Subtraction Worksheets
Welcome to the Subtraction Worksheets page at Math-Drills.com where you will get less of an experience than our other pages! This page includes Subtraction worksheets on topics such as five minute frenzies, one-, two-, three- and multi-digit subtraction and subtracting across zeros.
Subtraction has been around for several years now... well maybe more than a few, so it's probably a good thing for students to learn. People experience subtraction every minute of their lives from banks and the government taking away your money to the cookies in the jar mysteriously disappearing. With a good knowledge of subtraction, you can understand why your bank account reaches zero and do something to prevent it from happening.
Some students do have difficulty with subtraction, so take it easy on them. Help them to learn their addition facts first. Once they know those, they will need a few more strategies to successfully subtract. Teaching with manipulatives like base ten blocks or cereal or insects in the park can help students gain a deeper understanding of subtraction. The subtracting worksheets on this page are meant to support good teaching practices, so only use them for independent learning if students are practising skills they already know.
We use the words, minuend, subtrahend and difference on this page. Please refer to the following, so you know which word means which part of a subtraction question.
Minuend - Subtrahend = Difference

Most Popular Subtraction Worksheets this Week

Subtraction Facts Tables
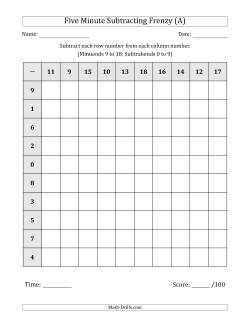
Five minute subtraction frenzies are timed practice charts that help students develop subtraction fact recall speed. These charts are similar to the addition and multiplication frenzy charts, but due to the nature of how subtraction works, we could not focus solely on the single digit fact families. For example, you might get questions like 18 - 4 = 14. You also have to be aware that you must subtract the row number from the column number to get a positive number (or zero). Other than that, they should be a nice way to practice some mental subtraction. As with most of these pages, please only use them as a timed activity with students who will experience success. If a student does not have the necessary skills to complete a frenzy in under five minutes, you may need to take a different approach to how you deliver this page. For all others, students should be able to complete this page in under five minutes with a 98% or greater accuracy and improve their time as they get more practice.
- Five Minute Subtraction Frenzies Five Minute Subtraction Frenzy (Minuends 9 to 18; Subtrahends 0 to 9) Five Minute Subtraction Frenzy (Minuends 29 to 38; Subtrahends 10 to 19) Five Minute Subtraction Frenzy (Minuends 41 to 50; Subtrahends 16 to 25)
Most of the subtraction tables in this section are meant to be used as a reference for students learning their subtraction facts. After a while, most students will remember the facts and recall them easily when completing math problems.
- Subtraction Facts Tables 0 to 11 Subtraction Facts 0 to 11 in Grey Subtraction Facts 0 to 11 in Color Subtraction Facts 0 to 11 with Facts Highlighted Subtraction Facts 0 to 11 in Montessori Colors Subtraction Facts 0 to 11 in Montessori Colors with Facts Highlighted
- Subtraction Facts Tables 1 to 12 Subtraction Facts Tables in Gray 1 to 12 Subtraction Facts Tables in Color 1 to 12 Subtraction Facts Tables in Montessori Colors 1 to 12 Subtraction Facts 1 to 12 with Facts Highlighted Subtraction Facts 1 to 12 in Montessori Colors with Facts Highlighted
- Compact Subtraction Facts Tables Compact Subtraction Table (Filled) Compact Subtraction Table (Blank)
Single-Digit Subtraction Facts
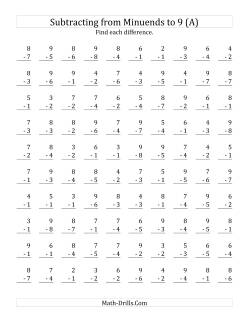
Subtracting single-digit facts is a skill that students generally learn after or while they are learning single-digit addition facts. The subtraction worksheets in this section are meant to be used for practice, testing or with teacher guidance. They will not teach students how to subtract or what the connection is between addition and subtraction; for that, students require a teacher or parent.
Some students might find it easier to start with subtraction facts with minuends (the first number) limited to 9 or lower. This way, they don't need to count across 10 eliminating that extra pesky digit... for now.
- Subtracting Single-Digit from Single-Digit Numbers 100 Subtraction Questions with Minuends up to 9 64 Subtraction Questions with Minuends up to 9 25 Subtraction Questions with Minuends up to 9
In relation to addition facts, the following worksheets cover the facts from 0 to 9, and the worksheets after that cover the addition facts from 1 to 9. The minuends are the amounts to be subtracted from, so a minuend of 18 means that both the subtrahend (the amount being subtracted) and the difference will be 9. The worksheets marked with an asterisk (*) include all possible questions in a random order on each version of the worksheet.
- Subtraction Facts from (0 − 0) to (18 − 9) Subtraction Facts from (0 − 0) to (18 − 9) (100* Questions) ✎ Subtraction Facts from (0 − 0) to (18 − 9) (81 Questions) ✎ Subtraction Facts from (0 − 0) to (18 − 9) (64 Questions) ✎ Subtraction Facts from (0 − 0) to (18 − 9) (50 Questions) ✎ Subtraction Facts from (0 − 0) to (18 − 9) (25 Large Print Questions) ✎ Subtraction Facts from (0 − 0) to (18 − 9) (12 Very Large Print Questions) ✎
- Subtraction Facts from (2 − 1) to (18 − 9) (No Zeros) Subtraction Facts from (2 − 1) to (18 − 9) (100 Questions) ✎ Subtraction Facts from (2 − 1) to (18 − 9) (81* Questions) ✎ Subtraction Facts from (2 − 1) to (18 − 9) (64 Questions) ✎ Subtraction Facts from (2 − 1) to (18 − 9) (50 Questions) ✎ Subtraction Facts from (2 − 1) to (18 − 9) (25 Large Print Questions) ✎ Subtraction Facts from (2 − 1) to (18 − 9) (12 Very Large Print Questions) ✎
- Subtraction Facts with Minuends from 10 to 18 100 Subtraction Questions with Minuends from 10 to 18 and All Regrouping (100 Questions) 64 Subtraction Questions with Minuends from 10 to 18 and All Regrouping (64 Questions) 25 Subtraction Questions with Minuends from 10 to 18 and All Regrouping (25 Large Print Questions)
Sometimes students just need to reinforce a single number at a time which is where these worksheets come in. There are three sets of worksheets in this section, each with a different number of questions. The last set is the most interesting as there are no questions repeated. Eleven and Twelve have been included as they are essentially subtracting by 10 and 1 or 2 more.
- Subtracting Individual Focus or Target Facts (50 Questions per Page) Subtracting 0 (50 Questions) ✎ Subtracting 1 (50 Questions) ✎ Subtracting 2 (50 Questions) ✎ Subtracting 3 (50 Questions) ✎ Subtracting 4 (50 Questions) ✎ Subtracting 5 (50 Questions) ✎ Subtracting 6 (50 Questions) ✎ Subtracting 7 (50 Questions) ✎ Subtracting 8 (50 Questions) ✎ Subtracting 9 (50 Questions) ✎ Subtracting 10 (50 Questions) ✎ Subtracting 11 (50 Questions) ✎ Subtracting 12 (50 Questions) ✎
- Subtracting Individual Focus or Target Facts (25 Questions per Page) Subtracting Zero (0) (25 Large Print Questions) ✎ Subtracting One (1) (25 Large Print Questions) ✎ Subtracting Two (2) (25 Large Print Questions) ✎ Subtracting Three (3) (25 Large Print Questions) ✎ Subtracting Four (4) (25 Large Print Questions) ✎ Subtracting Five (5) (25 Large Print Questions) ✎ Subtracting Six (6) (25 Large Print Questions) ✎ Subtracting Seven (7) (25 Large Print Questions) ✎ Subtracting Eight (8) (25 Large Print Questions) ✎ Subtracting Nine (9) (25 Large Print Questions) ✎
- Subtracting Individual Focus or Target Facts with Differences of 0 to 99 (100 Unique Questions per Page) Subtracting One (1) with Differences 0 to 99 (100 Unique Questions) ✎ Subtracting Two (2) with Differences 0 to 99 (100 Unique Questions) ✎ Subtracting Three (3) with Differences 0 to 99 (100 Unique Questions) ✎ Subtracting Four (4) with Differences 0 to 99 (100 Unique Questions) ✎ Subtracting Five (5) with Differences 0 to 99 (100 Unique Questions) ✎ Subtracting Six (6) with Differences 0 to 99 (100 Unique Questions) ✎ Subtracting Seven (7) with Differences 0 to 99 (100 Unique Questions) ✎ Subtracting Eight (8) with Differences 0 to 99 (100 Unique Questions) ✎ Subtracting Nine (9) with Differences 0 to 99 (100 Unique Questions) ✎ Subtracting Ten (10) with Differences 0 to 99 (100 Unique Questions) ✎ Subtracting Eleven (11) with Differences 0 to 99 (100 Unique Questions) ✎ Subtracting Twelve (12) with Differences 0 to 99 (100 Unique Questions) ✎
- Horizontally Arranged Subtraction Facts with Minuends to 18 Horizontal Subtraction Facts with Minuends to 18 (100 Questions) ✎ Horizontal Subtraction Facts with Minuends to 18 (50 Questions) ✎ Horizontal Subtraction Facts with Minuends to 18 (25 Questions; Large Print) ✎
- Horizontally Arranged Subtracting 1 to 5 from 1 to 10 Horizontal Subtracting 1 to 5 from 1 to 10 (100 Questions) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting 1 to 5 from 1 to 10 (50 Questions) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting 1 to 5 from 1 to 10 (25 Questions; Large Print) ✎
- Horizontally Arranged Subtracting 1s and 2s from Single-Digit Minuends Horizontal Subtracting Ones from Single-Digit Minuends (25 per page) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting Twos from Single-Digit Minuends (25 per page) ✎
- Horizontally Arranged Subtracting Individual Focus Facts Horizontal Subtracting 0s (100 per page) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting 1s (100 per page) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting 2s (100 per page) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting 3s (100 per page) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting 4s (100 per page) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting 5s (100 per page) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting 6s (100 per page) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting 7s (100 per page) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting 8s (100 per page) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting 9s (100 per page) ✎
- Horizontally Arranged Subtracting Pairs of Individual Focus Facts Horizontal Subtracting 0s and 1s (100 per page) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting 2s and 3s (100 per page) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting 4s and 5s (100 per page) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting 6s and 7s (100 per page) ✎ Horizontal Subtracting 8s and 9s (100 per page) ✎
- Subtracting a Number from Itself Subtracting a Number from Itself (Range 1 to 20)
The make ten subtraction strategy involves "spliting" the subtrahend (amount being subtracted) into two parts. The first part should be the exact amount that will reduce the minuend (the first number) to ten (or multiple of ten as the case may be) and the second part is the leftover amount. The strategy helps students internalize a mental strategy for subtracting across tens. For example, with the question 15 - 9, students first recognize that they need to subtract 5 to get 10, so they split the 9 into 5 and 4. Subtracting 5 from 15 results in 10 and subtracting 4 more results in 6, so 15 - 9 = 6. This strategy can be used any time students need to subtract "over" a multiple of ten and there are many worksheets in this section to practice it. For example, subtracting 84 - 8, students recognize that they must subtract 4 from 84 to get 80 which leaves 4 more to subtract from 80 to get 76.
- Make Ten Strategy Worksheets with 10 and Multiples of 10 Make 10 Subtraction Strategy Make 20 Subtraction Strategy Make 30 Subtraction Strategy Make 40 Subtraction Strategy Make 50 Subtraction Strategy Make 60 Subtraction Strategy Make 70 Subtraction Strategy Make 80 Subtraction Strategy Make 90 Subtraction Strategy Make Multiples of 10 Subtraction Strategy
Long Subtraction Worksheets

Try teaching a mental math strategy for subtraction called counting up. Here is how it is done:
Start with the second number (the subtrahend) and count up by tens until you find the closest value to the first number (the minuend). Keep track of how many tens you counted. Add or subtract a single digit number to get the minuend exactly then adjust the tens by that amount. For the question, 84 - 35, start at 35, and count, 45, 55, 65, 75, 85 (five tens) and one down to get 84. Five tens minus one is 49. For the question 65 - 22, start at 22 and count, 32, 42, 52, 62 (four tens) and three up to get 65. Four tens and three is 43. The previous examples used two-digit numbers, but the strategy can swiftly be modified for larger numbers. How far can your students go with it? Here is an example with three-digit numbers:
Let's use the question 927 - 648. First, count up by hundreds to 948 (that's 300). Then count down by tens to 928 (that's -20). Finally count down by ones to 927 (that's one). 300 - 20 - 1 = 279. That's almost easier than adding!
The multi-digit or long subtraction worksheets in the first part of this section are classic long subtraction worksheets with randomly generated numbers. Regrouping should be necessary about half of the time. Versions with ALL regrouping and NO regrouping follow. If you would like to see numbers with thousands separators, look a little further down and choose the appropriate version for your location.
- Subtracting up to 3-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping Subtracting 2-Digit from 2-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 2-Digit from 3-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 3-Digit from 3-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ✎ 3-Digit Expanded Form Subtraction Subtracting 3-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ✎
- Subtracting up to 3-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping (Large Print) Subtracting 1-Digit from 2-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 2-Digit from 2-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 1-Digit from 3-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 2-Digit from 3-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 3-Digit from 3-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 1- to 3-Digit from 1- to 3-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 3-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎
- Subtracting 4- to 9-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping Subtracting 4-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 4-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 5-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 5-Digit from 6-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 6-Digit from 6-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 6-Digit from 7-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 7-Digit from 7-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 7-Digit from 8-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 8-Digit from 8-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 8-Digit from 9-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 9-Digit from 9-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ✎
- Subtracting 4- to 6-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping (Large Print) Subtracting 4-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 4-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 5-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 5-Digit from 6-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 6-Digit from 6-Digit Numbers with Some Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎
For students who need a little extra help with lining things up, these long subtraction worksheets have the digits spaced farther apart on a grid. The answer keys also show the carrying values to help diagnose where things went wrong (but hopefully they won't).
- Long Subtraction Worksheets with Grid Support 2-Digit Minus 2-Digit Subtraction With Grid Support 3-Digit Minus 2-Digit Subtraction With Grid Support 3-Digit Minus 3-Digit Subtraction With Grid Support 4-Digit Minus 3-Digit Subtraction With Grid Support 4-Digit Minus 4-Digit Subtraction With Grid Support 5-Digit Minus 4-Digit Subtraction With Grid Support 5-Digit Minus 5-Digit Subtraction With Grid Support 6-Digit Minus 5-Digit Subtraction With Grid Support 6-Digit Minus 6-Digit Subtraction With Grid Support 2- to 4-Digit Minus 2- to 4-Digit Subtraction With Grid Support 3- to 6-Digit Minus 3- to 6-Digit Subtraction With Grid Support
The next long subtraction worksheets include questions that require regrouping at every step. They can be frustrating and difficult for students who are not familiar with the concept of subtraction. Try showing them with base ten blocks how regrouping works.
- Subtracting up to 3-Digit Numbers with All Regrouping Subtracting 1-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 2-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 3-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping ✎
- Subtracting up to 3-Digit Numbers with All Regrouping (Large Print) Subtracting 1-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 2-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 3-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎
- Subtracting 4- to 8-Digit Numbers with All Regrouping Subtracting 4-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 5-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 6-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 7-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 8-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping ✎
- Subtracting 4- to 6-Digit Numbers with All Regrouping (Large Print) Subtracting 4-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 5-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 6-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎
Some students require a little extra help when learning to subtract large numbers. These subtraction worksheets include questions where the regrouping step has been eliminated. This might help students learn a subtraction algorithm before learning about regrouping.
- Subtracting up to 3-Digit Numbers with No Regrouping Subtracting 2-Digit from 2-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 2-Digit from 3-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 3-Digit from 3-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 2-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 3-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ✎
- Subtracting up to 3-Digit Numbers with No Regrouping (Large Print) Subtracting 2-Digit from 2-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 2-Digit from 3-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 3-Digit from 3-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 2-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 3-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎
- Subtracting 4- to 9-Digit Numbers with No Regrouping Subtracting 4-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 5-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 6-Digit from 6-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 7-Digit from 7-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 8-Digit from 8-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ✎ Subtracting 9-Digit from 9-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ✎
- Subtracting 4- to 6-Digit Numbers with No Regrouping (Large Print) Subtracting 4-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 5-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎ Subtracting 6-Digit from 6-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping ( Large Print ) ✎
Why horizontal subtraction worksheets? Students can show their understanding of place value and number sense if they do not already have the numbers lined up. Vertical subtraction is often learned based on a student's understanding of single-digit subtraction, but looking at the whole number is lost in the algorithm.
- Horizontally Arranged 2-Digit Minus 1-Digit Questions 2-digit Minus 1-Digit Horizontal Subtraction (100 Questions) ✎ 2-digit Minus 1-Digit Horizontal Subtraction (50 Questions) ✎ 2-digit Minus 1-Digit Horizontal Subtraction (25 Questions; Large Print) ✎
- Horizontally Arranged 2-Digit Minus 2-Digit Questions 2-digit Minus 2-Digit Horizontal Subtraction (100 Questions) ✎ 2-digit Minus 2-Digit Horizontal Subtraction (50 Questions) ✎ 2-digit Minus 2-Digit Horizontal Subtraction (25 Questions; Large Print) ✎
- Horizontally Arranged 3-Digit Minus 1-Digit Questions 3-digit Minus 1-Digit Horizontal Subtraction (100 Questions) ✎ 3-digit Minus 1-Digit Horizontal Subtraction (50 Questions) ✎ 3-digit Minus 1-Digit Horizontal Subtraction (25 Questions; Large Print) ✎
- Horizontally Arranged 3-Digit Minus 2-Digit Questions 3-digit Minus 2-Digit Horizontal Subtraction (50 Questions) ✎ 3-digit Minus 2-Digit Horizontal Subtraction (25 Questions; Large Print) ✎ 3-Digit Minus 2-Digit Horizontal Subtraction ( All Regrouping ; 100 Questions)
- Horizontally Arranged 3-Digit Minus 3-Digit Questions 3-Digit Minus 3-Digit Horizontal Subtraction (50 Questions) ✎ 3-Digit Minus 3-Digit Horizontal Subtraction (25 Questions; Large Print) ✎
- Horizontally Arranged Various-Digit Minus Various-Digit Questions Various-Digit Minus Various-Digit Horizontal Subtraction (50 Questions) ✎ Various-Digit Minus Various-Digit Horizontal Subtraction (25 Questions; Large Print) ✎
Many students in English-speaking countries are used to seeing numbers with comma-separated thousands.
- Long Subtraction Worksheets with Comma Separated Thousands Subtracting 2-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers (Comma Separated) ✎ Subtracting 3-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers (Comma Separated) ✎ Subtracting 4-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers (Comma Separated) ✎ Subtracting 2-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers (Comma Separated) ✎ Subtracting 3-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers (Comma Separated) ✎ Subtracting 4-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers (Comma Separated) ✎ Subtracting 5-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers (Comma Separated) ✎ Mixture of Multi-Digit Subtraction from 2 to 4 digits (Comma Separated) ✎ Mixture of Multi-Digit Subtraction from 2 to 5 digits (Comma Separated) ✎
- Long Subtraction Worksheets with Comma Separated Thousands and All Regrouping Subtracting 4-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Comma Separated) ✎ Subtracting 5-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Comma Separated) ✎ Subtracting 6-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Comma Separated) ✎ Subtracting 7-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Comma Separated) ✎ Subtracting 8-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Comma Separated) ✎
- Long Subtraction Worksheets with Comma Separated Thousands and No Regrouping Subtracting 5-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Comma Separated) ✎ Subtracting 6-Digit from 6-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Comma Separated) ✎ Subtracting 7-Digit from 7-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Comma Separated) ✎ Subtracting 8-Digit from 8-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Comma Separated) ✎ Subtracting 9-Digit from 9-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Comma Separated) ✎
Space-separated thousands are becoming more widely used, including in the United States. Canadian students have used both comma separated and space separated thousands for many years.
- Long Subtraction Worksheets with Space Separated Thousands Subtracting 2-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers (Space Separated) ✎ Subtracting 3-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers (Space Separated) ✎ Subtracting 4-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers (Space Separated) ✎ Subtracting 2-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers (Space Separated) ✎ Subtracting 3-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers (Space Separated) ✎ Subtracting 4-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers (Space Separated) ✎ Subtracting 5-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers (Space Separated) ✎ Mixture of Multi-Digit Subtraction from 2 to 4 digits (Space Separated) ✎ Mixture of Multi-Digit Subtraction from 2 to 5 digits (Space Separated) ✎
- Long Subtraction Worksheets with Space Separated Thousands and All Regrouping Subtracting 4-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Space Separated) ✎ Subtracting 5-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Space Separated) ✎ Subtracting 6-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Space Separated) ✎ Subtracting 7-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Space Separated) ✎ Subtracting 8-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Space Separated) ✎
- Long Subtraction Worksheets with Space Separated Thousands and No Regrouping Subtracting 5-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Space Separated) ✎ Subtracting 6-Digit from 6-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Space Separated) ✎ Subtracting 7-Digit from 7-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Space Separated) ✎ Subtracting 8-Digit from 8-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Space Separated) ✎ Subtracting 9-Digit from 9-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Space Separated) ✎
Even though period separated thousands are not common in the English-speaking world, we provide these for our friends in other countries who may find them useful.
- Long Subtraction Worksheets with Period Separated Thousands Subtracting 2-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers (Period Separated) ✎ Subtracting 3-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers (Period Separated) ✎ Subtracting 4-Digit from 4-Digit Numbers (Period Separated) ✎ Subtracting 2-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers (Period Separated) ✎ Subtracting 3-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers (Period Separated) ✎ Subtracting 4-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers (Period Separated) ✎ Subtracting 5-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers (Period Separated) ✎ Mixture of Multi-Digit Subtraction from 2 to 4 digits (Period Separated) ✎ Mixture of Multi-Digit Subtraction from 2 to 5 digits (Period Separated) ✎
- Long Subtraction Worksheets with Period Separated Thousands and All Regrouping Subtracting 4-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Period Separated) ✎ Subtracting 5-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Period Separated) ✎ Subtracting 6-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Period Separated) ✎ Subtracting 7-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Period Separated) ✎ Subtracting 8-Digit Numbers with ALL Regrouping (Period Separated) ✎
- Long Subtraction Worksheets with Period Separated Thousands and No Regrouping Subtracting 5-Digit from 5-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Period Separated) ✎ Subtracting 6-Digit from 6-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Period Separated) ✎ Subtracting 7-Digit from 7-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Period Separated) ✎ Subtracting 8-Digit from 8-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Period Separated) ✎ Subtracting 9-Digit from 9-Digit Numbers with NO Regrouping (Period Separated) ✎
Various Other Long Subtraction Worksheets

