamental concept that plays a crucial role in shaping successful marketing strategies. The marketing mix refers to a set of tactical elements or variables that businesses use to influence the demand for their products or services in the marketplace. These variables are often referred to as the 4 Ps of marketing: product, price, promotion, and place.
The marketing mix represents the strategic combination of these four elements, which businesses can manipulate to create a compelling offering that meets the needs and desires of their target market. Each element of the marketing mix carries its own significance and contributes to the overall marketing strategy of a business.
Discover Fresh Marketing Insights!
Join other smart marketers to uncover amazing marketing strategies.
We will never give away, trade or sell your email address. You can unsubscribe at any time.
The product element focuses on designing, developing, and delivering a product or service that aligns with customer needs and preferences. The price element involves determining the optimal pricing strategy that reflects the value of the product while considering market dynamics and customer perceptions. Promotion encompasses all the activities undertaken to communicate and promote the product to the target audience, including advertising, public relations, and sales promotions. Lastly, the place element involves determining the most effective distribution channels to make the product accessible to customers.
The marketing mix is important because it provides a structured framework for businesses to effectively plan, execute, and control their marketing activities. It helps businesses identify and leverage their unique selling propositions, differentiate themselves from competitors, and create value for their target market. By carefully managing the marketing mix variables, businesses can optimize their marketing efforts, attract customers, and ultimately drive sales and revenue growth.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into each element of the marketing mix and explore their individual significance in developing a successful marketing strategy.
What are the 4Ps of marketing?
The 4Ps of marketing, also known as the marketing mix, are a set of four key elements that businesses use to formulate their marketing strategies. These elements include product, price, promotion, and place. Let’s explore each of these elements in detail:
- Product: The product element of the marketing mix refers to the goods or services that a business offers to its target market. It involves decisions related to product features, design, quality, packaging, and branding. Businesses need to consider the needs and preferences of their target customers and develop products that provide value and solve their problems. Product positioning is also important, which involves determining the unique selling points and differentiating the product from competitors.
- Price: Price refers to the amount of money customers are willing to pay for a product or service. Pricing decisions should consider factors such as production costs, desired profit margins, customer perceptions of value, and competitive pricing in the market. There are various pricing strategies businesses can employ, including cost-based pricing (setting prices based on production costs), value-based pricing (setting prices based on the perceived value to customers), and competition-based pricing (setting prices based on competitor pricing).
- Promotion: Promotion involves the various activities and communication channels that businesses use to promote their products or services and create awareness among their target audience. It includes advertising, which can be done through traditional channels like TV, radio, print media, or digital channels such as social media and online advertising. Public relations activities help build a positive image for the business through media coverage and events. Sales promotions, such as discounts, coupons, or loyalty programs, are used to stimulate immediate sales. Direct marketing involves reaching out to customers directly through email marketing, direct mail, or telemarketing.
- Place: Place refers to the distribution channels and locations where customers can access and purchase the product or service. It involves decisions about the best channels to reach the target market, such as retail outlets, wholesalers, distributors, or online channels. Businesses need to ensure that their products are available at convenient locations and through accessible channels that align with their target customers’ preferences.
By carefully considering and managing these four elements, businesses can create an effective marketing mix that positions their products or services in the market, attracts customers, and drives sales. It is important for businesses to continuously monitor and adjust their marketing mix strategies to adapt to market changes, customer preferences, and competitive dynamics.
In the next sections, we will explore different pricing strategies, promotion techniques, and distribution channels in more detail to understand how businesses can leverage these elements to create successful marketing strategies.
What are the 7Ps of Marketing?
The 7Ps of marketing, an extension of the traditional 4Ps, provide a comprehensive framework for businesses to develop and implement effective marketing strategies. In addition to product, price, promotion, and place, the 7Ps include people, process, and physical evidence. Let’s dive into each of these elements:
- People: The people element recognizes the importance of individuals involved in the marketing process, both within the organization and as customers. This includes understanding the target market and creating customer personas to tailor marketing efforts accordingly. Businesses should consider the customer journey and touchpoints to ensure positive interactions and experiences with their brand. Effective customer service and engagement strategies are crucial in building strong relationships with customers.
- Process: Process refers to the systems and procedures that businesses use to deliver their products or services to customers. It includes order fulfilment processes, inventory management, customer support systems, and other operational activities. Streamlining and optimizing these processes ensure efficient and consistent delivery, enhancing the overall customer experience.
- Physical Evidence: Physical evidence refers to the tangible elements that customers encounter when interacting with a brand. It includes the brand’s visual identity, packaging, retail environment, and any other physical aspects that shape customer perceptions. Strong brand identity and cohesive physical evidence help create a memorable and positive brand experience, contributing to customer loyalty and trust.
- Performance: Performance relates to measuring the effectiveness of marketing efforts and evaluating the return on investment (ROI). It involves tracking marketing metrics such as sales, conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, and customer satisfaction. By analyzing performance metrics, businesses can identify areas for improvement, optimize their marketing strategies, and make data-driven decisions.
The inclusion of people, process, and physical evidence in the 7Ps framework emphasizes the holistic nature of marketing. It recognizes the importance of customer-centricity, seamless operations, and creating a strong brand presence. By integrating these additional elements into their marketing strategies, businesses can create more comprehensive and impactful marketing campaigns.
It’s worth noting that while the 7Ps framework is widely recognized and used, different variations and interpretations may exist. Some variations may include additional Ps such as partnership and positioning. Ultimately, businesses should tailor the marketing mix framework to their specific industry, target market, and unique business needs.
In the following sections, we will explore each of the 7Ps in more detail, discussing strategies and considerations for effectively incorporating these elements into marketing plans.
What are the 4Cs of marketing?
The 4Cs of marketing is a customer-oriented framework that focuses on understanding and meeting the needs of customers. It complements the traditional marketing mix by shifting the perspective from the company’s offerings to the customer’s perspective. Let’s explore each element of the 4Cs:
1. Customer: The customer is at the core of the 4Cs. Understanding the customer is essential for developing effective marketing strategies. It involves identifying the target market, analyzing demographics, behaviors, preferences, and psychographics. By gaining deep insights into customers, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts to meet their specific needs. The following are ways to understand your customers:
- Needs : Needs refer to the fundamental requirements that customers have. It involves understanding what problem or desire the customer wants to fulfil with a product or service. By addressing these needs, businesses can provide value and satisfy customers, leading to customer loyalty and repeat business.
- Wants : Wants are the specific desires and preferences of customers. They go beyond basic needs and are influenced by personal tastes, aspirations, and social influences. Understanding customer wants helps businesses create products, services, and marketing messages that resonate with their target audience, increasing customer engagement and satisfaction.
- Expectations : Customer expectations are what customers anticipate and believe they will receive from a product or service. It includes factors such as quality, reliability, service, and overall experience. Meeting or exceeding customer expectations is crucial for building trust and long-term customer relationships.
2. Cost: Cost refers to what the customer is willing to pay for a product or service. It is not only limited to monetary value but also encompasses the perceived value customers receive in exchange for their investment. Understanding the customer’s perception of cost helps businesses set pricing strategies, create value propositions, and communicate the benefits and value of their offerings effectively.
3. Convenience: Convenience is about how easy it is for customers to access and purchase a product or service. It involves factors such as the availability of multiple purchase channels, user-friendly interfaces, and efficient customer service. By enhancing convenience, businesses can remove barriers to purchase, improve customer satisfaction, and drive customer loyalty.
4. Communication: Communication refers to the interaction between businesses and customers. It includes marketing messages, brand messaging, customer support, and engagement across various channels. Effective communication ensures that the brand message is clear, consistent, and resonates with the target audience, building trust and credibility.
In summary, the 4Cs of marketing emphasize the importance of understanding customer needs, wants, expectations, cost considerations, convenience, and effective communication. By focusing on these customer-centric elements, businesses can create tailored marketing strategies, deliver value to customers, and build strong, long-lasting relationships.
Note: The 4Cs framework is an extension of the traditional 4Ps marketing mix and provides a customer-oriented perspective. Different variations and interpretations of the 4Cs may exist, but the core idea remains the same – putting the customer at the forefront of marketing strategies.
Why Marketing Mix Is Important In Business
The marketing mix, also known as the “4Ps of marketing,” refers to a set of controllable marketing variables that a business can use to influence consumers’ buying decisions. It consists of product, price, place, and promotion. The marketing mix is crucial for businesses for several reasons:
- Product Development : The marketing mix helps businesses identify and develop products that meet customer needs and preferences. By understanding customer demands, businesses can create products that offer unique features and benefits, differentiating themselves from competitors and attracting target customers.
- Pricing Strategy: Pricing is a critical element of the marketing mix. It involves setting the right price for the product or service that reflects its value, covers costs, and remains competitive in the market. An effective pricing strategy can help maximize profits, attract customers, and create perceived value for the offering.
- Distribution and Placement: Place refers to the distribution channels and locations where customers can access the product. It involves determining the most suitable distribution channels, such as online platforms, retail stores, or direct sales, to ensure that the product is available to customers when and where they want it. Proper placement ensures convenience for customers and can increase sales and market reach.
- Promotional Activities: Promotion involves communication and marketing activities that create awareness, generate interest, and persuade customers to purchase the product or service. This includes advertising, public relations, sales promotions, and personal selling. Effective promotion helps businesses reach their target audience, build brand recognition, and drive sales.
- Consistency and Integration: The marketing mix provides a framework for businesses to align their marketing efforts and ensure consistency across all elements. It allows for a cohesive and integrated approach to marketing, where all aspects work together to deliver a unified message and brand experience to customers.
- Competitive Advantage: By carefully managing the marketing mix, businesses can gain a competitive edge in the market. Through product differentiation, pricing strategies, efficient distribution, and effective promotion, businesses can position themselves uniquely and attract customers away from competitors.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: The marketing mix is not a one-time decision but requires continuous monitoring and adjustment. It allows businesses to adapt to changes in the market, customer preferences, and competitive landscape. By evaluating and modifying the marketing mix elements as needed, businesses can remain relevant and responsive to market dynamics.
In summary, the marketing mix is important in business because it helps companies develop and market products effectively, set competitive prices, ensure product availability, communicate with customers, create a consistent brand experience, gain a competitive advantage, and adapt to changing market conditions. It serves as a strategic framework for businesses to make informed marketing decisions and achieve their business objectives.
In conclusion, understanding and implementing the marketing mix is crucial for the success of any business. The marketing mix, comprised of the 4Ps (Product, Price, Promotion, and Place), provides a framework for businesses to develop effective marketing strategies and drive their overall success.
By carefully analyzing and strategizing each element of the marketing mix, businesses can create compelling products or services, determine competitive pricing, develop impactful promotional campaigns, and establish appropriate distribution channels. This comprehensive approach ensures that businesses are aligning their offerings with customer needs, positioning themselves effectively in the market, and maximizing their chances of success.
Moreover, the marketing mix is not a one-time exercise, but an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adjustment. As market dynamics change and customer preferences evolve, businesses must adapt their marketing mix strategies to stay relevant and competitive.
Here are some additional tips for creating a successful marketing mix:
- Know your target market. The most important element of the marketing mix is the product. The product must be something that your target market wants and needs.
- Set realistic goals. When you are developing your marketing mix, it is important to set realistic goals. Don’t try to do too much at once, or you will end up spreading yourself too thin.
- Measure your results. Once you have implemented your marketing mix, it is important to measure the results. This will help you to see what is working and what is not so that you can make necessary adjustments.
Resources for further learning
For further learning, there are numerous resources available to deepen your understanding of the marketing mix. Books such as “Marketing Management” by Philip Kotler, “Principles of Marketing” by Gary Armstrong and Philip Kotler, and “The Marketing Mix: Master the 4 Ps of Marketing” by Thomas Lawson provide comprehensive insights into the principles and practical application of the marketing mix.
Additionally, staying updated with industry trends, attending marketing conferences, and engaging with online communities can further enhance your knowledge and keep you informed about the latest advancements in marketing strategies.
By leveraging the power of the marketing mix and continuously honing your marketing skills, you can effectively navigate the dynamic business landscape, meet customer needs, and drive the growth and success of your business.
Q: What are the 4 Ps of marketing?
A: The 4 Ps of marketing is a framework that businesses use to develop and execute their marketing strategies. The 4 Ps are:
- Product: The product is the good or service that a business offers for sale.
- Price: The price is the amount that customers pay for the product.
- Place: The place where the product is sold.
- Promotion: Promotion is the way that the product is communicated to potential customers.
Q: What are the 7 Ps of marketing?
A: The 7 Ps of marketing is an extension of the 4 Ps that includes three additional elements:
- People: The people are the employees who work for the business and interact with customers.
- Process: The process is the way that the business operates, from product development to customer service.
- Physical evidence: Physical evidence is the tangible aspects of the business, such as its branding, website, and physical location.
Q: What is the importance of the marketing mix?
A: The marketing mix is an important tool for businesses because it helps them to:
- Identify their target market: The marketing mix can help businesses to understand their target market’s needs and wants so that they can develop products and services that meet those needs.
- Set prices: The marketing mix can help businesses to set prices that are competitive and profitable.
- Distribute their products: The marketing mix can help businesses to find the right channels to distribute their products to their target market.
- Promote their products: The marketing mix can help businesses to communicate the value of their products to their target market.
Q: How do I create a marketing mix?
A: To create a marketing mix, businesses need to:
- Identify their target market: What are the needs and wants of their target market?
- Develop products and services that meet those needs: What products and services can the business offer that will meet the needs of its target market?
- Set prices that are competitive and profitable: What prices can the business charge for their products and services that will be competitive in the market and still be profitable?
- Distribute their products to their target market: Where can the business distribute their products so that they are accessible to their target market?
- Promote their products to their target market: How can the business communicate the value of their products to their target market?
Q: What are some tips for creating a successful marketing mix?
A: Here are some tips for creating a successful marketing mix:
- Make sure your marketing mix is aligned with your business goals: Your marketing mix should be designed to help you achieve your overall business goals.
- Tailor your marketing mix to your target market: Your marketing mix should be tailored to the specific needs and wants of your target market.
- Be flexible and adaptable: The marketing mix is not a static document. It should be updated regularly to reflect changes in the market and the needs of your target market.
- Measure the results of your marketing mix: It is important to measure the results of your marketing mix so that you can see what is working and what is not. This will help you to improve your marketing mix over time.
The marketing mix is a powerful tool that can be used to create a successful marketing strategy. By understanding the 4Ps (product, price, place, and promotion) and the 3Ps (people, process, and physical evidence), businesses can develop a marketing strategy that meets the needs of their target market and helps them achieve their marketing goals.
Similar Posts
How to create quality content for instagram.
Whether you’re a brand looking to engage your audience, an influencer seeking to grow your following, or simply an individual aiming to share your passions, the ability to create quality content for Instagram is a valuable skill. In this article, we’ll guide you through the art and science of crafting compelling posts that resonate with…
15 Best Social Media Communication Tools
Are you looking to supercharge your social media communication and take your online presence to the next level? In today’s fast-paced digital world, effective communication is the key to building meaningful connections with your audience. Whether you’re a small business owner, a social media manager, or a content creator, having the right tools at your…
Marketing Research Hypothesis Examples
What are marketing strategy models.
1.1. Understanding the Significance of Marketing Strategy Models In today’s competitive business landscape, having a well-defined and effective marketing strategy is crucial for the success and growth of any organization. Marketing strategy models play a pivotal role in guiding businesses to make informed decisions, allocate resources efficiently, and achieve their marketing objectives. Let’s delve deeper…

