Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 25 March 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core Collection This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: Jan 17, 2024 10:05 AM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews
How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
3 straightforward steps (with examples) + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

38 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very timely.
I appreciate.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: Mar 26, 2024 10:40 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

Research Methods and Design
- Action Research
- Case Study Design
Literature Review
- Quantitative Research Methods
- Qualitative Research Methods
- Mixed Methods Study
- Indigenous Research and Ethics This link opens in a new window
- Identifying Empirical Research Articles This link opens in a new window
- Research Ethics and Quality
- Data Literacy
- Get Help with Writing Assignments
A literature review is a discussion of the literature (aka. the "research" or "scholarship") surrounding a certain topic. A good literature review doesn't simply summarize the existing material, but provides thoughtful synthesis and analysis. The purpose of a literature review is to orient your own work within an existing body of knowledge. A literature review may be written as a standalone piece or be included in a larger body of work.
You can read more about literature reviews, what they entail, and how to write one, using the resources below.
Am I the only one struggling to write a literature review?
Dr. Zina O'Leary explains the misconceptions and struggles students often have with writing a literature review. She also provides step-by-step guidance on writing a persuasive literature review.
An Introduction to Literature Reviews
Dr. Eric Jensen, Professor of Sociology at the University of Warwick, and Dr. Charles Laurie, Director of Research at Verisk Maplecroft, explain how to write a literature review, and why researchers need to do so. Literature reviews can be stand-alone research or part of a larger project. They communicate the state of academic knowledge on a given topic, specifically detailing what is still unknown.
This is the first video in a whole series about literature reviews. You can find the rest of the series in our SAGE database, Research Methods:
Videos covering research methods and statistics
Identify Themes and Gaps in Literature (with real examples) | Scribbr
Finding connections between sources is key to organizing the arguments and structure of a good literature review. In this video, you'll learn how to identify themes, debates, and gaps between sources, using examples from real papers.
4 Tips for Writing a Literature Review's Intro, Body, and Conclusion | Scribbr
While each review will be unique in its structure--based on both the existing body of both literature and the overall goals of your own paper, dissertation, or research--this video from Scribbr does a good job simplifying the goals of writing a literature review for those who are new to the process. In this video, you’ll learn what to include in each section, as well as 4 tips for the main body illustrated with an example.
- Literature Review This chapter in SAGE's Encyclopedia of Research Design describes the types of literature reviews and scientific standards for conducting literature reviews.
- UNC Writing Center: Literature Reviews This handout from the Writing Center at UNC will explain what literature reviews are and offer insights into the form and construction of literature reviews in the humanities, social sciences, and sciences.
- Purdue OWL: Writing a Literature Review The overview of literature reviews comes from Purdue's Online Writing Lab. It explains the basic why, what, and how of writing a literature review.
Organizational Tools for Literature Reviews
One of the most daunting aspects of writing a literature review is organizing your research. There are a variety of strategies that you can use to help you in this task. We've highlighted just a few ways writers keep track of all that information! You can use a combination of these tools or come up with your own organizational process. The key is choosing something that works with your own learning style.
Citation Managers
Citation managers are great tools, in general, for organizing research, but can be especially helpful when writing a literature review. You can keep all of your research in one place, take notes, and organize your materials into different folders or categories. Read more about citations managers here:
- Manage Citations & Sources
Concept Mapping
Some writers use concept mapping (sometimes called flow or bubble charts or "mind maps") to help them visualize the ways in which the research they found connects.

There is no right or wrong way to make a concept map. There are a variety of online tools that can help you create a concept map or you can simply put pen to paper. To read more about concept mapping, take a look at the following help guides:
- Using Concept Maps From Williams College's guide, Literature Review: A Self-guided Tutorial
Synthesis Matrix
A synthesis matrix is is a chart you can use to help you organize your research into thematic categories. By organizing your research into a matrix, like the examples below, can help you visualize the ways in which your sources connect.
- Walden University Writing Center: Literature Review Matrix Find a variety of literature review matrix examples and templates from Walden University.
- Writing A Literature Review and Using a Synthesis Matrix An example synthesis matrix created by NC State University Writing and Speaking Tutorial Service Tutors. If you would like a copy of this synthesis matrix in a different format, like a Word document, please ask a librarian. CC-BY-SA 3.0
- << Previous: Case Study Design
- Next: Quantitative Research Methods >>
- Last Updated: Feb 6, 2024 9:20 AM
CityU Home - CityU Catalog

A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Stellar Literature Review (with Help from AI)

Table of contents

Aren’t all of us mini versions of Sherlock Holmes when browsing data and archives for a research piece? As we go through the process, a comprehensive literature review is an essential toolkit to make your research shine.
A literature review consists of scholarly sources that validate the content. Its primary objective is to offer a concise summary of the research and to let you explore relevant theories and methodologies. Through this review, you can identify gaps in the existing research and bridge them with your contribution.
The real challenge is how to write an excellent literature review. Let’s learn.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is an introduction to your research. It helps you put your perspective to the table, along with a summary of the theme.
What does my literature review communicate?
- Explanation of your research: how the information was collected, the research method, the justification of the chosen data sources, and an overview of the data analysis.
- Framework: the journey from where the concept began and how it is presented.
- Connects the previous and current research:
It presents the broader scope of your research by connecting it to the existing data and debates and underlining how your content fits the prevailing studies.
In an era of information overload, a literature review must be well-structured.
Let’s learn all about the structure and style of a literature review that’ll help you strengthen your research.
Literature review– structure and style
Begin with a question and end it with the solution– the key to structuring a literature review. It resembles an essay’s format, with the first paragraph introducing the readers to the topic and the following explaining the research in-depth.
The conclusion reiterates the question and summarizes the overall insights of your research. There’s no word count restriction. —it depends on the type of research. For example, a dissertation demands lengthy work, whereas a short paper needs a few pages.
In a literature review, maintaining high quality is vital, with a focus on academic writing style. Informal language should be avoided in favor of a more formal tone.
The content avoids contractions, clearly differentiating between previous and current research through the use of past and present tense. Wordtune assists in establishing a formal tone, enhancing your work with pertinent suggestions. This AI-powered tool ensures your writing remains genuine, lucid, and engaging.

The option of refining the tonality offers multiple possibilities for rephrasing a single sentence. Thus, pick the best and keep writing.
Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
Your friendly step-by-step guide to writing a literary review (with help from AI)
Do you find it challenging to begin the literature review? Don’t worry! We’re here to get you started with our step-by-step guide.
1. Narrow down the research scope
Simply begin with the question: What am I answering through my research?
Whether it’s cooking or painting, the real challenge is the prep-up for it rather than performing the task. Once you’re done, it smoothly progresses. Similarly, for your literature review, prepare the groundwork by narrowing down the research scope.
Browse and scoop out relevant data inclining well with your research. While you can’t cover every aspect of your research, pick a topic that isn’t too narrow nor too broad to keep your literature review well-balanced.
2. Hunt relevant literature
The next question: Does this data align with the issue I’m trying to address?
As you review sources of information, hunt out the best ones. Determine which findings help in offering a focused insight on your topic. The best way to pick primary sources is to opt for the ones featured in reliable publications. You can also choose secondary sources from other researchers from a reasonable time frame and a relevant background.
For example, if your research focuses on the Historical Architecture of 18th-century Europe, the first-hand accounts and surveys from the past would hold more weight than the new-age publications.
3. Observe the themes and patterns in sources
Next comes: What is the core viewpoint in most of the research? Has it stayed constant over time, or have the authors differed in their points of view?
Ensure to scoop out the essential aspects of what each source represents. Once you have collected all this information, combine it and add your interpretations at the end. This process is known as synthesis.
Synthesize ideas by combining arguments, findings and forming your new version.
4. Generate an outline
The next question: How can I organize my review effectively? When navigating multiple data sources, you must have noticed a structure throughout the research. Develop an outline to make the process easier. An outline is a skeletal format of the review, helping you connect the information more strategically.
Here are the three different ways to organize an outline– Chronologically, Thematically, or by Methodology.You can develop the outline chronologically, starting from the older sources and leading to the latest pieces. Another way of organizing is to thematically divide the sections and discuss each under the designated sub-heading.
You can even organize it per the research methods used by the respective authors. The choice of outline depends on the subject. For example, in the case of a science paper, you can divide the information into sections like introduction, types of equipment, method, procedure, findings, etc. In contrast, it’s best to present it in divisions based on timelines like Ancient, Middle Ages, Industrial revolutions, etc., for a history paper.
If you’re confused about how to structure the data, work with Wordtune.

With the Generate with AI feature, you can mention your research topic and let Wordtune curate a comprehensive outline for your study.

Having a precise prompt is the key to getting the best results.
5. Start filling!
Your next question must be: Am I ready to compose all the parts of the literature review?
Once you’re ready with the basic outline and relevant sources, start filling in the data. Go for an introductory paragraph first to ensure your readers understand the topic and how you will present it. Ensure you clearly explain the section in the first sentence.
However, if beginning from the first paragraph seems intimidating, don’t worry! Add the main body content to the sub-headings, then jump to the introduction.
Add headings wherever possible to make it more straightforward and guide your readers logically through different sources. Lastly, conclude your study by presenting a key takeaway and summarizing your findings. To make your task easier, work with Wordtune. It helps align your content with the desired tone and refine the structure.
6. Give attention to detail and edit
The last question: Am I satisfied with the language and content written in the literature review? Is it easy to understand?
Once you’re done writing the first draft of a literature review, it’s time to refine it. Take time between writing and reading the draft to ensure a fresh perspective. It makes it easier to spot errors when you disconnect from the content for some time. Start by looking at the document from a bird's eye to ensure the formatting and structure are in order.
After reviewing the content format, you must thoroughly check your work for grammar, spelling, and punctuation. One of the best approaches to editing and proofreading is to use Wordtune . It helps simplify complex sentences, enhance the content quality, and gain prowess over the tonality.
The dos and don’ts of writing a literature review
Writing a stellar literature review requires following a few dos and don'ts. Just like Sherlock Holmes would never overlook a hint, you must pay attention to every minute detail while writing a perfect narrative. To help you write, below are some dos and don'ts to remember.

Composing a literature review demands a holistic research summary, each part exhibiting your understanding and approach. As you write the content, make sure to cover the following points:
- Keep a historical background of the field of research. Highlight the relevant relation between the old studies and your new research.
- Discuss the core issue, question, and debate of your topic.
- Theories lay the foundation of research. While you’re writing a literature review, make sure to add relevant concepts and ideas to support your statements.
- Another critical thing to keep in mind is to define complex terminologies. It helps the readers understand the content with better clarity.
Examples of comprehensive literature reviews
Aren’t good examples the best way to understand a subject? Let’s look into a few examples of literature reviews and analyze what makes them well-written.
1. Critical Thinking and Transferability: A Review of the Literature (Gwendolyn Reece)
An overview of scholarly sources is included in the literature review, which explores critical thinking in American education. The introduction stating the subject’s importance makes it a winning literature review. Following the introduction is a well-defined purpose that highlights the importance of research.
As one keeps reading, there is more clarity on the pros and cons of the research. By dividing information into parts with relevant subheadings, the author breaks a lengthy literature review into manageable chunks, defining the overall structure.
Along with other studies and presented perspectives, the author also expresses her opinion. It is presented with minimal usage of ‘I,’ keeping it person-poised yet general. Toward the conclusion, the author again offers an overview of the study. A summary is further strengthened by presenting suggestions for future research as well.
2. The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review
This literature review is thematically organized on how technology affects language acquisition. The study begins with an introduction to the topic with well-cited sources. It presents the views of different studies to help readers get a sense of different perspectives. After giving these perspectives, the author offers a personalized opinion.
One of the critical aspects that makes this a good literature review is a dedicated paragraph for definitions. It helps readers proceed further with a clear understanding of the crucial terminologies. There’s a comparison of the modern and previous studies and approaches to give an overall picture of the research.
Once the main body is composed, the author integrates recommendations for action-based tips. Thus, the literature review isn’t just summarizing the sources but offering actions relevant to the topics. Finally, the concluding paragraph has a brief overview with key takeaways.
Wordtune: your writing buddy!
A literature review demands the right balance of language and clarity. You must refine the content to achieve a formal tone and clear structure. Do you know what will help you the most? Wordtune !.
The real-time grammar checker leaves no scope for errors and lets you retain precision in writing. This writing companion is all you need for stress-free working and comprehensive literature review development.
Let the narrative begin
A literary review isn't just about summarizing sources; it's about seamlessly bringing your perspective to the table. Always remember to set a narrative for added interest and a brilliant composition. With structure and style being the pillars of a stellar literature review, work with Wordtune to ensure zero compromises on the quality.
Share This Article:


The Official Wordtune Guide

An Expert Guide to Writing Effective Compound Sentences (+ Examples)
How I Turned Clutter into Cash: 10 Proven Instagram Copywriting Hacks
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Sample Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts
Have an exemplary literature review.
- Literature Review Sample 1
- Literature Review Sample 2
- Literature Review Sample 3
Have you written a stellar literature review you care to share for teaching purposes?
Are you an instructor who has received an exemplary literature review and have permission from the student to post?
Please contact Britt McGowan at [email protected] for inclusion in this guide. All disciplines welcome and encouraged.
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Mar 22, 2024 9:37 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 21 March 2024
Expert review of the science underlying nature-based climate solutions
- B. Buma ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2402-7737 1 , 2 na1 ,
- D. R. Gordon ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6398-2345 1 , 3 na1 ,
- K. M. Kleisner 1 ,
- A. Bartuska 1 , 4 ,
- A. Bidlack 5 ,
- R. DeFries ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3332-4621 6 ,
- P. Ellis ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7933-8298 7 ,
- P. Friedlingstein ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3309-4739 8 , 9 ,
- S. Metzger 10 nAff15 nAff16 ,
- G. Morgan 11 ,
- K. Novick ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8431-0879 12 ,
- J. N. Sanchirico 13 ,
- J. R. Collins ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5705-9682 1 , 14 ,
- A. J. Eagle ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0841-2379 1 ,
- R. Fujita 1 ,
- E. Holst 1 ,
- J. M. Lavallee ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3028-7087 1 ,
- R. N. Lubowski 1 nAff17 ,
- C. Melikov 1 nAff18 ,
- L. A. Moore ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0239-6080 1 nAff19 ,
- E. E. Oldfield ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6181-1267 1 ,
- J. Paltseva 1 nAff20 ,
- A. M. Raffeld ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5036-6460 1 ,
- N. A. Randazzo 1 nAff21 nAff22 ,
- C. Schneider 1 ,
- N. Uludere Aragon 1 nAff23 &
- S. P. Hamburg 1
Nature Climate Change ( 2024 ) Cite this article
9786 Accesses
43 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Climate-change ecology
- Climate-change mitigation
- Environmental impact
Viable nature-based climate solutions (NbCS) are needed to achieve climate goals expressed in international agreements like the Paris Accord. Many NbCS pathways have strong scientific foundations and can deliver meaningful climate benefits but effective mitigation is undermined by pathways with less scientific certainty. Here we couple an extensive literature review with an expert elicitation on 43 pathways and find that at present the most used pathways, such as tropical forest conservation, have a solid scientific basis for mitigation. However, the experts suggested that some pathways, many with carbon credit eligibility and market activity, remain uncertain in terms of their climate mitigation efficacy. Sources of uncertainty include incomplete GHG measurement and accounting. We recommend focusing on resolving those uncertainties before broadly scaling implementation of those pathways in quantitative emission or sequestration mitigation plans. If appropriate, those pathways should be supported for their cobenefits, such as biodiversity and food security.
Similar content being viewed by others

The principles of natural climate solutions
Peter Woods Ellis, Aaron Marr Page, … Susan C. Cook-Patton