Generally, a student would not regroup to determine the complements of 10, 100, 1000, etc. One strategy that could be used is as follows: working from left to right, a student would take each digit in the subtrahend and figure out its nines complement. If the digit was 3, for example, the nines complement of 3 is 6. For the last digit (ones), the student would use the tens complement. For example, a typical question is 1000 - 456. The nines complement of 4 is 5, the nines complement of 5 is 4 and the tens complement of 6 is 4. Putting it all together, the student would get 5 4 4 or 544 = 1000 - 456.
- Calculating Complements of Powers of Ten (Subtracting Across Zeros) Complements of 10 Complements of 100 Complements of 1000 Complements of 10000 Complements of 100 and 1000 Complements of 1000 and 10000 Complements of 100, 1000 and 10000
A similar strategy is employed with the next worksheets except students must adapt to calculating the largest place value number.
- Calculating Complements of Multiples of Powers of Ten (Subtracting Across Zeros) Subtracting from multiples of 10 Subtracting from multiples of 100 Subtracting from multiples of 1000 Subtracting from multiples of 10000 Subtracting from a mixture of multiples of 100 and 1000 Subtracting from a mixture of multiples of 1000 and 10000 Subtracting from a mixture of multiples of 100, 1000 and 10000
These worksheets are meant to give students practice dealing with 0's in the middles of subtraction questions. Whether using pencil and paper or mental arithmetic, it is always a good idea to make sure students know what to do when they encounter zeros.
- Subtracting Across Zeros in the Middle (Ones Always Need Regrouping) 3-Digit Subtraction across zeros in the middle ( Ones always need regrouping ) 4-Digit Subtraction across zeros in the middle ( Ones always need regrouping ) 5-Digit Subtraction across zeros in the middle ( Ones always need regrouping )
- Subtracting Across Zeros in the Middle (Ones Sometimes Need Regrouping) 3-Digit Subtraction across zeros in the middle ( Ones sometimes need regrouping ) 4-Digit Subtraction across zeros in the middle ( Ones sometimes need regrouping ) 5-Digit Subtraction across zeros in the middle ( Ones sometimes need regrouping )
Subtracting numbers in number systems other than decimal numbers including binary, quaternary, octal, duodecimal and hexadecimal numbers.
- Subtracting in Other Base Number Systems Subtracting Binary Numbers (Base 2) Subtracting Ternary Numbers (Base 3) Subtracting Quaternary Numbers (Base 4) Subtracting Quinary Numbers (Base 5) Subtracting Senary Numbers (Base 6) Subtracting Octal Numbers (Base 8) Subtracting Duodecimal Numbers (Base 12) Subtracting Hexadecimal Numbers (Base 16) Subtracting Vigesimal Numbers (Base 20) Subtracting Hexatrigesimal Numbers (Base 36) Subtracting Various Numbers (Various Bases)
Copyright © 2005-2024 Math-Drills.com You may use the math worksheets on this website according to our Terms of Use to help students learn math.
Problem Solving on Subtraction
Problem solving on subtraction will help us to get the idea on how to solve the basic subtraction statement problems.
1. Eight birds sat on a wire. Three birds flew away. How many were left?
Total number of birds sat on a wire = 8
Number of birds flew away = 3
Therefore, number of birds left = 8 - 3 = 5
2. Sam had 7 dollars. He spent 4 dollars. How many dollars is he left with?
Total amount of money Sam had = $7
He spent = $4
Therefore, amount of money left with him = $7 - $4 = $3
3. Five boats were tied up. Four of the boats sailed away. How many were left?
Total number of boats tied up = 5
Number of boats sailed away = 4
Therefore, number of boats were left = 5 - 4 = 1
4. Ron had 10 stamps. His father took 2 stamps. How many stamps does Ron have now?
Total number of stamps Ron had = 10
Number of stamps his father took = 2
Therefore, number of stamps he have now = 10 - 2 = 8
5. Diana had 18 toffees. She gave 5 toffees to her friend. How many toffees left with her?
Total number of toffees Diana had = 18
Number of toffees she gave to her friend = 5
Therefore, number of toffees left = 18 - 5 = 13
More examples on statement problem solving on subtraction:
6. Mr. Daniel had 39 goats in a pasture. When he opened the pasture gate, 13 goats went out. How many goats remained in?
Total number of goats in a pasture Mr. Daniel had = 39
Number of goats went out = 13
Therefore, number of goats remained in = 39 - 13 = 26
7. Derek’s father is 47 years old. His mother is 35 years old. What is the difference of their ages?
Age of Derek’s father = 47 years
Age of his mother = 35 years
Therefore, difference of their ages = 47 - 35 = 12 years
2nd Grade Math Practice From Problem Solving on Subtraction to HOME PAGE
New! Comments
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math . Use this Google Search to find what you need.
- Preschool Activities
- Kindergarten Math
- 1st Grade Math
- 2nd Grade Math
- 3rd Grade Math
- 4th Grade Math
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- 7th Grade Math
- 8th Grade Math
- 9th Grade Math
- 10th Grade Math
- 11 & 12 Grade Math
- Concepts of Sets
- Probability
- Boolean Algebra
- Math Coloring Pages
- Multiplication Table
- Cool Maths Games
- Math Flash Cards
- Online Math Quiz
- Math Puzzles
- Binary System
- Math Dictionary
- Conversion Chart
- Homework Sheets
- Math Problem Ans
- Free Math Answers
- Printable Math Sheet
- Funny Math Answers
- Employment Test
- Math Patterns
- Link Partners
- Privacy Policy

Recent Articles
Months of the Year | List of 12 Months of the Year |Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr
Apr 02, 24 02:08 PM

Division of Two-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers | Dividing Larger Numbers
Apr 02, 24 11:58 AM

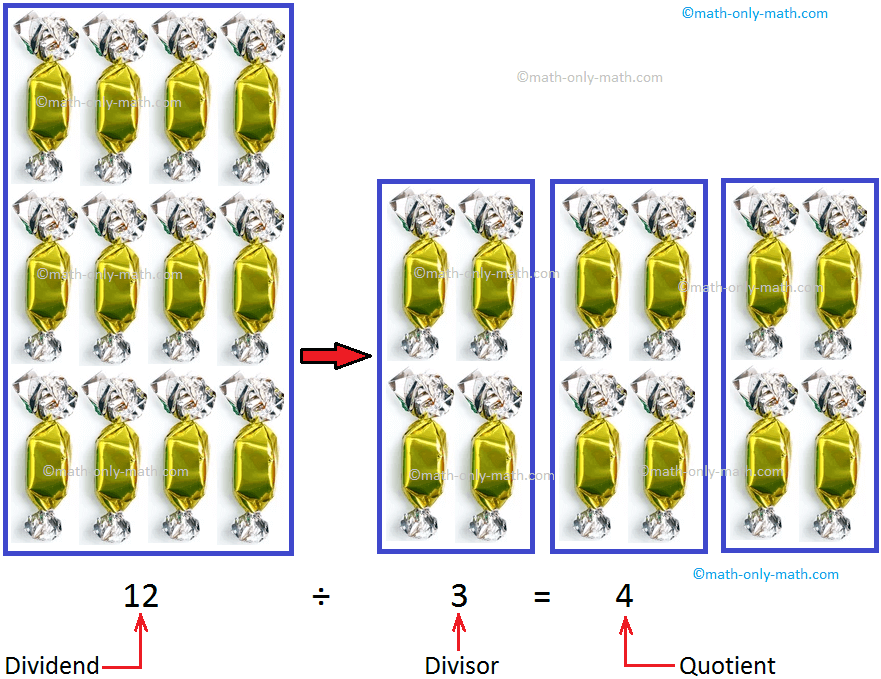
Terms Used in Division | Dividend | Divisor | Quotient | Remainder
Apr 01, 24 05:38 PM
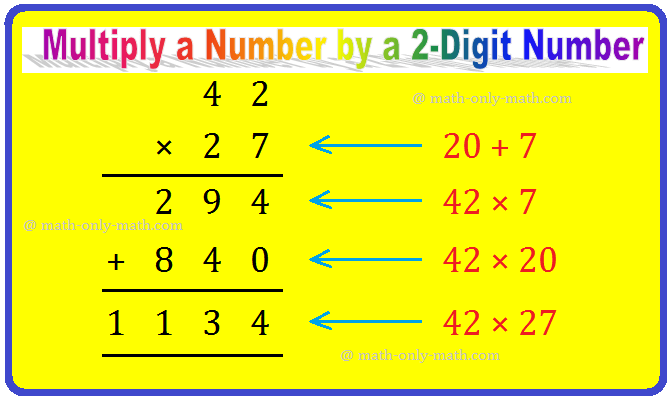
Multiply a Number by a 2-Digit Number | Multiplying 2-Digit by 2-Digit
Apr 01, 24 04:52 PM
Mental Math on Multiplication Worksheet | Multiplication Facts|Answers
Apr 01, 24 04:04 PM
© and ™ math-only-math.com. All Rights Reserved. 2010 - 2024.
Subtraction
Subtraction is the process of taking away a number from another. It is a primary arithmetic operation that is denoted by a subtraction symbol (-) and is the method of calculating the difference between two numbers.
What Is Subtraction?
Subtraction is an operation used to find the difference between numbers . When you have a group of objects and you take away a few objects from it, the group becomes smaller. For example, you bought 9 cupcakes for your birthday party and your friends ate 7 cupcakes. Now you are left with 2 cupcakes. This can be written in the form of a subtraction expression: 9 - 7 = 2 and is read as "nine minus seven equals two". When we subtract 7 from 9, (9 - 7) we get 2. Here, we performed the subtraction operation on two numbers 9 and 7 to get the difference of 2.
Subtraction Symbol
In mathematics, we have different symbols. The subtraction symbol is one of the important math symbols that we use while performing subtraction. In the above section, we read about subtracting two numbers 9 and 7. If we observe this subtraction: (9 - 7 = 2), the symbol (-) connects the two numbers and completes the given expression. This symbol is also known as the minus sign.
Subtraction Formula
When we subtract two numbers, we use some terms which are used in the subtraction expression:
- Minuend: The number from which the other number is subtracted.
- Subtrahend: The number which is to be subtracted from the minuend.
- Difference: The final result after subtracting the subtrahend from the minuend.
The subtraction formula is written as: Minuend - Subtrahend = Difference
Let us understand the subtraction formula or the mathematical equation of subtraction with an example.

Here, 9 is the minuend, 7 is the subtrahend, and 2 is the difference.
How To Solve Subtraction Problems?
While solving subtraction problems, one-digit numbers can be subtracted in a simple way, but for larger numbers, we split the numbers into columns using their respective place values , like Ones, Tens, Hundreds, Thousands, and so on. While solving such problems we may encounter some cases with borrowing and some without borrowing. Subtraction with borrowing is also known as subtraction with regrouping. When the minuend is smaller than the subtrahend, we use the regrouping method. While regrouping, we borrow 1 number from the preceding column to make the minuend bigger than the subtrahend. Let us understand this with the help of a few examples.
Subtraction Without Regrouping
Example: Subtract 25632 from 48756.
Note: In subtraction, we always subtract the smaller number from the larger number to get the correct answer.
Solution: Follow the given steps and try to relate them with the following figure.
Step 1: Start with the digit at ones place. (6 - 2 = 4) Step 2: Move to the tens place. (5 - 3 = 2) Step 3: Now subtract the digits at hundreds place. (7 - 6 = 1) Step 4: Now subtract the digits at thousands place. (8 - 5 = 3) Step 5: Finally, subtract the digits at ten thousands place. (4 - 2 = 2) Step 6: Therefore, the difference between the two given numbers is: 48756 - 25632 = 23124.

Subtraction With Regrouping
Example: Subtract 3678 from 8162.
Solution: Follow the given steps and try to relate them with the following figure. We need to solve: 8162 - 3678 Step 1: Start subtracting the digits at ones place. We can see that 8 is greater than 2. So, we will borrow 1 from the tens column which will make it 12. Now, 12 - 8 = 4 ones. Step 2: After giving 1 to the ones column in the previous step, 6 becomes 5. Now, let us subtract the digits at the tens place (5 - 7). Here, 7 is greater than 5, so we will borrow 1 from the hundreds column. This will make it 15. So,15 - 7 = 8 tens. Step 3: In step 2 we had given 1 to the tens column, so we are left with 0 at the hundreds place. To subtract the digits on the hundreds place, i.e., (0 - 6) we will borrow 1 from the thousands column. This will make it 10. So, 10 - 6 = 4 hundreds. Step 4: Now, let us subtract the digits at the thousands place. After giving 1 to the hundreds column, we have 7. So, 7 - 3 = 4 Step 5: Therefore, the difference between the two given numbers is: 8162 - 3678 = 4484

Subtraction Using Number Line
A number line is a visual aid that helps us understand subtraction because it allows us to jump backward and forward on each number. To understand how this works, let us explore subtraction using a number line. Let us subtract 4 from 9 using a number line. We will start by marking the number 9 on the number line. When we subtract using a number line, we count by moving one number at a time towards the left-hand side. Since we are subtracting 4 from 9, we will move 4 times to the left. The number on which you land after 4 backward jumps, is the answer. Thus, 9 - 4 = 5.

Real Life Subtraction Word Problems
The concept of subtraction is often used in our day-to-day activities. Let us understand how to solve real-life subtraction word problems with the help of an interesting example.
Example: A soccer match had a total of 4535 spectators. After the first innings, 2332 spectators left the stadium. Find the number of remaining spectators.
Solution: Given: The total number of spectators present in the first innings = 4535; The number of spectators who left the stadium after the first innings = 2332 Here, 4535 is the minuend and 2332 is the subtrahend.
Th H T O 4 5 3 5 -2 3 3 2 2 2 0 3
Therefore, the number of remaining spectators = 2203.
Important Notes on Subtraction:
Here are a few important notes that you can follow while performing subtraction in your everyday life.
- Any subtraction problem can be transformed into an addition problem and vice-versa.
- Subtracting 0 from any number gives the number itself as the difference.
- When 1 is subtracted from any number, the difference equals the predecessor of the number.
- Words like "Minus", "Less", "Difference", "Decrease", "Take Away" and "Deduct" indicate that you need to subtract one number from another.
Topics Related to Subtraction
Check out these interesting articles to know about subtraction and its related topics.
- Binary Subtraction
- Subtraction Calculator
- Addition and Subtraction of Fractions
- Subtraction of Complex Numbers
- Subtraction of Fractions
Subtraction Examples
Example 1: In an International cricket match, Sri Lanka scored 236 runs and India scored 126 runs. How many more runs should India score to be equal to the number of runs scored by Sri Lanka?
Runs scored by Sri Lanka = 236; Runs scored by India = 126 To find the number of runs that India should score more to be equal to the number of runs scored by Sri Lanka, we will subtract 126 from 236.
H T O 2 3 6 - 1 2 6 1 1 0
Therefore, India must score 110 more runs to be equal to Sri Lanka's runs.
Example 2: Jerry collected 189 seashells and Eva collected 54 shells. Who collected more seashells and by how much?
Number of shells collected by Jerry = 189; Number of shells collected by Eva = 54
This shows that Jerry collected more seashells. Let us subtract 189 - 54 to get the difference.
H T O 1 8 9 - 0 5 4 1 3 5
Therefore, Jerry collected 135 seashells more than Eva.
Example 3: During an annual Easter egg hunt, the participants found 2469 eggs in the clubhouse, out of which 54 Easter eggs were broken. Can you find out the number of unbroken eggs?
The number of easter eggs found in the Clubhouse = 2469; Number of easter eggs that were broken = 54; The total number of unbroken eggs=?
Now, we will subtract the number of broken eggs from the total number of eggs.
Th H T O 2 4 6 9 - 5 4 2 4 1 5
Therefore, the number of unbroken eggs are 2415.
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on Subtraction
go to slide go to slide
FAQs on Subtraction
Where do we use subtraction.
Subtraction is used in our day-to-day life. For example, if we want to know how much money we spent on the items that we bought, or, how much money is left with us, or, if we want to calculate the time left in finishing a task, we use subtraction.
What Are the Types of Subtraction?
The types of subtraction mean the various methods used in subtraction. For example, subtraction with and without regrouping, subtraction using number charts, subtraction using number line, the subtraction of small numbers using you fingers, and so on.
What Are Subtraction Strategies?
Subtraction strategies are different ways in which subtraction can be learned. For example, using a number line, with the help of a Place Value Chart, separating the Tens and Ones and then subtracting them separately, and many others.
Give Some Subtraction Examples.
There can be various real-life examples of subtraction. For example, if you have 5 apples and your friend ate 3 apples. Using subtraction, we can find out the number of remaining apples: 5 - 3 = 2. So, 2 apples are left with you. Similarly, if there are 16 students in a class, out of which 9 are girls, then we can find out the number of boys in the class by subtracting 9 from 16. (16 - 9 = 7). So, we know that there are 7 boys in the class.
What Are the Three Parts of Subtraction?
The 3 parts of subtraction are named as follows:
- Minuend: The number from which we subtract the other number is known as the minuend.
- Subtrahend: The number which is subtracted from the minuend is known as the subtrahend.
- Difference: The final result obtained after performing subtraction is known as the difference.
How Do You Write a Subtraction?
While writing subtraction, the two important symbols are '-' (minus) and '=' (equal to). The minus sign means when one number is being subtracted from the other number. And the equal to sign delivers the final result.
- 1st Grade Math
- 2nd Grade Math
- 3rd Grade Math
- 4th Grade Math
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- 7th Grade Math
- 8th Grade Math
- Knowledge Base
- Math for kids
Subtraction – Definition, Symbol, Examples, Practice Problems
Created: December 19, 2023
Last updated: January 10, 2024
Welcome to Brighterly – your trusted partner for making learning mathematics a delightful and exciting journey! We’re passionate about illuminating the path to knowledge and equipping young minds with the tools they need to succeed. Today, we’re focusing on a core concept in mathematics that plays a vital role in our daily lives – Subtraction. This fundamental operation is more than just a simple act of ‘taking away’; it’s a powerful tool that aids us in understanding and interacting with the world around us.
At Brighterly, we strive to break down complex topics into digestible, understandable pieces, and subtraction is no exception. Through this comprehensive guide, we will explore the definition of subtraction, its symbolic representation, examples, and practice problems. Whether you’re a curious learner, a supportive parent, or an inspiring teacher, this article has something to offer to help you or your child make strides in mathematical understanding. Join us as we dive into the world of subtraction, making learning brighter and more engaging, one step at a time!
What Is Subtraction?
Subtraction is one of the fundamental operations in arithmetic that children learn early in their education. It’s a process we use to find the difference between two numbers, quantities, or objects. For instance, if a basket contains five apples and you remove two, you’re left with three. This operation can be expressed as a subtraction problem: 5 – 2 = 3. The concept of taking away or finding the difference is central to subtraction. It’s not just useful in mathematical computations but also applicable in various real-life situations, such as calculating change in a store, or determining how much of a pizza is left after some slices have been eaten.
What is Subtraction in Math?
In mathematics, subtraction serves as one of the fundamental pillars of basic arithmetic. It’s an operation that helps us calculate the difference between two numbers or quantities. In essence, subtraction represents the process of taking one number away from another. For example, if you have ten chocolates and you eat four, you’re left with six. That situation, expressed mathematically, is 10 – 4 = 6. This operation is so central to our daily lives that we use it frequently, sometimes without even noticing. For instance, it’s used when we calculate how many hours of sleep we can get before the alarm rings, or how much money remains after making a purchase.
Definition of Subtraction
In mathematical terms, subtraction is defined as the operation that tells the amount or quantity that remains when a number or quantity is taken from another. The result of subtraction is called the difference. For instance, in the subtraction problem 8 – 3 = 5, eight is the minuend (the number from which another number is subtracted), three is the subtrahend (the number that is to be subtracted), and five is the difference.
Symbol of Subtraction
The most common symbol of subtraction is the minus sign (-). It’s placed between two numbers to indicate that the second number (subtrahend) is to be subtracted from the first number (minuend). For example, in the expression 7 – 2, the minus sign is the symbol of subtraction, showing that 2 is to be subtracted from 7.
Formula of Subtraction Operation
The formula for the subtraction operation involves a minuend, a subtrahend, and a difference. It’s written in the format: Minuend – Subtrahend = Difference. For example, in the subtraction problem 15 – 6 = 9, 15 is the minuend, 6 is the subtrahend, and 9 is the difference.
What Is Minus in Math?
The minus sign (-) in math is a symbol used to represent subtraction, as well as negative numbers and the opposite of a number. When used for subtraction, it signifies that a number (the subtrahend) is to be subtracted from another number (the minuend). For example, in 10 – 3, the minus sign signifies that 3 is to be subtracted from 10. When used to represent negative numbers, the minus sign is placed before the number to indicate that it is less than zero. For instance, -5 is a negative number.
Uses of Minus Sign
The minus sign (-) has several uses in mathematics. Apart from representing subtraction and negative numbers, it’s used to denote the opposite of a number. For instance, the opposite of +5 is -5. It’s also used in equations to balance the two sides. For example, to balance the equation x + 2 = 5, we subtract 2 from both sides to get x = 5 – 2. Moreover, in the context of temperature, the minus sign is used to indicate degrees below zero.
How To Solve Subtraction Problems?
Solving subtraction problems typically involves three steps: identifying the minuend and subtrahend, performing the subtraction operation, and writing down the difference. For instance, to solve the subtraction problem 13 – 4, identify 13 as the minuend and 4 as the subtrahend. Subtract 4 from 13 to get the difference, which is 9. So, 13 – 4 = 9.
Subtraction Without Regrouping
Subtraction without regrouping (also known as subtraction without borrowing) occurs when the minuend (top number) in each column is larger than or equal to the subtrahend (bottom number). In this case, you simply subtract the smaller number from the larger number. For example, in the subtraction problem 63 – 27, you can subtract 7 from 3 and 2 from 6 without needing to borrow or regroup.
Subtraction With Regrouping
Subtraction with regrouping (also known as subtraction with borrowing) is a method used when the minuend (top number) in a column is smaller than the subtrahend (bottom number). In this case, you borrow 1 from the next higher place value column. For instance, in the subtraction problem 53 – 28, you can’t subtract 8 from 3 without regrouping. So, you borrow 1 from the tens place (making it 4), and the 3 becomes 13. Then you can subtract 8 from 13 and 2 from 4 to get the difference, 25.
Subtraction Table
A subtraction table is a chart that shows the results of subtracting one number from another. The minuend (from which subtraction is made) is listed down the left column, and the subtrahend (which is subtracted) across the top row. The difference can be found where the row and column of the minuend and subtrahend meet. Subtraction tables are great tools for children learning subtraction, as they provide a visual representation of the operation and can help improve speed and accuracy.
Subtraction Sums
Subtraction sums refer to the problems or exercises that involve the operation of subtraction. They may consist of simple problems like 7 – 3, or more complex ones that involve larger numbers, decimals, fractions, or integers. Practice with a variety of subtraction sums can help children improve their fluency and understanding of the subtraction operation.
Subtraction of Fractions
The subtraction of fractions involves a few steps. If the fractions have the same denominator (also known as like fractions), you simply subtract the numerators and keep the denominator. For example, 5/8 – 3/8 = 2/8, which simplifies to 1/4. If the fractions have different denominators (also known as unlike fractions), you first need to find a common denominator, adjust the numerators accordingly, then subtract.
Subtraction of Integers
Subtraction of integers can be a bit tricky due to the presence of positive and negative numbers. However, it can be simplified by understanding that subtracting a number is the same as adding its opposite. For example, to subtract -3 from 5 (5 – (-3)), you add the opposite of -3 (which is 3) to 5, resulting in 8.
Subtraction on Number Line
Subtraction on a number line provides a visual method for subtracting numbers. To subtract a number, you start at the minuend and move to the left the number of steps equal to the subtrahend. For example, to subtract 3 from 7 on a number line, you start at 7 and move three steps to the left, landing on 4.
Subtraction Word Problems
Subtraction word problems are practical scenarios that require the use of subtraction to solve. They are often used in math education to apply subtraction skills to real-world situations. For example, “John has 15 candies. He gives 7 to his friend. How many candies does John have now?” requires the subtraction operation to solve (15 – 7 = 8).
Properties of Subtraction
There are several properties of subtraction, including the property of non-commutativity (changing the order of the numbers changes the result, i.e., a – b ≠ b – a) and the property of non-associativity (changing the grouping of the numbers changes the result, i.e., (a – b) – c ≠ a – (b – c)).
Solved Examples On Subtraction
Here are some solved examples on subtraction:
- 10 – 5 = 5
- 7 – 2 = 5
- 15 – 8 = 7
Each example follows the same format: Minuend – Subtrahend = Difference.
Practice Problems On Subtraction
Practice problems are an excellent way to reinforce your understanding of subtraction. Here are a few practice problems on subtraction:
- 12 – 7 = ?
- 9 – 4 = ?
- 6 – 3 = ?
Try solving these problems to test your subtraction skills!
In conclusion, subtraction is a fundamental mathematical operation, which plays a pivotal role in our everyday lives and in the broader realm of mathematics. At Brighterly, we believe in simplifying complex concepts, making subtraction an accessible and understandable topic for children. By understanding the concept, symbols, and methods of subtraction, such as without regrouping and with regrouping, learners can build a robust mathematical foundation. Our hands-on examples and intuitive explanations help students grasp these concepts effectively. Remember, practice is key in mastering subtraction. Therefore, we encourage learners to frequently use the practice problems and worked examples provided here on Brighterly to hone their subtraction skills. Together, let’s make learning math a fun, engaging, and brighter experience!
Frequently Asked Questions On Subtraction
What is subtraction.
Subtraction is a fundamental arithmetic operation that is integral to our daily mathematical calculations. It is the process of deducting a quantity, often referred to as the subtrahend, from a larger quantity known as the minuend. Subtraction is used to determine the difference between these two numbers or quantities. Conceptually, subtraction can be thought of as the operation of “taking away.” It’s crucial in various real-world scenarios, such as when we calculate the remaining amount of money after making a purchase or determining the time left for an event to start.
What is the symbol for subtraction?
The symbol for subtraction is the minus sign (-). It is used between two numbers to denote that the number following the sign should be subtracted from the number preceding it. This symbol is universally recognized in mathematics and signifies the operation of subtraction. For example, in the arithmetic expression “7 – 2”, the minus sign indicates that 2 should be subtracted from 7.
What is the formula for subtraction?
The standard formula for subtraction is expressed as: Minuend – Subtrahend = Difference. Here, the minuend is the initial quantity from which another quantity, the subtrahend, is subtracted. The result of this operation is known as the difference. To illustrate, let’s consider the subtraction operation “9 – 4 = 5”. Here, 9 is the minuend, 4 is the subtrahend, and 5 is the difference. This formula provides the basic framework for understanding and performing subtraction operations.
Information in this article was collated from reputable sources including:
- Wikipedia – Subtraction
- U.S. Department of Education – Helping Your Child Learn Mathematics
- Open University – Introduction to Subtraction
- Stanford Mathematics Education – Number & Operations
I am a seasoned math tutor with over seven years of experience in the field. Holding a Master’s Degree in Education, I take great joy in nurturing young math enthusiasts, regardless of their age, grade, and skill level. Beyond teaching, I am passionate about spending time with my family, reading, and watching movies. My background also includes knowledge in child psychology, which aids in delivering personalized and effective teaching strategies.
Troubles with Subtraction?
- Is your child finding it challenging to understand the concept of subtraction?
- An online tutor could be the answer.
Kid’s grade
Does your child struggle to master subtraction basics? Try learning with an online tutor.

