What is a scientific hypothesis?
It's the initial building block in the scientific method.


Hypothesis basics
What makes a hypothesis testable.
- Types of hypotheses
- Hypothesis versus theory
Additional resources
Bibliography.
A scientific hypothesis is a tentative, testable explanation for a phenomenon in the natural world. It's the initial building block in the scientific method . Many describe it as an "educated guess" based on prior knowledge and observation. While this is true, a hypothesis is more informed than a guess. While an "educated guess" suggests a random prediction based on a person's expertise, developing a hypothesis requires active observation and background research.
The basic idea of a hypothesis is that there is no predetermined outcome. For a solution to be termed a scientific hypothesis, it has to be an idea that can be supported or refuted through carefully crafted experimentation or observation. This concept, called falsifiability and testability, was advanced in the mid-20th century by Austrian-British philosopher Karl Popper in his famous book "The Logic of Scientific Discovery" (Routledge, 1959).
A key function of a hypothesis is to derive predictions about the results of future experiments and then perform those experiments to see whether they support the predictions.
A hypothesis is usually written in the form of an if-then statement, which gives a possibility (if) and explains what may happen because of the possibility (then). The statement could also include "may," according to California State University, Bakersfield .
Here are some examples of hypothesis statements:
- If garlic repels fleas, then a dog that is given garlic every day will not get fleas.
- If sugar causes cavities, then people who eat a lot of candy may be more prone to cavities.
- If ultraviolet light can damage the eyes, then maybe this light can cause blindness.
A useful hypothesis should be testable and falsifiable. That means that it should be possible to prove it wrong. A theory that can't be proved wrong is nonscientific, according to Karl Popper's 1963 book " Conjectures and Refutations ."
An example of an untestable statement is, "Dogs are better than cats." That's because the definition of "better" is vague and subjective. However, an untestable statement can be reworded to make it testable. For example, the previous statement could be changed to this: "Owning a dog is associated with higher levels of physical fitness than owning a cat." With this statement, the researcher can take measures of physical fitness from dog and cat owners and compare the two.
Types of scientific hypotheses

In an experiment, researchers generally state their hypotheses in two ways. The null hypothesis predicts that there will be no relationship between the variables tested, or no difference between the experimental groups. The alternative hypothesis predicts the opposite: that there will be a difference between the experimental groups. This is usually the hypothesis scientists are most interested in, according to the University of Miami .
For example, a null hypothesis might state, "There will be no difference in the rate of muscle growth between people who take a protein supplement and people who don't." The alternative hypothesis would state, "There will be a difference in the rate of muscle growth between people who take a protein supplement and people who don't."
If the results of the experiment show a relationship between the variables, then the null hypothesis has been rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis, according to the book " Research Methods in Psychology " (BCcampus, 2015).
There are other ways to describe an alternative hypothesis. The alternative hypothesis above does not specify a direction of the effect, only that there will be a difference between the two groups. That type of prediction is called a two-tailed hypothesis. If a hypothesis specifies a certain direction — for example, that people who take a protein supplement will gain more muscle than people who don't — it is called a one-tailed hypothesis, according to William M. K. Trochim , a professor of Policy Analysis and Management at Cornell University.
Sometimes, errors take place during an experiment. These errors can happen in one of two ways. A type I error is when the null hypothesis is rejected when it is true. This is also known as a false positive. A type II error occurs when the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is false. This is also known as a false negative, according to the University of California, Berkeley .
A hypothesis can be rejected or modified, but it can never be proved correct 100% of the time. For example, a scientist can form a hypothesis stating that if a certain type of tomato has a gene for red pigment, that type of tomato will be red. During research, the scientist then finds that each tomato of this type is red. Though the findings confirm the hypothesis, there may be a tomato of that type somewhere in the world that isn't red. Thus, the hypothesis is true, but it may not be true 100% of the time.
Scientific theory vs. scientific hypothesis
The best hypotheses are simple. They deal with a relatively narrow set of phenomena. But theories are broader; they generally combine multiple hypotheses into a general explanation for a wide range of phenomena, according to the University of California, Berkeley . For example, a hypothesis might state, "If animals adapt to suit their environments, then birds that live on islands with lots of seeds to eat will have differently shaped beaks than birds that live on islands with lots of insects to eat." After testing many hypotheses like these, Charles Darwin formulated an overarching theory: the theory of evolution by natural selection.
"Theories are the ways that we make sense of what we observe in the natural world," Tanner said. "Theories are structures of ideas that explain and interpret facts."
- Read more about writing a hypothesis, from the American Medical Writers Association.
- Find out why a hypothesis isn't always necessary in science, from The American Biology Teacher.
- Learn about null and alternative hypotheses, from Prof. Essa on YouTube .
Encyclopedia Britannica. Scientific Hypothesis. Jan. 13, 2022. https://www.britannica.com/science/scientific-hypothesis
Karl Popper, "The Logic of Scientific Discovery," Routledge, 1959.
California State University, Bakersfield, "Formatting a testable hypothesis." https://www.csub.edu/~ddodenhoff/Bio100/Bio100sp04/formattingahypothesis.htm
Karl Popper, "Conjectures and Refutations," Routledge, 1963.
Price, P., Jhangiani, R., & Chiang, I., "Research Methods of Psychology — 2nd Canadian Edition," BCcampus, 2015.
University of Miami, "The Scientific Method" http://www.bio.miami.edu/dana/161/evolution/161app1_scimethod.pdf
William M.K. Trochim, "Research Methods Knowledge Base," https://conjointly.com/kb/hypotheses-explained/
University of California, Berkeley, "Multiple Hypothesis Testing and False Discovery Rate" https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~hhuang/STAT141/Lecture-FDR.pdf
University of California, Berkeley, "Science at multiple levels" https://undsci.berkeley.edu/article/0_0_0/howscienceworks_19
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

AI-powered 'digital twin' of Earth could make weather predictions at super speeds
Part of the San Andreas fault may be gearing up for an earthquake
'Vampire' bacteria thirst for human blood — and cause deadly infections as they feed
Most Popular
- 2 NASA spacecraft snaps mysterious 'surfboard' orbiting the moon. What is it?
- 3 'Gambling with your life': Experts weigh in on dangers of the Wim Hof method
- 4 Viking Age women with cone-shaped skulls likely learned head-binding practice from far-flung region
- 5 'Exceptional' prosthesis of gold, silver and wool helped 18th-century man live with cleft palate
- 2 AI pinpoints where psychosis originates in the brain
- 3 NASA's downed Ingenuity helicopter has a 'last gift' for humanity — but we'll have to go to Mars to get it
- 4 Anglerfish entered the midnight zone 55 million years ago and thrived by becoming sexual parasites
- 5 2,500-year-old skeletons with legs chopped off may be elites who received 'cruel' punishment in ancient China
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

The Craft of Writing a Strong Hypothesis

Table of Contents
Writing a hypothesis is one of the essential elements of a scientific research paper. It needs to be to the point, clearly communicating what your research is trying to accomplish. A blurry, drawn-out, or complexly-structured hypothesis can confuse your readers. Or worse, the editor and peer reviewers.
A captivating hypothesis is not too intricate. This blog will take you through the process so that, by the end of it, you have a better idea of how to convey your research paper's intent in just one sentence.
What is a Hypothesis?
The first step in your scientific endeavor, a hypothesis, is a strong, concise statement that forms the basis of your research. It is not the same as a thesis statement , which is a brief summary of your research paper .
The sole purpose of a hypothesis is to predict your paper's findings, data, and conclusion. It comes from a place of curiosity and intuition . When you write a hypothesis, you're essentially making an educated guess based on scientific prejudices and evidence, which is further proven or disproven through the scientific method.
The reason for undertaking research is to observe a specific phenomenon. A hypothesis, therefore, lays out what the said phenomenon is. And it does so through two variables, an independent and dependent variable.
The independent variable is the cause behind the observation, while the dependent variable is the effect of the cause. A good example of this is “mixing red and blue forms purple.” In this hypothesis, mixing red and blue is the independent variable as you're combining the two colors at your own will. The formation of purple is the dependent variable as, in this case, it is conditional to the independent variable.
Different Types of Hypotheses

Types of hypotheses
Some would stand by the notion that there are only two types of hypotheses: a Null hypothesis and an Alternative hypothesis. While that may have some truth to it, it would be better to fully distinguish the most common forms as these terms come up so often, which might leave you out of context.
Apart from Null and Alternative, there are Complex, Simple, Directional, Non-Directional, Statistical, and Associative and casual hypotheses. They don't necessarily have to be exclusive, as one hypothesis can tick many boxes, but knowing the distinctions between them will make it easier for you to construct your own.
1. Null hypothesis
A null hypothesis proposes no relationship between two variables. Denoted by H 0 , it is a negative statement like “Attending physiotherapy sessions does not affect athletes' on-field performance.” Here, the author claims physiotherapy sessions have no effect on on-field performances. Even if there is, it's only a coincidence.
2. Alternative hypothesis
Considered to be the opposite of a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis is donated as H1 or Ha. It explicitly states that the dependent variable affects the independent variable. A good alternative hypothesis example is “Attending physiotherapy sessions improves athletes' on-field performance.” or “Water evaporates at 100 °C. ” The alternative hypothesis further branches into directional and non-directional.
- Directional hypothesis: A hypothesis that states the result would be either positive or negative is called directional hypothesis. It accompanies H1 with either the ‘<' or ‘>' sign.
- Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional hypothesis only claims an effect on the dependent variable. It does not clarify whether the result would be positive or negative. The sign for a non-directional hypothesis is ‘≠.'
3. Simple hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, “Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking.
4. Complex hypothesis
In contrast to a simple hypothesis, a complex hypothesis implies the relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. For instance, “Individuals who eat more fruits tend to have higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.” The independent variable is eating more fruits, while the dependent variables are higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.
5. Associative and casual hypothesis
Associative and casual hypotheses don't exhibit how many variables there will be. They define the relationship between the variables. In an associative hypothesis, changing any one variable, dependent or independent, affects others. In a casual hypothesis, the independent variable directly affects the dependent.
6. Empirical hypothesis
Also referred to as the working hypothesis, an empirical hypothesis claims a theory's validation via experiments and observation. This way, the statement appears justifiable and different from a wild guess.
Say, the hypothesis is “Women who take iron tablets face a lesser risk of anemia than those who take vitamin B12.” This is an example of an empirical hypothesis where the researcher the statement after assessing a group of women who take iron tablets and charting the findings.
7. Statistical hypothesis
The point of a statistical hypothesis is to test an already existing hypothesis by studying a population sample. Hypothesis like “44% of the Indian population belong in the age group of 22-27.” leverage evidence to prove or disprove a particular statement.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
Writing a hypothesis is essential as it can make or break your research for you. That includes your chances of getting published in a journal. So when you're designing one, keep an eye out for these pointers:
- A research hypothesis has to be simple yet clear to look justifiable enough.
- It has to be testable — your research would be rendered pointless if too far-fetched into reality or limited by technology.
- It has to be precise about the results —what you are trying to do and achieve through it should come out in your hypothesis.
- A research hypothesis should be self-explanatory, leaving no doubt in the reader's mind.
- If you are developing a relational hypothesis, you need to include the variables and establish an appropriate relationship among them.
- A hypothesis must keep and reflect the scope for further investigations and experiments.
Separating a Hypothesis from a Prediction
Outside of academia, hypothesis and prediction are often used interchangeably. In research writing, this is not only confusing but also incorrect. And although a hypothesis and prediction are guesses at their core, there are many differences between them.
A hypothesis is an educated guess or even a testable prediction validated through research. It aims to analyze the gathered evidence and facts to define a relationship between variables and put forth a logical explanation behind the nature of events.
Predictions are assumptions or expected outcomes made without any backing evidence. They are more fictionally inclined regardless of where they originate from.
For this reason, a hypothesis holds much more weight than a prediction. It sticks to the scientific method rather than pure guesswork. "Planets revolve around the Sun." is an example of a hypothesis as it is previous knowledge and observed trends. Additionally, we can test it through the scientific method.
Whereas "COVID-19 will be eradicated by 2030." is a prediction. Even though it results from past trends, we can't prove or disprove it. So, the only way this gets validated is to wait and watch if COVID-19 cases end by 2030.
Finally, How to Write a Hypothesis