Constraints and enablers for increasing carbon storage in the terrestrial biosphere
Connor J. Nolan, Christopher B. Field & Katharine J. Mach
On the optimality of 2°C targets and a decomposition of uncertainty
Kaj-Ivar van der Wijst, Andries F. Hof & Detlef P. van Vuuren
Nature-based climate solutions (NbCS) are conservation, restoration and improved management strategies (pathways) in natural and working ecosystems with the primary motivation to mitigate GHG emissions and remove CO 2 from the atmosphere 1 (similar to ecosystem-based mitigation 2 ). GHG mitigation through ecosystem stewardship is integral to meeting global climate goals, with the greatest benefit coming from near-term maximization of emission reductions, followed by CO 2 removal 3 . Many countries (for example, Indonesia, China and Colombia) use NbCS to demonstrate progress toward national climate commitments.
The scope of NbCS is narrower than that of nature-based solutions (NbS) which include interventions that prioritize non-climate benefits alongside climate (for example, biodiversity, food provisioning and water quality improvement) 4 . In many cases, GHG mitigation is considered a cobenefit that results from NbS actions focused on these other challenges 2 . In contrast, NbCS are broader than natural climate solutions, which are primarily focused on climate mitigation through conservation, restoration and improved land management, generally not moving ecosystems beyond their unmodified structure, function or composition 5 . NbCS may involve moving systems beyond their original function, for example by cultivating macroalgae in water deeper than their natural habitat.
The promise of NbCS has generated a proliferation of interest in using them in GHG mitigation plans 6 , 7 ; 104 of the 168 signatories to the Paris Accord included nature-based actions as part of their mitigation plans 8 . Success in long-term GHG management requires an accurate accounting of inputs and outputs to the atmosphere at scale, so NbCS credits must have robust, comprehensive and transparent scientific underpinnings 9 . Given the urgency of the climate problem, our goal is to identify NbCS pathways with a sufficient scientific foundation to provide broad confidence in their potential GHG mitigation impact, provide resources for confident implementation and identify priority research areas in more uncertain pathways. Evaluating implementation of mitigation projects is beyond our scope; this effort focuses on understanding the underlying science. The purpose is not evaluating any specific carbon crediting protocol or implementation framework but rather the current state of scientific understanding necessary to provide confidence in any NbCS.
In service of this goal, we first investigated nine biomes (boreal forests, coastal marine (salt marsh, mangrove, seagrass and coral reef), freshwater wetlands, grasslands, open ocean (large marine animal and mesopelagic zone biomass, seabed), peatlands, shrublands, temperate forests and tropical forests) and three cultivation types (agroforestry, croplands and macroalgae aquaculture); these were chosen because of their identified potential scale of global impact. In this context, impact is assessed as net GHG mitigation: the CO 2 sequestered or emissions reduced, for example, discounted by understood simultaneous emissions of other GHG (as when N 2 O is released simultaneously with carbon sequestration in cropland soils). From there, we identified 43 NbCS pathways which have been formally implemented (with or without market action) or informally proposed. We estimated the scale of mitigation impact for each pathway on the basis of this literature and, as a proxy measure of NbCS implementation, determined eligibility and activity under existing carbon crediting protocols. Eligibility means that the pathway is addressed by an existing GHG mitigation protocol; market activity means that credits are actively being bought under those eligibility requirements. We considered pathways across a spectrum from protection to improved management to restoration to manipulated systems, but some boundaries were necessary. We excluded primarily abiotically driven pathways (for example, ocean alkalinity enhancement) or where major land use or land-use trade-offs exist (for example, afforestation) 10 , 11 , 12 . Of the 43 pathways, 79% are at present eligible for carbon crediting (sometimes under several methodologies) and at least 65% of those have been implemented (Supplementary Table 1 ). This review was then appraised by 30 independent scholars (at least three per pathway; a complete review synthesis is given in the Supplementary Data ).
Consolidation of a broad body of scientific knowledge, with inherent variance, requires expert judgement. We used an expert elicitation process 13 , 14 , 15 with ten experts to place each proposed NbCS pathway into one of three readiness categories following their own assessment of the scientific literature, categorized by general sources of potential uncertainty: category 1, sufficient scientific basis to support a high-quality carbon accounting system or to support the development of such a system today; category 2, a >25% chance that focused research and reasonable funding would support development of high-quality carbon accounting (that is, move to category 1) within 5 years; or category 3, a <25% chance of development of high-quality carbon accounting within 5 years (for example, due to measurement challenges, unconstrained leakage, external factors which constrain viability).
If an expert ranked a pathway as category 2, they were also asked to rank general research needs to resolve: leakage/displacement (spillover to other areas), measuring, reporting and verification (the ability to quantify all salient stocks and fluxes), basic mechanisms of action (fundamental science), durability (ability to predict or compensate for uncertainty in timescale of effectiveness due to disturbances, climate change, human activity or other factors), geographic uncertainty (place-to-place variation), scaling potential (ability to estimate impact) and setting of a baseline (ability to estimate additionality over non-action; a counterfactual). To avoid biasing towards a particular a priori framework for evaluation of the scientific literature, reviewers could use their own framework for evaluating the NbCS literature about potential climate impact and so could choose to ignore or add relevant categorizations as well. Any pathway in category 1 would not need fundamental research for implementation; research gaps were considered too extensive for useful guidance on reducing uncertainty in category 3 pathways. Estimates of the global scale of likely potential impact (PgCO 2 e yr −1 ) and cobenefits were also collected from expert elicitors. See Methods and Supplementary Information for the survey instrument.
Four pathways with the highest current carbon market activity and high mitigation potential (tropical and temperate forest conservation and reforestation; Table 1 and Supplementary Data ), were consistently rated as high-confidence pathways in the expert elicitation survey. Other NbCS pathways, especially in the forestry sector, were rated relatively strongly by the experts for both confidence in scientific basis and scale of potential impact, with some spread across the experts (upper right quadrant, Fig. 1 ). Conversely, 13 pathways were consistently marked by experts as currently highly uncertain/low confidence (median score across experts: 2.5–3.0) and placed in category 3 (for example, cropland microbial amendments and coral reef restoration; Supplementary Tables 1 and 2 ). For the full review, including crediting protocols currently used, literature estimates of scale and details of sub-pathways, see Supplementary Data .
Pathways in the upper right quadrant have both high confidence in the scientific foundations and the largest potential scale of global impact; pathways in the lower left have the lowest confidence in our present scientific body of knowledge and an estimated smaller potential scale of impact. Designations of carbon credit eligibility under existing protocols and market activity at the present time are noted. Grassland enhanced mineral weathering (EMW) is not shown (mean category rating 2.9) as no scale of impact was estimated. See Supplementary Table 1 for specific pathway data. Bars represent 20th to 80th percentiles of individual estimates, if there was variability in estimates. A small amount of random noise was added to avoid overlap.
The experts assessed 26 pathways as having average confidence scores between 1.5 and 2.4, suggesting the potential for near-term resolution of uncertainties. This categorization arose from either consensus amongst experts on the uncertain potential (for example, boreal forest reforestation consistently rated category 2, with primary concerns about durability) or because experts disagreed, with some ranking category 1 and others category 3 (for example, pasture management). We note that where expert disagreement exists (seen as the spread of responses in Fig. 1 and Supplementary Table 1 ; also see Data availability for link to original data), this suggests caution against overconfidence in statements about these pathways. These results also suggest that confidence may be increased by targeted research on the identified sources of uncertainty (Supplementary Table 3 ).
Sources of uncertainty
Durability and baseline-setting were rated as high sources of uncertainty across all pathways ranked as category 2 by the experts (mean ratings of 3.6 and 3.4 out of 5, respectively; Supplementary Table 3 ). Understanding of mechanisms and geographic spread had the lowest uncertainty ratings (2.1 and 2.3, respectively), showing confidence in the basic science. Different subsets of pathways had different prioritizations, however, suggesting different research needs: forest-centric pathways were most uncertain in their durability and additionality (3.8 and 3.4, respectively), suggesting concerns about long-term climate and disturbance trajectories. Agricultural and grassland systems, however, had higher uncertainty in measurement methods and additionality (3.9 and 3.5 respectively). Although there were concerns about durability from some experts (for example, due to sea-level rise), some coastal blue carbon pathways such as mangrove restoration (mean category ranking: 1.7 (20th to 80th percentile 1.0–2.0)) have higher confidence than others (for example, seagrass restoration: mean category ranking 2.8, 20th to 80th percentile 2.6–3.0)), which are relatively poorly constrained in terms of net radiative forcing potential despite a potentially large carbon impact (seagrass median: 1.60 PgCO 2 e yr −1 ; see Supplementary Data for more scientific literature estimates).
Scale of impact
For those pathways with lower categorization by the expert elicitation (category 2 or 3) at the present time, scale of global impact is a potential heuristic for prioritizing further research. High variability, often two orders of magnitude, was evident in the mean estimated potential PgCO 2 e yr −1 impacts for the different pathways (Fig. 1 and Supplementary Table 2 ) and the review of the literature found even larger ranges produced by individual studies (Supplementary Data ). A probable cause of this wide range was different constraints on the estimated potential, with some studies focusing on potential maximum impact and others on more constrained realizable impacts. Only avoided loss of tropical forest and cropland biochar amendment were consistently estimated as having the likely potential to mitigate >2 PgCO 2 e yr −1 , although biochar was considered more uncertain by experts due to other factors germane to its overall viability as a climate solution, averaging a categorization of 2.2. The next four highest potential impact pathways, ranging from 1.6 to 1.7 PgCO 2 e yr −1 , spanned the spectrum from high readiness (temperate forest restoration) to moderate (cropland conversion from annual to perennial vegetation and grassland restoration) to low (seagrass restoration, with main uncertainties around scale of potential impact and durability).
There was high variability in the elicitors’ estimated potential scale of impact, even in pathways with strong support, such as tropical forest avoided loss (20th to 80th percentile confidence interval: 1–8 PgCO 2 e yr −1 ), again emphasizing the importance of consistent definitions and constraints on how NbCS are measured, evaluated and then used in broad-scale climate change mitigation planning and budgeting. Generally, as pathway readiness decreased (moving from category 1 to 3), the elicitor-estimated estimates of GHG mitigation potential decreased (Supplementary Fig. 1 ). Note that individual studies from the scientific literature may have higher or lower estimates (Supplementary Data ).
Expert elicitation meta-analyses suggest that 6–12 responses are sufficient for a robust and stable quantification of responses 15 . We tested that assumption via a Monte Carlo-based sensitivity assessment. Readiness categorizations by the ten experts were robust to a Monte Carlo simulation test, where further samples were randomly drawn from the observed distribution of responses: mean difference between the original and the boot-strapped data was 0.02 (s.d. = 0.05) with an absolute difference average of 0.06 (s.d. = 0.06). The maximum difference in readiness categorization means across all pathways was 0.20 (s.d. = 0.20) (Supplementary Table 2 ). The full dataset of responses is available online (see ʻData availabilityʼ).
These results highlight opportunities to accelerate implementation of NbCS in well-supported pathways and identify critical research needs in others (Fig. 1 ). We suggest focusing future efforts on resolving identified uncertainties for pathways at the intersection between moderate average readiness (for example, mean categorizations between ~1.5 and 2.0) and high potential impact (for example, median >0.5 PgCO 2 e yr −1 ; Supplementary Table 1 ): agroforestry, improved tropical and temperate forest management, tropical and boreal peatlands avoided loss and peatland restoration. Many, although not all, experts identified durability and baseline/additionality as key concerns to resolve in those systems; research explicitly targeted at those specific uncertainties (Supplementary Table 3 ) could rapidly improve confidence in those pathways.
We recommend a secondary research focus on the lower ranked (mean category 2.0 to 3.0) pathways with estimated potential impacts >1 PgCO 2 e yr −1 (Supplementary Fig. 2 ). For these pathways, explicit, quantitative incorporation into broad-scale GHG management plans will require further focus on systems-level carbon/GHG understandings to inspire confidence at all stages of action and/or identifying locations likely to support durable GHG mitigation, for example ref. 16 . Examples of this group include avoided loss and degradation of boreal forests (for example, fire, pests and pathogens and albedo 16 ) and effective mesopelagic fishery management, which some individual studies estimate would avoid future reductions of the currently sequestered 1.5–2.0 PgC yr −1 (refs. 17 , 18 ). These pathways may turn out to have higher or lower potential than the expert review suggests, on the basis of individual studies (Supplementary Data ) but strong support will require further, independent verification of that potential.
We note that category 3 rankings by expert elicitation do not necessarily imply non-viability but simply that much more research is needed to confidently incorporate actions into quantitative GHG mitigation plans. We found an unsurprising trend of lower readiness categorization with lower pathway familiarity (Supplementary Fig. 3 ). This correlation may result from two, non-exclusive potential causes: (1) lower elicitor expertise in some pathways (inevitable, although the panel was explicitly chosen for global perspectives, connections and diverse specialties) and (2) an actual lack of scientific evidence in the literature, which leads to that self-reported lack of familiarity, a common finding in the literature review (Supplementary Data ). Both explanations suggest a need to better consolidate, develop and disseminate the science in each pathway for global utility and recognition.
Our focus on GHG-related benefits in no way diminishes the substantial conservation, environmental and social cobenefits of these pathways (Supplementary Table 4 ), which often exceed their perceived climate benefits 1 , 19 , 20 , 21 . Where experts found climate impacts to remain highly uncertain but other NbS benefits are clear (for example, biodiversity and water quality; Supplementary Table 4 ), other incentives or financing mechanisms independent of carbon crediting should be pursued. While the goals here directly relate to using NbCS as a reliably quantifiable part of global climate action planning and thus strong GHG-related scientific foundations, non-climate NbS projects may provide climate benefits that are less well constrained (and thus less useful from a GHG budgeting standpoint) but also valuable. Potential trade-offs, if any, between ecosystem services and management actions, such as biodiversity and positive GHG outcomes, should be explored to ensure the best realization of desired goals 2 .
Finally, our focus in this study was on broad-scale NbCS potential in quantitative mitigation planning because of the principal and necessary role of NbCS in overall global warming targets. We recognize the range of project conditions that may increase, or decrease, the rigour of any pathway outside the global-scale focus here. We did not specifically evaluate the large and increasing number of crediting concepts (by pathway: Supplementary Data ), focusing rather on the underlying scientific body of knowledge within those pathways. Some broad pathways may have better defined sub-pathways within them, with a smaller potential scale of impact but potentially lower uncertainty (for example, macroalgae harvest cycling). Poorly enacted NbCS actions and/or crediting methodologies at project scales may result in loss of benefits even from high-ranking pathways 22 , 23 , 24 and attention to implementation should be paramount. Conversely, strong, careful project-scale methodologies may make lower readiness pathways beneficial for a given site.
Viable NbCS are vital to global climate change mitigation but NbCS pathways that lack strong scientific underpinnings threaten global accounting by potentially overestimating future climate benefits and eroding public trust in rigorous natural solutions. Both the review of the scientific literature and the expert elicitation survey identified high potential ready-to-implement pathways (for example, tropical reforestation), reinforcing present use of NbCS in planning.
However, uncertainty remains about the quantifiable GHG mitigation of some active and nascent NbCS pathways. On the basis of the expert elicitation survey and review of the scientific literature, we are concerned that large-scale implementation of less scientifically well-founded NbCS pathways in mitigation plans may undermine net GHG budget planning; those pathways require more study before they can be confidently promoted at broad scales and life-cycle analyses to integrate system-level emissions when calculating totals. The expert elicitation judgements suggest a precautionary approach to scaling lower confidence pathways until the scientific foundations are strengthened, especially for NbCS pathways with insufficient measurement and monitoring 10 , 24 , 25 or poorly understood or measured net GHG mitigation potentials 16 , 26 , 27 , 28 . While the need to implement more NbCS pathways for reducing GHG emissions and removing carbon from the atmosphere is urgent, advancing the implementation of poorly quantified pathways (in relation to their GHG mitigation efficacy) could give the false impression that they can balance ongoing, fossil emissions, thereby undermining overall support for more viable NbCS pathways. Explicitly targeting research to resolve these uncertainties in the baseline science could greatly bolster confidence in the less-established NbCS pathways, benefiting efforts to reduce GHG concentrations 29 .
The results of this study should inform both market-based mechanisms and non-market approaches to NbCS pathway management. Research and action that elucidates and advances pathways to ensure a solid scientific basis will provide confidence in the foundation for successfully implementing NbCS as a core component of global GHG management.
NbCS pathway selection
We synthesized scientific publications for nine biomes (boreal forests, coastal blue carbon, freshwater wetlands, grasslands, open ocean blue carbon, peatlands, shrublands, temperate forests and tropical forests) and three cultivation types (agroforestry, croplands and macroalgae aquaculture) (hereafter, systems) and the different pathways through which they may be able to remove carbon or reduce GHG emissions. Shrublands and grasslands were considered as independent ecosystems; nonetheless, we acknowledge that there is overlap in the numbers presented here because shrublands are often included with grasslands 5 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 .
The 12 systems were chosen because they have each been identified as having potential for emissions reductions or carbon removal at globally relevant scales. Within these systems, we identified 43 pathways which either have carbon credit protocols formally established or informally proposed for review (non-carbon associated credits were not evaluated). We obtained data on carbon crediting protocols from international, national and regional organizations and registries, such as Verra, American Carbon Registry, Climate Action Reserve, Gold Standard, Clean Development Mechanism, FAO and Nori. We also obtained data from the Voluntary Registry Offsets Database developed by the Berkeley Carbon Trading Project and Carbon Direct company 34 . While we found evidence of more Chinese carbon crediting protocols, we were not able to review these because of limited publicly available information. To maintain clarity and avoid misrepresentation, we used the language as written in each protocol. A full list of the organizations and registries for each system can be found in the Supplementary Data .
Literature searches and synthesis
We reviewed scientific literature and reviews (for example, IPCC special reports) to identify studies reporting data on carbon stocks, GHG dynamics and sequestration potential of each system. Peer-reviewed studies and meta-analyses were identified on Scopus, Web of Science and Google Scholar using simple queries combining the specific practice or pathway names or synonyms (for example, no-tillage, soil amendments, reduced stocking rates, improved forest management, avoided forest conversion and degradation, avoided mangrove conversion and degradation) and the following search terms: ‘carbon storage’, ‘carbon stocks’, ‘carbon sequestration’, ‘carbon sequestration potential’, ‘additional carbon storage’, ‘carbon dynamics’, ‘areal extent’ or ‘global’.
The full literature review was conducted between January and October 2021. We solicited an independent, external review of the syntheses (obtaining from at least three external reviewers per natural or working system; see p. 2 of the Supplementary Data ) as a second check against missing key papers or misinterpretation of data. The review was generally completed in March 2022. Data from additional relevant citations were added through October 2022 as they were discovered. For a complete list of all literature cited, see pp. 217–249 of the Supplementary Data .
From candidate papers, the papers were considered if their results/data could be applied to the following central questions:
How much carbon is stored (globally) at present in the system (total and on average per hectare) and what is the confidence?
At the global level, is the system a carbon source or sink at this time? What is the business-as-usual projection for its carbon dynamics?
Is it possible, through active management, to either increase net carbon sequestration in the system or prevent carbon emissions from that system? (Note that other GHG emissions and forcings were included here as well.)
What is the range of estimates for how much extra carbon could be sequestered globally?
How much confidence do we have in the present methods to detect any net increases in carbon sequestration in a system or net changes in areal extent of that?
From each paper, quantitative estimates for the above questions were extracted for each pathway, including any descriptive information/metadata necessary to understand the estimate. In addition, information on sample size, sampling scheme, geographic coverage, timeline of study, timeline of projections (if applicable) and specific study contexts (for example, wind-break agroforestry) were recorded.
We also tracked where the literature identified trade-offs between carbon sequestered or CO 2 emissions reduced and emissions of other GHG (for example, N 2 O or methane) for questions three and five above. For example, wetland restoration can result in increased CO 2 uptake from the atmosphere. However, it can also increase methane and N 2 O emissions to the atmosphere. Experts were asked to consider the uncertainty in assessing net GHG mitigation as they categorized the NbCS pathways.
Inclusion of each pathway in mitigation protocols and the specific carbon registries involved were also identified. These results are reported (grouped or individually as appropriate) in the Supplementary Data , organized by the central questions and including textual information for interpretation. The data and protocol summaries for each of the 12 systems were reviewed by at least three scientists each and accordingly revised.
These summaries were provided to the expert elicitation group as optional background information.
Unit conversions
Since this synthesis draws on literature from several sources that use different methods and units, all carbon measurements were standardized to the International System of Units (SI units). When referring to total stocks for each system, numbers are reported in SI units of elemental carbon (that is, PgC). When referring to mitigation potential, elemental carbon was converted to CO 2 by multiplying by 3.67. Differences in methodology, such as soil sampling depth, make it difficult to standardize across studies. Where applicable, the specific measurement used to develop each stock estimate is reported.
Expert elicitation process
To assess conclusions brought about by the initial review process described above, we conducted an expert elicitation survey to consolidate and add further, independent assessments to the original literature review. The expert elicitation survey design followed best practice recommendations 14 , with a focus on participant selection, explicitly defining uncertainty, minimizing cognitive and overconfidence biases and clarity of focus. Research on expert elicitation suggests that 6–12 responses are sufficient for a stable quantification of responses 15 . We identified >40 potential experts via a broad survey of leading academics, science-oriented NGO and government agency publications and products. These individuals have published on several NbCS pathways or could represent larger research efforts that spanned the NbCS under consideration. Careful attention was paid to the gender and sectoral breakdown of respondents to ensure equitable representation. Of the invitees, ten completed the full elicitation effort. Experts were offered compensation for their time.
Implementation of the expert elicitation process followed the IDEA protocol 15 . Briefly, after a short introductory interview, the survey was sent to the participants. Results were anonymized and standardized (methods below) and a meeting held with the entire group to discuss the initial results and calibrate understanding of questions. The purpose of this meeting was not to develop consensus on a singular answer but to discuss and ensure that all questions are being considered in the same way (for example, clarifying any potentially confusing language, discussing any questions that emerged as part of the process). The experts then revisited their initial rankings to provide final, anonymous rankings which were compiled in the same way. These final rankings are the results presented here and may be the same or different from the initial rankings, which were discarded.
Survey questions
The expert elicitation survey comprised five questions for each pathway. The data were collected via Google Forms and collated anonymously at the level of pathways, with each respondent contributing one datapoint for each pathway. The experts reported their familiarity (or the familiarity of the organization whose work they were representing) with the pathway and other cobenefits for the pathways.
The initial question ranked the NbCS pathway by category, from one to three.
Category 1 was defined as a pathway with sufficient scientific knowledge to support a high-quality carbon accounting system today (for example, meets the scientific criteria identified in the WWF-EDF-Oeko Institut and ICAO TAB) or to support the development of such a system today. The intended interpretation is that sufficient science is available for quantifying and verifying net GHG mitigation. Note that experts were not required to reference any given ‘high-quality’ crediting framework, which were provided only as examples. In other words, the evaluation was not intended to rank a given framework (for example, ref. 35 ) but rather expert confidence in the fundamental scientific understandings that underpin potential for carbon accounting overall. To this end, no categorization of uncertainty was required (reviewers could skip categorizations they felt were not necessary) and space was available to fill in new categories by individual reviewers (if they felt a category was missing or needed). Uncertainties at this category 1 level are deemed ‘acceptable’, for example, not precluding accounting now, although more research may further substantiate high-quality credits.
Category 2 pathways have a good chance (>25%) that with more research and within the next 5 years, the pathway could be developed into a high-quality pathway for carbon accounting and as a nature-based climate solution pathway. For these pathways, further understanding is needed for factors such as baseline processes, long-term stability, unconstrained fluxes, possible leakage or other before labelling as category 1 but the expert is confident that information can be developed, in 5 years or less, with more work. The >25% chance threshold and 5-year timeframe were determined a priori to reflect and identify pathways that experts identified as having the potential to meet the Paris Accord 2030 goal. Other thresholds (for example, longer timeframes) could have been chosen, which would impact the relative distribution of pathways in categories 2 and 3 (for example, a longer timeframe allowed could move some pathways from category 3 into category 2, for some reviewers). We emphasize that category 3 pathways do not necessarily mean non-valuable approaches but longer timeframes required for research than the one set here.
Category 3 responses denoted pathways that the expert thought had little chance (<25%) that with more research and within the next 5 years, this pathway could be developed into a suitable pathway for managing as a natural solutions pathway, either because present evidence already suggests GHG reduction is not likely to be viable, co-emissions or other biophysical feedbacks may offset those gains or because understanding of key factors is lacking and unlikely to be developed within the next 5 years. Notably, the last does not mean that the NbCS pathway is not valid or viable in the long-term, simply that physical and biological understandings are probably not established enough to enable scientific rigorous and valid NbCS activity in the near term.
The second question asked the experts to identify research gaps associated with those that they ranked as category 2 pathways to determine focal areas for further research. The experts were asked to rank concerns about durability (ability to predict or compensate for uncertainty in timescale of effectiveness due to disturbances, climate change, human activity or other factors), geographic uncertainty (place-to-place variation), leakage or displacement (spillover of activities to other areas), measuring, reporting and verification (MRV, referring to the ability to quantify all salient stocks and fluxes to fully assess climate impacts), basic mechanisms of action (fundamental science), scaling potential (ability to estimate potential growth) and setting of a baseline (ability to reasonably quantify additionality over non-action, a counterfactual). Respondents could also enter a different category if desired. For complete definitions of these categories, see the survey instrument ( Supplementary Information ). This question was not asked if the expert ranked the pathway as category 1, as those were deemed acceptable, or for category 3, respecting the substantial uncertainty in that rating. Note that responses were individual and so the same NbCS pathway could receive (for example) several individual category 1 rankings, which would indicate reasonable confidence from those experts, and several category 2 rankings from others, which would indicate that those reviewers have lingering concerns about the scientific basis, along with their rankings of the remaining key uncertainties in those pathways. These are important considerations, as they reflect the diversity of opinions and research priorities; individual responses are publicly available (anonymized: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7859146 ).
The third question involved quantification of the potential for moving from category 2 to 1 explicitly. Following ref. 14 , the respondents first reported the lowest plausible value for the potential likelihood of movement (representing the lower end of a 95% confidence interval), then the upper likelihood and then their best guess for the median/most likely probability. They were also asked for the odds that their chosen interval contained the true value, which was used to scale responses to standard 80% credible intervals and limit overconfidence bias 13 , 15 . This question was not asked if the expert ranked the pathway as category 3, respecting the substantial uncertainty in that rating.
The fourth question involved the scale of potential impact from the NbCS, given the range of uncertainties associated with effectiveness, area of applicability and other factors. The question followed the same pattern as the third, first asking about lowest, then highest, then best estimate for potential scale of impact (in PgCO 2 e yr −1 ). Experts were again asked to express their confidence in their own range, which was used to scale to a standard 80% credible interval. This estimate represents a consolidation of the best-available science by the reviewers. For a complete review including individual studies and their respective findings, see the Supplementary Data . This question was not asked if the expert ranked the pathway as category 3, respecting the substantial uncertainty in that rating.
Final results
After collection of the final survey responses, results were anonymized and compiled by pathway. For overall visualization and discussion purposes, responses were combined into a mean and 20th to 80th percentile range. The strength of the expert elicitation process lies in the collection of several independent assessments. Those different responses represent real differences in data interpretation and synthesis ascribed by experts. This can have meaningful impacts on decision-making by different individuals and organizations (for example, those that are more optimistic or pessimistic about any given pathway). Therefore, individual anonymous responses were retained by pathway to show the diversity of responses for any given pathway. The experts surveyed, despite their broad range of expertise, ranked themselves as less familiar with category 3 pathways than category 1 or 2 (linear regression, P < 0.001, F = 59.6 2, 394 ); this could be because of a lack of appropriate experts—although they represented all principal fields—or simply because the data are limited in those areas.
Sensitivity
To check for robustness against sample size variation, we conducted a Monte Carlo sensitivity analysis of the data on each pathway to generate responses of a further ten hypothetical experts. Briefly, the extra samples were randomly drawn from the observed category ranking mean and standard deviations for each individual pathway and appended to the original list; values <1 or >3 were truncated to those values. This analysis resulted in only minor differences in the mean categorization across all pathways: the mean difference between the original and the boot-strapped data was 0.02 (s.d. = 0.05) with an absolute difference average of 0.06 (s.d. = 0.06). The maximum difference in means across all pathways was 0.20 (s.d. = 0.20) (Supplementary Table 2 ). The results suggest that the response values are stable to additional responses.
