Generate accurate MLA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- MLA titles: Formatting and capitalization rules

MLA Titles | How to Format & Capitalize Source Titles
Published on April 2, 2019 by Courtney Gahan . Revised on March 5, 2024.
In MLA style , source titles appear either in italics or in quotation marks:
- Italicize the title of a self-contained whole (e.g. a book, film, journal, or website).
- Use quotation marks around the title if it is part of a larger work (e.g. a chapter of a book, an article in a journal, or a page on a website).
All major words in a title are capitalized . The same format is used in the Works Cited list and in the text itself.
When you use the Scribbr MLA Citation Generator , the correct formatting and capitalization are automatically applied to titles.
Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Capitalization in mla titles, punctuation in mla titles, titles within titles, exceptions to mla title formatting, sources with no title, abbreviating titles, titles in foreign languages, frequently asked questions about mla titles.
In all titles and subtitles, capitalize the first and last words, as well as any other principal words.
What to capitalize
What not to capitalize, receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting.
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Use the same punctuation as appears in the source title. However, if there is a subtitle, separate it from the main title with a colon and a space, even if different (or no) punctuation is used in the source.
Example of a work with a subtitle
The exception is when the title ends in a question mark, exclamation point or dash, in which case you keep the original punctuation:
Sometimes a title contains another title—for example, the title of an article about a novel might contain that novel’s title.
For titles within titles, in general, maintain the same formatting as you would if the title stood on its own.
Titles and names that fall into the following categories are not italicized or enclosed in quotation marks:
- Scripture (e.g. the Bible, the Koran, the Gospel)
- Laws, acts and related documents (e.g. the Declaration of Independence, the Constitution , the Paris Agreement)
- Musical compositions identified by form, number and key (e.g. Beethoven’s Symphony no. 5 in C minor, op. 67)
- Conferences, seminars, workshops and courses (e.g. MLA Annual Convention)
Sections of a work
Words that indicate a particular section of a work are not italicized or placed within quotation marks. They are also not capitalized when mentioned in the text.
Examples of such sections include:
- introduction
- list of works cited
- bibliography
Introductions, prefaces, forewords and afterwords
Descriptive terms such as “introduction”, “preface”, “foreword” and “afterword” are capitalized if mentioned in an MLA in-text citation or in the Works Cited list, but not when mentioned in the text itself.
Example of descriptive term capitalization
In-text citation: (Brontë, Preface )
In text: In her preface to the work, added in a later edition, Brontë debates the morality of creating characters such as those featured in Wuthering Heights .
If there is a unique title for the introduction, preface, foreword or afterword, include that title in quotation marks instead of the generic section name when referencing the source in the Works Cited list or an in-text citation.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
For sources with no title, a brief description of the source acts as the title.
Example of a source reference with no title
Follow these rules for capitalization:
- Capitalize the first word
- Capitalize proper nouns
- Ignore other MLA rules for capitalization
There are some exceptions to this general format: descriptions including titles of other works, such as comments on articles or reviews of movies; untitled short messages, like tweets; email messages; and untitled poems.
Exceptions to general format for sources with no title
If you need to mention the name of a work in the text itself, state the full title, but omit the subtitle.
If you need to refer to the work multiple times, you may shorten the title to something familiar or obvious to the reader. For example, Huckleberry Finn for The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn . If in doubt, prefer the noun phrase.
If the standalone abbreviation may not be clear, you can introduce it in parentheses, following the standard guidelines for abbreviations. For example, The Merchant of Venice ( MV ) . For Shakespeare and the Bible , there are well-established abbreviations you can use.
When you abbreviate a title, make sure you keep the formatting consistent. Even if the abbreviation consists only of letters, as in the MV example, it must be italicized or placed within quotation marks in the same way as it would be when written in full.
Abbreviating very long titles in the Works Cited list
Titles should normally be given in full in the Works Cited list, but if any of your sources has a particularly long title (often the case with older works), you can use an ellipsis to shorten it here. This is only necessary with extremely long titles such as the example below.
In the Works Cited list, if you are listing a work with a title in a language other than English, you can add the translated title in square brackets.
Example of a reference with a translated title
If you are using the foreign-language title in the text itself, you can also include the translation in parenthesis. For example, O Alquimista ( The Alchemist ) .
You don’t need to include a translation in your reference list or in the text if you expect your readers to be familiar with the original language. For example, you wouldn’t translate the title of a French novel you were writing about in the context of a French degree.
Non-Latin script languages
For works in a language that does not use the Latin alphabet, such as Arabic, Chinese, Greek, Hebrew, Japanese, or Russian, be consistent with how you mention the source titles and also quotations from within them.
For example, if you choose to write a Russian title in the Cyrillic form, do that throughout the document. If you choose to use the Romanized form, stick with that. Do not alternate between the two.
Yes. MLA style uses title case, which means that all principal words (nouns, pronouns , verbs, adjectives , adverbs , and some conjunctions ) are capitalized.
This applies to titles of sources as well as the title of, and subheadings in, your paper. Use MLA capitalization style even when the original source title uses different capitalization .
In MLA style , book titles appear in italics, with all major words capitalized. If there is a subtitle, separate it from the main title with a colon and a space (even if no colon appears in the source). For example:
The format is the same in the Works Cited list and in the text itself. However, when you mention the book title in the text, you don’t have to include the subtitle.
The title of a part of a book—such as a chapter, or a short story or poem in a collection—is not italicized, but instead placed in quotation marks.
When a book’s chapters are written by different authors, you should cite the specific chapter you are referring to.
When all the chapters are written by the same author (or group of authors), you should usually cite the entire book, but some styles include exceptions to this.
- In APA Style , single-author books should always be cited as a whole, even if you only quote or paraphrase from one chapter.
- In MLA Style , if a single-author book is a collection of stand-alone works (e.g. short stories ), you should cite the individual work.
- In Chicago Style , you may choose to cite a single chapter of a single-author book if you feel it is more appropriate than citing the whole book.
The title of an article is not italicized in MLA style , but placed in quotation marks. This applies to articles from journals , newspapers , websites , or any other publication. Use italics for the title of the source where the article was published. For example:
Use the same formatting in the Works Cited entry and when referring to the article in the text itself.
The MLA Handbook is currently in its 9th edition , published in 2021.
This quick guide to MLA style explains the latest guidelines for citing sources and formatting papers according to MLA.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Gahan, C. (2024, March 05). MLA Titles | How to Format & Capitalize Source Titles. Scribbr. Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/mla/titles/
Is this article helpful?
Courtney Gahan
Other students also liked, mla format for academic papers and essays, creating an mla header, author names in mla | citing one or multiple authors, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Learning Tips
- Exam Guides
- School Life
Are Essay Titles Italicized? A Guide for APA and MLA Titles
- by Michael Smart
- January 16, 2024
- Custom Essay writing

Have you ever written an essay and then question yourself whether you have used italics appropriately in the titles? Is the use of italics something that worries you to the extent of avoiding them?
Well, you are not alone because many students do not fully understand how to apply them in their essays, particularly in the titles.
This article will explain when to use italics in your essay and how to appropriately write them. However, before exploring this, it is important to note whether essay titles are italicized or not.
Are Essay Titles Italicized?
The answer to this question depends on the type of words in the title. Essay titles can be italicized. In case you have a title that includes names of vehicles, large works, television series, or movies, you should use italics when mentioning them.
Essay titles can be italicized if the words represent a literary work or are a quote that needs to be represented in italics. Essay titles can also be italicized if all the words or some of them represent certain non-English wordings that are not in the English dictionary.
Literary words are works of literature. Titles of plays, books, and other forms of works of art should also be italicized within the title to set them apart from the surrounding text.
When writing an essay, you will be required by your instructor to format it academically in either APA or MLA since the two formats are the most commonly used.
Instances When to Italicize Titles in an Essay
1. when words need to be emphasized within the title.
As we have noted, italics are used to set a word or phrase apart from other text within the title.
When the word or phrase is set apart, it means that the reader will easily notice it and even prioritize its meaning compared to the rest of the words.

Therefore, if you have a word or words that need to be emphasized within the title of your essay, you can italicize them.
There are some words or phrases that you will include in your title and you wish your readers to take note of them.
They can be part of the essay’s keywords that you might explain from a different perspective to that of the readers.
However, it should be noted that emphasizing words using italics within the title is not commonly used in academic writing.
2. When including Publication Names in your Title
Imagine you are writing an essay in which you are required to conduct an in-depth analysis of an article or case study within a publication.
In this case, you may need to include the name of the publication within your title to instantly communicate to the reader what the paper is all about. Such publication names include:
3. Standalone Works in the Essay Title
When you are including the title of a standalone work like complete plays and books, you should italicize them. Titles of sacred texts should also be italicized when they are included in the title of your essay. This is especially the case when analyzing the complete works in your essay.
For example, if your essay is analyzing a specific Harry Potter book, the title will appear like this: Elements of Style in Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows .
When it comes to places like Romeo and Juliet, your title will look like this: Elements of Style in Romeo and Juliet .
For sacred or religious texts like the King James Version of the Bible, the title may appear like this: Understanding the Meaning from the Language used in King James Bible .
4. When Writing Titles of Creative Works
In case you are required or find yourself in a situation where you need to include the title of creative work in the title of your essay, you should italicize it. This should only include titles of standalone creative works. Such include:
5. When Using Foreign and Unfamiliar Words
In case you have an essay title that requires you to include a foreign word, you should italicize it. The same case applies to words that you are not familiar with or words that are technical.
6. When Referring to Legal Cases
When you are writing an essay that explores or analyzes a legal case, you should include the name of the case within the title of your essay to separate it from the rest of the text. For example, “Analyzing the Outcomes of the Case of Brown v. Board of Education ”.
How to Write Titles in an APA Essay?
Titles in an APA essay will utilize a unique system of headings that help in classifying and separating the different sections in your essay. They take levels. Note that the aforementioned instances of italicization will still apply on the different levels.
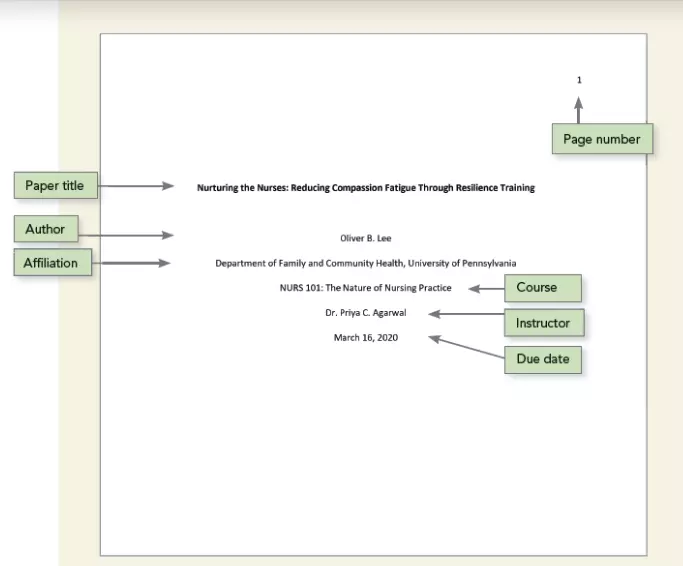
The first level or the main topic of your APA essay will be centered, boldface, and with a title-case heading.
Remember to capitalize the first word, all the principle words, and the last word in the title.
Avoid capitalizing prepositions (“above”, “on”, “to”, “below”, etc.), articles (“an”, “a”, and “the”), and coordinating conjunctions (“for”, “nor”, “and”, “but”, “so”, “or”, and “yet”).
The paragraph will be left justified with the first sentence indented.
The second level of the title should not be centered on your paper.
It should be flush left or it should begin at the left side of your page with no indentation.
It should also be typed in bold with a title case heading. The paragraph will also start from the left side of your paper with an indentation.
The third level of your titles should also begin at the left side of your page with no indentation. It should be boldface with a title case heading. However, the third level of your title should be italicized. The paragraph begins from the left side of your page with an indentation.
The fourth level of your titles should be indented, boldface, and with a title-case heading. This level is not italicized. However, it ends with a period because the text of the paragraph that follows should continue on the same line as that of the title level.
The fifth level of an APA title should also be indented, boldface, and with a title-case heading. However, this level is italicized. It also ends with a period since the next paragraph will start on the same line.
How to Write Titles for MLA Essay
Titles in an MLA essay have different levels with the first level being centered, boldface, and with a title, case heading. The second level should be written in the same way as the first level with the only difference being that the second level is flushed to the left side of the paper.

