- Our Mission


Why Students Cheat—and What to Do About It
A teacher seeks answers from researchers and psychologists.
“Why did you cheat in high school?” I posed the question to a dozen former students.
“I wanted good grades and I didn’t want to work,” said Sonya, who graduates from college in June. [The students’ names in this article have been changed to protect their privacy.]
My current students were less candid than Sonya. To excuse her plagiarized Cannery Row essay, Erin, a ninth-grader with straight As, complained vaguely and unconvincingly of overwhelming stress. When he was caught copying a review of the documentary Hypernormalism , Jeremy, a senior, stood by his “hard work” and said my accusation hurt his feelings.
Cases like the much-publicized ( and enduring ) 2012 cheating scandal at high-achieving Stuyvesant High School in New York City confirm that academic dishonesty is rampant and touches even the most prestigious of schools. The data confirms this as well. A 2012 Josephson Institute’s Center for Youth Ethics report revealed that more than half of high school students admitted to cheating on a test, while 74 percent reported copying their friends’ homework. And a survey of 70,000 high school students across the United States between 2002 and 2015 found that 58 percent had plagiarized papers, while 95 percent admitted to cheating in some capacity.
So why do students cheat—and how do we stop them?
According to researchers and psychologists, the real reasons vary just as much as my students’ explanations. But educators can still learn to identify motivations for student cheating and think critically about solutions to keep even the most audacious cheaters in their classrooms from doing it again.
Rationalizing It
First, know that students realize cheating is wrong—they simply see themselves as moral in spite of it.
“They cheat just enough to maintain a self-concept as honest people. They make their behavior an exception to a general rule,” said Dr. David Rettinger , professor at the University of Mary Washington and executive director of the Center for Honor, Leadership, and Service, a campus organization dedicated to integrity.
According to Rettinger and other researchers, students who cheat can still see themselves as principled people by rationalizing cheating for reasons they see as legitimate.
Some do it when they don’t see the value of work they’re assigned, such as drill-and-kill homework assignments, or when they perceive an overemphasis on teaching content linked to high-stakes tests.
“There was no critical thinking, and teachers seemed pressured to squish it into their curriculum,” said Javier, a former student and recent liberal arts college graduate. “They questioned you on material that was never covered in class, and if you failed the test, it was progressively harder to pass the next time around.”
But students also rationalize cheating on assignments they see as having value.
High-achieving students who feel pressured to attain perfection (and Ivy League acceptances) may turn to cheating as a way to find an edge on the competition or to keep a single bad test score from sabotaging months of hard work. At Stuyvesant, for example, students and teachers identified the cutthroat environment as a factor in the rampant dishonesty that plagued the school.
And research has found that students who receive praise for being smart—as opposed to praise for effort and progress—are more inclined to exaggerate their performance and to cheat on assignments , likely because they are carrying the burden of lofty expectations.
A Developmental Stage
When it comes to risk management, adolescent students are bullish. Research has found that teenagers are biologically predisposed to be more tolerant of unknown outcomes and less bothered by stated risks than their older peers.
“In high school, they’re risk takers developmentally, and can’t see the consequences of immediate actions,” Rettinger says. “Even delayed consequences are remote to them.”
While cheating may not be a thrill ride, students already inclined to rebel against curfews and dabble in illicit substances have a certain comfort level with being reckless. They’re willing to gamble when they think they can keep up the ruse—and more inclined to believe they can get away with it.
Cheating also appears to be almost contagious among young people—and may even serve as a kind of social adhesive, at least in environments where it is widely accepted. A study of military academy students from 1959 to 2002 revealed that students in communities where cheating is tolerated easily cave in to peer pressure, finding it harder not to cheat out of fear of losing social status if they don’t.
Michael, a former student, explained that while he didn’t need to help classmates cheat, he felt “unable to say no.” Once he started, he couldn’t stop.

Technology Facilitates and Normalizes It
With smartphones and Alexa at their fingertips, today’s students have easy access to quick answers and content they can reproduce for exams and papers. Studies show that technology has made cheating in school easier, more convenient, and harder to catch than ever before.
To Liz Ruff, an English teacher at Garfield High School in Los Angeles, students’ use of social media can erode their understanding of authenticity and intellectual property. Because students are used to reposting images, repurposing memes, and watching parody videos, they “see ownership as nebulous,” she said.
As a result, while they may want to avoid penalties for plagiarism, they may not see it as wrong or even know that they’re doing it.
This confirms what Donald McCabe, a Rutgers University Business School professor, reported in his 2012 book ; he found that more than 60 percent of surveyed students who had cheated considered digital plagiarism to be “trivial”—effectively, students believed it was not actually cheating at all.
Strategies for Reducing Cheating
Even moral students need help acting morally, said Dr. Jason M. Stephens , who researches academic motivation and moral development in adolescents at the University of Auckland’s School of Learning, Development, and Professional Practice. According to Stephens, teachers are uniquely positioned to infuse students with a sense of responsibility and help them overcome the rationalizations that enable them to think cheating is OK.
1. Turn down the pressure cooker. Students are less likely to cheat on work in which they feel invested. A multiple-choice assessment tempts would-be cheaters, while a unique, multiphase writing project measuring competencies can make cheating much harder and less enticing. Repetitive homework assignments are also a culprit, according to research , so teachers should look at creating take-home assignments that encourage students to think critically and expand on class discussions. Teachers could also give students one free pass on a homework assignment each quarter, for example, or let them drop their lowest score on an assignment.
2. Be thoughtful about your language. Research indicates that using the language of fixed mindsets , like praising children for being smart as opposed to praising them for effort and progress , is both demotivating and increases cheating. When delivering feedback, researchers suggest using phrases focused on effort like, “You made really great progress on this paper” or “This is excellent work, but there are still a few areas where you can grow.”
3. Create student honor councils. Give students the opportunity to enforce honor codes or write their own classroom/school bylaws through honor councils so they can develop a full understanding of how cheating affects themselves and others. At Fredericksburg Academy, high school students elect two Honor Council members per grade. These students teach the Honor Code to fifth graders, who, in turn, explain it to younger elementary school students to help establish a student-driven culture of integrity. Students also write a pledge of authenticity on every assignment. And if there is an honor code transgression, the council gathers to discuss possible consequences.
4. Use metacognition. Research shows that metacognition, a process sometimes described as “ thinking about thinking ,” can help students process their motivations, goals, and actions. With my ninth graders, I use a centuries-old resource to discuss moral quandaries: the play Macbeth . Before they meet the infamous Thane of Glamis, they role-play as medical school applicants, soccer players, and politicians, deciding if they’d cheat, injure, or lie to achieve goals. I push students to consider the steps they take to get the outcomes they desire. Why do we tend to act in the ways we do? What will we do to get what we want? And how will doing those things change who we are? Every tragedy is about us, I say, not just, as in Macbeth’s case, about a man who succumbs to “vaulting ambition.”
5. Bring honesty right into the curriculum. Teachers can weave a discussion of ethical behavior into curriculum. Ruff and many other teachers have been inspired to teach media literacy to help students understand digital plagiarism and navigate the widespread availability of secondary sources online, using guidance from organizations like Common Sense Media .
There are complicated psychological dynamics at play when students cheat, according to experts and researchers. While enforcing rules and consequences is important, knowing what’s really motivating students to cheat can help you foster integrity in the classroom instead of just penalizing the cheating.
- Trying to Conceive
- Signs & Symptoms
- Pregnancy Tests
- Fertility Testing
- Fertility Treatment
- Weeks & Trimesters
- Staying Healthy
- Preparing for Baby
- Complications & Concerns
- Pregnancy Loss
- Breastfeeding
- School-Aged Kids
- Raising Kids
- Personal Stories
- Everyday Wellness
- Safety & First Aid
- Immunizations
- Food & Nutrition
- Active Play
- Pregnancy Products
- Nursery & Sleep Products
- Nursing & Feeding Products
- Clothing & Accessories
- Toys & Gifts
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- How to Talk About Postpartum Depression
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
How Teens Use Technology to Cheat in School
Why teens cheat, text messaging during tests, storing notes, copying and pasting, social media, homework apps and websites, talk to your teen.
- Expectations and Consequences
When you were in school, teens who were cheating were likely looking at a neighbor’s paper or copying a friend’s homework. The most high-tech attempts to cheat may have involved a student who wrote the answers to a test on the cover of their notebook.
Cheating in today’s world has evolved, and unfortunately, become pervasive. Technology makes cheating all too tempting, common, and easy to pull off. Not only can kids use their phones to covertly communicate with each other, but they can also easily look up answers or get their work done on the Internet.
In one study, a whopping 35% of teens admit to using their smartphones to cheat on homework or tests. 65% of the same surveyed students also stated they have seen others use their phones to cheat in school. Other research has also pointed to widespread academic indiscretions among teens.
Sadly, academic dishonesty often is easily normalized among teens. Many of them may not even recognize that sharing answers, looking up facts online, consulting a friend, or using a homework app could constitute cheating. It may be a slippery slope as well, with kids fudging the honesty line a tiny bit here or there before beginning full-fledged cheating.
For those who are well aware that their behavior constitutes cheating, the academic pressure to succeed may outweigh the risk of getting caught. They may want to get into top colleges or earn scholarships for their grades. Some teens may feel that the best way to gain a competitive edge is by cheating.
Other students may just be looking for shortcuts. It may seem easier to cheat rather than look up the answers, figure things out in their heads, or study for a test. Plus, it can be rationalized that they are "studying" on their phone rather than actually cheating.
Teens with busy schedules may be especially tempted to cheat. The demands of sports, a part-time job , family commitments, or other after-school responsibilities can make academic dishonesty seem like a time-saving option.
Sometimes, there’s also a fairly low risk of getting caught. Some teachers rely on an honor system, and in some cases, technology has evolved faster than school policies. Many teachers lack the resources to detect academic dishonesty in the classroom. However, increasingly, there are programs and methods that let teachers scan student work for plagiarism.
Finally, some teens get confused about their family's values and may forget that learning is the goal of schooling rather than just the grades they get. They may assume that their parent would rather they cheat than get a bad grade—or they fear disappointing them. Plus, they see so many other kids cheating that it may start to feel expected.
It’s important to educate yourself about the various ways that today’s teens are cheating so you can be aware of the temptations your teen may face. Let's look at how teens are using phones and technology to cheat.
Texting is one of the fastest ways for students to get answers to test questions from other students in the room—it's become the modern equivalent of note passing. Teens hide their smartphones on their seats and text one another, looking down to view responses while the teacher isn't paying attention.
Teens often admit the practice is easy to get away with even when phones aren't allowed (provided the teacher isn't walking around the room to check for cellphones).
Some teens store notes for test time on their cell phones and access these notes during class. As with texting, this is done on the sly, hiding the phone from view. The internet offers other unusual tips for cheating with notes, too.
For example, several sites guide teens to print their notes out in the nutrition information portion of a water bottle label, providing a downloadable template to do so. Teens replace the water or beverage bottle labels with their own for a nearly undetectable setup, especially in a large class. This, of course, only works if the teacher allows beverages during class.
Rather than conduct research to find sources, some students are copying and pasting material. They may plagiarize a report by trying to pass off a Wikipedia article as their own paper, for example.
Teachers may get wise to this type of plagiarism by doing a simple internet search of their own. Pasting a few sentences of a paper into a search engine can help teachers identify if the content was taken from a website.
A few websites offer complete research papers for free based on popular subjects or common books. Others allow students to purchase a paper. Then, a professional writer, or perhaps even another student, will complete the report for them.
Teachers may be able to detect this type of cheating when a student’s paper seems to be written in a different voice. A perfectly polished paper may indicate a ninth-grade student’s work isn’t their own. Teachers may also just be able to tell that the paper just doesn't sound like the student who turned it in.
Crowdsourced sites such as Homework Helper also provide their share of homework answers. Students simply ask a question and others chime in to give them the answers.
Teenagers use social media to help one another on tests, too. It only takes a second to capture a picture of an exam when the teacher isn’t looking.
That picture may then be shared with friends who want a sneak peek of the test before they take it. The photo may be uploaded to a special Facebook group or simply shared via text message. Then, other teens can look up the answers to the exam once they know the questions ahead of time.
While many tech-savvy cheating methods aren’t all that surprising, some methods require very little effort on the student’s part. Numerous free math apps such as Photomath allow a student to take a picture of the math problem. The app scans the problem and spits out the answers, even for complex algebra problems. That means students can quickly complete the homework without actually understanding the material.
Other apps, such as HWPic , send a picture of the problem to an actual tutor, who offers a step-by-step solution to the problem. While some students may use this to better understand their homework, others just copy down the answers, complete with the steps that justify the answer.
Websites such as Cymayth and Wolfram Alpha solve math problems on the fly—Wolfram can even handle college-level math problems. While the sites and apps state they are designed to help students figure out how to do the math, they are also used by students who would rather have the answers without the effort required to think them through on their own.
Other apps quickly translate foreign languages. Rather than have to decipher what a recording says or translate written words, apps can easily translate the information for the student.
The American Academy of Pediatrics encourages parents to talk to teens about cheating and their expectations for honesty, school, and communication. Many parents may have never had a serious talk with their child about cheating. It may not even come up unless their child gets caught cheating. Some parents may not think it’s necessary to discuss because they assume their child would never cheat.
However, clearly, the statistics show that many kids do engage in academic discretions. So, don’t assume your child wouldn’t cheat. Often, "good kids" and "honest kids" make bad decisions. Make it clear to your teen that you value hard work and honesty.
Talk to your teen regularly about the dangers of cheating. Make it clear that cheaters tend not to get ahead in life.
Discuss the academic and social consequences of cheating, too. For example, your teen might get a zero or get kicked out of a class for cheating. Even worse, other people may not believe them when they tell the truth if they become known as dishonest or a cheater. It could also go on their transcripts, which could impair their academic future.
It’s important for your teen to understand that cheating—and heavy cell phone use—can take a toll on their mental health , as well. Additionally, studies make clear that poor mental health, particularly relating to self-image, stress levels, and academic engagement, makes kids more likely to indulge in academic dishonestly. So, be sure to consider the whole picture of why your child may be cheating or feel tempted to cheat.
A 2016 study found that cheaters actually cheat themselves out of happiness. Although they may think the advantage they gain by cheating will make them happier, research shows cheating causes people to feel worse.
Establish Clear Expectations and Consequences
Deciphering what constitutes cheating in today's world can be a little tricky. If your teen uses a homework app to get help, is that cheating? What if they use a website that translates Spanish into English? Also, note that different teachers have different expectations and will allow different levels of outside academic support.
Expectations
So, you may need to take it on a case-by-case basis to determine whether your teen's use of technology enhances or hinders their learning and/or is approved by their teacher. When in doubt, you can always ask the teacher directly if using technology for homework or other projects is acceptable.
To help prevent cheating, take a firm, clear stance so that your child understands your values and expectations. Also, make sure they have any needed supports in place so that they aren't tempted to cheat due to academic frustrations or challenges.
Tell your teen, ideally before an incident of academic dishonesty occurs, that you don’t condone cheating of any kind and you’d prefer a bad grade over dishonesty.
Stay involved in your teen’s education. Know what type of homework your teen is doing and be aware of the various ways your teen may be tempted to use their laptop or smartphone to cheat.
To encourage honesty in your child, help them develop a healthy moral compass by being an honest role model. If you cheat on your taxes or lie about your teen’s age to get into the movies for a cheaper price, you may send them the message that cheating is acceptable.
Consequences
If you do catch your teen cheating, take action . Just because your teen insists, “Everyone uses an app to get homework done,” don’t blindly believe it or let that give them a free pass. Instead, reiterate your expectations and provide substantive consequences. These may include removing phone privileges for a specified period of time. Sometimes the loss of privileges —such as your teen’s electronics—for 24 hours is enough to send a clear message.
Allow your teen to face consequences at school as well. If they get a zero on a test for cheating, don’t argue with the teacher. Instead, let your teen know that cheating has serious ramifications—and that they will not get away with this behavior.
However, do find out why your teen is cheating. Consider if they're over-scheduled or afraid they can’t keep up with their peers. Are they struggling to understand the material? Do they feel unhealthy pressure to excel? Ask questions to gain an understanding so you can help prevent cheating in the future and ensure they can succeed on their own.
It’s better for your teen to learn lessons about cheating now, rather than later in life. Dishonesty can have serious consequences. Cheating in college could get your teen expelled and cheating at a future job could get them fired or it could even lead to legal action. Cheating on a future partner could lead to the end of the relationship.
A Word From Verywell
Make sure your teen knows that honesty and focusing on learning rather than only on getting "good grades," at all costs, really is the best policy. Talk about honesty often and validate your teen’s feelings when they're frustrated with schoolwork—and the fact that some students who cheat seem to get ahead without getting caught. Assure them that ultimately, people who cheat truly are cheating themselves.
Common Sense Media. It's ridiculously easy for kids to cheat now .
Common Sense Media. 35% of kids admit to using cell phones to cheat .
Isakov M, Tripathy A. Behavioral correlates of cheating: environmental specificity and reward expectation . PLoS One . 2017;12(10):e0186054. Published 2017 Oct 26. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0186054
Marksteiner T, Nishen AK, Dickhäuser O. Students' perception of teachers' reference norm orientation and cheating in the classroom . Front Psychol . 2021;12:614199. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2021.614199
Khan ZR, Sivasubramaniam S, Anand P, Hysaj A. ‘ e’-thinking teaching and assessment to uphold academic integrity: lessons learned from emergency distance learning . International Journal for Educational Integrity . 2021;17(1):17. doi:10.1007/s40979-021-00079-5
Farnese ML, Tramontano C, Fida R, Paciello M. Cheating behaviors in academic context: does academic moral disengagement matter? Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences . 2011;29:356-365. doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.11.250
Pew Research Center. How parents and schools regulate teens' mobile phones .
Mohammad Abu Taleb BR, Coughlin C, Romanowski MH, Semmar Y, Hosny KH. Students, mobile devices and classrooms: a comparison of US and Arab undergraduate students in a middle eastern university . HES . 2017;7(3):181. doi:10.5539/hes.v7n3p181
Gasparyan AY, Nurmashev B, Seksenbayev B, Trukhachev VI, Kostyukova EI, Kitas GD. Plagiarism in the context of education and evolving detection strategies . J Korean Med Sci . 2017;32(8):1220-1227. doi:10.3346/jkms.2017.32.8.1220
Bretag T. Challenges in addressing plagiarism in education . PLoS Med . 2013;10(12):e1001574. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001574
American Academy of Pediatrics. Competition and cheating .
Korn L, Davidovitch N. The Profile of academic offenders: features of students who admit to academic dishonesty . Med Sci Monit . 2016;22:3043-3055. doi:10.12659/msm.898810
Abi-Jaoude E, Naylor KT, Pignatiello A. Smartphones, social media use and youth mental health . CMAJ . 2020;192(6):E136-E141. doi:10.1503/cmaj.190434
Stets JE, Trettevik R. Happiness and Identities . Soc Sci Res. 2016;58:1-13. doi:10.1016/j.ssresearch.2016.04.011
Lenhart A. Teens, Social Media & Technology Overview 2015 . Pew Research Center.
By Amy Morin, LCSW Amy Morin, LCSW, is the Editor-in-Chief of Verywell Mind. She's also a psychotherapist, an international bestselling author of books on mental strength and host of The Verywell Mind Podcast. She delivered one of the most popular TEDx talks of all time.
Trending Post : 12 Powerful Discussion Strategies to Engage Students