Unlocking Marketing Excellence: Role Of Integrated Marketing Communication
In today’s fast-paced and highly competitive business landscape, companies are continuously seeking innovative ways to effectively reach and engage their target audience. Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC) has emerged as a powerful and strategic approach that unifies all marketing efforts to deliver a consistent and compelling message to customers. In this introductory section, we will delve…
Why Is Brand Awareness Important In Marketing
In the highly competitive landscape of the modern business world, brand awareness has emerged as a pivotal factor that can make or break a company’s success. This section of the article will delve into the significance of brand awareness in marketing and shed light on why it holds such a prominent position in the minds…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Please enter an answer in digits: two × two =

What is a marketing mix? Definition and examples
A marketing mix is a planned mix of elements that make up the marketing plan of a product or service. There are typically four elements: P roduct, P rice, P lace, and P romotion. They all start with the letter ‘P.’ Hence, we can say the marketing mix or the 4Ps . Some people also call the mix the 4Ps Strategy or the 4Ps Marketing Matrix .
It should be noted that sometimes ‘Presentation’ substitutes ‘Product’ in the first ‘P.’
Companies adjust the 4Ps until they find the combination that is just right for the product. In other words, the marketing mix that generates the most profit and also satisfies customers’ needs, wants, and expectations.
Some marketing executives refer to the marketing mix of the 4Ps as the marketing principles . We use the marketing principles for the successful promotion of either goods or services.
Philip Kotler, an American marketing author, consultant, and professor, once said:
“The marketing mix is the set of marketing tools that the firm uses to pursue its marketing objectives in the target market.”
Prof. Kotler is the S. C. Johnson Distinguished Professor of International Marketing at the Kellogg School of Management at Northwestern University.
Marketing tools are tools that businesses use to promote their products and services. They also use them to determine what new products to develop and how to improve their existing ones.
Marketing and the marketing mix
Marketing is a management process through which goods and services move from concept to the final consumer , i.e., the end user. It includes the identification of a good or service, determining demand, deciding on a price, and choosing distribution channels.
It also includes the development and implementation of a promotional strategy. As a business strategy, marketing has been around for thousands of years.
Marketing theory, on the other hand, emerged at the beginning of the last century. The contemporary marketing mix of the 4Ps emerged in the 1960s. It has become a dominant framework for marketing management decisions (see the end of this article for the 7Ps) .
4 elements of the marketing mix
Below is an explanation of the four elements of the marketing mix – they all start with the letter ‘P’:
This term refers to an item that satisfies the needs or wants of the consumer. The word products , in this context, also includes services .
It, therefore, includes tangible items, i.e., goods, and intangible items, i.e., services, experiences, or ideas. If something is tangible, you can touch it, i.e., it is a physical item. The word intangible refers to something we cannot touch; it is abstract (not physical).
Typical product marketing decisions include branding, product range/mix, product lines, and packaging and labeling. It also includes guarantees, warranties, returns, and managing products through the life-cycle.
This term refers to how much buyers pay for the product. It may also refer to the sacrifice customers are prepared to make to purchase a product. Sacrifice includes, for example, time and effort.
This element of the marketing mix is the only one that has implications for revenue and profit margins. It also includes considerations of customers’ perceived value.
Typical marketing decisions include price strategy, price tactics, and price setting. They also include discounts for customers and payment terms.
Place is all about where the manufacturer makes and sells the product. In other words, the products’ place of origin and the provision of customer access.
Location can affect customer service as well as how rapidly the seller can respond to orders and requests.
Typical marketing decisions include where best to sell the product and where consumers are likely to look for it. They also include how to get the product to where consumers are.
Is it a B2B, B2C, or B2G business?
- B2B stands for business-to-business – in other words, the company’s customers are other companies.
- B2C stands for business-to-customer , i.e., the company sells to individual consumers (retail).
- B2G stands for business-to-government . Defense contractors, for example, are B2G – their customer is the government (mainly).
This element of the marketing mix is all about telling consumers about the product. In other words, marketing communications. Promotion may consist of public relations (PR), direct marketing, advertising, and sales promotion.
Marketing decisions include determining what promotion mix is best as well as the message strategy. They also include determining channel/media strategies and message frequency.
If the product is seasonal, for example, getting the timing of the promotional activities right is crucial.
Marketing mix – 7Ps
There is another marketing mix that has seven elements. We call them the 7Ps because they all start with the letter ‘P.’ The seven Ps are P roduct, P lace, P rice, P romotion, P eople, P hysical Environment, and P rocess.
Regarding the 7Ps marketing mix, P rofessional Academy says:
“ Though in place since the 1980’s , the 7Ps are still widely taught due to their fundamental logic being sound in the marketing environment and marketers abilities to adapt the marketing mix to include changes in communications.”
Social media, for example, is one of the changes in communication.
Compound phrases with ‘Marketing Mix’
The term ‘Marketing Mix’ is a 2-word compound phrase. From this term we can make many 3-word compound phrases. Let’s have a look at 5 of them:
- Marketing Mix Analysis – Reviewing the strategies in the marketing mix.
- Marketing Mix Modeling – Using statistics to forecast marketing outcomes.
- Marketing Mix Optimization – Adjusting the marketing mix for best results.
- Marketing Mix Strategy – Integrating the four Ps for marketing goals.
- Marketing Mix Adaptation – Tailoring the marketing mix for different markets.
Video – What is a Marketing Mix?
This video, from our sister channel on YouTube – Marketing Business Network , explains what a ‘Marketing Mix’ is using simple and easy-to-understand language and examples.
Share this:
- Renewable Energy
- Artificial Intelligence
- 3D Printing
- Financial Glossary
Hey there! Free trials are available for Standard and Essentials plans. Start for free today.
- Marketing Mix
Marketing Mix & The 7 P’s Of Marketing
The classic marketing mix, as established by Professor of Marketing at Harvard University, Prof. James Culliton in 1948 and expanded upon by Jerome McCarthy, incorporates Product, Price, Placement, and Promotion into a theory of marketing that has been important to the industry for more than 70 years. Since then, the theory has been expanded into the 7 P's of marketing. Which are: Product, Price, Promotion, Place, People, Packaging, and Process.

You’ve got this! We’ve got your back.
Mailchimp has the tools and resources to help you plan and run effective campaigns, so you can reach your goals.
Today, we refer to these interchangeably as the 7 P's or as the Marketing Mix. Here, we will discuss this concept, its components, and answer some common questions about the marketing mix and its applications.

What is a marketing mix?
Marketing mix is a selection of marketing tools that include several areas of focus that can be combined to create a comprehensive plan. The term refers to a classification that began as the 4 P’s: product, price, placement, and promotion, and has been expanded to Product, Price, Promotion, Place, People, Packaging, and Process.
What are the 7 Ps of Marketing?
The 4 P’s marketing mix concept (later known as the 7 P’s of marketing) was introduced by Jerome McCarthy in his book: "Basic Marketing: A Managerial Approach". It refers to the thoughtfully designed blend of strategies and practices a company uses to drive business and successful product promotion. Initially 4, these elements were Product, Price, Place and Promotion, which were later expanded by including People, Packaging and Process. These are now considered to be the “7 P’s” mix elements.
It can be difficult for a small business owner or marketing manager to know how to establish a unique selling proposition or to reach the right customers, especially on new platforms like the internet, with digital marketing.
Fortunately, the 7 Ps of marketing give you a framework to use in your marketing planning and essential strategy to effectively promote to your target market.
You can also take into consideration elements of the mix in your day to day marketing decision making process with the goal to attract the right audience to successfully market to through your marketing campaigns.
The 7 elements of the marketing mix include the following:
1. Product (or Service)
Your customer only cares about one thing: what your product or service can do for them. Because of this, prioritize making your product the best it can be and optimize your product lines accordingly. This approach is called “product-led marketing.” In a marketing mix, product considerations involve every aspect of what you're trying to sell. This includes:
- Market positioning

There are five components to successful product-led marketing that are important for product marketers to take into consideration:
- Get out of the way. Let your product or service sell itself . Focus your marketing efforts on getting consumers to try what you have to offer so they can learn its value for themselves.
- Be an expert (on your customers). Know your customer's needs and use that knowledge to help communicate your product's value.
- Always be helping. Position yourself as an ally by creating informative content that meets your target customers’ needs, and they'll be more likely to buy from you. (This is also called content marketing .)
- Share authentic stories. Encourage happy customers to share their experiences and tell others why they appreciate your brand.
- Grow a product mindset. Focus on your product before you consider how to sell it. Invest in development, and the product quality will take care of the rest.
Many factors go into a pricing model. Brands may:
- Price a product higher than competitors to create the impression of a higher-quality offering.
- Price a product similar to competitors, then draw attention to features or benefits other brands lack.
- Price a product lower than competitors to break into a crowded market or attract value-conscious consumers.
- Plan to raise the price after the brand is established or lower it to highlight the value of an updated model.
- Set the base price higher to make bundling or promotions more appealing.
Consider what you're trying to achieve with your pricing strategy and how price will work with the rest of your marketing strategy. Some questions to ask yourself when selling products:
- Will you be offering higher-end versions at an additional cost?
- Do you need to cover costs right away, or can you set a lower price and consider it an investment in growth?
- Will you offer sales promotions?
- How low can you go without people questioning your quality?
- How high can you go before customers think you’re overpriced?
- Are you perceived as a value brand or a premium brand?
3. Promotion
Promotion is the part of the marketing mix that the public notices most. It includes television and print advertising, content marketing, coupons or scheduled discounts, social media strategies , email marketing , display ads, digital strategies , marketing communication, search engine marketing, public relations and more.
All these promotional channels tie the whole marketing mix together into an omnichannel strategy that creates a unified experience for the customer base. For example:
- A customer sees an in-store promotion and uses their phone to check prices and read reviews.
- They view the brand's website , which focuses on a unique feature of the product.
- The brand has solicited reviews addressing that feature. Those reviews appear on high-ranking review sites.
- The customer buys the product and you’ve sent a thank you email using marketing automation .
Here are the ways you can use these channels together:
- Make sure you know all the channels available and make the most of them to reach your target audience.
- Embrace the move toward personalized marketing .
- Segment your promotional efforts based on your customers' behavior.
- Test responses to different promotions and adjust your marketing spend accordingly.
- Remember that promotion isn't a one-way street. Customers expect you to pay attention to their interests and offer them solutions when they need them.
Where will you sell your product? The same market research that informed your product and price decisions will inform your placement as well, which goes beyond physical locations. Here are some considerations when it comes to place:
- Where will people be looking for your product?
- Will they need to hold it in their hands?
- Will you get more sales by marketing directly to customers from your own e-commerce website, or will buyers be looking for you on third-party marketplaces?
- Do you want to converse directly with your customers as they purchase, or do you want a third party to solve customer service issues?