The third level should begin at the left side of your page with no indentation.
It should be boldface with a title case heading.
The third level of your title should be italicized.
The fourth level should be indented, boldface, and with a title, case heading.
This level is not italicized. However, it ends with a period.
The fifth level should also be indented, boldface, and with a title, case heading. This level is italicized. It also ends with a period.
In MLA, you should also capitalize the first word, all the principle words, and the last word in the title. Don’t capitalize prepositions, articles, and coordinating conjunctions.
Read our guide on how to write good essay titles to get further insight and tips that will help you sharpen your writing skills.

I am an educational writer and blogger focussing on tech, education, and life improvement.

- Research by Subject
- All Databases (A-Z)
- Course Reserves
- Journals by Title
- A book on the shelf
- Digital Collections
- Interlibrary Loan
- Make Appointment with Librarian
- Schedule a Class (faculty)
- Poster Production / Media
- Online / Distance Services
- Book a Study Room
- Special Collections
- Study Rooms
- All Policies
- Support the Library
- BuleyWise Blog
- Buley Bulletin
- Floor Plans
- Library Directory
- Library Hours
- The Director's Page
- Library Impact Dashboard
MLA Style Guide Eighth Edition
- MLA Style Guide Home
- Interactive Practice Template
- Automatically Generate Citations within the Databases!
- Free citation Software on the Web
- What's new in MLA 8th Edition?
- Title of Container
- Other Contributors
- Publication Date
- In-text Citation
- Annotated Bibliography
- Model MLA Paper
- EasyBib MLA 8th Edition
Title of Source. The title is usually taken from an authoritative location in the source such as the title page. It is the name of the source you are using. Capitalize the following parts of speech in a title: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, subordinating conjunctions (although, because, unless, after, until, when, where, while, etc.). Do not capitalize articles, prepositions, coordinating conjunctions, the "to" in infinitives if they appear in the middle of the title. A colon separates the title from the subtitle unless it ends in a question mark or exclamation. Titles should be italicized or enclosed in quotation marks. Titles that are independent and self-contained (e.g., books) and titles of containers (e.g., anthologies) should be italicized. Titles that are contained in larger works (e.g., short stories) should be in quotation s. Exceptions to the above rule are: 1) Scripture (Genesis, Bible, Gospels, Upanishads, Old Testament, Talmud, etc.) Titles of individualized scripture writings, however, should be italicized and treated like any other published work.(e.g. The Interlinear Bible) 2) Names of laws, acts and political documents (Bill of Rights, Declaration of Independence, Magna Carta, Treaty of Marseilles, etc.) 3) Musical compositions identified by form, number, and key (Beethoven's Symphony No. 7 in A, op. 92) 4) Series titles (Critical American Studies, Bollingen Series, etc.) 5) Conferences, seminars, workshops, and courses (MLA Annual Convention, English 110)
The title of the work follows the author and ends with a period . Mitchell, Margaret. Gone With the Wind . New York: Macmillan, 1961.
A sub-title is included after the main title . Joyce, Michael. Othermindedness: The Emergence of Network Culture. U of Michigan P, 2000. Baron, Sabrina Alcorn et al., editors. Agent of Change: Print Culture Studies after Elizabeth L. Eisenstein. U of Massachusetts P /Center for the Book, Library of Congress, 2007.
The title of a story, poem or essay in a collection, as part of a larger whole, is placed in quotation marks . Dewar, James A., and Peng Hwa Ang. "The Cultural Consequences of Printing and the Internet." Agent of Change: Print Culture Studies after Elizabeth L. Eisenstein. U of Massachusetts P /Center for the Book, Library of Congress, 2007, pp. 365-77.
Independent work in a collection When a work that is normally independent (such as a novel or play) appears in a collection, the work's title remains in italics. Euripides. The Trojan Women . Ten Plays, translated by Paul Roche, New American Library, 1998, pp. 457-512.
The title of a periodical (journal, magazine, or newspaper) is in italics and the title of the article is in quotation marks. Goldman, Anne. "Questions of Transport: Reading Primo Levi Reading Dante." The Georgia Review, vol. 64, no. 1, 2010 pp. 69-88. Note: This rule applies to all media forms such as the title of a television series, an episode in a television series, a song or piece of music in an album, a posting or article on a web page. See examples below. Television series Buffy the Vampire Slayer . Created by Joss Whedon, performance by Sarah Michelle Gellar, Mutant Enemy, 1997-2003. Episode in a television series "Hush." Buffy the Vampire Slayer , created by Joss Whedon, performance by Sarah Michelle Gellar, season 4, episode 10, Mutant Enemy, 1997-2003. Web site Hollmichel, Stefanie. So Many Books . 2003-13, somanybooksbkog.com Note: When giving a URL, omit http and https. Posting of an article on a web site Hollmichel, Stefanie. "The Reading Brain: Differences Between Digital and Print." So Many Books, 25 April 2013, somanybooksblog.com/2013/04/25/the-reading-brain-differences-between-digital- and-print/. A song or piece of music in an album Beyonce. "Pretty Hurts." Beyonce , Parkwood Entertainment, 2013, www.beyonce.com/album/beyonce/?media_view=songs.
Untitled Source In the place of the title, provide a generic description of the source without italics or quotation marks. Capitalize the first word in the title and any proper nouns in it. Mackintosh, Charles Rennie. Chair of Stained Oak. 1897-1900, Victoria and Albert Museum, London.
Comment or review of a title in an online forum Jeane. Comment on "The Reading Brain: Differences Between Digital and Print." So Many Books, 25 Apr. 2013, 10:30 p.m., somanybooksblog.com/2013/04/25/the-reading-brain-differences-between-digital-and- print/#comment-83030
Review of a title in an online forum Mackin, Joseph. Review of The Pleasures of Reading of an age of Distraction , by Alan Jacobs. New York Journal of Books, 2 June 2011, www.nyjournalofbooks.com/book-review/ pleasures-reading-age-distraction.
Tweet Reproduce the full text without changing anything and enclose within quotation marks. @persiankiwi."We have report of large street battles in east and west of Tehran now. - #Iranelection." Twitter , 23 June 2009, 11:15 a.m., twitter.com/persianwiki/status/2298106072.
E-mail message Use subject as the title. Subject is enclosed in quotation marks. Boyle, Anthony T. "Re: Utopia." Received by Daniel J. Cayhill, 21 June 1997.
Introduction, Preface, Foreword, or Afterword Capitalize the term in the works cited list but do not italicize or enclose in quotation marks. The term need not be capitalized in in-text discussion. Felstiner, John. Preface. Selected Poems and Prose of Paul Celan , by Paul Celan, translated by Felstiner W.W. Norton, 2001, pp.xix-xxxvi.
Translations of Titles Place translations of titles for foreign works in square brackets in the works cited list. The translation appears next to the title.
Shortened titles The first time a title is mentioned in your work, it should appear in full. If the title is repeated in the work, it can be shortened to a familiar one (e.g., Skylark for Ode to a Skylark).
- << Previous: Author
- Next: Title of Container >>
- Last Updated: Dec 15, 2023 1:48 PM
- URL: https://libguides.southernct.edu/mla

MLA Style Guide, 7th Edition: Titles
- About In-text Citations
- In-text Examples
- How to Paraphrase and Quote
- What to Include
- Editors, Translators, etc.
- Publication Date
- Volume/Issue
- Place of Publication
- Date of Access (when needed)
- Book with Personal Author(s)
- Book with Editor(s)
- Book with Organization as Author
- Work with No Author
- Parts of Books or Anthologies
- Multi-Volume Works
- Journal Article
- Newspaper Article
- Magazine Article
- Government Publication
- Web Publications
- Other Common Sources
- Formatting Your Paper
- Formatting Your 'Works Cited' List
- Annotated Bibliography
General Rules for Titles in Works Cited List (in progress)
In general, the title of a work is taken from the title page of the publication. Refer to section 3.6.4 of the MLA Manual for more about titles and quotations within titles. Section 3.6.5 discusses exceptions to the rules.
- Rules for capitalizing are strict. Capitalize all principal words (nouns, verbs, adjectives, etc.). Do not capitalize articles, prepostions, or conjunctions when they fall in the middle of a title.
- Separate a subtitle with a colon and a space.
- Italicize titles of larger works like books, periodicals, databases, and Web sites.
- Use quotation marks for titles published in larger works like articles, essays, chapters, poems, Web pages, songs, and speeches.
Book titles
Book titles are italicized.
- Writing Matters: A Handbook for Writing and Research (book)
- Their Eyes Were Watching God
- All the Pretty Horses
Chapter title in a book or anthology
The book title is italicized ; the title of the article or essay is enclosed in quotations.
Henderson, Carol E. "Refiguring the Flesh: The Word, the Body, and the Rituals of Being Loved in Beloved and Go Tell It on the Mountain ." Critical Insights: Toni Morrison . Ed. Solomon O. Iyasere and Marla W. Iyasere. Pasadena: Salem P, 2010. Print.
Beloved and Go Tell It on the Mountain (book titles) remain italicized in the article title.
Journals and Magazines
The title of the periodical (journal, magazine, or newspaper) is italicized. The title of the article or work is enclosed in quotations.
Danport, Sandra. " A Study of Malawian Households." Journal of Developing Areas ...
Gardiner, Andy. "Stanford Could Lose QB, Coach." USA Today ...
The title of the periodical (journal, magazine, or newspaper) is italicized. The title of the article or work is enclosed in quotations. Omit any introductory article in the newspaper title for English-language newspapers ( Palm Beach Post, not The Palm Beach Post ). Retain the article in non-English language newspapers ( Le monde ).
The title of the work is italicized if the work is independent. The title of the work is enclosed in quotation marks if it is part of a larger work. The title of the overall Web site is italicized if distinct from the the title of the work.
Park, Madison. "How Does a Baby Get To Be Obese." CNN.com ....
Salda, Michael N., ed. The Cinderella Project ...
- << Previous: Publication Date
- Next: Editions >>
- Last Updated: Dec 11, 2020 4:39 PM
- URL: https://irsc.libguides.com/mla7