Why Students Cheat on Homework and How to Prevent It
One of the most frustrating aspects of teaching in today’s world is the cheating epidemic. There’s nothing more irritating than getting halfway through grading a large stack of papers only to realize some students cheated on the assignment. There’s really not much point in teachers grading work that has a high likelihood of having been copied or otherwise unethically completed. So. What is a teacher to do? We need to be able to assess students. Why do students cheat on homework, and how can we address it?
Like most new teachers, I learned the hard way over the course of many years of teaching that it is possible to reduce cheating on homework, if not completely prevent it. Here are six suggestions to keep your students honest and to keep yourself sane.
ASSIGN LESS HOMEWORK
One of the reasons students cheat on homework is because they are overwhelmed. I remember vividly what it felt like to be a high school student in honors classes with multiple extracurricular activities on my plate. Other teens have after school jobs to help support their families, and some don’t have a home environment that is conducive to studying.
While cheating is never excusable under any circumstances, it does help to walk a mile in our students’ shoes. If they are consistently making the decision to cheat, it might be time to reduce the amount of homework we are assigning.
I used to give homework every night – especially to my advanced students. I wanted to push them. Instead, I stressed them out. They wanted so badly to be in the Top 10 at graduation that they would do whatever they needed to do in order to complete their assignments on time – even if that meant cheating.
When assigning homework, consider the at-home support, maturity, and outside-of-school commitments involved. Think about the kind of school and home balance you would want for your own children. Go with that.
PROVIDE CLASS TIME
Allowing students time in class to get started on their assignments seems to curb cheating to some extent. When students have class time, they are able to knock out part of the assignment, which leaves less to fret over later. Additionally, it gives them an opportunity to ask questions.
When students are confused while completing assignments at home, they often seek “help” from a friend instead of going in early the next morning to request guidance from the teacher. Often, completing a portion of a homework assignment in class gives students the confidence that they can do it successfully on their own. Plus, it provides the social aspect of learning that many students crave. Instead of fighting cheating outside of class , we can allow students to work in pairs or small groups in class to learn from each other.
Plus, to prevent students from wanting to cheat on homework, we can extend the time we allow them to complete it. Maybe students would work better if they have multiple nights to choose among options on a choice board. Home schedules can be busy, so building in some flexibility to the timeline can help reduce pressure to finish work in a hurry.
GIVE MEANINGFUL WORK
If you find students cheat on homework, they probably lack the vision for how the work is beneficial. It’s important to consider the meaningfulness and valuable of the assignment from students’ perspectives. They need to see how it is relevant to them.
In my class, I’ve learned to assign work that cannot be copied. I’ve never had luck assigning worksheets as homework because even though worksheets have value, it’s generally not obvious to teenagers. It’s nearly impossible to catch cheating on worksheets that have “right or wrong” answers. That’s not to say I don’t use worksheets. I do! But. I use them as in-class station, competition, and practice activities, not homework.
So what are examples of more effective and meaningful types of homework to assign?
- Ask students to complete a reading assignment and respond in writing .
- Have students watch a video clip and answer an oral entrance question.
- Require that students contribute to an online discussion post.
- Assign them a reflection on the day’s lesson in the form of a short project, like a one-pager or a mind map.
As you can see, these options require unique, valuable responses, thereby reducing the opportunity for students to cheat on them. The more open-ended an assignment is, the more invested students need to be to complete it well.
DIFFERENTIATE
Part of giving meaningful work involves accounting for readiness levels. Whenever we can tier assignments or build in choice, the better. A huge cause of cheating is when work is either too easy (and students are bored) or too hard (and they are frustrated). Getting to know our students as learners can help us to provide meaningful differentiation options. Plus, we can ask them!
This is what you need to be able to demonstrate the ability to do. How would you like to show me you can do it?

REDUCE THE POINT VALUE
If you’re sincerely concerned about students cheating on assignments, consider reducing the point value. Reflect on your grading system.
Are homework grades carrying so much weight that students feel the need to cheat in order to maintain an A? In a standards-based system, will the assignment be a key determining factor in whether or not students are proficient with a skill?
Each teacher has to do what works for him or her. In my classroom, homework is worth the least amount out of any category. If I assign something for which I plan on giving completion credit, the point value is even less than it typically would be. Projects, essays, and formal assessments count for much more.
CREATE AN ETHICAL CULTURE
To some extent, this part is out of educators’ hands. Much of the ethical and moral training a student receives comes from home. Still, we can do our best to create a classroom culture in which we continually talk about integrity, responsibility, honor, and the benefits of working hard. What are some specific ways can we do this?
Building Community and Honestly
- Talk to students about what it means to cheat on homework. Explain to them that there are different kinds. Many students are unaware, for instance, that the “divide and conquer (you do the first half, I’ll do the second half, and then we will trade answers)” is cheating.
- As a class, develop expectations and consequences for students who decide to take short cuts.
- Decorate your room with motivational quotes that relate to honesty and doing the right thing.
- Discuss how making a poor decision doesn’t make you a bad person. It is an opportunity to grow.
- Share with students that you care about them and their futures. The assignments you give them are intended to prepare them for success.
- Offer them many different ways to seek help from you if and when they are confused.
- Provide revision opportunities for homework assignments.
- Explain that you partner with their parents and that guardians will be notified if cheating occurs.
- Explore hypothetical situations. What if you have a late night? Let’s pretend you don’t get home until after orchestra and Lego practices. You have three hours of homework to do. You know you can call your friend, Bob, who always has his homework done. How do you handle this situation?
EDUCATE ABOUT PLAGIARISM
Many students don’t realize that plagiarism applies to more than just essays. At the beginning of the school year, teachers have an energized group of students, fresh off of summer break. I’ve always found it’s easiest to motivate my students at this time. I capitalize on this opportunity by beginning with a plagiarism mini unit .
While much of the information we discuss is about writing, I always make sure my students know that homework can be plagiarized. Speeches can be plagiarized. Videos can be plagiarized. Anything can be plagiarized, and the repercussions for stealing someone else’s ideas (even in the form of a simple worksheet) are never worth the time saved by doing so.
In an ideal world, no one would cheat. However, teaching and learning in the 21st century is much different than it was fifty years ago. Cheating? It’s increased. Maybe because of the digital age… the differences in morals and values of our culture… people are busier. Maybe because students don’t see how the school work they are completing relates to their lives.
No matter what the root cause, teachers need to be proactive. We need to know why students feel compelled to cheat on homework and what we can do to help them make learning for beneficial. Personally, I don’t advocate for completely eliminating homework with older students. To me, it has the potential to teach students many lessons both related to school and life. Still, the “right” answer to this issue will be different for each teacher, depending on her community, students, and culture.
STRATEGIES FOR ADDRESSING CHALLENGING BEHAVIORS IN SECONDARY
You may also enjoy:.

You are so right about communicating the purpose of the assignment and giving students time in class to do homework. I also use an article of the week on plagiarism. I give students points for the learning – not the doing. It makes all the difference. I tell my students why they need to learn how to do “—” for high school or college or even in life experiences. Since, they get an A or F for the effort, my students are more motivated to give it a try. No effort and they sit in my class to work with me on the assignment. Showing me the effort to learn it — asking me questions about the assignment, getting help from a peer or me, helping a peer are all ways to get full credit for the homework- even if it’s not complete. I also choose one thing from each assignment for the test which is a motivator for learning the material – not just “doing it.” Also, no one is permitted to earn a D or F on a test. Any student earning an F or D on a test is then required to do a project over the weekend or at lunch or after school with me. All of this reinforces the idea – learning is what is the goal. Giving students options to show their learning is also important. Cheating is greatly reduced when the goal is to learn and not simply earn the grade.
Thanks for sharing your unique approaches, Sandra! Learning is definitely the goal, and getting students to own their learning is key.
Comments are closed.
Get the latest in your inbox!

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the 5 best homework help websites (free and paid).
Other High School , General Education

Listen: we know homework isn’t fun, but it is a good way to reinforce the ideas and concepts you’ve learned in class. But what if you’re really struggling with your homework assignments?
If you’ve looked online for a little extra help with your take-home assignments, you’ve probably stumbled across websites claiming to provide the homework help and answers students need to succeed . But can homework help sites really make a difference? And if so, which are the best homework help websites you can use?
Below, we answer these questions and more about homework help websites–free and paid. We’ll go over:
- The basics of homework help websites
- The cost of homework help websites
- The five best homework websites out there
- The pros and cons of using these websites for homework help
- The line between “learning” and “cheating” when using online homework help
- Tips for getting the most out of a homework help website
So let’s get started!

The Basics About Homework Help Websites–Free and Paid
Homework help websites are designed to help you complete your homework assignments, plain and simple.
What Makes a Homework Help Site Worth Using
Most of the best sites allow users to ask questions and then provide an answer (or multiple possible answers) and explanation in seconds. In some instances, you can even send a photo of a particular assignment or problem instead of typing the whole thing out!
Homework help sites also offer more than just help answering homework questions. Common services provided are Q&A with experts, educational videos, lectures, practice tests and quizzes, learning modules, math solving tools, and proofreading help. Homework help sites can also provide textbook solutions (i.e. answers to problems in tons of different textbooks your school might be using), one-on-one tutoring, and peer-to-peer platforms that allow you to discuss subjects you’re learning about with your fellow students.
And best of all, nearly all of them offer their services 24/7, including tutoring!
What You Should Should Look Out For
When it comes to homework help, there are lots–and we mean lots –of scam sites out there willing to prey on desperate students. Before you sign up for any service, make sure you read reviews to ensure you’re working with a legitimate company.
A word to the wise: the more a company advertises help that veers into the territory of cheating, the more likely it is to be a scam. The best homework help websites are going to help you learn the concepts you’ll need to successfully complete your homework on your own. (We’ll go over the difference between “homework help” and “cheating” a little later!)

You don't need a golden piggy bank to use homework help websites. Some provide low or no cost help for students like you!
How Expensive Are the Best Homework Help Websites?
First of all, just because a homework help site costs money doesn’t mean it’s a good service. Likewise, just because a homework help website is free doesn’t mean the help isn’t high quality. To find the best websites, you have to take a close look at the quality and types of information they provide!
When it comes to paid homework help services, the prices vary pretty widely depending on the amount of services you want to subscribe to. Subscriptions can cost anywhere from $2 to $150 dollars per month, with the most expensive services offering several hours of one-on-one tutoring with a subject expert per month.
The 5 Best Homework Help Websites
So, what is the best homework help website you can use? The answer is that it depends on what you need help with.
The best homework help websites are the ones that are reliable and help you learn the material. They don’t just provide answers to homework questions–they actually help you learn the material.
That’s why we’ve broken down our favorite websites into categories based on who they’re best for . For instance, the best website for people struggling with math might not work for someone who needs a little extra help with science, and vice versa.
Keep reading to find the best homework help website for you!
Best Free Homework Help Site: Khan Academy
- Price: Free!
- Best for: Practicing tough material
Not only is Khan Academy free, but it’s full of information and can be personalized to suit your needs. When you set up your account , you choose which courses you need to study, and Khan Academy sets up a personal dashboard of instructional videos, practice exercises, and quizzes –with both correct and incorrect answer explanations–so you can learn at your own pace.
As an added bonus, it covers more course topics than many other homework help sites, including several AP classes.
Runner Up: Brainly.com offers a free service that allows you to type in questions and get answers and explanations from experts. The downside is that you’re limited to two answers per question and have to watch ads.
Best Paid Homework Help Site: Chegg
- Price: $14.95 to $19.95 per month
- Best for: 24/7 homework assistance
This service has three main parts . The first is Chegg Study, which includes textbook solutions, Q&A with subject experts, flashcards, video explanations, a math solver, and writing help. The resources are thorough, and reviewers state that Chegg answers homework questions quickly and accurately no matter when you submit them.
Chegg also offers textbook rentals for students who need access to textbooks outside of their classroom. Finally, Chegg offers Internship and Career Advice for students who are preparing to graduate and may need a little extra help with the transition out of high school.
Another great feature Chegg provides is a selection of free articles geared towards helping with general life skills, like coping with stress and saving money. Chegg’s learning modules are comprehensive, and they feature solutions to the problems in tons of different textbooks in a wide variety of subjects.
Runner Up: Bartleby offers basically the same services as Chegg for $14.99 per month. The reason it didn’t rank as the best is based on customer reviews that say user questions aren’t answered quite as quickly on this site as on Chegg. Otherwise, this is also a solid choice!

Best Site for Math Homework Help: Photomath
- Price: Free (or $59.99 per year for premium services)
- Best for: Explaining solutions to math problems
This site allows you to t ake a picture of a math problem, and instantly pulls up a step-by-step solution, as well as a detailed explanation of the concept. Photomath also includes animated videos that break down mathematical concepts to help you better understand and remember them.
The basic service is free, but for an additional fee you can get extra study tools and learn additional strategies for solving common math problems.
Runner Up: KhanAcademy offers in-depth tutorials that cover complex math topics for free, but you won’t get the same tailored help (and answers!) that Photomath offers.
Best Site for English Homework Help: Princeton Review Academic Tutoring
- Price: $40 to $153 per month, depending on how many hours of tutoring you want
- Best for: Comprehensive and personalized reading and writing help
While sites like Grammarly and Sparknotes help you by either proofreading what you write via an algorithm or providing book summaries, Princeton Review’s tutors provide in-depth help with vocabulary, literature, essay writing and development, proofreading, and reading comprehension. And unlike other services, you’ll have the chance to work with a real person to get help.
The best part is that you can get on-demand English (and ESL) tutoring from experts 24/7. That means you can get help whenever you need it, even if you’re pulling an all-nighter!
This is by far the most expensive homework site on this list, so you’ll need to really think about what you need out of a homework help website before you commit. One added benefit is that the subscription covers over 80 other subjects, including AP classes, which can make it a good value if you need lots of help!

Best Site for STEM Homework Help: Studypool
- Best for: Science homework help
- Price: Varies; you’ll pay for each question you submit
When it comes to science homework help, there aren’t a ton of great resources out there. The best of the bunch is Studypool, and while it has great reviews, there are some downsides as well.
Let’s start with the good stuff. Studypool offers an interesting twist on the homework help formula. After you create a free account, you can submit your homework help questions, and tutors will submit bids to answer your questions. You’ll be able to select the tutor–and price point–that works for you, then you’ll pay to have your homework question answered. You can also pay a small fee to access notes, lectures, and other documents that top tutors have uploaded.
The downside to Studypool is that the pricing is not transparent . There’s no way to plan for how much your homework help will cost, especially if you have lots of questions! Additionally, it’s not clear how tutors are selected, so you’ll need to be cautious when you choose who you’d like to answer your homework questions.

What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Homework Help Sites?
Homework help websites can be a great resource if you’re struggling in a subject, or even if you just want to make sure that you’re really learning and understanding topics and ideas that you’re interested in. But, there are some possible drawbacks if you don’t use these sites responsibly.
We’ll go over the good–and the not-so-good–aspects of getting online homework help below.
3 Pros of Using Homework Help Websites
First, let’s take a look at the benefits.
#1: Better Grades Beyond Homework
This is a big one! Getting outside help with your studies can improve your understanding of concepts that you’re learning, which translates into better grades when you take tests or write essays.
Remember: homework is designed to help reinforce the concepts you learned in class. If you just get easy answers without learning the material behind the problems, you may not have the tools you need to be successful on your class exams…or even standardized tests you’ll need to take for college.
#2: Convenience
One of the main reasons that online homework help is appealing is because it’s flexible and convenient. You don’t have to go to a specific tutoring center while they’re open or stay after school to speak with your teacher. Instead, you can access helpful resources wherever you can access the internet, whenever you need them.
This is especially true if you tend to study at off hours because of your extracurriculars, work schedule, or family obligations. Sites that offer 24/7 tutoring can give you the extra help you need if you can’t access the free resources that are available at your school.
#3: Variety
Not everyone learns the same way. Maybe you’re more of a visual learner, but your teacher mostly does lectures. Or maybe you learn best by listening and taking notes, but you’re expected to learn something just from reading the textbook .
One of the best things about online homework help is that it comes in a variety of forms. The best homework help sites offer resources for all types of learners, including videos, practice activities, and even one-on-one discussions with real-life experts.
This variety can also be a good thing if you just don’t really resonate with the way a concept is being explained (looking at you, math textbooks!).

Not so fast. There are cons to homework help websites, too. Get to know them below!
3 Cons of Using Homework Help Websites
Now, let’s take a look at the drawbacks of online homework help.
#1: Unreliable Info
This can be a real problem. In addition to all the really good homework help sites, there are a whole lot of disreputable or unreliable sites out there. The fact of the matter is that some homework help sites don’t necessarily hire people who are experts in the subjects they’re talking about. In those cases, you may not be getting the accurate, up-to-date, and thorough information you need.
Additionally, even the great sites may not be able to answer all of your homework questions. This is especially true if the site uses an algorithm or chatbot to help students…or if you’re enrolled in an advanced or college-level course. In these cases, working with your teacher or school-provided tutors are probably your best option.
#2: No Clarification
This depends on the service you use, of course. But the majority of them provide free or low-cost help through pre-recorded videos. Watching videos or reading info online can definitely help you with your homework… but you can’t ask questions or get immediate feedback if you need it .
#3: Potential For Scamming
Like we mentioned earlier, there are a lot of homework help websites out there, and lots of them are scams. The review comments we read covered everything from outdated or wrong information, to misleading claims about the help provided, to not allowing people to cancel their service after signing up.
No matter which site you choose to use, make sure you research and read reviews before you sign up–especially if it’s a paid service!