All processing was done in R 36 , with packages including fmsb 37 and forcats 38 .
Data availability
Anonymized expert elicitation responses are available on Zenodo 39 : https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7859146 .
Code availability
R code for analysis available on Zenodo 39 : https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7859146 .
Novick, K. A. et al. Informing nature‐based climate solutions for the United States with the best‐available science. Glob. Change Biol. 28 , 3778–3794 (2022).
Article Google Scholar
Cohen-Shacham, E., Walters, G., Janzen, C. & Maginnis, S. (eds) Nature-based Solutions to Address Global Societal Challenges (IUCN, 2016).
IPCC Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis (eds Masson-Delmotte, V. et al.) (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2021).
Seddon, N. et al. Understanding the value and limits of nature-based solutions to climate change and other global challenges. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 375 , 20190120 (2020).
Griscom, B. W. et al. Natural climate solutions. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114 , 11645–11650 (2017).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central ADS Google Scholar
Blaufelder, C., Levy, C., Mannion, P. & Pinner, D. A. Blueprint for Scaling Voluntary Carbon Markets to Meet the Climate Challenge (McKinsey & Company, 2021).
Arcusa, S. & Sprenkle-Hyppolite, S. Snapshot of the carbon dioxide removal certification and standards ecosystem (2021–2022). Clim. Policy 22 , 1319–1332 (2022).
Seddon, N. et al. Global recognition of the importance of nature-based solutions to the impacts of climate change Glob. Sustain. 3 , pe15 (2020).
Anderegg, W. R. Gambling with the climate: how risky of a bet are natural climate solutions? AGU Adv. 2 , e2021AV000490 (2021).
Article ADS Google Scholar
Gattuso, J. P. et al. Ocean solutions to address climate change and its effects on marine ecosystems. Front. Mar. Sci. 5 , p337 (2018).
Bach, L. T., Gill, S. J., Rickaby, R. E., Gore, S. & Renforth, P. CO 2 removal with enhanced weathering and ocean alkalinity enhancement: potential risks and co-benefits for marine pelagic ecosystems. Front. Clim. 1 , 7 (2019).
Doelman, J. C. et al. Afforestation for climate change mitigation: potentials, risks and trade‐offs. Glob. Change Biol. 26 , 1576–1591 (2019).
Speirs-Bridge, A. et al. Reducing overconfidence in the interval judgments of experts. Risk Anal. 30 , 512–523 (2010).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Morgan, M. G. Use (and abuse) of expert elicitation in support of decision making for public policy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 111 , 7176–7184 (2014).
Hemming, V., Burgman, M. A., Hanea, A. M., McBride, M. F. & Wintle, B. C. A practical guide to structured expert elicitation using the IDEA protocol. Methods Ecol. Evol. 9 , 169–180 (2018).
Anderegg, W. R. et al. Climate-driven risks to the climate mitigation potential of forests. Science 368 , eaaz7005 (2020).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Boyd, P. W., Claustre, H., Levy, M., Siegel, D. A. & Weber, T. Multi-faceted particle pumps drive carbon sequestration in the ocean. Nature 568 , 327–335 (2019).
Article CAS PubMed ADS Google Scholar
Saba, G. K. et al. Toward a better understanding of fish-based contribution to ocean carbon flux. Limnol. Oceanogr. 66 , 1639–1664 (2021).
Article CAS ADS Google Scholar
Seddon, N., Turner, B., Berry, P., Chausson, A. & Girardin, C. A. Grounding nature-based climate solutions in sound biodiversity science. Nat. Clim. Change 9 , 84–87 (2019).
Soto-Navarro, C. et al. Mapping co-benefits for carbon storage and biodiversity to inform conservation policy and action. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 375 , 20190128 (2020).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Schulte, I., Eggers, J., Nielsen, J. Ø. & Fuss, S. What influences the implementation of natural climate solutions? A systematic map and review of the evidence. Environ. Res. Lett. 17 , p013002 (2022).
West, T. A., Börner, J., Sills, E. O. & Kontoleon, A. Overstated carbon emission reductions from voluntary REDD+ projects in the Brazilian Amazon. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117 , 24188–24194 (2020).
Di Sacco, A. et al. Ten golden rules for reforestation to optimize carbon sequestration, biodiversity recovery and livelihood benefits. Glob. Change Biol. 27 , 1328–1348 (2021).
López-Vallejo, M. in Towards an Emissions Trading System in Mexico: Rationale, Design and Connections with the Global Climate Agenda (ed. Lucatello, S.) 191–221 (Springer, 2022)
Oldfield, E. E. et al. Realizing the potential of agricultural soil carbon sequestration requires more effective accounting. Science 375 , 1222–1225 (2022).
Burkholz, C., Garcias-Bonet, N. & Duarte, C. M. Warming enhances carbon dioxide and methane fluxes from Red Sea seagrass ( Halophila stipulacea ) sediments. Biogeosciences 17 , 1717–1730 (2020).
Guenet, B. et al. Can N 2 O emissions offset the benefits from soil organic carbon storage? Glob. Change Biol. 27 , 237–256 (2021).
Rosentreter, J. A., Al‐Haj, A. N., Fulweiler, R. W. & Williamson, P. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions complicate coastal blue carbon assessments. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 35 , pe2020GB006858 (2021).
Schwartzman, S. et al. Environmental integrity of emissions reductions depends on scale and systemic changes, not sector of origin. Environ. Res. Lett. 16 , p091001 (2021).
Crop and Livestock Products Database (FAO, 2022); https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL
Fargione, J. E. et al. Natural climate solutions for the United States. Sci. Adv. 4 , eaat1869 (2018).
Article PubMed PubMed Central ADS Google Scholar
Meyer, S. E. Is climate change mitigation the best use of desert shrublands? Nat. Resour. Environ. Issues 17 , 2 (2011).
Google Scholar
Lorenz, K. & Lal, R. Carbon Sequestration in Agricultural Ecosystems (Springer Cham, 2018).
Haya, B., So, I. & Elias, M. The Voluntary Registry Offsets Database (Univ. California, 2021); https://gspp.berkeley.edu/faculty-and-impact/centers/cepp/projects/berkeley-carbon-trading-project/offsets-database
Core Carbon Principles; CCP Attributes; Assessment Framework for Programs; and Assessment Procedure (ICVCM, 2023); https://icvcm.org/the-core-carbon-principles/
R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2022).
Nakazawa, M. fmsb: Functions for medical statistics book with some demographic data. R package version 0.7.4 https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=fmsb (2022).
Wickham, H. forcats: Tools for working with categorical variables (factors). R package version 0.5.2 https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=forcats (2022)
Buma, B. Nature-based climate solutions: expert elicitation data and analysis code. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7859146 (2023).
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was supported through gifts to the Environmental Defense Fund from the Bezos Earth Fund, King Philanthropies and Arcadia, a charitable fund of L. Rausing and P. Baldwin. We thank J. Rudek for help assembling the review and 30 experts who reviewed some or all of those data and protocol summaries (Supplementary Data ). S.M. was supported by a cooperative agreement between the National Science Foundation and Battelle that sponsors the National Ecological Observatory Network programme.
Author information
Present address: Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, USA
Present address: AtmoFacts, Longmont, CO, USA
R. N. Lubowski
Present address: Lombard Odier Investment Managers, New York, NY, USA
Present address: Ecological Carbon Offset Partners LLC, dba EP Carbon, Minneapolis, MN, USA
L. A. Moore
Present address: , San Francisco, CA, USA
J. Paltseva
Present address: ART, Arlington, VA, USA
N. A. Randazzo
Present address: NASA/GSFC, Greenbelt, MD, USA
Present address: University of Maryland, College Park, MD, USA
N. Uludere Aragon
Present address: Numerical Terradynamic Simulation Group, University of Montana, Missoula, MT, USA
These authors contributed equally: B. Buma, D. R. Gordon.
Authors and Affiliations
Environmental Defense Fund, New York, NY, USA
B. Buma, D. R. Gordon, K. M. Kleisner, A. Bartuska, J. R. Collins, A. J. Eagle, R. Fujita, E. Holst, J. M. Lavallee, R. N. Lubowski, C. Melikov, L. A. Moore, E. E. Oldfield, J. Paltseva, A. M. Raffeld, N. A. Randazzo, C. Schneider, N. Uludere Aragon & S. P. Hamburg
Department of Integrative Biology, University of Colorado, Denver, CO, USA
Department of Biology, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA
D. R. Gordon
Resources for the Future, Washington, DC, USA
A. Bartuska
International Arctic Research Center, University of Alaska, Fairbanks, AK, USA
Department of Ecology Evolution and Environmental Biology and the Climate School, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA
The Nature Conservancy, Arlington, VA, USA
Faculty of Environment, Science and Economy, University of Exeter, Exeter, UK
P. Friedlingstein
Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique/Institut Pierre-Simon Laplace, CNRS, Ecole Normale Supérieure/Université PSL, Sorbonne Université, Ecole Polytechnique, Palaiseau, France
National Ecological Observatory Network, Battelle, Boulder, CO, USA
Department of Engineering and Public Policy, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, USA
O’Neill School of Public and Environmental Affairs, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN, USA
Department of Environmental Science and Policy, University of California, Davis, CA, USA
J. N. Sanchirico
Department of Marine Chemistry & Geochemistry, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, MA, USA
J. R. Collins
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
D.R.G. and B.B. conceived of and executed the study design. D.R.G., K.M.K., J.R.C., A.J.E., R.F., E.H., J.M.L., R.N.L., C.M., L.A.M., E.E.O., J.P., A.M.R., N.A.R., C.S. and N.U.A. coordinated and conducted the literature review. G.M. and B.B. primarily designed the survey. A. Bartuska, A. Bidlack, B.B., J.N.S., K.N., P.E., P.F., R.D. and S.M. contributed to the elicitation. B.B. conducted the analysis and coding. S.P.H. coordinated funding. B.B. and D.R.G. were primary writers; all authors were invited to contribute to the initial drafting.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to B. Buma .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests. In the interest of full transparency, we note that while B.B., D.R.G., K.M.K., A.B., J.R.C., A.J.E., R.F., E.H., J.M.L., R.N.L., C.M., L.A.M., E.E.O., J.P., A.M.R., N.A.R., C.S., N.U.A., S.P.H. and P.E. are employed by organizations that have taken positions on specific NbCS frameworks or carbon crediting pathways (not the focus of this work), none have financial or other competing interest in any of the pathways and all relied on independent science in their contributions to the work.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Climate Change thanks Camila Donatti, Connor Nolan and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information.
Supplementary Tables 1–4, Figs. 1–3 and survey instrument.
Supplementary Data
Literature review and list of reviewers.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Buma, B., Gordon, D.R., Kleisner, K.M. et al. Expert review of the science underlying nature-based climate solutions. Nat. Clim. Chang. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-024-01960-0
Download citation
Received : 24 April 2023
Accepted : 20 February 2024
Published : 21 March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-024-01960-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
- Open access
- Published: 20 September 2023
Older adults’ experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative systematic literature review
- Elfriede Derrer-Merk ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7241-0808 1 ,
- Maria-Fernanda Reyes-Rodriguez ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2645-5092 2 ,
- Laura K. Soulsby ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9071-8654 1 ,
- Louise Roper ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2918-7628 3 &
- Kate M. Bennett ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3164-6894 1
BMC Geriatrics volume 23 , Article number: 580 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
1512 Accesses
5 Citations
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
Relatively little is known about the lived experiences of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic. We systematically review the international literature to understand the lived experiences of older adult’s experiences during the pandemic.
Design and methodology
This study uses a meta-ethnographical approach to investigate the included studies. The analyses were undertaken with constructivist grounded theory.
Thirty-two studies met the inclusion criteria and only five papers were of low quality. Most, but not all studies, were from the global north. We identified three themes: desired and challenged wellbeing; coping and adaptation; and discrimination and intersectionality.
Overall, the studies’ findings were varied and reflected different times during the pandemic. Studies reported the impact of mass media messaging and its mostly negative impact on older adults. Many studies highlighted the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on participants' social connectivity and well-being including missing the proximity of loved ones and in consequence experienced an increase in anxiety, feeling of depression, or loneliness. However, many studies reported how participants adapted to the change of lifestyle including new ways of communication, and social distancing. Some studies focused on discrimination and the experiences of sexual and gender minority and ethnic minority participants. Studies found that the pandemic impacted the participants’ well-being including suicidal risk behaviour, friendship loss, and increased mental health issues.
The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted and impacted older adults’ well-being worldwide. Despite the cultural and socio-economic differences many commonalities were found. Studies described the impact of mass media reporting, social connectivity, impact of confinement on well-being, coping, and on discrimination. The authors suggest that these findings need to be acknowledged for future pandemic strategies. Additionally, policy-making processes need to include older adults to address their needs. PROSPERO record [CRD42022331714], (Derrer-Merk et al., Older adults’ lived experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review, 2022).
Peer Review reports
Introduction
In March 2020 the World Health Organisation declared a pandemic caused by the virus SARS-CoV2 (COVID-19) [ 1 ]. At this time 118,000 cases in 114 countries were identified and 4,291 people had already lost their lives [ 2 ]. By July 2022, there were over 5.7 million active cases and over 6.4 million deaths [ 2 ]. Despite the effort to combat and eliminate the virus globally, new variants of the virus are still a concern. At the start of the pandemic, little was known about who would be most at risk, but emerging data suggested that both people with underlying health conditions and older people had a higher risk of becoming seriously ill [ 3 ]. Thus, countries worldwide imposed health and safety measures aimed at reducing viral transmission and protecting people at higher risk of contracting the virus [ 4 ]. These measures included: national lockdowns with different lengths and frequencies; targeted shopping times for older people; hygiene procedures (wearing masks, washing hands regularly, disinfecting hands); restricting or prohibiting social gatherings; working from home, school closure, and home-schooling.
Research suggests that lockdowns and protective measures impacted on people’s lives, and had a particular impact on older people. They were at higher risk from COVID-19, with greater disease severity and higher mortality compared to younger people [ 5 ]. Older adults were identified as at higher risk as they are more likely to have pre-existing conditions including heart disease, diabetes, and severe respiratory conditions [ 5 ]. Additionally, recent research highlights that COVID-19 and its safety measures led to increased mental health problems, including increased feelings of depression, anxiety, social isolation, and loneliness, potentially cognitive decline [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 ]. Other studies reported the consequences of only age-based protective health measures including self-isolation for people older people (e.g. feeling old, losing out the time with family) [ 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 ].
Over the past decade, the World Health Organisation (WHO) has recognised the importance of risk communication within public health emergency preparedness and response, especially in the context of epidemics and pandemics. Risk communication is defined as “the real-time exchange of information, advice and opinions between experts or officials, and people who face a threat (hazard) to their survival, health or economic or social well-being” ([ 31 ], p5). This includes reporting the risk and health protection measurements through media and governmental bodies. Constructing awareness and building trust in society are essential components of risk communication [ 32 ]. In the context of the pandemic, the WHO noted that individual risk perception helped to prompt problem-solving activities (such as wearing face masks, social distancing, and self-isolation). However, the prolonged perception of pandemic-related uncertainty and risk could also lead to heightened feelings of distress and anxiety [ 31 , 33 ], see also [ 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 ].
This new and unprecedented disease provided the ground for researchers worldwide to investigate the COVID-19 pandemic. To date (August 2022), approximately 8072 studies have been recorded on the U.S. National Library of Medicine ClinicalTrials.gov [ 38 ] and 12002 systematic reviews have been registered at PROSPERO, concerning COVID-19. However, to our knowledge, there is little known about qualitative research as a response to the COVID-19 pandemic and how it impacted older adults’ well-being [ 39 ]. In particular, little is known about how older people experienced the pandemic. Thus, our research question considers: How did older adults experience the COVID-19 pandemic worldwide?
We use a qualitative evidence synthesis (QES) recommended by Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group to identify peer-reviewed articles [ 40 ]. This provides an overview of existing research, identifies potential research gaps, and develops new cumulative knowledge concerning the COVID-19 pandemic and older adults’ experiences. QES is a valuable method for its potential to contribute to research and policy [ 41 ]. Flemming and Noyes [ 40 ] argue that the evidence synthesis from qualitative research provides a richer interpretation compared to single primary research. They identified an increasing demand for qualitative evidence synthesis from a wide range of “health and social professionals, policymakers, guideline developers and educationalists” (p.1).
Methodology
A systematic literature review requires a specific approach compared to other reviews. Although there is no consensus on how it is conducted, recent systematic literature reviews have agreed the following reporting criteria are addressed [ 42 , 43 ]: (a) a research question; (b) reporting database, and search strategy; (c) inclusion and exclusion criteria; (d) reporting selection methods; (e) critically appraisal tools; (f) data analysis and synthesis. We applied these criteria in our study and began by registering the research protocol with Prospero [ 44 ].
The study is registered at Prospero [ 44 ]. This systematic literature review incorporates qualitative studies concerning older adults’ experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Search strategy
The primary qualitative articles were identified via a systematic search as per the qualitative-specific SPIDER approach [ 45 ]. The SPIDER tool is designed to structure qualitative research questions, focusing less on interventions and more on study design, and ‘samples’ rather than populations, encompassing:
S-Sample. This includes all articles concerning older adults aged 60 + [ 1 ].
P-Phenomena of Interest. How did older adults experience the COVID-19 pandemic?
D-Design. We aim to investigate qualitative studies concerning the experiences of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic.
E-Evaluation. The evaluation of studies will be evaluated with the amended Critical Appraisal Skills Programme CASP [ 46 ].
R-Research type Qualitative
Information source
The following databases were searched: PsychInfo, Medline, CINAHL, Web of Science, Annual Review, Annual Review of Gerontology, and Geriatrics. A hand search was conducted on Google Scholar and additional searches examined the reference lists of the included papers. The keyword search included the following terms: (older adults or elderly) AND (COVID-19 or SARS or pandemic) AND (experiences); (older adults) AND (experience) AND (covid-19) OR (coronavirus); (older adults) AND (experience) AND (covid-19 OR coronavirus) AND (Qualitative). Additional hand search terms included e.g. senior, senior citizen, or old age.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Articles were included when they met the following criteria: primary research using qualitative methods related to the lived experience of older adults aged 60 + (i.e. the experiences of individuals during the COVID-19 pandemic); peer-reviewed journal articles published in English; related to the COVID-19 pandemic; empirical research; published from 2020 till August 2022.
Articles were excluded when: papers discussed health professionals’ experiences; diagnostics; medical studies; interventions; day-care; home care; or carers; experiences with dementia; studies including hospitals; quantitative studies; mixed-method studies; single-case studies; people under the age of 60; grey literature; scoping reviews, and systematic reviews. We excluded clinical/care-related studies as we wanted to explore the everyday experiences of people aged 60 + . Mixed-method studies were excluded as we were interested in what was represented in solely qualitative studies. However, we acknowledge, that mixed-method studies are valuable for future systematic reviews.
Meta-ethnography
The qualitative synthesis was undertaken by using meta-ethnography. The authors have chosen meta-ethnography over other methodologies as it is an inductive and interpretive synthesis analysis and is uniquely “suited to developing new conceptual models and theories” ([ 47 ], p 2), see also [ 48 ]. Therefore, it combines well with constructivist grounded theory methodology. Meta-ethnography also examines and identifies areas of disagreements between studies [ 48 ].
This is of particular interest as the lived experiences of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic were likely to be diverse. The method enables the researcher to synthesise the findings (e.g. themes, concepts) from primary studies, acknowledging primary data (quotes) by “using a unique translation synthesis method to transcend the findings of individual study accounts and create higher order” constructs ([ 47 ], p. 2). The following seven steps were applied:
Getting started (identify area of interest). We were interested in the lived experiences of older adults worldwide.
Deciding what was relevant to the initial interest (defining the focus, locating relevant studies, decision to include studies, quality appraisal). We decided on the inclusion and exclusion criteria and an appropriate quality appraisal.
Reading the studies. We used the screening process described below (title, abstract, full text)
Determining how the studies were related (extracting first-order constructs- participants’ quotes and second-order construct- primary author interpretation, clustering the themes from the studies into new categories (Table 3 ).
Translating the studies into one another (comparing and contrasting the studies, checking commonalities or differences of each article) to organise and develop higher-order constructs by using constant comparison (Table 3 ). Translating is the process of finding commonalities between studies [ 48 ].
Synthesising the translation (reciprocal and refutational synthesis, a lines of argument synthesis (interpretation of the relationship between the themes- leads to key themes and constructs of higher order; creating new meaning, Tables 2 , 3 ),
Expressing the synthesis (writing up the findings) [ 47 , 48 ].
Screening and Study Selection
A 4-stage screening protocol was followed (Fig. 1 Prisma). First, all selected studies were screened for duplicates, which were deleted. Second, all remaining studies were screened for eligibility, and non-relevant studies were excluded at the preliminary stage. These screening steps were as follows: 1. title screening; 2. abstract screening, by the first and senior authors independently; and 3. full-text screening which was undertaken for almost all papers by the first author. However, 2 papers [ 9 , 23 ] were assessed independently by LS, LR, and LMM to avoid a conflict of interest. The other co-authors also screened independently a portion of the papers each, to ensure that each paper had two independent screens to determine inclusion in the review [ 49 ]. This avoided bias and confirmed the eligibility of the included papers (Fig. 1 ). Endnote reference management was used to store the articles and aid the screening process.
Prisma flow diagram adapted from Page et al. [ 50 ]. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ, 372, n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71 )
Data extraction
After title and abstract screening, 39 papers were selected for reading the full article. 7 papers were excluded after the full-text assessment (1 study was conducted in 2017, but published in 2021; 2 papers were not fully available in English, 2 papers did not address the research question, 1 article was based on a conference abstract only, 1 article had only one participant age 65 +).
The full-text screening included 32 studies. All the included studies, alongside the CASP template, data extraction table, the draft of this article, and translation for synthesising the findings [ 47 , 48 ] were available and accessible on google drive for all co-authors. All authors discussed the findings in regular meetings.
Quality appraisal
A critical appraisal tool assesses a study for its trustworthiness, methodological rigor, and biases and ensures “transparency in the assessment of primary research” ([ 51 ], p. 5); see also [ 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 ]. There is currently no gold standard for assessing primary qualitative studies, but different authors agreed that the amended CASPS checklist was appropriate to assess qualitative studies [ 46 , 54 ]. Thus, we use the amended CASP appraisal tool [ 42 ]. The amended CASP appraisal tool aims to improve qualitative evidence synthesis by assessing ontology and epistemology (Table 1 CASP appraisal tool).
A numerical score was assigned to each question to indicate whether the criteria had been met (= 2), partially met (= 1), or not met (= 0) [ 54 ]; see also [ 55 ]. The score 16 – 22 are considered to be moderate and high-quality studies. The studies scored 15 and below were identified as low-quality papers. Although we focus on higher-quality papers, we did not exclude papers to avoid the exclusion of insightful and meaningful data [ 42 , 48 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 ]. The quality of the paper was considered in developing the evidence synthesis.
We followed the appraisal questions applied for each included study and answered the criteria either ‘Yes’, ‘Cannot tell’, or ‘No’. (Table 1 CASP appraisal criteria). The tenth question asking the value of the article was answered with ‘high’ of importance, ‘middle’, or low of importance. The new eleventh question in the CASP tool concerning ontology and epistemology was answered with yes, no, or partly (Table 1 ).
Data synthesis
The data synthesis followed the seven steps of Meta-Ethnography developed by Noblit & Hare [ 58 ], starting the data synthesis at step 3, described in detail by [ 47 ]. This encompasses: reading the studies; determining how the studies are related; translating the studies into one another; synthesis the translations; and expressing synthesis. This review provides a synthesis of the findings from studies related to the experiences of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic. The qualitative analyses are based on constructivist grounded theory [ 59 ] to identify the experiences of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic (non-clinical) populations. The analysis is inductive and iterative, uses constant comparison, and aims to develop a theory. The qualitative synthesis encompasses all text labelled as ‘results’ or ‘findings’ and uses this as raw data. The raw data includes participant’s quotes; thus, the synthesis is grounded in the participant's experience [ 47 , 48 , 60 , 61 ]. The initial coding was undertaken for each eligible article line by line. Please see Table 2 Themes per author and country. Focused coding was applied using constant comparison, which is a widely used approach in grounded theory [ 61 ]. In particular, common and recurring as well as contradicting concepts within the studies were identified, clustered into categories, and overarching higher order constructs were developed [ 47 , 48 , 60 ] (Tables 2 , 3 , 4 ).
We identified twenty-seven out of thirty-two studies as moderate-high quality; they met most of the criteria (scoring 16/22 or above on the CASP; [ 54 ]. Only five papers were identified as low qualitative papers scoring 15 and below [ 71 , 73 , 74 , 86 , 91 ]. Please see the scores provided for each paper in Table 4 . The low-quality papers did not provide sufficient details regarding the researcher’s relationship with the participants, sampling and recruitment, data collection, rigor in the analysis, or epistemological or ontological reasoning. For example, Yildirim [ 91 ] used verbatim notes as data without recording or transcribing them. This article described the analytical process briefly but was missing a discussion of the applied reflexivity of using verbatim notes and its limitations [ 92 ].
This systematic review found that many studies did not mention the relationship between the authors and the participant. The CASP critical appraisal tool asks: Has the relationship between the researcher and participants been adequately considered? (reflecting on own role, potential bias). Many studies reported that the recruitment was drawn from larger studies and that the qualitative study was a sub-study. Others reported that participants contacted the researcher after advertising the study. One study Goins et al., [ 72 ] reported that students recruited family members, but did not discuss how this potential bias impacted the results.
Our review brings new insights into older adults’ experiences during the pandemic worldwide. The studies were conducted on almost all continents. The majority of the articles were written in Europe followed by North America and Canada (4: USA; 3: Canada, UK; 2: Brazil, India, Netherlands, Sweden, Turkey 2; 1: Austria, China, Finland, India/Iran, Mauritius, New Zealand, Serbia, Spain, Switzerland, Uganda, UK/Ireland, UK/Colombia) (see Fig. 2 ). Note, as the review focuses on English language publications, we are unable to comment on qualitative research conducted in other languages see [ 72 ].
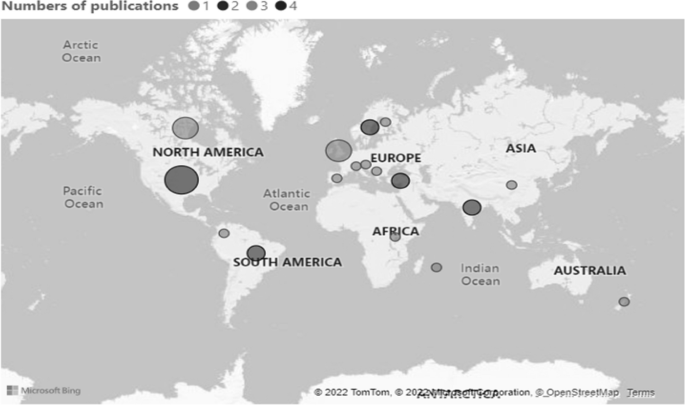
Numbers of publications by country
The characteristics of the included studies and the presence of analytical themes can be found in Table 4 . We used the following characteristics: Author and year of publication, research aims, the country conducted, Participant’s age, number of participants, analytical methodology, CASP score, and themes.
We identified three themes: desired and challenged wellbeing; coping and adaptation; discrimination and intersectionality. We will discuss the themes in turn.
Desired and challenged wellbeing
Most of the studies reported the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the well-being of older adults. Factors which influenced wellbeing included: risk communication and risk perception; social connectivity; confinement (at home); and means of coping and adapting. In this context, well-being refers to the evidence reported about participants' physical and mental health, and social connectivity.
Risk perception and risk communication
Politicians and media transmitted messages about the response to the pandemic to the public worldwide. These included mortality and morbidity reports, and details of health and safety regulations like social distancing, shielding- self-isolation, or wearing masks [ 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 ]. As this risk communication is crucial to combat the spread of the virus, it is also important to understand how people perceived the reporting during the pandemic.
Seven studies reported on how the mass media impacted participants' well-being [ 23 , 67 , 68 , 70 , 72 , 81 , 85 ]. Sangrar et al. [ 68 ] investigated how older adults responded to COVID-19 messaging: “My reaction was to try to make sure that I listen to everything and [I] made sure I was aware of all the suggestions and the precautions that were being expressed by various agencies …”. (p. 4). Other studies reported the negative impact on participants' well-being of constant messaging and as a consequence stopped watching the news to maintain emotional well-being [ 3 , 67 , 68 , 70 , 72 , 81 , 85 ]. Derrer-Merk et al. [ 23 ] reported one participant said that “At first, watching the news every day is depressing and getting more and more depressing by the day, so I’ve had to stop watching it for my own peace of mind” (p. 13). In addition, news reporting impacted participants’ risk perception. For example, “Sometimes we are scared to hear the huge coverage of COVID-19 news, in particular the repeated message ‘older is risky’, although the message is useful.” ([ 81 ], p5).
- Social connectivity
Social connectivity and support from family and community were found in fourteen of the studies as important themes [ 9 , 62 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 , 79 , 80 , 83 , 84 , 90 ].
The impact of COVID-19 on social networks highlighted the diverse experiences of participants. Some participants reported that the size of social contact was reduced: “We have been quite isolated during this corona time” ?([ 80 ], p. 3). Whilst other participants reported that the network was stable except that the method of contact was different: “These friends and relatives, they visited and called as often as before, but of course, we needed to use the telephone when it was not possible to meet” ([ 77 ], p. 5). Many participants in this study did not want to expand their social network see also [ 9 , 77 , 78 , 79 ]. Hafford-Letchfield et al. [ 76 ] reported that established social networks and relationships were beneficial for the participants: “Covid has affected our relationship (with partner), we spend some really positive close time together and support each other a lot” (p. 7).
On the other hand, other studies reported decreases of, and gaps in, social connectedness: “I couldn’t do a lot of things that I’ve been doing for years. That was playing competitive badminton three times a week, I couldn’t do that. I couldn’t get up early and go volunteer in Seattle” [ 9 , 67 , 75 ]. A loss of social connection with children and grandchildren was often mentioned: “We cannot see our grandchildren up close and personal because, well because they [the parents] don’t want us, they don’t want to risk our being with the kids … it’s been an emotional loss exacerbated by the COVID thing” ([ 68 ] p.10); see also [ 9 , 67 , 78 ]. On the contrary, Chemen & Gopalla [ 66 ] note that those older adults who were living with other family members reported that they were more valued: “Last night my daughter-in-law thanked me for helping with my granddaughter” (p.4).