After-School Math Program
Related math.
Rational numbers are commonly used in engineering, physics, and finance. However, they aren’t necessary just for niche fields and scenarios; understanding rational numbers is essential for everyday life. Thus, kids need to understand the properties and applications of rational numbers. What Are Rational Numbers? A rational number is any number that can be expressed […]
Welcome to another enlightening piece on Brighterly, your most reliable platform for illuminating mathematical concepts. We’re about to embark on a fascinating journey into the world of trigonometry. Our focus for today’s adventure? The trigonometric function Cos2x. This function is more than just an abstract mathematical concept—it’s a powerful tool for understanding the geometric relationships […]
Welcome to Brighterly, your gateway to the magical world of mathematics where learning becomes an exciting adventure! Today, we shall embark on a geometric journey to explore the fascinating realm of trapezoidal prisms. This shape may sound complex, but here at Brighterly, we believe in breaking down intricate subjects into fun and digestible pieces. A […]
We use cookies to help give you the best service possible. If you continue to use the website we will understand that you consent to the Terms and Conditions. These cookies are safe and secure. We will not share your history logs with third parties. Learn More
Subtraction Word Problems
These lessons look at simple examples of subtraction word problems.
Related Pages More Lessons for Arithmetic Math Worksheets
Words like ‘difference’, ‘less’, ‘take away’, ‘loss’ usually means that subtraction is involved.
For subtraction, take note which number has to be subtracted from which number. Subtracting in the wrong order will give you the wrong answer.
Example: Andy has 53 marbles. Sam has 105 marbles and lost 8 when his bag of marbles dropped. Find the difference between the number of marbles that Sam has left and Andy’s.
Solution: [Sam has 105 marbles] – [8 lost] – [Andy has 53 marbles]
105 – 8 – 53 = 44 marbles
Examples of subtraction word problems
- John has 12 apples, and he gives away 5 of them. How many apples does he have left?
- What is the difference between 17 and 38?
- Jennifer has eighteen apples, and Mike has twelve. How many more apples does Jennifer have than Mike?
Subtraction Word Problem
Example: A farmer grows 531 tomatoes and is able to sell 176 of them in three days. Given that his supply of tomatoes decreases by 176, how many tomatoes does he have remaining at the end of the three days?

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
Subtraction
Subtraction is ....
... taking one number away from another.
Try It Yourself
Train yourself.
You get good at subtraction with practice...
... so use Math Trainer - Subtraction to train yourself!
Subtraction Table
You can also "look up" answers for simple subtraction using this table:
Example: Find 8 − 5
- find the row starting with "8"
- move along till you are under the column "5"
- and there is the number "3", so 8 − 5 = 3
Other names used in subtraction are Minus, Less, Difference, Decrease, Take Away, Deduct.
The names of the numbers in a subtraction fact are:
Minuend − Subtrahend = Difference
Minuend : The number that is to be subtracted from.
Subtrahend : The number that is to be subtracted.
Difference : The result of subtracting one number from another.
Subtracting Larger Numbers
To subtract numbers with more than one digit (such as "42−25") use any of these methods, choose the one you prefer :
For practice try these Subtraction Worksheets

Child Login
- Kindergarten
- Number charts
- Skip Counting
- Place Value
- Number Lines
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Word Problems
- Comparing Numbers
- Ordering Numbers
- Odd and Even
- Prime and Composite
- Roman Numerals
- Ordinal Numbers
- In and Out Boxes
- Number System Conversions
- More Number Sense Worksheets
- Size Comparison
- Measuring Length
- Metric Unit Conversion
- Customary Unit Conversion
- Temperature
- More Measurement Worksheets
- Writing Checks
- Profit and Loss
- Simple Interest
- Compound Interest
- Tally Marks
- Mean, Median, Mode, Range
- Mean Absolute Deviation
- Stem-and-leaf Plot
- Box-and-whisker Plot
- Permutation and Combination
- Probability
- Venn Diagram
- More Statistics Worksheets
- Shapes - 2D
- Shapes - 3D
- Lines, Rays and Line Segments
- Points, Lines and Planes
- Transformation
- Quadrilateral
- Ordered Pairs
- Midpoint Formula
- Distance Formula
- Parallel, Perpendicular and Intersecting Lines
- Scale Factor
- Surface Area
- Pythagorean Theorem
- More Geometry Worksheets
- Converting between Fractions and Decimals
- Significant Figures
- Convert between Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
- Proportions
- Direct and Inverse Variation
- Order of Operations
- Squaring Numbers
- Square Roots
- Scientific Notations
- Speed, Distance, and Time
- Absolute Value
- More Pre-Algebra Worksheets
- Translating Algebraic Phrases
- Evaluating Algebraic Expressions
- Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
- Algebraic Identities
- Quadratic Equations
- Systems of Equations
- Polynomials
- Inequalities
- Sequence and Series
- Complex Numbers
- More Algebra Worksheets
- Trigonometry
- Math Workbooks
- English Language Arts
- Summer Review Packets
- Social Studies
- Holidays and Events
- Worksheets >
- Number Sense >
- Subtraction >
Subtraction Word Problem Worksheets
The extensive set of subtraction word problems featured here will require the learner to find the difference between minuends and subtrahends, which includes problems with regrouping and without regrouping. This large collection of printable word problem worksheets, ideal for children in kindergarten through grade 4 features scenarios that involve single-digit subtraction, two-digit subtraction, three-digit subtraction, and subtraction of large numbers up to six digits. Give yourself a head-start with our free subtraction worksheets!

Word Problems for Beginners: 0 to 10
Find the difference between the numbers that ranges from 0 to 10 in the set of kindergarten worksheets featured here. Use the answer key to verify your responses.
- Download the set

Subtraction within 20
Ascend from a beginner to a proficient in performing subtraction up to 20 as you explore this bunch of well-researched word problems and work out the difference within 20.

Two-digit Subtraction: No Regrouping (No Borrowing)
The series of worksheets for grade 1 and grade 2 presented here involve two-digit subtraction word problems that do not require regrouping. Find the differences between the two-digit subtrahends and minuends featured here.

Two-digit Subtraction: Regrouping (Borrowing)
The two-digit subtraction word problems presented in the 2nd grade worksheets here require regrouping (borrowing). Determine the difference between the two-digit numbers by following the place value columns correctly.

Theme based Subtraction Problems
The colorful theme-based worksheet pdfs for kids in 1st grade through 3rd grade are based on three engaging real-life themes - Beach, Italian Ice and Birthday Party.

Three-digit and Two-digit Subtraction
The set of subtraction word problem pdfs featured here will require grade 3 student to find the difference between three-digit minuends and two-digit subtrahends. Use the answer keys to verify your responses.

Three-digit Subtraction Word Problems
Each printable worksheet contains five word problems finding difference between three-digit numbers. Some problems may require regrouping.

Four-digit Subtraction Word Problems
This section contains subtraction word problems on finding the difference between four-digit numbers. Both borrowing and no borrowing problems are included. Some problems may involve subtraction across zero.

Advanced: Large Number Subtraction
The word problems featured in the 4th grade pdf worksheets here include large numbers with minuends and subtrahends up to six digits. Determine the difference between the large numbers by following the place value columns correctly.
Related Worksheets
» Addition Word Problems
» Subtraction within 10
» 2-Digit Subtraction
» Word Problems
Become a Member
Membership Information
Privacy Policy
What's New?
Printing Help
Testimonial
Copyright © 2024 - Math Worksheets 4 Kids
This is a members-only feature!


- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Addition and Subtraction - Subtracting Two- and Three-Digit Numbers
Addition and subtraction -, subtracting two- and three-digit numbers, addition and subtraction subtracting two- and three-digit numbers.

Addition and Subtraction: Subtracting Two- and Three-Digit Numbers
Lesson 5: subtracting two- and three-digit numbers.
/en/additionsubtraction/introduction-to-subtraction/content/
Subtracting larger numbers
In Introduction to Subtraction , we learned that counting and using visuals can be useful for solving basic subtraction problems. For instance, say you have 9 apples and you use 6 to make a pie. To find out how many apples are left, you could represent the situation like this:

It's easy to count and see that 3 apples are left.
What if you need to solve a subtraction problem that starts with a large number? For instance, let's say instead of making an apple pie, you want to pick apples from an apple tree. The tree has 30 apples and you pick 21 . We could write this as 30 - 21 .
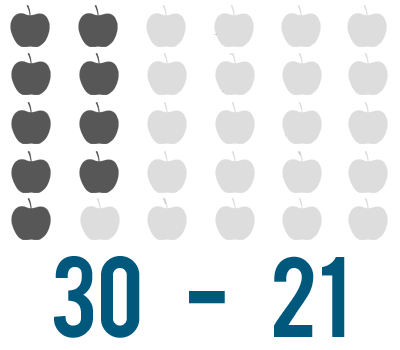
You might see why counting to solve this problem isn't a good idea. When you have a subtraction problem that starts with a large number, it could take a long time to set up the problem. Imagine the time it would take to count out 30 objects and then take away 21! Also, it would be easy to lose track as you counted. You could end up with the wrong answer.
For this reason, when people solve a subtraction problem with large numbers, they set up the problem in a way that makes it easy to solve one step at a time. Let's see how this works with another problem: 79 - 13 .
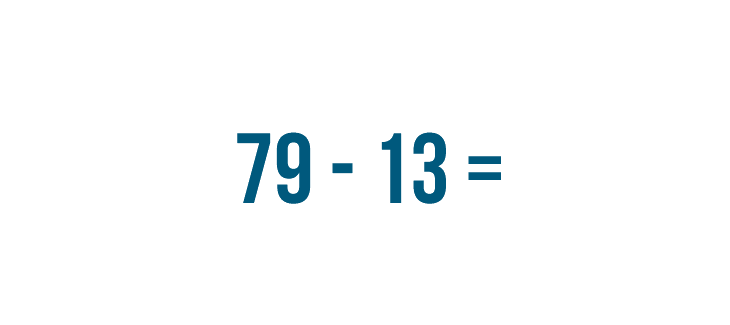
In the last lesson, we learned how to write expressions. However, subtracting with larger numbers is easier when the expressions are written in a different way.
Instead of writing the numbers side by side…
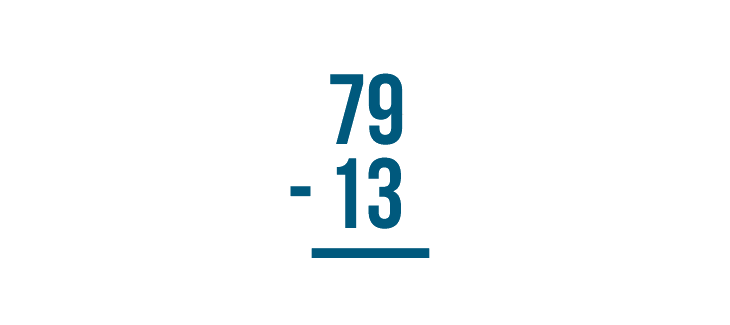
Place the numbers so they are stacked — one number on top and one number on the bottom.
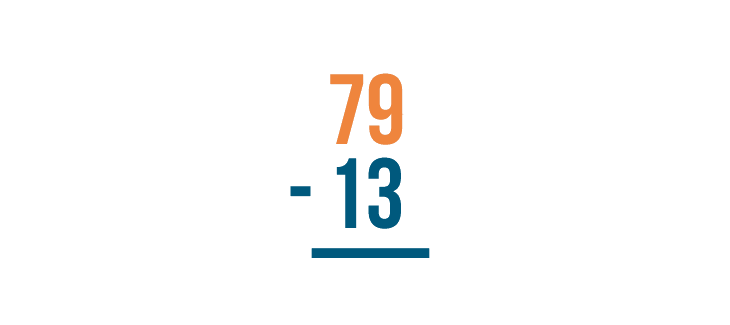
With a stacked subtraction expression, the larger number is always written on top. Here, that number is 79 .
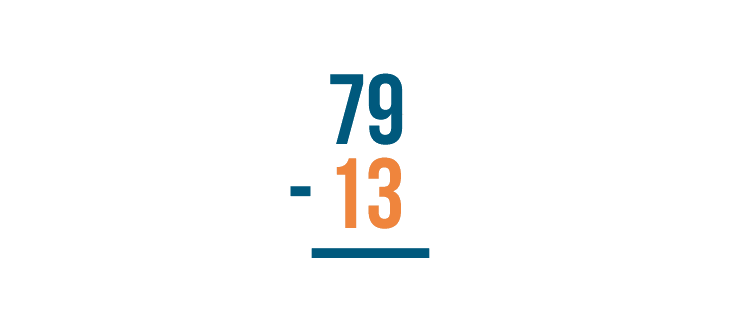
Write the amount being subtracted underneath the top number. That's 13 .

Put the minus sign to the left of the numbers.
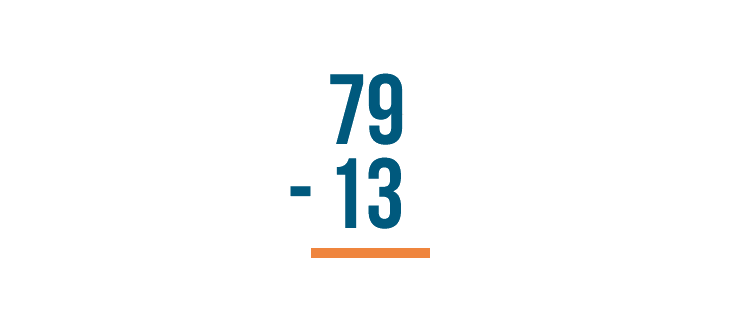
Instead of an equals sign, put a line underneath the bottom number.
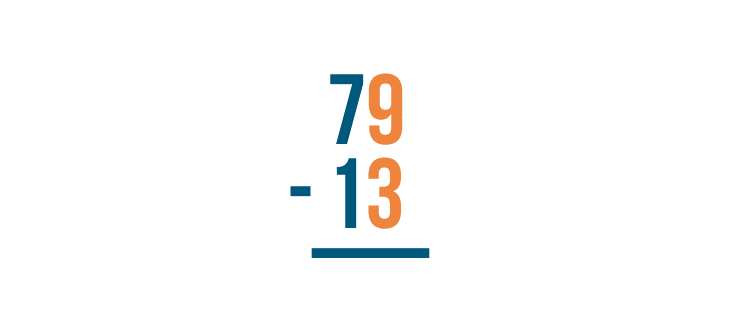
When you stack a subtraction expression, make sure the numbers are lined up correctly. They are always lined up on the right. Here, we lined up 9 and 3 .

Here's another problem, 576 - 2 . With this problem, see how we lined up the numbers to the right?
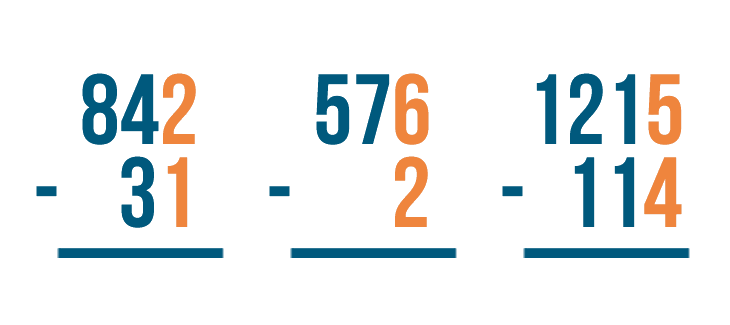
No matter how many digits are in the numbers, always line up the numbers to the right.

Solving Stacked Subtraction Problems
If you feel comfortable with the subtraction skills from Introduction to Subtraction , you're ready to start solving stacked subtraction problems.
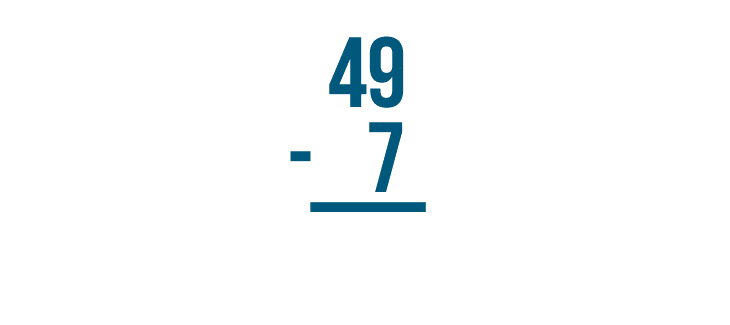
Let's try to solve 49 - 7 .
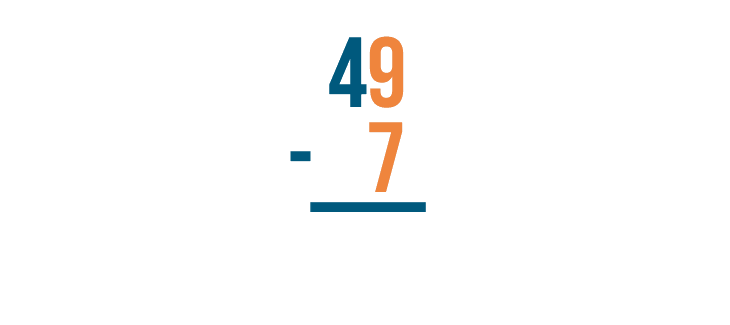
With all stacked subtraction problems, we start with the digits that are farthest to the right. Here, we'll begin with 9 and 7 .
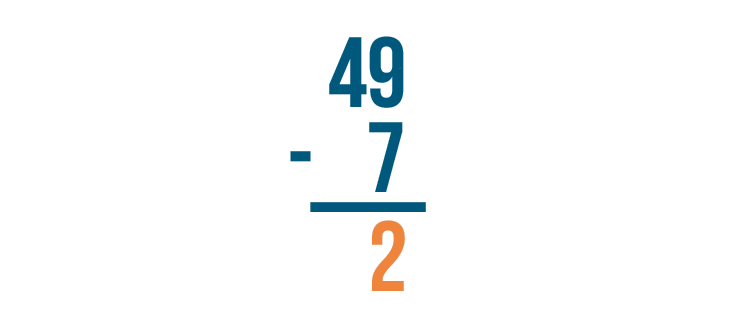
9 - 7 = 2 . The difference is 2 . It's important to write 2 directly beneath the digits we just subtracted.
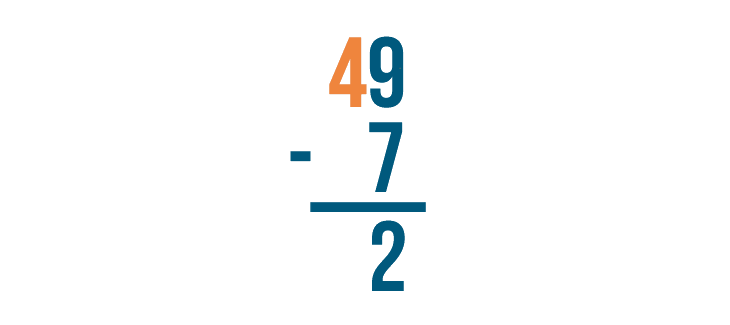
Now let's find the difference of the digits to the left. The top digit is 4 , but there's nothing beneath it.
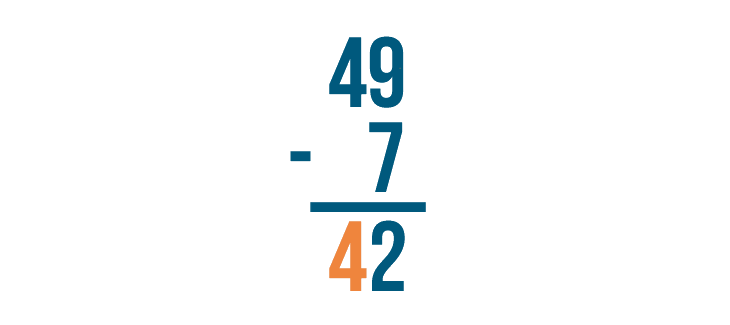
4 minus nothing is 4 , so we'll write 4 beneath the line.
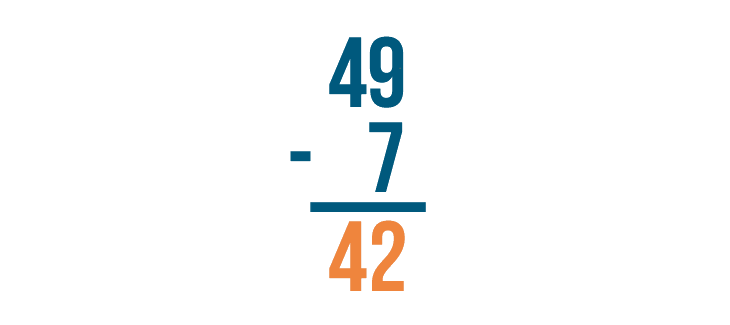
Our result is 42 . 49 - 7 = 42 .