When Does “Help” Become “Cheating”?
Admittedly, whether using homework help websites constitutes cheating is a bit of a grey area. For instance, is it “help” when a friend reads your essay for history class and corrects your grammar, or is it “cheating”? The truth is, not everyone agrees on when “help” crosses the line into “cheating .” When in doubt, it can be a good idea to check with your teacher to see what they think about a particular type of help you want to get.
That said, a general rule of thumb to keep in mind is to make sure that the assignment you turn in for credit is authentically yours . It needs to demonstrate your own thoughts and your own current abilities. Remember: the point of every homework assignment is to 1) help you learn something, and 2) show what you’ve learned.
So if a service answers questions or writes essays for you, there’s a good chance using it constitutes cheating.
Here’s an example that might help clarify the difference for you. Brainstorming essay ideas with others or looking online for inspiration is “help” as long as you write the essay yourself. Having someone read it and give you feedback about what you need to change is also help, provided you’re the one that makes the changes later.
But copying all or part of an essay you find online or having someone write (or rewrite) the whole thing for you would be “cheating.” The same is true for other subjects. Ultimately, if you’re not generating your own work or your own answers, it’s probably cheating.

5 Tips for Finding the Best Homework Help Websites for You
Now that you know some of our favorite homework help websites, free and paid, you can start doing some additional research on your own to decide which services might work best for you! Here are some top tips for choosing a homework help website.
Tip 1: Decide How You Learn Best
Before you decide which site or sites you’re going to use for homework help, y ou should figure out what kind of learning style works for you the most. Are you a visual learner? Then choose a site that uses lots of videos to help explain concepts. If you know you learn best by actually doing tasks, choose a site that provides lots of practice exercises.
Tip 2: Determine Which Subjects You Need Help With
Just because a homework help site is good overall doesn’t mean that it’s equally good for every subject. If you only need help in math, choose a site that specializes in that area. But if history is where you’re struggling, a site that specializes in math won’t be much help. So make sure to choose a site that you know provides high-quality help in the areas you need it most.
Tip 3: Decide How Much One-On-One Help You Need
This is really about cost-effectiveness. If you learn well on your own by reading and watching videos, a free site like Khan Academy is a good choice. But if you need actual tutoring, or to be able to ask questions and get personalized answers from experts, a paid site that provides that kind of service may be a better option.
Tip 4: Set a Budget
If you decide you want to go with a paid homework help website, set a budget first . The prices for sites vary wildly, and the cost to use them can add up quick.
Tip 5: Read the Reviews
Finally, it’s always a good idea to read actual reviews written by the people using these homework sites. You’ll learn the good, the bad, and the ugly of what the users’ experiences have been. This is especially true if you intend to subscribe to a paid service. You’ll want to make sure that users think it’s worth the price overall!

What’s Next?
If you want to get good grades on your homework, it’s a good idea to learn how to tackle it strategically. Our expert tips will help you get the most out of each assignment…and boost your grades in the process.
Doing well on homework assignments is just one part of getting good grades. We’ll teach you everything you need to know about getting great grades in high school in this article.
Of course, test grades can make or break your GPA, too. Here are 17 expert tips that’ll help you get the most out of your study prep before you take an exam.
Need more help? Check out Tutorbase!
Our vetted tutor database includes a range of experienced educators who can help you polish an essay for English or explain how derivatives work for Calculus. You can use dozens of filters and search criteria to find the perfect person for your needs.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Why Do Students Cheat?
- Posted July 19, 2016
- By Zachary Goldman

In March, Usable Knowledge published an article on ethical collaboration , which explored researchers’ ideas about how to develop classrooms and schools where collaboration is nurtured but cheating is avoided. The piece offers several explanations for why students cheat and provides powerful ideas about how to create ethical communities. The article left me wondering how students themselves might respond to these ideas, and whether their experiences with cheating reflected the researchers’ understanding. In other words, how are young people “reading the world,” to quote Paulo Freire , when it comes to questions of cheating, and what might we learn from their perspectives?
I worked with Gretchen Brion-Meisels to investigate these questions by talking to two classrooms of students from Massachusetts and Texas about their experiences with cheating. We asked these youth informants to connect their own insights and ideas about cheating with the ideas described in " Ethical Collaboration ." They wrote from a range of perspectives, grappling with what constitutes cheating, why people cheat, how people cheat, and when cheating might be ethically acceptable. In doing so, they provide us with additional insights into why students cheat and how schools might better foster ethical collaboration.
Why Students Cheat
Students critiqued both the individual decision-making of peers and the school-based structures that encourage cheating. For example, Julio (Massachusetts) wrote, “Teachers care about cheating because its not fair [that] students get good grades [but] didn't follow the teacher's rules.” His perspective represents one set of ideas that we heard, which suggests that cheating is an unethical decision caused by personal misjudgment. Umna (Massachusetts) echoed this idea, noting that “cheating is … not using the evidence in your head and only using the evidence that’s from someone else’s head.”
Other students focused on external factors that might make their peers feel pressured to cheat. For example, Michima (Massachusetts) wrote, “Peer pressure makes students cheat. Sometimes they have a reason to cheat like feeling [like] they need to be the smartest kid in class.” Kayla (Massachusetts) agreed, noting, “Some people cheat because they want to seem cooler than their friends or try to impress their friends. Students cheat because they think if they cheat all the time they’re going to get smarter.” In addition to pressure from peers, students spoke about pressure from adults, pressure related to standardized testing, and the demands of competing responsibilities.
When Cheating is Acceptable
Students noted a few types of extenuating circumstances, including high stakes moments. For example, Alejandra (Texas) wrote, “The times I had cheated [were] when I was failing a class, and if I failed the final I would repeat the class. And I hated that class and I didn’t want to retake it again.” Here, she identifies allegiance to a parallel ethical value: Graduating from high school. In this case, while cheating might be wrong, it is an acceptable means to a higher-level goal.
Encouraging an Ethical School Community
Several of the older students with whom we spoke were able to offer us ideas about how schools might create more ethical communities. Sam (Texas) wrote, “A school where cheating isn't necessary would be centered around individualization and learning. Students would learn information and be tested on the information. From there the teachers would assess students' progress with this information, new material would be created to help individual students with what they don't understand. This way of teaching wouldn't be based on time crunching every lesson, but more about helping a student understand a concept.”
Sam provides a vision for the type of school climate in which collaboration, not cheating, would be most encouraged. Kaith (Texas), added to this vision, writing, “In my own opinion students wouldn’t find the need to cheat if they knew that they had the right undivided attention towards them from their teachers and actually showed them that they care about their learning. So a school where cheating wasn’t necessary would be amazing for both teachers and students because teachers would be actually getting new things into our brains and us as students would be not only attentive of our teachers but also in fact learning.”
Both of these visions echo a big idea from “ Ethical Collaboration ”: The importance of reducing the pressure to achieve. Across students’ comments, we heard about how self-imposed pressure, peer pressure, and pressure from adults can encourage cheating.
Where Student Opinions Diverge from Research
The ways in which students spoke about support differed from the descriptions in “ Ethical Collaboration .” The researchers explain that, to reduce cheating, students need “vertical support,” or standards, guidelines, and models of ethical behavior. This implies that students need support understanding what is ethical. However, our youth informants describe a type of vertical support that centers on listening and responding to students’ needs. They want teachers to enable ethical behavior through holistic support of individual learning styles and goals. Similarly, researchers describe “horizontal support” as creating “a school environment where students know, and can persuade their peers, that no one benefits from cheating,” again implying that students need help understanding the ethics of cheating. Our youth informants led us to believe instead that the type of horizontal support needed may be one where collective success is seen as more important than individual competition.
Why Youth Voices Matter, and How to Help Them Be Heard
Our purpose in reaching out to youth respondents was to better understand whether the research perspectives on cheating offered in “ Ethical Collaboration ” mirrored the lived experiences of young people. This blog post is only a small step in that direction; young peoples’ perspectives vary widely across geographic, demographic, developmental, and contextual dimensions, and we do not mean to imply that these youth informants speak for all youth. However, our brief conversations suggest that asking youth about their lived experiences can benefit the way that educators understand school structures.
Too often, though, students are cut out of conversations about school policies and culture. They rarely even have access to information on current educational research, partially because they are not the intended audience of such work. To expand opportunities for student voice, we need to create spaces — either online or in schools — where students can research a current topic that interests them. Then they can collect information, craft arguments they want to make, and deliver their messages. Educators can create the spaces for this youth-driven work in schools, communities, and even policy settings — helping to support young people as both knowledge creators and knowledge consumers.
Additional Resources
- Read “ Student Voice in Educational Research and Reform ” [PDF] by Alison Cook-Sather.
- Read “ The Significance of Students ” [PDF] by Dana L. Mitra.
- Read “ Beyond School Spirit ” by Emily J. Ozer and Dana Wright.
Related Articles

Part of the Conversation: Rachel Hanebutt, MBE'16
Fighting for change: estefania rodriguez, l&t'16, notes from ferguson.

The Real Roots of Student Cheating
Let's address the mixed messages we are sending to young people..
Updated September 28, 2023 | Reviewed by Ray Parker
- Why Education Is Important
- Find a Child Therapist
- Cheating is rampant, yet young people consistently affirm honesty and the belief that cheating is wrong.
- This discrepancy arises, in part, from the tension students perceive between honesty and the terms of success.
- In an integrated environment, achievement and the real world are not seen as at odds with honesty.

The release of ChatGPT has high school and college teachers wringing their hands. A Columbia University undergraduate rubbed it in our face last May with an opinion piece in the Chronicle of Higher Education titled I’m a Student. You Have No Idea How Much We’re Using ChatGPT.
He goes on to detail how students use the program to “do the lion’s share of the thinking,” while passing off the work as their own. Catching the deception , he insists, is impossible.
As if students needed more ways to cheat. Every survey of students, whether high school or college, has found that cheating is “rampant,” “epidemic,” “commonplace, and practically expected,” to use a few of the terms with which researchers have described the scope of academic dishonesty.
In a 2010 study by the Josephson Institute, for example, 59 percent of the 43,000 high school students admitted to cheating on a test in the past year. According to a 2012 white paper, Cheat or Be Cheated? prepared by Challenge Success, 80 percent admitted to copying another student’s homework. The other studies summarized in the paper found self-reports of past-year cheating by high school students in the 70 percent to 80 percent range and higher.
At colleges, the situation is only marginally better. Studies consistently put the level of self-reported cheating among undergraduates between 50 percent and 70 percent depending in part on what behaviors are included. 1
The sad fact is that cheating is widespread.
Commitment to Honesty
Yet, when asked, most young people affirm the moral value of honesty and the belief that cheating is wrong. For example, in a survey of more than 3,000 teens conducted by my colleagues at the University of Virginia, the great majority (83 percent) indicated that to become “honest—someone who doesn’t lie or cheat,” was very important, if not essential to them.
On a long list of traits and qualities, they ranked honesty just below “hard-working” and “reliable and dependent,” and far ahead of traits like being “ambitious,” “a leader ,” and “popular.” When asked directly about cheating, only 6 percent thought it was rarely or never wrong.
Other studies find similar commitments, as do experimental studies by psychologists. In experiments, researchers manipulate the salience of moral beliefs concerning cheating by, for example, inserting moral reminders into the test situation to gauge their effect. Although students often regard some forms of cheating, such as doing homework together when they are expected to do it alone, as trivial, the studies find that young people view cheating in general, along with specific forms of dishonesty, such as copying off another person’s test, as wrong.
They find that young people strongly care to think of themselves as honest and temper their cheating behavior accordingly. 2
The Discrepancy Between Belief and Behavior
Bottom line: Kids whose ideal is to be honest and who know cheating is wrong also routinely cheat in school.
What accounts for this discrepancy? In the psychological and educational literature, researchers typically focus on personal and situational factors that work to override students’ commitment to do the right thing.
These factors include the force of different motives to cheat, such as the desire to avoid failure, and the self-serving rationalizations that students use to excuse their behavior, like minimizing responsibility—“everyone is doing it”—or dismissing their actions because “no one is hurt.”
While these explanations have obvious merit—we all know the gap between our ideals and our actions—I want to suggest another possibility: Perhaps the inconsistency also reflects the mixed messages to which young people (all of us, in fact) are constantly subjected.
Mixed Messages
Consider the story that young people hear about success. What student hasn’t been told doing well includes such things as getting good grades, going to a good college, living up to their potential, aiming high, and letting go of “limiting beliefs” that stand in their way? Schools, not to mention parents, media, and employers, all, in various ways, communicate these expectations and portray them as integral to the good in life.
They tell young people that these are the standards they should meet, the yardsticks by which they should measure themselves.
In my interviews and discussions with young people, it is clear they have absorbed these powerful messages and feel held to answer, to themselves and others, for how they are measuring up. Falling short, as they understand and feel it, is highly distressful.
At the same time, they are regularly exposed to the idea that success involves a trade-off with honesty and that cheating behavior, though regrettable, is “real life.” These words are from a student on a survey administered at an elite high school. “People,” he continued, “who are rich and successful lie and cheat every day.”

In this thinking, he is far from alone. In a 2012 Josephson Institute survey of 23,000 high school students, 57 percent agreed that “in the real world, successful people do what they have to do to win, even if others consider it cheating.” 3
Putting these together, another high school student told a researcher: “Grades are everything. You have to realize it’s the only possible way to get into a good college and you resort to any means necessary.”
In a 2021 survey of college students by College Pulse, the single biggest reason given for cheating, endorsed by 72 percent of the respondents, was “pressure to do well.”
What we see here are two goods—educational success and honesty—pitted against each other. When the two collide, the call to be successful is likely to be the far more immediate and tangible imperative.
A young person’s very future appears to hang in the balance. And, when asked in surveys , youths often perceive both their parents’ and teachers’ priorities to be more focused on getting “good grades in my classes,” than on character qualities, such as being a “caring community member.”
In noting the mixed messages, my point is not to offer another excuse for bad behavior. But some of the messages just don’t mix, placing young people in a difficult bind. Answering the expectations placed on them can be at odds with being an honest person. In the trade-off, cheating takes on a certain logic.
The proposed remedies to academic dishonesty typically focus on parents and schools. One commonly recommended strategy is to do more to promote student integrity. That seems obvious. Yet, as we saw, students already believe in honesty and the wrongness of (most) cheating. It’s not clear how more teaching on that point would make much of a difference.
Integrity, though, has another meaning, in addition to the personal qualities of being honest and of strong moral principles. Integrity is also the “quality or state of being whole or undivided.” In this second sense, we can speak of social life itself as having integrity.
It is “whole or undivided” when the different contexts of everyday life are integrated in such a way that norms, values, and expectations are fairly consistent and tend to reinforce each other—and when messages about what it means to be a good, accomplished person are not mixed but harmonious.
While social integrity rooted in ethical principles does not guarantee personal integrity, it is not hard to see how that foundation would make a major difference. Rather than confronting students with trade-offs that incentivize “any means necessary,” they would receive positive, consistent reinforcement to speak and act truthfully.
Talk of personal integrity is all for the good. But as pervasive cheating suggests, more is needed. We must also work to shape an integrated environment in which achievement and the “real world” are not set in opposition to honesty.
1. Liora Pedhazur Schmelkin, et al. “A Multidimensional Scaling of College Students’ Perceptions of Academic Dishonesty.” The Journal of Higher Education 79 (2008): 587–607.
2. See, for example, the studies in Christian B. Miller, Character and Moral Psychology. New York: Oxford University Press, 2014, Ch. 3.
3. Josephson Institute. The 2012 Report Card on the Ethics of American Youth (Installment 1: Honesty and Integrity). Josephson Institute of Ethics, 2012.