Despite reports of social disconnectedness, some studies highlighted the importance of support from family members and how support changed during the COVID-19 pandemic [ 9 , 62 , 81 , 83 , 90 ]. Yang et al. [ 90 ] argued that social support was essential during the Lockdown in China: “N6 said: ‘I asked my son-in-law to take me to the hospital” (p. 4810). Mahapatra et al. [ 81 ] found, in an Indian study, that the complex interplay of support on different levels (individual, family, and community) helped participants to adapt to the new situation. For example, this participant reported that: “The local police are very helpful. When I rang them for something and asked them to find out about it, they responded immediately” (p. 5).
Impact of confinement on well being
Most articles highlighted the impact of confinement on older adults’ well-being [ 9 , 62 , 63 , 65 , 67 , 69 , 70 , 72 , 75 , 77 , 78 , 79 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 85 , 89 , 90 ].
Some studies found that participants maintained emotional well-being during the pandemic and it did not change their lifestyle [ 79 , 80 , 82 , 83 , 89 , 92 ]: “Actually, I used this crisis period to clean my house. Bookcases are completely cleaned and I discarded old books. Well, we have actually been very busy with those kind of jobs. So, we were not bored at all” ([ 79 ], p. 5). In McKinlay et al. [ 82 ]’s study, nearly half of the participants found that having a sense of purpose helped to maintain their well-being: “You have to have a purpose you see. I think mental resilience is all about having a sense of purpose” (p. 6).
However, at the same time, the majority of the articles (12 out of 18) highlighted the negative impact of confinement and social distancing. Participants talked of increased depressive feelings and anxiety. For example, one of Akkus et al.’s [ 62 ] participants said: “... I am depressed; people died. Terrible disease does not give up, it always kills, I am afraid of it …” (p. 549). Similarly, one of Falvo et al.’s [ 67 ] participants remarked: “I am locked inside my house and I am afraid to go out” (p. 7).
Many of the studies reported the negative impact of loneliness as a result of confinement on participants’ well-being including [ 69 , 70 , 72 , 78 , 79 , 90 , 93 ]. Falvo et al. [ 67 ] reported that many participants experienced loneliness: “What sense does it make when you are not even able to see a family member? I mean, it is the saddest thing not to have the comfort of having your family next to you, to be really alone” (p. 8).
Not all studies found a negative impact on loneliness. For example, a “loner advantage” was found by Xie et al. ([ 82 ], p. 386). In this study participants found benefits in already being alone “It’s just a part of who I am, and I think that helps—if you can be alone, it really is an asset when you have to be alone” ([ 82 ], p. 386).
Bundy et al. [ 80 ] investigated loneliness from already lonely older adults and found that many participants did not attribute the loneliness to the pandemic: “It’s not been a whole lot, because I was already sitting around the house a whole lot anyway ( …). It’s basically the same, pretty well … I’d pretty well be like this anyway with COVID or without COVID” (p. 873) (see also [ 83 ]).
A study from Serbia investigated how the curfew was perceived 15 months afterward. Some participants were calm: “I realized that … well … it was simply necessary. For that reason, we accepted it as a measure that is for the common good” ([ 70 ], p.634). Others were shocked: “Above all, it was a huge surprise and sort of a shock, a complete shock because I have never, ever seen it in my life and I felt horrible, because I thought that something even worse is coming, that I even could not fathom” ([ 70 ], p. 634).
The lockdowns brought not only mental health issues to the fore but impacted the physical health of participants. Some reported they were fearful of the COVID-19 pandemic: “... For a little while I was afraid to leave, to go outside. I didn’t know if you got it from the air” ([ 75 ]. p. 6). Another study reported: “It’s been important for me to walk heartily so that I get a bit sweaty and that I breathe properly so that I fill my lungs—so that I can be prepared—and be as strong as possible, in case I should catch that coronavirus” ([ 77 ], p. 9); see also [ 70 , 78 , 82 , 85 ].
Coping and adaptation
Many studies mentioned older adults’ processes of coping and adaptation during the pandemic [ 63 , 64 , 68 , 69 , 72 , 75 , 79 , 81 , 85 , 87 , 88 , 89 , 90 ].
A variety of coping processes were reported including: acceptance; behavioural adaptation; emotional regulation; creating new routines; or using new technology. Kremers et al. [ 79 ] reported: “We are very realistic about the situation and we all have to go through it. Better days will come” (p. e71). Behavioural adaptation was reported: “Because I’m asthmatic, I was wearing the disposable masks, I really had trouble breathing. But I was determined to find a mask I could wear” ([ 68 ], p. 14). New routines with protective hygiene helped some participants at the beginning of the pandemic to cope with the health threat: “I am washing my hands all the time, my hands are raw from washing them all the time, I don't think I need to wash them as much as I do but I do it just in case, I don’t have anybody coming in, so there is nobody contaminating me, but I keep washing” ([ 69 ], p. 4391); see also [ 72 ]. Verhage et al. [ 87 ] reported strategies of coping including self-enhancing comparisons, distraction, and temporary acceptance: “There are so many people in worse circumstances …” (p. e294). Other studies reported how participants used a new technology: “I have recently learned to use WhatsApp, where I can make video phone calls.” ([ 88 ], p. 163); see also [ 89 ].
Discrimination -intersectionality (age and race/gender identity)
Seven studies reported ageism, racism, and gender discrimination experienced by older adults during the pandemic [ 23 , 63 , 67 , 70 , 76 , 84 , 88 ].
Prigent et al. [ 84 ], conducted in a New Zealand study, found that ageism was reciprocal. Younger people spoke against older adults: “why don’t you do everyone a favour and drop dead you f******g b**** it’s all because of ones like you that people are losing jobs” (p. 11). On the other hand, older adults spoke against the younger generation: “Shame to see the much younger generations often flout the rules and generally risk the gains made by the team. Sheer arrogance on their part and no sanctions applied” (p.11). Although one study reported benevolent ageism [ 23 ] most studies found hostile ageism [ 23 , 63 , 67 , 70 , 76 , 84 ]. One study from Canada exploring 15 older adult’s Chinese immigrants’ experiences reported racism as people around them thought they would bring the virus into the country. The negative impact on existing friendships was told by a Chinese man aged 69 “I can tell some people are blatantly despising us. I can feel it. When I talked with my Caucasian friends verbally, they would indirectly blame us for the problem. Eventually, many of our friendships ended because of this issue” ([ 88 ], p161). In addition, this study reported ageism when participants in nursing homes felt neglected by the Canadian government.
Two papers reported experiences of sexual and gender minorities (SGM) (e.g. transgender, queer, lesbian or gay) and found additional burdens during the pandemic [ 63 , 76 ]. People experienced marginalisation, stereotypes, and discrimination, as well as financial crisis: “I have faced this throughout life. Now people look at me in a way as if I am responsible for the virus.” ([ 63 ], p. 6). The consequence of marginalisation and ignorance of people with different gender identities was also noted by Hafford- Letchfield et al. [ 76 ]: “People have been moved out of their accommodation into hotels with people they don't know …. a gay man committed suicide, community members know of several that have attempted suicide. They are feeling pretty marginalised and vulnerable and you see what people are writing on the chat pages” (p.4). The intersection of ageism, racism, and heterosexism and its negative impact on people’s well-being during the pandemic reflects additional burden and stressors for older adults.
This systematic literature review is important as it provides new insights into the lived experiences of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic, worldwide. Our study highlights that the COVID-19 pandemic brought an increase in English-written qualitative articles to the fore. We found that 32 articles met the inclusion criteria but 5 were low quality. A lack of transparency reduces the trustworthiness of the study for the reader and the scientific community. This is particularly relevant as qualitative research is often criticised for its bias or lack of rigor [ 94 ]. However, their findings are additional evidence for our study.
Our aim was to explore, in a systematic literature review, the lived experiences of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic worldwide. The evidence highlights the themes of desired and challenged wellbeing, coping and adaptation, and discrimination and intersectionality, on wellbeing.
Perceived risk communication was experienced by many participants as overwhelming and anxiety-provoking. This finding supports Anwar et al.’s [ 37 ] study from the beginning of the pandemic which found, in addition to circulating information, that mass media influenced the public's behaviour and in consequence the spread of disease. The impact can be positive but has also been revealed to be negative as well. They suggest evaluating the role of the mass media in relation to what and how it has been conveyed and perceived. The disrupted social connectivity found in our review supports earlier studies that reported the negative impact of people’s well-being [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 ] at the beginning of the pandemic. This finding is important for future health crisis management, as the protective health measures such as confinement or self-isolation had a negative impact on many of the participants’ emotional wellbeing including increased anxiety, feelings of depression, and loneliness during the lockdowns. As a result of our review, future protective health measures should support people’s desire to maintain proximity with their loved ones and friends. However, we want to stress that our findings are mixed.
The ability of older adults to adapt and cope with the health crisis is important: many of the reported studies noted the diverse strategies used by older people to adapt to new circumstances. These included learning new technologies or changing daily routines. Politicians and the media and politicians should recognise both older adults' risk of disease and its consequences, but also their adaptability in the face of fast-changing health measures. This analysis supports studies conducted over the past decades on lifespan development, which found that people learn and adapt livelong to changing circumstances [ 95 , 96 , 97 ].
We found that discrimination against age, race, and gender identity was reported in some studies, in particular exploring participants’ experiences with immigration backgrounds and sexual and gender minorities. These studies highlighted the intersection of age and gender or race and were additional stressors for older adults and support the findings from Ramirez et al. [ 98 ] This review suggests that more research should be conducted to investigate the experiences of minority groups to develop relevant policies for future health crises.
Our review was undertaken two years after the pandemic started. At the cut-off point of our search strategy, no longitudinal studies had been found. However, in December 2022 a longitudinal study conducted in the USA explored older adult’s advice given to others [ 99 ]. They found that fostering and maintaining well-being, having a positive life perspective, and being connected to others were coping strategies during the pandemic [ 100 ]. This study supports the results of the higher order constructs of coping and adaptation in this study. Thus, more longitudinal studies are needed to enhance our understanding of the long-term consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic. The impact of the COVID-19 restrictions on older adults’ lives is evident. We suggest that future strategies and policies, which aim to protect older adults, should not only focus on the physical health threat but also acknowledge older adults' needs including psychological support, social connectedness, and instrumental support. The policies regarding older adult’s protections changed quickly but little is known about older adults’ involvement in decision making [ 100 ]. We suggest including older adults as consultants in policymaking decisions to ensure that their own self-determinism and independence are taken into consideration.
There are some limitations to this study. It did not include the lived experiences of older adults in care facilities or hospitals. The studies were undertaken during the COVID-19 pandemic and therefore data collection was not generally undertaken face-to-face. Thus, many studies included participants who had access to a phone, internet, or email, others could not be contacted. Additionally, we did not include published papers after August 2022. Even after capturing the most commonly used terms and performing additional hand searches, the search terms used might not be comprehensive. The authors found the quality of the papers to be variable, and their credibility was in question. We acknowledge that more qualitative studies might have been published in other languages than English and were not considered in this analysis.
To conclude, this systematic literature review found many similarities in the experiences of older adults during the Covid-19 pandemic despite cultural and socio-economic differences. However, we stress to acknowledge the heterogeneity of the experiences. This study highlights that the interplay of mass media reports of the COVID-19 pandemic and the policies to protect older adults had a direct impact on older adults’ well-being. The intersection of ‘isms’ (ageism, racism, and heterosexism) brought an additional burden for some older adults [ 98 ]. These results and knowledge about the drawbacks of health-protecting measures need to be included in future policies to maintain older adults’ well-being during a health crisis.
Availability of data and materials
The systematic literature review is based on already published articles. And all data analysed during this study are included in this manuscript. No additional data was used.
World Health Organisation (WHO): WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. 2020. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020.
WorldOMeter: Coronavirus toll update: Cases & deaths by country. 2022. Worldometers. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ .
World Health Organisation (WHO): Coronavirus disease. 2022. https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus#tab=tab . Aaccessed 5 Oct 2022.
Ayouni I, Maatoug J, Dhouib W, Zammit N, Fredj SB, Ghammam R, Ghannem H. Effective public health measures to mitigate the spread of COVID-19: a systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2021;21(1):1015.
PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Cerasoli B. The frail future of geriatrics. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2020;1(1):e11.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Allen K-A, Arslan G, Craig H, Arefi S, Yaghoobzadeh A, Sharif Nia H. The psychometric evaluation of the sense of belonging instrument (SOBI) with Iranian older adults. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):211.
Bailey L, Ward M, DiCosimo A, Baunta S, Cunningham C, Romero-Ortuno R, Kenny RA, Purcell R, Lannon R, McCarroll K, et al. Physical and mental health of older people while cocooning during the COVID-19 pandemic. QJM. 2021;114(9):648–53.
Dahlberg L. Loneliness during the COVID-19 pandemic. Aging Ment Health. 2021;25(7):1161–4.
PubMed Google Scholar
Derrer-Merk E, Ferson S, Mannis A, Bentall R, Bennett KM. Older people's family relationships in disequilibrium during the COVID-19 pandemic. What really matters? Ageing Soc. 2022:1–18.
Derrer-Merk E, Ferson S, Mannis A, Bentall RP, Bennett KM. Belongingness challenged: Exploring the impact on older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic. PLoS ONE. 2022;17(10):e0276561.
Heidinger T, Richter L. The effect of COVID-19 on loneliness in the elderly. An empirical comparison of pre-and peri-pandemic loneliness in community-dwelling elderly. Front Psychol. 2020;11:(585308).
Richter L, Heidinger T. Hitting close to home: the effect of COVID-19 illness in the social environment on psychological burden in older adults. Front Psychol. 2021;12:(737787).
Krendl AC, Perry BL. The impact of sheltering in place during the COVID-19 pandemic on older adults’ social and mental well-being. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2021;76(2):e53–8.
Litwin, H., & Levinsky, M. Social networks and mental health change in older adults after the Covid-19 outbreak. Aging Ment Health. 2021:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/13607863.2021.1902468 .
De Pue S, Gillebert C, Dierckx E, Vanderhasselt MA, De Raedt R, Van den Bussche E. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on wellbeing and cognitive functioning of older adults. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):4636.
Shahid Z, Kalayanamitra R, McClafferty B, Kepko D, Ramgobin D, Patel R, Aggarwal CS, Vunnam R, Sahu N, Bhatt D, et al. COVID-19 and older adults: what we know. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020;68(5):926–9.
Smith M, Steinman L, Casey E. Combatting social isolation among older adults in a time of physical distancing: the COVID-19 social connectivity paradox. Front Public Health. 2020;8:403.
Cohn-Schwartz E, Finlay JM, Kobayashi LC. Perceptions of societal ageism and declines in subjective memory during the COVID-19 pandemic: longitudinal evidence from US adults aged ≥55 years. J Soc Issues. 2022;78(4):924–38.
Tsoukalis-Chaikalis N, Demsia S, Stamatopoulou A, Chaniotis D, Tel Nu. Systematic Mapping Study of Covid-19 Psychological Impact. 2021;15(3):820.
van Gerwen M, Alsen M, Little C, Barlow J, Genden E, Naymagon L, Tremblay D. Risk factors and outcomes of COVID-19 in New York City; a retrospective cohort study. J Med Virol. 2021;93(2):907–15.
Victor CR, Rippon I, Barreto M, Hammond C, Qualter P. Older adults’ experiences of loneliness over the lifecourse: an exploratory study using the BBC loneliness experiment. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2022;102:104740.
Vrach IT, Tomar R. Mental health impacts of social isolation in older people during COVID pandemic. Prog Neurol Psychiatry. 2020;24(4):25–9.
Google Scholar
Derrer-Merk E, Reyes-Rodriguez M-F, Salazar A-M, Guevara M, Rodríguez G, Fonseca A-M, Camacho N, Ferson S, Mannis A, Bentall RP, et al. Is protecting older adults from COVID-19 Ageism? A comparative cross-cultural constructive grounded theory from the United Kingdom and Colombia. J Soc Issues. 2022;78(4):900–23.
Lytle A, Levy SR. Reducing ageism toward older adults and highlighting older adults as contributors during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Soc Issues. 2022;78(4):1066–84.
McDarby M, Ju CH, Picchiello MC, Carpenter BD. Older adults’ perceptions and experiences of ageism during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Soc Issues. 2022;78(4):939–64.
Drury L, Abrams D, Swift HJ. Intergenerational contact during and beyond COVID-19. J Soc Issues. 2022;78(4):860–82.
Kanık B, Uluğ ÖM, Solak N, Chayinska M. “Let the strongest survive”: Ageism and social Darwinism as barriers to supporting policies to benefit older individuals. J Soc Issues. 2022;00:1–25.
Spaccatini F, Giovannelli I, Pacilli MG. “You are stealing our present”: Younger people's ageism towards older people predicts attitude towards age-based COVID-19 restriction measures. J Soc Issues. 2022;78(4):769–89.
Sutter A, Vaswani M, Denice P, Choi KH, Bouchard H, Esses VM. Ageism toward older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic: Intergenerational conflict and support. J Soc Issues. 2022;78(4):815–41.
Swift H, Chasteen A. Ageism in the time of COVID-19. Group Process Intergroup Relat. 2021;24:246–52.
World Health Organisation (WHO): Risk Communication in times of an epidemic or pandemic. Asset paper series Epidemics and Pandemics: 2017. https://www.who.int/emergencies/risk-communicationsWHORCaCERaoSAo .
Bailey A, Harris MA, Bogle D, Jama A, Muir SA, Miller S, Walters CA, Govia I. Coping with COVID-19: health risk communication and vulnerable groups. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2021;17:e22.
Li X, Lyu H. Epidemic risk perception PS, and mental health during COVID-19 pandemic: a moderated mediating model. Front Psychol. 2021;11:563741. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.563741 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sandman P M & American Industrial Hygiene Association: Responding to community outrage: strategies for effective risk communication. American Industrial Hygiene Association. 2003.
Sandman, P M. Introduction and orientation index. https://www.psandman.com/index-intro.htm . Retrieved 13 October 2022.
Anderson M, Pitchforth E, Asaria M, Brayne C, Casadei B, Charlesworth A, Coulter A, Franklin BD, Donaldson C, Drummond M, et al. LSE-Lancet Commission on the future of the NHS: re-laying the foundations for an equitable and efficient health and care service after COVID-19. Lancet. 2021;397(10288):1915–78.
PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Anwar A, Malik M, Raees V, Anwar A. Role of mass media and public health communications in the COVID-19 pandemic. Cureus. 2020;12(9):e10453.
U.S. National Library of Medicine: COVID-19 - Search Details - ClinicalTrials.gov: Clinicaltrials.gov 2022. Retrieved October 13, 2022, from https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results/details?cond=COVID-19 .
Tremblay S, Castiglione S, Audet L-A, Desmarais M, Horace M, Peláez S. Conducting qualitative research to respond to COVID-19 challenges: reflections for the present and beyond. Int J Qual Methods. 2021;20:16094069211009680.
Flemming K, Noyes J. Qualitative evidence synthesis: where are we at? Int J Qual Methods. 2021;20:1609406921993276.
Booth A. Searching for qualitative research for inclusion in systematic reviews: a structured methodological review. Syst Rev. 2016;5(1):74.
Krnic Martinic M, Pieper D, Glatt A, Puljak L. Definition of a systematic review used in overviews of systematic reviews, meta-epidemiological studies and textbooks. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019;19(1):203.
Phillips V, Barker E. Systematic reviews: structure, form and content. J Perioper Pract. 2021;31(9):349–53.
Derrer-Merk E, Soulsby L, Reyes Rodriguez M, Ferson S, Mannis A, Bennett KM. Older adults' lived experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review. 2022. PROSPERO 2022 CRD42022331714. Available from: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42022331714 .
Cooke A, Smith D, Booth A. Beyond PICO: the SPIDER tool for qualitative evidence synthesis. Qual Health Res. 2012;22:1435–43.
Long HA, French DP, Brooks JM. Optimising the value of the critical appraisal skills programme (CASP) tool for quality appraisal in qualitative evidence synthesis. Res Methods Med Health Sci. 2020;1(1):31–42.
Sattar R, Lawton R, Panagioti M, Johnson J. Meta-ethnography in healthcare research: a guide to using a meta-ethnographic approach for literature synthesis. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):50.
Soundy A, Heneghan NR. Meta-ethnography. Int Rev Sport Exerc Psychol. 2022;15(1):266–86.
Fallon V, Groves R, Halford JCG, Bennett KM, Harrold JA. Postpartum anxiety and infant-feeding outcomes: a systematic review. J Hum Lact. 2016;32(4):740–58.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SE, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2021;18(3):e1003583.
Tod D, Booth A, Smith B. Critical appraisal. Int Rev Sport Exerc Psychol. 2022;15(1):52–72.
Morse J. Why the Qualitative Health Research (QHR) review process does not use checklists. Qual Health Res. 2021;31(5):819–21.
Munthe-Kaas HM, Glenton C, Booth A, Noyes J, Lewin S. Systematic mapping of existing tools to appraise methodological strengths and limitations of qualitative research: first stage in the development of the CAMELOT tool. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019;19(1):113.
Njau B, Covin C, Lisasi E, Damian D, Mushi D, Boulle A, Mathews C. A systematic review of qualitative evidence on factors enabling and deterring uptake of HIV self-testing in Africa. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):1289.
Butler A, Hall H, Copnell B. A guide to writing a qualitative systematic review protocol to enhance evidence-based practice in nursing and health care. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2016;13(3):241–9.
Soilemezi D, Linceviciute S. Synthesizing qualitative research: reflections and lessons learnt by two new reviewers. Int J Qual Methods. 2018;17(1):1609406918768014.
Booth A. Harnessing energies, resolving tensions: acknowledging a dual heritage for qualitative evidence synthesis. Qual Health Res. 2019;29(1):18–31.
Carroll C, Booth A. Quality assessment of qualitative evidence for systematic review and synthesis: Is it meaningful, and if so, how should it be performed? Res Synth Methods. 2015;6(2):149–54.
Charmaz K. Constructing Grounded Theory. 2nd ed. London: Sage; 2014.
Toye F, Seers K, Allcock N, Briggs M, Carr E, Barker K. Meta-ethnography 25 years on: challenges and insights for synthesising a large number of qualitative studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14(1):80.
Noblit GW, Hare RD. Meta-ethnography: synthesizing qualitative studies. California: Sage Publications Ltd; 1988.
Akkus Y, Parlak A, Karacan Y, Karatay G. Perceptions and experiences of older people regarding the COVID-19 pandemic process: a phenomenological study. Turk Geriatri Dergisi. 2021;24:546–56.
Banerjee D, Rao TSS. “The Graying Minority”: lived experiences and psychosocial challenges of older transgender adults during the COVID-19 pandemic in India, A qualitative exploration. Front Psychiatry. 2021;11:604472.
Brooke J, Jackson D. Older people and COVID-19: Isolation, risk and ageism. J Clin Nurs. 2020;29(13-14):2044–6.
Bundy H, Lee HM, Sturkey KN, Caprio AJ. The lived experience of already-lonely older adults during COVID-19. Gerontologist. 2021;61(6):870–7.
Chemen S, Gopalla YN. Lived experiences of older adults living in the community during the COVID-19 lockdown - The case of mauritius. J Aging Stud. 2021;57:100932.
Falvo I, Zufferey MC, Albanese E, Fadda M. Lived experiences of older adults during the first COVID-19 lockdown: a qualitative study. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(6):e0252101.
Fiocco AJ, Gryspeerdt C, Franco G. Stress and adjustment during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative study on the lived experience of Canadian older adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(24):12922.
Fristedt S, Carlsson G, Kylén M, Jonsson O, Granbom M. Changes in daily life and wellbeing in adults, 70 years and older, in the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. Scand J Occup Ther. 2022;29(6):511–21.
Gazibara T, Maksimovic N, Dotlic J, Jeremic Stojkovic V, Cvjetkovic S, Milic M. Experiences and aftermath of the COVID-19 lockdown among community-dwelling older people in Serbia: a qualitative study. J Eval Clin Pract. 2022;28(4):631–40.
Giebel C, Ivan B, Ddumba I. COVID-19 public health restrictions and older adults’ well-being in Uganda: psychological impacts and coping mechanisms. Clin Gerontol. 2022;45(1):97–105.
Goins RT, Anderson E, Minick H, Daniels H. Older adults in the United States and COVID-19: a qualitative study of perceptions, finances, coping, and emotions. Front Public Health. 2021;9:660536.
Gomes MACFC, Fontenele NAO, Galindo Neto NM, Barros LM, Frota NM. Elderly people’s experience facing social isolation in the COVID-19 pandemic. Rev Rene. 2021;22:e69236. https://doi.org/10.15253/2175-6783.20212269236 .
Article Google Scholar
Gonçalves AR, Barcelos JLM, Duarte AP, Lucchetti G, Gonçalves DR. Silva e Dutra FCM, Gonçalves JRL: Perceptions, feelings, and the routine of older adults during the isolation period caused by the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative study in four countries. Aging Ment Health. 2022;26(5):911–8.
Greenwood-Hickman MA, Dahlquist J, Cooper J, Holden E, McClure JB, Mettert KD, Perry SR, Rosenberg DE. “They’re Going to Zoom It”: a qualitative investigation of impacts and coping strategies during the COVID-19 pandemic among older adults. Front Public Health. 2021;9:679976.
Hafford-Letchfield T, Toze M, Westwood S. Unheard voices: a qualitative study of LGBT+ older people experiences during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in the UK. Health Soc Care Community. 2022;30(4):e1233–43.
Huntley R, Bratt AS. An interpretative phenomenological analysis of the lived experiences of older adults during the covid-19 pandemic in sweden. Nordic Psychol. 2022;75(1)3–19.
Jiménez-Etxebarria E, Bernaras Iturrioz E, Jaureguizar J. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic as perceived by older people in Northern Spain. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2021;14:1789–803.
Kremers EM, Janssen JHM, Nieuwboer MS, Olde Rikkert MGM, Peeters GMEE. The psychosocial adaptability of independently living older adults to COVID-19 related social isolation in the Netherlands: a qualitative study. Health Soc Care Community. 2022;30(1):e67–74.
Kulmala J, Tiilikainen E, Lisko I, Ngandu T, Kivipelto M, Solomon A. Personal social networks of community-dwelling oldest old during the Covid-19 pandemic—A qualitative study. Front Public Health. 2021;9:1–10.
Mahapatra P, Sahoo KC, Desaraju S, Pati S. Coping with COVID-19 pandemic: reflections of older couples living alone in urban Odisha India. Prim Health Care Res Dev. 2021;22:e64.
McKinlay AR, Fancourt D, Burton A. A qualitative study about the mental health and wellbeing of older adults in the UK during the COVID-19 pandemic. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):1–10.
Pfabigan J, Wosko P, Pichler B, Reitinger E, Pleschberger S. Under reconstruction: the impact of COVID-19 policies on the lives and support networks of older people living alone. Int J Care Caring. 2022;6(1-2):211–28.
Prigent C, Morgan T, Wiles J, Morgan K, Williams L, Gott M. Intergenerational tension or cohesion during the covid-19 pandemic?: A letter-writing study with older new zealanders. J Intergenerational Relationsh. 2022;20(4):386–405.
Sangrar R, Porter MM, Chesser S. Exploring the interpretation of COVID-19 messaging on older adults. Experiences of vulnerability. Can J Aging Rev Can Vieil. 2021;40(4):533–42.
Sattari S, Billore S. Bring it on Covid-19: being an older person in developing countries during a pandemic. Working Older People. 2020;24(4):281–91.
Verhage M, Thielman L, Kock L, Lindenberg J. Coping of older adults in times of COVID-19: considerations of temporality among dutch older adults. J Gerontol B. 2021;76(7):e290–9.
Wang Q, Liu JKK, Walsh CA. Identities: experiences and impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic from the perspectives of older Chinese immigrants in Canada. China J Soc Work. 2021;14(2):153–71.
Xie B, Shiroma K, De Main AS, Davis NW, Fingerman K, Danesh V. Living through the COVID-19 pandemic: community-dwelling older adults’ experiences. J Aging Soc Policy. 2021;33(4–5):380–97.
Yang Q, Wang Y, Tian C, Chen Y, Mao J. The Experiences of Community-dwelling older adults during the COVID-19 lockdown in Wuhan: a qualitative study. J Adv Nurs (John Wiley & Sons, Inc). 2021;77(12):4805–14.
Yıldırım H. Psychosocial status of older adults aged 65 years and over during lockdown in Turkey and their perspectives on the outbreak. Health Soc Care Community. 2022;30(3):899–907.
Hill Z, Tawiah-Agyemang C, Kirkwood B, Kendall C. Are verbatim transcripts necessary in applied qualitative research: experiences from two community-based intervention trials in Ghana. Emerg Themes Epidemiol. 2022;19(1):5.
Giles D. Performed across Europe and written up in English: the double challenge for qualitative psychologists. Qual Res Psychol. 2019;16(3):503–7.
Anderson C. Presenting and evaluating qualitative research. Am J Pharm Educ. 2010;74(8):141.
Nikitin J, Freund A. The Adaptation Process of Aging. The Cambridge Handbook of Successful Aging. Chapter: 17. Cambridge University Press. 2019. p. 281–98.
Deimling GT, Kahana B, Bowman KF, Schaefer ML. Cancer survivorship and psychological distress in later life. Psychooncology. 2002;11(6):479–94.
Baltes PB, Staudinger UM, Lindenberger U. Lifespan psychology: theory and application to intellectual functioning. Annu Rev Psychol. 1999;50:471–507.
Ramirez L, Monahan C, Palacios-Espinosa X, Levy SR. Intersections of ageism toward older adults and other isms during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Soc Issues. 2022;78(4):965–90.
Van Vleet B, Fuller HR, Hofmann B, Huseth-Zosel A. Untapped insight: a longitudinal qualitative analysis of older adults’ advice during the COVID-19 pandemic. Innov Aging. 2022;6(7):igac071.
Gietel-Basten S, Matus K, Mori R. COVID-19 as a trigger for innovation in policy action for older persons? Evid Asia Policy Soc. 2022;41(1):168–86.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Liverpool, Eleanor Rathbone Building, Bedford Street South, Liverpool, L697ZA, UK
Elfriede Derrer-Merk, Laura K. Soulsby & Kate M. Bennett
Universidad de los Andes, Carrera 1 No. 18A-12, Bogotá, Colombia
Maria-Fernanda Reyes-Rodriguez
Principal Health Psychologist, Resilience Hub, Lancashire & South Cumbria Foundation Hospital, Chorley, UK
Louise Roper
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Elfriede Derrer-Merk contributed to the design, analysis, and writing the draft. Maria-Fernanda Rodriguez-Reyes contributed to the analysis, revised the draft, and approved the submission. Laura K. Soulsby contributed to the analysis, revised the draft, and approved the submission. Louise Roper contributed to the analysis, revised the draft, and approved the submission. Kate M. Bennett contributed to the design, analysis, writing the draft, and approved the submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Elfriede Derrer-Merk .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Derrer-Merk, E., Reyes-Rodriguez, MF., Soulsby, L.K. et al. Older adults’ experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative systematic literature review. BMC Geriatr 23 , 580 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-023-04282-6
Download citation
Received : 16 November 2022
Accepted : 05 September 2023
Published : 20 September 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-023-04282-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Older adults
- Risk communication
- Discrimination
BMC Geriatrics
ISSN: 1471-2318
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Advertisement
Active Student Participation in Whole-School Interventions in Secondary School. A Systematic Literature Review
- REVIEW ARTICLE
- Open access
- Published: 04 May 2023
- Volume 35 , article number 52 , ( 2023 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Sara Berti ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5238-1077 1 ,
- Valentina Grazia 1 &
- Luisa Molinari 1
4286 Accesses
4 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This review presents a reasoned synthesis of whole-school interventions seeking to improve the overall school environment by fostering active student participation (ASP) in school activities and decision-making processes. The aims are to describe the selected programs, assess their methodological quality, and analyze the activities soliciting ASP. Among the 205 publications initially provided by the literature search in the academic databases PsycINFO and Education Research Complete, 22 reports met the inclusion criteria of presenting whole-school interventions that solicit ASP in secondary schools, and were thus included in the review. Such publications referred to 13 different whole-school programs, whose implemented activities were distinguished on a 5-point scale of ASP levels, ranging from Very high ASP , when students were involved in a decision-making role, to Very low ASP , when students were the passive recipients of content provided by adults. This review contributes to the literature by proposing an organizing structure based on different levels of ASP, which provides clarity and a common ground for future studies on student participation. Overall, the in-depth description of activities offers a framework to researchers and practitioners for planning interventions aimed at improving the learning environment and contributing meaningfully to the far-reaching goal of encouraging student participation in school life.
Similar content being viewed by others