Let's see how this works with another problem: 88 - 62 .
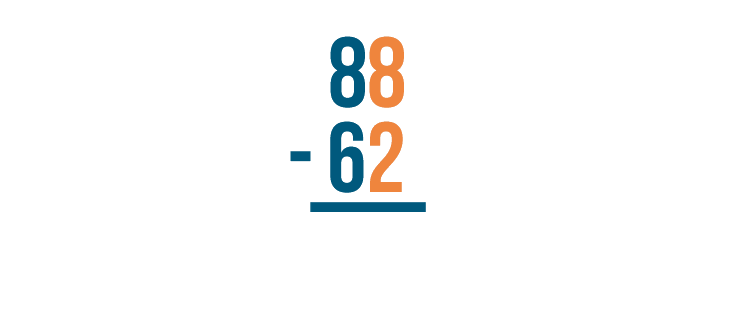
As always, start with the digits that are farthest to the right. Here, they are 8 and 2 .
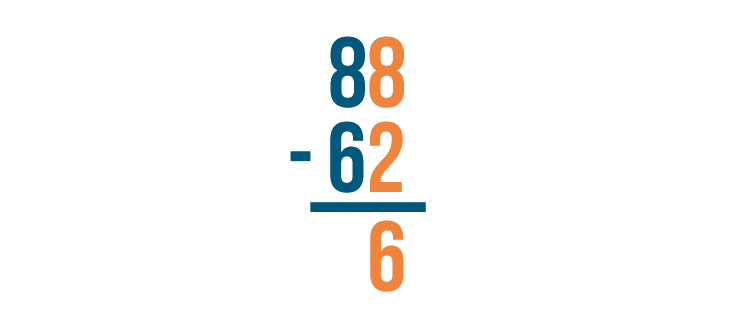
8 - 2 = 6 . Make sure to write 6 below the line.
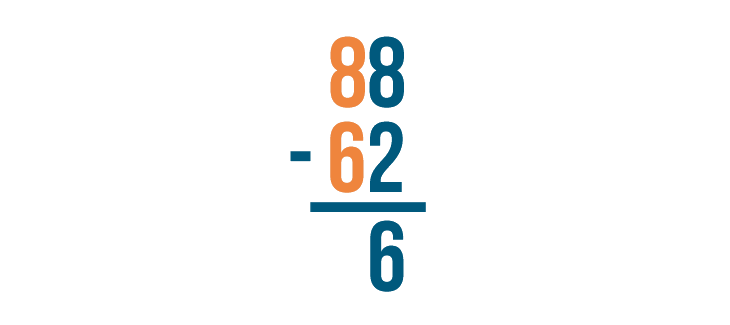
Next, find the difference of the digits to the left, 8 and 6 .
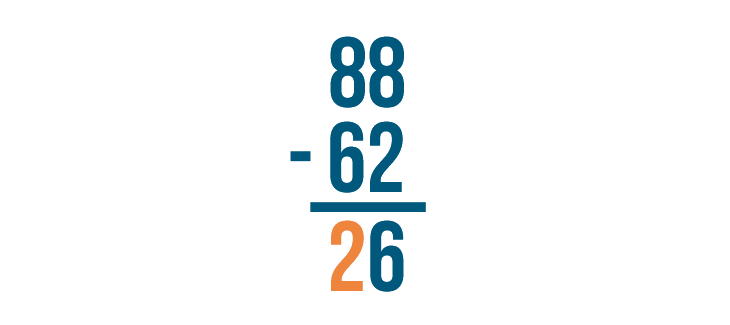
8 - 6 is 2 . Write 2 below the line.

The answer is 26 . 88 - 62 = 26 .
In the slideshow, you saw that stacked subtraction problems are always solved from right to left . The expressions below are solved the same way. First, the bottom right digit is subtracted from the top right digit. Then, the bottom left digit is subtracted from the top left digit.
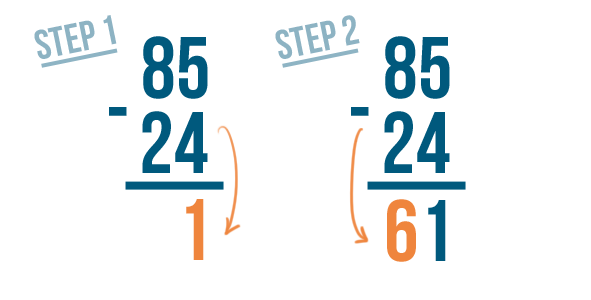
Stack these subtraction problems and solve them. Then, check your answer by typing it into the box.
Subtracting Larger Numbers
Stacked subtraction can also be used for finding the difference of larger numbers. No matter how many digits there are, you subtract the same way every time — from right to left.
These subtraction problems have larger numbers. Solve them, and then check your answer by typing it into the box.
Sometimes when you subtract, you will notice that the top digit is smaller than the bottom. For example, take a look at this problem:

Normally, we'd start on the right with 5 - 9. However, since 9 is bigger than 5, we can't subtract normally. Instead, we have to use a technique called borrowing .
Let's see how it works.

First, we'll make sure the expression is set up correctly. The larger number is stacked on top of the smaller number.
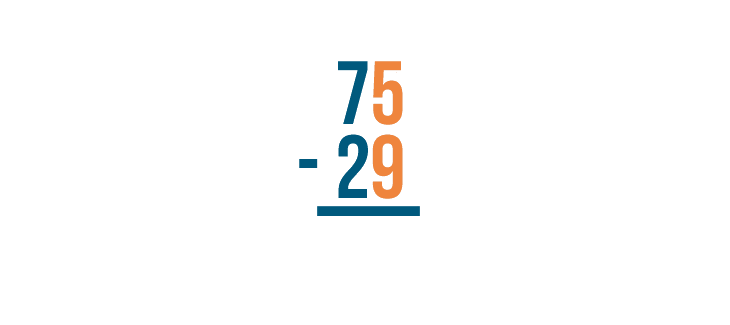
As with all stacked subtraction problems, begin with the digits farthest to the right. Here, they are 5 and 9 .
5 is smaller than 9 , so we'll need to borrow to make 5 larger.
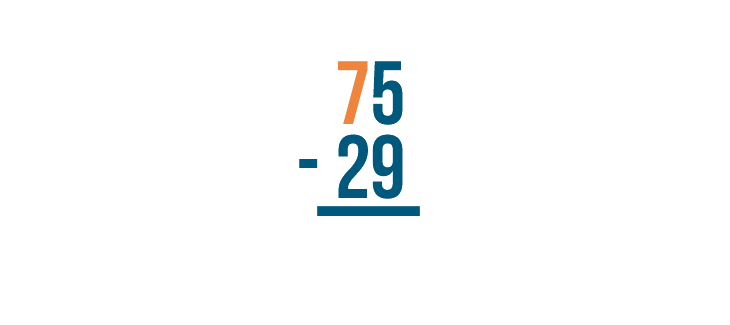
We'll borrow from the digit to the left of 5 . Here, it's 7 . We'll take 1 from it....
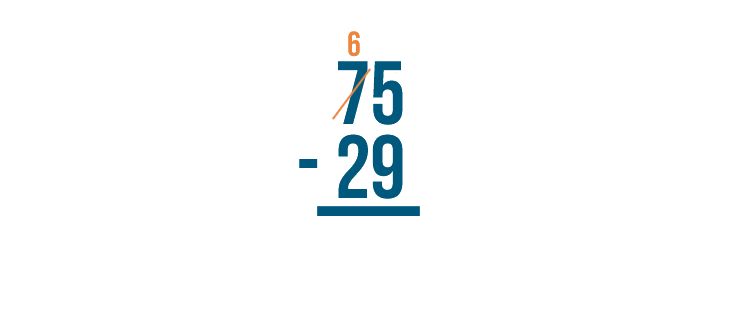
7 - 1 = 6 . To help us remember that we subtracted 1, we'll cross out the 7 and write 6 above it.

Then, we'll place the 1 we took next to the 5 ...
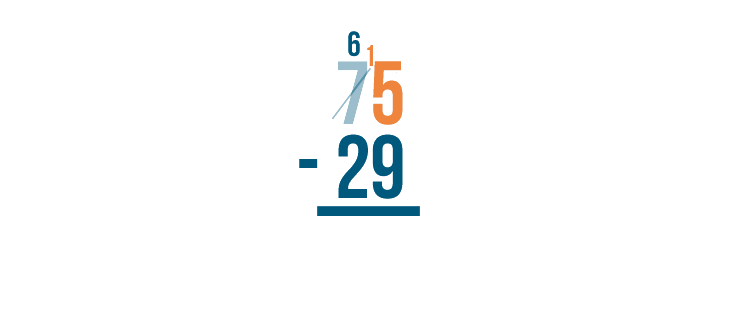
5 becomes 15 . See how it looks like 15?
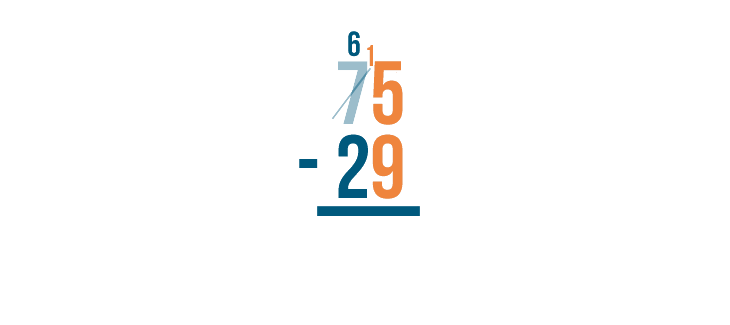
15 is larger than 9, which means we can subtract. We'll solve for 15 - 9 .
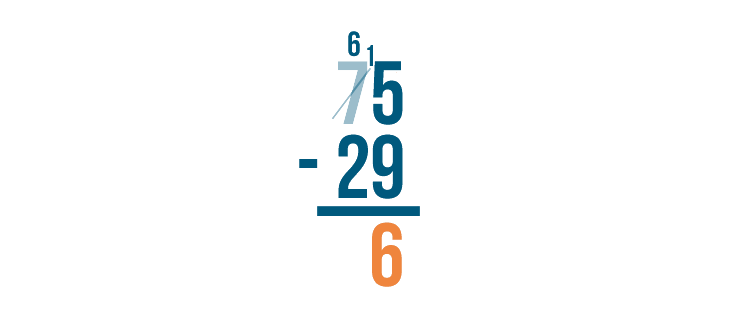
15 - 9 = 6 . We'll write 6 beneath the line.
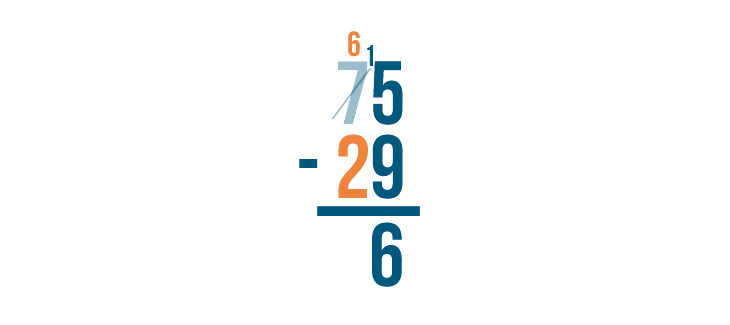
Next, find the difference of the digits to the left: 6 - 2 .
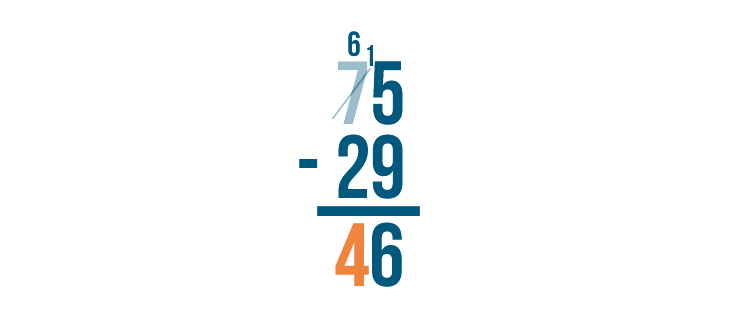
6 - 2 = 4 . We'll write 4 beneath the line.
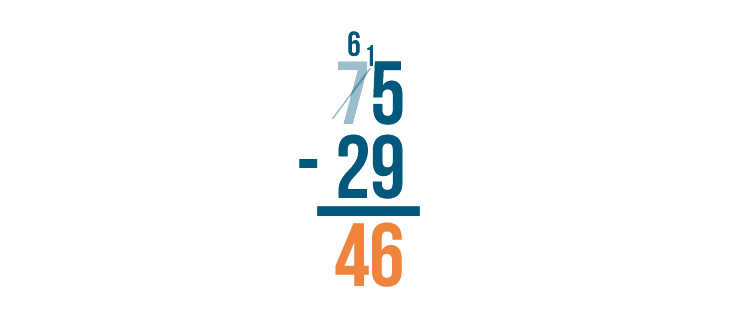
Our answer is 46 . 75 - 29 = 46 .
As you borrow, always cross out the digit you borrow from and write the new value above it. Remember to always place the 1 next to the smaller digit.
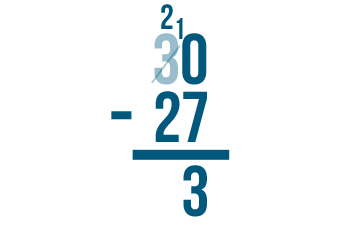
Try these problems to practice borrowing. Check your answer by typing it into the box.
Borrowing More Than Once
Sometimes the top number might have two or more digits that are smaller than the digits beneath them. In that case, you'll need to borrow more than once. It will always work the same way. You'll always subtract 1 from the digit to the left and place 1 next to the smaller digit.
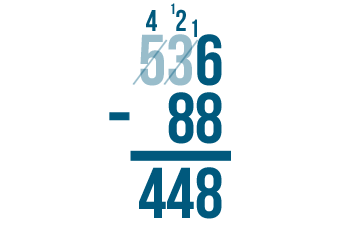
In some cases, you might notice that the number to the left is zero. Check out the slideshow below to see an example of what to do.
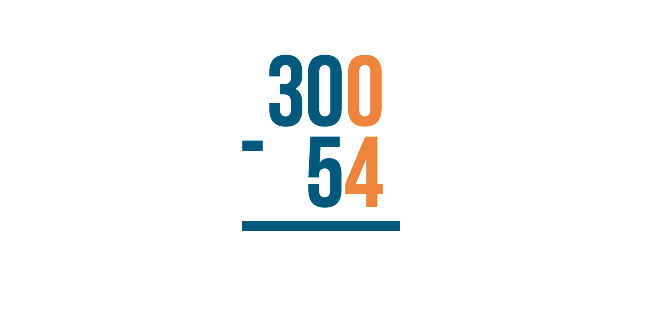
Let's look at the example 300 minus 54. We would begin on the right with 0 minus 4 . However, zero is smaller than 4, so we would need to borrow from the next digit to the left.
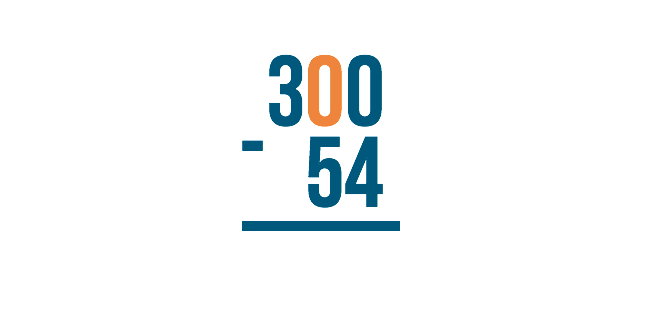
The next digit to the left, however, is zero ! We can't borrow if nothing is there. So what do we do?
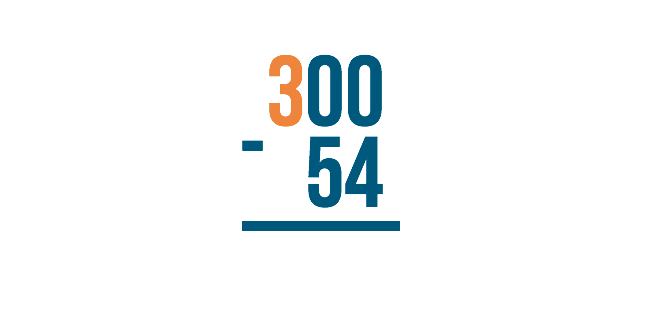
We have to go to the next digit to the left. Think of it like asking your neighbor for a cup of sugar. If the first neighbor doesn't have any, you would move to the next neighbor over to ask for some to borrow.
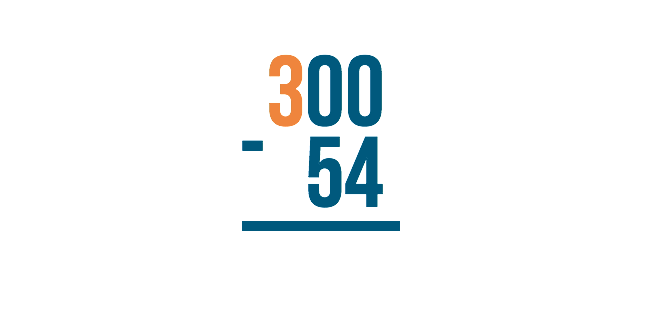
Since the next number over is 3 , we'll borrow from that.
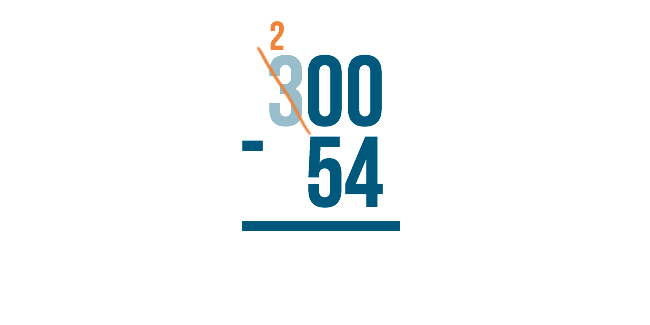
Just like when we borrow normally, we'll subtract 1 from 3 to make it 2 . We'll place the 1 next to the number on the right to make it 10 .

Remember though, we originally needed to borrow in order to do 0 minus 4 . Now that we have 10 in the middle, we can borrow from it.
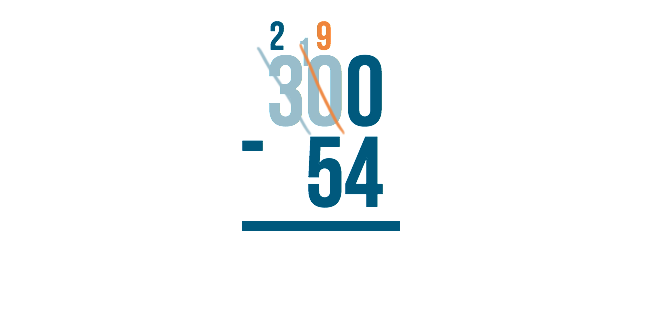
Cross out the 10 and subtract 1 to make it 9 .

Then, place the 1 next to the 0 in order to make it 10 . Now you're ready to subtract.
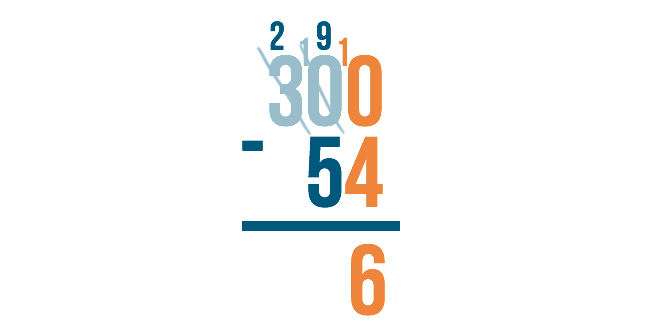
10 minus 4 is 6.
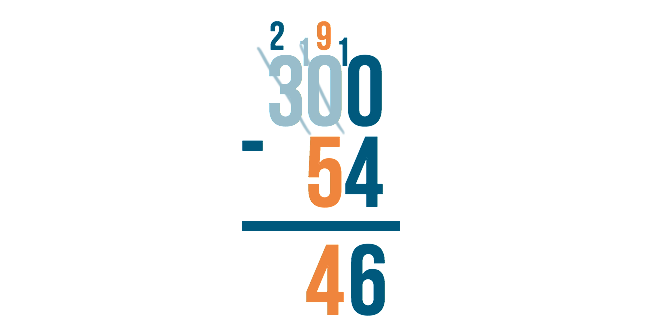
9 minus 5 is 4.
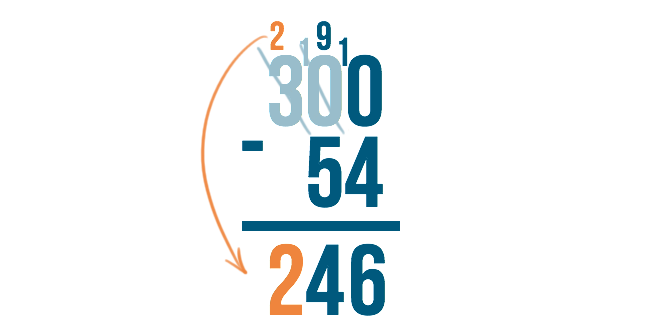
There is nothing to subtract from the 2, so we just bring it down, and we're finished!
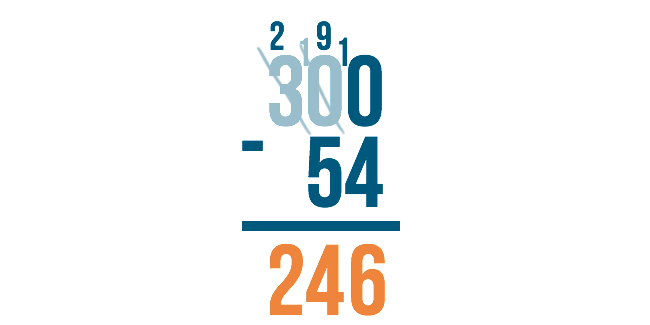
The answer is 246 .