Joseph E. Davis is Research Professor of Sociology and Director of the Picturing the Human Colloquy of the Institute for Advanced Studies in Culture at the University of Virginia.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Overcome burnout, your burdens, and that endless to-do list.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Advertisement
Academic dishonesty when doing homework: How digital technologies are put to bad use in secondary schools
- Open access
- Published: 23 July 2022
- Volume 28 , pages 1251–1271, ( 2023 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Juliette C. Désiron ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3074-9018 1 &
- Dominik Petko ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1569-1302 1
5340 Accesses
3 Citations
4 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
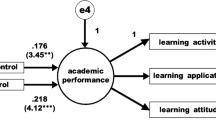
The growth in digital technologies in recent decades has offered many opportunities to support students’ learning and homework completion. However, it has also contributed to expanding the field of possibilities concerning homework avoidance. Although studies have investigated the factors of academic dishonesty, the focus has often been on college students and formal assessments. The present study aimed to determine what predicts homework avoidance using digital resources and whether engaging in these practices is another predictor of test performance. To address these questions, we analyzed data from the Program for International Student Assessment 2018 survey, which contained additional questionnaires addressing this issue, for the Swiss students. The results showed that about half of the students engaged in one kind or another of digitally-supported practices for homework avoidance at least once or twice a week. Students who were more likely to use digital resources to engage in dishonest practices were males who did not put much effort into their homework and were enrolled in non-higher education-oriented school programs. Further, we found that digitally-supported homework avoidance was a significant negative predictor of test performance when considering information and communication technology predictors. Thus, the present study not only expands the knowledge regarding the predictors of academic dishonesty with digital resources, but also confirms the negative impact of such practices on learning.
Similar content being viewed by others
The impact of smartphone use on learning effectiveness: A case study of primary school students
Jen Chun Wang, Chia-Yen Hsieh & Shih-Hao Kung

Adoption of online mathematics learning in Ugandan government universities during the COVID-19 pandemic: pre-service teachers’ behavioural intention and challenges
Geofrey Kansiime & Marjorie Sarah Kabuye Batiibwe
Effects of higher education institutes’ artificial intelligence capability on students' self-efficacy, creativity and learning performance
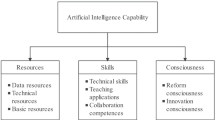
Shaofeng Wang, Zhuo Sun & Ying Chen
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Academic dishonesty is a widespread and perpetual issue for teachers made even more easier to perpetrate with the rise of digital technologies (Blau & Eshet-Alkalai, 2017 ; Ma et al., 2008 ). Definitions vary but overall an academically dishonest practices correspond to learners engaging in unauthorized practice such as cheating and plagiarism. Differences in engaging in those two types of practices mainly resides in students’ perception that plagiarism is worse than cheating (Evering & Moorman, 2012 ; McCabe, 2005 ). Plagiarism is usually defined as the unethical act of copying part or all of someone else’s work, with or without editing it, while cheating is more about sharing practices (Krou et al., 2021 ). As a result, most students do report cheating in an exam or for homework (Ma et al., 2008 ). To note, other research follow a different distinction for those practices and consider that plagiarism is a specific – and common – type of cheating (Waltzer & Dahl, 2022 ). Digital technologies have contributed to opening possibilities of homework avoidance and technology-related distraction (Ma et al., 2008 ; Xu, 2015 ).
The question of whether the use of digital resources hinders or enhances homework has often been investigated in large-scale studies, such as the Program for International Student Assessment (PISA), the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS), and the Progress in International Reading Literacy Study (PIRLS). While most of the early large-scale studies showed positive overall correlations between the use of digital technologies for learning at home and test scores in language, mathematics, and science (e.g., OECD, 2015 ; Petko et al., 2017 ; Skryabin et al., 2015 ), there have been more recent studies reporting negative associations as well (Agasisti et al., 2020 ; Odell et al., 2020 ). One reason for these inconclusive findings is certainly the complex interplay of related factors, which include diverse ways of measuring homework, gender, socioeconomic status, personality traits, learning goals, academic abilities, learning strategies, motivation, and effort, as well as support from teachers and parents. Despite this complexity, it needs to be acknowledged that doing homework digitally does not automatically lead to productive learning activities, and it might even be associated with counter-productive practices such as digital distraction or academic dishonesty. Digitally enhanced academic dishonesty has mostly been investigated regarding formal assessment-related examinations (Evering & Moorman, 2012 ; Ma et al., 2008 ); however, it might be equally important to investigate its effects regarding learning-related assignments such as homework. Although a large body of research exists on digital academic dishonesty regarding assignments in higher education, relatively few studies have investigated this topic on K12 homework. To investigate this issue, we integrated questionnaire items on homework engagement and digital homework avoidance in a national add-on to PISA 2018 in Switzerland. Data from the Swiss sample can serve as a case study for further research with a wider cultural background. This study provides an overview of the descriptive results and tries to identify predictors of the use of digital technology for academic dishonesty when completing homework.
1.1 Prevalence and factors of digital academic dishonesty in schools
According to Pavela’s ( 1997 ) framework, four different types of academic dishonesty can be distinguished: cheating by using unauthorized materials, plagiarism by copying the work of others, fabrication of invented evidence, and facilitation by helping others in their attempts at academic dishonesty. Academic dishonesty can happen in assessment situations, as well as in learning situations. In formal assessments, academic dishonesty usually serves the purpose of passing a test or getting a better grade despite lacking the proper abilities or knowledge. In learning-related situations such as homework, where assignments are mandatory, cheating practices equally qualify as academic dishonesty. For perpetrators, these practices can be seen as shortcuts in which the willingness to invest the proper time and effort into learning is missing (Chow, 2021; Waltzer & Dahl, 2022 ). The interviews by Waltzer & Dahl ( 2022 ) reveal that students do perceive cheating as being wrong but this does not prevent them from engaging in at least one type of dishonest practice. While academic dishonesty is not a new phenomenon, it has been changing together with the development of new digital technologies (Anderman & Koenka, 2017 ; Ercegovac & Richardson, 2004 ). With the rapid growth in technologies, new forms of homework avoidance, such as copying and plagiarism, are developing (Evering & Moorman, 2012 ; Ma et al., 2008 ) summarized the findings of the 2006 U.S. surveys of the Josephson Institute of Ethics with the conclusion that the internet has led to a deterioration of ethics among students. In 2006, one-third of high school students had copied an internet document in the past 12 months, and 60% had cheated on a test. In 2012, these numbers were updated to 32% and 51%, respectively (Josephson Institute of Ethics, 2012 ). Further, 75% reported having copied another’s homework. Surprisingly, only a few studies have provided more recent evidence on the prevalence of academic dishonesty in middle and high schools. The results from colleges and universities are hardly comparable, and until now, this topic has not been addressed in international large-scale studies on schooling and school performance.
Despite the lack of representative studies, research has identified many factors in smaller and non-representative samples that might explain why some students engage in dishonest practices and others do not. These include male gender (Whitley et al., 1999 ), the “dark triad” of personality traits in contrast to conscientiousness and agreeableness (e.g., Cuadrado et al., 2021 ; Giluk & Postlethwaite, 2015 ), extrinsic motivation and performance/avoidance goals in contrast to intrinsic motivation and mastery goals (e.g., Anderman & Koenka, 2017 ; Krou et al., 2021 ), self-efficacy and achievement scores (e.g., Nora & Zhang, 2010 ; Yaniv et al., 2017 ), unethical attitudes, and low fear of being caught (e.g., Cheng et al., 2021 ; Kam et al., 2018 ), influenced by the moral norms of peers and the conditions of the educational context (e.g., Isakov & Tripathy, 2017 ; Kapoor & Kaufman, 2021 ). Similar factors have been reported regarding research on the causes of plagiarism (Husain et al., 2017 ; Moss et al., 2018 ). Further, the systematic review from Chiang et al. ( 2022 ) focused on factors of academic dishonesty in online learning environments. The analyses, based on the six-components behavior engineering, showed that the most prominent factors were environmental (effect of incentives) and individual (effect of motivation). Despite these intensive research efforts, there is still no overarching model that can comprehensively explain the interplay of these factors.
1.2 Effects of homework engagement and digital dishonesty on school performance
In meta-analyses of schools, small but significant positive effects of homework have been found regarding learning and achievement (e.g., Baş et al., 2017 ; Chen & Chen, 2014 ; Fan et al., 2017 ). In their review, Fan et al. ( 2017 ) found lower effect sizes for studies focusing on the time or frequency of homework than for studies investigating homework completion, homework grades, or homework effort. In large surveys, such as PISA, homework measurement by estimating after-school working hours has been customary practice. However, this measure could hide some other variables, such as whether teachers even give homework, whether there are school or state policies regarding homework, where the homework is done, whether it is done alone, etc. (e.g., Fernández-Alonso et al., 2015 , 2017 ). Trautwein ( 2007 ) and Trautwein et al. ( 2009 ) repeatedly showed that homework effort rather than the frequency or the time spent on homework can be considered a better predictor for academic achievement Effort and engagement can be seen as closely interrelated. Martin et al. ( 2017 ) defined engagement as the expressed behavior corresponding to students’ motivation. This has been more recently expanded by the notion of the quality of homework completion (Rosário et al., 2018 ; Xu et al., 2021 ). Therefore, it is a plausible assumption that academic dishonesty when doing homework is closely related to low homework effort and a low quality of homework completion, which in turn affects academic achievement. However, almost no studies exist on the effects of homework avoidance or academic dishonesty on academic achievement. Studies investigating the relationship between academic dishonesty and academic achievement typically use academic achievement as a predictor of academic dishonesty, not the other way around (e.g., Cuadrado et al., 2019 ; McCabe et al., 2001 ). The results of these studies show that low-performing students tend to engage in dishonest practices more often. However, high-performing students also seem to be prone to cheating in highly competitive situations (Yaniv et al., 2017 ).
1.3 Present study and hypotheses
The present study serves three combined purposes.
First, based on the additional questionnaires integrated into the Program for International Student Assessment 2018 (PISA 2018) data collection in Switzerland, we provide descriptive figures on the frequency of homework effort and the various forms of digitally-supported homework avoidance practices.
Second, the data were used to identify possible factors that explain higher levels of digitally-supported homework avoidance practices. Based on our review of the literature presented in Section 1.1 , we hypothesized (Hypothesis 1 – H1) that these factors include homework effort, age, gender, socio-economic status, and study program.
Finally, we tested whether digitally-supported homework avoidance practices were a significant predictor of test score performance. We expected (Hypothesis 2 – H2) that technology-related factors influencing test scores include not only those reported by Petko et al. ( 2017 ) but also self-reported engagement in digital dishonesty practices. .
2.1 Participants
Our analyses were based on data collected for PISA 2018 in Switzerland, made available in June 2021 (Erzinger et al., 2021 ). The target sample of PISA was 15-year-old students, with a two-phase sampling: schools and then students (Erzinger et al., 2019 , p.7–8, OECD, 2019a ). A total of 228 schools were selected for Switzerland, with an original sample of 5822 students. Based on the PISA 2018 technical report (OECD, 2019a ), only participants with a minimum of three valid responses to each scale used in the statistical analyses were included (see Section 2.2 ). A final sample of 4771 responses (48% female) was used for statistical analyses. The mean age was 15 years and 9 months ( SD = 3 months). As Switzerland is a multilingual country, 60% of the respondents completed the questionnaires in German, 23% in French, and 17% in Italian.
2.2 Measures
2.2.1 digital dishonesty in homework scale.
This six-item digital dishonesty for homework scale assesses the use of digital technology for homework avoidance and copying (IC801 C01 to C06), is intended to work as a single overall scale for digital homework dishonesty practice constructed to include items corresponding to two types of dishonest practices from Pavela ( 1997 ), namely cheating and plagiarism (see Table 1 ). Three items target individual digital practices to avoid homework, which can be referred to as plagiarism (items 1, 2 and 5). Two focus more on social digital practices, for which students are cheating together with peers (items 4 and 6). One item target cheating as peer authorized plagiarism. Response options are based on questions on the productive use of digital technologies for homework in the common PISA survey (IC010), with an additional distinction for the lowest frequency option (6-point Likert scale). The scale was not tested prior to its integration into the PISA questionnaire, as it was newly developed for the purposes of this study.
2.2.2 Homework engagement scale
The scale, originally developed by Trautwein et al. (Trautwein, 2007 ; Trautwein et al., 2006 ), measures homework engagement (IC800 C01 to C06) and can be subdivided into two sub-scales: homework compliance and homework effort. The reliability of the scale was tested and established in different variants, both in Germany (Trautwein et al., 2006 ; Trautwein & Köller, 2003 ) and in Switzerland (Schnyder et al., 2008 ; Schynder Godel, 2015 ). In the adaptation used in the PISA 2018 survey, four items were positively poled (items 1, 2, 4, and 6), and two items were negatively poled (items 3 and 5) and presented with a 4-point Likert scale ranging from “Does not apply at all” to “Applies absolutely.” This adaptation showed acceptable reliability in previous studies in Switzerland (α = 0.73 and α = 0.78). The present study focused on homework effort, and thus only data from the corresponding sub-scale was analyzed (items 2 [I always try to do all of my homework], 4 [When it comes to homework, I do my best], and 6 [On the whole, I think I do my homework more conscientiously than my classmates]).
2.2.3 Demographics
Previous studies showed that demographic characteristics, such as age, gender, and socioeconomic status, could impact learning outcomes (Jacobs et al., 2002 ) and intention to use digital tools for learning (Tarhini et al., 2014 ). Gender is a dummy variable (ST004), with 1 for female and 2 for male. Socioeconomic status was analyzed based on the PISA 2018 index of economic, social, and cultural status (ESCS). It is computed from three other indices (OECD, 2019b , Annex A1): parents’ highest level of education (PARED), parents’ highest occupational status (HISEI), and home possessions (HOMEPOS). The final ESCS score is transformed so that 0 corresponds to an average OECD student. More details can be found in Annex A1 from PISA 2018 Results Volume 3 (OECD, 2019b ).
2.2.4 Study program
Although large-scale studies on schools have accounted for the differences between schools, the study program can also be a factor that directly affects digital homework dishonesty practices. In Switzerland, 15-year-old students from the PISA sampling pool can be part of at least six main study programs, which greatly differ in terms of learning content. In this study, study programs distinguished both level and type of study: lower secondary education (gymnasial – n = 798, basic requirements – n = 897, advanced requirements – n = 1235), vocational education (classic – n = 571, with baccalaureate – n = 275), and university entrance preparation ( n = 745). An “other” category was also included ( n = 250). This 6-level ordinal variable was dummy coded based on the available CNTSCHID variable.
2.2.5 Technologies and schools
The PISA 2015 ICT (Information and Communication Technology) familiarity questionnaire included most of the technology-related variables tested by Petko et al. ( 2017 ): ENTUSE (frequency of computer use at home for entertainment purposes), HOMESCH (frequency of computer use for school-related purposes at home), and USESCH (frequency of computer use at school). However, the measure of student’s attitudes toward ICT in the 2015 survey was different from that of the 2012 dataset. Based on previous studies (Arpacı et al., 2021 ; Kunina-Habenicht & Goldhammer, 2020 ), we thus included INICT (Student’s ICT interest), COMPICT (Students’ perceived ICT competence), AUTICT (Students’ perceived autonomy related to ICT use), and SOIACICT (Students’ ICT as a topic in social interaction) instead of the variable ICTATTPOS of the 2012 survey.
2.2.6 Test scores
The PISA science, mathematics, and reading test scores were used as dependent variables to test our second hypothesis. Following Aparicio et al. ( 2021 ), the mean scores from plausible values were computed for each test score and used in the test score analysis.
2.3 Data analyses
Our hypotheses aim to assess the factors explaining student digital homework dishonesty practices (H1) and test score performance (H2). At the student level, we used multilevel regression analyses to decompose the variance and estimate associations. As we used data for Switzerland, in which differences between school systems exist at the level of provinces (within and between), we also considered differences across schools (based on the variable CNTSCHID).
Data were downloaded from the main PISA repository, and additional data for Switzerland were available on forscenter.ch (Erzinger et al., 2021 ). Analyses were computed with Jamovi (v.1.8 for Microsoft Windows) statistics and R packages (GAMLj, lavaan).
3.1 Additional scales for Switzerland
3.1.1 digital dishonesty in homework practices.
The digital homework dishonesty scale (6 items), computed with the six items IC801, was found to be of very good reliability overall (α = 0.91, ω = 0.91). After checking for reliability, a mean score was computed for the overall scale. The confirmatory factor analysis for the one-dimensional model reached an adequate fit, with three modifications using residual covariances between single items χ 2 (6) = 220, p < 0.001, TLI = 0.969, CFI = 0.988, RMSEA (Root Mean Square Error of Approximation) = 0.086, SRMR = 0.016).
On the one hand, the practice that was the least reported was copying something from the internet and presenting it as their own (51% never did). On the other hand, students were more likely to partially copy content from the internet and modify it to present as their own (47% did it at least once a month). Copying answers shared by friends was rather common, with 62% of the students reporting that they engaged in such practices at least once a month.
When all surveyed practices were taken together, 7.6% of the students reported that they had never engaged in digitally dishonest practices for homework, while 30.6% reported cheating once or twice a week, 12.1% almost every day, and 6.9% every day (Table 1 ).
3.1.2 Homework effort
The overall homework engagement scale consisted of six items (IC800), and it was found to be acceptably reliable (α = 0.76, ω = 0.79). Items 3 and 5 were reversed for this analysis. The homework compliance sub-scale had a low reliability (α = 0.58, ω = 0.64), whereas the homework effort sub-scale had an acceptable reliability (α = 0.78, ω = 0.79). Based on our rationale, the following statistical analyses used only the homework effort sub-scale. Furthermore, this focus is justified by the fact that the homework compliance scale might be statistically confounded with the digital dishonesty in homework scale.
Descriptive weighted statistics per item (Table 2 ) showed that while most students (80%) tried to complete all of their homework, only half of the students reported doing those diligently (53.3%). Most students also reported that they believed they put more effort into their homework than their peers (77.7%). The overall mean score of the composite scale was 2.81 ( SD = 0.69).
3.2 Multilevel regression analysis: Predictors of digital dishonesty in homework (H1)
Mixed multilevel modeling was used to analyze predictors of digital homework avoidance while considering the effect of school (random component). Based on our first hypothesis, we compared several models by progressively including the following fixed effects: homework effort and personal traits (age, gender) (Model 2), then socio-economic status (Model 3), and finally, study program (Model 4). The results are presented in Table 3 . Except for the digital homework dishonesty and homework efforts scales, all other scales were based upon the scores computed according to the PISA technical report (OECD, 2019a ).
We first compared variance components. Variance was decomposed into student and school levels. Model 1 provides estimates of the variance component without any covariates. The intraclass coefficient (ICC) indicated that about 6.6% of the total variance was associated with schools. The parameter (b = 2.56, SE b = 0.025 ) falls within the 95% confidence interval. Further, CI is above 0 and thus we can reject the null hypothesis. Comparing the empty model to models with covariates, we found that Models 2, 3 and 4 showed an increase in total explained variance to 10%. Variance explained by the covariates was about 3% in Models 2 and 3, and about 4% in Model 4. Interestingly, in our models, student socio-economic status, measured by the PISA index, never accounted for variance in digitally-supported dishonest practices to complete homework.
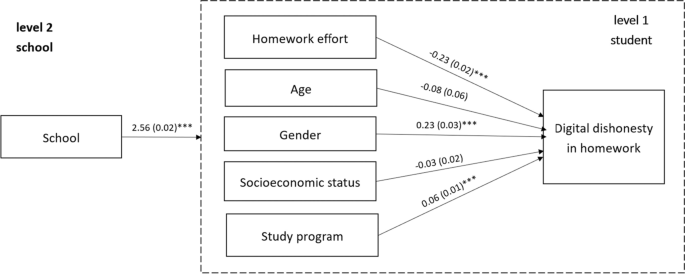
Summary of the two-steps Model 4 (estimates - β, with standard errors and significance levels, *** p < 0.001)
Further, model comparison based on AIC indicates that Model 4, including homework effort, personal traits, socio-economic status, and study program, was the better fit for the data. In Model 4 (Table 3 ; Fig. 1 ), we observed that homework effort and gender were negatively associated with digital dishonesty. Male students who invested less effort in their homework were more prone to engage in digital dishonesty. The study program was positively but weakly associated with digital dishonesty. Students in programs that target higher education were less likely to engage in digital dishonesty when completing homework.