Play-Based Learning: Evidence-Based Research to Improve Children’s Learning Experiences in the Kindergarten Classroom
Meaghan Elizabeth Taylor & Wanda Boyer
The Role of School in Adolescents’ Identity Development. A Literature Review
Monique Verhoeven, Astrid M. G. Poorthuis & Monique Volman
Social support in schools and related outcomes for LGBTQ youth: a scoping review
Enoch Leung, Gabriela Kassel-Gomez, … Tara Flanagan
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Research in educational psychology is consistent in showing that the quality of the school environment largely affects student well-being. Indeed, students’ experiences of a supportive school context have a significant impact on positive behaviors, such as academic achievement (Brand et al., 2008 ; Hoy, 2012 ) and good relationships among students and between students and staff (Cohen et al., 2009 ; Thapa et al., 2013 ). Conversely, the poor quality of the learning environment predicts negative outcomes, such as substance use (Weatherson et al., 2018 ) or bullying (Låftman et al., 2017 ).
In view of this, schools need to face the challenge of implementing interventions aimed at changing and improving the learning environment in the direction of promoting positive behaviors and reducing negative outcomes. One of the most promising directions in this regard is based on the adoption of whole-school approaches whose key features are the focus on overall school systems instead of on specific problems (Bonell et al., 2018 ).
The literature on whole-school interventions is broad (see, for example, Charlton et al., 2021 , for an extensive review on whole-school interventions focused on school climate), but it suffers from two major gaps. First, it relies primarily on programs applicable to elementary schools, while studies on high school populations are rarer, presumably because of the multiple challenges derived from the implementation of programs in such complex contexts (Estrapala et al., 2021 ; Vancel et al., 2016 ). Second, despite the importance generally attributed to the active involvement of students in the programs, to our knowledge, no previous reviews have specifically investigated the degree and the characteristics of student participation in such interventions. To address these limitations, in this article, we present a systematic literature review on whole-school interventions carried out in secondary schools and based on programs that envisage students’ active participation and involvement.
Whole-School Interventions for Improving the Learning Environment
In educational research, some reviews and meta-analyses (Charlton et al., 2021 ; Merrell et al., 2008 ; Voight & Nation, 2016 ) have critically synthesized and discussed studies on school interventions aimed at improving the learning environment. These programs have considered different outcomes of improvement, ranging from a general focus on school climate dimensions—e.g., relational aspects, institutional organization, and safety—to more specific aspects, such as bullying, violence, or substance use. However, the degree of effectiveness of such programs remains controversial. For example, a meta-analysis by Ttofi et al. ( 2008 ) indicated that school-based bullying prevention programs were able to bring about positive results, while another meta-analysis on the same topic (Merrel et al., 2008 ) concluded that evidence in this direction was only modest.
More positive results concerning the effectiveness of interventions were reported by Allen ( 2010 ) with reference to programs conducted by means of a whole-school approach. In her literature overview of studies designed to reduce bullying and victimization, the author concluded that whole-school interventions generally showed at least marginal evidence of improvement. Despite these encouraging findings, the studies conducted with a whole-school approach in secondary education contexts were rare. Among these, a well-established framework of whole-school interventions mostly implemented in middle schools is the School-Wide Positive Behavior Support program (for reviews, see Gage et al., 2018 ; Noltemeyer et al., 2019 ), which is a multi-tiered framework engaging students, school staff, and families for the delivery of evidence-based behavioral support aligned to students’ needs (Horner et al., 2004 ). By and large, the study results in this framework are again promising in suggesting a connection between such programs and school improvement, although the evidence is generally moderate and only regards a few of the considered outcome measures.
The mixed or weak results reported in the cited reviews solicit further exploration of the specific characteristics of whole-school interventions. In particular, a major limitation of the literature is the lack of an in-depth analysis of the types of activities proposed to students in each program, especially as far as their direct involvement is concerned. Given the importance attributed to student engagement in school life (Markham & Aveyard, 2003 ), this is a relevant area of inquiry that can inform researchers and practitioners willing to design and conduct whole-school interventions calling for students’ involvement.
Student Involvement in School Intervention
The importance of students’ involvement and participation finds a theoretical ground in the self-determination theory (see Ryan & Deci, 2017 ), according to which people who are self-determined perceive themselves as causal agents in life experiences, being proactive and engaged in the social environment. Studies examining such human disposition in adolescence supported the relevance of self-determination for quality of life and identity development (Griffin et al., 2017 ; Nota et al., 2011 ) and as a full mediator in the negative association between stress and school engagement (Raufelder et al., 2014 ).
In the light of these assumptions, educational and school psychologists have launched scientific and professional debates on the ways in which schools can implement favorable conditions for students to feel active and co-responsible for their educational and academic pathways (Carpenter & Pease, 2013 ; Helker & Wosnitza, 2016 ; Schweisfurth, 2015 ). These debates have reached consensus across-the-board on the recognition that school change and improvement are best fostered by intervention programs in which students are offered opportunities to get actively involved in school life (Baeten et al., 2016 ; Voight & Nation, 2016 ). For this goal to be achieved, all educational agencies are called upon to promote interventions capable of supporting activities that require student involvement and participation (Antoniou & Kyriakides, 2013 ).
The importance of students’ active participation in the school environment has also been confirmed by a substantial amount of literature investigating over time the association between high student involvement and positive learning environments. Mitchell ( 1967 ) reported that school climate is related to the extent of student participation and interaction during school life. Epstein and McPartland ( 1976 ) showed that student opportunities for school involvement were related to satisfactory outcomes. In a 1982 review published, Anderson claimed that “the type and extent of student interaction that is possible within a school appears to be a significant climate variable” (Anderson, 1982 ; p.401). A few years later, Power et al. ( 1989 ) described a program implemented in several contexts and characterized by high student involvement, whose results showed that a high rate of student participation led to their capacity to take on responsibility for building an effective learning environment and positive climate. More recent studies (Vieno et al., 2005 ) have confirmed that democratic school practices, such as student participation in decision-making processes, play a significant role in the development of a sense of community at individual, class, and school levels. The review by Thapa et al. ( 2013 ) confirmed the importance of student classroom participation as a variable affecting school climate and academic achievement.
On these theoretical and empirical grounds, providing space to student voices in decision-making and school change emerges as a powerful strategy for improving school environments and enforcing the success of programs (Mitra, 2004 ). The construct of student agency fits in well with this approach, as it refers to the students’ willingness and skill to act upon activities and circumstances in their school lives (Lipponen & Kumpulainen, 2011 ). Representing adolescents’ authentic, proactive, and transformative contributions to school life (Grazia et al., 2021 ), agency is fostered by school environments capable of soliciting and valorizing students’ active participation in educational practices and school decisions (Makitalo, 2016 ) and encouraging them to feel co-responsible with teachers and staff for their school lives (Mameli et al., 2019 ). The value of agency has been confirmed by research showing its positive associations with motivation and the fulfilment of basic psychological needs (Jang et al., 2012 ) as well as with the perception of supportive teaching (Matos et al., 2018 ).
Despite the agreement on student participation as a crucial feature for the success of programs capable of improving students’ school life, to our knowledge, previous literature reviews on school interventions have not focused specifically on the extent and way in which students are given a voice and are involved in the programs. In view of this, in the present work, we set out to search, in the existing literature, for interventions specifically based on activities in which students were not just the recipients of activities but rather took on an active and decision-making role. For our purposes, we use the notion of active student participation (ASP) to include the variety of ways in which students are given the opportunity to participate actively in school activities and decisions that will shape their own lives and those of their peers.
Review’s Aims
Previous reviews (Charlton et al., 2021 ; Estrapala et al., 2021 ; Voight & Nation, 2016 ) have provided extensive descriptions of whole-school interventions aimed at improving school environments or reducing school problems, suggesting their effectiveness. Moreover, a growing amount of literature has found that students’ active involvement in their school life is a crucial feature for improvement. Our general goal was to move forward by conducting an in-depth examination of existing whole-school interventions based on activities promoting ASP in secondary schools, by providing a reasoned synthesis of their characteristics and implementation. The choice to focus on secondary schools was driven by the evidence that this developmental stage has so far received less attention in whole-school intervention research (Estrapala et al., 2021 ; Vancel et al., 2016 ).
Given the large heterogeneity of existing intervention programs, both in terms of participants (specific subgroups vs general student population) and targets of improvement (specific abilities vs general school environment), it was essential to set clear boundaries for the study selection. As this was a novel undertaking, we chose to focus on whole-school interventions directed to the overall student population and aimed at improving the school climate as a whole. This allowed us to select a reasonably homogeneous sample of studies, with the confidence that future reviews will advance our knowledge by considering more specific fields and populations.
The review’s aims were (a) to describe the selected programs on the basis of their focus, country, duration, age of participants, and research design; (b) to assess the soundness of the research design and methodologies adopted in each study in order to provide evidence of the methodological quality of the selected programs; and (c) to differentiate among various levels of ASP in the program’s activities and, for each of these levels, to describe methods and activities carried out in the programs.
The present review was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses 2020 updated statement (PRISMA 2020; Page et al., 2021 ). In line with the terminology proposed by the authors, in the following sections, we use the term study for every investigation that includes a well-defined group of participants and one or more interventions and outcomes, report for every document supplying information about a particular study (a single study might have multiple reports), and record for the title and/or abstract of a report indexed in a database. In addition, for the specific purposes of the present review, we use the term program when referring to an implemented whole-school intervention that has specific characteristics and is usually named, since more than one study may be conducted with the same program.
Eligibility Criteria
Studies were eligible for inclusion in the review if they were (i) written in English language; (ii) published in peer-reviewed academic journals; and (iii) aimed at assessing psychological effects of whole-school interventions that solicit ASP in secondary schools; thus, studies in which students were involved solely as recipients of activities delivered by adults were excluded. Moreover, in line with the review’s aims described above, studies were excluded from the review if they were (i) focused on specific subgroups of students (e.g., ethnical minorities or LGBTQ students); (ii) solely aimed at improving specific skills (e.g., literacy or mathematics); and (iii) solely focused on physical health (e.g., nutrition or physical activity).
Information Sources and Search Strategy
A literature search was conducted via EBSCO, including the academic databases PsycINFO and Education Research Complete, last consulted on April 9, 2022. The entered search terms were school-wide interventions OR whole-school interventions OR school-wide programs OR whole-school programs OR school-wide trainings OR whole-school trainings AND secondary school OR high school OR secondary education. By means of the software’s automated procedure, we searched these terms in the abstracts and filtered the results according to the first two inclusion criteria, selecting articles in English and published in peer-reviewed academic journals.
Selection and Data Collection Process
The records of each study were screened by two researchers, and the potentially relevant studies were further assessed for eligibility by three researchers, who read the full text independently. Moreover, some records relevant to the purposes of the research were identified through the references of the included documents ( forward snowballing ; Wohlin, 2014 ). Data from each included report were searched by two researchers, who worked independently to extrapolate the information relevant to the review, which were (a) the study characteristics; (b) the indicators of methodological quality; and (c) the program activities.
Detailed information about the selection process is provided in the PRISMA flow diagram (Fig. 1 ). The literature search provided 205 total records, and reduced to 169 after the automatic deduplication provided by EBSCO. After the application of our inclusion and exclusion criteria, 62 records were selected for full text reading. Of the 107 excluded records, 37 did not report interventions (e.g., they presented only school surveys), 25 were informative papers on initiatives and/or interventions without assessments, 15 focused only on academic skills attainment, 11 referred to primary schools, 10 focused on minorities, 6 were reviews of books or DVDs, and 3 only evaluated physical health as an outcome. After the full text reading of the 62 selected reports, 48 were excluded as they only discussed aspects related to implementation (e.g., feasibility or fidelity) without assessing the psychological effects of the intervention on students ( n = 23) or did not solicit ASP during the intervention ( n = 25). Thus, 14 reports were included in the sample. In addition, 10 reports were identified by sifting through the references of the selected documents ( forward snowballing ; Wohlin, 2014 ). After the full text reading, two of them were excluded as they did not assess the effects of the intervention. At the end of the selection process, the final sample of the present review included 22 reports, which referred to 16 studies and 13 programs.
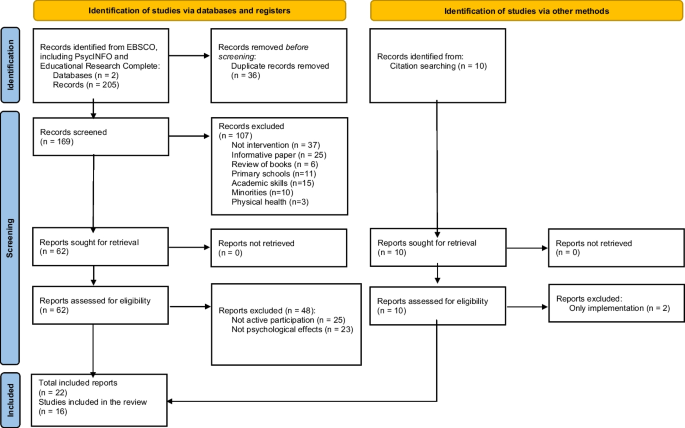
PRISMA flow diagram
Study Characteristics
The main information about each study is reported in Table 1 . As for the focus of the interventions, three macro-areas were identified: (a) prevention of violence (nine studies and twelve reports), including programs for less bullying, cyberbullying, dating violence, sexual violence, and aggression; (b) promotion of mental health (five studies and seven reports), including programs for addressing depression and suicide risk and for promoting general psychological health; (c) promotion of positive emotional and relational school climate (two studies and three reports), including programs for enhancing school connectedness and school climate.
Within each macro-area, in Table 1 , the programs are listed following the alphabetical order of the program name. Out of the studies focused on preventing violence, three referred to unnamed anti-bullying programs, which in the present review were labeled Anti-bullying_1 , Anti-bullying_2 , and Anti-bullying_3 ; the other studies on the topic referred to an anti-cyberbullying program named Cyber Friendly School ; an anti-bullying program named Friendly School ; a bystander program aimed at preventing dating violence and sexual violence, named Green Dots ; a program aimed at preventing bullying and aggression, named Learning Together ; and an anti-bullying program named STAC , which stands for Stealing the show, Turning it over, Accompanying others, Coaching compassion. The studies focused on promoting mental health comprised a school research initiative aimed at preventing depression, named Beyond blue ; an intervention aimed at promoting mental health, named Gatehouse Project ; and a program to prevent suicide risk, named Sources of Strengths . Out of the studies focused on promoting positive emotional and relational school climate, one referred to the Restorative Justice program, aimed at promoting healthy and trusting relationships within the school, and the other referred to a program aimed at the promotion of a good school climate, named SEHER , which stands for Strengthening Evidence base on scHool-based intErventions for pRomoting adolescent health.
A large majority of the studies were conducted in the USA, some were carried out in Australia and the UK, and a few studies in India and China. The studies varied in duration, ranging from one to seven school years, and the number of schools involved in the intervention, ranging from 1 to 75. About half of the studies involved students from all grades while the other half was targeted only for some grades. Lastly, the reports varied in its research design: the majority conducted experimental group comparisons (EGC), but also other quantitative research designs (O) were present along with some qualitative designs (QUAL). To make text and tables more readable, the 13 included programs were renamed with a program ID consisting of the initials of the program name. Similarly, the 22 included reports were renamed with a report ID , consisting in the program ID followed by the surname of the first author and the publication year, all separated by underscores. Report ID and Program ID are reported in Table 1 .
Assessment of Methodological Quality
To assess each report’s methodological quality, we searched in the literature for a rigorous and comprehensive set of indicators and eventually decided to use as a reference the standards for evidence-based practices identified by the Council for Exceptional Children (CEC, 2014 ), which include indicators on setting and program description, fidelity, and reliability of outcome measures. Although the standards were originally recommended for the specific field of special education, they are considered appropriate to evaluate studies in all educational settings and were previously used by Charlton et al. ( 2021 ) in a systematic review studying the effects of school-wide interventions on school climate perceptions. Given that our aim was not to identify evidence-based practices but more generally to assess the methodological quality of the reports included in the review, some of the identified indicators were not applicable to our material. For this reason, among all the indicators described in the document (CEC, 2014), we selected those that provided a general overview of each report’s methodological quality. The selected indicators, their corresponding number in the CEC document, and a short description for each are reported in Table 2 .
In more detail, we applied a more extensive set of indicators to reports which fit the CEC definition of experimental group comparison design (EGC, as reported in Table 1 ), where participants were divided into two or more groups, both randomly and non-randomly, to test the effects of the interventions. For reports based on qualitative analyses and on quantitative analyses not consistent with the EGC design (QUAL and O, as reported in Table 1 ), we used a more limited set of indicators (indicators 1 to 6, as described in Table 2 ) and included a brief description of the research aims and methods. In the assessment of methodological quality, interrater reliability was achieved as three independent researchers read each report in detail, and the attribution of each indicator was discussed and agreed upon.
The assessment of methodological quality for the EGC reports is summarized in Table 3 . The findings show that most studies were strong in contextualizing the research, clearly describing the intervention program (either directly or with references to previous work) and conducting quality analyses. Weak points emerged to be related to the assessment of fidelity implementation (indicators 4 and 5 in Table 3 ), both with reference to adherence to the intervention program and to the dosage received by participants. Results for studies with qualitative analyses or quantitative analyses not EGC are reported in Table 4 . Like the ECG reports, most of these studies appeared strong in contextualizing the research and describing the intervention program, while fidelity of implementation received less attention (indicators 4 and 5 in Table 4 ).
Levels of Active Student Participation
As required by our inclusion criteria, all the selected programs were based on interventions that solicited ASP. However, from the careful analysis of the studies, we realized that the program activities promoted very different forms of ASP. Three independent researchers thus considered in detail each activity described in the programs and eventually agreed to score it on a 5-point scale (see Table 5 ), distinguishing among activities that solicit various levels of ASP. The scale partly followed the school participation scale of the HBSC questionnaire as defined by De Róiste et al. ( 2012 ). It ranged from Very high levels of ASP, attributed to activities in which students were given a fully decision-making role, to Very low levels of ASP, given to activities in which students were just the recipients of activities delivered by adults. In line with our inclusion criteria, in no programs, students were involved solely as recipients of activities delivered by adults (Very low ASP). Moreover, levels were not mutually exclusive, so that each program might include different levels of ASP.
In Table 5 , we report all the considered ASP levels, with the specifically related activities, and the coding of each program. It should be specified that the distribution of activities in the various levels was based on a qualitative accurate analysis of the role attributed to students and not on the number of students involved in each program’s activities, which varied to a great extent. In more detail, Very high ASP was attributed to interventions in which students were involved in processes with a direct organizational impact on school roles, curricula, and policies; this included two types of activities, i.e., student involvement in decision-making processes and the formation of school action teams comprising students. High ASP was recognized when students were still involved in organizational activities, but their role was limited to the implementation of activities and did not directly impact on school curricula and policies; it consisted of three activities, i.e., presentation of students’ works, leading of activities for peers, and leading of activities for adults. Moderate ASP was attributed when students were asked to express their viewpoints and opinions, without having a decision-making power, however; it comprised activities in which students were called to express their points of view on various school issues, either by the provision of platforms to share ideas, concerns, or suggestions, or by the organization of interactive school assemblies, or by their involvement in surveys based on data collection (e.g., by means of questionnaires) on specific aspects of their school life. Low ASP was attributed when the students’ activation was limited to a specific task required within a structured format designed by other people, including training for student leaders, interactive group activities, and individual activities. Finally, activities were coded as Very low ASP when students were involved as the passive recipients of contents provided by adults, through lecture-style lessons, viewing of videos, or distribution of didactic material. The activities provided for in each program are described at length in the following paragraphs, considering activities scored in every specific level of ASP.
For the sake of completeness, in Table 5 , we added a final column in which we indicated additional program activities that involved the staff. They comprised the formation of school action teams made up of adults, training, and the provision of materials for the staff. As the description of these activities goes beyond the scope of our investigation, we will not describe them in detail.
Very High ASP: Making School Rules
As can be seen in Table 5 , activities implying involvement of students in decision-making processes were identified in six programs. In AB3, during a school assembly, students were invited to develop a whole-school anti-bullying policy, while in later activities, they were asked to identify strategies to be implemented in the school to prevent bullying. In CFS, school staff and student leaders conducted whole-school activities helping students to review school policies to promote a positive use of technology. In FS, the intervention aimed to help the transition between primary and secondary school was co‐developed with students who had already made such a transition. In GP, the use of peer support and leadership was encouraged to increase opportunities and skills for students to participate in decision-making processes within the school; in addition, at a classroom level, rules were negotiated by teachers and students and displayed in each classroom. In RJ, during the first year of implementation, staff and students developed a plan for pathways of primary, secondary, and tertiary restorative interventions; in the following years, students’ leadership roles and collective decision-making activities increased, so that students themselves were able to advance whole-school initiatives and activities, to map out course goals and determine which projects they would embrace. Finally, in SE, some health policies were discussed with the principal, teachers, and students before being finalized in a school action team meeting and disseminated at whole-school level.
Activities consisting in the creation of school action teams (or school action groups) including students and teachers were identified in three programs (see Table 5 ). In AB2, a school action group with both students and staff was formed to define action plans and training for staff on restorative practices at whole-school level and to implement a new school curriculum focusing on social and emotional skills. In LT, a school action group comprising around six students and six staff was formed to lay down school policies and coordinate interventions, based on the feedback from the student data collection. In SE, a school health promotion committee, consisting of representatives from the school board, parents, teachers, and students, was formed to discuss issues submitted by the students and to plan the activities for the future years based on the feedback from the activities already carried out. In addition, a peer group of 10 and 15 students from each class discussed health topics and student concerns with adult facilitators, in order to develop an action plan and to help in organizing various activities, such as contests and school assemblies.
High ASP: Organizing School Events
Three types of activities were included in this level of ASP. As reported in Table 5 , five programs solicited the creation of different student artifacts . AB1 included a student-made video on bullying to be presented to all the students. In GP, student artifacts were presented to audiences such as parents, other students, teachers, and members of the community. In SS, student leaders made presentations for peers to share personal examples of using the strengths provided by the program. In RJ, students engaged in collaborative, interactive writing activities based on analytical reflection for the realization of a rubric co-developed by students. SE included the contribution of all the students, teachers, and the principal in the realization of works like write-ups, poems, pictures, or artwork, on specific topics for a monthly wall magazine publication. SE also envisaged contests among students, such as poster-making and essay writing, linked to the monthly topic of the wall magazine.
Activities regarding the organization of student-led activities for peers were found in four programs (see Table 5 ). In CFS, student leaders (four to six in each intervention school) conducted at least three important whole-school activities to promote students’ positive use of technology for raising students’ awareness of their rights and responsibilities online; they also provided cyberbullying prevention trainings for peers. In SS, student leaders (up to six in the school) conducted activities aimed at raising awareness of Sources of Strengths , generating conversations with other students, providing presentations about the strengths proposed by the program, and engaging peers to identify their own trusted adults. RJ included student-led restorative circles with students, workshops for students, and peer-to-peer mentorship on restorative practices. In SE, student leaders (between 10 and 15 in each class) conducted peer group meetings to discuss on relevant health topics.
In two programs, student-led activities for adults were organized (see Table 5 ). In CFS, student-led activities provided information to the teaching staff about the technologies used by students and cyberbullying prevention training given to parents. In RJ, circles and workshops on restorative practices were implemented by the students for the staff.
Moderate ASP: Expressing Personal Views
Three types of activities were included in this level of ASP. As can be seen in Table 5 , two programs provided platforms where students could express their personal views on various topics. In BB, students, families, and school staff were provided with platforms to share information and communication on mental health issues. In SE, platforms were used to raise concerns, make complaints, and give suggestions, either anonymously or by self-identifying, on the intervention topics.
Interactive assemblies for students to discuss on the main intervention topics were organized in three programs (see Table 5 ). AB1 provided a first interactive school assembly to discuss respect and bullying, and later assemblies at class level to further discuss the themes emerged during the whole-school assembly. Similarly, AB3 included a school assembly where students were encouraged to get involved in the development of a whole-school anti-bullying policy, followed by three lessons during which the class teacher facilitated a discussion in each class aimed to raise awareness about bullying and to think about school-based solutions. SE included group discussions for generating awareness about health issues, to be discussed during the school assemblies that took place four times a month.
In six programs, students were given a voice by data collections to be used in the process of school changes (see Table 5 ). AB1 included a bullying report form that students, in addition to staff and parents, filled in to report bullying incidents. AB3 provided feedback from student data collection during the school assembly as a basis for discussing whole-school anti-bullying strategies. In LT, annual reports on students’ needs, drawing from student surveys in relation to bullying, aggression, and school experiences, guided the action teams to define school policies and coordinate interventions. In BB, summaries of student and staff data on current school structures, policies, programs, and practices related to student well-being, collected annually, were used by the team to create an “action plan” for changes across the school, both at the classroom and whole-school level. In GP, the profile emerging from the student surveys on school environment guided school teams in the definition of priority areas and strategies within each school, both by coordinating existing health promotional work and introducing new strategies that met the needs of a specific school. In SE, the school action team planned school activities based on reports and discussions on issues presented by the students.
Low ASP: Trainings
A low level of ASP was identified in three types of activities. As can be seen in Table 5 , four programs included trainings for student peer leaders . CFS provided a 10-h training for peer leaders to lead whole-school activities on the positive use of technology. GD provided a 5-h bystander training for student leaders to recognize situations and behaviors that could lead to violence or abuse and to identify active bystander behaviors to be performed either individually or collectively to reduce the risk or effect of violence. ST provided a 90-min training session and two 15-min booster sessions on bullying, which included icebreaker exercises, hands-on activities, and role plays. SS provided a 4-h interactive training for peer leaders aimed at developing protective resources in themselves and encouraging peers to grow such resources as well.
Eight programs included interactive group activities (see Table 5 ). In AB3, students worked in small groups to identify the types of bullying in the school and to discuss strategies to prevent bullying, with the support of bullying scenarios with discussion questions. In CFS, interactive activities included problem-solving, quizzes, and case studies on the use of technology to prevent cyberbullying. LT included various interactive activities aimed at preventing violence, ranging from informal practice, for example, using “affective” statements to communicate feelings, to formal practices, for example hosting a restorative “circle” where participants were encouraged to express emotions and create emotional bonds after problematic or disruptive behavior. BB provided a range of interactive teaching methods, such as small-group exercises, role plays, and quizzes, for reflecting on mental health issues. GP provided activities as small group work and class discussion, by also implementing interactive teaching strategies, such as using questions to kindle discussions and emphasizing the importance to consider different perspectives on a topic, encourage challenges, and debate ideas. SS included peer-to-peer messages and activities wherein student leaders shared examples of strengths that have helped them to overcome personal challenges and invited their peers to participate in interactive tasks. RJ included many interactive practices, such as restorative circles, interactive writing activities, and peer-to-peer mentorship to broaden the impact of restorative practices. SE included monthly contests for students, such as elocution, debates, and quiz games.
Finally, in BB program, some individual activities , in addition to group tasks, were conducted (see Table 5 ). Such activities consisted of individual writings and self-reflection on specific topics, aimed at building or enhancing sense of self-worth, belonging, control, purpose, future, and humor, which were considered to protect against mental health problems.
Very Low ASP: Students as Recipients
Activities in which student’s role was overall that of the recipients of actions taken from adults were of three types. As can be seen in Table 5 , six programs included lecture-style lessons . AB1 included the speech by a nationally known speaker about respect and bullying and the presentation of the Social Support System to students by their English teachers. AB3 included the presentation of summary feedback from the pre-test questionnaires during a school assembly and three lessons, delivered by the class teachers, on school bullying. CFS included lessons led by class teachers, aimed at improving online social skills, focusing, in particular, on positive communication, resilience, self-management, conflict resolution, and social responsibility. GD included a 50-min persuasive lesson led by adults focused on violence victimization, perpetration, and prosocial behaviors. LT included adult-led lessons on social and emotional skills. SE organized workshops led by teachers or program facilitators on effective study skills, such as time management, learning style, note-taking, reading comprehension, memorization techniques, and concentration techniques.
Three programs included the viewing of videos during the implementation (see Table 5 ). AB1 and AB3 provided a video on school bullying for all the students. BB provided video or DVD materials on mental health issues.
Finally, three programs provided students with informative materials (see Table 5 ). AB1 provided a form with several responses for intervening against bullying, which offered alternatives to the traditional method of apportioning blame and punishing bullies. Similarly, AB3 provided a worksheet on possible responses to bullying. FS provided educational magazines on bullying issues. BB provided many materials, such as individual student workbooks, a review poster, master copies of resources for all activities, and homework worksheets.
The aim of this systematic review was to provide a reasoned synthesis of whole-school interventions in secondary school capable of improving the school environment by assigning an active role to students. The first result that warrants consideration regards the number of publications that met our eligibility criteria to select whole-school interventions based on activities soliciting ASP in secondary schools. Despite the wide interest of researchers on the topic of whole-school interventions in general (see Bonell et al., 2018 ; Charlton et al., 2021 ), our selection and data collection process eventually provided only 22 reports referring to 16 studies that fostered ASP during the intervention. This result calls for further work in the field. Based on the emphasis given by educational and political agendas about the importance of empowering students in their role as active participants in schools, first of all, and in societies, subsequently, research should not overlook the question of how to improve their participatory skills by involving them in school activities and decisions (Markham & Aveyard, 2003 ). More investment in this direction is needed to evaluate the consistency and efficacy of the existing programs, to eventually reach consensus on the intervention protocols that schools can implement to improve their learning environment. Results related to each of our specific aims will be discussed in the following paragraphs.
Characteristics of the Selected Programs
As for the first aim of the review, concerning the description of the identified literature, several reflections arise from our results. Considering the year of publication, we found growing interest by researchers in the field, as most reports were published in the last few years, i.e., from 2018 to 2021. This may be considered positive indication that research has identified student participation in school interventions as a crucial topic on which to invest for future works. As for the focus of the selected literature, most of the included studies concerned the reduction of violent behaviors, referring for the most part to bullying, while the promotion of a more general positive emotional and relational school climate is the less investigated topic. Notwithstanding the overall need to fill in this limitation of research, these results suggest that future studies should address the issue of how it is possible to create better school environments for students starting from their own involvement and decision-making roles. This is consistent with the direction indicated by Bonell et al. ( 2018 ), who upheld the importance of focusing more on overall school systems rather than on specific problems. The implementation of a larger number of programs fostering ASP in order to improve school climate and learning environments would thus be important to understand how to support students in dealing with the variety of non-specific problems that can arise during school life. Indeed, as confirmed by the literature, a positive school climate is related to higher academic achievement (Berkowitz et al., 2017 ; Kutsyuruba et al., 2015 ) and fewer problematic behaviors, violence (Reaves et al., 2018 ), and psychological malaise at school (Aldridge and McChesney, 2018 ). Finally, looking at the country of the selected program implementation, most of the studies were conducted in the USA, some in Australia and the UK, and a few in India and China. To our knowledge, with the exception of the two anti-bullying programs carried out in the UK and included in the current review, no other studies were conducted in European countries. With caution, as in many other countries researchers may have developed programs that could not be included in this review due to the inclusion criteria, we consider this as a gap in the literature that future work should fill, especially considering that school policies and organizations are very different between continents. In this regard, it would be interesting both to replicate existing programs and to develop revisited or new interventions specifically adapted to the context of the country’s school system, a work that would also fulfil the aim to increase the ecological validity of the proposed activities.
Methodological Quality of the Selected Reports
The second aim of the review was to assess the soundness of the research design and methodologies adopted in the selected studies. In this regard, we found that the considered reports were robust overall, as they met most of the considered indicators of methodological quality. In particular, most of the studies, based both on EGC or on other designs, described and contextualized the intervention and provided adequate analyses. Beyond the generally good methodological quality of the included studies, consistently with previous examinations of intervention programs (Charlton et al., 2021 ), we found a weakness concerning the fidelity of implementation, as this indicator was observed in only about half of the considered programs. Given that fidelity is a fundamental aspect for the evaluation of the intervention efficacy (O’Donnell, 2008 ), future studies should consider this important factor, by adding it to the evaluation of the programs for providing adequate monitoring tools that include qualitative and process indicators. Overall, however, the literature on the interventions meeting the criteria for our review, albeit limited, relies on methodologically sound grounds that allow us to draw some conclusions on programs and activities actively involving students and to offer suggestions for researchers and practitioners in the field.
Program Activities and Levels of ASP
As for the third and last aim of the review, i.e., concerning the analysis and description of ASP activities proposed in the various programs, our results offer material for an innovative way to look at the programs and points the way to future research in the field. In particular, some points should be highlighted. First, we were able to show that a variety of ASP activities can be used in interventions, from those requiring students to directly act on school programs and policies to those in which students are merely involved as recipients of contents delivered by school staff. From the careful and independently conducted analysis of all program activities, we were also able to grade such activities on a scale ranging from very high to very low levels of ASP. This may be a useful tool for researchers, as it advances a way to develop and organize interventions fostering different levels of ASP activities, to be selected on the basis of the research focus and aims. The effort to identify different levels of ASP also has the merit of introducing some degree of clarity and order in the great variability of program activities. While the importance of student involvement and participation was generally recognized in the literature (Baeten et al., 2016 ; Schweisfurth, 2015 ), our in-depth description shows that not all forms of participation are equal, and thus offers a tool to differentiate between them. This advances our understanding of the concept of student participation both on a theoretical and methodological level.
Beyond this general picture of ASP activities, our findings show that the interventions based on the highest levels of ASP are those aimed at generally improving the school environment, i.e., the Restorative Justice and SEHER programs. These programs included all but one of the activities defined as Very High ASP or High ASP , while all other programs usually provided only one or two of them. This result can offer interesting insights if taken together with the above-reported considerations on the importance to promote overall school improvement, and not to restrict the focus on one or few specific problems. On the basis of this result, we tentatively advance that when the study scope is broad and the theoretical approach is systemic, interventions are more directly centered on lending a voice to students and assigning to them a decision-making role. This again supports the importance of promoting whole-school interventions targeted toward the general learning environment.
Limitations and Conclusion
We are aware that the findings of the present literature review should be considered in the light of certain limitations. First of all, our choice to include only studies published in peer-reviewed journals in English requires some caution. While this selection criteria allowed us to provide a picture of the international literature, this might entail the loss of programs published in other languages that nonetheless contribute to the issue and deserve to be explored in future reviews. Secondly, in the present work, we did not address the issue of cross-cultural similarities and differences in schooling and education, which may influence the way ASP is conceived and valorized in the school context. However, the levels of ASP activities we proposed have the strength of resulting from the analysis of programs from several countries and may thus offer a basis for future discussions on the cross-cultural validity of practices fostering ASP. Furthermore, the present review has focused only on secondary school programs. While this choice was needed for guaranteeing clear references and boundaries to our findings, it also leaves to be explored whether our proposed classification of ASP activities could also be applied to younger students. Given the developmental and organizational differences between primary and secondary levels of education, this issue certainly merits further exploration in future reviews.
As the aim of our review was to provide an in-depth and reasoned description of existing studies based on ASP and of the activities adopted to promote the active role of students, testing the efficacy of these studies was beyond the scope of the present work. While future research may advance this line of inquiry, based on the evidence that different outcomes are considered in such a small number of studies, it seems premature to move toward extensive efficacy testing such as meta-analyses. Rather, at present, it is probably more feasible and desirable to have an increasing amount of literature focusing on ASP in whole-school interventions, to collect further evidence of robust programs and activities, especially with regard to high ASP. As a possible further research question in this direction, we suggest it would also be useful to assess whether the ways of actively involving students may change depending on the intervention target outcomes or on the number of students taking part in the activities. Lastly, while this is true for any review of the literature, it should nonetheless be acknowledged that our syntheses and reflections are dependent upon the choices made in the article selection process. For example, our inclusion and exclusion criteria (i.e., focusing on general participants and targets of intervention) may have restricted our sample. With this in mind, we followed closely the PRISMA guidelines and detailed each step of the process, so that readers can be well informed and future research may build as seamlessly as possible from our work.
Despite the mentioned limitations, this review provides a literature advance in its in-depth examination of existing whole-school interventions that include active student participation in secondary school. Their description and reasoned synthesis make available to researchers and practitioners an overview of specific programs and activities that are being used to actively involve students in processes of change. This in turn can inform reflections and experimentations as to how to integrate and improve the existing provision. In this direction, the major effort and contribution of the present review is the proposal of an organizing structure based on different levels of ASP for analyzing interventions, which allows to classify the specific activities included in each program. Such an effort provides a common ground for reflections and future studies on active student participation, as a shared classification can be instrumental for planning new interventions or evaluating the actual degree of students’ active involvement in the implemented programs. Overall, this work significantly contributes to the far-reaching goal of encouraging student participation in school life, and more specifically in the transformation of their learning environment, so that they can be empowered in shaping it to be increasingly responsive to their insights, ideas, and needs.
Aldridge, J. M., & McChesney, K. (2018). The relationships between school climate and adolescent mental health and wellbeing: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Educational Research, 88 , 121–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2018.01.012
Article Google Scholar
Allen, K. P. (2010). A bullying intervention system in high school: A two-year school-wide follow-up. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 36 (3), 83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stueduc.2011.01.002
Anderson, C. S. (1982). The search for school climate: A review of the research. Review of Educational Research, 52 (3), 368–420. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543052003368
Antoniou, P., & Kyriakides, L. (2013). A dynamic integrated approach to teacher professional development: Impact and sustainability of the effects on improving teacher behavior and student outcomes. Teaching and Teacher Education, 29 (1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2012.08.001
Baeten, M., Dochy, F., Struyven, K., Parmentier, E., & Vanderbruggen, A. (2016). Student-centred learning environments: An investigation into student teachers’ instructional preferences and approaches to learning. Learning Environments Research, 19 (1), 43–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10984-015-9190-5
Berkowitz, R., Moore, H., Astor, R. A., & Benbenishty, R. (2017). A research synthesis of the associations between socioeconomic background, inequality, school climate, and academic achievement. Review of Educational Research, 87 (2), 425–469. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654316669821
Bond, L., Patton, G., Glover, S., Carlin, J. B., Butler, H., Thomas, L., & Bowes, G. (2004). The Gatehouse Project: Can a multilevel school intervention affect emotional wellbeing and health risk behaviours? Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health, 58 (12), 997–1003. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.2003.009449
Bonell, C., Allen, E., Warren, E., McGowan, J., Bevilacqua, L., Jamal, F., ... & Viner, R. M. (2018). Effects of the Learning Together intervention on bullying and aggression in English secondary schools (INCLUSIVE): A cluster randomised controlled trial. The Lancet , 392 (10163), 2452–2464. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31782-3
Brand, S., Felner, R. D., Seitsinger, A., Burns, A., & Bolton, N. (2008). A large scale study of the assessment of the social environment of middle and secondary schools: The validity and utility of teachers’ ratings of school climate, cultural pluralism, and safety problems for understanding school effects and school improvement. Journal of School Psychology, 46 (5), 507–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2007.12.001
Carpenter, J. P., & Pease, J. S. (2013). Preparing students to take responsibilities for learning: The role of non-curricular learning strategies. Journal of Curriculum and Instruction, 7 (2), 38–55. https://doi.org/10.3776/joci.2013.v7n2p38-55
Charlton, C. T., Moulton, S., Sabey, C. V., & West, R. (2021). A systematic review of the effects of schoolwide intervention programs on student and teacher perceptions of school climate. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 23 (3), 185–200. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098300720940168
Cohen, J., Mccabe, E. M., Michelli, N. M., & Pickeral, T. (2009). School climate: Research, policy, practice, and teacher education. Teachers College Record, 111 (1), 180–213. https://doi.org/10.1177/016146810911100108
Coker, A. L., Bush, H. M., Brancato, C. J., Clear, E. R., & Recktenwald, E. A. (2019). Bystander program effectiveness to reduce violence acceptance: RCT in high schools. Journal of Family Violence, 34 (3), 153–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10896-018-9961-8
Council for Exceptional Children (CEC): Standards for evidence-based practices in special education. (2014). Exceptional Children, 80 (4), 504–511. https://doi.org/10.1177/0014402914531388
Cross, D., Shaw, T., Hadwen, K., Cardoso, P., Slee, P., Roberts, C., Thomas, L., & Barnes, A. (2016). Longitudinal impact of the cyber friendly schools program on adolescents’ cyberbullying behavior. Aggressive Behavior, 42 (2), 166–180. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.21609
Cross, D., Shaw, T., Epstein, M., Pearce, N., Barnes, A., Burns, S., Waters, S., Lester, L., & Runions, K. (2018). Impact of the friendly schools whole-school intervention on transition to secondary school and adolescent bullying behaviour. European Journal of Education, 53 (4), 495–513. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejed.12307
De Róiste, A., Kelly, C., Molcho, M., Gavin, A., & Gabhainn, S. N. (2012). Is school participation good for children? Associations with health and wellbeing. Health Education, 112 (2), 88–104. https://doi.org/10.1108/09654281211203394
Doumas, D. M., Midgett, A., & Watts, A. D. (2019a). The impact of a brief, bullying bystander intervention on internalizing symptoms: Is gender a moderator of intervention effects? School Psychology International, 40 (3), 275–293. https://doi.org/10.1177/0143034319830149
Doumas, D. M., Midgett, A., & Watts, A. D. (2019b). A pilot evaluation of the social validity of a bullying bystander program adapted for high school students. Psychology in the Schools, 56 (7), 1101–1116. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.22249
Epstein, J. L., & McPartland, J. M. (1976). The concept and measurement of the quality of school life. American Educational Research Journal, 13 (1), 15–30. https://doi.org/10.1037/e435912004-001
Estrapala, S., Rila, A., & Bruhn, A. L. (2021). A systematic review of Tier I PBIS implementation in high schools. Journal of Positive Psychology, 23 (4), 288–302. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098300720929684
Fletcher, A., Fitzgerald-Yau, N., Wiggins, M., Viner, R. M., & Bonell, C. (2015). Involving young people in changing their school environment to make it safer: Findings from a process evaluation in English secondary schools. Health Education, 115 (3–4), 322–338. https://doi.org/10.1108/HE-04-2014-0063
Gage, N., Whitford, D. K., & Katsiyannis, A. (2018). A review of schoolwide positive behavior interventions and supports as a framework for reducing disciplinary exclusions. The Journal of Special Education, 52 , 142–151. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022466918767847
González, T., Sattler, H., & Buth, A. J. (2019). New directions in whole-school restorative justice implementation. Conflict Resolution Quarterly, 36 (3), 207–220. https://doi.org/10.1002/crq.21236
Grazia, V., Mameli, C., & Molinari, L. (2021). Adolescents’ profiles based on student agency and teacher autonomy support: Does interpersonal justice matter? European Journal of Psychology of Education, 36 (4), 1117–1134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-020-00504-2
Griffin, L. K., Adams, N., & Little, T. D. (2017). Self determination theory, identity development, and adolescence. Development of self-determination through the life-course , 189–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-1042-6_14
Helker, K., & Wosnitza, M. (2016). The interplay of students’ and parents’ responsibility judgements in the school context and their associations with student motivation and achievement. International Journal of Educational Research, 76 , 34–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2016.01.001
Horner, R. H., Todd, A. W., Lewis-Palmer, T., Irvin, L., Sugai, G., & Boland, J. B. (2004). The school-wide evaluation tool (SET): A research instrument for assessing school-wide positive behavior support. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 6 , 3–12. https://doi.org/10.1177/10983007040060010201
Hoy, W. K. (2012). School characteristics that make a difference for the achievement of all students: A 40-year odyssey. Journal of Educational Administration, 50 (1), 76–97. https://doi.org/10.1108/09578231211196078
Jang, H., Kim, E. J., & Reeve, J. (2012). Longitudinal test of self-determination theory’s motivation mediation model in a naturally occurring classroom context. Journal of Educational Psychology, 104 , 1175–1188. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0028089
Johnston, A. D., Midgett, A., Doumas, D. M., & Moody, S. (2018). A mixed methods evaluation of the “aged-up” STAC bullying bystander intervention for high school students. The Professional Counselor, 8 (1), 73–87. https://doi.org/10.15241/adj.8.1.73
Kutsyuruba, B., Klinger, D. A., & Hussain, A. (2015). Relationships among school climate, school safety, and student achievement and well-being: A review of the literature. Review of Education, 3 , 103–135. https://doi.org/10.1002/rev3.3043
Låftman, S. B., Östberg, V., & Modin, B. (2017). School climate and exposure to bullying: A multilevel study. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 28 (1), 153–164. https://doi.org/10.1080/09243453.2016.1253591
Lipponen, L., & Kumpulainen, K. (2011). Acting as accountable authors: Creating interactional space for agency work in teacher education. Teaching and Teachers Education, 27 (5), 821–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2011.01.001
Makitalo, A. (2016). On the notion of agency in studies of interaction and learning. Learning, Culture, and Social Interaction, 10 , 64–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lcsi.2016.07.003
Mameli, C., Molinari, L., & Passini, S. (2019). Agency and responsibility in adolescent students: A challenge for the societies of tomorrow. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 89 (1), 41–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12215
Markham, W. A., & Aveyard, P. (2003). A new theory of health promoting schools based on human functioning, school organization and pedagogic practices. Social Sciences & Medicine, 56 , 1209–1220. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0277-9536(02)00120-x
Matos, L., Reeve, J., Herrera, D., & Claux, M. (2018). Students’ agentic engagement predicts longitudinal increases in perceived autonomy-supportive teaching: The squeaky wheel gets the grease. The Journal of Experimental Education, 86 (4), 579–596. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220973.2018.1448746
Melendez-Torres, G. J., Allen, E., Viner, R., & Bonell, C. (2021). Effects of a whole-school health intervention on clustered adolescent health risks: Latent transition analysis of data from the inclusive trial. Prevention Science, 23 , 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-021-01237-4
Merrell, K. W., Gueldner, B. A., Ross, S. W., & Isava, D. M. (2008). How effective are school bullying intervention programs? A meta-analysis of intervention research. School Psychology Quarterly, 23 (1), 26–42. https://doi.org/10.1037/1045-3830.23.1.26
Midgett, A., & Doumas, D. M. (2019). The impact of a brief bullying bystander intervention on depressive symptoms. Journal of Counseling & Development, 97 (3), 270–280. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcad.12267
Mitchell, J. V. (1967). A study of high school learning environments and their impact on students. Report, U.S. Office of Education, Project No. 5–8032. University of Rochester.
Mitra, D. L. (2004). The significance of students: Can increasing “student voice” in schools lead to gains in youth development? Teacher College Record, 106 (4), 651–688. https://doi.org/10.1177/016146810410600402
Noltemeyer, A., Palmer, K., James, A. G., & Wiechman, S. (2019). School-wide positive behavioral interventions and supports (SWPBIS): A synthesis of existing research. International Journal of School & Educational Psychology, 7 , 253–262. https://doi.org/10.1080/21683603.2018.1425169
Nota, L., Soresi, S., Ferrari, L., & Wehmeyer, M. L. (2011). A multivariate analysis of the self-determination of adolescents. Journal of Happiness Studies, 12 , 245–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-010-9191-0
O’Donnell, C. L. (2008). Defining, conceptualizing, and measuring fidelity of implementation and its relationship to outcomes in K–12 curriculum intervention research. Review of Educational Research, 78 (1), 33–84. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654307313793
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., ... & Moher, D. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. International Journal of Surgery , 88 , 105906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.105906
Patton, G. C., Bond, L., Carlin, J. B., Thomas, L., Butler, H., Glover, S., ... & Bowes, G. (2006). Promoting social inclusion in schools: A group-randomized trial of effects on student health risk behavior and well-being. American journal of public health, 96(9) , 1582–1587. https://doi.org/10.2105/ajph.2004.047399
Petrova, M., Wyman, P. A., Schmeelk-Cone, K., & Pisani, A. R. (2015). Positive-themed suicide prevention messages delivered by adolescent peer leaders: Proximal impact on classmates’ coping attitudes and perceptions of adult support. Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior, 45 (6), 651–663. https://doi.org/10.1111/sltb.12156
Pickering, T. A., Wyman, P. A., Schmeelk-Cone, K., Hartley, C., Valente, T. W., Pisani, A. R., Rulison, K. L., Brown, C. H., & LoMurray, M. (2018). Diffusion of a peer-led suicide preventive intervention through school-based student peer and adult networks. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 9 , 598. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00598
Power, F. C., Higgins, A., & Kohlberg, L. (1989). Lawrence Kohlberg’s approach to moral education . Columbia University Press.
Google Scholar
Raufelder, D., Kittler, F., Braun, S. R., Lätsch, A., Wilkinson, R. P., & Hoferichter, F. (2014). The interplay of perceived stress, self-determination and school engagement in adolescence. School Psychology International, 35 (4), 405–420. https://doi.org/10.1177/0143034313498953
Reaves, S., McMahon, S. D., Duffy, S. N., & Ruiz, L. (2018). The test of time: A meta-analytic review of the relation between school climate and problem behavior. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 39 , 100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2018.01.006
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2017). Self-determination theory. Basic psychological needs in motivation, development, and wellness. Guilford Publications.
Sawyer, M. G., Pfeiffer, S., Spence, S. H., Bond, L., Graetz, B., Kay, D., ... & Sheffield, J. (2010). School‐based prevention of depression: A randomised controlled study of the beyondblue schools research initiative. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry , 51 (2), 199–209. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2009.02136.x
Schweisfurth, M. (2015). Learner-centred pedagogy: Towards a post-2015 agenda for teaching and learning. International Journal of Educational Development, 40 , 259–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedudev.2014.10.011
Shinde, S., Weiss, H. A., Varghese, B., Khandeparkar, P., Pereira, B., Sharma, A., Gupta, R., Ross, D. A., Patton, G., & Patel, V. (2018). Promoting school climate and health outcomes with the SEHER multi-component secondary school intervention in Bihar, India: A cluster-randomised controlled trial. The Lancet, 392 (10163), 2465–2477. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31615-5
Singla, D. R., Shinde, S., Patton, G., & Patel, V. (2021). The mediating effect of school climate on adolescent mental health: Findings from a randomized controlled trial of a school-wide intervention. Journal of Adolescent Health, 69 (1), 90–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2020.09.030
Thapa, A., Cohen, J., Guffey, S., & Higgins-D’Alessandro, A. (2013). A review of school climate research. Review of Educational Research, 83 (3), 357–385. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654313483907
Ttofi, M. M., Farrington, D. P., & Baldry, A. C. (2008). Effectiveness of programmes to reduce school bullying . Swedish Council for Crime Prevention, Information, and Publications.
Vancel, S. M., Missall, K. N., & Bruhn, A. L. (2016). Teacher ratings of the social validity of Schoolwide Positive Behavior Interventions and Supports: A comparison of school groups. Preventing School Failure, 60 , 320–328. https://doi.org/10.1080/1045988x.2016.1157784
Vieno, A., Perkins, D. D., Smith, T. M., & Santinello, M. (2005). Democratic school climate and sense of community in school: A multilevel analysis. American Journal of Community Psychology, 36 (3–4), 327–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10464-005-8629-8
Voight, A., & Nation, M. (2016). Practices for improving secondary school climate: A systematic review of research literature. American Journal of Community Psychology, 58 , 174–191. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajcp.12074
Weatherson, K. A., O’Neill, M., Lau, E. Y., Qian, W., Leatherdale, S. T., & Faulkner, G. E. (2018). The protective effects of school connectedness on substance use and physical activity. Journal of Adolescent Health, 63 (6), 724–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2018.07.002
Williford, A., Yoder, J., Fulginiti, A., Ortega, L., LoMurray, S., Duncan, D., & Kennedy, N. (2021). Peer leaders as gatekeepers and agents of change: Understanding how sources of strength reduces suicide risk and promotes wellness. Child & Youth Care Forum, 51 (3), 539–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10566-021-09639-9
Wohlin, C. (2014, May). Guidelines for snowballing in systematic literature studies and a replication in software engineering. In Proceedings of the 18th international conference on evaluation and assessment in software engineering (1–10). https://doi.org/10.1145/2601248.2601268
Wurf, G. (2012). High school anti-bullying interventions: An evaluation of curriculum approaches and the method of shared concern in four Hong Kong international schools. Australian Journal of Guidance and Counselling, 22 (1), 139–149. https://doi.org/10.1017/jgc.2012.2
Wyman, P. A., Brown, C. H., LoMurray, M., Schmeelk-Cone, K., Petrova, M., Yu, Q., ... & Wang, W. (2010). An outcome evaluation of the Sources of Strength suicide prevention program delivered by adolescent peer leaders in high schools. American journal of public health , 100 (9), 1653–1661. https://doi.org/10.2105/ajph.2009.190025
Download references
Open access funding provided by Università degli Studi di Parma within the CRUI-CARE Agreement. The research leading to these results received funding from the Program “FIL-Quota Incentivante” of the University of Parma co-sponsored by Fondazione Cariparma.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Humanities, Social Sciences and Cultural Industries, University of Parma, Borgo Carissimi 10, 43121, Parma, PR, Italy
Sara Berti, Valentina Grazia & Luisa Molinari
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Literature search was conducted by Sara Berti; assessment of methodological quality was supervised by Valentina Grazia; draft of the introduction and overall supervision were performed by Luisa Molinari. All the authors contributed to data analyses, draft of the manuscript, and critical revisions of the work and they eventually approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sara Berti .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Berti, S., Grazia, V. & Molinari, L. Active Student Participation in Whole-School Interventions in Secondary School. A Systematic Literature Review. Educ Psychol Rev 35 , 52 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-023-09773-x
Download citation
Accepted : 19 April 2023
Published : 04 May 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-023-09773-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Active student participation
- Whole-school intervention
- Secondary school
- Student involvement
- Program activities
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Grad Med Educ
- v.8(3); 2016 Jul
The Literature Review: A Foundation for High-Quality Medical Education Research
a These are subscription resources. Researchers should check with their librarian to determine their access rights.
Despite a surge in published scholarship in medical education 1 and rapid growth in journals that publish educational research, manuscript acceptance rates continue to fall. 2 Failure to conduct a thorough, accurate, and up-to-date literature review identifying an important problem and placing the study in context is consistently identified as one of the top reasons for rejection. 3 , 4 The purpose of this editorial is to provide a road map and practical recommendations for planning a literature review. By understanding the goals of a literature review and following a few basic processes, authors can enhance both the quality of their educational research and the likelihood of publication in the Journal of Graduate Medical Education ( JGME ) and in other journals.
The Literature Review Defined
In medical education, no organization has articulated a formal definition of a literature review for a research paper; thus, a literature review can take a number of forms. Depending on the type of article, target journal, and specific topic, these forms will vary in methodology, rigor, and depth. Several organizations have published guidelines for conducting an intensive literature search intended for formal systematic reviews, both broadly (eg, PRISMA) 5 and within medical education, 6 and there are excellent commentaries to guide authors of systematic reviews. 7 , 8
- A literature review forms the basis for high-quality medical education research and helps maximize relevance, originality, generalizability, and impact.
- A literature review provides context, informs methodology, maximizes innovation, avoids duplicative research, and ensures that professional standards are met.
- Literature reviews take time, are iterative, and should continue throughout the research process.
- Researchers should maximize the use of human resources (librarians, colleagues), search tools (databases/search engines), and existing literature (related articles).
- Keeping organized is critical.
Such work is outside the scope of this article, which focuses on literature reviews to inform reports of original medical education research. We define such a literature review as a synthetic review and summary of what is known and unknown regarding the topic of a scholarly body of work, including the current work's place within the existing knowledge . While this type of literature review may not require the intensive search processes mandated by systematic reviews, it merits a thoughtful and rigorous approach.
Purpose and Importance of the Literature Review
An understanding of the current literature is critical for all phases of a research study. Lingard 9 recently invoked the “journal-as-conversation” metaphor as a way of understanding how one's research fits into the larger medical education conversation. As she described it: “Imagine yourself joining a conversation at a social event. After you hang about eavesdropping to get the drift of what's being said (the conversational equivalent of the literature review), you join the conversation with a contribution that signals your shared interest in the topic, your knowledge of what's already been said, and your intention.” 9
The literature review helps any researcher “join the conversation” by providing context, informing methodology, identifying innovation, minimizing duplicative research, and ensuring that professional standards are met. Understanding the current literature also promotes scholarship, as proposed by Boyer, 10 by contributing to 5 of the 6 standards by which scholarly work should be evaluated. 11 Specifically, the review helps the researcher (1) articulate clear goals, (2) show evidence of adequate preparation, (3) select appropriate methods, (4) communicate relevant results, and (5) engage in reflective critique.
Failure to conduct a high-quality literature review is associated with several problems identified in the medical education literature, including studies that are repetitive, not grounded in theory, methodologically weak, and fail to expand knowledge beyond a single setting. 12 Indeed, medical education scholars complain that many studies repeat work already published and contribute little new knowledge—a likely cause of which is failure to conduct a proper literature review. 3 , 4
Likewise, studies that lack theoretical grounding or a conceptual framework make study design and interpretation difficult. 13 When theory is used in medical education studies, it is often invoked at a superficial level. As Norman 14 noted, when theory is used appropriately, it helps articulate variables that might be linked together and why, and it allows the researcher to make hypotheses and define a study's context and scope. Ultimately, a proper literature review is a first critical step toward identifying relevant conceptual frameworks.
Another problem is that many medical education studies are methodologically weak. 12 Good research requires trained investigators who can articulate relevant research questions, operationally define variables of interest, and choose the best method for specific research questions. Conducting a proper literature review helps both novice and experienced researchers select rigorous research methodologies.
Finally, many studies in medical education are “one-offs,” that is, single studies undertaken because the opportunity presented itself locally. Such studies frequently are not oriented toward progressive knowledge building and generalization to other settings. A firm grasp of the literature can encourage a programmatic approach to research.
Approaching the Literature Review
Considering these issues, journals have a responsibility to demand from authors a thoughtful synthesis of their study's position within the field, and it is the authors' responsibility to provide such a synthesis, based on a literature review. The aforementioned purposes of the literature review mandate that the review occurs throughout all phases of a study, from conception and design, to implementation and analysis, to manuscript preparation and submission.
Planning the literature review requires understanding of journal requirements, which vary greatly by journal ( table 1 ). Authors are advised to take note of common problems with reporting results of the literature review. Table 2 lists the most common problems that we have encountered as authors, reviewers, and editors.
Sample of Journals' Author Instructions for Literature Reviews Conducted as Part of Original Research Article a