Try solving these subtraction problems to practice borrowing more than one time. Check your answer by typing it in the box.
Checking Your Work
In the last few lessons, you learned how to solve addition and subtraction problems. As you practice these math skills, it's a good idea to get into the habit of checking your work . Checking will help you know if your answers are correct. When you're ready to check the answer to subtraction problems, you'll need to use addition.
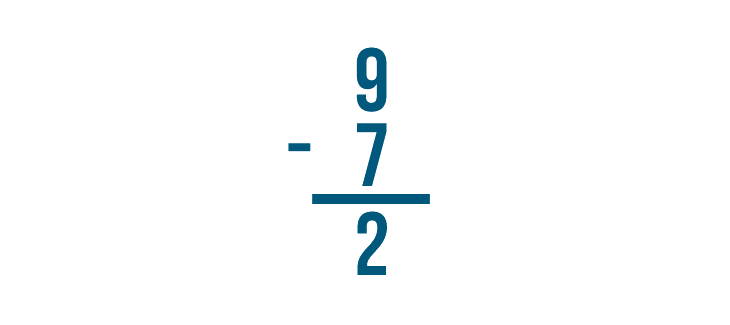
Let's look at this problem: 9 - 7 = 2 .
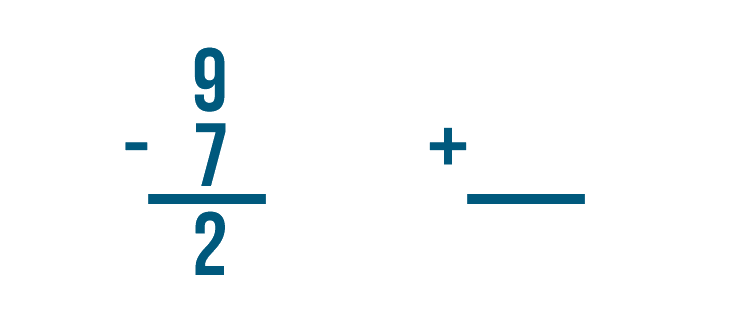
How do we know that 2 is the correct answer? We can check by adding.
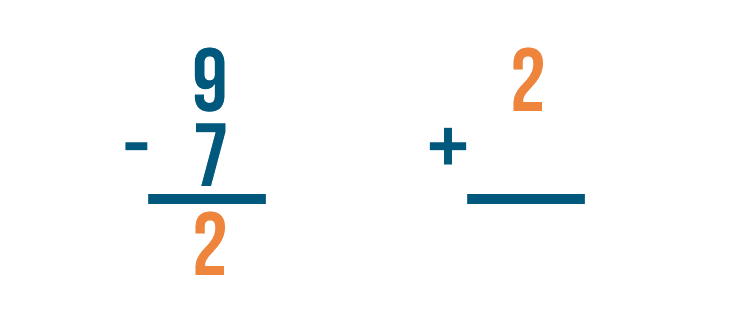
Let's set up our addition problem. First, we'll write the subtraction problem's answer. That means we'll write 2 .
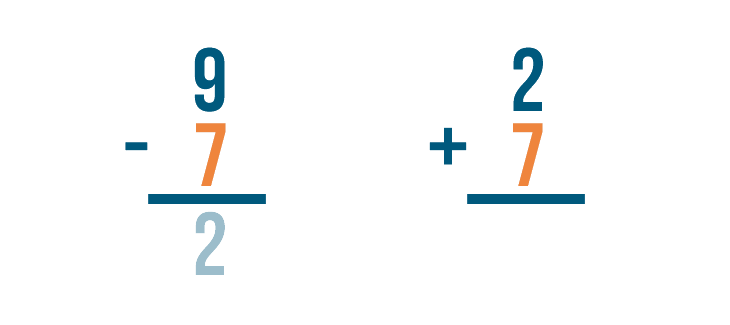
Next, we'll add the amount that was subtracted, 7 .
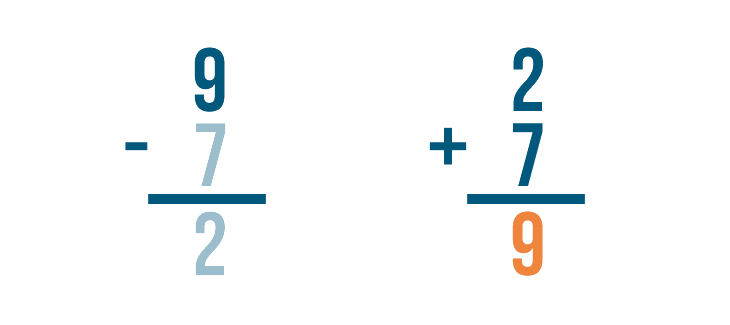
Time to add. 2 + 7 = 9 .
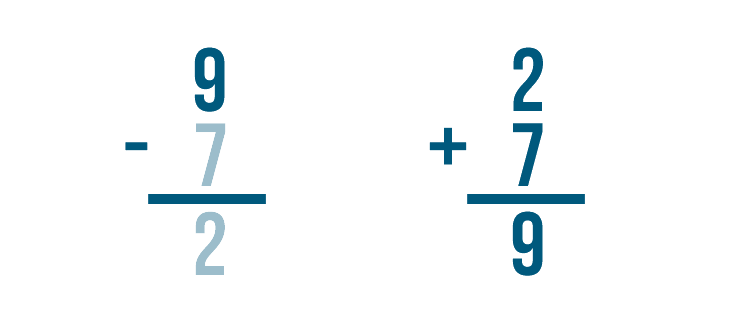
If we subtracted correctly, the answer will match the larger number in our subtraction problem.
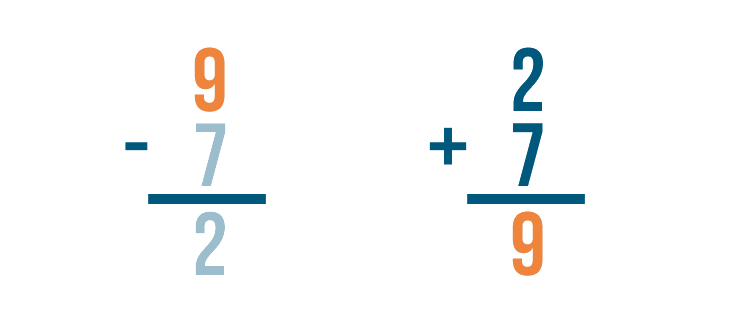
They match — 9 and 9 . Our answer was correct.
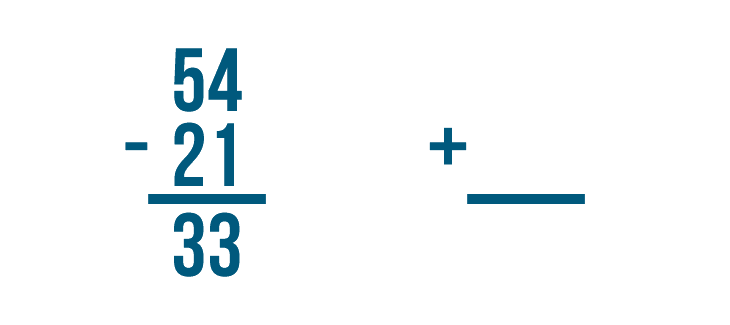
Let's try using addition to check the answer to another subtraction problem: 54 - 21 = 33 .
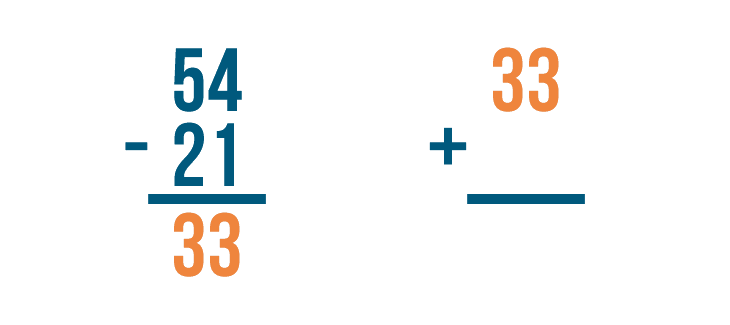
Let's set up our addition problem. First write the answer to the subtraction problem, 33 .
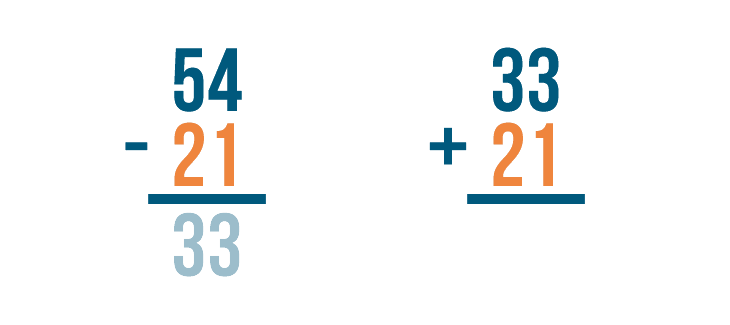
Then add back the number that was subtracted, 21 .
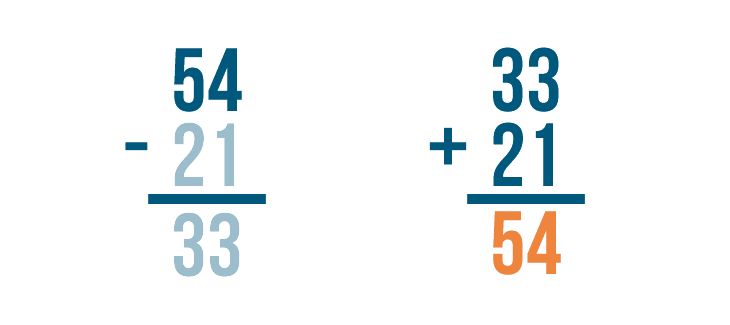
Now it's time to add. 33 + 21 = 54 .
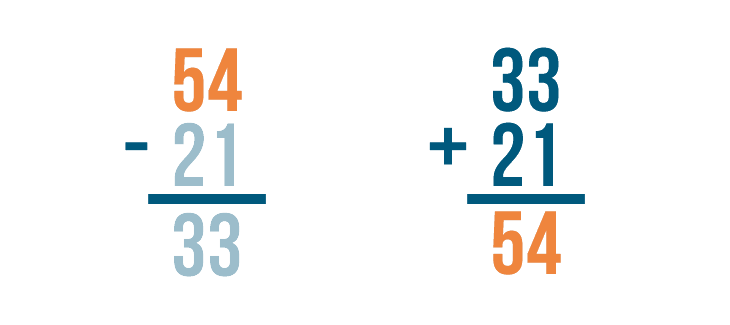
Finally, we'll check to see if 54 matches the larger number in our subtraction problem. It does!
Practice subtracting these problems. You'll have to use borrowing to solve some of the problems. There are 4 sets of problems with 3 problems each.
/en/additionsubtraction/video-subtraction/content/
Subtraction With Regrouping
Solve more complex subtraction problems with regrouping, also known as borrowing or carrying!

Author Taylor Hartley

Expert Reviewer Jill Padfield
Published: August 24, 2023

- Key takeaways
- Subtraction with regrouping is a key building block for learning mathematics – It allows you to solve double and triple digit subtraction problems.
- It’s important to learn subtraction with regrouping – That way, you can better understand and solve complex word problems.
- Subtraction with regrouping is also referred to as borrowing or carrying – It’s a skill you’ll need for higher level math.
Table of contents
What is subtraction with regrouping?
Important terms to know, how to subtract with regrouping, in 5 easy steps, let’s practice together, practice problems.
Subtraction is one of the most important building blocks for learning more complicated math problems. Subtracting 8 from 10 gives us 2, which is pretty easy to follow, but what happens when we need to solve multi-digit subtraction problems?
To prepare for more involved subtraction problems, we can use a handy skill called regrouping. Subtraction with regrouping lets you tackle problems where the number you must subtract from is smaller than the number you are subtracting.
We know that sounds confusing right now, but once we work through a few examples together, you’ll get the hang of it in no time.
Subtraction with regrouping, also called borrowing or carrying, is used to solve subtraction problems where the equation is written vertically This might look something like:

See how, in the top number, the 8 in the 1s place is smaller than the 9 in the 1s place in the bottom number? This means we can’t subtract…unless we use regrouping!
Let’s look at some terms that will help us better understand this skill.
These terms are going to be an important part of understanding regrouping, so pay close attention. We’ll be discussing three different terms: subtrahends, minuends, and differences.
- Subtrahend – The number we subtract from the minuend.
- Minuend – The number we’re subtracting another number from.
- Difference – The end value of subtracting the subtrahend from the minuend.
These terms will appear in the following format every time you subtract:
Minuend – Subtrahend = Difference
For example, let’s take a look at this subtraction equation: 14 – 5 = 9
In this instance, the minuend would be 14 , the subtrahend would be 5 , and the difference would be 9 .
Now, let’s walk through the basic steps of how to use regrouping when we are subtracting. This involves setting up our subtraction equation using the column method.
After we do that, we will identify which numbers are in which place values, then finish with our borrowing/carrying. Once we’ve borrowed from the tens place and carried to the ones, it’ll make it much easier to subtract.
Let’s take a look at the following problem:
23 – 8 = 15
1. Place the numbers you are subtracting vertically
First, we need to set up our equation in vertical form. This will make it easier for us to borrow our numbers and show our work in the process. Just write the 8 write under your 23, but make sure the 8 falls right under the 3 within the ones place.
It should look like this:
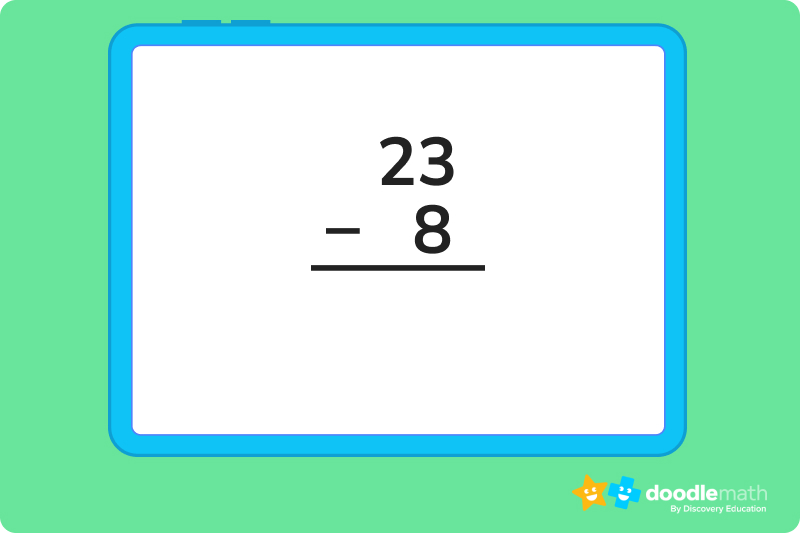
2. Read the problem and look at the different place values
Now, let’s identify which numbers are in which place values. This will be important for knowing which number to borrow from within the minuend, and where it should be carried.
You should always be borrowing from the tens place, and carrying to the ones. For our minuend 23, 2 is in the tens place and 3 is in the ones.
3. Since we can’t subtract 8 from 3, borrow 1 from the tens column
Here is the most important step of this process. Now, we just have to borrow one from the tens column and carry it into the ones. We will always only borrow 1 from the tens column, remember that!
So the equation becomes:

4. Now, do your subtraction, first on the ones side
Now that we’ve taken 1 away from the tens column, we only have 1 left in the tens column. However, we can write that same 1 right next to the three in the ones column, making 13.
5. Then, subtract from the tens side
Now, we’re ready to do our subtraction. Since we turned the three in the ones column into a thirteen in the step before, we can subtract 8 from 13 instead of 8 from 3!
13 minus 8 equals 5, and the 1 left over in the tens column has no subtrahend, so it stays the same. That means we have a 1 in the tens column and a 5 in the ones column, giving us a difference of 15.
Here’s three practice problems we can work through together to make sure you have the basics down.
1. Write 24 – 5 as a vertical equation
a. We know that the minuend is 24, and the subtrahend is 5, which means 24 goes on the top of the equation with 5 on the bottom.
b. We also know that both 4 and 5 are in the ones place, meaning they should be placed in the same column.
c. Now, we’re ready to write our finished equation:
2. Simon got 35 toy cars for his birthday this year. His brother Charles also loves toy cars, so Simon decides to give Charles 6 cars as a present. How many cars is Simon left with?
a. Let’s start by identifying our minuend and subtrahend. The number we’re subtracting from is 35, and the number being subtracted is 6.
b. That means we’ll need to set up our column method with 35 on the top, and 6 right below it.
c. We also know that both 5 and 6 are in the ones place, meaning they should be put in the same column. The setup for our vertical equation should look like this:
d. Now that we have our equation, we can do our regrouping. First, we’ll borrow the one from the tens column of the 35, and carry it into the ones column.
e. That means we subtract 1 from the 3, leaving a two in the tens column. We write that one next to the 5 in the ones column, giving us a 15.
f. Now we can subtract 6 from 15 much easier, giving us a difference of 9 in the ones column. And since we aren’t subtracting anything from the 2, we can place that 2 in the tens column, giving us a total difference of 29.
3. Robert has 21 marbles in his box. His sister Margaret decides to take 3 marbles for herself. How many marbles is Robert left with?
a. Here, we’ll need to set up our vertical equation with 21 on the top, and 3 on the bottom. 21 is the minuend, here, and 3 is the subtrahend. It should look like the following:
b. Since we’ve lined up the 3 and the 1 in the ones place, we’re ready to regroup. We’ll borrow a 1 from the tens place, and carry it into the ones, leaving a one leftover in the tens place, and an 11 in the ones.
c. Now we can subtract 3 from 11 in the ones column, giving us 8, and drag the 1 in the tens place down to form a difference of 18.
Ready to give it a go?
Now it’s time for you to give a few of these problems a shot on your own. Feel free to consult the explanations, definitions, and practice problems above if you get confused or stumped on a question. And remember, practice makes perfect, so don’t get discouraged. Keep working through these problems and we promise you’ll get the hang of regrouping in no time!
Click to reveal the answer.
The answer is 8 .
The answer is 18 .
The answer is 14 .
Parent Guide
How did we get here?
- We’ve identified that the minuend is 13, while the subtrahend is 7.
- That means we can set up our vertical equation with the minuend (13) on top, and the subtrahend (7) on the bottom.
- We also know that both 3 and 7 are in the ones place, so they should be in the same column within our equation. This gives us the vertical equation written above.
- First, we need to identify that the 3 and the 5 are in the ones place, so we’ll be subtracting 5 from 3 in this equation.
- 5 is greater than 3, so we know we’ll need to borrow a one from the tens column so we can actually subtract.
- So, we borrow a 1 from the tens column and place it next to the 3 in the ones column, making thirteen. Since we’ve technically subtracted 1 from the tens column, the two there becomes a one.
- Now, we can subtract in the ones column. 13 – 5 = 8.
- The tens column is left as 1 – 1, which gives us a difference of 0. That means the total difference for this problem is 8.
- First, we identify the minuend and the subtrahend so that we know which number to place on top, and which number to put on the bottom.
- Since we’re subtracting 17 cups away from the 45 already in the cabinet, we know that the minuend is 45 and the subtrahend is 17.
- We also need to identify which numbers are in which places. Both 4 and 1 are in the tens place, and 5 and 7 are in the ones, so these numbers should be in the same respective columns.
- We’re now ready to write our formula.
How did we get here?
- Here, we know that the minuend is 32 and the subtrahend is 14, since we are taking away 14 pencils from the total of 32.
- That means we can set up the following vertical equation: 32 -14
- Since the 4 in the ones column is bigger than the 2, we know we’ll need to regroup. Now, we’ll borrow a one from the tens column and carry it to the ones, giving us a 12 to subtract the four from.
- The 3 in the ones column loses the 1 we borrowed, decreasing it to 2.
- Now, we can subtract the 1 from the 2 in the tens column, and the 4 from the 12 in the ones column.
- 2 – 1 = 1, and 12 – 4 = 8. We now write the 1 in the tens and the 8 in the ones, giving us a difference of 18.
- The minuend for this problem is 22, and the subtrahend is 8. That means the 22 goes on top, and the 8 goes underneath it for our vertical equation.
- Since the 2 and the 8 are both in the ones column, we know we’ll have to borrow from the tens column, since 8 is greater than 2.
- That means we borrow a one, leaving a 1 leftover in the tens column, and carry it to the ones column, giving us a 12.
- Now we can solve 12 – 8, giving us 4. We aren’t subtracting anything from the 1 in the minuend since the subtrahend has no value in the tens column. We can simply write the 1 next to our 4 for a solved difference of 14.
Sign up for the DoodleMath app today!
Turn math into an adventure when you sign up for DoodleMath.
Click here to get started for free!
FAQs about math strategies for kids
We understand that diving into new information can sometimes be overwhelming, and questions often arise. That’s why we’ve meticulously crafted these FAQs, based on real questions from students and parents. We’ve got you covered!
If you know how to do subtraction with regrouping – also known as borrowing or carrying – then you will be able to subtract any number from any other number.
This will help you as you progress from more basic level mathematics to more complicated mathematics!
Look at the number in the 10s place as being the number of 10s that exist in the number itself.
So, let’s say we have the number 24. To make the number 20, you need two 10s, right? That’s why there is a 2 in the 10s place!
Negative numbers do exist! When you’re subtracting a large number from a smaller number, you will get a negative answer. For example, 13 – 17 = -4, right?
But, when we use subtraction with regrouping, we are almost always subtracting a smaller number from a larger number. For example, in 13 – 4, 13 is still larger than 4. The issue is that, when you stack these numbers vertically, 3 is smaller than 4, so we need to borrow to make it easier to calculate.
When we borrow from the 10s column, the 3 becomes 13, and 13 – 4 is 9 .