People refers to anyone who comes in contact with your customer, even indirectly, so make sure you're recruiting the best talent at all levels—not just in customer service and sales force.
Here’s what you can do to ensure your people are making the right impact on your customers:
- Develop your marketers’ skills so they can carry out your marketing mix strategy
- Think about company culture and brand personality .
- Hire professionals to design and develop your products or services.
- Focus on customer relationship management, or CRM , which creates genuine connections and inspires loyalty on a personal level.
6. Packaging
A company's packaging catches the attention of new buyers in a crowded marketplace and reinforces value to returning customers . Here are some ways to make your packaging work harder for you:
- Design for differentiation. A good design helps people recognize your brand at a glance, and can also highlight particular features of your product. For example, if you’re a shampoo company, you can use different colors on the packaging to label different hair types.
- Provide valuable information. Your packaging is the perfect place for product education or brand reinforcement. Include clear instructions, or an unexpected element to surprise and delight your customers.
- Add more value. Exceed expectations for your customers and give them well-designed, branded extras they can use, like a free toothbrush from their dentist, a free estimate from a roofer, or a free styling guide from their hairdresser.
Prioritize processes that overlap with the customer experience. The more specific and seamless your processes are, the more smoothly your staff can carry them out. If your staff isn't focused on navigating procedures, they have more attention available for customers—translating directly to personal and exceptional customer experiences.
Some processes to consider:
- Are the logistics in your main distribution channel cost-efficient?
- How are your scheduling and delivery logistics?
- Will your third-party retailers run out of product at critical times?
- Do you have enough staff to cover busy times?
- Do items ship reliably from your website?
If you get more than one customer complaint about any process, pinpoint what's going wrong and figure out how to fix it.
Marketing mix FAQs
Understanding marketing mix and the 7 P’s can bring up a lot of questions. Below, we’ve answered some frequently asked questions to help you identify and establish your own marketing mix.

What is a marketing mix example?
A good example of the marketing mix might be a convenience store. In this instance, we might consider a chain of convenience outlets that provide a wide range of products including fresh and packaged food, tools, household, and kitchen items, novelties, magazines, etc.
- Product : Chiefly, foods and various items located and packaged in a way that provides convenience and utility.
- Price : Pricing will be considered competitive with supermarkets, with some exceptions where convenience, novelty, and fun add special appeal.
- Place : Locations should be amenable to the value proposition of convenience. As such, locations should be strategically positioned near residential areas, shopping centers, educational centers, etc.
- Promotion : Advertising will be largely constrained to posted promotional material, the outlet buildings themselves, local social media pages, and so on.
Here, we will consider the customer experience as the opportunity to access simple food items, snacks, and a range of useful products for home, recreation, and more.
Another example might be a streaming service. Here our 4 P's are as follows:
- Product : Original quality entertainment and convenient viewing access.
- Price : Free trial offer, premium packages, and a commercial free subscription level.
- Place : The subscriber's digital device.
- Promotion : Extended advertising across a range of channels and platforms, including high-value metropolitan billboards, magazines, and word of mouth.
Here, the customer experience is appealing, long-form video content primarily in the form of popular TV, films, comedy specials, and more with an emphasis on convenient home viewing.
What are the types of marketing mix?
In reality, there are as many types of marketing mixes as there are functioning businesses in the world. To make things simpler, we might try to make our model fit within one of 7 common, established marketing mix types as listed below.
- Product Mix
- Product Progression and Product Life Cycle
- Market Coverage Mix (aka Positioning Mix)
- Service Mix
- Marketing Program Mix (or Promotional Mix)
- Channel Mix/Vertical Integration
- Global Marketing Mix (or International Marketing Mix)
As you can see, making a given company's value proposition and promotional needs fit into one of these categories might not work well. Our convenient store example might fit into the service mix since convenience is the primary value we would be offering. But our streaming service might also be called a "service mix,” or even a "product mix."
In most cases, it is best to generate an original marketing mix that describes the marketing needs of a real life organization.
What are the 4 P’s of marketing mix?
The 4 P's are Product, Price, Place, and Promotion.
- Product : The product is an item or service for sale. For marketing purposes, we should consider who it is for and why they would want it. We should also consider and compare our offering to that of the competition.
- Price : This is the amount customers will be willing or required to pay. Often, making prices competitive is a significant challenge. In cases where prices cannot be lowered below the market benchmark, additional value may need to be added to the offer.
- Place : This is the location/s where the product or service can be accessed and where it is used. For a restaurant, location is everything. For a streaming service, it is the user's home or the location where they buy computer devices and services.
- Promotion : This describes how, where, and how frequently advertising materials will be produced and where they appear. With our convenience store, the promotional material is largely on and in the store itself. With our streaming service, it would be in locations all over the web and any other appropriate location/media.
The takeaway
The marketing mix and the 7 P's of marketing are a guide to drafting and creating an outreach campaign for any given commercial enterprise. They are guidelines that help us cover all of our bases when it comes to brand outreach. It should be borne in mind that branding considerations are not covered in the concepts covered by these promotional frameworks.
The elements of these guidelines work together to create a functional framework for the creation of a complete marketing plan.
Develop your marketing mix and integrate it into your marketing essentials. As you develop your marketing mix, consider how each element affects the rest to create a unified brand experience for your consumers, from the user experience to the perceived value of your product. Think about how a product's price changes its promotion strategy, how specifications will contribute to pricing, and how your people carry out processes. Ensure that your people and the tools they use can communicate with each other, and use the right tools to reach the right people.
Take your business to the next level
- The Program
- Manufacturing
- Construction

The 4 P’s of Marketing Mix and how to master it in today's world (updated with example and template)
This article addresses how to use one of the oldest marketing concepts in today's online world: "The Marketing Mix," which is based on the 4 P's: Product, Price, Place and Promotion.
If you’re ready to take your marketing seriously, you’ll need to start with a marketing plan. A classic marketing concept called “The Marketing Mix” or “The 4 P’s” of Marketing is a perfect place to start.
The original concept of the 4 P's marketing mix

The original marketing mix, or 4 P's, as originally proposed by marketer and academic Jerome E. McCarthy , provides a framework for marketing decision-making. Effectively summing up the 4 pillars of the business cycle, McCarthy's marketing mix has since become one of the most enduring and widely accepted frameworks in business.
The essential base ingredients of the 4 P’s are: Product , Price , Place and Promotion . While this combination doesn’t appear to be rocket science, a company’s ability or lack thereof to embrace and implement the 4 P’s can make all the difference between thriving and failing as a business.
Each of the 4 P’s build upon and interact with one another, and are governed by both internal and external factors within the business itself, and our ever-changing marketplace. The 4 P’s of marketing primary purpose is to help us take into consideration potential roadblocks to widespread product adaptation and ongoing success.
So let’s get to them, shall we?
4 P's of marketing in simple and familiar terms:
A PRODUCT is a service or good offered to meet consumer interest or demand. It could come in the form of occupational therapy or a fidget spinner - choices are only limited to the imagination, BUT, are highly dependent on marketplace curiosity or need.
PRICE is the cost people pay for a product. This includes base costs (materials, manufacturing, and shipping) plus expenses (rent, office supplies, healthcare, etc.). While you should always look to the competition, a smart business will tap into what people will actually pay for it. That's the only thing that counts. If you can't rise above your bottom line and make your target profit, then it’s a losing proposition.
PLACE is the “home” where the product resides, and that “home” can live in many different channels, such as a physical store display, a newspaper, radio or TV ad, or a website or blog spotlight. Really, a place is anywhere you can get your product in front of your target customers that compliments your budget, including the price point.
PROMOTION is product exposure and public relations efforts via advertising (through the channels mentioned above) as well as word of mouth, direct mail, email marketing and social media. Promotion is a communication tool that encapsulates the first 3 P’s by putting the right product in the right place, at the right price, at the right time, with the goal of it being irresistible to customers.
The 4 P's example and template for a service business
The Marketing Mix of “HVAC Plumber” reflects a real life example of how a service company covers the 4 P’s (Product, Price, Place, Promotion) in their marketing strategy.
“HVAC plumber” (a fictitious company) provides heating and cooling services in the Chicago Metropolitan Area.
HVAC Plumber marketing mix elements strategy and example:
HVAC Plumber offers industry standard services, but also innovates to provide more value to our customers and captures more of the market. We are insured, licensed and provide warranties for our work. Our high quality services and focus on a pleasant customer experience helps us get repeat clients, referrals, and builds our reputation. Also, our motto is: “Leave the place cleaner than we found it” - so you’ll always see us with a broom in our hands before we leave.
At present, the following are the main categories of HVAC Plumber products:
- Furnace installation and repair
- Water heater maintenance, installation and repair
- Air conditioning installation, maintenance and repair
- Complete plumbing system design and installation
- Drain, sink and toilet unclogging and jet rodding and repairs
Our extra value added products:
- Emergency services
- Indoor air quality testing services
- Air duct and dryer vent cleaning services
- Warranty services
- Equipment sales
Our reputation and successful marketing generates more demand than we can handle, so it allows us to charge premium for our services. We train our service technicians to upsell our other services. We also have a customer loyalty program in place to reward our long-term clients with better rates and provide coupons to first time clients. We also seek partnerships with organizations such as: homeowner associations, insurance companies, builders and general contractors, and offer exclusive pricing options based on quantity.
The company has offices in downtown Chicago, but walk-in customers are unusual. We are physically represented by our company vans, uniforms and warranty stickers. We consistently attend industry trade shows, and belong to the Chicago Chamber of Commerce.
We nurture partnerships with our equipment vendors, participate in their trainings, and have certifications, which allow us to be listed “licensed technicians” on their websites. We serve the Chicagoland Area, which is about a 30 mile radius from our warehouse, but we do make travel exceptions for long-term clients and bigger projects.
Our company website is the most important communication tool, and is a place where our clients learn about our services and make initial contact. We invest a great deal of money and time to keep it updated and useful to our audience. We plan to expand our website to include ecommerce and make some of the package services, equipment and accessories available for purchase online. None of our competitors are doing this at the moment, so we’ll take advantage of being pioneers in this regard.
Most new business comes through our website and we focus all of our promotion efforts to drive more traffic to it. Our promotional mix is as follows:
- Search engine optimization
- Paid traffic
- Social media marketing
- Content marketing
- Email marketing
Our value proposition statement
HVAC Plumber is an industry-leading HVAC and plumbing service provider serving the Chicago area since 1999. We specialize in new installations, repairs, and 24 hour emergency services.
Start with 4 P's of marketing template
Check out our 4 P's of marketing template to help you work through your first few ideas.
But why stop there?
The 7 P’s of marketing mix
Since the inception of the original 4 P’s of marketing, marketing experts have expounded upon the mix to include three additional P’s to enhance brand exposure and sales performance.
These additional P’s include: People , Process and Physical evidence .
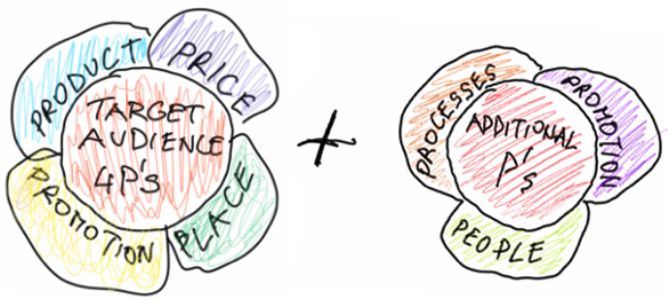
PEOPLE have always been at the epicenter of the business world. Whether it’s the company visionaries, the movers and shakers, or the daily doers, unless (or until) commerce is fully automated, you’re only as good as the people who keep the business operational and flowing. And believe you me, customers are quick to notice when there’s a glitch in the matrix.
PROCESSES ensure consistent service delivery to every customer, at any time of day, on any given day. And, a successful business incorporates scenarios where customer preferences can be accommodated to provide them a unique experience.
PHYSICAL EVIDENCE – Almost all services include physical proof of a transaction, even if the bulk of what the consumer bought isn’t tangible. It’s something the customer can hold onto and recall about working with you. Physical evidence also describes consistent branding across communication channels.
How can you actually use this?
How the 4 P’s apply in today’s online marketing
The how’s and why’s of how we approach marketing have become much more dynamic since the inception of the internet. However, the driving factor is still and should always remain: PEOPLE. Actually, it’s more about people than ever before. Having an honest marketing approach has never been more important and is both emotionally and financially rewarding if you do it right.