Quick tips on writing a hypothesis
1. Be clear about your research question
A hypothesis should instantly address the research question or the problem statement. To do so, you need to ask a question. Understand the constraints of your undertaken research topic and then formulate a simple and topic-centric problem. Only after that can you develop a hypothesis and further test for evidence.
2. Carry out a recce
Once you have your research's foundation laid out, it would be best to conduct preliminary research. Go through previous theories, academic papers, data, and experiments before you start curating your research hypothesis. It will give you an idea of your hypothesis's viability or originality.
Making use of references from relevant research papers helps draft a good research hypothesis. SciSpace Discover offers a repository of over 270 million research papers to browse through and gain a deeper understanding of related studies on a particular topic. Additionally, you can use SciSpace Copilot , your AI research assistant, for reading any lengthy research paper and getting a more summarized context of it. A hypothesis can be formed after evaluating many such summarized research papers. Copilot also offers explanations for theories and equations, explains paper in simplified version, allows you to highlight any text in the paper or clip math equations and tables and provides a deeper, clear understanding of what is being said. This can improve the hypothesis by helping you identify potential research gaps.
3. Create a 3-dimensional hypothesis
Variables are an essential part of any reasonable hypothesis. So, identify your independent and dependent variable(s) and form a correlation between them. The ideal way to do this is to write the hypothetical assumption in the ‘if-then' form. If you use this form, make sure that you state the predefined relationship between the variables.
In another way, you can choose to present your hypothesis as a comparison between two variables. Here, you must specify the difference you expect to observe in the results.
4. Write the first draft
Now that everything is in place, it's time to write your hypothesis. For starters, create the first draft. In this version, write what you expect to find from your research.
Clearly separate your independent and dependent variables and the link between them. Don't fixate on syntax at this stage. The goal is to ensure your hypothesis addresses the issue.
5. Proof your hypothesis
After preparing the first draft of your hypothesis, you need to inspect it thoroughly. It should tick all the boxes, like being concise, straightforward, relevant, and accurate. Your final hypothesis has to be well-structured as well.
Research projects are an exciting and crucial part of being a scholar. And once you have your research question, you need a great hypothesis to begin conducting research. Thus, knowing how to write a hypothesis is very important.
Now that you have a firmer grasp on what a good hypothesis constitutes, the different kinds there are, and what process to follow, you will find it much easier to write your hypothesis, which ultimately helps your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace Discover . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
It includes everything you need, including a repository of over 270 million research papers across disciplines, SEO-optimized summaries and public profiles to show your expertise and experience.
If you found these tips on writing a research hypothesis useful, head over to our blog on Statistical Hypothesis Testing to learn about the top researchers, papers, and institutions in this domain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is the definition of hypothesis.
According to the Oxford dictionary, a hypothesis is defined as “An idea or explanation of something that is based on a few known facts, but that has not yet been proved to be true or correct”.
2. What is an example of hypothesis?
The hypothesis is a statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables. An example: "If we increase the number of new users who join our platform by 25%, then we will see an increase in revenue."
3. What is an example of null hypothesis?
A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between two variables. The null hypothesis is written as H0. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect. For example, if you're studying whether or not a particular type of exercise increases strength, your null hypothesis will be "there is no difference in strength between people who exercise and people who don't."
4. What are the types of research?
• Fundamental research
• Applied research
• Qualitative research
• Quantitative research
• Mixed research
• Exploratory research
• Longitudinal research
• Cross-sectional research
• Field research
• Laboratory research
• Fixed research
• Flexible research
• Action research
• Policy research
• Classification research
• Comparative research
• Causal research
• Inductive research
• Deductive research
5. How to write a hypothesis?
• Your hypothesis should be able to predict the relationship and outcome.
• Avoid wordiness by keeping it simple and brief.
• Your hypothesis should contain observable and testable outcomes.
• Your hypothesis should be relevant to the research question.
6. What are the 2 types of hypothesis?
• Null hypotheses are used to test the claim that "there is no difference between two groups of data".
• Alternative hypotheses test the claim that "there is a difference between two data groups".
7. Difference between research question and research hypothesis?
A research question is a broad, open-ended question you will try to answer through your research. A hypothesis is a statement based on prior research or theory that you expect to be true due to your study. Example - Research question: What are the factors that influence the adoption of the new technology? Research hypothesis: There is a positive relationship between age, education and income level with the adoption of the new technology.
8. What is plural for hypothesis?
The plural of hypothesis is hypotheses. Here's an example of how it would be used in a statement, "Numerous well-considered hypotheses are presented in this part, and they are supported by tables and figures that are well-illustrated."
9. What is the red queen hypothesis?
The red queen hypothesis in evolutionary biology states that species must constantly evolve to avoid extinction because if they don't, they will be outcompeted by other species that are evolving. Leigh Van Valen first proposed it in 1973; since then, it has been tested and substantiated many times.
10. Who is known as the father of null hypothesis?
The father of the null hypothesis is Sir Ronald Fisher. He published a paper in 1925 that introduced the concept of null hypothesis testing, and he was also the first to use the term itself.
11. When to reject null hypothesis?
You need to find a significant difference between your two populations to reject the null hypothesis. You can determine that by running statistical tests such as an independent sample t-test or a dependent sample t-test. You should reject the null hypothesis if the p-value is less than 0.05.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
What Is A Research (Scientific) Hypothesis? A plain-language explainer + examples
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
If you’re new to the world of research, or it’s your first time writing a dissertation or thesis, you’re probably noticing that the words “research hypothesis” and “scientific hypothesis” are used quite a bit, and you’re wondering what they mean in a research context .
“Hypothesis” is one of those words that people use loosely, thinking they understand what it means. However, it has a very specific meaning within academic research. So, it’s important to understand the exact meaning before you start hypothesizing.
Research Hypothesis 101
- What is a hypothesis ?
- What is a research hypothesis (scientific hypothesis)?
- Requirements for a research hypothesis
- Definition of a research hypothesis
- The null hypothesis
What is a hypothesis?
Let’s start with the general definition of a hypothesis (not a research hypothesis or scientific hypothesis), according to the Cambridge Dictionary:
Hypothesis: an idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved.
In other words, it’s a statement that provides an explanation for why or how something works, based on facts (or some reasonable assumptions), but that has not yet been specifically tested . For example, a hypothesis might look something like this:
Hypothesis: sleep impacts academic performance.
This statement predicts that academic performance will be influenced by the amount and/or quality of sleep a student engages in – sounds reasonable, right? It’s based on reasonable assumptions , underpinned by what we currently know about sleep and health (from the existing literature). So, loosely speaking, we could call it a hypothesis, at least by the dictionary definition.
But that’s not good enough…
Unfortunately, that’s not quite sophisticated enough to describe a research hypothesis (also sometimes called a scientific hypothesis), and it wouldn’t be acceptable in a dissertation, thesis or research paper . In the world of academic research, a statement needs a few more criteria to constitute a true research hypothesis .
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes – specificity , clarity and testability .
Let’s take a look at these more closely.
Need a helping hand?
Hypothesis Essential #1: Specificity & Clarity
A good research hypothesis needs to be extremely clear and articulate about both what’ s being assessed (who or what variables are involved ) and the expected outcome (for example, a difference between groups, a relationship between variables, etc.).
Let’s stick with our sleepy students example and look at how this statement could be more specific and clear.
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
As you can see, the statement is very specific as it identifies the variables involved (sleep hours and test grades), the parties involved (two groups of students), as well as the predicted relationship type (a positive relationship). There’s no ambiguity or uncertainty about who or what is involved in the statement, and the expected outcome is clear.
Contrast that to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – and you can see the difference. “Sleep” and “academic performance” are both comparatively vague , and there’s no indication of what the expected relationship direction is (more sleep or less sleep). As you can see, specificity and clarity are key.

Hypothesis Essential #2: Testability (Provability)
A statement must be testable to qualify as a research hypothesis. In other words, there needs to be a way to prove (or disprove) the statement. If it’s not testable, it’s not a hypothesis – simple as that.
For example, consider the hypothesis we mentioned earlier:
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
We could test this statement by undertaking a quantitative study involving two groups of students, one that gets 8 or more hours of sleep per night for a fixed period, and one that gets less. We could then compare the standardised test results for both groups to see if there’s a statistically significant difference.
Again, if you compare this to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – you can see that it would be quite difficult to test that statement, primarily because it isn’t specific enough. How much sleep? By who? What type of academic performance?
So, remember the mantra – if you can’t test it, it’s not a hypothesis 🙂

Defining A Research Hypothesis
You’re still with us? Great! Let’s recap and pin down a clear definition of a hypothesis.
A research hypothesis (or scientific hypothesis) is a statement about an expected relationship between variables, or explanation of an occurrence, that is clear, specific and testable.
So, when you write up hypotheses for your dissertation or thesis, make sure that they meet all these criteria. If you do, you’ll not only have rock-solid hypotheses but you’ll also ensure a clear focus for your entire research project.
What about the null hypothesis?
You may have also heard the terms null hypothesis , alternative hypothesis, or H-zero thrown around. At a simple level, the null hypothesis is the counter-proposal to the original hypothesis.
For example, if the hypothesis predicts that there is a relationship between two variables (for example, sleep and academic performance), the null hypothesis would predict that there is no relationship between those variables.
At a more technical level, the null hypothesis proposes that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations and that any differences are due to chance alone.
And there you have it – hypotheses in a nutshell.
If you have any questions, be sure to leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to help you. If you need hands-on help developing and testing your hypotheses, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research journey.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

16 Comments
Very useful information. I benefit more from getting more information in this regard.
Very great insight,educative and informative. Please give meet deep critics on many research data of public international Law like human rights, environment, natural resources, law of the sea etc
In a book I read a distinction is made between null, research, and alternative hypothesis. As far as I understand, alternative and research hypotheses are the same. Can you please elaborate? Best Afshin
This is a self explanatory, easy going site. I will recommend this to my friends and colleagues.
Very good definition. How can I cite your definition in my thesis? Thank you. Is nul hypothesis compulsory in a research?
It’s a counter-proposal to be proven as a rejection
Please what is the difference between alternate hypothesis and research hypothesis?
It is a very good explanation. However, it limits hypotheses to statistically tasteable ideas. What about for qualitative researches or other researches that involve quantitative data that don’t need statistical tests?
In qualitative research, one typically uses propositions, not hypotheses.
could you please elaborate it more
I’ve benefited greatly from these notes, thank you.
This is very helpful
well articulated ideas are presented here, thank you for being reliable sources of information
Excellent. Thanks for being clear and sound about the research methodology and hypothesis (quantitative research)
I have only a simple question regarding the null hypothesis. – Is the null hypothesis (Ho) known as the reversible hypothesis of the alternative hypothesis (H1? – How to test it in academic research?
this is very important note help me much more
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is Research Methodology? Simple Definition (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and objectives are confirmatory in nature. For example,…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Hypothesis n., plural: hypotheses [/haɪˈpɑːθəsɪs/] Definition: Testable scientific prediction
Table of Contents
What Is Hypothesis?
A scientific hypothesis is a foundational element of the scientific method . It’s a testable statement proposing a potential explanation for natural phenomena. The term hypothesis means “little theory” . A hypothesis is a short statement that can be tested and gives a possible reason for a phenomenon or a possible link between two variables . In the setting of scientific research, a hypothesis is a tentative explanation or statement that can be proven wrong and is used to guide experiments and empirical research.