Related Posts
Helpful description
Lesson credits
Taylor Hartley
Taylor Hartley is an author and an English teacher based in Charlotte, North Carolina. When she's not writing, you can find her on the rowing machine or lost in a good novel.

Parents, sign up for a DoodleMath subscription and see your child become a math wizard!
What we offer
Quick links
All rights reserved.

Are you a parent, teacher or student?
Get started for free!

Maths information pack
We ask for your contact info so we can send our info pack directly to your inbox for your convenience, exam prep information pack, case studies information pack.
Book a chat with our team

I’m new to Doodle

My school is already using Doodle

Information pack
We ask for your contact info so that our education consultants can get in touch with you and let you know a bit more about doodle., student login, which programme would you like to use.
DoodleMaths
DoodleTables
DoodleEnglish
DoodleSpell
If you’d like to use Doodle’s browser version, please visit this page on a desktop.
To log in to Doodle on this device, you can do so through our apps. You can find out how to download them here:
- Administrator
- Teacher How To's
- How It works
- All Worksheets
- Math Worksheets
- ELA Worksheets
Subtraction Activities
Teach your child all about subtraction with amazing educational resources for children. These online subtraction learning resources break down the topic into smaller parts for better conceptual understanding and grasp. Get started now to make subtraction practice a smooth, easy and fun process for your child!

CONTENT TYPE
- Lesson Plans
- Math (8,010)
- Number Sense (1,465)
- Number Recognition (515)
- Number Recognition Within 3 (82)
- Number Recognition Within 5 (75)
- Number Recognition Within 10 (146)
- Number Recognition Within 20 (216)
- Number Sequence (86)
- Number Sequence Within 3 (6)
- Number Sequence Within 5 (15)
- Number Sequence Within 10 (28)
- Number Sequence Within 20 (15)
- Number Sequence Within 50 (5)
- Number Sequence Within 100 (5)
- Number Sequence Within 120 (4)
- Backward Sequence from 20 (10)
- Counting (330)
- Counting Objects Within 3 (13)
- Counting Objects Within 5 (54)
- Counting Objects Within 10 (86)
- Counting Objects Within 20 (13)
- Writing Numbers (470)
- Writing Numbers Within 3 (70)
- Writing Numbers Within 5 (65)
- Writing Numbers Within 10 (125)
- Writing Numbers Within 20 (210)
- Number Representation (82)
- Represent Numbers Using Place Value Blocks (10)
- Compare and Order Numbers (205)
- Compare Numbers (163)
- Compare Numbers within 10 (45)
- Compare Objects within 10 (16)
- Compare Without Visual Support (10)
- Compare Numbers within 20 (31)
- Compare Numbers Using Place Value Blocks (10)
- Compare Numbers Without Visual Support (10)
- Compare Numbers within 100 (46)
- Use Place Value Blocks to Compare Numbers (10)
- Compare Two 2-Digit Numbers (10)
- Compare 3-Digit Numbers (10)
- Compare Multi-Digit Numbers (10)
- Order Numbers (44)
- Order Numbers within 10 (3)
- Order Numbers within 20 (3)
- Order 3-Digit Numbers (10)
- Order Multi-Digit Numbers (11)
- Skip Counting (37)
- Skip Count by 2 (6)
- Skip Count by 5 (7)
- Skip Count by 10 (18)
- Skip Count by 100 (3)
- Even and Odd Numbers (28)
- Place Value (335)
- Read and Write Numbers (177)
- Numbers up to 10 (55)
- Numbers up to 20 (6)
- Numbers up to 50 (7)
- Numbers up to 100 (17)
- Identify Teen Numbers (12)
- Expanded Form (8)
- 3-Digit Numbers in Expanded Form (6)
- 4-Digit Numbers in Expanded Form (1)
- 5-Digit Numbers in Expanded Form (1)
- Standard Form (11)
- 3-Digit Numbers in Standard Form (6)
- 4-Digit Numbers in Standard Form (4)
- 5-Digit Numbers in Standard Form (1)
- Word Form (3)
- 3-Digit Numbers in Word Form (1)
- 4-Digit Numbers in Word Form (1)
- 5-Digit Numbers in Word Form (1)
- Unit Form (17)
- 3-Digit Numbers in Unit Form (5)
- 4-Digit Numbers in Unit Form (4)
- 5-Digit Numbers in Unit Form (3)
- Place Value Chart (17)
- 3-Digit Numbers on Place Value Chart (14)
- 4-Digit Numbers on Place Value Chart (1)
- 5-Digit Numbers on Place Value Chart (1)
- Round Numbers (47)
- Round Numbers to the Nearest 10 (18)
- Round Numbers to the Nearest 100 (14)
- Addition (1,331)
- Embedded Numbers (13)
- Addition Sentences (64)
- Addition Sentence within 5 (20)
- Addition Sentence within 10 (44)
- Add with Pictures (33)
- Add with Pictures within 5 (22)
- Add with Pictures within 10 (11)
- Model Addition (235)
- Addition Properties (16)
- Commutative Property of Addition (10)
- Add Using Models (18)
- Addition Strategies (500)
- Addition Strategies within 10 (287)
- Count All to Add (21)
- Count All to add within 5 (5)
- Count All to add within 10 (16)
- Count On to Add Strategy (40)
- Add using number line (10)
- Compose and Decompose Numbers (226)
- Number Bonds (197)
- Addition Strategies within 20 (130)
- Anchor 5 and 10 (21)
- Count On Strategy (24)
- Add with 10 (13)
- Make 10 Strategy (20)
- Doubles and Near Doubles Strategy to Add (38)
- Doubles Facts (13)
- Add Three Whole Numbers (18)
- Addition Strategies within 100 (54)
- Add using multiples of 10 (19)
- Addition Strategies within 1000 (36)
- Add using multiples of 100 (25)
- Addition Facts (208)
- Fluently Add within 5 (16)
- Fluently Add within 10 (83)
- Fluently Add within 20 (116)
- Equal Expressions (33)
- Addition Without Regrouping (238)
- Add within 100 without Regrouping (72)
- Add 2-digit number to 1-digit (17)
- Add 2-digit number to 2-digit (54)
- Add within 1000 without Regrouping (124)
- Add 10 to 3-digit numbers (15)
- Add 100 to 3-digit numbers (16)
- Add 3-digit number to 1-digit (16)
- Add 3-digit number to 2-digit (24)
- Add two 3-digit numbers (44)
- Add within 10000 without Regrouping (42)
- Addition With Regrouping (152)
- Add within 100 with Regrouping (51)
- Regroup and add 2-digit number to 1-digit (17)
- Regroup and add 2-digit numbers (17)
- Add within 1000 with Regrouping (57)
- Regroup ones and add (13)
- Regroup ones and tens and add (13)
- Regroup tens and add (3)
- Add within 10000 with Regrouping (44)
- Multi-digit Addition (108)
- Addition within 100000 (53)
- Addition within 1000000 (53)
- Subtraction (943)
- Subtraction Sentences (52)
- Subtraction Sentences within 5 (19)
- Subtraction Sentences within 10 (32)
- Subtract with Pictures (52)
- Subtract with Pictures within 5 (33)
- Subtract with Pictures within 10 (19)
- Model Subtraction (49)
- Subtract using Models (14)
- Subtraction Strategies (172)
- Subtraction Strategies within 10 (32)
- Count Back Strategy within 10 (25)
- Relate Addition and Subtraction within 10 (6)
- Subtraction Strategies within 20 (84)
- Count Back Strategy within 20 (44)
- Subtract using number line (10)
- Relate Addition and Subtraction within 20 (13)
- Doubles and Near Doubles Strategy to Subtract (4)
- Subtract from 10 Strategy (12)
- Subtraction Strategies within 100 (36)
- Subtract using multiples of 10 (20)
- Subtraction Strategies within 1000 (22)
- Subtract using multiples of 100 (11)
- Subtraction Facts (198)
- Fluently Subtract within 5 (17)
- Fluently Subtract within 10 (82)
- Fluently Subtract within 20 (110)
- Equal Expressions in Subtraction (28)
- Subtraction Without Regrouping (227)
- Subtract within 100 without Regrouping (83)
- Subtract Multiples of 10 (19)
- Subtract within 1000 without Regrouping (104)
- Subtract within 10000 without Regrouping (40)
- Subtraction With Regrouping (137)
- Subtract within 100 with Regrouping (49)
- Subtract within 1000 with Regrouping (52)
- Subtract across Zeros (5)
- Subtract within 10000 with Regrouping (36)
- Multi-digit Subtraction (110)
- Subtraction within 100000 (56)
- Subtraction within 1000000 (52)
- Multiplication (670)
- Arrays (23)
- Equal Groups (26)
- Multiplication Sentences (53)
- Repeated Addition to Multiply (18)
- Multiplication on Number Line (6)
- Multi-digit Multiplication (162)
- Multiply 2-digit by 1-digit Numbers (35)
- Multiply 2-digit by 2-digit numbers (55)
- Multiply 3-digit by 1-digit Numbers (18)
- Multiply 3-digit by 2-digit numbers (25)
- Multiply 4-digit by 1-digit Numbers (17)
- Multiplication Properties (105)
- Associative Property (12)
- Commutative Property (14)
- Distributive Property (61)
- Multiply by 0 and 1 (13)
- Estimate Products (12)
- Multiply by multiples of 10 (27)
- Times Tables (206)
- Multiplication Facts (193)
- Multiplication Facts of 2 (19)
- Multiplication Facts of 3 (19)
- Multiplication Facts of 4 (19)
- Multiplication Facts of 5 (19)
- Multiplication Facts of 6 (19)
- Multiplication Facts of 7 (18)
- Multiplication Facts of 8 (18)
- Multiplication Facts of 9 (19)
- Multiplication Facts of 10 (17)
- Multiply by 11 (15)
- Multiply by 12 (15)
- Division (383)
- Division Facts (138)
- Division Facts of 2 (15)
- Division Facts of 3 (17)
- Division Facts of 4 (17)
- Division Facts of 5 (15)
- Division Facts of 6 (18)
- Division Facts of 7 (15)
- Division Facts of 8 (16)
- Division Facts of 9 (15)
- Division Facts of 10 (14)
- Divide on a Number Line (13)
- Long Division (116)
- Divide 2-digit by 1-digit Numbers (21)
- Divide 3-digit by 1-digit Numbers (19)
- Divide 4-digit by 1-digit Numbers (15)
- Divide Multiples of 10 or 100 (20)
- Estimate Quotients (29)
- Fractions (609)
- Identify Fractions (54)
- Identify fractions using models (18)
- Identify fractions on the number line (17)
- Represent Fractions (44)
- Represent fractions on the number line (10)
- Mark fractions on the number line (10)
- Represent fractions using models (10)
- Represent fractions using real-word objects (10)
- Represent Mixed Numbers (10)
- Represent mixed numbers using models (10)
- Compare Fractions (65)
- Compare fractions using visual models (13)
- Compare fractions using number lines (14)
- Compare fractions without visual models (11)
- Benchmark Fractions (16)
- Order Fractions (20)
- Order fractions using visual models (10)
- Order fractions without visual models (10)
- Equivalent Fractions (52)
- Equivalent fractions using models (10)
- Equivalent fractions using number lines (10)
- Equivalent fractions without visual models (15)
- Identify equivalent fractions (10)
- Convert Fractions (35)
- Fractions as Mixed Numbers (10)
- Mixed Numbers as Fractions (25)
- Fractions Operations (324)
- Add and Subtract Fractions (110)
- Add Fractions (57)
- Represent Fraction Addition (9)
- Add fractions using models (12)
- Add like fractions (12)
- Add unlike fractions (10)
- Estimate fraction sums (13)
- Subtract Fractions (39)
- Represent Fraction Subtraction (9)
- Subtract fractions using models (9)
- Subtract like fractions (12)
- Subtract unlike fractions (10)
- Add and Subtract mixed numbers (81)
- Add mixed numbers (40)
- Add mixed numbers using models (10)
- Add a mixed number to a fraction (12)
- Add two mixed numbers (11)
- Subtract mixed numbers (41)
- Subtract mixed numbers using models (10)
- Subtract a fraction from a mixed number (14)
- Subtract two mixed numbers (10)
- Multiply Fractions (122)
- Multiply fractions by whole numbers (14)
- Multiply fractions by whole numbers without models (10)
- Multiply two fractions (20)
- Multiply fractions using models (10)
- Multiply fractions without models (10)
- Multiply mixed numbers (32)
- Multiply mixed numbers by whole numbers (10)
- Multiply mixed numbers by fractions (10)
- Multiply two mixed numbers (10)
- Fraction multiplication as scaling (10)
- Divide fractions (8)
- Decimals (1,729)
- Identify tenths (7)
- Identify hundredths (8)
- Represent Decimals (32)
- Represent Decimals Using Models (18)
- Represent Decimals on Number Lines (14)
- Read and Write Decimals (42)
- Decimals Expanded Form (20)
- Compose Decimals (10)
- Decompose Decimals (10)
- Decimals Standard Form (11)
- Decimals Word Form (10)
- Decimal Place Value (34)
- Digits at the given decimal place (10)
- Place values of digits in decimals (10)
- Compare and Order Decimals (76)
- Compare decimals (45)
- Compare decimals using models (20)
- Compare using decimal grids (10)
- Compare using decimal number lines (10)
- Compare decimals using place value (10)
- Order decimals (31)
- Order decimals using place value (10)
- Round Decimals (42)
- Round decimals to the nearest whole (12)
- Round decimals to the nearest tenths (10)
- Round decimals to the nearest hundredths (10)
- Convert Between Decimals and Fractions (7)
- Convert Decimals to Fractions (7)
- Equivalent Decimals (27)
- Tenths to hundredths (9)
- Hundredths to tenths (8)
- Decimal Operations (1,459)
- Add Decimals (699)
- Add tenths and hundredths (360)
- Add decimals without regrouping (194)
- Add decimals with regrouping (188)
- Subtract Decimals (705)
- Subtract decimals without regrouping (194)
- Subtract decimals with regrouping (184)
- Multiply Decimals (237)
- Multiply decimals by powers of 10 (83)
- Multiply decimals by whole numbers (128)
- Multiply decimals by decimals (72)
- Divide Decimals (161)
- Divide decimals by powers of 10 (20)
- Divide decimals by whole numbers (41)
- Divide whole numbers by decimals (45)
- Divide decimals by decimals (41)
- Types of Decimals (12)
- Geometry (292)
- Parallel lines (5)
- Angles (15)
- Positional Words (15)
- Sides and Corners (12)
- Corners (11)
- Shapes (200)
- 2d Shapes (162)
- Identify Quadrilaterals (24)
- Trapezoids (10)
- Identify triangles (14)
- Identify polygons (10)
- Attributes of 2D shapes (20)
- Sort 2D shapes (14)
- Partition 2D Shapes (28)
- Partition into equal parts (24)
- Halves, Thirds, and Fourths (18)
- 3d Shapes (20)
- Flat and Solid Shapes (23)
- Match 2D Shapes (9)
- Match 3D Shapes (10)
- 3D Shapes in real life (10)
- Coordinate Planes (28)
- Identify Points on the Coordinate Plane (10)
- Plot on the Coordinate Plane (11)
- Measurement (282)
- Capacity (22)
- Comparing Measurements (53)
- Compare Weights (13)
- Group of Objects (4)
- Compare Lengths (24)
- Compare Heights (14)
- Conversion of Measurement Units (16)
- Data Handling (73)
- Organize and Interpret Data (57)
- Organize data in bar graphs (7)
- Organize data in line plots (6)
- Organize data in picture graphs (4)
- Interpret data in bar graphs (5)
- Interpret data in line plots (7)
- Interpret data in picture graphs (6)
- Sort Objects (11)
- Length (39)
- Measure Lengths (19)
- Measure Lengths using the ruler (17)
- Estimate Lengths (4)
- Area of Shapes (18)
- Area of 2D Shapes (5)
- Area as Additive (5)
- Perimeter (19)
- Perimeter of Shapes (19)
- AM and PM (12)
- Analog Clock (32)
- Hour hand (12)
- Set time (10)
- Digital Clock (9)
- Elapsed Time (3)
- Time in Half Hours (19)
- Time in Hours (17)
- Time in Quarter Hours (19)
- Time to the Nearest 5 Minutes (21)
- Time to the Nearest Minute (2)
- Money (128)
- Identify Coins (20)
- Value of the Coins (10)
- Make Amounts (10)
- Counting Money (103)
- Compare Money (15)
- Count Money with Coins (37)
- Penny, Nickel, and Dime (20)
- Quarters and Half Dollar (9)
- Operations With Money (24)
- Add and Subtract Money (12)
- Multiply and Divide Money (7)
- Algebra (146)
- Patterns (35)
- Number Patterns (35)
- Extend Number Patterns (10)
- Generate Number Patterns (10)
- Relationship Between Patterns (10)
- Numerical Expressions (41)
- Interpret Numerical Expressions (10)
- Evaluate Numerical Expressions (21)
- Evaluate Exponents (10)
- Order of Operations (10)
- Factors and Multiples (51)
- Factors (30)
- Multiples (14)
- Prime and Composite Numbers (15)
- Word Problems (705)
- Addition and Subtraction Word Problems (396)
- Addition Word Problems (174)
- Addition Word Problems within 10 (29)
- Addition Word Problems within 20 (28)
- Addition Word Problems within 100 (44)
- Add to Compare Word Problems (21)
- Subtraction Word Problems (112)
- Subtraction Word Problems within 10 (17)
- Subtraction Word Problems within 20 (14)
- Subtraction Word Problems within 100 (28)
- Subtract to Compare Word Problems (16)
- Decimal Subtraction Word Problems (25)
- Multiplication and Division Word Problems (180)
- Multiplication Word Problems (104)
- Division Word Problems (73)
- Fraction Word Problems (34)
- Multi-step Word Problems (81)
- Money Word Problems (10)
- ELA (7,781)
- Reading (5,206)
- Phonics (4,916)
- Bossy R (27)
- Words with AR (10)
- Words with ER (8)
- Words With IR (8)
- Words with OR (7)
- Words with UR (8)
- Diphthongs (28)
- Words with OI (11)
- Words with OU (11)
- Words with OW (11)
- Words with OY (11)
- Ending Consonant Blends (91)
- CK Blend (7)
- LF Blend (13)
- LK Blend (14)
- LT Blend (13)
- MP Blend (12)
- ND Blend (13)
- NK Blend (14)
- SK Blend (12)
- ST Blend (12)
- NG Blend (7)
- Beginning Consonant Blends (101)
- L Blend Words (40)
- BL Blend (14)
- CL Blend (13)
- FL Blend (13)
- GL Blend (10)
- PL Blend (11)
- SL Blend (10)
- R Blend Words (36)
- CR Blend (12)
- FR Blend (12)
- GR Blend (11)
- PR Blend (13)
- TR Blend (12)
- SPL Blend (9)
- SQU Blend (8)
- STR Blend (8)
- Alphabet (581)
- Letter A (23)
- Letter B (27)
- Letter C (22)
- Letter D (28)
- Letter E (22)
- Letter F (23)
- Letter G (28)
- Letter H (24)
- Letter I (26)
- Letter J (26)
- Letter K (22)
- Letter L (22)
- Letter M (23)
- Letter N (25)
- Letter O (22)
- Letter P (29)
- Letter Q (27)
- Letter R (22)
- Letter S (22)
- Letter T (23)
- Letter U (22)
- Letter V (22)
- Letter W (22)
- Letter X (22)
- Letter Y (22)
- Letter Z (22)
- Letter Sequence (64)
- ABC Song (20)
- Alphabetical Order (34)
- Letter Sounds (468)
- Letter Sound A (21)
- Letter Sound B (21)
- Letter Sound C (21)
- Letter Sound D (22)
- Letter Sound E (20)
- Letter Sound F (21)
- Letter Sound G (22)
- Letter Sound H (22)
- Letter Sound I (19)
- Letter Sound J (19)
- Letter Sound K (21)
- Letter Sound L (20)
- Letter Sound M (21)
- Letter Sound N (17)
- Letter Sound O (20)
- Letter Sound P (21)
- Letter Sound Q (17)
- Letter Sound R (21)
- Letter Sound S (21)
- Letter Sound T (21)
- Letter Sound U (17)
- Letter Sound V (18)
- Letter Sound W (20)
- Letter Sound X (16)
- Letter Sound Y (19)
- Letter Sound Z (17)
- Beginning and Ending Sounds (25)
- Letter Recognition (365)
- Lowercase Letters (78)
- Uppercase Letters (78)
- Matching Lowercase and Uppercase Letters (209)
- Match Aa - Dd (9)
- Match Ee - Gg (7)
- Match Hh - Kk (9)
- Match Ll - Pp (11)
- Match Qq - Ss (7)
- Match Tt - Vv (7)
- Match Ww - Zz (9)
- Vowels (321)
- Long Vowel Sounds (128)
- Long A Vowel Sound (28)
- Long E Vowel Sound (27)
- Long I Vowel Sound (26)
- Long O Vowel Sound (24)
- Long U Vowel Sound (25)
- Magic - E (37)
- Magic E Words with Long Vowel A (12)
- Magic E Words with Long Vowel E (6)
- Magic E Words with Long Vowel I (12)
- Magic E Words with Long Vowel O (11)
- Magic E Words with Long Vowel U (11)
- Short Vowel Sounds (151)
- Short A Vowel Sound (77)
- Short E Vowel Sound (38)
- Short I Vowel Sound (77)
- Short O Vowel Sound (55)
- Short U Vowel Sound (35)
- Vowel Teams (49)
- Words with AI and AY (13)
- Words with EA and EE (14)
- Words with IE and Y (11)
- Words with OA and OW (13)
- Words with OO (11)
- Words with UE and UI (9)
- Blending (955)
- CCVC Words (64)
- CCVCC Words (36)
- CVC Words (453)
- CVCC Words (156)
- Beginning Blending (34)
- CCVC and CCVCC Words (28)
- CVCC and CCVCC Words (46)
- Words With Bossy R (45)
- Words With Diphthongs (18)
- Words With Three Letter Blends (14)
- Words With Trigraphs (28)
- Words With Vowel Teams (50)
- Consonant Digraphs (39)
- Digraph CH (17)
- Digraph CK (5)
- Digraph NG (5)
- Digraph PH (11)
- Digraph SH (18)
- Digraph TH (17)
- Digraph WH (17)
- Double Consonants (43)
- FF Words (13)
- LL Words (17)
- SS Words (15)
- ZZ Words (12)
- Rhyming Words (174)
- Trigraphs (29)
- Trigraph DGE (9)
- Trigraph IGH (7)
- Trigraph SHR (8)
- Trigraph TCH (7)
- Trigraph THR (7)
- Soft Sounds (2)
- Words with Soft C (1)
- Words with Soft G (1)
- Three Letter Blends (5)
- Sight Words (1,943)
- Dolch Sight Words (567)
- Fry Sight Words (444)
- Syllables (8)
- Hard and Soft Sounds of C and G (2)
- Segmenting Phonemes (1)
- Adding Deleting and Substituting Phonemes (6)
- Silent Letter Words (11)
- Reading Skills (276)
- Cause and Effect (21)
- Inference (19)
- Identify the Main Idea (40)
- Categorize Pictures into Groups (4)
- Choose a Suitable Heading (5)
- Prediction (14)
- Sequencing (28)
- Arrange Pictures in Order (3)
- Arrange Sentences in Order (4)
- Story Elements (20)
- Authors Purpose (9)
- Compare and Contrast (14)
- Ask and Answer Questions (6)
- Central Message (4)
- Point of View (12)
- Sensory Words (3)
- Comprehension (21)
- Character Analysis (16)
- Text Structure (9)
- Fact or Opinion (2)
- Reality and Fantasy (6)
- Using Illustrations (15)
- Using Text Features (8)
- Context Clues (13)
- Evaluating Authors Argument and Evidence (6)
- Communication Skills (14)
- Listening Skills (3)
- Speaking Skills (11)
- Writing (1,836)
- Handwriting (1,652)
- Letter Tracing (356)
- Letter Tracing A (33)
- Letter Tracing B (34)
- Letter Tracing C (33)
- Letter Tracing D (33)
- Letter Tracing E (33)
- Letter Tracing F (34)
- Letter Tracing G (33)
- Letter Tracing H (34)
- Letter Tracing I (33)
- Letter Tracing J (33)
- Letter Tracing K (33)
- Letter Tracing L (33)
- Letter Tracing M (34)
- Letter Tracing N (33)
- Letter Tracing O (33)
- Letter Tracing P (33)
- Letter Tracing Q (33)
- Letter Tracing R (33)
- Letter Tracing S (33)
- Letter Tracing T (33)
- Letter Tracing U (33)
- Letter Tracing V (33)
- Letter Tracing W (33)
- Letter Tracing X (33)
- Letter Tracing Y (33)
- Letter Tracing Z (33)
- Word Tracing (300)
- Cursive Writing (742)
- Writing Sight Words (60)
- Creative Writing (124)
- Grammar (392)
- Adverbs and Adjectives (71)
- Nouns and Pronouns (135)
- Pronouns (25)
- Parts of Speech (12)
- Prepositions and Conjunctions (36)
- Conjunctions (6)
- Prepositions (13)
- Punctuation (23)
- Sentences (27)
- Verbs and Tenses (100)
- Determiners (2)
- Article A An The (2)
- Spelling (29)
- Common Misspellings (10)
- Unscramble (16)
- Vocabulary (307)
- Abbreviations and Contractions (11)
- Affixes (17)
- Inflectional Endings (2)
- Commonly Confused Words (28)
- Compound Words (10)
- Figures of Speech (14)
- Similes and Metaphors (6)
- Alliteration (2)
- Synonyms and Antonyms (23)
- Word Puzzles (81)
- Shades of Meaning (4)
- Sorting Words into Categories (21)
- Making Connections in Reading (6)
- Flashcards (45)
- Vocabulary Flashcards (1)
- Phonics Flashcards (42)
- Grammar Flashcards (2)
- General Knowledge (295)
- Vegetables (19)
- Fruits (24)
- Dessert (9)
- Animals (58)
- Underwater (9)
- Dinosaurs (8)
- Reptiles (9)
- Seasonal (28)
- Christmas (12)
- Halloween (8)
- Kitchen (11)
- Utensils (6)
- Musical Instruments (30)
- Transport (9)
- Vehicles (9)
- Insects (9)
- Professions (8)
- Monuments (8)
- Household Items (8)
- Flowers (8)
- Buildings (8)
- Art & Creativity (236)
- Coloring (181)
- Animals (32)
- Underwater (8)
- Reptiles (8)
- Vegetables (8)
- Transport (8)
- Vehicles (8)
- Musical Instruments (8)
- Kitchen (8)
- Utensils (5)
- Insects (8)
- Rhymes (25)
- Cooking (7)
- Stories (10)
- Logic & Thinking (16)
- Puzzles (11)
- Matching (3)
- Multiplayer (12)
- Time Based (12)
- Player vs Player (12)
- Motor Skills (16)
- Fine Finger Movement (9)
- Aiming and Precision (6)
Subtraction Sentences