Formatting Titles
by Purdue Global Academic Success Center and Writing Center · Published October 2, 2020 · Updated November 5, 2020

Let’s face it: For whatever reason, formatting titles can be confusing, especially if you think about all the titles that need proper formatting–the title placed on the title page of a paper, the title of a journal article mentioned in the body of a paper, the title of a newspaper or a website on the list of references. There are titles of books and titles of chapters in those books; titles of blogs and titles of blog entries. Some titles are italicized and some are put in quotation marks. Titles on the list of references require formatting–some titles use title case, some sentence case; some titles are italicized and some are not. And then there are those situations where titles are used in in-text citations–some titles are truncated and italicized; some are put in quotation marks–you get the idea.
First off, I am not going to address how to format titles when citing in the paper or listing on the list of references—those are formatting guidelines for another time. I am going to focus on titles on the title page, the first page of the paper, and within a paper. Here is what you need to keep straight:
Titles require special capitalization called title case. Title case requires one to
- capitalize the first letter of the first and last words of a title;
- capitalize the first letter of all verbs;
- capitalize all words of four or more letters;
- capitalize the first letter of all other words except a, an, the, short conjunctions such as “for, and, but,” and prepositions of fewer than four letters (words like “up, in, off”);
- capitalize the first letter of a word following a colon or dash;
- capitalize the first letter of a subtitle.
When a title appears on the title page of an APA Style 7th edition student paper, that title should be centered, bolded, and in title case—no need to use all caps, no need to italicize or underline, and no need to use quotation marks or place a period at the end.
Simply type out the title using title case and bold it–that’s it.
On the first page of the essay, center and repeat the title, bold it, and use title case. Again, do not use any special formatting. Do not use a bigger font size or style. Do not underline or italicize and so forth. Just use title case, bold, and center the title on the first page of the essay.
Easy enough, right?
Titles that appear within an essay require special formatting in addition to title case. If the title is for an article—content that is part of a greater whole—then the title should have quotation marks around it. If the title is for a book, journal, newspaper, or some other whole work, then the title is italicized.
Let’s say you have an article titled “The New Coffee Culture” that appears in the journal Studies in Popular Culture . Let’s also say that for whatever reason, you name both titles in the body of your paper. The article “The New Coffee Culture” appears in the journal Studies in Popular Culture , so the article is content that appears in a greater whole, right?
Both titles would be in title case. The article “The New Coffee Culture” would have quotation marks around it, and the title of the journal, Studies in Popular Culture , would be italicized.
I hope this blogcast clarifies exactly what you need to do when formatting titles in typical usage situations in APA style.
Until next week–
Kurtis Clements

Share this:
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Next story APA Style Formatting in PowerPoint
- Previous story Bias-Free Language
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / Citation Basics / Do You Italicize Article Titles?
Do You Italicize Article Titles?
No, typically you don’t italicize article titles. Instead, you may enclose article titles in double quotation marks (MLA 9: “Article Title”) or simply use regular font without quotation marks (APA 7: Article title). The exact format for article titles depends on the style guide you’re using. Different academic disciplines use different style manuals that follow differing rules. However, generally, you do italicize the larger work of which the article is a part ( Journal/Magazine/Newspaper Title ) .
Let’s look at how MLA 9, APA 7, and Chicago styles handle title formatting for articles.
MLA 9 Style for Article Titles
Since journal, magazine, and newspaper articles are part of a larger standalone work, you use regular font (not italics) for article titles and double quotation marks in MLA 9 style.
Here is a template for a magazine article in MLA 9-style:
Author Last Name, First Name. “Title of the Article.” Magazine Title , Publication Month. Year, pp. #-# or URL.
Here is an MLA 9-style reference list entry example for a magazine article:
Parker, James. “An Ode to My Thesaurus.” The Atlantic , July-Aug. 2022, https://www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2022/07/an-ode-to-my-thesaurus/638453/
Notice the regular font for the magazine article and the italics for the magazine title:
- Article title: “An Ode to My Thesaurus”
- Magazine title : The Atlantic
MLA 9’s style manual uses the term containers for larger standalone works. For example, a book is a container for a chapter. Here are more container examples:
- Container –> Item in container
- Album –> Song
- Book –> Chapter
- Journal –> Article
- Television show/series –> Episode
- Newspaper or Magazine Publication –> Interview
Standalone works or containers are italicized . That includes the titles of the following:
- Journal Titles
- Magazine Titles
- Newspaper Titles
- Photo/Image/Painting
- Television series
- Webpages/Websites
Works contained within a standalone work should be enclosed in double quotation marks. In the works-cited entry, these titles are placed before the container’s, or standalone work’s, title. Titles of works that are part of larger standalone works include the following:
- Book chapters
- Interviews in a magazine
- Journal articles
- Magazine article
- Newspaper article
- Short stories
- Song on an album
- Webpage/Website articles
APA 7 Style for Article Titles
Since journal, magazine, and newspaper articles are part of a larger standalone work, you use regular font (not italics) for article titles in APA style.
Here is a template for a journal article in APA 7-style:
Author Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Publication Year). Title of the journal article: Subtitle of article. Title of the Journal, VolumeNumber (IssueNumber), Page#-#. URL.
Here is an APA 7-style reference list entry example for a journal article:
Jacoby, W. G. (1994). Public attitudes toward government spending. American Journal of Political Science, 38 (2), 336-361. https://doi.org/10.2307/2111407
Notice the regular font for the journal article and the italics for the journal title:
- Article title: Public attitudes toward government spending.
- Journal title : American Journal of Political Science
In APA 7, you italicize titles of sources that stand alone. Standalone sources are not part of another work. Standalone works that you italicize in APA include:
- Journal Titles ( not journal articles)
- Magazine Title
- Music Album ( not a song on the album)
- Newspaper Title
- Podcast ( not a podcast episode)
- Television Series
- YouTube Video
Works that are just a part of another work, like a chapter in a book, are not italicized. Sources that are part of another work and in regular font in APA include:
- Edited Book Chapters
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Podcast episodes
- Songs on an album
- Television episodes
Chicago Style (17th ed. notes-bibliography format)
Since journal, magazine, and newspaper articles are part of a larger standalone work, you use regular font (not italics) and quotation marks for article titles in Chicago style.
Here is a template for a newspaper article in Chicago-style:
- Author First Name Last Name, “Newspaper Article Title,” Newspaper Title , Publication Month Day, Year, URL.
Bibliography:
Author Last Name, First Name. “Newspaper Article Title.” Newspaper Title , Publication Month Day, Year. URL.
Here are Chicago-style note and bibliography entry examples for a newspaper article:
- Emmett Lindner, “Keeping Up With Crypto,” New York Times , June 3, 2022, https://www.nytimes.com/2022/06/03/insider/keeping-up-with-crypto.html.
Lindner. Emmett. “Keeping Up With Crypto.” New York Times , June 3, 2022. https://www.nytimes.com/2022/06/03/insider/keeping-up-with-crypto.html.
Notice the regular font for the newspaper article and the italics for the newspaper title:
- Article title: “Keeping Up With Crypto”
- Newspaper title : New York Times
In Chicago style, you italicize titles of sources that stand alone. Standalone sources are not part of another work. Standalone works that you italicize in Chicago include:
Works that are just a part of another work, like a chapter in a book, are not italicized. Sources that are part of another work and in regular font in Chicago style include:
Citation Guides
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- Citation Examples
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Page Numbers
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
- Bibliography
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- View MLA Guide
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
The article title does not appear in in-text citations. It appears only in the corresponding works-cited-list entry. To cite the article title in MLA style in your works cited list, you need to follow the format given in the below template. An example of an article written by a single author is given for your understanding.
Works cited list template and example
The title of the article is in plain text and title case; it is placed inside quotation marks. Follow the punctuation and formatting as given in the example.
Surname, First Name. “Title of the Article.” Journal Title , volume #, issue #, publication date, page range.
Etchells, Tim. “On the Skids: Some Years of Acting Animals.” Performance Research , vol. 5, no. 2, 2000, pp. 55–60.
The article title of a journal, newspaper, or magazine is never italicized in either APA or MLA style. In APA style, the article title is given in plain text and sentence case. In MLA style, the article title is written in title case and given in quotation marks.
Citation Basics
Harvard Referencing
Plagiarism Basics
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
If a book title within an essay title is not italicized in the source, should I italicize it in my works-cited-list entry?
Note: This post relates to content in the eighth edition of the MLA Handbook . For up-to-date guidance, see the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Yes. A title within a title should be styled according to the guidelines in section 1.2.4 of the MLA Handbook , regardless of how a title within a title is styled in the source.
For example, the title of an essay about Gone with the Wind is styled in EBSCOHost as follows:
“Painfully Southern”: “Gone with the Wind,” the Agrarians, and the Battle for the New South
Since Gone with the Wind is the title of a novel, if you were to include this essay in your works-cited list, you would set it in italics instead of enclosing it in quotation marks:
Adams, Amanda. “‘Painfully Southern’: Gone with the Wind , the Agrarians, and the Battle for the New South.” Southern Literary Journal , vol. 40, no. 1, Fall 2007, p. 58. EBSCOHost Connection , connection.ebscohost.com/c/literary-criticism/28439869/painfully-southern-gone-wind-agrarians-battle-new-south.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Titles in Essays (Italics or Quote Marks?)
4-minute read
- 26th February 2018
Formatting your own essay title is easy (just bung a Heading style on it). Unfortunately, the rules about formatting the titles of existing published works (e.g. a textbook or an article from a journal) are more complicated. Usually, though, it comes down to one question: italics or quote marks?
But most students will need to name a book, journal or website in an essay at some point, so it’s important to know how this works. To help you out, we’ve prepared this guide on when to use italics and when to use quote marks for titles.
When to Use Italics
Titles of longer works are usually italicised. A ‘longer work’ in this case is something presented as a standalone publication. Charles Dickens’ famous novel, for example, would be written as Great Expectations if it were named in an essay.
Other examples of longer works that should be italicised include:
- Books and book-length poems (e.g. ‘An analysis of The Wasteland shows…’)
- Journals, newspapers and magazines (e.g. ‘According to The Guardian …’)
- Websites and blogs (e.g. ‘The project was funded via Unbound …’)
- Films (e.g. ‘ Jaws broke several box-office records…’)
- TV series (e.g. ‘Many fans of The X-Files claim…’)
- Plays and other stage shows (e.g. ‘This production of Swan Lake is…’)
- Paintings and works of art (e.g. ‘The Mona Lisa is currently housed…’)
- Music albums (e.g. ‘The album Sticky Fingers was released in…’)
The key factor is that all of these are standalone products, not part of a greater whole. The main exceptions to this rule are holy texts, such as the Bible, which are not typically italicised.
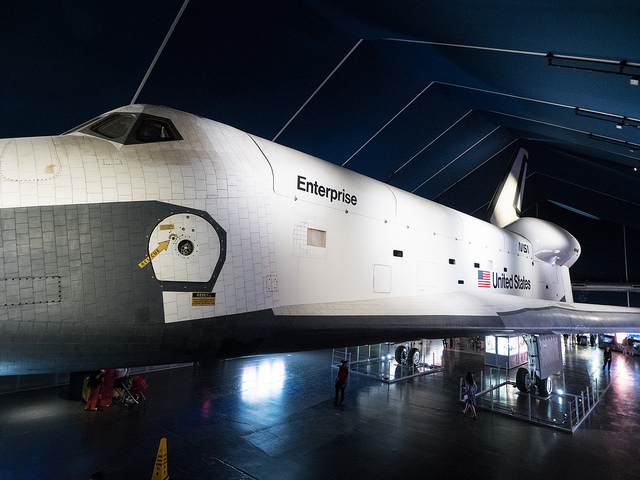
Italics are also used for the names of particular vehicles in some cases, especially ships and spacecraft. For example, we might write about the space shuttle Enterprise or the HMS Beagle (note that the ‘HMS’ is not italicised, since this is an abbreviation).