It is an important part of the scientific method because it gives a basis for planning tests, gathering data, and judging evidence to see if it is true and could help us understand how natural things work. Several hypotheses can be tested in the real world, and the results of careful and systematic observation and analysis can be used to support, reject, or improve them.
Researchers and scientists often use the word hypothesis to refer to this educated guess . These hypotheses are firmly established based on scientific principles and the rigorous testing of new technology and experiments .
For example, in astrophysics, the Big Bang Theory is a working hypothesis that explains the origins of the universe and considers it as a natural phenomenon. It is among the most prominent scientific hypotheses in the field.
“The scientific method: steps, terms, and examples” by Scishow:
Biology definition: A hypothesis is a supposition or tentative explanation for (a group of) phenomena, (a set of) facts, or a scientific inquiry that may be tested, verified or answered by further investigation or methodological experiment. It is like a scientific guess . It’s an idea or prediction that scientists make before they do experiments. They use it to guess what might happen and then test it to see if they were right. It’s like a smart guess that helps them learn new things. A scientific hypothesis that has been verified through scientific experiment and research may well be considered a scientific theory .
Etymology: The word “hypothesis” comes from the Greek word “hupothesis,” which means “a basis” or “a supposition.” It combines “hupo” (under) and “thesis” (placing). Synonym: proposition; assumption; conjecture; postulate Compare: theory See also: null hypothesis
Characteristics Of Hypothesis
A useful hypothesis must have the following qualities:
- It should never be written as a question.
- You should be able to test it in the real world to see if it’s right or wrong.
- It needs to be clear and exact.
- It should list the factors that will be used to figure out the relationship.
- It should only talk about one thing. You can make a theory in either a descriptive or form of relationship.
- It shouldn’t go against any natural rule that everyone knows is true. Verification will be done well with the tools and methods that are available.
- It should be written in as simple a way as possible so that everyone can understand it.
- It must explain what happened to make an answer necessary.
- It should be testable in a fair amount of time.
- It shouldn’t say different things.
Sources Of Hypothesis
Sources of hypothesis are:
- Patterns of similarity between the phenomenon under investigation and existing hypotheses.
- Insights derived from prior research, concurrent observations, and insights from opposing perspectives.
- The formulations are derived from accepted scientific theories and proposed by researchers.
- In research, it’s essential to consider hypothesis as different subject areas may require various hypotheses (plural form of hypothesis). Researchers also establish a significance level to determine the strength of evidence supporting a hypothesis.
- Individual cognitive processes also contribute to the formation of hypotheses.
One hypothesis is a tentative explanation for an observation or phenomenon. It is based on prior knowledge and understanding of the world, and it can be tested by gathering and analyzing data. Observed facts are the data that are collected to test a hypothesis. They can support or refute the hypothesis.
For example, the hypothesis that “eating more fruits and vegetables will improve your health” can be tested by gathering data on the health of people who eat different amounts of fruits and vegetables. If the people who eat more fruits and vegetables are healthier than those who eat less fruits and vegetables, then the hypothesis is supported.
Hypotheses are essential for scientific inquiry. They help scientists to focus their research, to design experiments, and to interpret their results. They are also essential for the development of scientific theories.
Types Of Hypothesis
In research, you typically encounter two types of hypothesis: the alternative hypothesis (which proposes a relationship between variables) and the null hypothesis (which suggests no relationship).
Simple Hypothesis
It illustrates the association between one dependent variable and one independent variable. For instance, if you consume more vegetables, you will lose weight more quickly. Here, increasing vegetable consumption is the independent variable, while weight loss is the dependent variable.
Complex Hypothesis
It exhibits the relationship between at least two dependent variables and at least two independent variables. Eating more vegetables and fruits results in weight loss, radiant skin, and a decreased risk of numerous diseases, including heart disease.
Directional Hypothesis
It shows that a researcher wants to reach a certain goal. The way the factors are related can also tell us about their nature. For example, four-year-old children who eat well over a time of five years have a higher IQ than children who don’t eat well. This shows what happened and how it happened.
Non-directional Hypothesis
When there is no theory involved, it is used. It is a statement that there is a connection between two variables, but it doesn’t say what that relationship is or which way it goes.
Null Hypothesis
It says something that goes against the theory. It’s a statement that says something is not true, and there is no link between the independent and dependent factors. “H 0 ” represents the null hypothesis.
Associative and Causal Hypothesis
When a change in one variable causes a change in the other variable, this is called the associative hypothesis . The causal hypothesis, on the other hand, says that there is a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more factors.
Examples Of Hypothesis
Examples of simple hypotheses:
- Students who consume breakfast before taking a math test will have a better overall performance than students who do not consume breakfast.
- Students who experience test anxiety before an English examination will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety.
- Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone, is a statement that suggests that drivers who talk on the phone while driving are more likely to make mistakes.
Examples of a complex hypothesis:
- Individuals who consume a lot of sugar and don’t get much exercise are at an increased risk of developing depression.
- Younger people who are routinely exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces, according to a new study.
- Increased levels of air pollution led to higher rates of respiratory illnesses, which in turn resulted in increased costs for healthcare for the affected communities.
Examples of Directional Hypothesis:
- The crop yield will go up a lot if the amount of fertilizer is increased.
- Patients who have surgery and are exposed to more stress will need more time to get better.
- Increasing the frequency of brand advertising on social media will lead to a significant increase in brand awareness among the target audience.
Examples of Non-Directional Hypothesis (or Two-Tailed Hypothesis):
- The test scores of two groups of students are very different from each other.
- There is a link between gender and being happy at work.
- There is a correlation between the amount of caffeine an individual consumes and the speed with which they react.
Examples of a null hypothesis:
- Children who receive a new reading intervention will have scores that are different than students who do not receive the intervention.
- The results of a memory recall test will not reveal any significant gap in performance between children and adults.
- There is not a significant relationship between the number of hours spent playing video games and academic performance.
Examples of Associative Hypothesis:
- There is a link between how many hours you spend studying and how well you do in school.
- Drinking sugary drinks is bad for your health as a whole.
- There is an association between socioeconomic status and access to quality healthcare services in urban neighborhoods.
Functions Of Hypothesis
The research issue can be understood better with the help of a hypothesis, which is why developing one is crucial. The following are some of the specific roles that a hypothesis plays: (Rashid, Apr 20, 2022)
- A hypothesis gives a study a point of concentration. It enlightens us as to the specific characteristics of a study subject we need to look into.
- It instructs us on what data to acquire as well as what data we should not collect, giving the study a focal point .
- The development of a hypothesis improves objectivity since it enables the establishment of a focal point.
- A hypothesis makes it possible for us to contribute to the development of the theory. Because of this, we are in a position to definitively determine what is true and what is untrue .
How will Hypothesis help in the Scientific Method?
- The scientific method begins with observation and inquiry about the natural world when formulating research questions. Researchers can refine their observations and queries into specific, testable research questions with the aid of hypothesis. They provide an investigation with a focused starting point.
- Hypothesis generate specific predictions regarding the expected outcomes of experiments or observations. These forecasts are founded on the researcher’s current knowledge of the subject. They elucidate what researchers anticipate observing if the hypothesis is true.
- Hypothesis direct the design of experiments and data collection techniques. Researchers can use them to determine which variables to measure or manipulate, which data to obtain, and how to conduct systematic and controlled research.
- Following the formulation of a hypothesis and the design of an experiment, researchers collect data through observation, measurement, or experimentation. The collected data is used to verify the hypothesis’s predictions.
- Hypothesis establish the criteria for evaluating experiment results. The observed data are compared to the predictions generated by the hypothesis. This analysis helps determine whether empirical evidence supports or refutes the hypothesis.
- The results of experiments or observations are used to derive conclusions regarding the hypothesis. If the data support the predictions, then the hypothesis is supported. If this is not the case, the hypothesis may be revised or rejected, leading to the formulation of new queries and hypothesis.
- The scientific approach is iterative, resulting in new hypothesis and research issues from previous trials. This cycle of hypothesis generation, testing, and refining drives scientific progress.

Importance Of Hypothesis
- Hypothesis are testable statements that enable scientists to determine if their predictions are accurate. This assessment is essential to the scientific method, which is based on empirical evidence.
- Hypothesis serve as the foundation for designing experiments or data collection techniques. They can be used by researchers to develop protocols and procedures that will produce meaningful results.
- Hypothesis hold scientists accountable for their assertions. They establish expectations for what the research should reveal and enable others to assess the validity of the findings.
- Hypothesis aid in identifying the most important variables of a study. The variables can then be measured, manipulated, or analyzed to determine their relationships.
- Hypothesis assist researchers in allocating their resources efficiently. They ensure that time, money, and effort are spent investigating specific concerns, as opposed to exploring random concepts.
- Testing hypothesis contribute to the scientific body of knowledge. Whether or not a hypothesis is supported, the results contribute to our understanding of a phenomenon.
- Hypothesis can result in the creation of theories. When supported by substantive evidence, hypothesis can serve as the foundation for larger theoretical frameworks that explain complex phenomena.
- Beyond scientific research, hypothesis play a role in the solution of problems in a variety of domains. They enable professionals to make educated assumptions about the causes of problems and to devise solutions.
Research Hypotheses: Did you know that a hypothesis refers to an educated guess or prediction about the outcome of a research study?
It’s like a roadmap guiding researchers towards their destination of knowledge. Just like a compass points north, a well-crafted hypothesis points the way to valuable discoveries in the world of science and inquiry.
Choose the best answer.
Send Your Results (Optional)

Further Reading
- RNA-DNA World Hypothesis
- BYJU’S. (2023). Hypothesis. Retrieved 01 Septermber 2023, from https://byjus.com/physics/hypothesis/#sources-of-hypothesis
- Collegedunia. (2023). Hypothesis. Retrieved 1 September 2023, from https://collegedunia.com/exams/hypothesis-science-articleid-7026#d
- Hussain, D. J. (2022). Hypothesis. Retrieved 01 September 2023, from https://mmhapu.ac.in/doc/eContent/Management/JamesHusain/Research%20Hypothesis%20-Meaning,%20Nature%20&%20Importance-Characteristics%20of%20Good%20%20Hypothesis%20Sem2.pdf
- Media, D. (2023). Hypothesis in the Scientific Method. Retrieved 01 September 2023, from https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-a-hypothesis-2795239#toc-hypotheses-examples
- Rashid, M. H. A. (Apr 20, 2022). Research Methodology. Retrieved 01 September 2023, from https://limbd.org/hypothesis-definitions-functions-characteristics-types-errors-the-process-of-testing-a-hypothesis-hypotheses-in-qualitative-research/#:~:text=Functions%20of%20a%20Hypothesis%3A&text=Specifically%2C%20a%20hypothesis%20serves%20the,providing%20focus%20to%20the%20study.
©BiologyOnline.com. Content provided and moderated by Biology Online Editors.
Last updated on September 8th, 2023
You will also like...

Gene Action – Operon Hypothesis

Water in Plants

Growth and Plant Hormones

Sigmund Freud and Carl Gustav Jung

Population Growth and Survivorship
Related articles....

RNA-DNA World Hypothesis?

On Mate Selection Evolution: Are intelligent males more attractive?

Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use

Dead Man Walking
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.36(50); 2021 Dec 27

Formulating Hypotheses for Different Study Designs
Durga prasanna misra.
1 Department of Clinical Immunology and Rheumatology, Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India.
Armen Yuri Gasparyan
2 Departments of Rheumatology and Research and Development, Dudley Group NHS Foundation Trust (Teaching Trust of the University of Birmingham, UK), Russells Hall Hospital, Dudley, UK.
Olena Zimba
3 Department of Internal Medicine #2, Danylo Halytsky Lviv National Medical University, Lviv, Ukraine.
Marlen Yessirkepov
4 Department of Biology and Biochemistry, South Kazakhstan Medical Academy, Shymkent, Kazakhstan.
Vikas Agarwal
George d. kitas.
5 Centre for Epidemiology versus Arthritis, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK.
Generating a testable working hypothesis is the first step towards conducting original research. Such research may prove or disprove the proposed hypothesis. Case reports, case series, online surveys and other observational studies, clinical trials, and narrative reviews help to generate hypotheses. Observational and interventional studies help to test hypotheses. A good hypothesis is usually based on previous evidence-based reports. Hypotheses without evidence-based justification and a priori ideas are not received favourably by the scientific community. Original research to test a hypothesis should be carefully planned to ensure appropriate methodology and adequate statistical power. While hypotheses can challenge conventional thinking and may be controversial, they should not be destructive. A hypothesis should be tested by ethically sound experiments with meaningful ethical and clinical implications. The coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic has brought into sharp focus numerous hypotheses, some of which were proven (e.g. effectiveness of corticosteroids in those with hypoxia) while others were disproven (e.g. ineffectiveness of hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin).
Graphical Abstract

DEFINING WORKING AND STANDALONE SCIENTIFIC HYPOTHESES
Science is the systematized description of natural truths and facts. Routine observations of existing life phenomena lead to the creative thinking and generation of ideas about mechanisms of such phenomena and related human interventions. Such ideas presented in a structured format can be viewed as hypotheses. After generating a hypothesis, it is necessary to test it to prove its validity. Thus, hypothesis can be defined as a proposed mechanism of a naturally occurring event or a proposed outcome of an intervention. 1 , 2
Hypothesis testing requires choosing the most appropriate methodology and adequately powering statistically the study to be able to “prove” or “disprove” it within predetermined and widely accepted levels of certainty. This entails sample size calculation that often takes into account previously published observations and pilot studies. 2 , 3 In the era of digitization, hypothesis generation and testing may benefit from the availability of numerous platforms for data dissemination, social networking, and expert validation. Related expert evaluations may reveal strengths and limitations of proposed ideas at early stages of post-publication promotion, preventing the implementation of unsupported controversial points. 4
Thus, hypothesis generation is an important initial step in the research workflow, reflecting accumulating evidence and experts' stance. In this article, we overview the genesis and importance of scientific hypotheses and their relevance in the era of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
DO WE NEED HYPOTHESES FOR ALL STUDY DESIGNS?
Broadly, research can be categorized as primary or secondary. In the context of medicine, primary research may include real-life observations of disease presentations and outcomes. Single case descriptions, which often lead to new ideas and hypotheses, serve as important starting points or justifications for case series and cohort studies. The importance of case descriptions is particularly evident in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic when unique, educational case reports have heralded a new era in clinical medicine. 5
Case series serve similar purpose to single case reports, but are based on a slightly larger quantum of information. Observational studies, including online surveys, describe the existing phenomena at a larger scale, often involving various control groups. Observational studies include variable-scale epidemiological investigations at different time points. Interventional studies detail the results of therapeutic interventions.
Secondary research is based on already published literature and does not directly involve human or animal subjects. Review articles are generated by secondary research. These could be systematic reviews which follow methods akin to primary research but with the unit of study being published papers rather than humans or animals. Systematic reviews have a rigid structure with a mandatory search strategy encompassing multiple databases, systematic screening of search results against pre-defined inclusion and exclusion criteria, critical appraisal of study quality and an optional component of collating results across studies quantitatively to derive summary estimates (meta-analysis). 6 Narrative reviews, on the other hand, have a more flexible structure. Systematic literature searches to minimise bias in selection of articles are highly recommended but not mandatory. 7 Narrative reviews are influenced by the authors' viewpoint who may preferentially analyse selected sets of articles. 8
In relation to primary research, case studies and case series are generally not driven by a working hypothesis. Rather, they serve as a basis to generate a hypothesis. Observational or interventional studies should have a hypothesis for choosing research design and sample size. The results of observational and interventional studies further lead to the generation of new hypotheses, testing of which forms the basis of future studies. Review articles, on the other hand, may not be hypothesis-driven, but form fertile ground to generate future hypotheses for evaluation. Fig. 1 summarizes which type of studies are hypothesis-driven and which lead on to hypothesis generation.