PRODUCT and how it lives online versus the shelf
It seems like not much has changed as far as the product or services goes, right? Wrong. No matter what type of product you offer, the landscape shifted majorly to the consumer benefit. The majority of customers now prefer to shop online, and perform in-depth research before making their buying decisions.
Besides the original, product-related marketing factors such as: product quality and design, branding, packaging, returns and guarantees, in your marketing plan, you should also consider NEW factors.
User-centric customer support - your product now has a digital voice. And it must talk to your audience and be both personalized and timely. Not only across all the common channels such as phone or email, but also should be proactively involved in social media. Resource: Social media customer service 101: the beginner's guide
New PRICING models to consider

Pricing your product or service is never an easy task. It sure helps if you can find a unique product positioning on the market, otherwise you fall into price comparison wars with your competition. And, to compare prices has never been easier than today. The original Marketing Mix suggests considering pricing strategy and tactics, discount structure, payment terms and options for both customers and distributors.
Competition pricing research - this is an in-depth review of the pricing models of your direct competitors. In comparing products, you should focus worldwide. With local services, of course, should compare within your own service area. Remember that you don’t have to anchor your pricing based on competition, but it helps to know the market.
Shipping and handling strategy - it’s not an obvious, but very important factor in online sales conversions no matter the item price. Offering free shipping is one of the most effective purchase incentives. Resource: How to offer free shipping and still make money

"9 out of 10 online shoppers consider free shipping as one of the main reasons why they shop at a particular online store. To offer free shipping is not a new thing, thanks to Amazon it became essential running an online store. The main question now is how to make it profitable. It looks impossible, but with the right approach - offering it most, not all, of the time, setting a flat shipping or order threshold, it is possible."
Diana Bukevicius - Scube Marketing
Product positioning - I know I’m repeating myself, but I have to. Positioning is strongly engraved into each pillar of The Marketing Mix. As far as pricing goes, having strong niche positioning eliminates the number of competitors that your product or service can be compared with and it opens up an opportunity to go for value pricing . Resource: Everything you need to know about pricing
Upsell strategy - this is an underestimated source of cash flow. It’s always easier to sell to the people that already bought something from you and were happy with the product. It can be an additional items or warranties, maintenance or a product upgrade.
PLACE for marketing is now on the mobile screens
Back in the 1940’s “place” was all about brick and mortar. Location, distribution, and logistics are still part of the process, but it heavily shifted from the marketing department to operations. No doubt you’ll boost sales if your product gets featured in physical Walmart stores, but you also can sell at Walmart Marketplace online with way less effort for the approval process. Same goes for Amazon. Online selling has undoubtedly taken over as the place to peddle your wares. Resource: How to sell on Walmart marketplace in 7 easy steps

Website - this is by far your most important marketing piece. It’s your 24/7 storefront and your sales rep that never sleeps. Any marketing efforts that you take will end up on your website. I mentioned 3rd party sources like Walmart Marketplace or Amazon, but I still highly recommend you focus on your own website first and use other sources as secondary. Why? Because you own it and you control it.
Any 3rd party retailer could change their policies tomorrow and you might be out of business. Plus, websites grow more powerful over time if supported by thoughtful and consistent marketing decisions. When you build your website, the decisions on design, structure and content should be made based on your promotional strategies.

3rd party platforms - Your audience is on or a few of these platforms already. Identify those platforms and utilize them. It can take the form of direct eCommerce platforms like Amazon, or it can be social channels like LinkedIn or Facebook etc.
PROMOTION is in your inbox
Search engine optimization (SEO), social media, email marketing and paid search. I hear that Super Bowl ads are worth their weight in gold, but if you can afford a Superbowl ad, you are on the wrong blog!
Jokes aside, make sure your marketing strategy is built around driving traffic to your website and converting it to leads or sales.

Traffic generation - getting targeted visitors to come to your website is the ultimate #1 goal. There are numerous ways you can achieve that, and they’re all worth considering:
Search engine optimization (SEO) - is the practice driving traffic to your website through organic search engine results by optimizing (making relevant) your website for targeted keyphrases. SEO is an ongoing process that requires patience and consistent efforts.
Paid search - in other words - “bought traffic.” Platforms like Google AdWords, Bing Ads or Facebook Ads allows you to buy highly targeted traffic in an auction-type of fashion. It’s typically based on “per click” pricing, where each visitors cost you x amount of dollars.
Social media marketing - is the process of gaining traffic or attention through social media sites. If you sell to people then it’s a great idea to invest time and effort (and sometimes money) into one or several social media sites. That’s where the people hang-out these days. Resource: Welcome to the beginner's guide to social media!
Email marketing - is the modern equivalent of oldschool direct mail, I believe. Even if one more email in our inbox is the last thing we want or need - email is still one of the best performing marketing tools. Resource: A beginner’s guide to successful email marketing Resource: A comprehensive guide to email marketing platforms
Conversion rate optimization - converting website visitors into leads is the ultimate goal #2 to achieve. Firstly, to be able to calculate conversions you need to have Google Analytics or other tracking system integrated to your website. Conversion rate optimization are an ongoing process where you optimize your website and measure the outcome looking for the optimal version of each page. Resource: Conversion optimization made simple: a step-by-step guide Resource: Learn Google Analytics with free online courses
2 extra P’s from Angle180
The team at Angle180 takes the “4 P's of marketing (Plus 3)” two steps further, to include Positioning and Positive Reviews.
Positioning - again and again. Positioning is a fundamental piece of your marketing plan and your overall business success. Essentially, if you answer all the questions related to each P you’ll arrive to your business positioning statement.
Positioning is how you differentiate your product or service from your competitors in your niche market.
A good positioning statement is the first thing people read when they visit your website. Typically, it’s a 7-10 word sentence on your Home Page that succinctly answers:
There’s a science behind positioning, and it’s wise to research how others in your field describe themselves.

Positive reviews - positive online reviews are pretty self explanatory, but I recommend creating a strategy for collecting positive reviews, as well as dealing with negative ones.
Unfortunately, it’s human nature to take positive experiences for granted and feel revengeful about the negative ones.
Reviews definitely affect local search rankings and customer buying decisions.
Local consumer review survey by BrightLocal reveals the importance of reviews:
97% of consumers read online reviews for local businesses in 2017
85% of consumers trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations
49% of consumers need at least a four-star rating before they choose to use a business
Responding to reviews is more important than ever, with 30% naming this as key when judging local businesses
4 P's of Marketing Mix in a slideshow presentation (PPT) and downloadable PDF
Here is a PDF version of 4 P's of marketing presentation.
Our conclusion? The original 4 P’s of the marketing mix withstand the test of time
There is one common trait to all classic things - they never get old or obsolete. So, even with all the changes that technology has brought us, the 80 year concept of The 4 P’s of marketing mix are still relevant and applicable today. Marketing platforms and tools have certainly changed, but the foundation is rock solid. And, let’s hope it always remains personalized and people-driven.

I'm Sarunas Budrikas, CEO of Angle180, a B2B marketing company delivering results through high performance web design and traffic generation.
You can also find me on LinkedIn and Twitter .

Get news and tips to grow your business
© 2009-2024 Angle180 141 W. Jackson Blvd., Chicago, IL 60604 (720) 575-0003 , (847) 439-6226 Privacy Policy
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. By continuing to use the site, you consent to the use of these cookies and agree to our privacy policy .
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Market Analysis for a Business Plan

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
A lot of preparation goes into starting a business before you can open your doors to the public or launch your online store. One of your first steps should be to write a business plan . A business plan will serve as your roadmap when building your business.
Within your business plan, there’s an important section you should pay careful attention to: your market analysis. Your market analysis helps you understand your target market and how you can thrive within it.
Simply put, your market analysis shows that you’ve done your research. It also contributes to your marketing strategy by defining your target customer and researching their buying habits. Overall, a market analysis will yield invaluable data if you have limited knowledge about your market, the market has fierce competition, and if you require a business loan. In this guide, we'll explore how to conduct your own market analysis.
How to conduct a market analysis: A step-by-step guide
In your market analysis, you can expect to cover the following:
Industry outlook
Target market
Market value
Competition
Barriers to entry
Let’s dive into an in-depth look into each section:
Step 1: Define your objective
Before you begin your market analysis, it’s important to define your objective for writing a market analysis. Are you writing it for internal purposes or for external purposes?
If you were doing a market analysis for internal purposes, you might be brainstorming new products to launch or adjusting your marketing tactics. An example of an external purpose might be that you need a market analysis to get approved for a business loan .
The comprehensiveness of your market analysis will depend on your objective. If you’re preparing for a new product launch, you might focus more heavily on researching the competition. A market analysis for a loan approval would require heavy data and research into market size and growth, share potential, and pricing.
Step 2: Provide an industry outlook
An industry outlook is a general direction of where your industry is heading. Lenders want to know whether you’re targeting a growing industry or declining industry. For example, if you’re looking to sell VCRs in 2020, it’s unlikely that your business will succeed.
Starting your market analysis with an industry outlook offers a preliminary view of the market and what to expect in your market analysis. When writing this section, you'll want to include:
Market size
Are you chasing big markets or are you targeting very niche markets? If you’re targeting a niche market, are there enough customers to support your business and buy your product?
Product life cycle
If you develop a product, what will its life cycle look like? Lenders want an overview of how your product will come into fruition after it’s developed and launched. In this section, you can discuss your product’s:
Research and development
Projected growth
How do you see your company performing over time? Calculating your year-over-year growth will help you and lenders see how your business has grown thus far. Calculating your projected growth shows how your business will fare in future projected market conditions.
Step 3: Determine your target market
This section of your market analysis is dedicated to your potential customer. Who is your ideal target customer? How can you cater your product to serve them specifically?
Don’t make the mistake of wanting to sell your product to everybody. Your target customer should be specific. For example, if you’re selling mittens, you wouldn’t want to market to warmer climates like Hawaii. You should target customers who live in colder regions. The more nuanced your target market is, the more information you’ll have to inform your business and marketing strategy.
With that in mind, your target market section should include the following points:
Demographics
This is where you leave nothing to mystery about your ideal customer. You want to know every aspect of your customer so you can best serve them. Dedicate time to researching the following demographics:
Income level
Create a customer persona
Creating a customer persona can help you better understand your customer. It can be easier to market to a person than data on paper. You can give this persona a name, background, and job. Mold this persona into your target customer.
What are your customer’s pain points? How do these pain points influence how they buy products? What matters most to them? Why do they choose one brand over another?
Research and supporting material
Information without data are just claims. To add credibility to your market analysis, you need to include data. Some methods for collecting data include:
Target group surveys
Focus groups
Reading reviews
Feedback surveys
You can also consult resources online. For example, the U.S. Census Bureau can help you find demographics in calculating your market share. The U.S. Department of Commerce and the U.S. Small Business Administration also offer general data that can help you research your target industry.
Step 4: Calculate market value
You can use either top-down analysis or bottom-up analysis to calculate an estimate of your market value.
A top-down analysis tends to be the easier option of the two. It requires for you to calculate the entire market and then estimate how much of a share you expect your business to get. For example, let’s assume your target market consists of 100,000 people. If you’re optimistic and manage to get 1% of that market, you can expect to make 1,000 sales.
A bottom-up analysis is more data-driven and requires more research. You calculate the individual factors of your business and then estimate how high you can scale them to arrive at a projected market share. Some factors to consider when doing a bottom-up analysis include:
Where products are sold
Who your competition is
The price per unit
How many consumers you expect to reach
The average amount a customer would buy over time
While a bottom-up analysis requires more data than a top-down analysis, you can usually arrive at a more accurate calculation.
Step 5: Get to know your competition
Before you start a business, you need to research the level of competition within your market. Are there certain companies getting the lion’s share of the market? How can you position yourself to stand out from the competition?
There are two types of competitors that you should be aware of: direct competitors and indirect competitors.
Direct competitors are other businesses who sell the same product as you. If you and the company across town both sell apples, you are direct competitors.
An indirect competitor sells a different but similar product to yours. If that company across town sells oranges instead, they are an indirect competitor. Apples and oranges are different but they still target a similar market: people who eat fruits.
Also, here are some questions you want to answer when writing this section of your market analysis:
What are your competitor’s strengths?
What are your competitor’s weaknesses?
How can you cover your competitor’s weaknesses in your own business?
How can you solve the same problems better or differently than your competitors?
How can you leverage technology to better serve your customers?
How big of a threat are your competitors if you open your business?
Step 6: Identify your barriers
Writing a market analysis can help you identify some glaring barriers to starting your business. Researching these barriers will help you avoid any costly legal or business mistakes down the line. Some entry barriers to address in your marketing analysis include:
Technology: How rapid is technology advancing and can it render your product obsolete within the next five years?
Branding: You need to establish your brand identity to stand out in a saturated market.
Cost of entry: Startup costs, like renting a space and hiring employees, are expensive. Also, specialty equipment often comes with hefty price tags. (Consider researching equipment financing to help finance these purchases.)
Location: You need to secure a prime location if you’re opening a physical store.
Competition: A market with fierce competition can be a steep uphill battle (like attempting to go toe-to-toe with Apple or Amazon).
Step 7: Know the regulations
When starting a business, it’s your responsibility to research governmental and state business regulations within your market. Some regulations to keep in mind include (but aren’t limited to):
Employment and labor laws
Advertising
Environmental regulations
If you’re a newer entrepreneur and this is your first business, this part can be daunting so you might want to consult with a business attorney. A legal professional will help you identify the legal requirements specific to your business. You can also check online legal help sites like LegalZoom or Rocket Lawyer.
Tips when writing your market analysis
We wouldn’t be surprised if you feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information needed in a market analysis. Keep in mind, though, this research is key to launching a successful business. You don’t want to cut corners, but here are a few tips to help you out when writing your market analysis:
Use visual aids
Nobody likes 30 pages of nothing but text. Using visual aids can break up those text blocks, making your market analysis more visually appealing. When discussing statistics and metrics, charts and graphs will help you better communicate your data.
Include a summary
If you’ve ever read an article from an academic journal, you’ll notice that writers include an abstract that offers the reader a preview.
Use this same tactic when writing your market analysis. It will prime the reader of your market highlights before they dive into the hard data.
Get to the point
It’s better to keep your market analysis concise than to stuff it with fluff and repetition. You’ll want to present your data, analyze it, and then tie it back into how your business can thrive within your target market.
Revisit your market analysis regularly
Markets are always changing and it's important that your business changes with your target market. Revisiting your market analysis ensures that your business operations align with changing market conditions. The best businesses are the ones that can adapt.
Why should you write a market analysis?
Your market analysis helps you look at factors within your market to determine if it’s a good fit for your business model. A market analysis will help you:
1. Learn how to analyze the market need
Markets are always shifting and it’s a good idea to identify current and projected market conditions. These trends will help you understand the size of your market and whether there are paying customers waiting for you. Doing a market analysis helps you confirm that your target market is a lucrative market.
2. Learn about your customers
The best way to serve your customer is to understand them. A market analysis will examine your customer’s buying habits, pain points, and desires. This information will aid you in developing a business that addresses those points.
3. Get approved for a business loan
Starting a business, especially if it’s your first one, requires startup funding. A good first step is to apply for a business loan with your bank or other financial institution.
A thorough market analysis shows that you’re professional, prepared, and worth the investment from lenders. This preparation inspires confidence within the lender that you can build a business and repay the loan.
4. Beat the competition
Your research will offer valuable insight and certain advantages that the competition might not have. For example, thoroughly understanding your customer’s pain points and desires will help you develop a superior product or service than your competitors. If your business is already up and running, an updated market analysis can upgrade your marketing strategy or help you launch a new product.
Final thoughts
There is a saying that the first step to cutting down a tree is to sharpen an axe. In other words, preparation is the key to success. In business, preparation increases the chances that your business will succeed, even in a competitive market.
The market analysis section of your business plan separates the entrepreneurs who have done their homework from those who haven’t. Now that you’ve learned how to write a market analysis, it’s time for you to sharpen your axe and grow a successful business. And keep in mind, if you need help crafting your business plan, you can always turn to business plan software or a free template to help you stay organized.
This article originally appeared on JustBusiness, a subsidiary of NerdWallet.
On a similar note...