When to Use Quote Marks
Quote marks , meanwhile, are usually saved for shorter works. These are often part of a larger publication, such as an article in a newspaper or a chapter in an edited book. For example, if we were to name a book and a chapter in one place we’d write:
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Hugh Wilder’s ‘Interpretive Cognitive Ethology’ was first published in Readings in Animal Cognition , edited by Marc Bekoff and Dale Jamieson.
As indicated by the italics, the book here is called Readings in Animal Cognition . ‘Interpretive Cognitive Ethology’, meanwhile, is an essay from the book, so we use quote marks for this title.
Cases where quotation marks are used for titles include:
- Chapters from books
- Articles in newspapers, magazines and journals
- Particular pages or articles from a website
- Individual poems and short stories
- Episodes from a TV show
It is also common to use quote marks for unpublished writing regardless of length. For example, if you were referring to an unfinished manuscript or a PhD dissertation, you would put the title in quote marks; but if these same documents were published, you would use italics.
Look Out for Exceptions!
The guidelines above will apply in most cases, but there are exceptions. The APA style guide, for example, recommends italicising book titles in the main text of an essay, but not in the reference list. As such, it is wise to check your style guide to see if it has specific advice on formatting titles.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Get help from a language expert. Try our proofreading services for free.
The benefits of using an online proofreading service.
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
3-minute read
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Formatting Titles in Essays
2-minute read
- 8th May 2018
Handling your own headings is one thing, but how should you write the titles of other works? You need to mark them out somehow, and you have two standard options: italics or quote marks.
This is especially important in academic writing , as you’ll often have to discuss books and papers written by other people. Here, then, are some guidelines you should follow when formatting titles.
When to Use Italics
You can often spot a title from the capitalisation , but we still format titles to distinguish between different types of source. Titles of longer sources, for example, typically use italics:

Here, Kerrang! is italicised because it is the title of a magazine (i.e. a standalone work that is not one part of a larger whole). Other publications and productions that this applies to include:
- Academic journals
- Newspapers and magazines
- Websites and blogs
- Films and TV shows
- Radio programmes
- Plays and other stage shows
- Book-length poems
- Paintings and other works of art
- Music albums
The key here, then, is that italics are used for longer published works .
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
When to Use Quote Marks
We use quote marks for the title of anything that doesn’t fit in the list above. Usually, this will be something that is part of a more substantial publication, such as an article from a magazine:
In this case, we see both the magazine title and an article title. Using italics on the former and quote marks on the latter makes it immediately obvious which is which. Other cases where quote marks are required include:
- Chapters from books
- Academic papers and journal articles
- Articles from newspapers and magazines
- Single pages from a website or posts from a blog
- Individual poems and short stories
- Single episodes of a TV series
- Single poems from a collection
- Songs and other short recordings
In this case, the key is that quote marks are used for shorter works . However, quote marks are also used for unpublished works regardless of length (e.g. a draft manuscript or a PhD dissertation).
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Get help from a language expert. Try our proofreading services for free.
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
3-minute read
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

When writing a paper, do I use italics for all titles?
Simply put: no .
APA's Publication Manual (2020) indicates that, in the body of your paper , you should use italics for the titles of:
- "books, reports, webpages, and other stand-alone works" (p. 170)
- periodicals (journals, magazines, newspapers)
Beyond APA's specific examples, know that certain types of titles are almost always written in italics.
A general rule of thumb is that within the text of a paper, italicize the title of complete works but put quotation marks around titles of parts within a complete work.
The table below isn't comprehensive, but it's a good starting point
On an APA-style reference page , the rules for titles are a little different. In short, a title you would italicize within the body of a paper will also be italicized on a reference page. However, a title you'd place in quotation marks within the body of the paper (such as the title of an article within a journal) will be written without italics and quotation marks on the references page.
Here are some examples:
Smith's (2001) research is fully described in the Journal of Higher Education.
Smith's (2001) article "College Admissions See Increase" was published in the Journal of Higher Education after his pivotal study on the admissions process.
Visit the APA Style's " Use of Italics " page to learn more!
- Reading and Writing
- Last Updated Jun 12, 2022
- Views 2131207
- Answered By Kate Anderson, Librarian
FAQ Actions
- Share on Facebook
Comments (8)
- Nice, quick, concise listing. Good format to save for quick reference by AlonzoQuixano on May 14, 2015
- Thank you so much for the information. It was so helpful and easily understandable. by mary woodard on Jun 29, 2015
- Is it the same for MLA writing? Thanks Sara, Librarian: Lesa, Rasmussen College doesn't teach or focus on MLA for students. But if you have specific MLA formatting questions, I recommend you take a look at the MLA FAQ website here: https://www.mla.org/MLA-Style/FAQ-about-MLA-Style by Lesa D.W on Dec 04, 2015
- What about the name of a community program, for example Friend's Read. Would you use quotations or italics? Sara, Librarian: Adriana, great question. for organization or program names in the text of a paper you don't need to use italics or quotation marks. Just capitalize the major words of the organization or program like you did above with Friend's Read. by Adriana on Apr 11, 2016
- Thank you for this posting. I am writing a paper on The Crucible and, surprisingly, I couldn't find on the wonderfully thorough Purdue Owl APA guide whether titles of plays are italicized or in quotes. by J.D. on Apr 18, 2016
- this was really helpful, thank you by natalie on Dec 11, 2016
- thank you so much, this is very helpful and easy to understand. by Mendryll on Jan 24, 2017
- Thank you! I am also wondering, do you capitalize only the first word of the title when using it in the text of your paper, like you are supposed to do in the references list? Or do you capitalize all the "important" words like usual? Sara, Librarian Reply: Ashley, within the text of your paper you should capitalize all the important words like you normally would. Thank you for your question! by Ashley on Dec 04, 2017
Hello! We're here to help! Please log in to ask your question.
Need an answer now? Search our FAQs !
How can I find my course textbook?
You can expect a prompt response, Monday through Friday, 8:00 AM-4:00 PM Central Time (by the next business day on weekends and holidays).
Questions may be answered by a Librarian, Learning Services Coordinator, Instructor, or Tutor.

Writing Nestling

Do You Italicize Titles? (Easy Guide & Explained)
Welcome to the intriguing realm of typographical finesse – the nuanced practice of italicizing titles. In the vast landscape of written expression, the question of whether to italicize titles can be a labyrinthine endeavor, navigating the subtle nuances that distinguish literary works.
As we embark on this linguistic odyssey, we’ll unravel the conventions, explore the historical threads that weave through italics, and delve into the practicalities of emphasizing titles within the written tapestry.
So, do you italicize titles? Join us on this literary sojourn as we demystify the art of italicization and unveil the stylistic symphony that it brings to the written word.
Whether you’re a seasoned wordsmith or a burgeoning scribe, this exploration promises to shed light on the intricacies of title formatting, inviting you to wield italics with finesse and purpose in the vast expanse of language.
Table of Contents
Do You Italicize Titles?
Yes, you italicize titles when writing to indicate the title of a longer work, such as a book, movie, play, or magazine. Follow these steps:
Books, Magazines, Newspapers, Journals
Italicize the titles of complete works like books (e.g., To Kill a Mockingbird), magazines (e.g., National Geographic), newspapers (e.g., The New York Times), and journals (e.g., Journal of Psychology).
Movies and TV Shows
Italicize the titles of films (e.g., The Shawshank Redemption) and TV shows (e.g., Stranger Things).
Plays and Operas
Italicize the titles of plays (e.g., Hamlet) and operas (e.g., Carmen).
Albums and Songs
Italicize the titles of albums (e.g., The Dark Side of the Moon) and songs (e.g., Bohemian Rhapsody).
Artworks and Sculptures
Italicize the titles of paintings (e.g., Starry Night) and sculptures (e.g., David).
Websites and Online Publications
Italicize the names of websites (e.g., Wikipedia) and online publications (e.g., The Huffington Post).
Names of Ships and Aircraft
Italicize the names of ships (e.g., Titanic) and aircraft (e.g., Spirit of St. Louis).
Foreign Words and Phrases
Italicize foreign words or phrases that are not part of common English usage.
Remember, when writing by hand or in a situation where italics are not possible, you can underline titles instead. Additionally, short works like poems, articles, and short stories are typically placed in quotation marks rather than italicized.