Subtraction Equations Game
Unearth the wisdom of mathematics by learning how to complete subtraction equations.

Subtraction Symbol Game
Take the first step towards building your math castle by practicing the subtraction symbol.
Complete Subtraction Sentence Using Pictures Worksheet
Help your child revise subtraction by completing subtraction sentences using pictures.

Represent Subtraction Sentences Worksheet
Make math practice a joyride by solving problems to represent subtraction sentences.
Subtract with Pictures

Count to Tell One Less Game
Take a look at how to count to tell 'one less' with this subtraction game.

Subtract using Counters Game
Begin the exciting journey of becoming a math wizard by learning how to subtract using counters.

Use Pictures to Subtract Worksheet
Learners must use pictures to subtract to enhance their math skills.

Solve Subtraction Sentences Using Pictures Worksheet
Pack your math practice time with fun by solving subtraction sentences using pictures.
Subtract using Models

Decompose 10 to Make Numbers Game
Apply your knowledge of subtraction to decompose 10 to make a number.

Identify the Correct Expression Game
Practice the superpower of subtraction by learning how to identify the correct expression.

Find 1 Less than a Number Worksheet
Solidify your math skills by practicing to find 1 less than a number.

Subtract Using Part-Part-Whole Model Worksheet
Combine math learning with adventure by solving to subtract using 'Part-Part-Whole' model.
Subtraction Strategies

Count Backward From 10 Game
Ask your little one to count backward from 10 to play this game.

Decompose a Number within 5 Game
Ask your little one to decompose a number within 5 to play this game.

Three More or Three Less within 10: Vertical Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
Learn subtraction at the speed of lightning by finding three more or three less within 10.

One More or One Less within 10: Vertical Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
In this worksheet, learners will get to find one more or one less within 10.
Subtraction Facts

Subtract Two Numbers (Up to 5) Game
Take a deep dive into the world of math by subtracting two numbers (up to 5).

Subtract Within 5 Game
Practice the superpower of subtraction by learning how to subtract within 5.

Three More or Three Less within 10: Horizontal Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
Use this printable worksheet to find three more or three less within 10.

Add and Subtract Numbers within 10: Horizontal Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
Focus on core math skills with this fun worksheet by solving to add and subtract numbers within 10.
Subtraction Without Regrouping

Subtract Multiples to 10 using Visuals Game
Enjoy the marvel of mathematics by exploring how to subtract multiples of 10 using visuals.

Subtract Tens Game
Take a deep dive into the world of math by subtracting tens.

Add and Subtract Multiples of 10: Horizontal Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
Dive into this printable worksheet by practicing to add and subtract multiples of 10.

Add and Subtract Multiples of 10: Vertical Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
Reinforce math concepts by practicing to add and subtract multiples of 10.
Subtraction With Regrouping

Use Place Value to Subtract Game
Take the first step towards building your math castle by practicing to use place values to subtract.

Subtract By Regrouping Game
Learn to solve math problems through subtracting by regrouping.

Add and Subtract 2-Digit and 1-Digit Numbers with Regrouping: Horizontal Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
This worksheet will help kids add and subtract 2-digit and 1-digit numbers with regrouping.

Add and Subtract 2-Digit and 1-Digit Numbers with Regrouping: Vertical Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
Solve this worksheet to add and subtract 2-digit and 1-digit numbers with regrouping.
Multi-digit Subtraction

Subtract Two 4-Digit Numbers Using Model Game
Learn to solve math problems by subtracting two 4-digit numbers using models.

Regroup to Subtract Two 4-Digit Numbers Game
Learn to solve math problems by regrouping to subtract two 4-digit numbers.

Add and Subtract 5-Digit and 3-Digit Numbers without Regrouping: Horizontal Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
Use this printable worksheet to add and subtract 5-digit and 3-digit numbers without regrouping.

Add and Subtract 5-Digit and 4-Digit Numbers without Regrouping: Horizontal Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
Focus on core math skills by adding and subtracting 5-digit and 4-digit numbers without regrouping.
All Subtraction Resources

Add Using Fingers Worksheet
Learners must add using fingers to enhance their math skills.

Add and Subtract Numbers within 5: Vertical Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
Use this printable worksheet to add and subtract numbers within 5 to strengthen your math skills.

Add and Subtract 2-Digit and 1-Digit Numbers without Regrouping: Horizontal Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
In this worksheet, learners will add and subtract 2-digit and 1-digit numbers without regrouping.

Subtract and FInd the DIfference Game
Add more arrows to your child’s math quiver by subtracting to find the difference.

Subtract the Numbers using the Column Method Worksheet
Help your child revise number sense by solving to subtract the numbers using the column method.

One More or One Less within 5: Vertical Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
Pack your math practice time with fun by finding one more or one less within 5.

Add and Subtract 2-Digit and 1-Digit Numbers without Regrouping: Vertical Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
Practice math skills by adding and subtracting 2-digit and 1-digit numbers without regrouping.

Use Column Method to Subtract and Find the Difference Game
Unearth the wisdom of mathematics by using the column method to subtract and find the difference.

Add and Subtract Two 2-Digit Numbers with Regrouping: Vertical Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
Learners must add and subtract two 2-digit numbers with regrouping to enhance their math skills.

Estimate the Sum or the Difference Worksheet
Solidify your math skills by practicing to estimate the sum or the difference.

Solve Subtraction Scenarios Game
Apply your knowledge to solve subtraction scenarios.

Identify One Less within 10 Game
Add more arrows to your child’s math quiver by identifying one less within 10.

Subtraction Word Problems with Pictures Worksheet
Print this worksheet to practice subtraction word problems with pictures like a math legend!

Solve Subtraction Problems using Apples Worksheet
Pack your math practice time with fun by solving subtraction problems using apples.

Missing Number in Subtraction Sentence Game
Practice the superpower of math by learning how to find the missing number in subtraction sentences.

Count Back on a Number Line Game
Have your own math-themed party by learning how to count back on a number line.

Solve Using Part-Part-Whole Model Worksheet
Learn subtraction at the speed of lightning by practicing to solve using 'Part-Part-Whole' model.

Finding the Difference (within 10) Game
Ask your little one to find the difference (within 10) to play this game.

Identify the Difference of Multiples of 10 Game
Unearth the wisdom of mathematics by learning how to identify the difference of multiples of 10.

Single Digit Subtraction within 5: Vertical Subtraction Worksheet
This downloadable worksheet is designed to practice single digit subtraction within 5.

Add and Subtract Two 2-Digit Numbers without Regrouping: Horizontal Addition and Subtraction Worksheet
Reinforce math concepts by practicing to add and subtract two 2-digit numbers without regrouping.

Subtract the Numbers by Regrouping Game
Begin the exciting journey of becoming a math wizard by learning to subtract numbers by regrouping.

Fill the Missing Number and Complete the Subtraction Solution Game
Kids must fill the missing number and complete the subtraction solution.

Subtract 1-Digit Numbers from 2-Digit Numbers with Regrouping: Vertical Subtraction Worksheet
Dive into this fun worksheet by subtracting 1-digit numbers from 2-digit numbers with regrouping.
Your one stop solution for all grade learning needs.

Reading & Math for K-5
- Kindergarten
- Learning numbers
- Comparing numbers
- Place Value
- Roman numerals
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Order of operations
- Drills & practice
- Measurement
- Factoring & prime factors
- Proportions
- Shape & geometry
- Data & graphing
- Word problems
- Children's stories
- Leveled Stories
- Context clues
- Cause & effect
- Compare & contrast
- Fact vs. fiction
- Fact vs. opinion
- Main idea & details
- Story elements
- Conclusions & inferences
- Sounds & phonics
- Words & vocabulary
- Reading comprehension
- Early writing
- Numbers & counting
- Simple math
- Social skills
- Other activities
- Dolch sight words
- Fry sight words
- Multiple meaning words
- Prefixes & suffixes
- Vocabulary cards
- Other parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Capitalization
- Narrative writing
- Opinion writing
- Informative writing
- Cursive alphabet
- Cursive letters
- Cursive letter joins
- Cursive words
- Cursive sentences
- Cursive passages
- Grammar & Writing
Breadcrumbs
- Word Problems

Download & Print Only $7.90
Subtraction word problems for 3rd grade
Simple subtraction.
These grade 3 word problems use simple (horizontal) subtraction. The student should read the problem, write a subtraction equation from it and then answer the problem. Students should understand the meaning of subtraction and have studied their subtraction math facts prior to attempting these worksheets.

These worksheets are available to members only.
Join K5 to save time, skip ads and access more content. Learn More
More word problem worksheets
Explore all of our math word problem worksheets , from kindergarten through grade 5.
What is K5?
K5 Learning offers free worksheets , flashcards and inexpensive workbooks for kids in kindergarten to grade 5. Become a member to access additional content and skip ads.
Our members helped us give away millions of worksheets last year.
We provide free educational materials to parents and teachers in over 100 countries. If you can, please consider purchasing a membership ($24/year) to support our efforts.
Members skip ads and access exclusive features.
Learn about member benefits
This content is available to members only.
- Forgot Password?

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.5: Subtraction Algorithms
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 82999

- Julie Harland
- MiraCosta College
You will need: Base Blocks (Material Cards 4-15)
The most common subtraction algorithm is the Right to Left Standard Subtraction Algoithm , which is where you start in the ones column and subtract, then move to the left and subtract at each column. The problem, of course, is when the top digit is less than the bottom digit and you have to regroup. Get out your Base Ten blocks now to see what is really going on.
Consider the subtraction problem 425 –158. From our knowledge of place value, we know that 425 is is 4 \(\times\) 100 + 2 \(\times\) 10 + 5 (or 400 + 20 + 5) and 158 is 1 \(\times\) 100 + 5 \(\times\) 10 + 8 (or 100 + 50 + 8). Using Base Ten blocks, 425 would be represented with 4 flats, 2 longs and 5 units whereas 158 would be represented with 1 flat, 5 longs and 8 units. So, the subtraction problem can be thought of in the following way:
Using Base Blocks \[\begin{aligned} (4 \text{ flat(s) } + 2 \text{ long(s) } + 5 \text{ unit(s) }) \\ \underline{– (1 \text{ flat(s) } + 5 \text{ long(s) } + 8 \text{ unit(s) })} \end{aligned} \nonumber \]
Using blocks, the subtraction problem is shown below:
We can't subtract 8 units from 5 units, so a long is exchanged for ten units, which gives 4 flats, 1 long and 15 units in the minuend. Now, we also can't subtract 5 longs from 1 long, so 1 flat is exchanged for ten longs, which gives 3 flats, 11 longs and 15 units in the minuend. Now we can subtract at each column, which is shown on the next page. You can use either the take away approach or the missing addends approach to subtract. Use your base blocks to work through these problems.
Using Base Blocks \[\begin{aligned} &(3 \text{ flat(s) } + 11 \text{ long(s) } + 15 \text{ unit(s)}) \\ -& (1 \text{ flat(s) } + 5 \text{ long(s) } + 8 \text{ unit(s)}) \\ \hdashline &2 \text{ flat(s) } + 6 \text{ long(s) } + 7 \text{ unit(s)}) = \underline{267} \end{aligned} \nonumber \]
The subtraction problem using blocks is shown below:
Since we are working in Base Ten, the answer (difference) is 267. So, 425 –158 = 267.
The problem can be worked using a chart where enough space is left between the minuend and subtrahend so exchanges can be made in the minuend. Notice the steps shown if you work this problem using a Base chart as shown below.

Now, we'll perform this basic algorithm in different bases. Pay attention to the base when you subtract! For instance, in the first example below you have to exchange a flat for 9 more longs (since it is Base Nine). One way to show this is to actually add 9 (the base) to the amount of longs already there, so I cross off the 5, and add 9 to get 14. If you write it that way, remember the number you are writing is in Base Ten and not in the Base you are working in. Writing it this way is probably easiest when you first start to subtract. A more elegant way is to write it the same way you do when working in Base Ten, which is by putting a 1 in front of the 5 in the longs column so it looks like 15 (it doesn't mean fifteen), which in Base Nine represents 14 longs (5 longs + 9 more from the exchange)! Both ways of writing it are shown. You might want to use your Base Blocks to help visualize the actual exchanges being made. Study the following examples. Check each answer by adding the answer to the subtrahend and see that you get the minuend!
Check: \(\begin{aligned} 11_{\text{two}} \\ \underline{+111_{\text{two}}} \\ 1010_{\text{two}} \end{aligned}\)
In Examples 3 and 4, when I needed to make an exchange and there was a zero in the place value to the left, the exchange had to be made at a higher place value first. Then, exchanges are made down the line until you can subtract. This case happens in Base Ten all the time when you subtract a number from 100, 1000, 10000, etc. Most people just start crossing off each zero and putting 9's above them out of habit, without having any idea why they are doing it. To subtract 235 from 1000, first you should cross off the 1, put a zero above it and put a 1 in front of the zero in the hundred's place (which is trading in 1000 for 10 hundreds), then you should cross off that 10 in the hundred's place, put a 9 above it and put a 1 in front of the zero in the ten's place (which is exchanging 10 hundreds for 9 hundreds and 10 tens), then you should cross off that 10, put a 9 above it and a 1 in front of the zero in the one's place (which is exchanging 10 tens for 9 tens and 10 ones). Then, you can subtract as shown in the example to the right. It's important to really understand what's going on here because children usually have a very hard time when there is a zero to cross off.

Perform the following subtraction problems. You can use blocks or charts to help visualize the problem, but you eventually want to work toward being able to do them without the manipulatives. Underneath each problem, check by adding the difference (answer) to the subtrahend (number being subtracted) and see if the sum is the minuend (the number on top). Use any addition algorithm you prefer.
Check each problem here:
The traditional, standard subtraction algorithm is not necessarily the best one and there are many other ones you'll be learning in the rest of this Exercise Set.
The next algorithm was taught to many people before the "new math" and so I call it the Oldtimer's Algorithm . It's similar to the Standard Algorithm in that you start on the right and move to the left. But you don't regroup (formally known as borrowing). First look again at an example of using the Standard Algorithm to subtract 95 – 28. Since, you can't subtract 8 from 5, you regroup from the 9 by crossing out the 9 and writing 8 so you can put a 1 in front of the 2. Now, in the unit's column, 15 – 8 = 7 and in the ten's column, 8 – 2 = 6. The answer is 67. This new method starts out the same way. You can't subtract 8 from 5, but instead of regrouping from the 9, you add a 1 to the number under the 9, and put a 1 in front of the 5. Notice that in the unit's column, 15 – 8 = 7 and in the ten's column, instead of 8 –2, you have 9 –3 which is the same answer of 6. The advantage of this method is if you put a 1 at the top of one column, you compensate by adding a 1 to the bottom of the next column. You don't have to worry about crossing things off and making a mess and you don't have to think about the digit in the column to the left until you go to that column to subtract – no trying to regroup and getting hung up there! Look at the two methods side by side. If you use the new method, you have to leave space between the subtrahend and subtraction bar in case you need to put a 1 there.

What I really like about the Oldtimer's method is that it is much easier to check. Just add up each column. There is no carrying : 7 + 8 = 15 and 6 + 1 + 2 = 9. It's a breeze. To check the Standard Algorithm, well it's something of a mess and you would need to write it down somewhere else and check it. Study the following examples.
You still have to be very careful to pay close attention to the base. When you put a 1 in front of a digit, remember that it stands for the number that is the base. Another way to indicate the same thing is to write out what it stands for as shown below. The same five examples are illustrated again doing it this way. It's not as elegant but if it helps drive home what is really going on, do it this way.

Subtract the following using the Oldtimer's Algorithm. Check your answers by adding up.
Now that you have mastered that algorithm, here is another one for you. This is a Left to Right Algorithm where no regrouping takes place until the end of the problem – you regroup from the answer! Here's how it works. Start with the left-most column and subtract. Move to the next column. Subtract if possible. If you need to regroup, put a 1 in front of the top digit as usual, and put a slash through the previous digit in the answer. You'll take away from the answer in the end. Continue on to the next column until you've done the unit's column. Then go back and subtract one from all digits with a slash through them. Study the following example which is shown step by step.

Here are some examples in other bases. If you prefer, instead of putting the 1 in front of the digit when you regroup, you can put, for example, +4 if it's in Base Four, like was shown for the previous algorithm on the bottom of the last page.