Common Problem Areas for Reporting Literature Reviews in the Context of Scholarly Articles

Locating and Organizing the Literature
Three resources may facilitate identifying relevant literature: human resources, search tools, and related literature. As the process requires time, it is important to begin searching for literature early in the process (ie, the study design phase). Identifying and understanding relevant studies will increase the likelihood of designing a relevant, adaptable, generalizable, and novel study that is based on educational or learning theory and can maximize impact.
Human Resources
A medical librarian can help translate research interests into an effective search strategy, familiarize researchers with available information resources, provide information on organizing information, and introduce strategies for keeping current with emerging research. Often, librarians are also aware of research across their institutions and may be able to connect researchers with similar interests. Reaching out to colleagues for suggestions may help researchers quickly locate resources that would not otherwise be on their radar.
During this process, researchers will likely identify other researchers writing on aspects of their topic. Researchers should consider searching for the publications of these relevant researchers (see table 3 for search strategies). Additionally, institutional websites may include curriculum vitae of such relevant faculty with access to their entire publication record, including difficult to locate publications, such as book chapters, dissertations, and technical reports.
Strategies for Finding Related Researcher Publications in Databases and Search Engines

Search Tools and Related Literature
Researchers will locate the majority of needed information using databases and search engines. Excellent resources are available to guide researchers in the mechanics of literature searches. 15 , 16
Because medical education research draws on a variety of disciplines, researchers should include search tools with coverage beyond medicine (eg, psychology, nursing, education, and anthropology) and that cover several publication types, such as reports, standards, conference abstracts, and book chapters (see the box for several information resources). Many search tools include options for viewing citations of selected articles. Examining cited references provides additional articles for review and a sense of the influence of the selected article on its field.
Box Information Resources
- Web of Science a
- Education Resource Information Center (ERIC)
- Cumulative Index of Nursing & Allied Health (CINAHL) a
- Google Scholar
Once relevant articles are located, it is useful to mine those articles for additional citations. One strategy is to examine references of key articles, especially review articles, for relevant citations.
Getting Organized
As the aforementioned resources will likely provide a tremendous amount of information, organization is crucial. Researchers should determine which details are most important to their study (eg, participants, setting, methods, and outcomes) and generate a strategy for keeping those details organized and accessible. Increasingly, researchers utilize digital tools, such as Evernote, to capture such information, which enables accessibility across digital workspaces and search capabilities. Use of citation managers can also be helpful as they store citations and, in some cases, can generate bibliographies ( table 4 ).
Citation Managers