General Rules for Italics
Unlock the door to a world of typographic elegance as we delve into the enchanting realm of italicization. Like the subtle curve of a dancer’s silhouette, italics bestow a touch of sophistication upon the written word, transforming mere titles into majestic declarations.
The general rules for italics are akin to the seasoned conductor guiding a symphony—each element plays a crucial part.
Whether it’s the weighty volumes of books demanding attention, the silver screen allure of movies, or the captivating drama scripted within plays, italics paint a canvas of distinction.
This typographic magic extends to the sonorous notes of long poems and the rhythmic beats of music albums, creating a harmonious symphony of visual eloquence.
Prepare to be transported to a world where words don’t just speak; they pirouette, leaving an indelible mark on the reader’s imagination. Welcome to the theatre of italics, where every title is a leading star in the grand production of language.
Titles of Books
Titles of books, those literary treasures that beckon us into worlds unknown, stand as the heralds of intellectual exploration.
In the vast tapestry of written expression, books emerge as the venerable monarchs, their titles encapsulating the essence of entire universes waiting to be unfurled.
The careful italicization of these titles not only pays homage to their significance but also acts as a visual cue, inviting readers to embark on a journey of wordsmithing wonder.
Each italicized title becomes a portal, a gateway to realms where characters breathe life, and narratives weave tapestries of emotions.
Whether it’s the whispering secrets of fiction, the bold expositions of non-fiction, or the lyrical verses of poetry, the italicized titles of books are the keys to unlocking the boundless potential of human imagination.
In the hallowed halls of literature, the artful presentation of book titles in italics is an invitation—an invitation to traverse the limitless landscapes of knowledge and creativity.
Specific Cases for Italics
Within the labyrinth of language, italics emerge as the enigmatic sorcerers, casting spells of emphasis and distinction. In the realm of specific cases for italics, their prowess becomes even more apparent.
Picture this: titles within titles become nesting dolls of emphasis, a literary matryoshka capturing layers of significance within words.
As your eyes dance across the page, italics gracefully encircle foreign words and phrases , offering linguistic passports to exotic realms of expression.
And behold the italicized flourish when words crave emphasis, as if they donned a bespoke suit for a grand entrance onto the stage of sentences.
Specific cases for italics are the hidden alcoves in the mansion of typography, where the ordinary becomes extraordinary, and every word is a protagonist in its own narrative.
Brace yourself for a typographic spectacle, where italics don’t just punctuate; they pirouette through the prose, leaving an indelible mark on the reader’s psyche.
Titles within Titles
Titles within titles, a literary rendezvous where words engage in a delicate dance of emphasis and distinction. Like Russian nesting dolls of language, the italicized inception of one title within another creates a mesmerizing effect, a literary echo that resonates with nuanced significance.
Picture a story within a story, a tantalizing narrative inception, where each layer of italics serves as a threshold to a new dimension of meaning.
It’s not just about words; it’s a typographic artistry that invites readers to explore the labyrinthine corridors of a tale within the tale.
The subtlety of italicized titles within titles is akin to an eloquent whisper amid the cacophony of words, urging readers to pay heed to the nuanced layers beneath the surface.
This typographic play within the pages is a testament to the kaleidoscopic nature of language, where each title is not just a signpost but a gateway to a literary universe within.
Alternatives to Italics
In the symphony of typographic choices, where italics wield their elegant baton, alternatives to this classic maestro emerge as bold soloists, each playing a distinctive note in the composition of written expression.
Quotation marks, the rebellious rockstars of punctuation, strut onto the stage, offering a dynamic alternative to the italicized subtlety.
Capitalization, the regal monarch of written form, asserts its authority, standing tall as a formidable contender. These alternatives aren’t mere understudies; they are the co-stars in the typographic drama, challenging the status quo with their unique flair.
Imagine a narrative where words gleam in the spotlight of quotation marks or where the grandiosity of capitalization commands attention.
These alternatives to italics are not just substitutes; they are stylistic choices that infuse the written word with a distinctive rhythm, making each sentence a memorable verse in the symphony of storytelling.
Step into the arena of typographic experimentation, where alternatives to italics are the avant-garde artists, injecting vibrancy into the canvas of language.

Use of Quotation Marks
The use of quotation marks, those nimble acrobats of punctuation, introduces a captivating rhythm to the written symphony.
Quotation marks are not just functional signposts; they are the stage upon which dialogue, excerpts, and verbatim expressions take center spotlight.
Like a pair of literary parentheses, they cradle the spoken words, giving them a distinctive identity within the narrative tapestry.
Picture the flutter of quotation marks as characters engage in a verbal ballet, their voices resonating with a unique cadence.
It’s not merely about delineating speech; it’s an intimate choreography where the dance of words is adorned with the elegant grace of punctuation.
In the theater of language, the use of quotation marks is akin to a director’s cue, signaling the entrance of dialogue and lending an animated quality to the written script.
Whether crafting fiction or relaying real-world conversations, the judicious use of quotation marks transforms the written word into a symphony of voices, each note resonating with the reader’s imagination.
Style Guides and Their Recommendations
Enter the realm of literary sherpas, where style guides stand as wise guides, illuminating the treacherous path of punctuation and formatting.
These literary luminaries, be it the stern commander of the Modern Language Association (MLA), the discerning tactician of the American Psychological Association (APA), or the eloquent maestro of the Chicago Manual of Style, don’t just wield rules; they conduct a symphony of writing conventions.
Style guides are the Gandalfs of the manuscript, whispering, “You shall not pass!” to inconsistencies and haphazard formatting.
Each guide, with its own set of commandments, becomes the North Star in the inky expanse of authorial uncertainty.
Embarking on a writing journey without consulting these sages is like navigating a stormy sea without a compass.
In the grand tapestry of language, style guides aren’t just advisors; they are the keepers of the sacred flame of consistency, ensuring that every word, every comma, adheres to the hallowed doctrines of the written craft.
Modern Language Association (MLA)
The Modern Language Association (MLA), a venerable institution in the world of academia and literary scholarship, stands as a guiding beacon for writers navigating the labyrinth of citation and formatting.
Founded in 1883, the MLA has evolved into a stalwart guardian of scholarly communication, shaping the standards for research papers, essays, and manuscripts.
With its iconic parenthetical citations and meticulous guidelines, the MLA acts as a linguistic architect, constructing a framework that ensures clarity, consistency, and intellectual rigor in written discourse.
Academics and students alike bow to the MLA as a steadfast mentor, offering a roadmap through the intricate terrain of documentation and citation, allowing ideas to flow seamlessly from one mind to another.
In the grand mosaic of writing conventions, the MLA is a cornerstone, a testament to the timeless pursuit of precision and elegance in the written word.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
In the captivating ballet of language, where every word pirouettes across the stage, common mistakes can be likened to missteps that disrupt the rhythm of the narrative waltz.
Picture this literary dancefloor, where the misplaced twirl of a comma or the clumsy stumble of inconsistent formatting can lead to a typographic fiasco.
One of the cardinal sins is the mischievous misuse of italics, turning what should be a graceful emphasis into a chaotic cacophony.
Beware the overzealous italicizer, for too much emphasis can be as jarring as a poorly tuned instrument in a symphony.
Another pitfall is the sly inconsistency that lurks in the shadows, waiting to trip up unsuspecting writers. It’s a masquerade ball where punctuation masquerades as its grammatical counterpart, leaving sentences in disarray.
In this intricate dance of syntax, let’s not forget the dangers of neglecting the meticulous proofreading tango—a dance with typos and errors that can mar the elegance of the written performance.
In the grand theater of writing, these common mistakes aren’t just blunders; they are the mischievous sprites that threaten to turn eloquence into chaos. Dance wisely, dear writers, and may your prose glide gracefully through the literary ballroom.
Misuse of Italics
The misuse of italics in the written landscape is akin to a misplaced spotlight on the stage; instead of highlighting brilliance, it casts a glaring distraction.
This typographic misdemeanour is a subtle saboteur, transforming what should be a nuanced emphasis into an unwarranted spectacle.
A heavy-handed approach turns prose into a visual rollercoaster, where every word clamors for attention, robbing the reader of the gentle cadence that italics should provide.
It’s the equivalent of shouting in a library when a hushed whisper would suffice. The misuse of italics disrupts the delicate dance of language, diminishing the impact of truly significant words by drowning them in a sea of slanting letters.
Writers beware, for in the labyrinth of emphasis, a misstep with italics can turn a literary ballet into a chaotic mosh pit, leaving readers bewildered rather than captivated.

Practical Examples
Imagine the world of writing as a grand culinary expedition, and practical examples are the delectable ingredients that add flavor to the prose feast.
They are the saffron strands in a literary paella, the truffle shavings on the linguistical risotto. Practical examples aren’t just garnishes; they are the succulent bites that elucidate complex ideas and infuse the narrative with the richness of real-world application.
Much like master chefs crafting a gastronomic symphony, writers utilize practical examples to elevate their storytelling to a sensory experience.
These examples aren’t mere illustrations; they are the vibrant strokes that paint vivid images in the reader’s mind, turning abstract concepts into palpable realities.
So, as you embark on your literary banquet, savor the practical examples, for they are the secret sauce that transforms words into a literary feast for the mind.
Correct Italics Usage
Correct italics usage is the secret handshake of eloquent communication, a nuanced dance that adds finesse to the written language.
It is the judicious art of emphasis, guiding the reader’s gaze to the heart of the narrative with a subtle slant. Like a skilled conductor orchestrating a symphony, correct italics usage ensures that titles of books, movies, and plays step onto the stage with the regal flair they deserve.
It’s a typographic ballet where foreign words and phrases, adorned in italics, pirouette with grace amidst the prose.
Correct italics usage isn’t just about adherence to rules; it’s about infusing the written word with a visual melody that resonates in the reader’s mind.
It’s a punctuation ballet where every italicized note plays a vital role in harmonizing the symphony of expression. In the realm of language, correct italics usage is the well-timed crescendo, enhancing the resonance of each written composition.
Evolution of Italics Usage
Dive into the riveting narrative of italics, where each slanting serif tells a tale of evolution in the grand tapestry of language.
Once a humble tool for emphasis, italics have donned many masks over the centuries, morphing from typographic wallflowers into bold trendsetters.
Picture the Renaissance, where italics burst forth like eager buds in the spring, breathing life into the manuscripts of scholars and poets.
Fast forward to the digital age, and italics become the chameleons of expression, adapting seamlessly to the screens of our electronic devices.
No longer confined to the solemnity of the printed page, italics have become the graffiti artists of the written word, splashing slanted flair across social media and digital platforms.
The evolution of italics is a literary journey, a metamorphosis from quill and parchment to the pixelated playgrounds of modern communication.
In this typographic saga, italics aren’t just punctuation marks; they are shape-shifters, navigating the currents of evolving expression with unmatched finesse.
Historical Perspective
Embark on a voyage through the corridors of time, where the historical perspective of italics unfolds like an ancient manuscript waiting to be deciphered.
Italics, with its roots reaching back to the 15th century Italy, emerges as a testament to the craftsmanship of early typographers.
Initially conceived as a handwriting style to emulate the elegance of calligraphy, italics found its way into the printing press, becoming the hallmark of emphasis in early manuscripts.
The Renaissance saw italics bloom, with scholars and printers recognizing its potential to lend emphasis and visual harmony to written works.
Through quills and printing presses, italics became a silent witness to the epochs, adapting to the changing winds of writing conventions.
As the epochs unfolded, italics transcended the ink-and-paper realm, finding a new life in the digital age. In the historical tapestry of typographic evolution, italics stand as a timeless artifact, weaving a narrative that spans centuries and continents.
Frequently Asked Questions about Do You Italicize Titles?
When should i italicize titles.
Titles of longer works, such as books, movies, plays, and magazines, should be italicized. This helps distinguish them from shorter works like poems or articles .
Do I italicize titles in all writing styles?
Yes, most writing styles, including MLA, APA, and Chicago, recommend italicizing titles for longer works. However, styles may vary, so it’s essential to follow the guidelines of the specific style you’re using.
Are there exceptions to italicizing titles?
Yes, shorter works like poems, articles, and short stories are usually placed in quotation marks instead of being italicized. Additionally, specific style guides may have exceptions for certain types of works.
Can I use underlining instead of italics for titles?
Yes, when typing is not possible or practical, you can underline titles as an alternative to italics. However, it’s essential to be consistent in your choice throughout your writing.
How about titles of TV shows and songs? Do they follow the same rule?
Yes, titles of TV shows (e.g., Breaking Bad) and songs (e.g., Bohemian Rhapsody) should be italicized or placed in quotation marks, depending on the preference of your chosen writing style.
What about titles in social media posts or informal writing?
In more casual writing, such as social media posts or informal emails, italics may be less strictly adhered to. However, maintaining consistency in your formatting enhances clarity and professionalism.
Do foreign words or phrases need to be italicized?
Yes, foreign words or phrases that are not part of common English usage should be italicized. This helps readers recognize and distinguish them in the text.
How do I format titles if I’m writing by hand?
If italics are not feasible, you can underline titles when writing by hand. The goal is to visually set the title apart from the rest of the text.
Should I italicize titles of online publications and websites?
Yes, titles of websites (e.g., CNN) and online publications (e.g., The Guardian) should be italicized to indicate they are longer, standalone works.
Can you provide examples of when to italicize and when to use quotation marks?
Certainly! For instance, you italicize a book title (The Great Gatsby) but use quotation marks for a short story title (“The Lottery”). Consistency in applying these rules is key for clarity and correctness in writing.
In conclusion, understanding when to italicize titles is a fundamental aspect of proper writing conventions.
Whether you are crafting an academic paper, a creative work, or even a social media post, the consistent application of italicizing titles for longer works like books, movies, and plays, and using quotation marks for shorter works like poems and articles, contributes to the clarity and professionalism of your writing.
While variations exist among different writing styles, maintaining awareness of these guidelines ensures that your titles are appropriately formatted, making it easier for readers to navigate and comprehend your content.
So, the next time you find yourself pondering whether to italicize a title, consider the type of work and adhere to the conventions of the writing style you are following for a polished and well-structured piece.
Related Posts:
- How To Write A Job Posting Ad (11 Effective Ways And…
- How To Write A French Accent (10 Important Steps You…
- Do Authors Use Ghost Writers? (Explained with 05 Reasons)
- Why Does Academic Writing Require Strict Formatting?
- What Is A Snapshot In Writing? (Easy Guide & Explained)
- How To Write An Australian Accent (10 Best Ways You…
Similar Posts