3.3 Multilevel regression analysis: Cheating and test scores (H2)
Our first hypothesis aimed to provide insights into characteristics of students reporting that they regularly use digital resources dishonestly when completing homework. Our second hypothesis focused on whether digitally-supported homework avoidance practices was linked to results of test scores. Mixed multilevel modeling was used to analyze predictors of test scores while considering the effect of school (random component). Based on the study by Petko et al. ( 2017 ), we compared several models by progressively including the following fixed effects ICT use (three measures) (Model 2), then attitude toward ICT (four measures) (Model 3), and finally, digital dishonesty in homework (single measure) (Model 4). The results are presented in Table 4 for science, Table 5 for mathematics, and Table 6 for reading.
Variance components were decomposed into student and school level. ICC for Model 1 indicated that 37.9% of the variance component without covariates was associated with schools.
Taking Model 1 as a reference, we observed an increase in total explained variance to 40.5% with factors related to ICT use (Model 2), to 40.8% with factors related to attitude toward ICT (Model 3), and to 41.1% with the single digital dishonesty factor. It is interesting to note that we obtained different results from those reported by Petko et al. ( 2017 ). In their study, they found significant effects on the explained variances of ENTUSE, USESCH, and ICTATTPOS but not of HOMESCH for Switzerland. In the present study (Model 3), HOMESCH and USESCH were significant predictors but not ENTUSE, and for attitude toward ICT, all but INTICT were significant predictors of the variance. However, factors corresponding to ICT use were negatively associated with test performance, as in the study by Petko et al. ( 2017 ). Similarly, all components of attitude toward ICT positively affected science test scores, except for students’ ICT as a topic in social interaction.
Based on the AIC values, Model 4, including ICT use, attitude toward ICT, and digital dishonesty, was the better fit for the data. The parameter ( b = 498.00, SE b = 3.550) shows that our sample falls within the 95% confidence interval and that we can reject the null hypothesis. In this model, all factors except the use of ICT outside of school for leisure were significant predictors of explained variance in science test scores. These results are consistent with those reported by Petko et al. ( 2017 ), in which more frequent use of ICT negatively affected science test scores, with an overall positive effect of positive attitude toward ICT. Further, we observed that homework avoidance with digital resources strongly negatively affected performance, with lower performance associated with students reporting a higher frequency of engagement in digital dishonesty practices.
For mathematics test scores, results from Models 2 and 3 showed a similar pattern than those for science, and Model 4 also explained the highest variance (41.2%). The results from Model 4 contrast with those found by Petko et al. ( 2017 ), as in this study, HOMESCH was the only significant variable of ICT use. Regarding attitudes toward ICT, only two measures (COMPICT and AUTICT) were significant positive factors in Model 4. As for science test scores, digital dishonesty practices were a significantly strong negative predictor. Students who reported cheating more frequently were more likely to perform poorly on mathematics tests.
The analyses of PISA test scores for reading in Model 2 was similar to that of science and mathematics, with ENTUSE being a non-significant predictor when we included only measures of ICT use as predictors. In Model 3, contrary to the science and mathematics test scores models, in which INICT was non-significant, all measures of attitude toward ICT were positively significant predictors. Nevertheless, as for science and mathematics, Model 4, which included digital dishonesty, explained the greater variance in reading test scores (42.2%). We observed that for reading, all predictors were significant in Model 4, with an overall negative effect of ICT use, a positive effect of attitude toward ICT—except for SOIAICT, and a negative effect of digital dishonesty on test scores. Interestingly, the detrimental effect of using digital resources to engage in dishonest homework completion was the strongest in reading test scores.
4 Discussion
In this study, we were able to provide descriptive statistics on the prevalence of digital dishonesty among secondary students in the Swiss sample of PISA 2018. Students from this country were selected because they received additional questions targeting both homework effort and the frequency with which they engaged in digital dishonesty when doing homework. Descriptive statistics indicated that fairly high numbers of students engage in dishonest homework practices, with 49.6% reporting digital dishonesty at least once or twice a week. The most frequently reported practice was copying answers from friends, which was undertaken at least once a month by more than two-thirds of respondents. Interestingly, the most infamous form of digital dishonesty, that is plagiarism by copy-pasting something from the internet (Evering & Moorman, 2012 ), was admitted to by close to half of the students (49%). These results for homework avoidance are close to those obtained by previous research on digital academic plagiarism (e.g., McCabe et al., 2001 ).
We then investigated what makes a cheater, based on students’ demographics and effort put in doing their homework (H1), before looking at digital dishonesty as an additional ICT predictor of PISA test scores (mathematics, reading, and science) (H2).
The goal of our first research hypothesis was to determine student-related factors that may predict digital homework avoidance practices. Here, we focused on factors linked to students’ personal characteristics and study programs. Our multilevel model explained about 10% of the variance overall. Our analysis of which students are more likely to digital resources to avoid homework revealed an increased probability for male students who did not put much effort into doing their homework and who were studying in a program that was not oriented toward higher education. Thus, our findings tend to support results from previous research that stresses the importance of gender and motivational factors for academic dishonesty (e.g., Anderman & Koenka, 2017 ; Krou et al., 2021 ). Yet, as our model only explained little variance and more research is needed to provide an accurate representation of the factors that lead to digital dishonesty. Future research could include more aspects that are linked to learning, such as peer-related or teaching-related factors. Possibly, how closely homework is embedded in the teaching and learning culture may play a key role in digital dishonesty. Additional factors might be linked to the overall availability and use of digital tools. For example, the report combining factors from the PISA 2018 school and student questionnaires showed that the higher the computer–student ratio, the lower students scored in the general tests (OECD, 2020b ). A positive association with reading disappeared when socio-economic background was considered. This is even more interesting when considering previous research indicating that while internet access is not a source of divide among youths, the quality of use is still different based on gender or socioeconomic status (Livingstone & Helsper, 2007 ). Thus, investigating the usage-related “digital divide” as a potential source of digital dishonesty is an interesting avenue for future research (Dolan, 2016 ).
Our second hypothesis considered that digital dishonesty in homework completion can be regarded as an additional ICT-related trait and thus could be included in models targeting the influence of traditional ICT on PISA test scores, such as Petko et al. ( 2017 ) study. Overall, our results on the influence of ICT use and attitudes toward ICT on test scores are in line with those reported by Petko et al. ( 2017 ). Digital dishonesty was found to negatively influence test scores, with a higher frequency of cheating leading to lower performance in all major PISA test domains, and particularly so for reading. For each subject, the combined models explained about 40% of the total variance.
4.1 Conclusions and recommendations
Our results have several practical implications. First, the amount of cheating on homework observed calls for new strategies for raising homework engagement, as this was found to be a clear predictor of digital dishonesty. This can be achieved by better explaining the goals and benefits of homework, the adverse effects of cheating on homework, and by providing adequate feedback on homework that was done properly. Second, teachers might consider new forms of homework that are less prone to cheating, such as doing homework in non-digital formats that are less easy to copy digitally or in proctored digital formats that allow for the monitoring of the process of homework completion, or by using plagiarism software to check homework. Sometimes, it might even be possible to give homework and explicitly encourage strategies that might be considered cheating, for example, by working together or using internet sources. As collaboration is one of the 21st century skills that students are expected to develop (Bray et al., 2020 ), this can be used to turn cheating into positive practice. There is already research showing the beneficial impact of computer-supported collaborative learning (e.g., Janssen et al., 2012 ). Zhang et al. ( 2011 ) compared three homework assignment (creation of a homepage) conditions: individually, in groups with specific instructions, and in groups with general instructions. Their results showed that computer supported collaborative homework led to better performance than individual settings, only when the instructions were general. Thus, promoting digital collaborative homework could support the development of students’ digital and collaborative skills.
Further, digital dishonesty in homework needs to be considered different from cheating in assessments. In research on assessment-related dishonesty, cheating is perceived as a reprehensible practice because grades obtained are a misrepresentation of student knowledge, and cheating “implies that efficient cheaters are good students, since they get good grades” (Bouville, 2010 , p. 69). However, regarding homework, this view is too restrictive. Indeed, not all homework is graded, and we cannot know for sure whether students answered this questionnaire while considering homework as a whole or only graded homework (assessments). Our study did not include questions about whether students displayed the same attitudes and practices toward assessments (graded) and practice exercises (non-graded), nor did it include questions on how assessments and homework were related. By cheating on ungraded practice exercises, students will primarily hamper their own learning process. Future research could investigate in more depth the kinds of homework students cheat on and why.
Finally, the question of how to foster engaging homework with digital tools becomes even more important in pandemic situations. Numerous studies following the switch to home schooling at the beginning of the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic have investigated the difficulties for parents in supporting their children (Bol, 2020 ; Parczewska, 2021 ); however, the question of digital homework has not been specifically addressed. It is unknown whether the increase in digital schooling paired with discrepancies in access to digital tools has led to an increase in digital dishonesty practices. Data from the PISA 2018 student questionnaires (OECD, 2020a ) indicated that about 90% of students have a computer for schoolwork (OECD average), but the availability per student remains unknown. Digital homework can be perceived as yet another factor of social differences (see for example Auxier & Anderson, 2020 ; Thorn & Vincent-Lancrin, 2022 ).
4.2 Limitations and directions
The limitations of the study include the format of the data collected, with the accuracy of self-reports to mirror actual practices restricted, as these measures are particularly likely to trigger response bias, such as social desirability. More objective data on digital dishonesty in homework-related purposes could, for example, be obtained by analyzing students’ homework with plagiarism software. Further, additional measures that provide a more complete landscape of contributing factors are necessary. For example, in considering digital homework as an alternative to traditional homework, parents’ involvement in homework and their attitudes toward ICT are factors that have not been considered in this study (Amzalag, 2021 ). Although our results are in line with studies on academic digital dishonesty, their scope is limited to the Swiss context. Moreover, our analyses focused on secondary students. Results might be different with a sample of younger students. As an example, Kiss and Teller ( 2022 ) measured primary students cheating practices and found that individual characteristics were not a stable predictor of cheating between age groups. Further, our models included school as a random component, yet other group variables, such as class and peer groups, may well affect digital homework avoidance strategies.
The findings of this study suggest that academic dishonesty when doing homework needs to be addressed in schools. One way, as suggested by Chow et al. ( 2021 ) and Djokovic et al. ( 2022 ), is to build on students’ practices to explain which need to be considered cheating. This recommendation for institutions to take preventive actions and explicit to students the punishment faced in case of digital academic behavior was also raised by Chiang et al. ( 2022 ). Another is that teachers may consider developing homework formats that discourage cheating and shortcuts (e.g., creating multimedia documents instead of text-based documents, using platforms where answers cannot be copied and pasted, or using advanced forms of online proctoring). It may also be possible to change homework formats toward more open formats, where today’s cheating practices are allowed when they are made transparent (open-book homework, collaborative homework). Further, experiences from the COVID-19 pandemic have stressed the importance of understanding the factors related to the successful integration of digital homework and the need to minimize the digital “homework gap” (Auxier & Anderson, 2020 ; Donnelly & Patrinos, 2021 ). Given that homework engagement is a core predictor of academic dishonesty, students should receive meaningful homework in preparation for upcoming lessons or for practicing what was learned in past lessons. Raising student’s awareness of the meaning and significance of homework might be an important piece of the puzzle to honesty in learning.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in SISS base at https://doi.org/10.23662/FORS-DS-1285-1 , reference number 1285.
Agasisti, T., Gil-Izquierdo, M., & Han, S. W. (2020). ICT Use at home for school-related tasks: What is the effect on a student’s achievement? Empirical evidence from OECD PISA data. Education Economics, 28 (6), 601–620. https://doi.org/10.1080/09645292.2020.1822787
Article Google Scholar
Amzalag, M. (2021). Parent attitudes towards the integration of digital learning games as an alternative to traditional homework. International Journal of Information and Communication Technology Education, 17 (3), 151–167. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJICTE.20210701.oa10
Anderman, E. M., & Koenka, A. C. (2017). The relation between academic motivation and cheating. Theory into Practice, 56 (2), 95–102. https://doi.org/10.1080/00405841.2017.1308172
Aparicio, J., Cordero, J. M., & Ortiz, L. (2021). Efficiency analysis with educational data: How to deal with plausible values from international large-scale assessments. Mathematics, 9 (13), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9131579
Arpacı, S., Mercan, F., & Arıkan, S. (2021). The differential relationships between PISA 2015 science performance and, ICT availability, ICT use and attitudes toward ICT across regions: evidence from 35 countries. Education and Information Technologies, 26 (5), 6299–6318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10576-2
Auxier, B., & Anderson, M. (2020, March 16). As schools close due to the coronavirus, some U.S. students face a digital “homework gap”. Pew Research Center, 1–8. http://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2018/10/19/5-charts-on-global-views-of-china/ . Retrieved November 29th, 2021
Baş, G., Şentürk, C., & Ciğerci, F. M. (2017). Homework and academic achievement: A meta-analytic review of research. Issues in Educational Research, 27 (1), 31–50.
Google Scholar
Blau, I., & Eshet-Alkalai, Y. (2017). The ethical dissonance in digital and non-digital learning environments: Does technology promotes cheating among middle school students? Computers in Human Behavior, 73, 629–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.03.074
Bol, T. (2020). Inequality in homeschooling during the Corona crisis in the Netherlands. First results from the LISS Panel. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/hf32q
Bouville, M. (2010). Why is cheating wrong? Studies in Philosophy and Education, 29 (1), 67–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11217-009-9148-0
Bray, A., Byrne, P., & O’Kelly, M. (2020). A short instrument for measuring students’ confidence with ‘key skills’ (SICKS): Development, validation and initial results. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 37 (June), 100700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2020.100700
Chen, C. M., & Chen, F. Y. (2014). Enhancing digital reading performance with a collaborative reading annotation system. Computers and Education, 77, 67–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2014.04.010
Cheng, Y. C., Hung, F. C., & Hsu, H. M. (2021). The relationship between academic dishonesty, ethical attitude and ethical climate: The evidence from Taiwan. Sustainability (Switzerland), 13 (21), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132111615
Chiang, F. K., Zhu, D., & Yu, W. (2022). A systematic review of academic dishonesty in online learning environments. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning , 907–928. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12656
Chow, H. P. H., Jurdi-Hage, R., & Hage, H. S. (2021). Justifying academic dishonesty: A survey of Canadian university students. International Journal of Academic Research in Education , December. https://doi.org/10.17985/ijare.951714
Cuadrado, D., Salgado, J. F., & Moscoso, S. (2019). Prevalence and correlates of academic dishonesty: Towards a sustainable university. Sustainability (Switzerland) , 11 (21). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11216062
Cuadrado, D., Salgado, J. F., & Moscoso, S. (2021). Personality, intelligence, and counterproductive academic behaviors: A meta-analysis. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 120 (2), 504–537. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspp0000285
Djokovic, R., Janinovic, J., Pekovic, S., Vuckovic, D., & Blecic, M. (2022). Relying on technology for countering academic dishonesty: the impact of online tutorial on students’ perception of academic misconduct. Sustainability (Switzerland) , 14 (3). https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031756
Dolan, J. E. (2016). Splicing the divide: A review of research on the evolving digital divide among K–12 students. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 48 (1), 16–37.
Donnelly, R., & Patrinos, H. A. (2021). Learning loss during Covid-19: An early systematic review. Prospects , 0123456789 . https://doi.org/10.1007/s11125-021-09582-6
Ercegovac, Z., & Richardson, J. V. (2004). Academic dishonesty, plagiarism included, in the digital age: A literature review. College & Research Libraries, 65 (4), 301–318. https://doi.org/10.5860/crl.65.4.301
Erzinger, A. B., Verner, M., König, N., Petrucci, F., Nidegger, C., Roos, E., & Salvisberg, M. (2019). PISA 2018: Les élèves de Suisse en comparaison internationale . SEFRI/CDIP et Consortium PISA.ch.
Erzinger, A. B., Verner, M., Salvisberg, M., Nidegger, C., & Seiler, S. (2021). PISA 2018 in Switzerland, add-on to the international dataset: Swiss specific variables [Dataset] . FORS. https://doi.org/10.23662/FORS-DS-1285-1
Evering, L. C., & Moorman, G. (2012). Rethinking plagiarism in the digital age. Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy, 56 (1), 35–44.
Fan, H., Xu, J., Cai, Z., He, J., & Fan, X. (2017). Homework and students’ achievement in math and science: A 30-year meta-analysis, 1986–2015. Educational Research Review, 20, 35–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2016.11.003
Fernández-Alonso, R., álvarez-Díaz, M., Suárez-álvarez, J., & Muñiz, J. (2017). Students’ achievement and homework assignment strategies. Frontiers in Psychology, 8 (MAR), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00286
Fernández-Alonso, R., Suárez-Álvarez, J., & Muñiz, J. (2015). Adolescents’ homework performance in mathematics and science: Personal factors and teaching practices. Journal of Educational Psychology, 107 (4), 1075–1085. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000032
Giluk, T. L., & Postlethwaite, B. E. (2015). Big Five personality and academic dishonesty: A meta-analytic review. Personality and Individual Differences, 72, 59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2014.08.027
Husain, F. M., Al-Shaibani, G. K. S., & Mahfoodh, O. H. A. (2017). Perceptions of and attitudes toward plagiarism and factors contributing to plagiarism: A review of studies. Journal of Academic Ethics, 15 (2), 167–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10805-017-9274-1
Isakov, M., & Tripathy, A. (2017). Behavioral correlates of cheating: Environmental specificity and reward expectation. PLoS One1, 12 (10), 6–11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186054
Jacobs, J. E., Lanza, S., Osgood, D. W., Eccles, J. S., & Wigfield, A. (2002). Changes in children’s self-competence and values: Gender and domain differences across grades one through twelve. Child Development, 73 (2), 509–527. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00421
Janssen, J., Erkens, G., Kirschner, P., & Kanselaar, G. (2012). Task-related and social regulation during online collaborative learning. Metacognition and Learning, 7 (1), 25–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-010-9061-5
Josephson Institute of Ethics (2012). 2012 Report card on the ethics of American youth . https://charactercounts.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/ReportCard-2012-DataTables.pdf . Retrieved January 24th, 2022
Kam, C. C. S., Hue, M. T., & Cheung, H. Y. (2018). Academic dishonesty among Hong Kong secondary school students: Application of theory of planned behavior. Educational Psychology, 38 (7), 945–963. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410.2018.1454588
Kapoor, H., & Kaufman, J. C. (2021). Are cheaters common or creative?: Person-situation interactions of resistance in learning contexts. Journal of Academic Ethics, 19 (2), 157–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10805-020-09379-w
Kiss, H. J., & Keller, T. J. (2022). Individual characteristics do (not) matter in cheating. Available at SSRN 4001278. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4001278
Krou, M. R., Fong, C. J., & Hoff, M. A. (2021). Achievement motivation and academic dishonesty: A meta-analytic investigation. Educational Psychology Review, 33 (2), 427–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-020-09557-7
Kunina-Habenicht, O., & Goldhammer, F. (2020). ICT engagement: A new construct and its assessment in PISA 2015. Large-Scale Assessments in Education , 8 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40536-020-00084-z
Livingstone, S., & Helsper, E. (2007). Gradations in digital inclusion: Children, young people and the digital divide. New Media and Society, 9 (4), 671–696. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444807080335
Ma, H. J., Wan, G., & Lu, E. Y. (2008). Digital cheating and plagiarism in schools. Theory into Practice, 47 (3), 197–203. https://doi.org/10.1080/00405840802153809
Martin, A. J., Ginns, P., & Papworth, B. (2017). Motivation and engagement: Same or different? Does it matter? Learning and Individual Differences, 55, 150–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2017.03.013
McCabe, D. L. (2005). It takes a village: Academic dishonesty & educational opportunity. Liberal Education, 91 (3), 26–31.
McCabe, D. L., Treviño, L. K., & Butterfield, K. D. (2001). Cheating in academic institutions: A decade of research. Ethics and Behavior, 11 (3), 219–232. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327019EB1103_2
Moss, S. A., White, B., & Lee, J. (2018). A systematic review into the psychological causes and correlates of plagiarism. Ethics and Behavior, 28 (4), 261–283. https://doi.org/10.1080/10508422.2017.1341837
Nora, W. L. Y., & Zhang, K. C. (2010). Motives of cheating among secondary students: The role of self-efficacy and peer influence. Asia Pacific Education Review, 11 (4), 573–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12564-010-9104-2
Odell, B., Cutumisu, M., & Gierl, M. (2020). A scoping review of the relationship between students’ ICT and performance in mathematics and science in the PISA data. Social Psychology of Education , 23 (6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11218-020-09591-x
OECD, & Publishing, O. E. C. D. (2015). Students, computers and learning: Making the connection . PISA. https://doi.org/10.1787/factbook-2015-68-en
OECD (2019a). Chapter 16. Scaling procedures and construct validation of context questionnaire data. In PISA 2018 Technical Report . OECD.
OECD (2019b). PISA 2018 Results - What school life means for students’ life (Vol. III). OECD Publishing. https://www.oecd.org/pisa/publications/PISA2018_CN_IDN.pdf . Retrieved October 20th, 2021
OECD (2020a). Learning remotely when schools close . 1–13. https://read.oecd-ilibrary.org/view/?ref=127_127063-iiwm328658&title=Learning-remotely-when-schools-close . Retrieved November 29th, 2021
OECD (2020b). PISA 2018 Results: Effective policies, successful schools (Vol. V). PISA, OECD Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1787/ca768d40-en
Parczewska, T. (2021). Difficult situations and ways of coping with them in the experiences of parents homeschooling their children during the COVID-19 pandemic in Poland. Education 3–13 , 49 (7), 889–900. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004279.2020.1812689
Pavela, G. (1997). Applying the power of association on campus: A model code of academic integrity. Law and Policy, 24 (1), 1–22.
Petko, D., Cantieni, A., & Prasse, D. (2017). Perceived quality of educational technology matters: A secondary analysis of students ICT use, ICTRelated attitudes, and PISA 2012 test scores. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 54 (8), 1070–1091. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633116649373
Rosário, P., Carlos Núñez, J., Vallejo, G., Nunes, T., Cunha, J., Fuentes, S., & Valle, A. (2018). Homework purposes, homework behaviors, and academic achievement. Examining the mediating role of students’ perceived homework quality. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 53 (April), 168–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2018.04.001
Schnyder, I., Niggli, A., & Trautwein, U. (2008). Hausaufgabenqualität im Französischunterricht aus der Sicht von Schülern, Lehrkräften und Experten und die Entwicklung von Leistung, Hausaufgabensorgfalt und Bewertung der Hausaufgaben. Zeitschrift Fur Padagogische Psychologie, 22 (3–4), 233–246. https://doi.org/10.1024/1010-0652.22.34.233
Schynder Godel, I. (2015). Die Hausaufgaben unter der Lupe. Eine empirische Untersuchung im Fach Französisch als Fremdsprache.
Skryabin, M., Zhang, J., Liu, L., & Zhang, D. (2015). How the ICT development level and usage influence student achievement in reading, mathematics, and science. Computers and Education, 85, 49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2015.02.004
Tarhini, A., Hone, K., & Liu, X. (2014). Measuring the moderating effect of gender and age on e-learning acceptance in England: A structural equation modeling approach for an extended technology acceptance model. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 51 (2), 163–184. https://doi.org/10.2190/EC.51.2.b
Thorn, W., & Vincent-Lancrin, S. (2022). Education in the time of COVID-19 in France, Ireland, the Unites Kingdom and the United States: The nature and impact of remote learning. In F. M. Reimers (Ed.), Primary and secondary education during Covid-19 (pp. 383–420). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2632-5_2
Trautwein, U. (2007). The homework-achievement relation reconsidered: Differentiating homework time, homework frequency, and homework effort. Learning and Instruction, 17 (3), 372–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2007.02.009
Trautwein, U., & Köller, O. (2003). Was lange währt, wird nicht immer gut: Zur Rolle selbstregulativer Strategien bei der Hausaufgabenerledigung. Zeitschrift Für Pädagogische Psychologie German Journal of Educational Psychology, 17 (3–4), 199–209.
Trautwein, U., Lüdtke, O., Schnyder, I., & Niggli, A. (2006). Predicting homework effort: Support for a domain-specific, multilevel homework model. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98 (2), 438–456. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.98.2.438
Trautwein, U., Schnyder, I., Niggli, A., Neumann, M., & Lüdtke, O. (2009). Chameleon effects in homework research: The homework-achievement association depends on the measures used and the level of analysis chosen. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 34 (1), 77–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2008.09.001
Waltzer, T., & Dahl, A. (2022). Why do students cheat? Perceptions, evaluations, and motivations. Ethics and Behavior , 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/10508422.2022.2026775
Whitley, B. E., Nelson, A. B., & Jones, C. J. (1999). Gender differences in cheating attitudes and classroom cheating behavior: A meta-analysis. Sex Roles, 41 (9–10), 657–680. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018863909149
Xu, J. (2015). Investigating factors that influence conventional distraction and tech-related distraction in math homework. Computers and Education, 81, 304–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2014.10.024
Xu, J., Du, J., Cunha, J., & Rosário, P. (2021). Student perceptions of homework quality, autonomy support, effort, and math achievement: Testing models of reciprocal effects. Teaching and Teacher Education , 108 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2021.103508
Yaniv, G., Siniver, E., & Tobol, Y. (2017). Do higher achievers cheat less? An experiment of self-revealing individual cheating. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Economics, 68, 91–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socec.2017.04.005
Zhang, L., Ayres, P., & Chan, K. (2011). Examining different types of collaborative learning in a complex computer-based environment: A cognitive load approach. Computers in Human Behavior, 27 (1), 94–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.03.038
Download references
Open access funding provided by University of Zurich
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Education, University of Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland
Juliette C. Désiron & Dominik Petko
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Juliette C. Désiron: Formal analysis, Writing (Original, Review and Editing), Dominik Petko: Conceptualization, Writing (Original, Review and Editing), Supervision.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Juliette C. Désiron .
Ethics declarations
Competing of interests, additional information, publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
List of abbreviations related to PISA datasets
students’ perceived autonomy related to ICT use
students’ perceived ICT competence
frequency of computer use at home for entertainment purposes
index of economic, social, and cultural status (computed from PARED, HISEI and HOMEPOS)
parents’ highest occupational status
home possessions
frequency of computer use for school-related purposes at home
digital cheating for homework items for Switzerland
homework engagement items for Switzerland
positive attitude towards ICT as a learning tool
student’s ICT interest
parents’ highest level of education
students’ ICT as a topic in social interaction
frequency of computer use at school
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Désiron, J.C., Petko, D. Academic dishonesty when doing homework: How digital technologies are put to bad use in secondary schools. Educ Inf Technol 28 , 1251–1271 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11225-y
Download citation
Received : 11 May 2022
Accepted : 05 July 2022
Published : 23 July 2022
Issue Date : February 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11225-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Academic dishonesty
- Digitally-supported cheating
- Secondary education
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
How Cheating in College Hurts Students
Academic integrity is important, experts say, as plagiarism and other cheating may have severe consequences.