STANDARDS OF WORKING AND SCIENTIFIC HYPOTHESES
A review of the published literature did not enable the identification of clearly defined standards for working and scientific hypotheses. It is essential to distinguish influential versus not influential hypotheses, evidence-based hypotheses versus a priori statements and ideas, ethical versus unethical, or potentially harmful ideas. The following points are proposed for consideration while generating working and scientific hypotheses. 1 , 2 Table 1 summarizes these points.
Evidence-based data
A scientific hypothesis should have a sound basis on previously published literature as well as the scientist's observations. Randomly generated (a priori) hypotheses are unlikely to be proven. A thorough literature search should form the basis of a hypothesis based on published evidence. 7
Unless a scientific hypothesis can be tested, it can neither be proven nor be disproven. Therefore, a scientific hypothesis should be amenable to testing with the available technologies and the present understanding of science.
Supported by pilot studies
If a hypothesis is based purely on a novel observation by the scientist in question, it should be grounded on some preliminary studies to support it. For example, if a drug that targets a specific cell population is hypothesized to be useful in a particular disease setting, then there must be some preliminary evidence that the specific cell population plays a role in driving that disease process.
Testable by ethical studies
The hypothesis should be testable by experiments that are ethically acceptable. 9 For example, a hypothesis that parachutes reduce mortality from falls from an airplane cannot be tested using a randomized controlled trial. 10 This is because it is obvious that all those jumping from a flying plane without a parachute would likely die. Similarly, the hypothesis that smoking tobacco causes lung cancer cannot be tested by a clinical trial that makes people take up smoking (since there is considerable evidence for the health hazards associated with smoking). Instead, long-term observational studies comparing outcomes in those who smoke and those who do not, as was performed in the landmark epidemiological case control study by Doll and Hill, 11 are more ethical and practical.
Balance between scientific temper and controversy
Novel findings, including novel hypotheses, particularly those that challenge established norms, are bound to face resistance for their wider acceptance. Such resistance is inevitable until the time such findings are proven with appropriate scientific rigor. However, hypotheses that generate controversy are generally unwelcome. For example, at the time the pandemic of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and AIDS was taking foot, there were numerous deniers that refused to believe that HIV caused AIDS. 12 , 13 Similarly, at a time when climate change is causing catastrophic changes to weather patterns worldwide, denial that climate change is occurring and consequent attempts to block climate change are certainly unwelcome. 14 The denialism and misinformation during the COVID-19 pandemic, including unfortunate examples of vaccine hesitancy, are more recent examples of controversial hypotheses not backed by science. 15 , 16 An example of a controversial hypothesis that was a revolutionary scientific breakthrough was the hypothesis put forth by Warren and Marshall that Helicobacter pylori causes peptic ulcers. Initially, the hypothesis that a microorganism could cause gastritis and gastric ulcers faced immense resistance. When the scientists that proposed the hypothesis themselves ingested H. pylori to induce gastritis in themselves, only then could they convince the wider world about their hypothesis. Such was the impact of the hypothesis was that Barry Marshall and Robin Warren were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2005 for this discovery. 17 , 18
DISTINGUISHING THE MOST INFLUENTIAL HYPOTHESES
Influential hypotheses are those that have stood the test of time. An archetype of an influential hypothesis is that proposed by Edward Jenner in the eighteenth century that cowpox infection protects against smallpox. While this observation had been reported for nearly a century before this time, it had not been suitably tested and publicised until Jenner conducted his experiments on a young boy by demonstrating protection against smallpox after inoculation with cowpox. 19 These experiments were the basis for widespread smallpox immunization strategies worldwide in the 20th century which resulted in the elimination of smallpox as a human disease today. 20
Other influential hypotheses are those which have been read and cited widely. An example of this is the hygiene hypothesis proposing an inverse relationship between infections in early life and allergies or autoimmunity in adulthood. An analysis reported that this hypothesis had been cited more than 3,000 times on Scopus. 1
LESSONS LEARNED FROM HYPOTHESES AMIDST THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC
The COVID-19 pandemic devastated the world like no other in recent memory. During this period, various hypotheses emerged, understandably so considering the public health emergency situation with innumerable deaths and suffering for humanity. Within weeks of the first reports of COVID-19, aberrant immune system activation was identified as a key driver of organ dysfunction and mortality in this disease. 21 Consequently, numerous drugs that suppress the immune system or abrogate the activation of the immune system were hypothesized to have a role in COVID-19. 22 One of the earliest drugs hypothesized to have a benefit was hydroxychloroquine. Hydroxychloroquine was proposed to interfere with Toll-like receptor activation and consequently ameliorate the aberrant immune system activation leading to pathology in COVID-19. 22 The drug was also hypothesized to have a prophylactic role in preventing infection or disease severity in COVID-19. It was also touted as a wonder drug for the disease by many prominent international figures. However, later studies which were well-designed randomized controlled trials failed to demonstrate any benefit of hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19. 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 Subsequently, azithromycin 27 , 28 and ivermectin 29 were hypothesized as potential therapies for COVID-19, but were not supported by evidence from randomized controlled trials. The role of vitamin D in preventing disease severity was also proposed, but has not been proven definitively until now. 30 , 31 On the other hand, randomized controlled trials identified the evidence supporting dexamethasone 32 and interleukin-6 pathway blockade with tocilizumab as effective therapies for COVID-19 in specific situations such as at the onset of hypoxia. 33 , 34 Clues towards the apparent effectiveness of various drugs against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in vitro but their ineffectiveness in vivo have recently been identified. Many of these drugs are weak, lipophilic bases and some others induce phospholipidosis which results in apparent in vitro effectiveness due to non-specific off-target effects that are not replicated inside living systems. 35 , 36
Another hypothesis proposed was the association of the routine policy of vaccination with Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) with lower deaths due to COVID-19. This hypothesis emerged in the middle of 2020 when COVID-19 was still taking foot in many parts of the world. 37 , 38 Subsequently, many countries which had lower deaths at that time point went on to have higher numbers of mortality, comparable to other areas of the world. Furthermore, the hypothesis that BCG vaccination reduced COVID-19 mortality was a classic example of ecological fallacy. Associations between population level events (ecological studies; in this case, BCG vaccination and COVID-19 mortality) cannot be directly extrapolated to the individual level. Furthermore, such associations cannot per se be attributed as causal in nature, and can only serve to generate hypotheses that need to be tested at the individual level. 39
IS TRADITIONAL PEER REVIEW EFFICIENT FOR EVALUATION OF WORKING AND SCIENTIFIC HYPOTHESES?
Traditionally, publication after peer review has been considered the gold standard before any new idea finds acceptability amongst the scientific community. Getting a work (including a working or scientific hypothesis) reviewed by experts in the field before experiments are conducted to prove or disprove it helps to refine the idea further as well as improve the experiments planned to test the hypothesis. 40 A route towards this has been the emergence of journals dedicated to publishing hypotheses such as the Central Asian Journal of Medical Hypotheses and Ethics. 41 Another means of publishing hypotheses is through registered research protocols detailing the background, hypothesis, and methodology of a particular study. If such protocols are published after peer review, then the journal commits to publishing the completed study irrespective of whether the study hypothesis is proven or disproven. 42 In the post-pandemic world, online research methods such as online surveys powered via social media channels such as Twitter and Instagram might serve as critical tools to generate as well as to preliminarily test the appropriateness of hypotheses for further evaluation. 43 , 44
Some radical hypotheses might be difficult to publish after traditional peer review. These hypotheses might only be acceptable by the scientific community after they are tested in research studies. Preprints might be a way to disseminate such controversial and ground-breaking hypotheses. 45 However, scientists might prefer to keep their hypotheses confidential for the fear of plagiarism of ideas, avoiding online posting and publishing until they have tested the hypotheses.
SUGGESTIONS ON GENERATING AND PUBLISHING HYPOTHESES
Publication of hypotheses is important, however, a balance is required between scientific temper and controversy. Journal editors and reviewers might keep in mind these specific points, summarized in Table 2 and detailed hereafter, while judging the merit of hypotheses for publication. Keeping in mind the ethical principle of primum non nocere, a hypothesis should be published only if it is testable in a manner that is ethically appropriate. 46 Such hypotheses should be grounded in reality and lend themselves to further testing to either prove or disprove them. It must be considered that subsequent experiments to prove or disprove a hypothesis have an equal chance of failing or succeeding, akin to tossing a coin. A pre-conceived belief that a hypothesis is unlikely to be proven correct should not form the basis of rejection of such a hypothesis for publication. In this context, hypotheses generated after a thorough literature search to identify knowledge gaps or based on concrete clinical observations on a considerable number of patients (as opposed to random observations on a few patients) are more likely to be acceptable for publication by peer-reviewed journals. Also, hypotheses should be considered for publication or rejection based on their implications for science at large rather than whether the subsequent experiments to test them end up with results in favour of or against the original hypothesis.
Hypotheses form an important part of the scientific literature. The COVID-19 pandemic has reiterated the importance and relevance of hypotheses for dealing with public health emergencies and highlighted the need for evidence-based and ethical hypotheses. A good hypothesis is testable in a relevant study design, backed by preliminary evidence, and has positive ethical and clinical implications. General medical journals might consider publishing hypotheses as a specific article type to enable more rapid advancement of science.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Data curation: Gasparyan AY, Misra DP, Zimba O, Yessirkepov M, Agarwal V, Kitas GD.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Biology library
Course: biology library > unit 1, the scientific method.
- Controlled experiments
- The scientific method and experimental design
Introduction
- Make an observation.
- Ask a question.
- Form a hypothesis , or testable explanation.
- Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
- Test the prediction.
- Iterate: use the results to make new hypotheses or predictions.
Scientific method example: Failure to toast
1. make an observation..
- Observation: the toaster won't toast.
2. Ask a question.
- Question: Why won't my toaster toast?
3. Propose a hypothesis.
- Hypothesis: Maybe the outlet is broken.
4. Make predictions.
- Prediction: If I plug the toaster into a different outlet, then it will toast the bread.
5. Test the predictions.
- Test of prediction: Plug the toaster into a different outlet and try again.
- If the toaster does toast, then the hypothesis is supported—likely correct.
- If the toaster doesn't toast, then the hypothesis is not supported—likely wrong.
Logical possibility
Practical possibility, building a body of evidence, 6. iterate..
- Iteration time!
- If the hypothesis was supported, we might do additional tests to confirm it, or revise it to be more specific. For instance, we might investigate why the outlet is broken.
- If the hypothesis was not supported, we would come up with a new hypothesis. For instance, the next hypothesis might be that there's a broken wire in the toaster.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation.
Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments and the collection and analysis of data. It is an essential element of the scientific method, as it allows researchers to make predictions about the outcome of their experiments and to test those predictions to determine their accuracy.
Types of Hypothesis
Types of Hypothesis are as follows:
Research Hypothesis
A research hypothesis is a statement that predicts a relationship between variables. It is usually formulated as a specific statement that can be tested through research, and it is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is no significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as a starting point for testing the research hypothesis, and if the results of the study reject the null hypothesis, it suggests that there is a significant difference or relationship between variables.
Alternative Hypothesis
An alternative hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is a significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as an alternative to the null hypothesis and is tested against the null hypothesis to determine which statement is more accurate.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the direction of the relationship between variables. For example, a researcher might predict that increasing the amount of exercise will result in a decrease in body weight.
Non-directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between variables but does not specify the direction. For example, a researcher might predict that there is a relationship between the amount of exercise and body weight, but they do not specify whether increasing or decreasing exercise will affect body weight.
Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a statement that assumes a particular statistical model or distribution for the data. It is often used in statistical analysis to test the significance of a particular result.
Composite Hypothesis
A composite hypothesis is a statement that assumes more than one condition or outcome. It can be divided into several sub-hypotheses, each of which represents a different possible outcome.
Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is a statement that is based on observed phenomena or data. It is often used in scientific research to develop theories or models that explain the observed phenomena.
Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement that assumes only one outcome or condition. It is often used in scientific research to test a single variable or factor.
Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is a statement that assumes multiple outcomes or conditions. It is often used in scientific research to test the effects of multiple variables or factors on a particular outcome.
Applications of Hypothesis
Hypotheses are used in various fields to guide research and make predictions about the outcomes of experiments or observations. Here are some examples of how hypotheses are applied in different fields:
- Science : In scientific research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain natural phenomena. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular variable on a natural system, such as the effects of climate change on an ecosystem.
- Medicine : In medical research, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of treatments and therapies for specific conditions. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new drug on a particular disease.
- Psychology : In psychology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of human behavior and cognition. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular stimulus on the brain or behavior.
- Sociology : In sociology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of social phenomena, such as the effects of social structures or institutions on human behavior. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of income inequality on crime rates.
- Business : In business research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain business phenomena, such as consumer behavior or market trends. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new marketing campaign on consumer buying behavior.
- Engineering : In engineering, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of new technologies or designs. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the efficiency of a new solar panel design.
How to write a Hypothesis
Here are the steps to follow when writing a hypothesis:
Identify the Research Question
The first step is to identify the research question that you want to answer through your study. This question should be clear, specific, and focused. It should be something that can be investigated empirically and that has some relevance or significance in the field.
Conduct a Literature Review
Before writing your hypothesis, it’s essential to conduct a thorough literature review to understand what is already known about the topic. This will help you to identify the research gap and formulate a hypothesis that builds on existing knowledge.
Determine the Variables
The next step is to identify the variables involved in the research question. A variable is any characteristic or factor that can vary or change. There are two types of variables: independent and dependent. The independent variable is the one that is manipulated or changed by the researcher, while the dependent variable is the one that is measured or observed as a result of the independent variable.
Formulate the Hypothesis
Based on the research question and the variables involved, you can now formulate your hypothesis. A hypothesis should be a clear and concise statement that predicts the relationship between the variables. It should be testable through empirical research and based on existing theory or evidence.
Write the Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is the opposite of the alternative hypothesis, which is the hypothesis that you are testing. The null hypothesis states that there is no significant difference or relationship between the variables. It is important to write the null hypothesis because it allows you to compare your results with what would be expected by chance.
Refine the Hypothesis
After formulating the hypothesis, it’s important to refine it and make it more precise. This may involve clarifying the variables, specifying the direction of the relationship, or making the hypothesis more testable.
Examples of Hypothesis
Here are a few examples of hypotheses in different fields:
- Psychology : “Increased exposure to violent video games leads to increased aggressive behavior in adolescents.”
- Biology : “Higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will lead to increased plant growth.”
- Sociology : “Individuals who grow up in households with higher socioeconomic status will have higher levels of education and income as adults.”
- Education : “Implementing a new teaching method will result in higher student achievement scores.”
- Marketing : “Customers who receive a personalized email will be more likely to make a purchase than those who receive a generic email.”
- Physics : “An increase in temperature will cause an increase in the volume of a gas, assuming all other variables remain constant.”
- Medicine : “Consuming a diet high in saturated fats will increase the risk of developing heart disease.”
Purpose of Hypothesis
The purpose of a hypothesis is to provide a testable explanation for an observed phenomenon or a prediction of a future outcome based on existing knowledge or theories. A hypothesis is an essential part of the scientific method and helps to guide the research process by providing a clear focus for investigation. It enables scientists to design experiments or studies to gather evidence and data that can support or refute the proposed explanation or prediction.
The formulation of a hypothesis is based on existing knowledge, observations, and theories, and it should be specific, testable, and falsifiable. A specific hypothesis helps to define the research question, which is important in the research process as it guides the selection of an appropriate research design and methodology. Testability of the hypothesis means that it can be proven or disproven through empirical data collection and analysis. Falsifiability means that the hypothesis should be formulated in such a way that it can be proven wrong if it is incorrect.
In addition to guiding the research process, the testing of hypotheses can lead to new discoveries and advancements in scientific knowledge. When a hypothesis is supported by the data, it can be used to develop new theories or models to explain the observed phenomenon. When a hypothesis is not supported by the data, it can help to refine existing theories or prompt the development of new hypotheses to explain the phenomenon.
When to use Hypothesis
Here are some common situations in which hypotheses are used:
- In scientific research , hypotheses are used to guide the design of experiments and to help researchers make predictions about the outcomes of those experiments.
- In social science research , hypotheses are used to test theories about human behavior, social relationships, and other phenomena.
- I n business , hypotheses can be used to guide decisions about marketing, product development, and other areas. For example, a hypothesis might be that a new product will sell well in a particular market, and this hypothesis can be tested through market research.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Here are some common characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable : A hypothesis must be able to be tested through observation or experimentation. This means that it must be possible to collect data that will either support or refute the hypothesis.
- Falsifiable : A hypothesis must be able to be proven false if it is not supported by the data. If a hypothesis cannot be falsified, then it is not a scientific hypothesis.
- Clear and concise : A hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner so that it can be easily understood and tested.
- Based on existing knowledge : A hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and research in the field. It should not be based on personal beliefs or opinions.
- Specific : A hypothesis should be specific in terms of the variables being tested and the predicted outcome. This will help to ensure that the research is focused and well-designed.
- Tentative: A hypothesis is a tentative statement or assumption that requires further testing and evidence to be confirmed or refuted. It is not a final conclusion or assertion.
- Relevant : A hypothesis should be relevant to the research question or problem being studied. It should address a gap in knowledge or provide a new perspective on the issue.
Advantages of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have several advantages in scientific research and experimentation:
- Guides research: A hypothesis provides a clear and specific direction for research. It helps to focus the research question, select appropriate methods and variables, and interpret the results.
- Predictive powe r: A hypothesis makes predictions about the outcome of research, which can be tested through experimentation. This allows researchers to evaluate the validity of the hypothesis and make new discoveries.
- Facilitates communication: A hypothesis provides a common language and framework for scientists to communicate with one another about their research. This helps to facilitate the exchange of ideas and promotes collaboration.
- Efficient use of resources: A hypothesis helps researchers to use their time, resources, and funding efficiently by directing them towards specific research questions and methods that are most likely to yield results.
- Provides a basis for further research: A hypothesis that is supported by data provides a basis for further research and exploration. It can lead to new hypotheses, theories, and discoveries.
- Increases objectivity: A hypothesis can help to increase objectivity in research by providing a clear and specific framework for testing and interpreting results. This can reduce bias and increase the reliability of research findings.
Limitations of Hypothesis
Some Limitations of the Hypothesis are as follows:
- Limited to observable phenomena: Hypotheses are limited to observable phenomena and cannot account for unobservable or intangible factors. This means that some research questions may not be amenable to hypothesis testing.
- May be inaccurate or incomplete: Hypotheses are based on existing knowledge and research, which may be incomplete or inaccurate. This can lead to flawed hypotheses and erroneous conclusions.
- May be biased: Hypotheses may be biased by the researcher’s own beliefs, values, or assumptions. This can lead to selective interpretation of data and a lack of objectivity in research.
- Cannot prove causation: A hypothesis can only show a correlation between variables, but it cannot prove causation. This requires further experimentation and analysis.
- Limited to specific contexts: Hypotheses are limited to specific contexts and may not be generalizable to other situations or populations. This means that results may not be applicable in other contexts or may require further testing.
- May be affected by chance : Hypotheses may be affected by chance or random variation, which can obscure or distort the true relationship between variables.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
Hero Images/Getty Images
- Scientific Method
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
A hypothesis is an educated guess or prediction of what will happen. In science, a hypothesis proposes a relationship between factors called variables. A good hypothesis relates an independent variable and a dependent variable. The effect on the dependent variable depends on or is determined by what happens when you change the independent variable . While you could consider any prediction of an outcome to be a type of hypothesis, a good hypothesis is one you can test using the scientific method. In other words, you want to propose a hypothesis to use as the basis for an experiment.
Cause and Effect or 'If, Then' Relationships
A good experimental hypothesis can be written as an if, then statement to establish cause and effect on the variables. If you make a change to the independent variable, then the dependent variable will respond. Here's an example of a hypothesis:
If you increase the duration of light, (then) corn plants will grow more each day.
The hypothesis establishes two variables, length of light exposure, and the rate of plant growth. An experiment could be designed to test whether the rate of growth depends on the duration of light. The duration of light is the independent variable, which you can control in an experiment . The rate of plant growth is the dependent variable, which you can measure and record as data in an experiment.
Key Points of Hypothesis
When you have an idea for a hypothesis, it may help to write it out in several different ways. Review your choices and select a hypothesis that accurately describes what you are testing.
- Does the hypothesis relate an independent and dependent variable? Can you identify the variables?
- Can you test the hypothesis? In other words, could you design an experiment that would allow you to establish or disprove a relationship between the variables?
- Would your experiment be safe and ethical?
- Is there a simpler or more precise way to state the hypothesis? If so, rewrite it.
What If the Hypothesis Is Incorrect?
It's not wrong or bad if the hypothesis is not supported or is incorrect. Actually, this outcome may tell you more about a relationship between the variables than if the hypothesis is supported. You may intentionally write your hypothesis as a null hypothesis or no-difference hypothesis to establish a relationship between the variables.
For example, the hypothesis:
The rate of corn plant growth does not depend on the duration of light.
This can be tested by exposing corn plants to different length "days" and measuring the rate of plant growth. A statistical test can be applied to measure how well the data support the hypothesis. If the hypothesis is not supported, then you have evidence of a relationship between the variables. It's easier to establish cause and effect by testing whether "no effect" is found. Alternatively, if the null hypothesis is supported, then you have shown the variables are not related. Either way, your experiment is a success.
Need more examples of how to write a hypothesis ? Here you go:
- If you turn out all the lights, you will fall asleep faster. (Think: How would you test it?)
- If you drop different objects, they will fall at the same rate.
- If you eat only fast food, then you will gain weight.
- If you use cruise control, then your car will get better gas mileage.
- If you apply a top coat, then your manicure will last longer.
- If you turn the lights on and off rapidly, then the bulb will burn out faster.
- Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples
- Six Steps of the Scientific Method
- What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
- Understanding Simple vs Controlled Experiments
- The Role of a Controlled Variable in an Experiment
- Dependent Variable Definition and Examples
- How To Design a Science Fair Experiment
- Null Hypothesis Examples
- Independent Variable Definition and Examples
- Scientific Method Vocabulary Terms
- Scientific Method Flow Chart
- What Are Independent and Dependent Variables?
- Definition of a Hypothesis
- Scientific Variable
- What Is an Experiment? Definition and Design
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization
Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.