Can I Blog About Random Things? (12 Important Tips)
Embarking on the digital odyssey of blogging opens up a world of possibilities, and a common question that often arises is, “Can I blog about random things?” The short answer? Absolutely. In fact, the beauty of blogging lies in its inherent versatility, offering creators the freedom to explore an eclectic array of topics. Imagine your…

Talking About The Weather In English (11 Steps You Need To Know)
Talking about the weather in English may seem like a simple and mundane endeavor, yet it’s a conversation topic that transcends linguistic borders and cultural boundaries. It’s an art form, an everyday ritual, and a universal connector. Weather talk is the small talk that opens doors to more profound discussions, the social glue that bonds…

How Do Websites Make Money With Ads? (12 Best Ways)
In the bustling digital landscape, the question of how websites make money with ads unveils a fascinating tapestry of strategies, innovations, and symbiotic relationships. As the heartbeat of the online ecosystem, websites navigate the intricate dance between user experience and revenue generation. From the bold strokes of display ads to the nimble precision of programmatic…

How To Write For Bustle (15 Best Ways You Need To Know)
Introducing the fascinating world of writing for Bustle, where words come alive to capture the ever-evolving essence of contemporary life. Writing for Bustle offers a unique opportunity to become a part of a dynamic storytelling ecosystem, reaching a diverse and engaged audience hungry for fresh perspectives on a vast array of subjects. Whether you’re a…

Can Content Writing Make You Rich? 12 Best Ways
In the ever-evolving landscape of the digital age, the question resonates with aspiring wordsmiths and seasoned content creators alike: Can content writing make you rich? Beyond the mere arrangement of words, content creation has emerged as a dynamic force in the vast galaxy of online communication. This inquiry is not just about financial aspirations; it…

What Is Creative Writing? (Definition & 11 Best Steps)
Creative writing is the celestial dance of words, an art form that transcends the ordinary to forge literary constellations that illuminate the human experience. At its core, creative writing is a cosmic exploration of imagination, a journey into the uncharted realms where storytelling becomes a vehicle for self-expression, creativity, and connection. It encompasses a diverse…

Do You Italicize Article Titles? (Ultimate Citation Guide)
Do you italicize article titles? Put them in quotes? Underline them? If you’ve ever struggled with how to format titles, this blog post is for you.
Do you italicize article titles?
No, you do not italicize article titles. You place article titles in double quotation marks. This formatting rule applies to article titles in MLA, APA, Chicago Style, scholarly journals, magazines, newspapers, online, and most reference sections.
In this article, we’ll look at 11 specific scenarios so that we cover all the bases and answer all of your questions (Hint: only one scenario has an exception).
Do You Italicize Article Titles: Summary of Answers
I thought you might appreciate a summary table right here at the beginning.
I wanted to keep the table super simple so I only included two categories—type of content and whether or not you italicize it.
Check it out below:
Table of Contents
You might consider bookmarking this article in your favorite internet browser so that you can come back to this information anytime you want for a quick refresher.
Do Article Titles Get Italicized? (The One Exception)

You do not italicize article titles. You almost always place double quotation marks around article titles.
The only time you detour from quotation marks is when you write titles in an APA-style reference list. In that case, you write the title without any special formatting (italics, quotation marks, or underlining).
That’s the simple, direct answer.
Here are two simple examples of a properly formatted article title:
Wrong: Is Superman a Pisces
Right: “Is Superman a Pisces?”
Now, let’s look at other specific questions you might ask yourself when writing.
Do You Italicize Article Titles in MLA?
No, you do not italicize the titles of articles in MLA. You place the article title in quotes.
Here are two examples:
Wrong: 5 Signs He’s Too Tall For You
Right: “5 Signs He’s Too Tall For You”
Here’s an example of a complete MLA citation from a real article:
Kokoski, Christopher. “How To Become a Fortune Cookie Writer.” Christopher Kokoski, 16 Apr. 2021, www.writingbeginner.com/how-to-become-a-fortune-cookie-writer.
MLA , by the way, stands for Modern Language Association. The MLA Handbook is basically a stylebook for how to write information, format documents, and cite sources.
Do You Italicize Article Titles in APA?
You do not italicize article titles in APA. You place double quotation marks around the titles of articles.
Wrong: Will Ferrell Loves Baby Jesus
Right: “Will Ferrell Loves Baby Jesus”
APA stands for the American Psychological Association . APA is another style of writing, formatting, and citing information.
Do You Italicize Article Titles in APA References?
No, you do not italicize article titles in APA references or citation lists. You also don’t need to underline the title or put the title in quotes. You simply write the article title without any special formatting.
I understand the confusion when it comes to referencing sources in a list of citations at the end of a paper or article. The rule on titles is still “No, don’t italicize article titles,” but that doesn’t tell you WHAT to do.
The answer is that you don’t need to do anything at all. You simply list the title. Note that this is the ONLY exception to the answer in the answer box image at the beginning of this post.
Still, you don’t italicize the article title.
Wrong: Kokoski, C. (2021, April 16). How To Become a Fortune Cookie Writer . Christopher Kokoski. https://www.writingbeginner.com/how-to-become-a-fortune-cookie-writer/
Right: Kokoski, C. (2021, April 16). How To Become a Fortune Cookie Writer . Christopher Kokoski. https://www.writingbeginner.com/how-to-become-a-fortune-cookie-writer/
Keep in mind that style handbooks, like APA, tend to change over time. It’s a good idea to always check with the latest version of the APA style guide.
Do Journal Article Titles Get Italicized?
You do not italicize journal articles. You place double quotation marks around the title of journal articles in MLA and do not format the title of the journal articles at all in APA.
The confusion with scholarly journals is that you italicize the name of the journal, but you place quotes around the title of the articles in the journal. There is also a difference between the rules for MLA and APA-style reference lists.
However, in all cases, you do not italicize the title of journal articles.
Here are examples from MLA:
Wrong: Shamblen, Stephen & Kokoski, Christopher & Collins, David & Strader, Ted & Mckiernan, Patrick. (2017). Implementing Creating Lasting Family Connections with reentry fathers: A partial replication during a period of policy change . Journal of Offender Rehabilitation. 56. 1-13. 10.1080/10509674.2017.1327917.
Right: Shamblen, Stephen & Kokoski, Christopher & Collins, David & Strader, Ted & Mckiernan, Patrick. (2017). “Implementing Creating Lasting Family Connections with reentry fathers: A partial replication during a period of policy change.” Journal of Offender Rehabilitation. 56. 1-13. 10.1080/10509674.2017.1327917.
Do You Italicize Article Titles in Chicago Style?
What about Chicago Style? This is a good question since some of the “rules” are different between the style guides. However, the rule for italicizing article titles is the same.
You do not italicize article titles in Chicago Style. You place the title of the article in quotation marks.
Here are a few examples of Chicago Style :
Wrong: His article, Writing Love Squares: 13 Things You Need To Know , made some fascinating points!
Right: His article, “Writing Love Squares: 13 Things You Need To Know,” made some fascinating points!
Do Newspaper Article Titles Get Italicized?
You do not italicize the title of articles in newspapers. You place the title in double quotation marks. However, you do italicize the name of the newspaper.
Here are examples:
Wrong: Her article, Salvation by Dessert , appeared in The New York Times .
Right: Her article, “Salvation by Dessert,” appeared in The New York Times .
Note that, in these examples, the title of the specific article is in quotes but the title of the newspaper is italicized.
Should Any Article Titles Be Italicized?
You never italicize any entire article titles. You might, however, italicize unfamiliar foreign words or the titles of books you mention within an article title. But you do not italicize the entire article title under any circumstance.
I know this is somewhat of a repeat of the first question in the article, but sometimes I find it helpful to ask (and answer) the silly questions that summarize the information in a blog post.
Hopefully, this slight repeat helps you as it might help others.
For the sake of clarity, here are more examples of how to format article titles:
Wrong: The Problem With Smurfette
Right: “The Problem With Smurfette”
Since we’re about to look at a few rare scenarios you might face, here is a short video from Khan Academy to really nail down how to use quotation marks in titles:
Do You Italicize Foreign Words in Article Titles?
What about foreign words within the title of your article?
The Chicago Manual of Style says:
Italicize individual foreign words or short phrases that readers might not understand. Therefore, you should italicize only the unfamiliar foreign word or phrase within the title. Place quotation marks around the complete title of the article.
How do you know if a foreign word will confuse readers?
You check the English dictionary. If a foreign word or short phrase appears in the English dictionary, you probably don’t need to italicize it. If the word or phrase doesn’t appear in the English dictionary, then you can safely italicize it.
Just remember to place double quotation marks around the entire article title.
Wrong: The Best Teachers Embrace Juegos in the Classroom
Right: “The Best Teachers Embrace Juegos in the Classroom”
Do You Italicize the Title of Books in Your Article Title?
This is another very special circumstance.
You do not italicize article titles. If you name a book in the title of your article, you italicize only the name of the book. The entire article title is placed in quotation marks.
Here is an example:
Wrong: How Wicker Hollow Changed the Way I View Thriller Fiction
Right: “How Wicker Hollow Changed the Way I View Thriller Fiction”
Note: Wicker Hollow is the title of a book (in this case, it’s a book I wrote).
Do You Italicize the Title of Other Articles in Your Article Title?
This is a somewhat confusing question to ask, but I’ll try to clarify.
Sometimes you include the title of another article inside your article title. For example, imagine that you want to write an article about another, separate article.
When you reference another article in your article title, you italicize only the other, referenced article. However, the overall title of your article is not italicized. Rather, you place your article title in quotes.
Let’s look at a concrete example. Perhaps you read an article titled, “Fan Fiction 101,” and want to write about it. You decide to write your own article that references, “Fan Fiction 101”.
Here is the wrong and right way to format your article title:
Wrong: “My Take on the ‘Fan Fiction 101’ Viral Trend”
Right: “My Take on the Fan Fiction 101 Viral Trend”
Automatic Citation Generator
By the way, even though we already answered the question “Do you italicize article titles?”, I thought you might like a quick shortcut I use for citing sources.
My favorite automatic citation generator is made by Scribbr . It’s not perfect, but it usually works like a charm when I need a quick, accurate citation.
Best of all, it is free and generates:
- MLA citations
- APA citations
- Chicago Style citations
Final Thoughts: Do You Italicize Article Titles?
Thank you for reading this article. I hope you found all the answers you wanted (and then some).
If you enjoyed this post, you might also like these other articles:
- Why Do Writers Hate Adverbs (The Final Answer)
- Is Social Media Good or Bad For Writers? (The Final Answer)
- My Most Recommended Tools for Writers
1 thought on “Do You Italicize Article Titles? (Ultimate Citation Guide)”
Pingback: Does Scrivener Check Grammar? (Fully Explained for Beginners) -
Comments are closed.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Reference List: Basic Rules