Plan Projections
ideas to numbers .. simple financial projections
Home > Business Plan > Marketing Strategy in a Business Plan

Marketing Strategy in a Business Plan
… we will get this market share by …
- Product USP : Why buy our product? What characteristics does the product have to meet customer needs?
- Promotion : What marketing activities will be undertaken? What means of communication will the business use to persuade customers of the benefits of the product? Will it use above the line promotion or below the line promotion?
- Place : What are the distribution channels? How is the business going to reach customers with its product?
- Price : What price will the business charge for the product, and what goal is it pursuing with the pricing strategy? Will the business use premium, penetration, economy or skimming pricing strategies.
Marketing Strategy Presentation
The marketing strategy section of the business plan can be presented in four sections relating to each of the four P’s product, promotion, place, and price as shown in the example layout below.
The marketing strategy is a key section of the business plan, at this stage you are not trying to present a complete marketing plan, but simply trying to show the investor that each major section of the marketing strategy has been thought about and that you have a good marketing mix.
All of the four sections should be consistent with and support each other, for example, if you are planning to adopt a high price strategy, then the product would be aimed at an upmarket target customer, distributed at high end stores, and make use of one to one personal selling.
This is part of the financial projections and Contents of a Business Plan Guide , a series of posts on what each section of a simple business plan should include. The next post in this series sets out the business model which the business intends to use to generate revenue.
About the Author
Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Plan Projections. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University.
You May Also Like
- Revolutionizing Digital Communication: The Power of Olly and AI
- AI-Powered Video Editing with Snapy.ai: The Future of Content Creation is Here
- Dawn of AI-Powered Video Editing: Transform Your Videos with Silence Remover Online
- The Dawn of Generative AI: Why and How to Adopt it for your Business
- Harnessing the Power of Generative AI for Business Innovation: An Exclusive Consultancy Approach
Original content with a single minded focus on value addition.
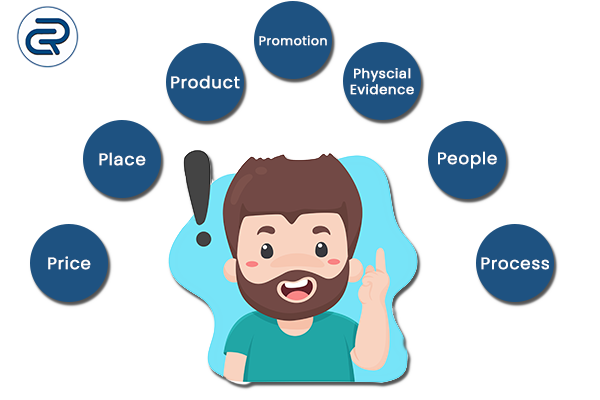
7Ps of Marketing Mix: Explained well with examples
Learn everything about the 7Ps of Marketing mix, Understand why this concept is still relevant today and will be relevant for the foreseeable future. The 7Ps of Marketing is the Price, Place, Promotion, Product, People, Process and finally, Physical Evidence.
It originally started as 4 Ps, but as the world, and the complexities of marketing grew; 3 more were added to formulate an effective marketing strategy. The ‘P’s stand for each of the pillars of a marketing strategy, and together are a part of the concept called the ‘marketing mix’. The term ‘marketing mix’ sounds a little confusing, but in essence, it is a foundation model for businesses. More easily explained, it is the operational part of a marketing plan- the nuts and bolts of it.
Funfact, there are actually 9Ps of Marketing: The above 7+2 viz. Packaging and Payments. But the 7Ps are popular given their wide and timeless application in the World of Marketing. Anyway, let’s just straight in the post.

The 7Ps of Marketing: With Examples
We can understand this with the example of a rainbow. The 7 colours of a rainbow and the 7Ps in a marketing mix bear a resemblance. Just as not all rainbows have the same the composition of the VIBGYOR colours, the same way every marketing plan is unique and contains varying amounts of the 7Ps of the marketing mix. The components are explained in the following points
One very important aspect of any product/success being a success in the market is the price at which it is marketed. The first colour of the marketing mix rainbow is one of the determining factors of what the people will see. Marketers tread very carefully while setting a price that is a win-win situation for both the company as well as the consumers.
There are several pricing models. One of the most famous ones is Competitive Pricing Strategy as is used by Coca-Cola. Coca-Cola’s main aim is to penetrate the markets and achieve the highest market share without compromising on its customer base and product positioning. Thus, the company charges its consumers what its competitor Pepsi is charging. It’s a simple, yet highly competitive strategy as the name suggests.
It is the channel through which your company’s goods/services get moved from the manufacturer to the consumer. Your good/service will need to be brought into the market through a mechanism, and ‘place’ is exactly that- a way for your offering to be seen by the correct audience. An example of this element of the marketing mix can be the numerous branches of McDonald’s all over the world. Almost every country in the world either has a McDonald’s franchisee, or knows of it. And each country has its unique menu, with the standard guarantee of tasty food, served fast, at low prices.
The Product
This is the P that starts it all. The need for this P to be known, positioned, and showcased gets the marketers working hard at strategies. ‘Product’ is the offering that your company has for the market whether it is a tangible good or intangible good (services). The product development has various stages, and it is instrumental in being the deciding factor in many strategies. Various aspects of a product like the product life cycle, the type of need it services, and its positioning come into play with this P.
We can consider the example of Starbucks here, which was solely established to make good quality coffee and coffee beverages accessible to people. Starbucks’ approach to marketing is very focused on its product and the quality of the product provided to its customers.
The Promotion
Directly speaking, the mainstream meaning of the word ‘Promotion’ also applies here. The essence of promotion lies in the activities that a marketer does in order to showcase the product in the market in the right sense. Promotional activities involve multi-channel, multi-level marketing communications in the technical sense. In a more simplistic sense, these activities are the communications that the companies indulge in like advertising, direct calling, using social media channels, as well as print media. There are many instances of how promotional activities have set a product apart from its competitors in the industry. One such is the launch of Sony Xperia Z3 Dual in 2014 as an underwater pop-up store.
The Physical Evidence
Physical evidence is a part of the product. If your product is a tangible offering, then all of its material cues (packaging, business cards, brochures, company branding) will be taken notice of, by the consumers. However, these tangible cues are also attached to a product that is intangible. The example can be, every time you encounter a FedEx delivery vehicle, you’ll immediately recognize it because of its purple and orange color scheme. That’s how they’re set apart from all the other delivery companies.
All the people involved in the making, distributing, and selling of your company’s product are also essential. Mostly, services (intangible offerings) have marketing mixes which are focused on the people presenting the product. The employees you have in the store, the delivery personnels, the sales executives, all of it and more leave a lasting impression on the people. Hotels like Taj, Hyatt, JW Marriott are known for the people that work there to serve the consumers. These brands have established themselves and built loyal customer bases due to the kind of people they employ.
The Process
Process involves all the ways the company and its customers can engage in order to facilitate the product to reach the consumer. It’s a map of how the company and its offerings are accessible to the market. It isn’t just a means to an end, but a roadmap of the company’s operations.
Here again, we can consider Starbucks as it has so many different ways in which the company operates- joint ventures, retail store licensing operations, food service accounts, depending on which country they’re operating in. They have an interactive website in order to collect customer feedback and suggestions, which also tells people how accessible the company is for the consumers.
Now, rounding up these 7 colors of the rainbow. We see that all these aspects ring in something essential for the business to gain competitive advantage. Though every product, every industry will have a unique marketing mix, the underlying structure will always be based on these 7 elements.
The 9Ps of Marketing you say?
Well yes, in the recent times, there appears to have introduced 2 more Ps vs earlier mix, now making the concept 9Ps of Marketing mix. We’ll keep this one short given you’ve gotten the gist. The 8th P is Packaging. Why? Given how connected the packaging has become to a customers journey, we cannot really let this one go, can we? Take the example of Paper Boat, the reason it connects so well is because of the simple packaging.
The 9th P of Marketing is Payments, it talks about the initiatives that companies can undertake in order to make your payment procedure a little more simple. That is introduce one click payment, EMI options, etc.
Anyway, that is all.
And well, the Author
No, this isn’t the 10th P of marketing. However, we believe, given the world has evolved today, there must exist a new P, a new dimension of Marketing. Something around Data Analytics, maybe, Programming? eh?
Anyway, the piece was written by Mahek Mirchandani , a co-author at Casereads. We’ve uploaded 10+ MBA starter concepts to kick start your MBA journey, directly click here .
Before you go, if you liked this piece, and if you have a friend starting their MBA; Why not be a good friend and share this with them on WhatsApp ?
7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 9Ps of marketing, 9Ps of marketing, 9Ps of marketing, 9Ps of marketing, 9Ps of marketing, 9Ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing
- What is WACC in Finance? Everything you need to know
- Ola case study: The story of a Millionaire without a car
You May Also Like

What is the Iceberg principle in Marketing?

Understanding the meaning of Financial Markets

The 101 of Packaging Design
2 thoughts on “ 7ps of marketing mix: explained well with examples ”.
Pingback: Story Of Paper Boat: A Nostalgic Walk Down The Memory Lane
Pingback: McKinsey 7s Framework With Examples
Comments are closed.