The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Thompson WH, Skau S. On the scope of scientific hypotheses . R Soc Open Sci . 2023;10(8):230607. doi:10.1098/rsos.230607
Taran S, Adhikari NKJ, Fan E. Falsifiability in medicine: what clinicians can learn from Karl Popper [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun 17;:]. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47(9):1054-1056. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06432-z
Eyler AA. Research Methods for Public Health . 1st ed. Springer Publishing Company; 2020. doi:10.1891/9780826182067.0004
Nosek BA, Errington TM. What is replication ? PLoS Biol . 2020;18(3):e3000691. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000691
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
5 Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis: A Guide for Researchers
- by Brian Thomas
- October 10, 2023
Are you a curious soul, always seeking answers to the whys and hows of the world? As a researcher, formulating a hypothesis is a crucial first step towards unraveling the mysteries of your study. A well-crafted hypothesis not only guides your research but also lays the foundation for drawing valid conclusions. But what exactly makes a hypothesis a good one? In this blog post, we will explore the five key characteristics of a good hypothesis that every researcher should know.
Here, we will delve into the world of hypotheses, covering everything from their types in research to understanding if they can be proven true. Whether you’re a seasoned researcher or just starting out, this blog post will provide valuable insights on how to craft a sound hypothesis for your study. So let’s dive in and uncover the secrets to formulating a hypothesis that stands strong amidst the scientific rigor!
(Keywords: characteristics of a good hypothesis, important characteristics of a good hypothesis quizlet, types of hypothesis in research, can a hypothesis be proven true, 6 parts of hypothesis, how to start a hypothesis sentence, examples of hypothesis, five key elements of a good hypothesis, hypothesis in research papers, is a hypothesis always a question, three things needed for a good hypothesis, components of a good hypothesis, formulate a hypothesis, characteristics of a hypothesis mcq, criteria for a scientific hypothesis, steps of theory development in scientific methods, what makes a good hypothesis, characteristics of a good hypothesis quizlet, five-step p-value approach to hypothesis testing , stages of hypothesis, good hypothesis characteristics, writing a good hypothesis example, difference between hypothesis and hypotheses, good hypothesis statement, not a characteristic of a good hypothesis)
5 Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
Clear and specific.
A good hypothesis is like a GPS that guides you to the right destination. It needs to be clear and specific so that you know exactly what you’re testing. Avoid vague statements or general ideas. Instead, focus on crafting a hypothesis that clearly states the relationship between variables and the expected outcome. Clarity is key, my friend!
Testable and Falsifiable
A hypothesis might sound great in theory, but if you can’t test it or prove it wrong, then it’s like chasing unicorns. A good hypothesis should be testable and falsifiable – meaning there should be a way to gather evidence to support or refute it. Don’t be afraid to challenge your hypothesis and put it to the test. Only when it can be proven false can it truly be considered a good hypothesis.
Based on Existing Knowledge
Imagine trying to build a Lego tower without any Lego bricks. That’s what it’s like to come up with a hypothesis that has no basis in existing knowledge. A good hypothesis is grounded in previous research, theories, or observations. It shows that you’ve done your homework and understand the current state of knowledge in your field. So, put on your research hat and gather those building blocks for a solid hypothesis!
Specific Predictions
No, we’re not talking about crystal ball predictions or psychic abilities here. A good hypothesis includes specific predictions about what you expect to happen. It’s like making an educated guess based on your understanding of the variables involved. These predictions help guide your research and give you something concrete to look for. So, put on those prediction goggles, my friend, and let’s get specific!
Relevant to the Research Question
A hypothesis is a road sign that points you in the right direction. But if it’s not relevant to your research question, then you might end up in a never-ending detour. A good hypothesis aligns with your research question and addresses the specific problem or phenomenon you’re investigating. Keep your focus on the main topic and avoid getting sidetracked by shiny distractions. Stay relevant, my friend, and you’ll find the answers you seek!
And there you have it: the five characteristics of a good hypothesis. Remember, a good hypothesis is clear, testable, based on existing knowledge, makes specific predictions, and is relevant to your research question. So go forth, my friend, and hypothesize your way to scientific discovery!
FAQs: Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
In the realm of scientific research, a hypothesis plays a crucial role in formulating and testing ideas. A good hypothesis serves as the foundation for an experiment or study, guiding the researcher towards meaningful results. In this FAQ-style subsection, we’ll explore the characteristics of a good hypothesis, their types, formulation, and more. So let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries of hypothesis-making!
What Are Two Important Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
A good hypothesis possesses two important characteristics:
Testability : A hypothesis must be testable to determine its validity. It should be formulated in a way that allows researchers to design and conduct experiments or gather data for analysis. For example, if we hypothesize that “drinking herbal tea reduces stress,” we can easily test it by conducting a study with a control group and a group drinking herbal tea.
Falsifiability : Falsifiability refers to the potential for a hypothesis to be proven wrong. A good hypothesis should make specific predictions that can be refuted or supported by evidence. This characteristic ensures that hypotheses are based on empirical observations rather than personal opinions. For instance, the hypothesis “all swans are white” can be falsified by discovering a single black swan.
What Are the Types of Hypothesis in Research
In research, there are three main types of hypotheses:
Null Hypothesis (H0) : The null hypothesis is a statement of no effect or relationship. It assumes that there is no significant difference between variables or no effect of a treatment. Researchers aim to reject the null hypothesis in favor of an alternative hypothesis.
Alternative Hypothesis (HA or H1) : The alternative hypothesis is the opposite of the null hypothesis. It asserts that there is a significant difference between variables or an effect of a treatment. Researchers seek evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
Directional Hypothesis : A directional hypothesis predicts the specific direction of the relationship or difference between variables. For example, “increasing exercise duration will lead to greater weight loss.”
Can a Hypothesis Be Proven True
In scientific research, hypotheses are not proven true; they are supported or rejected based on empirical evidence . Even if a hypothesis is supported by multiple studies, new evidence could arise that contradicts it. Scientific knowledge is always subject to revision and refinement. Therefore, the goal is to gather enough evidence to either support or reject a hypothesis, rather than proving it absolutely true.
What Are the Six Parts of a Hypothesis
A hypothesis typically consists of six essential parts:
Research Question : A clear and concise question that the hypothesis seeks to answer.
Variables : Identification of the independent (manipulated) and dependent (measured) variables involved in the hypothesis.
Population : The specific group or individuals the hypothesis is concerned with.
Relationship or Comparison : The expected relationship or difference between variables, often indicated by directional terms like “more,” “less,” “higher,” or “lower.”
Predictability : A statement of the predicted outcome or result based on the relationship between variables.
Testability : The ability to design an experiment or gather data to support or reject the hypothesis.
How Do You Start a Hypothesis Sentence
When starting a hypothesis sentence, it is essential to use clear and concise language to express your ideas. A common approach is to use the phrase “If…then…” to establish the conditional relationship between variables. For example:
- If [independent variable], then [dependent variable] because [explanation of expected relationship].
This structure allows for a straightforward and logical formulation of the hypothesis.
What Are Examples of Hypotheses
Here are a few examples of well-formulated hypotheses:
If exposure to sunlight increases, then plants will grow taller because sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis.
If students receive praise for good grades, then their motivation to excel will increase because they seek recognition and approval.
If the dose of a painkiller is increased, then the relief from pain will last longer because a higher dosage has a prolonged effect.
What Are the Five Key Elements to a Good Hypothesis
A good hypothesis should include the following five key elements:
Clarity : The hypothesis should be clear and specific, leaving no room for interpretation.
Testability : It should be possible to test the hypothesis through experimentation or data collection.
Relevance : The hypothesis should be directly tied to the research question or problem being investigated.
Specificity : It must clearly state the relationship or difference between variables being studied.
Falsifiability : The hypothesis should make predictions that can be refuted or supported by empirical evidence.
What Makes a Good Hypothesis in a Research Paper
In a research paper, a good hypothesis should have the following characteristics:
Relevance : It must directly relate to the research topic and address the objectives of the study.
Clarity : The hypothesis should be concise and precisely worded to avoid confusion.
Unambiguous : It must leave no room for multiple interpretations or ambiguity.
Logic : The hypothesis should be based on rational and logical reasoning, considering existing theories and observations.
Empirical Support : Ideally, the hypothesis should be supported by prior empirical evidence or strong theoretical justifications.
Is a Hypothesis Always a Question
No, a hypothesis is not always in the form of a question. While some hypotheses can take the form of a question, others may be statements asserting a relationship or difference between variables. The form of a hypothesis depends on the research question being addressed and the researcher’s preferred style of expression.
What Are the Three Things Needed for a Good Hypothesis
For a hypothesis to be considered good, it must fulfill the following three criteria:
Testability : The hypothesis should be formulated in a way that allows for empirical testing through experimentation or data collection.
Falsifiability : It must make specific predictions that can be potentially refuted or supported by evidence.
Relevance : The hypothesis should directly address the research question or problem being investigated.
What Are the Four Components to a Good Hypothesis
A good hypothesis typically consists of four components:
Independent Variable : The variable being manipulated or controlled by the researcher.
Dependent Variable : The variable being measured or observed to determine the effect of the independent variable.
Directionality : The predicted relationship or difference between the independent and dependent variables.
Population : The specific group or individuals to which the hypothesis applies.
How Do You Formulate a Hypothesis
To formulate a hypothesis, follow these steps:
Identify the Research Topic : Clearly define the area or phenomenon you want to study.
Conduct Background Research : Review existing literature and research to gain knowledge about the topic.
Formulate a Research Question : Ask a clear and focused question that you want to answer through your hypothesis.
State the Null and Alternative Hypotheses : Develop a null hypothesis to assume no effect or relationship, and an alternative hypothesis to propose a significant effect or relationship.
Decide on Variables and Relationships : Determine the independent and dependent variables and the predicted relationship between them.
Refine and Test : Refine your hypothesis, ensuring it is clear, testable, and falsifiable. Then, design experiments or gather data to support or reject it.
What Is a Characteristic of a Hypothesis MCQ
Multiple-choice questions (MCQ) regarding the characteristics of a hypothesis often assess knowledge on the testability and falsifiability of hypotheses. They may ask about the criteria that distinguish a good hypothesis from a poor one or the importance of making specific predictions. Remember to choose answers that emphasize the empirical and testable nature of hypotheses.
What Five Criteria Must Be Satisfied for a Hypothesis to Be Scientific
For a hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must satisfy the following five criteria:
Testability : The hypothesis must be formulated in a way that allows it to be tested through experimentation or data collection.
Falsifiability : It should make specific predictions that can be potentially refuted or supported by empirical evidence.
Empirical Basis : The hypothesis should be based on empirical observations or existing theories and knowledge.
Relevance : It must directly address the research question or problem being investigated.
Objective : A scientific hypothesis should be free from personal biases or subjective opinions, focusing on objective observations and analysis.
What Are the Steps of Theory Development in Scientific Methods
In scientific methods, theory development typically involves the following steps:
Observation : Identifying a phenomenon or pattern worthy of investigation through observation or empirical data.
Formulation of a Hypothesis : Constructing a hypothesis that explains the observed phenomena or predicts a relationship between variables.
Data Collection : Gathering relevant data through experiments, surveys, observations, or other research methods.
Analysis : Analyzing the collected data to evaluate the hypothesis’s predictions and determine their validity.
Revision and Refinement : Based on the analysis, refining the hypothesis, modifying the theory, or formulating new hypotheses for further investigation.
Which of the Following Makes a Good Hypothesis
A good hypothesis is characterized by:
Testability : The ability to form experiments or gather data to support or refute the hypothesis.
Falsifiability : The potential for the hypothesis’s predictions to be proven wrong based on empirical evidence.
Clarity : A clear and concise statement or question that leaves no room for ambiguity.
Relevancy : Directly addressing the research question or problem at hand.
Remember, it is important to select the option that encompasses all these characteristics.
What Are the Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
A good hypothesis possesses several characteristics, such as:
Testability : It should allow for empirical testing through experiments or data collection.
Falsifiability : The hypothesis should make specific predictions that can be potentially refuted or supported by evidence.
Clarity : It must be clearly and precisely formulated, leaving no room for ambiguity or multiple interpretations.
Relevance : The hypothesis should directly relate to the research question or problem being investigated.
What Is the Five-Step p-value Approach to Hypothesis Testing
The five-step p-value approach is a commonly used framework for hypothesis testing:
Step 1: Formulating the Hypotheses : The null hypothesis (H0) assumes no effect or relationship, while the alternative hypothesis (HA) proposes a significant effect or relationship.
Step 2: Setting the Significance Level : Decide on the level of significance (α), which represents the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. The commonly used level is 0.05 (5%).
Step 3: Collecting Data and Performing the Test : Acquire and analyze the data, calculating the test statistic and the corresponding p-value.
Step 4: Comparing the p-value with the Significance Level : If the p-value is less than the significance level (α), reject the null hypothesis. Otherwise, fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Step 5: Drawing Conclusions : Based on the comparison in Step 4, interpret the results and draw conclusions about the hypothesis.
What Are the Stages of Hypothesis
The stages of hypothesis generally include:
Observation : Identifying a pattern, phenomenon, or research question that warrants investigation.
Formulation : Developing a hypothesis that explains or predicts the relationship or difference between variables.
Testing : Collecting data, designing experiments, or conducting studies to gather evidence supporting or refuting the hypothesis.
Analysis : Assessing the collected data to determine whether the results support or reject the hypothesis.
Conclusion : Drawing conclusions based on the analysis and making further iterations, refinements, or new hypotheses for future research.
What Is a Characteristic of a Good Hypothesis
A characteristic of a good hypothesis is its ability to make specific predictions about the relationship or difference between variables. Good hypotheses avoid vague statements and clearly articulate the expected outcomes. By doing so, researchers can design experiments or gather data that directly test the predictions, leading to meaningful results.
How Do You Write a Good Hypothesis Example
To write a good hypothesis example, follow these guidelines:
If possible, use the “If…then…” format to express a conditional relationship between variables.
Be clear and concise in stating the variables involved, the predicted relationship, and the expected outcome.
Ensure the hypothesis is testable, meaning it can be evaluated through experiments or data collection.
For instance, consider the following example:
If students study for longer periods of time, then their test scores will improve because increased study time allows for better retention of information and increased proficiency.
What Is the Difference Between Hypothesis and Hypotheses
The main difference between a hypothesis and hypotheses lies in their grammatical number. A hypothesis refers to a single statement or proposition that is formulated to explain or predict the relationship between variables. On the other hand, hypotheses is the plural form of the term hypothesis, commonly used when multiple statements or propositions are proposed and tested simultaneously.
What Is a Good Hypothesis Statement
A good hypothesis statement exhibits the following qualities:
Clarity : It is written in clear and concise language, leaving no room for confusion or ambiguity.
Testability : The hypothesis should be formulated in a way that enables testing through experiments or data collection.
Specificity : It must clearly state the predicted relationship or difference between variables.
By adhering to these criteria, a good hypothesis statement guides research efforts effectively.
What Is Not a Characteristic of a Good Hypothesis
A characteristic that does not align with a good hypothesis is subjectivity . A hypothesis should be objective, based on empirical observations or existing theories, and free from personal bias. While personal interpretations and opinions can inspire the formulation of a hypothesis, it must ultimately rely on objective observations and be open to empirical testing.
By now, you’ve gained insights into the characteristics of a good hypothesis, including testability, falsifiability, clarity,
- characteristics
- falsifiable
- good hypothesis
- hypothesis testing
- null hypothesis
- observations
- scientific rigor
Brian Thomas
Is july really a 31-day month unraveling the puzzling calendar quirk, how long does it take to become l5 at amazon, you may also like, jessie holmes: the life below zero star’s journey and injury updates.
- by Mr. Gilbert Preston
- October 14, 2023
Did the Actress Who Plays Sasha on General Hospital Have Her Baby? – Exciting News for Soap Fans!
- by Daniel Taylor
- October 9, 2023
Who is Pom Pom to Bowser
- October 28, 2023
What Colour is 0xffff0000? A Comprehensive Guide to Color Codes
- October 8, 2023
Can Vampires Drink Water? Unraveling the Mysteries of Vampire Biology
- by Laura Rodriguez
- October 29, 2023
Was Venus Iced by Vicario? Unraveling the Truth Behind a Tennis Match
- by Brandon Thompson
- October 19, 2023