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resourse, revised according to the 7 th edition APA Publication Manual, offers basic guidelines for formatting the reference list at the end of a standard APA research paper. Most sources follow fairly straightforward rules. However, because sources obtained from academic journals carry special weight in research writing, these sources are subject to special rules . Thus, this page presents basic guidelines for citing academic journals separate from its "ordinary" basic guidelines. This distinction is made clear below.
Note: Because the information on this page pertains to virtually all citations, we've highlighted one important difference between APA 6 and APA 7 with an underlined note written in red. For more information, please consult the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , (7 th ed.).
Formatting a Reference List
Your reference list should appear at the end of your paper. It provides the information necessary for a reader to locate and retrieve any source you cite in the body of the paper. Each source you cite in the paper must appear in your reference list; likewise, each entry in the reference list must be cited in your text.
Your references should begin on a new page separate from the text of the essay; label this page "References" in bold, centered at the top of the page (do NOT underline or use quotation marks for the title). All text should be double-spaced just like the rest of your essay.
Basic Rules for Most Sources
- All lines after the first line of each entry in your reference list should be indented one-half inch from the left margin. This is called hanging indentation.
- All authors' names should be inverted (i.e., last names should be provided first).
- For example, the reference entry for a source written by Jane Marie Smith would begin with "Smith, J. M."
- If a middle name isn't available, just initialize the author's first name: "Smith, J."
- Give the last name and first/middle initials for all authors of a particular work up to and including 20 authors ( this is a new rule, as APA 6 only required the first six authors ). Separate each author’s initials from the next author in the list with a comma. Use an ampersand (&) before the last author’s name. If there are 21 or more authors, use an ellipsis (but no ampersand) after the 19th author, and then add the final author’s name.
- Reference list entries should be alphabetized by the last name of the first author of each work.
- For multiple articles by the same author, or authors listed in the same order, list the entries in chronological order, from earliest to most recent.
- Note again that the titles of academic journals are subject to special rules. See section below.
- Italicize titles of longer works (e.g., books, edited collections, names of newspapers, and so on).
- Do not italicize, underline, or put quotes around the titles of shorter works such as chapters in books or essays in edited collections.
Basic Rules for Articles in Academic Journals
- Present journal titles in full.
- Italicize journal titles.
- For example, you should use PhiloSOPHIA instead of Philosophia, or Past & Present instead of Past and Present.
- This distinction is based on the type of source being cited. Academic journal titles have all major words capitalized, while other sources' titles do not.
- Capitalize the first word of the titles and subtitles of journal articles , as well as the first word after a colon or a dash in the title, and any proper nouns .
- Do not italicize or underline the article title.
- Deep blue: The mysteries of the Marianas Trench.
- Oceanographic Study: A Peer-Reviewed Publication
Please note: While the APA manual provides examples of how to cite common types of sources, it does not cover all conceivable sources. If you must cite a source that APA does not address, the APA suggests finding an example that is similar to your source and using that format. For more information, see page 282 of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 7 th ed.

Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students
Knowing When To Underline Or Italicize: Your Go-To Guide

Knowing when to underline or italicize can be confusing. But it doesn’t have to be! In this article, we’ll lay out all the basics, plus a few common difficulties that confuse many writers, so you’ll be an expert in no time.
At the end of the article, you’ll get the chance to practice your hand at some sample sentences, so you’ll be sure that you know the ins and outs of using italics and underlines.
Italics Vs Underline: Clarifying The Confusion
In the past (before computers and MLA handbooks), italics and underlines were used to emphasize certain words or titles within the text. It let the reader know what was important, or what was separate from the rest of the sentence. They were both used interchangeably, as long as they were consistent.
Now, with the ability to change formatting with the click of a button, italics are generally used to indicate titles, and only sometimes for emphasis. Meanwhile, underlining is mostly reserved to replace italics in handwritten papers. Manuals and guidebooks, such as the MLA handbook, are now widely used in large institutions or according to the country’s standards, so that specific writing conventions, grammar rules, and formatting styles have become uniform.
With that said, the general rule is that italics are used for titles of books, movies, TV and radio shows, magazines, works of art, and long poems. As mentioned before, underlining is a substitute for italics when writing titles by hand.

Proper formatting in an essay can be confusing for many students: https://www.pexels.com/photo/woman-in-blue-blazer-holding-white-paper-3727468/
Titles of long works.
Titles that should be italicized are longer works. These include titles of books, movies, TV and radio shows, journals and magazines, and long poems. In the next section, we’ll see how these works differ from titles of shorter works which are put in quotations instead.
- The novel Jane Eyre, by Charlotte Bronte, was published in 1847 under the pen name of Currer Bell.
- The movie Home Alone , released in 1990, made a worldwide total of $476,684,675 in box office revenue.
Titles Of Smaller Works
The titles of smaller works are put in “quotations” in order to differentiate them from longer works. These smaller works include titles of chapters, short stories, TV or radio show episodes, articles, and short poems.
In the examples below, note how you can recognize the difference between the shorter works and larger works just by seeing how they are emphasized in the sentence. This makes it impossible to confuse the title of a chapter with the book that it belongs to, or the episode from its TV show.
- The chapter entitled “The Castaway” in Moby Dick describes the near-death experience of a character named Pip.
- Edgar Allen Poe’s short story, “The Fall of the House of Usher,” was originally published in a Burton’s Gentleman’s Magazine.
- The pilot episode of Friends , which was released on September 22, 1994, is called “The One Where Monica Gets A Roommate.”
Punctuation In Titles: Common Confusions
Question marks.
Confusion can come up when a title includes a question mark or an exclamation mark in the title itself. For example, the book Who Has Seen the Wind? includes a question mark in it.
The way to deal with these titles is to italicize the question mark as well, just as it is above. By doing so, you can differentiate this title from an actual question, such as writing: Have you read Gone With the Wind ?
The same idea applies to exclamation marks — for example, the movie Mamma Mia! , which includes an exclamation mark in the title. Note the italicization, and the difference between writing Mamma Mia! , the movie, and writing: I can’t believe that you never watched The Parent Trap !
Commas and periods
The confusion of commas and periods when it comes to quotations is a debate between different handbooks and countries. According to the MLA (Modern Language Association) handbook, commas and periods are placed inside of quotation marks.
- “The Seinfeld Chronicles , ” the first episode of Seinfeld , had 15.4 million viewers in America.
- Among the short stories of James Joyce included in the collection Dubliners are “Araby , ” “The Sisters , ” and “The Encounter.”

Solidify your new skills by completing practice sentences: https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-wearing-black-and-white-stripe-shirt-looking-at-white-printer-papers-on-the-wall-212286/
Let’s practice.
Try your hand at your new skills! Below are five sentences without any italics or quotations. Italicize the longer works and put the shorter works in quotations. If you get stuck, check back in the article, and you’ll be an expert in no time. Be sure to pay attention to tricky commas, periods, and question marks.
- The Lazy Controller, chapter two of Thinking Fast and Slow, talks about multitasking and its effect on thinking.
- The Yellow Wallpaper, a short story by Catherine Perkins Gilman, was originally published in The New England Magazine in January 1892.
- John Lennon’s album Imagine included favorites such as Gimme Some Truth, How Do You Sleep?, and, of course, Imagine.
- The premiere episode of Family Matters is called The Mama Who Came To Dinner, and relays the drama of Carl’s mother coming to live with him.
- The short story Hills Like White Elephants by Ernest Hemingway was first published in a magazine called Transition, and was only later published in his book Men Without Women.
Why Is Proper Indentation Important?
College essays .
No matter what you study in college, most students write a lot of essays during their school years. While some degrees may put more of an emphasis on writing proper essays , most teachers and professors will expect a certain level of basic grammar and formatting knowledge. Before you even step foot into college, you’ll most likely be expected to write an application essay . It’s important to put your best foot forward, and small formatting rules can go a long way in making a good first impression.
Landing your dream job
In addition to college essays, prospective employers and job positions will require and look for basic (or advanced, depending on the position) writing skills. Whether you think your dream job requires writing skills or not, writing is a part of everyday life and work, from emails and text messages, to presentations and reports. Having good writing skills will help you make a good first impression, land your dream job, and do your best work.