- List of Commerce Articles
- Marketing Mix
What Is Marketing Mix - 4 P and and 7 P of Marketing
Definition of marketing mix.
The marketing mix is defined by the use of a marketing tool that combines a number of components in order to become harden and solidify a product’s brand and to help in selling the product or service. Product based companies have to come up with strategies to sell their products, and coming up with a marketing mix is one of them.
Table of Content
- Marketing Mix 4P
- 7Ps of Marketing
- Marketing Mix Example
Marketing Mix Product
Importance of marketing mix, questions on marketing mix, what is marketing mix.
Marketing Mix is a set of marketing tool or tactics, used to promote a product or services in the market and sell it. It is about positioning a product and deciding it to sell in the right place, at the right price and right time. The product will then be sold, according to marketing and promotional strategy. The components of the marketing mix consist of 4Ps Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. In the business sector, the marketing managers plan a marketing strategy taking into consideration all the 4Ps. However, nowadays, the marketing mix increasingly includes several other Ps for vital development.
What is 4 P of Marketing

A product is a commodity, produced or built to satisfy the need of an individual or a group. The product can be intangible or tangible as it can be in the form of services or goods. It is important to do extensive research before developing a product as it has a fluctuating life cycle, from the growth phase to the maturity phase to the sales decline phase.
A product has a certain life cycle that includes the growth phase, the maturity phase, and the sales decline phase. It is important for marketers to reinvent their products to stimulate more demand once it reaches the sales decline phase. It should create an impact in the mind of the customers, which is exclusive and different from the competitor’s product. There is an old saying stating for marketers, “what can I do to offer a better product to this group of people than my competitors”. This strategy also helps the company to build brand value.
Price in Marketing Mix:
Price is a very important component of the marketing mix definition. The price of the product is basically the amount that a customer pays for to enjoy it. Price is the most critical element of a marketing plan because it dictates a company’s survival and profit. Adjusting the price of the product, even a little bit has a big impact on the entire marketing strategy as well as greatly affecting the sales and demand of the product in the market. Things to keep on mind while determining the cost of the product are, the competitor’s price, list price, customer location, discount, terms of sale, etc.,
Place in Marketing Mix:
Placement or distribution is a very important part of the marketing mix strategy. We should position and distribute our product in a place that is easily accessible to potential buyers/customers.
Promotion in Marketing Mix:
It is a marketing communication process that helps the company to publicize the product and its features to the public. It is the most expensive and essential components of the marketing mix, that helps to grab the attention of the customers and influence them to buy the product. Most of the marketers use promotion tactics to promote their product and reach out to the public or the target audience. The promotion might include direct marketing, advertising, personal branding, sales promotion, etc.
What is 7 P of Marketing:
The 7Ps model is a marketing model that modifies the 4Ps model. As Marketing mix 4P is becoming an old trend, and nowadays, marketing business needs deep understanding of the rise in new technology and concept. So, 3 more new P’s were added in the old 4Ps model to give a deep understanding of the concept of the marketing mix.
People in Marketing Mix:
The company’s employees are important in marketing because they are the ones who deliver the service to clients. It is important to hire and train the right people to deliver superior service to the clients, whether they run a support desk, customer service, copywriters, programmers…etc. It is very important to find people who genuinely believe in the products or services that the particular business creates, as there is a huge chance of giving their best performance. Adding to it, the organisation should accept the honest feedback from the employees about the business and should input their own thoughts and passions which can scale and grow the business.
Process in Marketing Mix:
We should always make sure that the business process is well structured and verified regularly to avoid mistakes and minimize costs. To maximise the profit, Its important to tighten up the enhancement process.
Physical Evidence in Marketing Mix:
In the service industries, there should be physical evidence that the service was delivered. A concept of this is branding. For example, when you think of “fast food”, you think of KFC. When you think of sports, the names Nike and Adidas come to mind.
Marketing Mix Example:
This article will go through a marketing mix example of a popular cereals company. At first, the company targeted older individuals who need to keep their diet under control, this product was introduced. However, after intense research, they later discovered that even young people need to have a healthy diet. So, this led to the development of a cereals product catered to young people. In accordance with all the elements of the marketing mix strategy, the company identified the product, priced it correctly, did tremendous promotions and availed it to the customers. This marketing mix example belongs to Honeycomb, one of the most renowned companies in the cereal niche. Following these rules clearly has managed to make the company untouchable by all the other competitors in the market. This makes Honeycomb, the giant we know and love today to eat as morning breakfast!
Related read:
- Why planning in marketing is important?
- What are the principles of Management?
All products can be broadly classified into 3 main categories. These are :
- Tangible products: These are items with an actual physical presence such as a car, an electronic device, and an item of clothing or a consumer good.
- Intangible products: These are items that have no physical presence but can be felt indirectly. An insurance policy is an example of this. Online items such as software, applications or even music and video files are also intangible products.
- Services: Services are also intangible products but they are the result of an economic activity that does not result in ownership. It is a process that creates benefits for customers. Services depend highly on who is performing them and remain difficult to reproduce exactly.
The marketing mix is a remarkable tool for creating the right marketing strategy and its implementation through effective tactics. The assessment of the roles of your product, promotion, price, and place plays a vital part in your overall marketing approach. Whereas the marketing mix strategy goes hand in hand with positioning, targeting, and segmentation. And at last, all the elements, included in the marketing mix and the extended marketing mix, have an interaction with one another.
Q.1 State Any One Advantage of Personal Branding
- It is because of branding that customers are able to identify the products.
- Example, a customer who is satisfied with ‘Dove’ beauty bar need not inspect it every time she buys the product.
Q.2 State the Components of Product Mix.
Q.3 A Company Has to Decide About Its Price Policy, Credit Policy; Terms of Payment Etc. Name the Concept Which the Company is Trying to Decide.
The above mentioned is the concept, that is elucidated in detail about ‘Marketing Mix’ for the Commerce students. To know more, stay tuned to BYJU’S.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

- Frequently Asked Questions
- Business Credit Cards
- Talk to Us 1-800-496-1056

How to Write the Marketing Plan in Business Plan?
A marketing plan in business plan is one of the very important sections of a business plan. Marketing is done to spread awareness about your business and its product/service.
What is a marketing plan?
Marketing plan vs marketing strategy, how to write a marketing plan for a business plan.
An effective marketing strategy helps you achieve early success.
Use this article to write an effective marketing plan section in a business plan.
A marketing section of a business plan gives you a roadmap to organize, execute and track the progress of your marketing efforts.
Your marketing plan helps you align your marketing efforts with your business goals. It gives your marketing effort a direction and you can evaluate your efforts at any point.
Types of marketing plan
A perfect type of marketing plan in business plan will depend on your business, your goals, and how soon you want to achieve them.
We have outlined some marketing plans that most businesses need to use. Since this is the age of the internet, we have also included online marketing plans and digital marketing plans.
Want to write a business plan?
Hire our professional business plan writers to prepare your business plan!
Quarterly or Annual Marketing Plans
These are your business marketing plans with a timeline. Every business has its quarterly, bi-yearly, and yearly goals. You will use these goals to monitor the effectiveness of your marketing efforts over time.
Paid Marketing Plans
Paid marketing plans include online advertising, buying billboards, or marketing on vehicles. Pay Per Click marketing and social media marketing for your small business.
Social Media Marketing Plan
Social media marketing plan for business plan can be done in two ways. You can hire a team and raise awareness about your business by sharing regular updates.
You can also do paid marketing on social media. You will need to invest in buying ads on that social media platform and pay for a team of social media marketers.
You can also leverage these effective digital marketing channels for your business.
Content Marketing Plan
A content marketing plan is about attracting potential customers to your website with the help of SEO. You create value for your potential customer first and then by extension, market your business. It can be offline in the form of free workshops etc or online in the form of guides and resources.
Product Launch Marketing Plan
A product lunch sales and marketing plan in business plan will help you decide on the marketing tools, tactics, and tracking you will do when launching a new product or service.
You can also hire WiseBusinessPlans Digital Marketing Services to run successful marketing campaigns for your business.
The difference between a marketing plan and a marketing strategy is simple; a marketing plan is what methods, tools, and tactics you will use for marketing, and a market strategy in business plan is how you will implement your plan.
Learn how to develop an effective marketing strategy with this detailed guide.
Access our free business plan examples now!

Follow these simple steps to write a marketing plan in business plan.
Business Mission
Write your business mission statement and translate it into the efforts the marketing department will make.
For example, your business mission is to help people with home gardening. Your marketing department version will be to attract people who want to do home gardening.
These are performance indicators. These metrics will help you evaluate performance and progress. An example of KPIs for marketing is customer visits to your website, social media page, or brick-and-mortar store.
Create Buyer Personas
A buyer persona is a short description of your average customer. When you have no data, a buyer persona will describe the customer you want to attract.
Decide on Marketing Strategies and Content
Go through the marketing strategies you can use and select the one that will produce the best return on investment for your business.
Similarly, think about the content type that is attractive to your target audience . For example, video format may attract your audience or you may need to share more about your business on social media to grab their attention.
Define Marketing Plan Scope
Define the scope and limits of your marketing plan. Clearly mention what your marketing team will do and will not do.
This will help you save time, cost, and effort in wasted resources.
Set Marketing Budget
You can only spend a set amount on marketing. Set your marketing budget and be creative in that budget to produce the best return.
Your budget is directly related to your marketing goals. Set your marketing budget in a way that does not hamper marketing efforts.
Know your Competition
Knowing and profiling your customer helps you market better. See what are strong spots of competitors’ marketing plans, are and how they are attracting audiences to make a plan to compete effectively.
Appoint your Team & their Responsibilities
Decide on job roles for your team. Set their KPIs, marketing channels they will manage, what content they will create, etc.
Bonus Tip: Here is a step by step guide on how to write a marketing plan executive summary with example and template.
Example of Marketing Plan in Business Plan PDF
See this example of a marketing plan in a business plan to understand how it is done. You can create your marketing plan in the same way.
In the marketing plan section, include details about your target market, competition analysis, marketing strategies, pricing, promotion, and distribution channels. It should outline your approach to reaching and engaging your target audience.
Conduct market research by analyzing your target audience, understanding their needs and preferences, studying your competitors, and identifying market trends. Use surveys, interviews, and industry reports to gather relevant data for your marketing plan.
Consider including a mix of marketing strategies such as digital marketing, social media marketing, content marketing, email marketing, advertising, public relations, and networking. Choose strategies that align with your target audience and business goals.
Determine pricing by considering factors such as production costs, competitor pricing, market demand, and perceived value. Conduct a pricing analysis to ensure your prices are competitive and profitable for your business.
It is recommended to review and update your marketing plan regularly, at least annually or whenever there are significant changes in your business or market conditions. This allows you to adapt your strategies, stay relevant, and capitalize on new opportunities.
WiseBusinessPlans is the company that writes business plans
One comment.
It is a very useful guide. I was wondering If your site offers marketing plan writers for businesses. If any, kindly reply.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077