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Developing a Hypothesis
Rajiv S. Jhangiani; I-Chant A. Chiang; Carrie Cuttler; and Dana C. Leighton
Learning Objectives
- Distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis.
- Discover how theories are used to generate hypotheses and how the results of studies can be used to further inform theories.
- Understand the characteristics of a good hypothesis.
Theories and Hypotheses
Before describing how to develop a hypothesis, it is important to distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis. A theory is a coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena. Although theories can take a variety of forms, one thing they have in common is that they go beyond the phenomena they explain by including variables, structures, processes, functions, or organizing principles that have not been observed directly. Consider, for example, Zajonc’s theory of social facilitation and social inhibition (1965) [1] . He proposed that being watched by others while performing a task creates a general state of physiological arousal, which increases the likelihood of the dominant (most likely) response. So for highly practiced tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make correct responses, but for relatively unpracticed tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make incorrect responses. Notice that this theory—which has come to be called drive theory—provides an explanation of both social facilitation and social inhibition that goes beyond the phenomena themselves by including concepts such as “arousal” and “dominant response,” along with processes such as the effect of arousal on the dominant response.
Outside of science, referring to an idea as a theory often implies that it is untested—perhaps no more than a wild guess. In science, however, the term theory has no such implication. A theory is simply an explanation or interpretation of a set of phenomena. It can be untested, but it can also be extensively tested, well supported, and accepted as an accurate description of the world by the scientific community. The theory of evolution by natural selection, for example, is a theory because it is an explanation of the diversity of life on earth—not because it is untested or unsupported by scientific research. On the contrary, the evidence for this theory is overwhelmingly positive and nearly all scientists accept its basic assumptions as accurate. Similarly, the “germ theory” of disease is a theory because it is an explanation of the origin of various diseases, not because there is any doubt that many diseases are caused by microorganisms that infect the body.
A hypothesis , on the other hand, is a specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate. It is an explanation that relies on just a few key concepts. Hypotheses are often specific predictions about what will happen in a particular study. They are developed by considering existing evidence and using reasoning to infer what will happen in the specific context of interest. Hypotheses are often but not always derived from theories. So a hypothesis is often a prediction based on a theory but some hypotheses are a-theoretical and only after a set of observations have been made, is a theory developed. This is because theories are broad in nature and they explain larger bodies of data. So if our research question is really original then we may need to collect some data and make some observations before we can develop a broader theory.
Theories and hypotheses always have this if-then relationship. “ If drive theory is correct, then cockroaches should run through a straight runway faster, and a branching runway more slowly, when other cockroaches are present.” Although hypotheses are usually expressed as statements, they can always be rephrased as questions. “Do cockroaches run through a straight runway faster when other cockroaches are present?” Thus deriving hypotheses from theories is an excellent way of generating interesting research questions.
But how do researchers derive hypotheses from theories? One way is to generate a research question using the techniques discussed in this chapter and then ask whether any theory implies an answer to that question. For example, you might wonder whether expressive writing about positive experiences improves health as much as expressive writing about traumatic experiences. Although this question is an interesting one on its own, you might then ask whether the habituation theory—the idea that expressive writing causes people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings—implies an answer. In this case, it seems clear that if the habituation theory is correct, then expressive writing about positive experiences should not be effective because it would not cause people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings. A second way to derive hypotheses from theories is to focus on some component of the theory that has not yet been directly observed. For example, a researcher could focus on the process of habituation—perhaps hypothesizing that people should show fewer signs of emotional distress with each new writing session.
Among the very best hypotheses are those that distinguish between competing theories. For example, Norbert Schwarz and his colleagues considered two theories of how people make judgments about themselves, such as how assertive they are (Schwarz et al., 1991) [2] . Both theories held that such judgments are based on relevant examples that people bring to mind. However, one theory was that people base their judgments on the number of examples they bring to mind and the other was that people base their judgments on how easily they bring those examples to mind. To test these theories, the researchers asked people to recall either six times when they were assertive (which is easy for most people) or 12 times (which is difficult for most people). Then they asked them to judge their own assertiveness. Note that the number-of-examples theory implies that people who recalled 12 examples should judge themselves to be more assertive because they recalled more examples, but the ease-of-examples theory implies that participants who recalled six examples should judge themselves as more assertive because recalling the examples was easier. Thus the two theories made opposite predictions so that only one of the predictions could be confirmed. The surprising result was that participants who recalled fewer examples judged themselves to be more assertive—providing particularly convincing evidence in favor of the ease-of-retrieval theory over the number-of-examples theory.
Theory Testing
The primary way that scientific researchers use theories is sometimes called the hypothetico-deductive method (although this term is much more likely to be used by philosophers of science than by scientists themselves). Researchers begin with a set of phenomena and either construct a theory to explain or interpret them or choose an existing theory to work with. They then make a prediction about some new phenomenon that should be observed if the theory is correct. Again, this prediction is called a hypothesis. The researchers then conduct an empirical study to test the hypothesis. Finally, they reevaluate the theory in light of the new results and revise it if necessary. This process is usually conceptualized as a cycle because the researchers can then derive a new hypothesis from the revised theory, conduct a new empirical study to test the hypothesis, and so on. As Figure 2.3 shows, this approach meshes nicely with the model of scientific research in psychology presented earlier in the textbook—creating a more detailed model of “theoretically motivated” or “theory-driven” research.
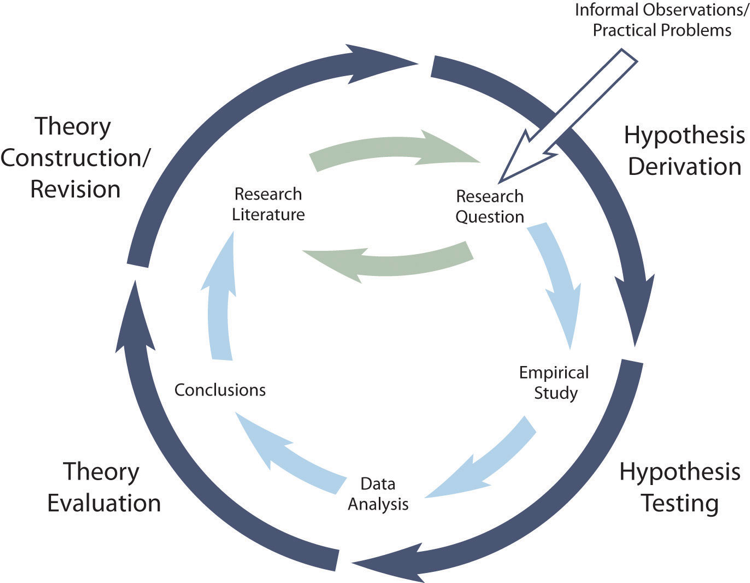
As an example, let us consider Zajonc’s research on social facilitation and inhibition. He started with a somewhat contradictory pattern of results from the research literature. He then constructed his drive theory, according to which being watched by others while performing a task causes physiological arousal, which increases an organism’s tendency to make the dominant response. This theory predicts social facilitation for well-learned tasks and social inhibition for poorly learned tasks. He now had a theory that organized previous results in a meaningful way—but he still needed to test it. He hypothesized that if his theory was correct, he should observe that the presence of others improves performance in a simple laboratory task but inhibits performance in a difficult version of the very same laboratory task. To test this hypothesis, one of the studies he conducted used cockroaches as subjects (Zajonc, Heingartner, & Herman, 1969) [3] . The cockroaches ran either down a straight runway (an easy task for a cockroach) or through a cross-shaped maze (a difficult task for a cockroach) to escape into a dark chamber when a light was shined on them. They did this either while alone or in the presence of other cockroaches in clear plastic “audience boxes.” Zajonc found that cockroaches in the straight runway reached their goal more quickly in the presence of other cockroaches, but cockroaches in the cross-shaped maze reached their goal more slowly when they were in the presence of other cockroaches. Thus he confirmed his hypothesis and provided support for his drive theory. (Zajonc also showed that drive theory existed in humans [Zajonc & Sales, 1966] [4] in many other studies afterward).
Incorporating Theory into Your Research
When you write your research report or plan your presentation, be aware that there are two basic ways that researchers usually include theory. The first is to raise a research question, answer that question by conducting a new study, and then offer one or more theories (usually more) to explain or interpret the results. This format works well for applied research questions and for research questions that existing theories do not address. The second way is to describe one or more existing theories, derive a hypothesis from one of those theories, test the hypothesis in a new study, and finally reevaluate the theory. This format works well when there is an existing theory that addresses the research question—especially if the resulting hypothesis is surprising or conflicts with a hypothesis derived from a different theory.
To use theories in your research will not only give you guidance in coming up with experiment ideas and possible projects, but it lends legitimacy to your work. Psychologists have been interested in a variety of human behaviors and have developed many theories along the way. Using established theories will help you break new ground as a researcher, not limit you from developing your own ideas.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable . We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you’ll recall Popper’s falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false. Second, a good hypothesis must be logical. As described above, hypotheses are more than just a random guess. Hypotheses should be informed by previous theories or observations and logical reasoning. Typically, we begin with a broad and general theory and use deductive reasoning to generate a more specific hypothesis to test based on that theory. Occasionally, however, when there is no theory to inform our hypothesis, we use inductive reasoning which involves using specific observations or research findings to form a more general hypothesis. Finally, the hypothesis should be positive. That is, the hypothesis should make a positive statement about the existence of a relationship or effect, rather than a statement that a relationship or effect does not exist. As scientists, we don’t set out to show that relationships do not exist or that effects do not occur so our hypotheses should not be worded in a way to suggest that an effect or relationship does not exist. The nature of science is to assume that something does not exist and then seek to find evidence to prove this wrong, to show that it really does exist. That may seem backward to you but that is the nature of the scientific method. The underlying reason for this is beyond the scope of this chapter but it has to do with statistical theory.
- Zajonc, R. B. (1965). Social facilitation. Science, 149 , 269–274 ↵
- Schwarz, N., Bless, H., Strack, F., Klumpp, G., Rittenauer-Schatka, H., & Simons, A. (1991). Ease of retrieval as information: Another look at the availability heuristic. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61 , 195–202. ↵
- Zajonc, R. B., Heingartner, A., & Herman, E. M. (1969). Social enhancement and impairment of performance in the cockroach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 13 , 83–92. ↵
- Zajonc, R.B. & Sales, S.M. (1966). Social facilitation of dominant and subordinate responses. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 2 , 160-168. ↵
A coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena.
A specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate.
A cyclical process of theory development, starting with an observed phenomenon, then developing or using a theory to make a specific prediction of what should happen if that theory is correct, testing that prediction, refining the theory in light of the findings, and using that refined theory to develop new hypotheses, and so on.
The ability to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and the possibility to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false.
Developing a Hypothesis Copyright © 2022 by Rajiv S. Jhangiani; I-Chant A. Chiang; Carrie Cuttler; and Dana C. Leighton is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