Proper writing is an important skill for any job: https://www.pexels.com/photo/writing-notes-idea-class-7103/
Having a successful career.
Though different students earn a degree for different reasons, many are hoping to work toward a successful career. In order to do this, the right preparation is key. Preparation may be earning a degree, gaining specific skills, or having the right guidance along the way.
University of the People prepares our students for successful careers by providing program advising , mentorship , and an emphasis on career development . We know that these extra details, much like formatting in an essay, make a big difference for the future success of our students. University of the People is a tuition-free online university that offers degree programs in business administration, computer science, health science, and education.
Wrapping Up
Now you know when to underline or italicize, and much more. To wrap up, italics should be used for the titles of longer works such as movies, books, and TV shows, and underlining for handwritten papers.
In addition, we hope you’ve learned the more tricky rules such as question marks and commas, and that you’ve given some thought to the importance of writing for your future education and success.
Related Articles
Do You Italicize Book Titles? MLA, Chicago Manual, and APA Rules (Examples)

Whether you are writing a book, a business blog, a research paper, or a magazine article, staying true (and consistent) to grammar and style is extremely important. It makes the entire article/ manuscript consistent and reading easy !
But with so many styles and style guides around, losing track is very common. This is especially true when you are writing titles – of books, stories, poems, chapters, and more – in your articles. Don’t you wonder whether you should underline the book titles, put them in italics, write them in quotation marks , or follow the traditional capital letter style? Well, we all do, and we often find ourselves hovering over different options, completely unsure of which one to choose .
So, should you italicize book titles or underline them?
The general rule says, always italicize book titles, if they are long and complete work. This keeps them distinct and makes them easily recognizable, especially when you are mentioning a book within your content. Italicizing also helps the reader to understand that this particular book is separate from the rest of the work they are reading. However, short titles – of poems, stories, articles, and chapters are often written in quotation marks.
For example:
Long title: Have you read In Search of Lost Time by Marcel Proust?
Short title: Grab your copy of “War and Peace” by Leo Tolstoy.
Now, this sometimes, can get very confusing and can put your writing all over the place. So when you are stuck between a right and a wrong, always follow the rule of thumb – How you write book titles in your work is a matter of choice (style). It is not governed by any grammarian law. There is no single source that governs how you must handle titled works and mostly depends on the style guide your publication is following – APA, Chicago, MLA, or any other.
So ask your editor his/ her preference and stick to it across your content. After all, consistency is the key to turning your writing into the most professional-looking copy .
In this article, we’ll help you learn the styling parameters that different style guides follow while writing book titles:
MLA rules for italicizing book titles
MLA stands for Modern Language Association – a United States-based society that styles manuals for students and scholars across the world. The MLA Handbook follows a particular style for documenting book titles, in the text as well as at the end of the article. As per the MLA style guide:
- Titles that are independent and self-contained are italicized.
- If the book title has a subtitle, the subtitle is italicized and separated by a colon (:).
- Titles that are contained in larger works ( e.g. , short stories, chapters) are put in quotations.
- However, when it comes to series titles, the MLA rules are a little confusing. In MLA, if a series title forms a part of the book title, then it is italicized. Otherwise, it is left in plain text. For example, the ‘Twilight Saga’ is a series title that you won’t italicize because it is not the tile of the book. But Harry Potter (a series title) you will italicize because it also forms a part of the title.
- Godfrey, Wyck., et al. The Twilight Saga : New Moon . Two-disc special ed. [Los Angeles, CA], Summit Entertainment, 2010.
- Rowling, J. K. Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone. New York: Arthur A. Levine Books, 1998.
Chicago Manual of style rules
The Chicago Manual of Style is another widely accepted and used citation system. It is used across various disciplines like the humanities, sciences, social sciences, and more. It has its own style for citing books , titles, and full-length and freestanding works. If you want to follow the Chicago Manual of Style while formatting your book titles, here are some points to remember:
- Always italicize and capitalize the titles of your full-length, freestanding works. These include books, magazines, journals, blogs, research papers, and more.
- Online book citation also follows the same format.
- Chapter titles are always written in quotations and are not italicized.
APA style guide rules
The American Psychological Association (APA) is one of the most common and widely used reference styles. It is mostly used as a citation style for books and manuals written in the field of social sciences, psychology, sociology, and more. It has its own set of rules for in-text and reference list citations. But when it comes to italicizing the books’ titles, the rules are pretty similar.
- Though in the APA, italicizing is kept to the bare minimum, long book titles, periodicals, webpages, reports, and standalone work are all italicized.
- Chapter titles in the APA are neither italicized nor written within quotes; the book titles however are. Also, the name of the chapter’s author is written in the first position.
7th Edition rules
The seventh edition of the APA is the latest edition and its purpose is to help students, scholars, and researchers write and communicate more effectively. Some of the biggest changes brought by the APA in its seventh edition include:
- The first letter (of the first word) of the title is capitalized.
- If there is a colon (:) in the title, the first letter after the colon is also capitalized.
- Proper names in titles are always capital
- Titles of books, magazines, journals, and newspapers are always italicized.
- Titles of articles or book chapters are not italicized.
- The title of the webpage is always italicized.
- The publisher’s location is no longer included in the reference.
When to Italicize Book Titles
As you could see , when it comes to writing book titles, a common rule applies across all styles ( barring a few exceptions ). So, if you are not following a particular citation style that asks you to do otherwise, this is a general rule that you can easily fall back on:
- Always italicize the titles of self-contained, independent work: books, albums
- Always italicize the titles of large books, like Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone
- Always italicize magazine names, like The New Yorker
- Always italicize newspapers, like The New York Times
Italicizing titles creates a visual hierarchy and helps a reference source stand out from the rest of the text.
When to Avoid Italicizing Book Titles?
While most book titles should be italicized, there are some exceptions to the rule:
- Short titles or titles of smaller works are not italicized. These include titles of short stories, poems, and chapters.
- The title of the series is not italicized. For example, while you would italicize Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets , you would not highlight the Harry Potter Series.
- Holy Books like The Bible and Quran, along with their sections, are not italicized.
- Headlines and course titles are also not italicized.
Do You Underline Book Titles?
No, we do not underline book titles . Underlining is an old formatting style that was once extensively used to emphasize certain words, phrases, and titles. But today, due to the availability of extensive formatting options, underlining has lost its mark and is not used as a preferred formatting option.
However, if you are writing with a medium that does not offer the option to italicize, you may underline the text to emphasize it.
Do You Quote Book Titles?
Books, magazines, newspapers, and series all comprise many smaller parts, like a short poem, a chapter, a short story, and an episode. When citing these small pieces of work, we prefer writing them in quotation marks.
The teacher read a story titled “Lamb to the Slaughter” by Roald Dahl.
I missed the last episode of “Shaun the Sheep”.
Susan is reading “The Fellowship of the Ring” from the Lord of the Rings .
Do You Italicize Book Series Titles?
While italics are used to emphasize book titles, trilogies and book series titles are only capitalized, not italicized.
What About Children’s Book Titles, Do Those Get Italicized?
Children’s books in style guides get the same treatment as other authored books. That is, titles of full works are italicized but short titles of poems, short stories, articles, or chapters are put within quotation marks. Also, in addition to the author’s name, they also include the illustrator’s name.
- Italics and Underlining: Titles of Works
- Treatment of titles
- Do You Italicize Book Titles In APA? A Must Read
- Should You Underline Or Italicise Book Titles?
- Do You Italicize Book Titles? Essay Secrets Revealed
- Should You Italicize Book Titles? A Guide to Formatting Titles
Inside this article
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Use quotation marks around the title if it is part of a larger work (e.g. a chapter of a book, an article in a journal, or a page on a website). All major words in a title are capitalized. The same format is used in the Works Cited list and in the text itself. Place in quotation marks. Italicize.
The answer to this question depends on the type of words in the title. Essay titles can be italicized. In case you have a title that includes names of vehicles, large works, television series, or movies, you should use italics when mentioning them. Essay titles can be italicized if the words represent a literary work or are a quote that needs ...
When to use italics. In APA Style papers, use italics for the following cases: Case. Example. First use of key terms or phrases, often accompanied by a definition. Mindfulness is defined as "the act of noticing new things, a process that promotes flexible responding to the demands of the environment" (Pagnini et al., 2016, p. 91).
Titles should be italicized or enclosed in quotation marks. Titles that are independent and self-contained (e.g., books) and titles of containers (e.g., anthologies) should be italicized. ... The title of a story, poem or essay in a collection, as part of a larger whole, is placed in quotation marks. Dewar, James A., and Peng Hwa Ang. ...
Refer to section 3.6.4 of the MLA Manual for more about titles and quotations within titles. Section 3.6.5 discusses exceptions to the rules. Rules for capitalizing are strict. Capitalize all principal words (nouns, verbs, adjectives, etc.). Do not capitalize articles, prepostions, or conjunctions when they fall in the middle of a title.
Titles that appear within an essay require special formatting in addition to title case. If the title is for an article—content that is part of a greater whole—then the title should have quotation marks around it. If the title is for a book, journal, newspaper, or some other whole work, then the title is italicized. Let's say you have an ...
Titles and Subtitles. Section 1.2.1 of the eighth edition of the MLA Handbook says, "Use a colon and a space to separate a title from a subtitle, unless the title ends in a question mark or an exclamation point. Include other punctuation only if it is part of the title or subtitle.". The handbook provides the following examples:
No, typically you don't italicize article titles. Instead, you may enclose article titles in double quotation marks (MLA 9: "Article Title") or simply use regular font without quotation marks (APA 7: Article title). The exact format for article titles depends on the style guide you're using. Different academic disciplines use different ...
Yes. A title within a title should be styled according to the guidelines in section 1.2.4 of the MLA Handbook, regardless of how a title within a title is styled in the source. For example, the title of an essay about Gone with the Wind is styled in EBSCOHost as follows: "Painfully Southern": "Gone with the Wind," the Agrarians, and the Battle for the New South
As indicated by the italics, the book here is called Readings in Animal Cognition. 'Interpretive Cognitive Ethology', meanwhile, is an essay from the book, so we use quote marks for this title. Cases where quotation marks are used for titles include: Chapters from books. Articles in newspapers, magazines and journals.
Do Not Use Italics. For the title of book series - i.e., "the Dan Brown series" Punctuation around italics - i.e., "(extremely dissatisfied)" Words from foreign languages that are in the dictionary of the language you are writing - i.e., "per se" Things To Remember. This list of rules and exceptions can feel overwhelming.
When to Use Italics. You can often spot a title from the capitalisation, but we still format titles to distinguish between different types of source. Titles of longer sources, for example, typically use italics: Here, Kerrang! is italicised because it is the title of a magazine (i.e. a standalone work that is not one part of a larger whole).
Italics and quotation marks are used to draw attention to text. For example, italics are used to draw attention to key terms and phrases when providing definitions and to format parts of reference list entries (e.g., titles of books and periodicals). Quotation marks are used to present linguistic examples and titles of book chapters and ...
Using italics vs. quotation marks in titles depends on your style guide. But the general rule is to italicize long titles, such as titles of books, movie titles, or album titles. Meanwhile, you must write titles in quotation marks for shorter pieces like musical titles, magazines, TV series, and articles. Note that the AP style does not put ...
On an APA-style reference page, the rules for titles are a little different.In short, a title you would italicize within the body of a paper will also be italicized on a reference page. However, a title you'd place in quotation marks within the body of the paper (such as the title of an article within a journal) will be written without italics and quotation marks on the references page.
Italicize foreign words or phrases that are not part of common English usage. Remember, when writing by hand or in a situation where italics are not possible, you can underline titles instead. Additionally, short works like poems, articles, and short stories are typically placed in quotation marks rather than italicized.
The rule on titles is still "No, don't italicize article titles," but that doesn't tell you WHAT to do. The answer is that you don't need to do anything at all. You simply list the title. Note that this is the ONLY exception to the answer in the answer box image at the beginning of this post. Still, you don't italicize the article ...
Note again that the titles of academic journals are subject to special rules. See section below. Italicize titles of longer works (e.g., books, edited collections, names of newspapers, and so on). Do not italicize, underline, or put quotes around the titles of shorter works such as chapters in books or essays in edited collections.
Now you know when to underline or italicize, and much more. To wrap up, italics should be used for the titles of longer works such as movies, books, and TV shows, and underlining for handwritten papers. In addition, we hope you've learned the more tricky rules such as question marks and commas, and that you've given some thought to the ...
If there is a colon (:) in the title, the first letter after the colon is also capitalized. Proper names in titles are always capital. Titles of books, magazines, journals, and newspapers are always italicized. Titles of articles or book chapters are not italicized. The title of the webpage is always italicized.