Getty Images | Westend61
Experts say the number of students engaging in academic dishonesty during the coronavirus pandemic is soaring.
Cheating in college is risky business loaded with potential consequences – failing classes, suspension, possible expulsion – yet it's common and perhaps more accessible than ever.
"A lot of people cheat a little," says David Pritchard, a physics professor emeritus at Massachusetts Institute of Technology who has studied academic dishonesty in online classes. "There's also a few people who cheat a lot."
Though it may be tempting and feel harmless, experts caution college students to think twice before cheating on coursework. Here's how to know what is typically considered cheating and the potential consequences.
How College Students Cheat
Cheating is a multibillion-dollar business, with some educational technology companies making money off students who use their products to break or bend academic integrity rules and others earning revenue from colleges trying to prevent academic dishonesty.
Students also use classic classroom moves like scribbling hidden notes somewhere or using technology such as smartwatches. Copying a classmate's assignment or plagiarizing parts of published works for a paper remain popular methods.
Many of those tactics appear to have been replaced by artificial intelligence and generative language models like ChatGPT and Google Bard, which offer some services like writing, editing and idea generation for free.
Pritchard notes that ChatGPT has performed well on exams in certain subjects, and the American Bar Association reported in March 2023 that it passed the Uniform Bar Exam by "a significant margin." While some professors say they're keeping an open mind about ChatGPT and similar tools, others say it's impossible to ignore the reality that students are using them to cheat.
ChatGPT "is the future of cheating," Pritchard says.
Rebecca Hamlin, a professor of legal studies and political science at the University of Massachusetts—Amherst , recently joined the university's academic honesty board and has seen cases of students caught cheating with ChatGPT. She caught 12 in her own classes during the spring 2023 semester.
“If students are genuinely interested in learning how to become writers, I’m very resistant to the idea that ChatGPT can help them," she says. “It’s really risky because it’s actually way more obvious to someone who reads really good writing all day long. I can immediately tell."
But plenty of students slip through undetected or cheat in other inconspicuous ways, she says.
Most instructors underestimate just how rampant the issue is, says Eric Anderman, a professor at The Ohio State University and interim dean at its Mansfield campus. "We think we're underestimating it because people don't want to admit to it."
Here's what academic integrity experts say college students should know about the immediate and long-term consequences of cheating.
The Consequences of Cheating in College
Regardless of the cheating method, students are only harming themselves and their learning process, experts say.
“I know that sounds really cheesy, but I kind of don’t really understand why someone is going to waste their time and money going to college if they don’t want to learn how to write," Hamlin says. "That’s probably one of the top two to three skills that you gain when you go to college."
Students also deprive themselves of a genuine feeling of achievement when they cheat, says Russell Monroe, director of academic integrity at Liberty University in Virginia.
"There’s a sense of dignity in knowing that I got a grade that I earned, whether that’s for an assignment or a class," he says. "You can look at your degree with pride knowing this is something I achieved on my own merit and didn’t have to outsource anything to anyone else or steal or plagiarize."
Some penalties can have a lasting effect and financial repercussions. They are often less severe for first-time offenders, but colleges keep records of such behavior. Students who continue to cheat and get caught risk failing a class, receiving academic suspension or being expelled from the school, which may come with a note on their transcript explaining why they were dismissed. This designation will likely make it harder to enroll at another college , experts say.
Students who fail a class due to academic dishonesty are usually allowed to retake it. If it's a class required for graduation, they don't have a choice. Either way, that means more money out of pocket, perhaps in student loans .
Failing a course also typically harms a student's GPA , particularly if they don't retake it and earn a higher grade. This could jeopardize eligibility for financial aid or scholarships and lead to academic probation .
Each school has its own policies and disciplinary measures, and professors may vary in how they address academic dishonesty. Some may handle it on their own while others may send it to a disciplinary committee. It often depends on the severity of cheating, Monroe says. For example, cheating on a discussion board assignment isn't seen as as serious as plagiarizing a dissertation or final exam paper, or cheating on a credential or certification exam, he says.
Plagiarizing on capstone course papers or other assignments tied to graduation is a particularly egregious offense that could jeopardize a student's ability to graduate, experts say.
“We are putting our stamp of approval on you to move on to the next step," Monroe says. "That next step might be graduation, but if we’re doing that based upon bad information or false information, that’s a serious problem.”
Even students who think they got away with cheating may suffer consequences, such as missing out on foundational information that they need to learn and apply in higher-level classes.
Additionally, graduates who cheated and perhaps even ended up with good grades may find themselves starting their career unprepared and lacking needed knowledge and skills. And for jobs that have a safety component, unprepared workers could put themselves and others at risk.
Then there are occasions when academic dishonesty is revealed later and torpedoes a career, sometimes in a public and humiliating way.
Know What Is and Isn't Cheating
While some students are well aware that they're cheating and see it as merely a means to an end, not all forms of academic dishonesty are intentional. In many cases, it's an accident made while under stress or when a student has procrastinated , experts say.
Sometimes students make mistakes because they aren't properly prepared to engage with college-level work. For example, improperly citing sources on a term paper can lead to charges of plagiarism.
"I think part of what happens is students aren't always taught in high school how to cite and evaluate information from the internet," Anderman says. "And I think a lot of them, when they get to college – and this is not an excuse – truly don't realize that you can't just look something up on the internet and put it in your paper, that you still have to cite it, and they get caught."
Colleges commonly use a variety of plagiarism-checking software, such as Turnitin, which flags written work that may be uncited or improperly cited. These tools help keep students honest and significantly decrease plagiarism, experts say.
Some forms of cheating, such as intentional plagiarism, buying papers online or paying someone to complete course work, should be fairly obvious, experts say. This is often referred to as "contract cheating," Monroe says, and it's an offense that can lead to expulsion from Liberty.
"It’s very difficult for us to know when that’s happening, but when we do find out, we view that very seriously because there are significant portions of your entire degree that may not have been done by the student at all," he says.
Other areas aren't as clear-cut, particularly what is permissible when it comes to collaborating with classmates, sharing information and using AI products. Monroe says Liberty doesn't ban the use of AI or tools like ChatGPT, but there are boundaries around their ethical use. Students can use these tools to edit and get inspiration, but any assignment turned in must be the student's original work.
Experts also caution against using online companies that position themselves as tutoring organizations but largely help students cheat. Colleges offer many academic resources that students can use instead, and at no extra cost.
“I would definitely encourage a student who’s facing a tough situation or feels that they can’t do their work on time to contact their professor and see if there’s some kind of alternate arrangement that can be made," Monroe says.
Many professors are willing to accept work late, he says. Liberty’s policy is to take 10% off of an assignment's overall grade if it’s late.
“We definitely prefer a timely submission of work," Monroe says, "but contact your professor. They are definitely willing to work with students within the scope that they’re allowed to. That would definitely be a better situation than turning to cheating."
Searching for a college? Get our complete rankings of Best Colleges.
10 Steps to Choosing the Right College

Tags: colleges , students , education , academics , cheating , college admissions , college applications , high school
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
College Admissions: Get a Step Ahead!
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S. News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Ask an Alum: Making the Most Out of College
You May Also Like
The complete guide to the toefl.
Sarah Wood March 8, 2024

Unique College Campus Visits
Sarah Wood March 7, 2024

MBA Programs Fail to Attract Women
Joy Jones March 7, 2024

12 Colleges With the Most NBA Players
Cole Claybourn March 1, 2024

Higher Education on the Edge
Alan Mallach Feb. 29, 2024

Disability Accommodations in College
Anayat Durrani Feb. 23, 2024

Why Do Colleges Close?
Sarah Wood Feb. 20, 2024

Online Programs With Diverse Faculty
Sarah Wood Feb. 16, 2024

U.S. and Europe Degree Differences
Anayat Durrani Feb. 13, 2024

How to Perform Well on SAT, ACT Test Day
Cole Claybourn Feb. 13, 2024

Students cheat for good grades. Why not make the classroom about learning and not testing?
Professor, Educational Psychology, The Ohio State University
Disclosure statement
Eric Anderman received funding from National Institutes of Health.
The Ohio State University provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation US.
View all partners

We have been hearing stories about academic cheating: from students caught cheating on homework assignments as well as college entrance exams to teachers being caught in cheating scandals, such as the ones in Atlanta , Georgia, and Columbus , Ohio.
Today, between 75% and 98% of college students surveyed each year report having cheated in high school. So, if cheating is happening at that large a scale, is it just inevitable? And can we even blame our students?
In order to figure out how to answer these questions, it’s important to consider why students cheat in the first place. Although the obvious reason seems to be the desire of students to get ahead (eg, to get a good grade, or to avoid a punishment), the real reason is actually a bit more complicated.
Academic goals matter
When students do their schoolwork (which includes everything from daily homework assignments to major examinations), they usually have certain goals in mind. These goals vary from one academic task to another.
In other words, if you were to ask a student, “What is your goal in taking next week’s chemistry test?”, the student should be able to tell you what she wants to get out of the experience.
My colleagues and I have been studying the psychology behind academic cheating for the past two decades, and we have found that students’ goals in their academic tasks are related in very predictable ways to their likelihood of cheating. Research also indicates that teachers and parents can influence those goals, and thus potentially deter cheating.
If the sole reason for engaging in an academic task is to get a good grade, then it’s probably easy for a student to justify the act of cheating.
As my colleagues and I found , some students might have short-term reasons. For instance, for some students, it might be as simple a motivation as the desire to go to a friend’s party on Saturday night. If they think that their parents will not let them go if they fail the test, they might take the easier option to cheat, to be able to go to the party.
For some others, it might be a longer-term reason: They might want a good salary and other luxuries in their adult life and believe that the only path to those things would be a good college. And they might be willing to cheat on their tests to be able to get ahead in their future.
Students have different goals
Whereas these reasons may seem selfish and shortsighted to some adults, to many adolescents, who are still unable to consider the consequences of their actions, these goals may seem perfectly reasonable.
We refer to these goals as “extrinsic” goals. Research indicates that students who experience classrooms in which extrinsic goals are common are more likely to cheat.
Clearly, not all students have these goals. Some students are motivated by their desire to learn.