Check the above examples by doing the following addition problems.
Subtract the following using the Left to Right Algorithm..
Check the answers to Exercise 4 by doing the corresponding addition problem
In this algorithm, there is one more little detail. If you cross out a zero, you must continue crossing off the digit to the left of the zero. If there is more than one zero in a row as you go left, cross off each zero until you get to a nonzero digit. Then, subtract 1 from each number crossed off as before. Pay attention to the base: In the second example below, the number before 40five is 34five. In the third example, the number before 100two is 11two. Study the following examples.
Subtract the following using the Left to Right Algorithm.
Check the answers to Exercise 6 by doing the corresponding addition problem.
Algebra will help you understand the next algorithm:
M – S = M – S + x – x = M + x – S – x = (M + x) – (S + x)
M – S = M – S + x – x = M – x – S + x = (M –x) – (S – x)
Basically, this states that to subtract two numbers, M (minuend) and S (subtrahend), you get the same answer if you first add (or subtract) the same number to both M and S before subtracting. The Oldtimer's Algorithm works because of this fact. For instance, when you put a 1 in front of the minuend's unit's digit and a 1 below the subtrahend's ten's digit, you are adding both a 10 to the minuend and to the subtrahend; then, you subtract.
This algorithm is particularly useful if the minuend has a string of zeros at the end. Subtract 1 from the minuend and subtrahend first and then do the subtraction. Look at how this works:
Well, what do you think? Isn't the second subtraction shown in each pair easier to do than the first one? I just subtracted 1 from the minuend and subtrahend first!
Make up two of your own subtraction problems using this method to subtract.
This algorithm also works well if the subtrahend is close to a power of the base, like 100, 1000, etc. For instance, for the subtraction problem 4503 – 997, add 3 to the minuend and subtrahend so that the problem becomes 4506 – 1000 = 3506. In the Base Four problem, \(2302_{\text{four}} – 333_{\text{four}}\), add 1 to both to get \(2303_{\text{four}} – 1000_{\text{four}} = 1303_{\text{four}}\)
Make up two of your own subtraction problems using this method to subtract. Use a base other than 10.
The above method is sometimes called the Complementary Method . There is yet a more specific approach called the Complementary Algorithm . It relies on the idea of complements that we defined in an earlier exercise set. In Base Ten, pairs of complements were 1 & 9, 2 & 8, 3 & 7, 4 & 6 and 5 & 5. For the complementary method, you find a very specific complement of the subtrahend and add it to both the minuend and subtrahend before subtracting. The complement, in this case, is a 1 followed only by zeros such that the number of zeros is the same number of digits in the minuend. First, you'll have to come up with an easy way to find the complement of a given number.
Below are examples showing how to find the complement (C) of a given number (A), given you want A + C to add up to a number B.
A = 74 and B = 1000.
To find C, add 6 to 74 to get 80, then 20 to get 100 and 900 to get 1000. C = 926.
A = \(24_{\text{six}}\) and B = \(1000_{\text{six}}\).
To find C, add 2 units to get 3 longs, then 3 longs to get 1 flat and 5 flats to get 1 block. Then C = \(532_{\text{six}}\).
There are other ways to figure out the complement. For instance, in Base Ten, if A is 28403 and you want a C such that A + C = 1000000, you can find the answer by writing the actual complement of 3, which is 7, for the unit's digit. Move to the left. You want a digit for each place value that when added to the digit there gives a sum of 9. Do this until the number has as many digits as there are zeros in 1000000. In this case, the answer is 971597. It's harder to explain than do! If you have your own way of figuring out the complement, that's great! Don't keep it a secret.
Exercise 10
Find the complement (C) of the given number (A) such that A + C = B.
a. A = 538 and B = 10000
b. A = \(212_{\text{four}}\) and B = \(1000_{\text{four}}\)
c. A = \(1011_{\text{two}}\) and B = \(10000_{\text{two}}\)
Here is how this complementary method works. Consider the problem 452 – 74. We need to find the number that when added to 74 is 1000. How do you choose what it should add up to, as in 1000? If the first number (minuend) is a 2 digit numeral, you want a 1 with 2 zeroes (100). If the first number (minuend) is a 3 digit numeral, you want a 1 with 3 zeroes (1000), and so on. This step is the same in all bases. Back to the problem: 452 – 74: 926 is what should be added to 74 to get 1000 (from Example 1). Add 926 to the minuend and subtrahend to get the new subtraction problem which is: 1378 – 1000 = 378. The answer is the new minuend without the first digit: 378. Pretty wild! Look at \(402_{\text{six}} –24_{\text{six}}\). We need to find the number that when added to \(24_{\text{six}}\) is \(1000_{\text{six}}\)., which is \(532_{\text{six}}\) from Example 2. Add \(532_{\text{six}}\) to the minuend and subtrahend to get the new subtraction problem which is \(1304 – 1000_{\text{six}} = 304_{\text{six}}\). Again, the answer is the new minuend without the first digit: \(304_{\text{six}}\). So here's the trick – Just add the complement to the minuend, take off the first digit and that's the answer! There is no subtracting.
Subtract using the complementary method: 912 – 573
427 is the number that when added to 573 equals 1000. Add to the minuend: 427 + 912 = 1339. Take off the first digit and the answer is 339.
Subtract \(301_{\text{four}} – 212_{\text{four}}\) using the complementary algorithm.
From 10.b., the complement is \(122_{\text{four}}\). \(301_{\text{four}} + 122_{\text{four}} = 1023_{\text{four}}\). So the answer is \(23_{\text{four}}\).
Exercise 11
Subtract \(1100_{\text{two}} – 1011_{\text{two}}\) using the complementary algorithm and your answer from 10.c.
Exercise 12
Perform the following subtraction problems using the complementary method.
The complementary method is actually easier to do with the blocks –once you get the hang of it. Take out your Base Three blocks to do the following example and problems.
To compute \(212_{\text{three}} – 120_{\text{three}}\), represent \(212_{\text{three}}\) and \(120_{\text{three}}\) with the blocks as shown below.
The minuend is shown on the left. Since its biggest "block" is a flat, the next "place value" up a block. So the problem is to figure out what needs to be added to the subtrahend (shown on the right) to make a block. It would be 1 more long and 1 more flat. In other words, if you added a long and flat to the subtrahend, you would have a block, right? Add that same amount to the minuend, shown on the left above. It should look like this:
If you subtract now, the answer is the new minuend with the largest block removed. Therefore, the answer is 2 longs and 2 units, or \(22_{\text{three}}\) The crucial step is to figure out what needs to be added to the subtrahend to make the block. Then, also add it to the minuend, remove the largest block from the new minuend and that's the answer! Ta da!
Since drawing the blocks out is sometimes cumbersome, another way to pictorially show what is going on is to use abbreviated pictures for the Base Three blocks, flats, longs and units (3B, 3F, 3L, U) as shown below.

Exercise 13
On the next page, use the appropriate base blocks to subtract \(120_{\text{three}} - 12_{\text{three}}\) and \(213_{\text{four}} - 133_{\text{four}}\) using the complementary method . Explain how to do it and show full or abbreviated pictures with the base blocks.
a. Use Base Three Blocks and complementary method to subtract \(120_{\text{three}} – 12_{\text{three}}\).
b. Use Base Four Blocks and complementary method to subtract \(213_{\text{four}} – 133_{\text{four}}\).
Exercise 14
Explain how each student is doing the subtraction problem 634 – 152.
a. Mary does the subtraction in her head by thinking out loud "534, 484, 482". What is her reasoning?
b. Pedro does the subtraction by thinking out loud " 634 and 48 is 682, take away 200 is 482". What is his reasoning?
Another method to subtract is called the Subtract from the Base Algorithm . This one is especially nice for working in other bases. In this method you never need to subtract from a number larger than the base.
Standard algorithm:
Using the Subtract from the Base method if you have a place where the bottom number is bigger than the top number, regroup as in the traditional method then subtract the bottom number from the base and add the result to the top number. The advantage of this method is you never subtract a number from any number larger than the base. This is a good method for people who need to use fingers to subtract.
Subtract from the base algorithm:
When using this method in other bases circle the base number when regrouping. For example when working in base six, 6 does not exist and writing 10 can be confusing even though it is correct.
Exercise 15
Subtract the following using the Subtract from the Base Algorithm. These are the same problems from #6. Don’t forget to circle the base number when regrouping.
Do you know of another algorithm for addition or subtraction? If so, post it with an explanation on the Forum for extra credit.

80 Educational Children's Math Picture Books
R eady for the biggest list of math picture books ? Because I’ve found SO MANY amazing math books, I can’t wait to tell you about them!
Use these at home, in the classroom, or with your homeschool. You’ll discover books about counting , addition, subtraction, number sense, the 100th day, sorting, fractions, division, geometry, problem-solving, money, telling time, multiplication , and algebra.
Three cheers for math!
Table of Contents
Counting math books, the 100th day books, number sense books, telling time books, addition and subtraction books, sorting and pattern books, measurement books, multiplication books, division and fraction books, geometry books, money books, algebra books, math problem-solving books, best math books.
One Big Pair of Underwear
HAHA — this is the silliest “counting” picture book you’ll read! It’s counting, subtracting, and patterns silliness that your kids will adore.
Count your way from one to ten as this family gets ready for dinner including shopping and cooking the food.
You’ll love the clever creations Medina makes with vegetables — 1 avocado deer and 2 radish mice, just to name a few.
Anno’s Counting Book by Mitsumasa Anno
Bold graphic images help children find the black dots from one to ten in different images. Fun!
What’s more relatable than candy? And brightly colored illustrations? This tasty book about large numbers is pitch-perfect.
How Many Bugs in a Box
We love this engaging book. Lift the flaps and see what pops out!
Rhyme and count with these naughty monkeys.
The snake wants to count the mice — for his dinner. Count up and count down.
Monkey counts to ten and back as she bravely faces the crocodile-infested waters in order to get to a banana tree.
Alice needs to find 100 things to bring for the 100th day — but she’s having lots of trouble deciding what.
What is he going to bring for the 100th day of school? You’ll love this delightful rhyming book.
It’s not only the kids that get to bring 100 things to school, Miss Bindergarten is getting together 100 things, too.
Learn about counting by tens as the queens plan a special birthday surprise for the king.
Grapes of Math
Fun and rhyming riddles to help kids learn problem-solving strategies.
Learn about odd and even numbers with this silly story about a boy who discovers that everything in his life is ODD! (Also read: My Even Day and My Half Day .)
Hungry for Math: Poems to Munch On
Just like numbers, ideas are infinite. This is fun story of making the challenging concept of infinity more understandable.
Even Steven is all about, you guessed it, even-numbered things. Then one day, his cousin Odd Todd comes to visit. Which terrifies Even Steven. Because even Odd Todd knocks in odd numbers. . .
Learn about a boy who loved numbers and was known as The Magician from Budapest in this playful mathematical biography.
Go Figure!: A Totally Cool Book About Numbers
Learn more about the numbers in our everyday life, their purpose, and history. Then try some of the fun number magic tricks, puzzles, and activities.
365 Penguins
Penguins are arriving every single day at their doorstep. What are they doing to do?!
How Much Is a Million?
David M. Schwartz, illustrated by Steven Kellogg
Marvelosissimo the mathematical magician will teach you about really BIG numbers.
Skip count and estimate with pumpkins.
This is a fun book that offers 100 math riddles, each with adaptations for young kids and bigger kids.
Telling Time with Big Mama Cat by Dan Harper
Follow along with the daily schedule and use the movable hands to practice telling time.
Learn about the different measurements of time (seconds, minutes), go through a day and take mini-quizzes to figure out how much you’re learning.
This funny book is all about Mr. Crocodile’s schedule which includes finding and catching some pesky monkeys.
Pigeon Math
Hilarious! Addition and subtraction never felt so fun!! An increasingly exasperated narrator is TRYING to tell the story about ten pigeons but it’s not going well. Visual support, goofy humor, and plenty of kid-appeal make this a 100% must-own, must-read STEM picture book.
Add the baby animals with the grown-ups to see how many all together.
Jen Arena (Author), Stephen Gilpin
A winter addition adventure of snowmen that will get you to 100 total.
A loving family shares a favorite cultural sweet treat and practices counting and subtracting in this beautifully written, Indian-flavored math story! Mama makes 10 gulab jamuns for guests. But, one child eats three. Now there are only 7 for the guests. And another child eats 3 more. Now there are only 4 left. Mamma wonders how she will have time to make more treats for her guests. The kids will help her make them!
The Chicken Problem
This is a Peg and Cat picture book story their perfect picnic that goes totally crazy with runaway chickens. Peg is “ totally freaking out ” and needs to get the one hundred chickens back in the coop. Peg and Cat must solve the chicken problem fast. I love the illustrations, the problem-solving characters, and the silly story.
Comic Book Math ~ Fun-Schooling Journal: Adding, Writing & Subtracting Games
by Sarah Janisse Brown
Use your imagination and practice math skills in a fun way.
Subtract your way through this goofy story about an elevator going down.
Animal stories help kids learn the basics of putting numbers in groups and taking numbers away.
Count and add the animals on the back of the trucks.
Go on a butterfly addition hunt and see who will win.
When the music stops, someone is out. Subtract to see how many are left.
The O’Malleys pass the time on a long car trip by counting up different color cars using tally marks. The winner is the one who tallies the most.
Arithmechicks Take Away: A Math Story
This gives kids photographs from which they can make decisions about sorting. Use with actual physical objects to make the lessons more concrete.
Blockhead: The Life of Fibonacci
Fibonacci sees patterns in nature and develops the Fibonacci Sequence.
Learn about all the spirals in nature.
What groups can you sort out of Packy the Packrat’s stuff?
Fannie in the Kitchen: The Whole Story from Soup to Nuts of How Fannie Farmer Invented Recipes with Precise Measurements
Kitchen measurements equal delicious foods.
Measuring Penny by Loreen Leedy
Lisa loves measurement, so she starts measuring her dog, Penny.
How Big is a Foot by Rolf Myller
The king needs to figure out how big of a bed to make for his queen. This introduces standardizing measurements.
An inchworm shows the bird why he shouldn’t be eaten — because he can measure anything!
Amanda learns that multiplication is the fastest way to count.
Kings Chessboard
Multiplying Menace: The Revenge of Rumpelstiltskin
by Pam Calvert and Wayne Geehan
This is a fun multiplication story about mischievous Rumplestiltskin and his multiplication stick.
Gorgeous illustrations illustrate this fable about a smart girl who outsmarts a king.
This is an introduction to multiplication and factorals.
Spaghetti And Meatballs For All!
by Marilyn Burns and Debbie Tilley
Yummy! It’s time for spaghetti. But how much does everyone get to eat?
Equal Shmequal
, illustrated by Philomena O’Neill
Mouse helps her friends how to equally divide up teams for a game of tug of war.
Elinor J Pinczes , illustrated by Bonnie MacKain
If 100 ants are marching to a picnic, how should they sort themselves into a line? 1 line of 100? 2 lines of 50?
The Doorbell Rang
Pat Hutchins
More and more friends arrive to share Ma’s cookies. How many cookies should each person get?
The Lion’s Share
The shared meal keeps getting divided in half leaving only a crumb for the ant. So she and the other guests bake cakes for the king. Which they have to divide.
Using the illustrations, readers get to answer division and fraction questions. What fraction of the cow is blue? Fun farm math!
Fractions in Disguise
by Edward Einhorn and David Clark
This is a mystery story about finding a missing fraction — clever!
by Dayle Ann Dodds , illustrated by Abby Carter
The Strawberry Inn is filled with five visitors who all want a piece of one cake. How will Miss Blue solve this problem?
Learn the basic shapes with this cute introductory book.
Lia and Luis Puzzled by Ana Crespo, illustrated by Giovana Medeiros
Grandma gives the twins a puzzle they must complete to discover what the surprise is. What will it be? First, the twins will have to collaborate and use geometry and sorting to put the puzzle together. Lia and Luis are Brazilian American and the story includes words in Portuguese like the word for Grandma and yay.
by Cindy Neuschwander and Bryan Langdo
To get to the pharaoh’s burial tomb, the kids must decode the geometric hieroglyphics.
Sir Cumference and the First Round Table by
Cindy Neuschwander and Wayne Geehan
The king needs a place for his your knights to sit and discuss battle and peace plans. Luckily Sir Cumference, Lady Di of Ameter, and their son Radius can help.
by Cindy Neuschwander and Wayne Geehan
Radius must use his wits and math skills to rescue the missing king.
When a Line Bends . . . A Shape Begins
Learn about shapes in this brightly illustrated beginning circus story.
The name says it all — learn about perimeter, area, and volume with this crew of monsters.
What’s Your Angle, Pythagoras?
Pythagoras discovered through experimentation that there are mathematical principles that always stay the same — like with right triangles.
The Greedy Triangle
Marilyn Burns , illustrated by Gordon Silveria
This triangle doesn’t just want to have three angles, he is greedy for more angles which changes his shape completely.
To successfully journey back to earth, Captain Invincible must use his knowledge of 3D shapes.
Grandfather Tang’s Story by Ann Tonpert, illustrated by Robert Andrew Parker
Moving the tangram shapes, help narrate the story of two fox fairies.
In this Three Little Pigs math story, the pigs must learn geometric shapes and tangrams.
Alexander trades his one dollar for many coins because he misses the point of how much things are worth, placing importance on the number of monies he has more than the value. Hilarious.
Count five pennies, count two nickels, and add them up.
Grandma’s birthday is coming. Watch as Max and Ruby learn about how much things cost and what the best presents really are.
From the history of bartering things to the creation of different types of money, this is a great informational math book about money.
Little Critter needs to earn money so that he can buy a skateboard.
Interesting information about collecting coins, plus a place to start collecting.
Pigs Will Be Pigs: Fun with Math and Money by Amy Axelrod, illustrated by Sharon McGinley-Nally
David A. Adler , Edward Miller
Find the unknown number of creepy things by using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
The Deductive Detective
This entertaining math picture book incorporates math with the mystery genre. Detective Duck needs to use his deductive reasoning to figure out which of the twelve animal bakers stole the cake from the cake contest. He follows the clues, subtracting each suspect as he rules them out. Until only one animal is left! Can you use your thinking skills to figure out the culprit before Detective Duck?
Frank adopts Lucky from a shelter. Together, they have fun, educational adventures around the neighborhood. For example, Frank learns about math and puzzles, thinking about how much hair Lucky sheds and dividing up and sharing the bed with Lucky. The author makes the duo’s learning fun and embedded throughout the day, whether it’s geography, science, or math. Love it.
One Minute Mysteries: 65 Short Mysteries You Solve With Math!
by Eric Yoder and Natalie Yoder
Real-world math brainteasers.
by Jon Scieszka and Lane Smith
If you’ve ever been a victim of a MATH CURSE, you know how horrible it can be. Because you can break the curse. FUN and funny!
by Greg Tang and Greg Paprocki
Using real artwork, this is a math picture book where kids solve math problems and appreciate famous art.
The Book of Perfectly Perilous Math: 24 Death-Defying Challenges for Young Mathematicians
Math for All Seasons
Put on your thinking caps. Look closely at the illustrations to solve the math problems.
Find books about place value , too!
KEEP READING
Cookbooks for Kids
Bedtime Stories for Kids
Memory Games
Book Series
Science Books
The post 80 Educational Children’s Math Picture Books appeared first on Imagination Soup .

If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Course: 2nd grade > Unit 3
- Adding and subtracting on number line word problems
- Adding two digit numbers on a number line
- Add and subtract on the number line word problems
- Multi step addition word problem
- 2-step addition word problems within 100
- Multi-step subtraction word problem
2-step subtraction word problems within 100
- Your answer should be
- an integer, like 6
- a simplified proper fraction, like 3 / 5
- a simplified improper fraction, like 7 / 4
- a mixed number, like 1 3 / 4
- an exact decimal, like 0.75
- a multiple of pi, like 12 pi or 2 / 3 pi

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Long Subtraction Worksheets. Try teaching a mental math strategy for subtraction called counting up. Here is how it is done: Start with the second number (the subtrahend) and count up by tens until you find the closest value to the first number (the minuend). Keep track of how many tens you counted.
Learn the definition and examples of subtraction as the opposite of addition, and how to use a number line to solve problems. Watch a video by Sal Khan and join the conversation with other learners.
Learn how to add and subtract whole numbers within 1000 with regrouping, number lines, and word problems. Practice with interactive exercises and quizzes on Khan Academy.
Problem Solving on Subtraction. Problem solving on subtraction will help us to get the idea on how to solve the basic subtraction statement problems. 1. Eight birds sat on a wire. Three birds flew away. How many were left? Total number of birds sat on a wire = 8. Number of birds flew away = 3. Therefore, number of birds left = 8 - 3 = 5.
Definition: Subtraction. Subtraction is the process of determining the remainder when part of the total is removed. Suppose the sum of two whole numbers is 11, and from 11 we remove 4. Using the number line to help our visualization, we see that if we are located at 11 and move 4 units to the left, and thus remove 4 units, we will be located at 7.
The concept of subtraction is often used in our day-to-day activities. Let us understand how to solve real-life subtraction word problems with the help of an interesting example. Example: A soccer match had a total of 4535 spectators. After the first innings, 2332 spectators left the stadium. Find the number of remaining spectators.
That 8 plus 9 are 17. Or the difference between 17 and 9 is 8. Or the difference between 17 and 8 is 9. Hopefully I'm not confusing you. So for most of these subtraction problems where the answer is a one-digit answer, you should eventually have them memorized, but in your head it's good to be imagining this number line. Let's do a couple more ...
Solving subtraction problems typically involves three steps: identifying the minuend and subtrahend, performing the subtraction operation, and writing down the difference. For instance, to solve the subtraction problem 13 - 4, identify 13 as the minuend and 4 as the subtrahend. Subtract 4 from 13 to get the difference, which is 9.
8 - 3 = 5 is a mathematical equation. You could read it like this: five minus three equals two. As we learned in Introduction to Addition, a mathematical equation is basically a math sentence that uses numbers and symbols. When we write a subtraction equation, we use two symbols: - and =. The minus sign ( -) means one thing is being subtracted ...
A visual way to solve world problems using bar modeling. This type of word problem uses the part-whole model. Because the part is missing, this is a subtraction problem. Example: There are 98 hats, 20 of them are pink and the rest are yellow. How many yellow hats are there? Show Video Lesson.
These lessons look at simple examples of subtraction word problems. Words like 'difference', 'less', 'take away', 'loss' usually means that subtraction is involved. For subtraction, take note which number has to be subtracted from which number. Subtracting in the wrong order will give you the wrong answer. Andy has 53 marbles.
The answer is there were less. Therefore, the operation that we have to do is SUBTRACTION. 16 - 9 = 7. In the beginning, there were 7 cars. We hope you enjoyed this post about subtraction problems. If you want to learn much more elementary math, try Smartick for free! Fun is our brain's favorite way of learning.
Names. Other names used in subtraction are Minus, Less, Difference, Decrease, Take Away, Deduct.. The names of the numbers in a subtraction fact are: Minuend − Subtrahend = Difference. Minuend: The number that is to be subtracted from.. Subtrahend: The number that is to be subtracted.. Difference: The result of subtracting one number from another. ...
Find printable worksheets for subtraction word problems with different levels of difficulty and themes. Learn how to subtract single-digit, two-digit, three-digit, four-digit and large numbers with or without regrouping.
Solving Stacked Subtraction Problems. If you feel comfortable with the subtraction skills from Introduction to Subtraction, you're ready to start solving stacked subtraction problems. Let's try to solve 49 - 7. With all stacked subtraction problems, we start with the digits that are farthest to the right. Here, we'll begin with 9 and 7. 9 - 7 = 2.
Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. ... Break apart 3-digit subtraction problems. Adding and subtracting on number line. Subtract on a number line. Methods for subtracting 3-digit numbers. Select strategies for subtracting within 1000. Math >
Subtracting a positive number from a negative number will always give a negative number. If we subtract a positive number from a negative number, we start at the negative number and count backwards. Negative $−$ Positive $=$ Negative. Using the number line, let's start at $− 3$. For example: Say, we have the problem $(− 2) − 3$.
Subtraction with regrouping is a key building block for learning mathematics - It allows you to solve double and triple digit subtraction problems. It's important to learn subtraction with regrouping - That way, you can better understand and solve complex word problems. Subtraction with regrouping is also referred to as borrowing or ...
Learn to solve math problems through subtracting by regrouping. 2 2.NBT.5. VIEW DETAILS. Multi-digit Subtraction. Use Column Method to Subtract and Find the Difference Game Unearth the wisdom of mathematics by using the column method to subtract and find the difference. 4 4.NBT.4.
Practice simple subtraction with these grade 3 word problems. Read the problem, write an equation and answer it. Explore more math word problems for kindergarten to grade 5.
Use cube trains to solve subtraction word problems - up to 5 X.4 Subtraction word problems - numbers up to 5 X.5 Model and write subtraction sentences for word problems - up to 5 Y.1 Take away cubes - numbers up to 10 Y.2 ...
This step is the same in all bases. Back to the problem: 452 - 74: 926 is what should be added to 74 to get 1000 (from Example 1). Add 926 to the minuend and subtrahend to get the new subtraction problem which is: 1378 - 1000 = 378. The answer is the new minuend without the first digit: 378.
Mystery Math: A First Book of Algebra by . David A. Adler, Edward Miller . Find the unknown number of creepy things by using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Math Problem ...
Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. ... Lesson 6: Addition and subtraction within 100 word problems (multi-step) Adding and subtracting on number line word problems. Adding two digit numbers on a number line.