Knowing When to Say When
Researchers often ask how to know when they have located enough citations. Unfortunately, there is no magic or ideal number of citations to collect. One strategy for checking coverage of the literature is to inspect references of relevant articles. As researchers review references they will start noticing a repetition of the same articles with few new articles appearing. This can indicate that the researcher has covered the literature base on a particular topic.
Putting It All Together
In preparing to write a research paper, it is important to consider which citations to include and how they will inform the introduction and discussion sections. The “Instructions to Authors” for the targeted journal will often provide guidance on structuring the literature review (or introduction) and the number of total citations permitted for each article category. Reviewing articles of similar type published in the targeted journal can also provide guidance regarding structure and average lengths of the introduction and discussion sections.
When selecting references for the introduction consider those that illustrate core background theoretical and methodological concepts, as well as recent relevant studies. The introduction should be brief and present references not as a laundry list or narrative of available literature, but rather as a synthesized summary to provide context for the current study and to identify the gap in the literature that the study intends to fill. For the discussion, citations should be thoughtfully selected to compare and contrast the present study's findings with the current literature and to indicate how the present study moves the field forward.
To facilitate writing a literature review, journals are increasingly providing helpful features to guide authors. For example, the resources available through JGME include several articles on writing. 17 The journal Perspectives on Medical Education recently launched “The Writer's Craft,” which is intended to help medical educators improve their writing. Additionally, many institutions have writing centers that provide web-based materials on writing a literature review, and some even have writing coaches.
The literature review is a vital part of medical education research and should occur throughout the research process to help researchers design a strong study and effectively communicate study results and importance. To achieve these goals, researchers are advised to plan and execute the literature review carefully. The guidance in this editorial provides considerations and recommendations that may improve the quality of literature reviews.
Systematic review study protocol of literature from 2018 to end of 2022 of stated preference studies about HIV care and prevention services around the world
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of Health Promotion Sciences, The University of Arizona Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health, Tucson, Arizona, USA [email protected].
- 2 Department of Health Promotion Sciences, The University of Arizona Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health, Tucson, Arizona, USA.
- 3 Department of Epidemiology, The University of Arizona Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health, Tucson, Arizona, USA.
- PMID: 38548370
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-072661
Background: There are currently over 38 million individuals around the globe living with the HIV and AIDS. As many HIV prevention and care services emerging for public use services become available to a wider audience, there is a growing need for more information about willingness to engage in these care and services. Stated preference research methods have been shown to be useful methods to help predict factors that influence health behaviours in the future.
Research question: This is a systematic review of findings from stated preference studies regarding the choices of people living with HIV or people at risk of contracting HIV to engage in HIV prevention or care.
Methods: Our team plans to compile stated preference studies studying the choice to engage in HIV prevention or care services. Studies will be included from 1 January 2018 until 28 October 2022. There will be no restrictions on the language or location of the study. We will search databases including PubMed, PsycINFO, Embase, Scopus, Tufts CEA registry and CINAHL. Two researchers will review each article's title, abstract, then full-text and finally extract relevant data based on a predetermined process. Data will be presented in a narrative review and in an exploratory meta-analysis by subgroups of studies.
Ethics and dissemination of research: There is no need for an ethical review process of this study since all data used is available publicly. The findings of this study will be reported in relevant conferences and submitted for publication in a peer-reviewed journal.
Prospero registration number: CRD42023397785.
Keywords: HIV & AIDS; International health services; PUBLIC HEALTH; Protocols & guidelines; Public health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Advertisement
Supported by
Henry Louis Gates Jr. Unpacks Black Literature’s ‘Black Box’
In his latest book, the Harvard scholar shows how African American writers have used the written word to shape their reality despite constraints imposed on them from outside.
- Share full article