So, for some students, the goal might be to truly understand and master the material that is being studied. In other words, whereas some students might have a goal of getting a good grade on a chemistry test in order to get something (eg, to go to a party), others might have the goal of truly learning chemistry: “I want to understand chemistry because I want to develop drugs to help fight cancer; I know that understanding chemistry is essential for me to be successful in this career.”
We refer to these goals as “mastery” goals. Research indicates that students who experience classrooms in which mastery goals are valued and encouraged are less likely to cheat .
If one thinks about this, it starts to make sense. When students are learning in classrooms where the teacher truly values mastery of the academic content (as opposed to getting a good grade on an assessment), then “cheating” really doesn’t offer any benefits to the students.
Teachers can help
The ways in which assessments of student learning are administered are particularly relevant in discussions of academic cheating. If results of assessments ultimately come down to a grade on a test or an assignment (eg, an “A” or an “F”), then students often will come to value the grade more than what they are actually learning.
However, if, in contrast, the assessment truly focuses on a demonstration of mastery of content, then students will focus on mastering that content and not just on getting an “A.”
When students have to demonstrate mastery of material, cheating doesn’t serve much of a purpose – if you truly have to show the teacher that you understand and can apply the information that you learned, then cheating won’t buy you any shortcuts.
Fortunately, there are strategies that educators can use to facilitate students’ adoption of mastery goals instead of extrinsic goals.
Here are a few suggestions, based on our research :
Make sure that assignments and exams require students to demonstrate mastery of content, as opposed to just requiring the regurgitation of memorized facts.
When students do not demonstrate mastery on an assignment or a test, allow them to redo the assignment. Educators sometimes don’t think that this recommendation is fair – after all, if one student gets all of the answers right the first time, why should someone else get a second chance? But, if the goal is really to learn or “master” the content, then does it really matter if the student gets a second chance?
Avoid high-stakes, one-time assessments.
Always provide students’ grades privately – don’t share results publicly or display distributions of scores; students often will cheat in order to avoid looking “dumb.”
Ultimately, some students will inevitably cheat. But, by considering why students are doing various academic tasks in the first place and helping them set their “mastery” goals, educators can make a significant dent in the epidemic of academic cheating.
- Adolescents
- high stakes testing
- Atlanta Cheating scandal
- Academic cheating
- Intrinsic goals
- Student learning
- Good grades
- Learning motivation

School of Social Sciences – Academic appointment opportunities

Union Organiser (part-time 0.8)

Director, Indigenous Education Research Centre

Communications Specialist

AUSTRALIAN PESTICIDES AND VETERINARY MEDICINES AUTHORITY (APVMA) BOARD CHAIR
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
What do ai chatbots really mean for students and cheating.

The launch of ChatGPT and other artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots has triggered an alarm for many educators, who worry about students using the technology to cheat by passing its writing off as their own. But two Stanford researchers say that concern is misdirected, based on their ongoing research into cheating among U.S. high school students before and after the release of ChatGPT.
“There’s been a ton of media coverage about AI making it easier and more likely for students to cheat,” said Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at Stanford Graduate School of Education (GSE). “But we haven’t seen that bear out in our data so far. And we know from our research that when students do cheat, it’s typically for reasons that have very little to do with their access to technology.”
Pope is a co-founder of Challenge Success , a school reform nonprofit affiliated with the GSE, which conducts research into the student experience, including students’ well-being and sense of belonging, academic integrity, and their engagement with learning. She is the author of Doing School: How We Are Creating a Generation of Stressed-Out, Materialistic, and Miseducated Students , and coauthor of Overloaded and Underprepared: Strategies for Stronger Schools and Healthy, Successful Kids.
Victor Lee is an associate professor at the GSE whose focus includes researching and designing learning experiences for K-12 data science education and AI literacy. He is the faculty lead for the AI + Education initiative at the Stanford Accelerator for Learning and director of CRAFT (Classroom-Ready Resources about AI for Teaching), a program that provides free resources to help teach AI literacy to high school students.
Here, Lee and Pope discuss the state of cheating in U.S. schools, what research shows about why students cheat, and their recommendations for educators working to address the problem.

Denise Pope
What do we know about how much students cheat?
Pope: We know that cheating rates have been high for a long time. At Challenge Success we’ve been running surveys and focus groups at schools for over 15 years, asking students about different aspects of their lives — the amount of sleep they get, homework pressure, extracurricular activities, family expectations, things like that — and also several questions about different forms of cheating.
For years, long before ChatGPT hit the scene, some 60 to 70 percent of students have reported engaging in at least one “cheating” behavior during the previous month. That percentage has stayed about the same or even decreased slightly in our 2023 surveys, when we added questions specific to new AI technologies, like ChatGPT, and how students are using it for school assignments.

Isn’t it possible that they’re lying about cheating?
Pope: Because these surveys are anonymous, students are surprisingly honest — especially when they know we’re doing these surveys to help improve their school experience. We often follow up our surveys with focus groups where the students tell us that those numbers seem accurate. If anything, they’re underreporting the frequency of these behaviors.
Lee: The surveys are also carefully written so they don’t ask, point-blank, “Do you cheat?” They ask about specific actions that are classified as cheating, like whether they have copied material word for word for an assignment in the past month or knowingly looked at someone else’s answer during a test. With AI, most of the fear is that the chatbot will write the paper for the student. But there isn’t evidence of an increase in that.
So AI isn’t changing how often students cheat — just the tools that they’re using?
Lee: The most prudent thing to say right now is that the data suggest, perhaps to the surprise of many people, that AI is not increasing the frequency of cheating. This may change as students become increasingly familiar with the technology, and we’ll continue to study it and see if and how this changes.
But I think it’s important to point out that, in Challenge Success’ most recent survey, students were also asked if and how they felt an AI chatbot like ChatGPT should be allowed for school-related tasks. Many said they thought it should be acceptable for “starter” purposes, like explaining a new concept or generating ideas for a paper. But the vast majority said that using a chatbot to write an entire paper should never be allowed. So this idea that students who’ve never cheated before are going to suddenly run amok and have AI write all of their papers appears unfounded.
But clearly a lot of students are cheating in the first place. Isn’t that a problem?
Pope: There are so many reasons why students cheat. They might be struggling with the material and unable to get the help they need. Maybe they have too much homework and not enough time to do it. Or maybe assignments feel like pointless busywork. Many students tell us they’re overwhelmed by the pressure to achieve — they know cheating is wrong, but they don’t want to let their family down by bringing home a low grade.
We know from our research that cheating is generally a symptom of a deeper, systemic problem. When students feel respected and valued, they’re more likely to engage in learning and act with integrity. They’re less likely to cheat when they feel a sense of belonging and connection at school, and when they find purpose and meaning in their classes. Strategies to help students feel more engaged and valued are likely to be more effective than taking a hard line on AI, especially since we know AI is here to stay and can actually be a great tool to promote deeper engagement with learning.
What would you suggest to school leaders who are concerned about students using AI chatbots?
Pope: Even before ChatGPT, we could never be sure whether kids were getting help from a parent or tutor or another source on their assignments, and this was not considered cheating. Kids in our focus groups are wondering why they can't use ChatGPT as another resource to help them write their papers — not to write the whole thing word for word, but to get the kind of help a parent or tutor would offer. We need to help students and educators find ways to discuss the ethics of using this technology and when it is and isn't useful for student learning.
Lee: There’s a lot of fear about students using this technology. Schools have considered putting significant amounts of money in AI-detection software, which studies show can be highly unreliable. Some districts have tried blocking AI chatbots from school wifi and devices, then repealed those bans because they were ineffective.
AI is not going away. Along with addressing the deeper reasons why students cheat, we need to teach students how to understand and think critically about this technology. For starters, at Stanford we’ve begun developing free resources to help teachers bring these topics into the classroom as it relates to different subject areas. We know that teachers don’t have time to introduce a whole new class, but we have been working with teachers to make sure these are activities and lessons that can fit with what they’re already covering in the time they have available.
I think of AI literacy as being akin to driver’s ed: We’ve got a powerful tool that can be a great asset, but it can also be dangerous. We want students to learn how to use it responsibly.
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
Improving lives through learning
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Looking For Your Next Teacher Job? You'll Want This Email Series!
How Do I Stop Students From Copying Each Other’s Homework Assignments?
Five steps that worked for me.

My students, like students everywhere, are smart and funny and creative and wonderful in so many ways. Also like students everywhere, they constantly seem to be looking for shortcuts on their homework. One of the bus drivers told me last year that the kids openly ask her to turn the interior lights on so they can finish copying homework before they get to school! Sigh. At least they’re motivated enough to copy, right?
This year, I made it a major goal to stop students from cheating. I put this five-step process in place, and it really cut down on the homework copying in my classroom. Here it is.
Step 1: Check the quality of your assignments.
First of all, it’s worth taking a close look at the kind of homework you assign. If you do a lot of worksheets, you might find those work better for in-class activities. Instead, try focusing homework on in-depth writing assignments and individual written responses.
If you’re a math teacher, having kids respond in writing about how they solved a problem always works, as does having them write their own problems or exemplars for what they’ve been learning. Anything that requires student-generated content is automatically going to be harder to copy.
Step 2: Check the quantity.
Of course, this creates a lot more grading than worksheets, which led me to reflect on the amount of homework I assigned. At first, I found myself overwhelmed. I had to wonder if this was how my students felt when they looked at a night’s homework load. If there had been someone whose grading I could have copied, I probably would have done it!
The result? I assigned a lot less homework as the year went on. Put your homework to this test: If it’s not worth your time to grade carefully, it’s not worth the students’ time to do it.
Step 3: Explain the changes.
Once you’ve started assigning less homework, you’ll want to make your reasons explicit to your students. “I’m assigning less homework because I don’t want to waste your time. That means that anything I do assign is really important, and it’s important for you to actually do it on your own.” This speech went a long way with many of my students, but I had another trick up my sleeve.
Step 4: Allow time to learn and make mistakes.
You might also want to try a few get-out-of-jail-free cards when it comes to homework. My middle schoolers are still in the process of learning how to budget their time and stay organized, and sometimes they make mistakes. I gave each kid three one-day extensions that they could use over the course of the year to avoid a penalty for late homework.
There were certain assignments on which these could not be used, like rough drafts we needed to edit or group projects. It lowered the general stress level and set a culture of respect and accountability that encouraged my kids to plan ahead. For the naysayers who say, “The real world won’t give them extensions,” I would respectfully offer my disagreement. What? You’ve never posted your grades after the deadline?
Step 5: Bring the pain.
Although this cut down on copying substantially, kids will always test your limits. That’s when you move on to the final step. It works like this: Read every word of every assignment. Make sure you grade an entire class at once so you’ll know if a phrase or a creatively spelled word seems familiar, and then hunt back through 35 other papers until you find the one it’s copied from. It is important that you identify when students cheat and that your justice is swift and merciless.
I had an escalating system of consequences for cheating. First time, you split the grade. If the assignment gets a 90, each person gets a 45. Second time, each person gets a zero and a lunch detention. Third time, it’s a phone call home in addition to a zero and an after-school detention. Not a single kid made it to the third offense. They have to believe that you’re documenting this and you’ll follow through. Let them see you putting their names in your file so they know you know what offense they’re on. It is a logistical pain, but it’s effective.
So did my kids ace the standardized test because they had done their homework all year? Not to brag, but their writing scores were pretty high. And I don’t think they missed out on many valuable educational experiences when I stopped assigning worksheets. After all, they’d have just copied them anyway!
How do you stop students from cheating? Come and share in our WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.
Plus, check out how to give meaningful homework, even when it’s not graded ..

You Might Also Like

How to Give Meaningful Homework, Even When It’s Not Graded
“Is this going to be graded?” Oh, how we love to hear this. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

- Instructors
- Institutions
- Teaching Strategies
- Higher Ed Trends
- Academic Leadership
- Affordability
- Product Updates
Why Do Students Cheat? One Student’s Perspective

Sarah Gido is a Marketing and Communications major at Anglo-American University in Prague, Czech Republic
Cheating has always been an issue in school. When I asked my friends if they had ever cheated in school, the response was almost always yes. Some said that in high school they wrote answers on water bottle wrappers or even on their legs to be seen through the holes of their jeans. Another said they took an online public speaking course and had their script written above their computer. But if we all know it’s morally wrong, why do students cheat? And why are more students cheating now in 2023 than ever before?
Online learning makes cheating easier
The shift to online learning in 2020 drastically changed the relationship between students and learning. From a student perspective, it is much easier to cheat on virtual tests and homework assignments. With any answer at their fingertips on the internet, students turn to search engines for help on exams. Digital learning puts a barrier between students and professors, but also between students and learning content.
It’s difficult to feel connected and interested in information through independent learning that arises from digital assignments. When students don’t have an emotional stake in the learning process, they retain less of what they learn and cheating is an easy solution. From splitting screens between tabs and studying websites, technology has made student cheating easier—and harder for instructors to detect—than ever before. When it’s that easy, students often find that it doesn’t feel as wrong. Furthermore, it’s easier on the conscience to cheat without a professor or your peers looking at you.
Students are losing motivation
Students’ plates are fuller than ever before. The switch back to fully in-person learning was jarring but a welcome change for many! However, many students fell into a cycle of choosing convenience over studying during virtual and hybrid learning courses. Being back in the classroom meant the return of intense schedules, public speaking, and rising stress levels. Staying motivated in class is much more difficult when balancing the stress of a job, relationships, sickness, or hunting for an internship. According to a survey completed by the American Addiction Centers, 88 percent of students reported their school life to be stressful. Dwindling levels of motivation can lead to procrastination and resistance to do assignments that weigh on students’ minds. Homework, essays, and exams turn into dreaded obligations completed with haste by cheating rather than opportunities for enhancement.
Students are focused on passing courses
In the minds of many students, there’s more emphasis on passing classes than there is on learning. In the stress of coursework, focus on exam scores can be overwhelming. Finishing a degree is difficult and there has been a distinct shift in the perception of college courses and the end goal. The COVID-19 pandemic put an abrupt halt to the “normal” progression of school life, and many students now are just looking to finish.
Curb your students’ desire to cheat
The students of today are unique and are looking to regain motivation. Making content relatable is the best way to tap into the minds of students and have them invest time and energy into the course. This is as simple as using relevant real-world resources and references. I look forward to courses that challenge me in a fun way as a learner and individual. As a Marketing student, my favorite college course I have taken utilized nontraditional assignments, including oral exams and examining current advertisements. Fostering a classroom that welcomes opportunities for career and personal development may energize your students and make them less likely to cheat.
Want to learn more about how and why students cheat, plus strategies for preventing and detecting cheating? Download our free eBook, “Cheating and Academic Dishonesty: How to Spot it — and What to Do About It.”
Related articles.

- UB Directory
Common Reasons Students Cheat

Poor Time Management
The most common reason students cite for committing academic dishonesty is that they ran out of time. The good news is that this is almost always avoidable. Good time management skills are a must for success in college (as well as in life). Visit the Undergraduate Academic Advisement website for tips on how to manage your time in college.
Stress/Overload
Another common reason students engage in dishonest behavior has to do with overload: too many homework assignments, work issues, relationship problems, COVID-19. Before you resort to behaving in an academically dishonest way, we encourage you to reach out to your professor, your TA, your academic advisor or even UB’s counseling services .
Wanting to Help Friends
While this sounds like a good reason to do something, it in no way helps a person to be assisted in academic dishonesty. Your friends are responsible for learning what is expected of them and providing evidence of that learning to their instructor. Your unauthorized assistance falls under the “ aiding in academic dishonesty ” violation and makes both you and your friend guilty.
Fear of Failure
Students report that they resort to academic dishonesty when they feel that they won’t be able to successfully perform the task (e.g., write the computer code, compose the paper, do well on the test). Fear of failure prompts students to get unauthorized help, but the repercussions of cheating far outweigh the repercussions of failing. First, when you are caught cheating, you may fail anyway. Second, you tarnish your reputation as a trustworthy student. And third, you are establishing habits that will hurt you in the long run. When your employer or graduate program expects you to have certain knowledge based on your coursework and you don’t have that knowledge, you diminish the value of a UB education for you and your fellow alumni.
"Everyone Does it" Phenomenon
Sometimes it can feel like everyone around us is dishonest or taking shortcuts. We hear about integrity scandals on the news and in our social media feeds. Plus, sometimes we witness students cheating and seeming to get away with it. This feeling that “everyone does it” is often reported by students as a reason that they decided to be academically dishonest. The important thing to remember is that you have one reputation and you need to protect it. Once identified as someone who lacks integrity, you are no longer given the benefit of the doubt in any situation. Additionally, research shows that once you cheat, it’s easier to do it the next time and the next, paving the path for you to become genuinely dishonest in your academic pursuits.
Temptation Due to Unmonitored Environments or Weak Assignment Design
When students take assessments without anyone monitoring them, they may be tempted to access unauthorized resources because they feel like no one will know. Especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, students have been tempted to peek at online answer sites, Google a test question, or even converse with friends during a test. Because our environments may have changed does not mean that our expectations have. If you wouldn’t cheat in a classroom, don’t be tempted to cheat at home. Your personal integrity is also at stake.
Different Understanding of Academic Integrity Policies
Standards and norms for academically acceptable behavior can vary. No matter where you’re from, whether the West Coast or the far East, the standards for academic integrity at UB must be followed to further the goals of a premier research institution. Become familiar with our policies that govern academically honest behavior.
To revisit this article, visit My Profile, then View saved stories .
- Backchannel
- Wired World
- Artificial Intelligence
- Newsletters
- Wired Insider
Cevin Soling
Why I Think Students Should Cheat

You have been kidnapped and dragged off to a remote location where your abductors have tied you to a chair. One of your captors is seated in front of you. He holds up ten flash cards and informs you that he is going to ask you a series of questions and the answers are printed on the backs of the cards. He assures you that once he has finished asking these questions, you will be released. There is a catch, though. For every question you get wrong, he will signal his accomplice to cut off one of your fingers. As he begins to read the first question, you notice there is a mirror on the opposite wall where you can see the reflection of the text on the card. Because you have been taught that cheating is dishonest, you interrupt your kidnapper and let him know that you are able to read the card and that he must conceal them better so that you cannot inadvertently cheat. He adjusts himself accordingly and proceeds to ask you a series of dry and uninspired questions on topics that hold no interest for you, while his accomplice menacingly holds out a set of cutting pliers.
While cheating is technically wrong, everyone should cringe at this conception of morality because it fails to account for context. In this example, cheating is not only justified, it is necessary because it aids a helpless victim who has been involuntarily subjected to unreasonable conditions. Unfortunately, this kind of clarity is absent when it comes to compulsory education.
One of the most salient features of all public schools is the importance of grades. Because grades are the currency and sole commodity of schools, they are used both to motivate and punish. They are a major component of a student’s portfolio and have the potential to impact their future. Educators might try to stress the value of “learning” over grades, but that is a complete farce. When learning is not commensurately represented by grades, students rightly feel cheated by the system and become apathetic. To insist on valuing learning over grades is offensively disingenuous and hypocritical. It is akin to telling workers at McDonald’s that they should care more about doing their job than their salary.
Students have no input regarding how or what they learn, and they are alienated from the work they do at school. Except for a few rare assignments, students are not inspired by their work, and any personal attachment they could have is undermined by the fact that they must compromise their efforts to meet the demands and expectations of the person who grades their work.
It's important to bear in mind that students prepare for tests with the intention that they will retain the material just long enough to take the test and then forget most of what they learned soon afterwards. This completely undermines the purpose and value of testing. Advocates of testing who denigrate cheating conveniently fail to acknowledge this. Testing demands that students view knowledge as a disposable commodity that is only relevant when it is tested. This contributes to the process of devaluing education.
The benefits of cheating are obvious – improved grades in an environment where failure is not an opportunity for learning, but rather a badge of shame. When students do poorly on a test, there is no reason for students to review their responses because they will likely never be tested on the same thing ever again. The test itself is largely arbitrary and often not meaningful. Organizations such as FairTest are devoted to sharing research that exposes the problems of bad testing practices.
The main arguments against cheating in school are that it is unethical, promotes bad habits, and impacts self-esteem through the attainment of an unearned reward. None of these concerns are even remotely valid because none consider the environment. Children are routinely rounded up and forcibly placed in an institution where they are subjected to a hierarchy that places them at the bottom. Like the hostage, they are held captive even if they are not physically bound. They are deprived of any power over their own lives, including the ability to pursue their interests, and are subjected to a barrage of tests that have consequences for each wrong answer.