Beyond launch day: How to plan successful B2B product rollouts

Believe it or not, rolling out a new product can be a lot trickier for B2B companies. And there are several reasons why. For one, in an ideal scenario, any new feature release requires a healthy amount of testing and, unlike B2C companies which build for general consumers and might have millions of users, most B2Bs are lucky to have a few thousand people regularly using their products. With such small sample sizes, you can’t be constantly mass testing like you would in B2C. This fact inherently increases the risk involved with launching new features.
Further, most B2B tools are productivity-boosting tools, which means when you do launch a new feature, you don’t always want to try to drive adoption with what could be noisy in-product messaging or tours. This is why go-to-market (GTM) teams play a large role in B2B rollouts, whether it’s running training with their account teams or answering basic support questions. B2B launches are very much a cross-functional effort.
In this article, I’ll show you how my team and I approach product rollouts at Mixpanel in four major stages—and why no step should go skipped.
The 4 stages of a successful product rollout
The best way to ensure a smooth product rollout is to have a phased approach supported by ample prep work. You don’t want to roll out a big feature to your entire customer base just to realize that there was a bug that the QA team missed.
Stage 1: The pre-rollout
In B2B, planning the launch of a new feature or product should happen weeks—sometimes even months—before the product team even starts building anything. This is largely because of the challenges that are inherent in B2B.
B2B products often have to appeal to many different personas. Take Mixpanel, for example. We have a wide range of user types, from marketers to engineers to product managers and more. Any new features we build have to appeal to some combination—and sometimes all—of these personas.
Before a line of code is written or a button is designed, we need to understand the personas that will be using this new feature and their true needs. This is crucial because it determines how we might position and market that feature, how we enable our sales team, and so on. Writing up the press release for your theoretical new feature can be a helpful exercise here.
Working backward, the product team (engineering, product, and design) can decide how we might build the feature to ensure it’s a success based on the positioning.
With positioning work done and building underway, we start preparing our internal teams with enablement materials and training. For example:
- What is the feature?
- Who is it designed for?
- How does it work?
- What is the pricing?
And other technical gotchas…
We have to be ready with answers for any questions that our customer success, support, solution engineers, sales, and post-sales teams might get. So it’s very helpful to collaborate with those teams to anticipate these questions. They’re the end consumers of this training, after all.
Whereas building the right feature could be 60% to 70% of the work in B2C, it’s closer to only 20% of the effort in B2B rollouts.
Key teams to involve: Product Marketing, Sales Enablement, Customer Success & Support
Key Mixpanel reports used: Flows (to look at workarounds being used today)
Stage 2: The phased rollout
Now, we can start actually rolling out the new product or feature. We’d recommend doing this in three phases.
Phase 1: 10%
First, make it available to a small percentage of your user base—we usually go with 10%. Don’t worry too much about adoption yet. Your goal for now is just to monitor your core user metrics in product analytics and make sure you haven’t broken anything. For example, if you were getting five support tickets a day and then suddenly began getting 100 after your 10% rollout, that would be a problem.
In addition to monitoring data, it’s important to start gathering feedback as soon as you start your 10% rollout. We even go as far as having the support team join our standups to talk about tickets concerning the new feature. The sooner you can get customer reactions from your support and account teams, the sooner you can understand what is (and isn’t) working and start iterating on the product.
Phase 2: 50%
Once you’ve determined that your metrics are still looking good, initial feedback is stable, and you haven’t broken anything, you can make the feature available to more users—our team typically expands availability to 50%.
It’s ideal to maintain this rollout phase for two to three weeks. That way you have enough time to spot trends and get an idea of whether your hypotheses were right or need to be modified. For example, you might expect X users a day, but you aren’t hitting that number. Perhaps you need to beef up your internal and external promotion strategy.
At this point, your customer-facing teams are also likely getting more questions from users and customers. This is valuable feedback and your product team should continue to iterate at this stage because if a user tries your new feature and it’s not good (first impressions are important), it’s highly unlikely that they’ll come back to use it again.
Phase 3: 100%
By now, you’ve made all the iterations you wanted to make and the product is truly ready for the big time.
You can open up the new product or feature to everyone now. Continue to get feedback from users, but focus more on changes that you can make on a larger scale going forward—how can you meaningfully improve the product in the future?
It shouldn’t be about small iterative changes anymore because the bulk of those should’ve come during your 10% and 50% rollout phases.
Key teams to involve: Support, Engineering, Product, Design, Customer Success
Key Mixpanel reports used: Insights (to monitor core metrics and trends), Funnels (to see drop-offs at key stages)
Stage 3: Demand gen and marketing
Now that your product is out in the world, it’s time for a big marketing push to get the word out to all your customers (and prospective customers) and get them excited.
It’s good to have a range of content like launch blogs and videos. We’ve found Looms are very effective, and we see a lot more adoption from using them to explain new features to users. If producing a beautiful video means waiting a few weeks on your marketing team, it might be better to get scrappy and have something functional out there in the meantime because making sure your audience knows about the right feature at the right time takes top importance. Most people won’t seek out new features on their own unless they really need it, so it takes a continuous cadence to catch them when ready.
(For larger launches and flagship features, of course, you might just have to take the time and wait for more polished videos.)
You’ll also want to make sure your marketing team has all the information they need to create ad campaigns (for large pushes), publish content on the blog, and communicate the benefits of the new product to prospects. Arm them with information like:
- Ideal customer profile (ICP) and industry or personas
- Use cases and details about product benefits
- Pricing and packaging (if applicable)
Key teams to involve: All marketing teams (including Product Marketing, Demand Gen, Content, Video, Brand, and so on)
Key Mixpanel reports used: Monitor the rollout dashboard built with reports above to see which hypothesis worked and amplify that message. Also, heavily use View Users to reach out to power users and get feedback/ customer stories for marketing content.
Stage 4: Continuous customer feedback
You’ve successfully launched your product (congratulations!), but the work isn’t done.
Make sure to continue monitoring customer feedback via different channels—support tickets, events, case study interviews—sometimes you’ll even see product feedback on social media channels.
Have a standing monthly check-in to review feedback and metrics for the next 4–6 months with the larger product team (including some GTM representatives) to determine the future direction post-launch and the level of further investment we may or may not want to put into this in the next planning cycle(s).
Key teams to involve: Support, Customer Success, Sales, Product Marketing
Key Mixpanel reports used: Retention report (to see Month 1+ retention), the rollout dashboard, and a support tickets dashboard ( which we also have built in Mixpanel internally )
Make your next product rollout a success
Even though B2B user bases tend to be smaller, a successful feature or product rollout can be a lot more impactful for B2B companies—and it’s a much bigger achievement for product teams that can pull it off.
As we’ve covered, getting it right demands meticulous planning. With the right tools, even small, resource-constrained teams can ensure every product rollout goes as smoothly as possible. Solutions like Mixpanel are designed to support every step in the process, from helping product teams monitor key adoption metrics to providing marketing teams with user insights that inform their campaigns.
Learn more about using Mixpanel’s reporting and analytics in your next product rollout— request a demo today .
- product management
Related articles

You are a builder. Can AI replace you?
You are a builder. And what makes you a builder is not just your ability to code, sketch an illustration, …

What most teams get wrong when choosing an A/B testing solution
Most companies, whether they have a mature data or product organization or not, are already doing some form of A/B …

How fintech companies can use product analytics to improve customer lifetime value
The banking and finance industries have seen a lot of disruption in the last 15 years that’s brought financial services …

- Side Hustles
- Power Players
- Young Success
- Save and Invest
- Become Debt-Free
- Land the Job
- Closing the Gap
- Science of Success
- Pop Culture and Media
- Psychology and Relationships
- Health and Wellness
- Real Estate
- Most Popular
Related Stories
- Work No. 1 question to ask before accepting a job, according to LinkedIn expert
- Work This soft skill is the new Harvard degree, says expert
- Get Ahead The No. 1 soft skill you need to get hired right now, according to LinkedIn
- Land the Job Don't use these phrases in a job interview, they are ‘major red flags'
- Land the Job The No. 1 trait employers are looking for right now—and how to show you have it
'Where do you see yourself in five years?': Recruitment expert on why you shouldn't care about this age-old question

"Where do you see yourself in five years?"
It's a question that most people have asked themselves or been asked in job interviews, by mentors, career advisors or even just their parents.
But it's not a question people should really be worried about, Aneesh Raman, vice president and workforce expert at LinkedIn, told CNBC Make It in a conversation on the sidelines of LinkedIn's U.K. Talent Connect event last month.
"Don't worry about five years or 10 years from now," he said.
That might seem counterintuitive at first, but as the labor market and jobs themselves are evolving rapidly thanks to technological developments like artificial intelligence, planning for the future can be tricky.
Put simply, we just do not know which jobs will even exist in a few years, Raman said. "The only constant for the coming decade will be change," he added.
But where does that leave those who are about to start their career?
Instead of thinking about what job title or role you want, Raman suggests focusing on what you want to do, what skills to develop, and using them in an impactful way.
"The thing that matters most is skills," Raman said. Developing those should be the focus of anyone's early career, he explained, adding that where and how that happens is secondary.
"Employers are interested in all the skills you'll bring to the organization, regardless of where you've learned them," he said. "Take stock of your top skills and get really good at telling a story around where you built them and, more importantly, where you applied them."
Data shows that employers are placing an increasing amount of attention on skills — for example, recruiters are five times more likely to search for candidates based on skills than other accolades like college degrees, LinkedIn has found.
"Once you've built up some true expertise, the next step is to ask yourself how you can apply what you know to a specific issue or a topic you're passionate about," Raman said.
Next to skills, learning should be another key focal point and goes hand in hand with being able to adapt in an ever-changing job market.
"Find your way to a love of learning, where you are excited about learning because you are curious and determined to get better at certain skills or in certain areas of expertise," Raman said.
He has said that asking about the culture of learning is the most important question job seekers can ask in interviews. This is due to the changing nature of jobs and the labor market, Raman said. LinkedIn research has also found that learning boost workers' sense of connection to their employer and adds purpose to their jobs.
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Target Market?
- Defining a Product's Target Market
- 4 Target Markets
Why Are Target Markets Important?
What are market segments, target market and product sales.
- Target Market FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Marketing Essentials
Target Market: Definition, Purpose, Examples, Market Segments
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Group1805-3b9f749674f0434184ef75020339bd35.jpg)
Investopedia / Mira Norian
A target market is a group of people that have been identified as the most likely potential customers for a product because of their shared characteristics, such as age, income, and lifestyle.
Identifying the target market is a key part of the decision-making process when a company designs, packages, and advertises its product.
Key Takeaways
- A target market is a group of customers with shared demographics who have been identified as the most likely buyers of a company's product or service.
- Identifying the target market is important in the development and implementation of a successful marketing plan for any new product.
- The target market also can inform a product's specifications, packaging, and distribution.
How Do I Define My Product's Target Market?
Part of creating a new product is envisioning the consumers who will want it.
A new product must satisfy a need or solve a problem, or both. That need or problem is probably not universal unless it reaches the level of indoor plumbing. More likely, it is needed by a subset of consumers, such as environmentally-conscious vegetarians, or science nerds, or outdoor enthusiasts. It may appeal to a teenager or a middle-aged professional, a bargain-hunter or a snob.
Envisioning your likely target market is part of the process of creating and refining a product, and informs decisions about its packaging, marketing, and placement.
What Are the 4 Target Markets?
Market researchers use activity, interest, and opinion (AIO) surveys to construct psychographic profiles of their target customers. Marketing professionals divide consumers into four major segments:
Demographic: These are the main characteristics that define your target market. Everyone can be identified as belonging to a specific age group, income level, gender, occupation, and education level.
Geographic: This segment is increasingly relevant in the era of globalization. Regional preferences need to be taken into account.
Psychographic: This segment goes beyond the basics of demographics to consider lifestyle, attitudes, interests, and values.
Behavioral: This is the one segment that relies on research into the decisions of a company's current customers. New products may be introduced based on research into the proven appeal of past products.
What Is an Example of a Target Market?
Each of the four target markets can be used to consider who the customer for a new product is.
For example, there are an estimated 100,000 Italian restaurants in the U.S. Clearly, they have enormous appeal.
But a corner pizza joint might appeal mostly, although by no means entirely, to a younger and more budget-conscious consumer, while an old-fashioned white tablecloth place might be dominated by older folks and families who live in the neighborhood. Meanwhile, a newer place down the street might cater to an upscale and trend-conscious crowd who will travel a good distance for the restaurant's innovative menu and fancy wine list.
In each successful case, a savvy business person has consciously considered the ideal target market for the restaurant and has tweaked the menu, decor, and advertising strategy to appeal to that market.
Few products today are designed to appeal to absolutely everyone. The Aveda Rosemary Mint Bath Bar, available for $26 a bar at Aveda beauty stores, is marketed to the upscale and eco-conscious woman who will pay extra for quality. Cle de Peau Beaute Synactif Soap retails for $110 a bar and is marketed to wealthy, fashion-conscious women who are willing to pay a premium for a luxury product. An eight-pack of Dial soap costs $12 at CVS, and it is known to get the job done.
Part of the success of selling a good or service is knowing to whom it will appeal and who will ultimately buy it. Its user base can grow over time through additional marketing, advertising, and word of mouth.
That's why businesses spend a lot of time and money in defining their initial target markets, and why they follow through with special offers, social media campaigns , and specialized advertising.
Dividing a target market into segments means grouping the population according to the key characteristics that drive their spending decisions. Some of these are gender, age, income level, race, education level, religion, marital status, and geographic location.
Consumers with the same demographics tend to value the same products and services, which is why narrowing down the segments is one of the most important factors in determining target markets.
For example, people who fall into a higher income bracket may be more likely to buy specialty coffee from Starbucks instead of Dunkin' Donuts. The parent companies of both of these brands need to know that in order to decide where to locate their stores, where to stock their products, and where to advertise their brand.
A business may have more than one target market—a primary target market, which is the main focus, and a secondary target market, which is smaller but has growth potential. Toy commercials are targeted directly to children. Their parents are the secondary market.
Identifying the target market is an essential part of a product development plan, along with manufacturing, distribution, price, and promotion planning. The target market determines significant factors about the product itself. A company may tweak certain aspects of a product, such as the amount of sugar in a soft drink or the style of the packaging, so that it appeals more to consumers in its target group.
As a company’s product sales grow, it may expand its target market internationally. International expansion allows a company to reach a broader subset of its target market in other regions of the world.
In addition to international expansion, a company may find its domestic target market expands as its products gain more traction in the marketplace. Expanding a product's target market is a revenue opportunity worth pursuing.
How Detailed Should a Target Market Be?
It depends. Broadly speaking, a product may be designed for a mass market or a niche market, and a niche market can be a very small group indeed, especially in a product's early introductory phase.
Some carbonated beverages aim for a practically universal market. Coca-Cola had to branch out to 200 markets abroad to continue growing its customer base. Gatorade is owned by Pepsi Cola, but the brand is positioned as a drink for athletes. The soda brand Poppi, which is branded as a "Healthy, Sparkling, Prebiotic Soda with Real Fruit Juice, Gut Health, and Immunity Benefits," is clearly aimed at a younger, healthier, and more trend-conscious target market.
Consider a casual apparel company that is working to build its distribution channels abroad. In order to determine where its apparel will be most successful, it conducts some research to identify its primary target market. It discovers that the people most likely to buy their products are middle-class women between the ages of 35 and 55 who live in cold climates.
It's reasonable for the company to focus its advertising efforts on northern European websites that have a strong female audience.
But first, the company may consider how its apparel can be most attractive to that target market. It may revise its styles and colors and tweak its advertising strategy to optimize its appeal to this new prospective market.
What Is the Purpose of a Target Market?
A target market defines a product as well as vice versa.
Once a target market is identified, it can influence a product's design, packaging, price, promotion, and distribution.
A product aimed at men won't be packaged in pink plastic. A luxury cosmetic won't be sold in a pharmacy. An expensive pair of shoes comes with a branded cloth drawstring bag as well as a shoebox. All of those factors are signals to the target audience that they have found the right product.
Identifying the target market is part of the process of creating and refining a new product.
A target market can be translated into a profile of the consumer to whom a product is most likely to appeal. The profile considers four main characteristics of that person: demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral.
National Geographic. " How Italian Cuisine Became as American as Apple Pie ."
Aveda. " Rosemary Mint Bath Bar ."
Cle de Peau. " Synactif Soap ."
CVS. " Dial Antibacterial Deodorant Bar Soap, White ."
Coca-Cola Australia. " Coca-Cola: From Start-Up to Global Enterprise ."
Pepsico Partners. " Gatorade ."
DrinkPoppi. " Home ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Market-Segmenation-76c1fe9e48ff4906bc2a565bb67c6862.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
California Sees Two More Property Insurers Exit From Market (1)
By Nadia Lopez