By Tope Folarin
Tope Folarin is a writer and critic. He is the executive director of the Institute for Policy Studies and the author of the novel “A Particular Kind of Black Man.”
- Barnes and Noble
- Books-A-Million
When you purchase an independently reviewed book through our site, we earn an affiliate commission.
THE BLACK BOX: Writing the Race , by Henry Louis Gates Jr.
By way of explaining the metaphor that serves as the title of his latest book, “The Black Box,” the Harvard scholar Henry Louis Gates Jr. transcribes a conversation he had with his son-in-law after the birth of his granddaughter 10 years ago:
“Did you check the box?” I asked, apropos of nothing we had just discussed. Without missing a beat, my good son-in-law responded, “Yes, sir. I did.” “Very good,” I responded, as I poured a second shot of Pappy Van Winkle.
The box that Gates’s son-in-law checked on a birth registration form indicates that his granddaughter is Black, even though his daughter’s genetic admixture is 75 percent European, and his son-in-law is 100 percent European. In other words, as Gates notes, his granddaughter “will test about 87.5 percent European when she spits in the test tube.”
Gates offers this anecdote to suggest the arbitrariness of racial categories, and to focus our attention on the image of the box — a container that can function simultaneously as a “circumscribed enclosure” and a zone in which the confined can create a thriving “social and cultural world.”
For Gates, the box is a supple concept. Not only does it appear with surprising frequency in literature by Black Americans — from the fugitive slave author Henry Box Brown (who escaped slavery in a box) to Booker T. Washington (who described the box as a barrel) to the contemporary poet Terrance Hayes — but Gates extends the metaphor to other kinds of boxes that relate to Black experience, to ordeals withstood and survived. He cites an airplane’s flight recorder box, a device that “preserves a record of the truth amid disastrous circumstances,” and the slave ship, before arriving at his thesis: African Americans have consistently relied on the written word to express and shape their reality despite the constraints imposed on them from outside, which they have endured since they were first brought to this continent.
“The Black Box” is based on lectures Gates has delivered for many years in his Introduction to African American Studies class at Harvard. From the beginning, he shows, African Americans have turned to literary forms to validate their humanity. He quickly sketches the childhood of Phillis Wheatley — her journey to America via slave ship, her rapid mastery of English — and the varied responses to her poetry, which she began to publish as a precocious teenager.
Wheatley’s success undermined the prevailing sentiment that Black Americans were less intelligent than their white counterparts, and in response to her art some thinkers, such as Voltaire, revised their formerly negative perspectives on Black people, while others, including Thomas Jefferson, remained steadfast in their views. (Jefferson on Wheatley: “The compositions published under her name are below the dignity of criticism.”)
Gates traces the history of slave narratives, a genre that “always told the story” of how enslaved authors “learned to read and write, and always, always, of course, of their escape to freedom.” And he describes the intense conversations within the Black American community around self-definition: “They stood on uncertain ground. Were they Africans, Americans, both, or neither?” In each of these instances, as throughout his book, Gates adroitly demonstrates how literature served as a site of self-interrogation and a pathway to liberation.
In other chapters, Gates writes about the manifold contributions of W.E.B. Du Bois; the boldness and flair of the Harlem Renaissance generation; the fierce debate between Zora Neale Hurston and Richard Wright over the proper way to represent the Black experience in literature; and the politics of passing.
Many of these ideas will be familiar to readers — Gates has written about them before. The allure of this book, and the reason for its existence, are the narrative links he draws among these people and events, and his insistence that a survey of African American history is incomplete without a special consideration of how writing has undergirded and powered it. This is a literary history of Black America, but it is also an argument that African American history is inextricable from the history of African American literature.
“The Black Box” arrives at an auspicious moment. This year marks the 100th anniversary of the birth of a great man of American and African American letters: James Baldwin. Next year marks the 100th anniversary of the publication of “The New Negro,” an anthology of fiction, poetry, art and essays edited by Alain Locke that is widely regarded as a defining text of the Harlem Renaissance.
This is also a moment when many politicians are hard at work revising our shared history in order to justify present-day policy agendas. Gates addresses this phenomenon in his concluding chapter, portions of which appeared in The New York Times a year ago. He invokes the story of Mildred Lewis Rutherford, the historian general of the United Daughters of the Confederacy, who argued throughout her career that the Civil War was simply “the War Between the States,” and had nothing to do with slavery.
As Gates notes, it is important to repeat the truth about history as often as possible, and to repel efforts to redefine it, because “what is inscribed on the blackboard translates directly to social practices unfolding on the street.”
THE BLACK BOX : Writing the Race | By Henry Louis Gates Jr. | Penguin Press | 262 pp. | $30
Explore More in Books
Want to know about the best books to read and the latest news start here..
James McBride’s novel sold a million copies, and he isn’t sure how he feels about that, as he considers the critical and commercial success of “The Heaven & Earth Grocery Store.”
How did gender become a scary word? Judith Butler, the theorist who got us talking about the subject , has answers.
You never know what’s going to go wrong in these graphic novels, where Circus tigers, giant spiders, shifting borders and motherhood all threaten to end life as we know it .
When the author Tommy Orange received an impassioned email from a teacher in the Bronx, he dropped everything to visit the students who inspired it.
Do you want to be a better reader? Here’s some helpful advice to show you how to get the most out of your literary endeavor .
Each week, top authors and critics join the Book Review’s podcast to talk about the latest news in the literary world. Listen here .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
In addition, they state that a quality literature review needs to be replicable, that is, the method must be described such that an external reader could replicate the study and reach similar findings. Lastly, they state that a literature review must be useful for scholars and practitioners. However, evaluating different types of literature ...
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
Example: Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398 ; Systematic review: "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139).
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources.
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it ...
Okay - with the why out the way, let's move on to the how. As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter.
In this study guide, I will begin by clearing up some misconceptions about what a literature review is and what it is not. Then, I will break the process down into a series of simple steps, looking at examples along the way. In the end, I hope you will have a simple, practical strategy to write an effective literature review.
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
Literature reviews can take two major forms. The most prevalent one is the "literature review" or "background" section within a journal paper or a chapter in a graduate thesis. This section synthesizes the extant literature and usually identifies the gaps in knowledge that the empirical study addresses (Sylvester, Tate, & Johnstone, 2013).
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
A literature review is defined as "a critical analysis of a segment of a published body of knowledge through summary, classification, and comparison of prior research studies, reviews of literature, and theoretical articles." (The Writing Center University of Winconsin-Madison 2022) A literature review is an integrated analysis, not just a summary of scholarly work on a specific topic.
A literature review is probably the most common academic writing activity that is performed by scholars and graduate students. Imel [] identified a literature review as being either part of a larger study or as a research effort on its own.As a part of a larger study, Imel [] identified the literature is "the foundation for the study."It has been suggested that the literature review for a ...
A literature review is a discussion of the literature (aka. the "research" or "scholarship") surrounding a certain topic. ... friendly approach to offer complete novices a simple review of a process which is often central to producing a research study. Writing the Literature Review by Sara Efrat Efron; Ruth Ravid. ISBN: 9781462536900.
A literature review is an overview of the previously published works on a topic. The term can refer to a full scholarly paper or a section of a scholarly work such as a book, or an article. Either way, a literature review is supposed to provide the researcher /author and the audiences with a general image of the existing knowledge on the topic ...
A literature review should connect to the study question, guide the study methodology, and be central in the discussion by indicating how the analyzed data advances what is known in the field. A theoretical framework drives the question, guides the types of methods for data collection and analysis, informs the discussion of the findings, and ...
Literature review is an essential feature of academic research. Fundamentally, knowledge advancement must be built on prior existing work. To push the knowledge frontier, we must know where the frontier is. By reviewing relevant literature, we understand the breadth and depth of the existing body of work and identify gaps to explore.
A literature review consists of scholarly sources that validate the content. Its primary objective is to offer a concise summary of the research and to let you explore relevant theories and methodologies. Through this review, you can identify gaps in the existing research and bridge them with your contribution. ... The study begins with an ...
Steps for Conducting a Lit Review; Finding "The Literature" Organizing/Writing; APA Style This link opens in a new window; Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window; MLA Style This link opens in a new window; Sample Literature Reviews. Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts; Have an exemplary literature review? Get Help!
The study method entails two main factors, purpose and the research synthesis process of the study. This study aims to explore the understanding and awareness of the teachers and students about STEM education; the challenges faced by them and their solutions in the light of literature review and research amalgamation and the abilities and skills to overcome these challenges.
Nature-based climate solutions are widely incorporated into climate change mitigation plans and need firm scientific foundations. Through literature review and expert elicitation, this analysis ...
Relatively little is known about the lived experiences of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic. We systematically review the international literature to understand the lived experiences of older adult's experiences during the pandemic. This study uses a meta-ethnographical approach to investigate the included studies. The analyses were undertaken with constructivist grounded theory.
The present review was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses 2020 updated statement (PRISMA 2020; Page et al., 2021).In line with the terminology proposed by the authors, in the following sections, we use the term study for every investigation that includes a well-defined group of participants and one or more interventions and outcomes ...
Purpose and Importance of the Literature Review. An understanding of the current literature is critical for all phases of a research study. Lingard 9 recently invoked the "journal-as-conversation" metaphor as a way of understanding how one's research fits into the larger medical education conversation. As she described it: "Imagine yourself joining a conversation at a social event.
By Sadie Stein. Sadie Stein is an editor at the Book Review. March 29, 2024. We have a complicated relationship with bunnies. On the one hand, we keep them as preschool companions, expect them to ...
Systematic review study protocol of literature from 2018 to end of 2022 of stated preference studies about HIV care and prevention services around the world ... There is no need for an ethical review process of this study since all data used is available publicly. The findings of this study will be reported in relevant conferences and submitted ...
By way of explaining the metaphor that serves as the title of his latest book, "The Black Box," the Harvard scholar Henry Louis Gates Jr. transcribes a conversation he had with his son-in-law ...