Paresh Dave

Joel Khalili

Aarian Marshall

Andy Greenberg
Maintaining ethics is part of an unwritten contract of being a willing participant in a community. Students placed in school against their will and routinely disrespected have no obligation to adhere to the ethical codes of their oppressors. Cheating is an act of resistance, and resistance against oppressive powers should be encouraged and celebrated, rather than deemed a “bad habit” or an unethical act. The concern regarding self-esteem that is highlighted by The Child Study Center as promoting the “worst damage,” lacks any scientific support whatsoever.
If students feel bad for cheating, it is because the environment has created a set of conditions where cheating is necessary and justifiable. For this same reason, many students are proud that they cheat. Cheating often requires creativity in terms of execution as well as ingenuity to avoid being caught. It also serves as a statement of disdain against an arbitrary and repressive institution. For these reasons, cheating can be a source for pride that boosts self-esteem. Given this construct, cheating is not simply something many students do; it is something all students in compulsory schools should do. Cheating is a moral imperative.
Punishing students for cheating is completely misguided. People should be most concerned about the student who does not cheat. They are the ones who appear to have internalized their oppression and might lack the necessary skills to rally and lobby against abuses of power that are perpetrated by governing bodies. Cheating should be recognized as the necessary and logical outcome of an arbitrary and oppressive institution. Punishing students who cheat is yet another abuse of autocratic power. In a healthy society, people ridicule and shame those who force children to endure the kind of environment that demands they must cheat.

Elliot Ackerman
Amit Katwala

Jennifer M. Wood

Garrett M. Graff

Vadim Smyslov
Nicole Tisdale

Jason Parham

- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- School Stuff
- Academic Dishonesty
How to Cheat on Homework
Last Updated: January 4, 2024
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 65 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time. This article has been viewed 137,913 times. Learn more...
Sometimes it's just easier to not do the work. According to a recent study, 42% of freshmen at Harvard admitted to cheating on homework assignments, putting you in good company if you often feel like you've got better things to do than another worksheet. [1] X Research source Instead of going about it foolishly and copying off your friend right before class starts, get smart about your cheating. You can learn the best ways to finish off your math homework, your reading, and even cut some serious corners on your essays.
Cheating on Math or Short-Answer Homework

- First, you've got to make friends with the smartest kids in class, who always do the work correctly. It helps if you can share in the workload sometimes, alternating who does the homework and who copies, night to night. Don't be totally useless.
- The best times to copy homework are on the bus on the way home, or on the way to school. It's usually better to do it on the way home, so you can still try to actually do the homework if you need to. Never copy homework in class before class starts. Never talk about copying the answers in public, to your parents, or to other students. Keep it quiet.
- If you use this method, paraphrase. It does cause a little suspicion when two students have the exact same answer.

- To make the homework go faster, split up all the answers among the group. Have one person do the first five, another do the next five, and so on. You should be able to finish before the bus ride is over. Try to keep the group as small as possible.
- Don't make the group too big. If everyone names the first president of the United States as "George Washington Carver" on the homework, your teacher might be suspicious that something strange was happening. After you copy it, go back over it once by yourself to fix any obvious mistakes and make little changes to make it your own.

- Even just fixing the order of words in short answers can throw a teacher off the scent, if the answer is correct. Change "John Glenn was the first American in space" to "The first American in space was John Glenn."
- To stay extra covert, try to copy off of someone that your teacher doesn't think you're friends with. The teacher may be more likely to look more closely at the homework for signs of cheating if you're neighbors with someone, or if you're sitting next to someone.

- If you find your answers off the internet, make sure to paraphrase it so your teachers don't find out. Teachers are smart these days, so if you copy it directly, they could definitely find out.

- Online tutoring even exists in some places. Some college students will sometimes answer homework questions or offer assistance online, sometimes for a price. [2] X Research source If you can send copies of the questions, you might at least get some help figuring out the answer for yourself.
Reading Fast

- Skip everything but the vocab words in a textbook. The skipping-around method tends to work better with textbooks, in which the actual explanations aren't that important, but the names and the vocab words are. You can read the textbook very fast this way, and not miss much information.
- Alternatively, depending on the kind of class, it might be better to read the first and last chapter of a novel, or focus all your attention on a single small part of the book and bring it up in class, to look as if you've read the whole thing and are prepared for discussion.

- It's also easy to find a long plot synopsis online, so you can at least get a good list of the characters and the style of the novel.

- Ask your friends to summarize their 50 assigned pages (or however many it works out to be) and take good notes on the section, then copy out the notes for everyone in the group. After that, each person's work will be done. It's like reading a whole book by only reading 1/3 or a 1/2.

- It's still a good idea to do some research and figure out whether or not the movie is accurate. Lots of movies take serious liberties with the plot lines of books, and you'll likely miss the names of characters and other minor plot points that might get cut out of the movie but be important for the book.
- Good movies based on books commonly assigned for school include: Grapes of Wrath , Romeo & Juliet , Lord of the Flies,' Pride & Prejudice , Wuthering Heights , Of Mice and Men , and To Kill a Mockingbird .
- Bad movies to watch instead of reading the book include The Iliad ('don't watch 'Troy , starring Brad Pitt), Fahrenheit 451 , Catcher in the Rye , Beowulf , Romeo & Juliet , and The Great Gatsby . These are good ways to prove you haven't read the book.

- It's also a good idea to look for possible talking-points online before you even do the reading, so you can know what to look for and have a good idea of something to say in class. Participation points with no actual work.
Cheating on Essays

- Many older teachers will assign the same papers year after year, and won't keep copies of them, making it very difficult for them to remember one students paper after a year or two. Never do this if your teacher collects essays online, or saves digital copies. This makes it very easy to do a quick file search and find copied passages.
- Buying essays online is basically a scam for chumps, so don't get schemed out of your hard-earned lunch money by some enterprising con artist. If you don't know the person you're getting the essay from, write it yourself. In general, paying to cheat is a bad idea, friend, sibling, or otherwise.

- Make sure the response to the topic is still up-to-date and not incriminating. If you see opportunities to expand and make more current references, do it to bring everything together.
- Never copy-paste from online and turn it in without revising. If you do, go over the font and the size to make sure everything is uniform.
- Copying passages or whole chunks of text from online is always easy to find quickly. If you try this, you risk lots of trouble.

- Read the assignment sheet closely as you go over the copied essay, making sure that it does everything that it needs to for you to get a good grade. If it doesn't, you need to add that in. Hey, at least you didn't have to start from scratch.

Did You Know? In countries such as Bangladesh and Singapore, this is criminalized and carries severe penalties.
Expert Q&A
- Copy down friend's work the day its assigned because most people do it in class. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If your homework questions are straight from a textbook, the internet will most likely have answers for them. If you are lucky, you can find a PDF of the teacher’s textbook, which has all the answers. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
Tips from our Readers
- If your homework questions come straight from a textbook, you can often find the answers online or in a PDF version of the teacher's book. But just copying the textbook's answers word-for-word is dishonest. Use any answers you find as a guide, but explain things in your own words.
- If an assignment's got you stumped, get help ASAP instead of waiting until the last minute. Talk to your teacher, go to tutoring, or study with friends who get the material. Being proactive will leave you truly prepared, not desperately seeking shortcuts.
- With group projects, make sure everyone pulls their weight. Don't let some kids copy your work while they slack off. Set ground rules for dividing up the work and keeping each other accountable.
- If you get busted copying someone's work, don't make excuses or blame others. Own up to your mistake, take the consequences, and learn from it. Your character matters more than one assignment.
- Prioritize homework by due dates and percentage of each one's worth. It is better to fully complete a big project than rush through busy work just to check it off. Use your time wisely.
- Break up long readings into 30-45 minute chunks. Take short breaks between sessions to stay focused and absorb more than just cramming it all in one mega study blast.

- Be discreet. Don't suddenly start getting top marks, ensure you make a slow and steady transition or everyone will know you are cheating. Thanks Helpful 4 Not Helpful 0
- Some teachers understand that there isn't much they can do to prevent students from copying solutions either from friends or off the internet. Instead, well-written exams will enforce the no copying solutions policy better than the teacher can. Homework will be worth only a small portion of the grade while exams will be the main grade determiner. If you have been copying homework solutions, you may be in trouble when it comes to the exams. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 1
- Just because you aren't caught directly cheating doesn't mean that people don't know that you're cheating. News about who cheats gets around the school fast. Don't be surprised if people seem to not want to trust you anymore. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 2
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.washingtonpost.com/lifestyle/on-parenting/harvard-freshmen-who-admitted-cheating-on-homework-did-nothing-wrong/2013/09/17/3aedb5d0-18a4-11e3-8685-5021e0c41964_story.html
- ↑ http://www.tutor-homework.com/homework-cheat.html
About This Article
- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
StudyMonkey
Your personal ai tutor.
Learn Smarter, Not Harder with AI
Introducing StudyMonkey, your AI-powered tutor .
StudyMonkey AI can tutor complex homework questions, enhance your essay writing and assess your work—all in seconds.
No more long all-nighters
24/7 solutions to questions you're stumped on and essays you procrastinated on.
No more stress and anxiety
Get all your assignments done with helpful answers in 10 seconds or less.
No more asking friends for help
StudyMonkey is your new smart bestie that will never ghost you.
No more staying after school
AI tutoring is available 24/7, on-demand when you need it most.
AI Tutor for any subject
American college testing (act), anthropology, advanced placement exams (ap exams), arabic language, archaeology, biochemistry, chartered financial analyst (cfa) exam, communications, computer science, certified public accountant (cpa) exam, cultural studies, cyber security, dental admission test (dat), discrete mathematics, earth science, elementary school, entrepreneurship, environmental science, farsi (persian) language, fundamentals of engineering (fe) exam, gender studies, graduate management admission test (gmat), graduate record examination (gre), greek language, hebrew language, high school entrance exam, high school, human geography, human resources, international english language testing system (ielts), information technology, international relations, independent school entrance exam (isee), linear algebra, linguistics, law school admission test (lsat), machine learning, master's degree, medical college admission test (mcat), meteorology, microbiology, middle school, national council licensure examination (nclex), national merit scholarship qualifying test (nmsqt), number theory, organic chemistry, project management professional (pmp), political science, portuguese language, probability, project management, preliminary sat (psat), public policy, public relations, russian language, scholastic assessment test (sat), social sciences, secondary school admission test (ssat), sustainability, swahili language, test of english as a foreign language (toefl), trigonometry, turkish language, united states medical licensing examination (usmle), web development, step-by-step guidance 24/7.
Receive step-by-step guidance & homework help for any homework problem & any subject 24/7
Ask any question
StudyMonkey supports every subject and every level of education from 1st grade to masters level.
Get an answer
StudyMonkey will give you an answer in seconds—multiple choice questions, short answers, and even an essays are supported!
Review your history
See your past questions and answers so you can review for tests and improve your grades.
It's not cheating...
You're just learning smarter than everyone else
How Can StudyMonkey Help You?
Hear from our happy students.
"The AI tutor is available 24/7, making it a convenient and accessible resource for students who need help with their homework at any time."
"Overall, StudyMonkey is an excellent tool for students looking to improve their understanding of homework topics and boost their academic success."
Upgrade to StudyMonkey Premium!
You have used all of your answers for today!
Why not upgrade to StudyMonkey Premium and get access to all features?
Take advantage of our 14 day free trial and try it out for yourself!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Cheating also appears to be almost contagious among young people—and may even serve as a kind of social adhesive, at least in environments where it is widely accepted. ... Repetitive homework assignments are also a culprit, according to research, so teachers should look at creating take-home assignments that encourage students to think ...
Copying and Pasting. Social Media. When you were in school, teens who were cheating were likely looking at a neighbor's paper or copying a friend's homework. The most high-tech attempts to cheat may have involved a student who wrote the answers to a test on the cover of their notebook.
If you find students cheat on homework, they probably lack the vision for how the work is beneficial. It's important to consider the meaningfulness and valuable of the assignment from students' perspectives. They need to see how it is relevant to them. In my class, I've learned to assign work that cannot be copied.
The line between "learning" and "cheating" when using online homework help ; Tips for getting the most out of a homework help website; So let's get started! The Basics About Homework Help Websites-Free and Paid. Homework help websites are designed to help you complete your homework assignments, plain and simple.
Sometimes they have a reason to cheat like feeling [like] they need to be the smartest kid in class.". Kayla (Massachusetts) agreed, noting, "Some people cheat because they want to seem cooler than their friends or try to impress their friends. Students cheat because they think if they cheat all the time they're going to get smarter.".
A lot of students don't even realize it's an easy way to catch a student cheating.". Online exams appear to be seen as more sacred by students, with the majority of survey respondents saying that using unapproved technology or tools in exams is very unacceptable and only 17 percent seeing it as somewhat or very acceptable.
According to a 2012 white paper, Cheat or Be Cheated? prepared by Challenge Success, 80 percent admitted to copying another student's homework. The other studies summarized in the paper found ...
Cheating on homework can hurt students in long run. Instructors say shared homework answers are easy to pick out. (Courtesy of Kristin Dudley and Anastasia Foster) Whether it takes five minutes or ...
First, the amount of cheating on homework observed calls for new strategies for raising homework engagement, as this was found to be a clear predictor of digital dishonesty. This can be achieved by better explaining the goals and benefits of homework, the adverse effects of cheating on homework, and by providing adequate feedback on homework ...
Academic integrity is important, experts say, as plagiarism and other cheating may have severe consequences. Experts say the number of students engaging in academic dishonesty during the ...
We have been hearing stories about academic cheating: from students caught cheating on homework assignments as well as college entrance exams to teachers being caught in cheating scandals, such as ...
What do we know about how much students cheat? Pope: We know that cheating rates have been high for a long time.At Challenge Success we've been running surveys and focus groups at schools for over 15 years, asking students about different aspects of their lives — the amount of sleep they get, homework pressure, extracurricular activities, family expectations, things like that — and also ...
Step 1: Check the quality of your assignments. First of all, it's worth taking a close look at the kind of homework you assign. If you do a lot of worksheets, you might find those work better for in-class activities. Instead, try focusing homework on in-depth writing assignments and individual written responses.
Excessive homework can also lead to cheating: 90% of middle school students and 67% of high school students admit to copying someone else's homework, and 43% of college students engaged in "unauthorized collaboration" on out-of-class assignments. Even parents take shortcuts on homework: 43% of those surveyed admitted to having completed a ...
Online learning makes cheating easier. The shift to online learning in 2020 drastically changed the relationship between students and learning. From a student perspective, it is much easier to cheat on virtual tests and homework assignments. With any answer at their fingertips on the internet, students turn to search engines for help on exams.
Another common reason students engage in dishonest behavior has to do with overload: too many homework assignments, work issues, relationship problems, COVID-19. Before you resort to behaving in an academically dishonest way, we encourage you to reach out to your professor, your TA, your academic advisor or even UB's counseling services.
A recent survey published by The International Center for Academic Integrity reports alarming results with respect to cheating by students. More than 70,000 students, both graduates and undergraduates, took part in the study that reported 95 percent of the surveyed students admitted to cheating on a test, on homework and/or committing plagiarism.
Cheating is an act of resistance, and resistance against oppressive powers should be encouraged and celebrated, rather than deemed a "bad habit" or an unethical act. The concern regarding self ...
The ultimate homework cheat? How teachers are facing up to ChatGPT. ChatGPT took the internet by storm when it launched in late 2022, impressing by generating stories, poems, coding solutions, and ...
Slader. Slader is a crowdsourcing app for high school and college students to post and answer questions in math and science. While students can post original homework for help, many questions in ...
2. Work on the assignment with a group. Doing an assignment in a big group in which everyone contributes is a good way to make sure that everyone gets the right answers and the assignment gets done quickly. Do it in the safety of someone's home, or on the bus after school to stay safe. Never try to do this in class.
Homework Helper Plan. "The AI tutor is available 24/7, making it a convenient and accessible resource for students who need help with their homework at any time." Anonymous. Basic Plan. A 24/7 free homework AI tutor that instantly provides personalized step-by-step guidance, explanations, and examples for any homework problem.
Learn the ramifications of homework cheating. Take a friend's responses and copy them. Collaborate on the assignment as a collective. Change the way you say things in your answers. Look them up on the internet. Consider enlisting the help of a mentor instead. to confuse your instructor, Make a few mistakes.
87 likes, 3 comments - codewithriyaa on March 8, 2024: "#reelsdaily #reelsexplore #codeeditors #reelsindia #reelsinstagram #educationalreels #100daysofco..."