California’s already strained property insurance market is facing a new challenge as two more insurers, Tokio Marine America Insurance Co. and Trans Pacific Insurance Co., plan to withdraw from the wildfire-prone state entirely starting in July.
The two companies, units of Japan-based Tokio Marine Holdings Inc., disclosed their plans in filings submitted to the California Department of Insurance . They said the decision will affect 12,556 policies with premiums of $11.3 million.
“Given the small segment of personal lines business we write and escalating costs, we cannot sustainably support personal lines coverages and do not plan to return,” the company ...
Learn more about Bloomberg Law or Log In to keep reading:
Learn about bloomberg law.
AI-powered legal analytics, workflow tools and premium legal & business news.
Already a subscriber?
Log in to keep reading or access research tools.
- New Terms of Use
- New Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Closed Captioning Policy
Quotes displayed in real-time or delayed by at least 15 minutes. Market data provided by Factset . Powered and implemented by FactSet Digital Solutions . Legal Statement .
This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed. ©2024 FOX News Network, LLC. All rights reserved. FAQ - New Privacy Policy
Majority of US couples do not have an estate plan, study finds
Ameriprise survey finds couples overwhelmingly tend to trust each other, but many have serious details to work out when it comes to retirement.

Diners weigh in on retirement as new study shows what it would take to retire comfortably
FOX Business' Ashley Webster talks to diners at The Villages in Florida about retirement after a Northwestern Mutual survey claims it will take $1.46M to retire comfortably.
American investors in committed relationships overwhelmingly say they trust their partners and share the same retirement goals , but most have not put an estate plan in place, new data suggests.
Ameriprise Financial's "Couples, Money & Retirement" report released Wednesday found 95% of couples agree they are honest and transparent with one another when it comes to their finances, and 91% said they share the same financial values.

A new survey by Ameriprise found most American investors in committed relationships have some significant details to work out with their partners when it comes to retirement. (Annette Riedl/picture alliance via Getty Images / Getty Images)
But many have not reached a consensus on a number of emotionally-charged decisions about money .
The survey, which polled more than 1,500 American couples with $100,000 or more in investable assets, focused primarily on those between the ages of 45-70 who have retired within the last decade or plan to do so in the next 10 years.
TAX REFUNDS ARE NOT FREE MONEY: RACHEL CRUZE
While it found that 93% of couples share similar goals for retirement and agree on when to retire, 24% of respondents said they have not come to an agreement on how much money they will need to save or how much they should spend on children and grandchildren, both today and as part of their estates.

Most couples do not have an estate plan in place, according to a new study by Ameriprise. (iStock / iStock)
In fact, more than half (52%) of couples surveyed said they have not yet set up an estate plan.
Marcy Keckler, senior vice president of financial advice strategy at Ameriprise Financial and a certified financial planner, offers the following advice for couples who still need to set up an estate plan:
1. Don't be intimidated by the concept of estate planning
"Estate planning is for everyone, no matter their wealth or complexity of their financial situation ," Keckler told FOX Business. "At some point, all of us will need an estate plan."
She explained that, at its core, estate planning is about making decisions about what you want to happen after you die or in the event you’re incapacitated and can’t make health-related or financial decisions on your own, even temporarily.
SHOULD YOU TELL YOUR KIDS ABOUT THEIR INHERITANCE?
2. Engage professionals
"A qualified financial adviser and estate planning attorney can help you initiate important, yet often emotional conversations and ensure you have decisions documented to cover a variety of potential scenarios that may arise,' Keckler said.
"Guidance from professionals can ensure your wishes for the legacy you want to leave your heirs and other loved ones are carried out."

Financial advisers can provide expert-led guidance for individuals or couples who have complex finances. (iStock / iStock)
Keckler recommends selecting professionals willing to collaborate, noting that one of the biggest mistakes couples can make is creating a will that specifies beneficiaries and then forgetting to update their accounts to actually identify the correct beneficiary.
She added that financial advisers and attorneys can work together to help ensure you’ve taken all the steps necessary to have your plan executed according to your wishes.
3. Once you complete your estate plan, be proud of yourself
" Estate planning is an important part of protecting your family and financial legacy," Keckler said. "It’s a big accomplishment that should be celebrated once it’s completed."
She recommends ensuring you know where the original documents and any physical or digital copies are, so you can refer to them in the event they become needed.
"If you have a doctor or hospital of choice, send them a copy, so they can keep it on file," Keckler suggested. "This can save valuable time and stress you or a loved one would otherwise spend trying to find them in an emergency."
GET FOX BUSINESS ON THE GO BY CLICKING HERE
4. Revisit your estate plan at least every five years, and more frequently if a big life event happens
"Estate plans need to be updated as your life evolves to ensure they reflect your wishes," Keckler added. "Moments in life such as the birth of a child or grandchild, major shifts in income, a divorce, acquisition of new property and a child reaching the age of 18 are a few examples of when your estate plan may need to be revisited."

COMMENTS
Marketing Mix: A marketing mix usually refers to E. Jerome McCarthy's four P classification for developing an effective marketing strategy: product, price, placement, or distribution, and ...
When perfected and synchronized, the core elements of a marketing mix provide a well-rounded approach to marketing strategy. 1. Product. Product refers to what your business is selling - product (s), service (s), or both. The bulk of the work in this element is typically done by product marketers or managers.
The marketing mix is a term to describe the multi-faceted approach to a complete and effective marketing plan. Traditionally, this plan included the four Ps of marketing: price, product, promotion, and place. But the exact makeup of a marketing mix has undergone various changes in response to new technologies and ways of thinking. Additions to the four Ps include physical evidence, people ...
3. Red Bull Marketing Mix Example. Since entering the market in 1987, Red Bull has remained the most popular energy drink brand worldwide. Over the years, Red Bull has sold over 100 billion cans and, as of 2020, held 43% of the global energy drinks market share.
The four Ps are product, price, place, and promotion. They are an example of a "marketing mix," or the combined tools and methodologies used by marketers to achieve their marketing objectives. The 4 Ps were first formally conceptualized in 1960 by E. Jerome McCarthy in the highly influential text, Basic Marketing, A Managerial Approach [ 1 ].
A marketing mix is a blend of business strategies brought into execution that make up the overall marketing strategy for a product. ... 4 P's of Marketing Mix with Examples. A marketing plan must be based on thorough market research and analysis of the many factors of marketing. A marketing design without a solid blueprint is like aiming in the ...
A marketing mix refers to a set of controllable variables that a company strategically chooses to influence the target buyers' responses. The elements of a marketing mix include four P's, i.e., product, price, promotion, and place. These elements work in conjunction to help brands create brand positioning, marketing plan, and advertising ...
A: The 4 Ps of marketing is a framework that businesses use to develop and execute their marketing strategies. The 4 Ps are: Product: The product is the good or service that a business offers for sale. Price: The price is the amount that customers pay for the product. Place: The place where the product is sold.
Four Ps: The four Ps are the categories that are involved in the marketing of a good or service, and they include product, price, place and promotion. Often referred to as the marketing mix, the ...
A marketing mix is a planned mix of elements that make up the marketing plan of a product or service. There are typically four elements: P roduct, P rice, P lace, and P romotion. They all start with the letter 'P.'. Hence, we can say the marketing mix or the 4Ps. Some people also call the mix the 4Ps Strategy or the 4Ps Marketing Matrix.
Show more. The four Ps of marketing—product, price, place and promotion—serve as a framework for marketing success. Sometimes referred to as the marketing mix, the four Ps help guide ...
Marketing mix is a selection of marketing tools that include several areas of focus that can be combined to create a comprehensive plan. The term refers to a classification that began as the 4 P's: product, price, placement, and promotion, and has been expanded to Product, Price, Promotion, Place, People, Packaging, and Process.
It's an essential part of a marketing plan structure that defines the tactics to be used to implement the marketing strategy. The traditional 7Ps of marketing consist of: Product. Promotion. Price. Place. People. Process. Physical evidence.
The 4 P's example and template for a service business. The Marketing Mix of "HVAC Plumber" reflects a real life example of how a service company covers the 4 P's (Product, Price, Place, Promotion) in their marketing strategy. "HVAC plumber" (a fictitious company) provides heating and cooling services in the Chicago Metropolitan Area.
Plan several rounds of edits or have someone else review it. Keep everything in the context of your business. Make sure all the statistics and data you use in your market analysis relate back to your business. Your focus should be on how you are uniquely positioned to meet the needs of the target market.
Step 4: Calculate market value. You can use either top-down analysis or bottom-up analysis to calculate an estimate of your market value. A top-down analysis tends to be the easier option of the ...
The marketing strategy section of the plan describes the marketing mix, the measures the business will take to enable it to obtain its market share. The simplest approach to the marketing strategy is to split the process into four sections, sometimes referred to as the fours P's, as follows:
The marketing plan usually assists in the growth of the business by stating appropriate marketing strategies, such as plans for increasing the customer base. State and review the marketing mix in terms of the 8Ps of marketing - Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, Physical Evidence, and Performance.
Marketing Plan: A marketing plan is a business's operational document for advertising campaigns designed to reach its target market . A marketing plan pulls together all the campaigns that will be ...
The 7Ps of Marketing is the Price, Place, Promotion, Product, People, Process and finally, Physical Evidence. It originally started as 4 Ps, but as the world, and the complexities of marketing grew; 3 more were added to formulate an effective marketing strategy. The 'P's stand for each of the pillars of a marketing strategy, and together ...
The components of the marketing mix consist of 4Ps Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. In the business sector, the marketing managers plan a marketing strategy taking into consideration all the 4Ps. However, nowadays, the marketing mix increasingly includes several other Ps for vital development.
Marketing plan in business plan explains your marketing efforts for your business, marketing techniques, resources, timeline and expected ROI. Skip to content. Talk to Wise | 1-800-496-1056. Company. ... Consider including a mix of marketing strategies such as digital marketing, social media marketing, content marketing, email marketing ...
Stage 1: The pre-rollout. In B2B, planning the launch of a new feature or product should happen weeks—sometimes even months—before the product team even starts building anything. This is largely because of the challenges that are inherent in B2B. B2B products often have to appeal to many different personas.
The stock market suffered heavy losses this past week, especially the Nasdaq and leading growth plays. The Dow Jones Industrial Average edged up 0.01% in last week's stock market trading. The S&P ...
Business Editor. IKEA is opening its latest plan and order point, which is located in Sligo, today. It is the sixth such outlet that the Swedish furniture retailer has opened here and its first in ...
A quickly evolving job market means having a five year career plan has become difficult. ... Business woman working at office with laptop and documents on his desk, financial adviser analyzing ...
April 18, 2024 at 10:43 AM PDT. Listen. 1:39. California's already strained property insurance market is facing a new challenge as two more insurers, Tokio Marine America Insurance Co. and Trans ...
Target Market: A target market is the market a company wants to sell its products and services to, and it includes a targeted set of customers for whom it directs its marketing efforts ...
California's already strained property insurance market is facing a new challenge as two more insurers, Tokio Marine America Insurance Co. and Trans Pacific Insurance Co., plan to withdraw from the wildfire-prone state entirely starting in July. The two companies, units of Japan-based Tokio Marine Holdings Inc., disclosed their plans in ...
Ameriprise Financial's latest "Couples, Money & Retirement" survey found U.S. couples overwhelmingly agree on retirement goals, but most do not have an estate plan in place.