What is Hypothesis? Definition, Meaning, Characteristics, Sources
- Post last modified: 10 January 2022
- Reading time: 18 mins read
- Post category: Research Methodology

What is Hypothesis?
Hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a study. Hypotheses are drawn from theories and research questions or from direct observations. In fact, a research problem can be formulated as a hypothesis. To test the hypothesis we need to formulate it in terms that can actually be analysed with statistical tools.
As an example, if we want to explore whether using a specific teaching method at school will result in better school marks (research question), the hypothesis could be that the mean school marks of students being taught with that specific teaching method will be higher than of those being taught using other methods.
In this example, we stated a hypothesis about the expected differences between groups. Other hypotheses may refer to correlations between variables.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Hypothesis?
- 2 Hypothesis Definition
- 3 Meaning of Hypothesis
- 4.1 Conceptual Clarity
- 4.2 Need of empirical referents
- 4.3 Hypothesis should be specific
- 4.4 Hypothesis should be within the ambit of the available research techniques
- 4.5 Hypothesis should be consistent with the theory
- 4.6 Hypothesis should be concerned with observable facts and empirical events
- 4.7 Hypothesis should be simple
- 5.1 Observation
- 5.2 Analogies
- 5.4 State of Knowledge
- 5.5 Culture
- 5.6 Continuity of Research
- 6.1 Null Hypothesis
- 6.2 Alternative Hypothesis
Thus, to formulate a hypothesis, we need to refer to the descriptive statistics (such as the mean final marks), and specify a set of conditions about these statistics (such as a difference between the means, or in a different example, a positive or negative correlation). The hypothesis we formulate applies to the population of interest.
The null hypothesis makes a statement that no difference exists (see Pyrczak, 1995, pp. 75-84).
Hypothesis Definition
A hypothesis is ‘a guess or supposition as to the existence of some fact or law which will serve to explain a connection of facts already known to exist.’ – J. E. Creighton & H. R. Smart
Hypothesis is ‘a proposition not known to be definitely true or false, examined for the sake of determining the consequences which would follow from its truth.’ – Max Black
Hypothesis is ‘a proposition which can be put to a test to determine validity and is useful for further research.’ – W. J. Goode and P. K. Hatt
A hypothesis is a proposition, condition or principle which is assumed, perhaps without belief, in order to draw out its logical consequences and by this method to test its accord with facts which are known or may be determined. – Webster’s New International Dictionary of the English Language (1956)
Meaning of Hypothesis
From the above mentioned definitions of hypothesis, its meaning can be explained in the following ways.
- At the primary level, a hypothesis is the possible and probable explanation of the sequence of happenings or data.
- Sometimes, hypothesis may emerge from an imagination, common sense or a sudden event.
- Hypothesis can be a probable answer to the research problem undertaken for study. 4. Hypothesis may not always be true. It can get disproven. In other words, hypothesis need not always be a true proposition.
- Hypothesis, in a sense, is an attempt to present the interrelations that exist in the available data or information.
- Hypothesis is not an individual opinion or community thought. Instead, it is a philosophical means which is to be used for research purpose. Hypothesis is not to be considered as the ultimate objective; rather it is to be taken as the means of explaining scientifically the prevailing situation.
The concept of hypothesis can further be explained with the help of some examples. Lord Keynes, in his theory of national income determination, made a hypothesis about the consumption function. He stated that the consumption expenditure of an individual or an economy as a whole is dependent on the level of income and changes in a certain proportion.
Later, this proposition was proved in the statistical research carried out by Prof. Simon Kuznets. Matthus, while studying the population, formulated a hypothesis that population increases faster than the supply of food grains. Population studies of several countries revealed that this hypothesis is true.
Validation of the Malthus’ hypothesis turned it into a theory and when it was tested in many other countries it became the famous Malthus’ Law of Population. It thus emerges that when a hypothesis is tested and proven, it becomes a theory. The theory, when found true in different times and at different places, becomes the law. Having understood the concept of hypothesis, few hypotheses can be formulated in the areas of commerce and economics.
- Population growth moderates with the rise in per capita income.
- Sales growth is positively linked with the availability of credit.
- Commerce education increases the employability of the graduate students.
- High rates of direct taxes prompt people to evade taxes.
- Good working conditions improve the productivity of employees.
- Advertising is the most effecting way of promoting sales than any other scheme.
- Higher Debt-Equity Ratio increases the probability of insolvency.
- Economic reforms in India have made the public sector banks more efficient and competent.
- Foreign direct investment in India has moved in those sectors which offer higher rate of profit.
- There is no significant association between credit rating and investment of fund.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Not all the hypotheses are good and useful from the point of view of research. It is only a few hypotheses satisfying certain criteria that are good, useful and directive in the research work undertaken. The characteristics of such a useful hypothesis can be listed as below:
Conceptual Clarity
Need of empirical referents, hypothesis should be specific, hypothesis should be within the ambit of the available research techniques, hypothesis should be consistent with the theory, hypothesis should be concerned with observable facts and empirical events, hypothesis should be simple.
The concepts used while framing hypothesis should be crystal clear and unambiguous. Such concepts must be clearly defined so that they become lucid and acceptable to everyone. How are the newly developed concepts interrelated and how are they linked with the old one is to be very clear so that the hypothesis framed on their basis also carries the same clarity.
A hypothesis embodying unclear and ambiguous concepts can to a great extent undermine the successful completion of the research work.
A hypothesis can be useful in the research work undertaken only when it has links with some empirical referents. Hypothesis based on moral values and ideals are useless as they cannot be tested. Similarly, hypothesis containing opinions as good and bad or expectation with respect to something are not testable and therefore useless.
For example, ‘current account deficit can be lowered if people change their attitude towards gold’ is a hypothesis encompassing expectation. In case of such a hypothesis, the attitude towards gold is something which cannot clearly be described and therefore a hypothesis which embodies such an unclean thing cannot be tested and proved or disproved. In short, the hypothesis should be linked with some testable referents.
For the successful conduction of research, it is necessary that the hypothesis is specific and presented in a precise manner. Hypothesis which is general, too ambitious and grandiose in scope is not to be made as such hypothesis cannot be easily put to test. A hypothesis is to be based on such concepts which are precise and empirical in nature. A hypothesis should give a clear idea about the indicators which are to be used.
For example, a hypothesis that economic power is increasingly getting concentrated in a few hands in India should enable us to define the concept of economic power. It should be explicated in terms of measurable indicator like income, wealth, etc. Such specificity in the formulation of a hypothesis ensures that the research is practicable and significant.
While framing the hypothesis, the researcher should be aware of the available research techniques and should see that the hypothesis framed is testable on the basis of them. In other words, a hypothesis should be researchable and for this it is important that a due thought has been given to the methods and techniques which can be used to measure the concepts and variables embodied in the hypothesis.
It does not however mean that hypotheses which are not testable with the available techniques of research are not to be made. If the problem is too significant and therefore the hypothesis framed becomes too ambitious and complex, it’s testing becomes possible with the development of new research techniques or the hypothesis itself leads to the development of new research techniques.
A hypothesis must be related to the existing theory or should have a theoretical orientation. The growth of knowledge takes place in the sequence of facts, hypothesis, theory and law or principles. It means the hypothesis should have a correspondence with the existing facts and theory.
If the hypothesis is related to some theory, the research work will enable us to support, modify or refute the existing theory. Theoretical orientation of the hypothesis ensures that it becomes scientifically useful. According to Prof. Goode and Prof. Hatt, research work can contribute to the existing knowledge only when the hypothesis is related with some theory.
This enables us to explain the observed facts and situations and also verify the framed hypothesis. In the words of Prof. Cohen and Prof. Nagel, “hypothesis must be formulated in such a manner that deduction can be made from it and that consequently a decision can be reached as to whether it does or does not explain the facts considered.”
If the research work based on a hypothesis is to be successful, it is necessary that the later is as simple and easy as possible. An ambition of finding out something new may lead the researcher to frame an unrealistic and unclear hypothesis. Such a temptation is to be avoided. Framing a simple, easy and testable hypothesis requires that the researcher is well acquainted with the related concepts.
Sources of Hypothesis
Hypotheses can be derived from various sources. Some of the sources is given below:
Observation
State of knowledge, continuity of research.
Hypotheses can be derived from observation from the observation of price behavior in a market. For example the relationship between the price and demand for an article is hypothesized.
Analogies are another source of useful hypotheses. Julian Huxley has pointed out that casual observations in nature or in the framework of another science may be a fertile source of hypotheses. For example, the hypotheses that similar human types or activities may be found in similar geophysical regions come from plant ecology.
This is one of the main sources of hypotheses. It gives direction to research by stating what is known logical deduction from theory lead to new hypotheses. For example, profit / wealth maximization is considered as the goal of private enterprises. From this assumption various hypotheses are derived’.
An important source of hypotheses is the state of knowledge in any particular science where formal theories exist hypotheses can be deduced. If the hypotheses are rejected theories are scarce hypotheses are generated from conception frameworks.
Another source of hypotheses is the culture on which the researcher was nurtured. Western culture has induced the emergence of sociology as an academic discipline over the past decade, a large part of the hypotheses on American society examined by researchers were connected with violence. This interest is related to the considerable increase in the level of violence in America.
The continuity of research in a field itself constitutes an important source of hypotheses. The rejection of some hypotheses leads to the formulation of new ones capable of explaining dependent variables in subsequent research on the same subject.
Null and Alternative Hypothesis
Null hypothesis.
The hypothesis that are proposed with the intent of receiving a rejection for them are called Null Hypothesis . This requires that we hypothesize the opposite of what is desired to be proved. For example, if we want to show that sales and advertisement expenditure are related, we formulate the null hypothesis that they are not related.
Similarly, if we want to conclude that the new sales training programme is effective, we formulate the null hypothesis that the new training programme is not effective, and if we want to prove that the average wages of skilled workers in town 1 is greater than that of town 2, we formulate the null hypotheses that there is no difference in the average wages of the skilled workers in both the towns.
Since we hypothesize that sales and advertisement are not related, new training programme is not effective and the average wages of skilled workers in both the towns are equal, we call such hypotheses null hypotheses and denote them as H 0 .
Alternative Hypothesis
Rejection of null hypotheses leads to the acceptance of alternative hypothesis . The rejection of null hypothesis indicates that the relationship between variables (e.g., sales and advertisement expenditure) or the difference between means (e.g., wages of skilled workers in town 1 and town 2) or the difference between proportions have statistical significance and the acceptance of the null hypotheses indicates that these differences are due to chance.
As already mentioned, the alternative hypotheses specify that values/relation which the researcher believes hold true. The alternative hypotheses can cover a whole range of values rather than a single point. The alternative hypotheses are denoted by H 1 .
Business Ethics
( Click on Topic to Read )
- What is Ethics?
- What is Business Ethics?
- Values, Norms, Beliefs and Standards in Business Ethics
- Indian Ethos in Management
- Ethical Issues in Marketing
- Ethical Issues in HRM
- Ethical Issues in IT
- Ethical Issues in Production and Operations Management
- Ethical Issues in Finance and Accounting
- What is Corporate Governance?
- What is Ownership Concentration?
- What is Ownership Composition?
- Types of Companies in India
- Internal Corporate Governance
- External Corporate Governance
- Corporate Governance in India
- What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
- What is Assessment of Risk?
- What is Risk Register?
- Risk Management Committee
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
- Theories of CSR
- Arguments Against CSR
- Business Case for CSR
- Importance of CSR in India
- Drivers of Corporate Social Responsibility
- Developing a CSR Strategy
- Implement CSR Commitments
- CSR Marketplace
- CSR at Workplace
- Environmental CSR
- CSR with Communities and in Supply Chain
- Community Interventions
- CSR Monitoring
- CSR Reporting
- Voluntary Codes in CSR
- What is Corporate Ethics?
Lean Six Sigma
- What is Six Sigma?
- What is Lean Six Sigma?
- Value and Waste in Lean Six Sigma
- Six Sigma Team
- MAIC Six Sigma
- Six Sigma in Supply Chains
- What is Binomial, Poisson, Normal Distribution?
- What is Sigma Level?
- What is DMAIC in Six Sigma?
- What is DMADV in Six Sigma?
- Six Sigma Project Charter
- Project Decomposition in Six Sigma
- Critical to Quality (CTQ) Six Sigma
- Process Mapping Six Sigma
- Flowchart and SIPOC
- Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility
- Statistical Diagram
- Lean Techniques for Optimisation Flow
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- What is Process Audits?
- Six Sigma Implementation at Ford
- IBM Uses Six Sigma to Drive Behaviour Change
- Research Methodology
- What is Research?
- Sampling Method
Research Methods
- Data Collection in Research
- Methods of Collecting Data
- Application of Business Research
- Levels of Measurement
- What is Sampling?
- Hypothesis Testing
Research Report
- What is Management?
- Planning in Management
- Decision Making in Management
- What is Controlling?
- What is Coordination?
- What is Staffing?
- Organization Structure
- What is Departmentation?
- Span of Control
- What is Authority?
- Centralization vs Decentralization
- Organizing in Management
- Schools of Management Thought
- Classical Management Approach
- Is Management an Art or Science?
- Who is a Manager?
Operations Research
- What is Operations Research?
- Operation Research Models
- Linear Programming
- Linear Programming Graphic Solution
- Linear Programming Simplex Method
- Linear Programming Artificial Variable Technique
- Duality in Linear Programming
- Transportation Problem Initial Basic Feasible Solution
- Transportation Problem Finding Optimal Solution
- Project Network Analysis with Critical Path Method
- Project Network Analysis Methods
- Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
- Simulation in Operation Research
- Replacement Models in Operation Research
Operation Management
- What is Strategy?
- What is Operations Strategy?
- Operations Competitive Dimensions
- Operations Strategy Formulation Process
- What is Strategic Fit?
- Strategic Design Process
- Focused Operations Strategy
- Corporate Level Strategy
- Expansion Strategies
- Stability Strategies
- Retrenchment Strategies
- Competitive Advantage
- Strategic Choice and Strategic Alternatives
- What is Production Process?
- What is Process Technology?
- What is Process Improvement?
- Strategic Capacity Management
- Production and Logistics Strategy
- Taxonomy of Supply Chain Strategies
- Factors Considered in Supply Chain Planning
- Operational and Strategic Issues in Global Logistics
- Logistics Outsourcing Strategy
- What is Supply Chain Mapping?
- Supply Chain Process Restructuring
- Points of Differentiation
- Re-engineering Improvement in SCM
- What is Supply Chain Drivers?
- Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) Model
- Customer Service and Cost Trade Off
- Internal and External Performance Measures
- Linking Supply Chain and Business Performance
- Netflix’s Niche Focused Strategy
- Disney and Pixar Merger
- Process Planning at Mcdonald’s
Service Operations Management
- What is Service?
- What is Service Operations Management?
- What is Service Design?
- Service Design Process
- Service Delivery
- What is Service Quality?
- Gap Model of Service Quality
- Juran Trilogy
- Service Performance Measurement
- Service Decoupling
- IT Service Operation
- Service Operations Management in Different Sector
Procurement Management
- What is Procurement Management?
- Procurement Negotiation
- Types of Requisition
- RFX in Procurement
- What is Purchasing Cycle?
- Vendor Managed Inventory
- Internal Conflict During Purchasing Operation
- Spend Analysis in Procurement
- Sourcing in Procurement
- Supplier Evaluation and Selection in Procurement
- Blacklisting of Suppliers in Procurement
- Total Cost of Ownership in Procurement
- Incoterms in Procurement
- Documents Used in International Procurement
- Transportation and Logistics Strategy
- What is Capital Equipment?
- Procurement Process of Capital Equipment
- Acquisition of Technology in Procurement
- What is E-Procurement?
- E-marketplace and Online Catalogues
- Fixed Price and Cost Reimbursement Contracts
- Contract Cancellation in Procurement
- Ethics in Procurement
- Legal Aspects of Procurement
- Global Sourcing in Procurement
- Intermediaries and Countertrade in Procurement
Strategic Management
- What is Strategic Management?
- What is Value Chain Analysis?
- Mission Statement
- Business Level Strategy
- What is SWOT Analysis?
- What is Competitive Advantage?
- What is Vision?
- What is Ansoff Matrix?
- Prahalad and Gary Hammel
- Strategic Management In Global Environment
- Competitor Analysis Framework
- Competitive Rivalry Analysis
- Competitive Dynamics
- What is Competitive Rivalry?
- Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy
- What is PESTLE Analysis?
- Fragmentation and Consolidation Of Industries
- What is Technology Life Cycle?
- What is Diversification Strategy?
- What is Corporate Restructuring Strategy?
- Resources and Capabilities of Organization
- Role of Leaders In Functional-Level Strategic Management
- Functional Structure In Functional Level Strategy Formulation
- Information And Control System
- What is Strategy Gap Analysis?
- Issues In Strategy Implementation
- Matrix Organizational Structure
- What is Strategic Management Process?
Supply Chain
- What is Supply Chain Management?
- Supply Chain Planning and Measuring Strategy Performance
- What is Warehousing?
- What is Packaging?
- What is Inventory Management?
- What is Material Handling?
- What is Order Picking?
- Receiving and Dispatch, Processes
- What is Warehouse Design?
- What is Warehousing Costs?
You Might Also Like
What is research types, purpose, characteristics, process, types of hypotheses, what is causal research advantages, disadvantages, how to perform, what is scaling techniques types, classifications, techniques, what is research design features, components, what is sample size determination, formula, determining,, steps in questionnaire design, data processing in research, primary data and secondary data, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
World's Best Online Courses at One Place
We’ve spent the time in finding, so you can spend your time in learning
Digital Marketing
Personal growth.

Development
Theories, Hypotheses, and Laws: Definitions, examples, and their roles in science
by Anthony Carpi, Ph.D., Anne E. Egger, Ph.D.
Listen to this reading
Did you know that the idea of evolution had been part of Western thought for more than 2,000 years before Charles Darwin was born? Like many theories, the theory of evolution was the result of the work of many different scientists working in different disciplines over a period of time.
A scientific theory is an explanation inferred from multiple lines of evidence for some broad aspect of the natural world and is logical, testable, and predictive.
As new evidence comes to light, or new interpretations of existing data are proposed, theories may be revised and even change; however, they are not tenuous or speculative.
A scientific hypothesis is an inferred explanation of an observation or research finding; while more exploratory in nature than a theory, it is based on existing scientific knowledge.
A scientific law is an expression of a mathematical or descriptive relationship observed in nature.
Imagine yourself shopping in a grocery store with a good friend who happens to be a chemist. Struggling to choose between the many different types of tomatoes in front of you, you pick one up, turn to your friend, and ask her if she thinks the tomato is organic . Your friend simply chuckles and replies, "Of course it's organic!" without even looking at how the fruit was grown. Why the amused reaction? Your friend is highlighting a simple difference in vocabulary. To a chemist, the term organic refers to any compound in which hydrogen is bonded to carbon. Tomatoes (like all plants) are abundant in organic compounds – thus your friend's laughter. In modern agriculture, however, organic has come to mean food items grown or raised without the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, or other additives.
So who is correct? You both are. Both uses of the word are correct, though they mean different things in different contexts. There are, of course, lots of words that have more than one meaning (like bat , for example), but multiple meanings can be especially confusing when two meanings convey very different ideas and are specific to one field of study.
- Scientific theories
The term theory also has two meanings, and this double meaning often leads to confusion. In common language, the term theory generally refers to speculation or a hunch or guess. You might have a theory about why your favorite sports team isn't playing well, or who ate the last cookie from the cookie jar. But these theories do not fit the scientific use of the term. In science, a theory is a well-substantiated and comprehensive set of ideas that explains a phenomenon in nature. A scientific theory is based on large amounts of data and observations that have been collected over time. Scientific theories can be tested and refined by additional research , and they allow scientists to make predictions. Though you may be correct in your hunch, your cookie jar conjecture doesn't fit this more rigorous definition.
All scientific disciplines have well-established, fundamental theories . For example, atomic theory describes the nature of matter and is supported by multiple lines of evidence from the way substances behave and react in the world around us (see our series on Atomic Theory ). Plate tectonic theory describes the large scale movement of the outer layer of the Earth and is supported by evidence from studies about earthquakes , magnetic properties of the rocks that make up the seafloor , and the distribution of volcanoes on Earth (see our series on Plate Tectonic Theory ). The theory of evolution by natural selection , which describes the mechanism by which inherited traits that affect survivability or reproductive success can cause changes in living organisms over generations , is supported by extensive studies of DNA , fossils , and other types of scientific evidence (see our Charles Darwin series for more information). Each of these major theories guides and informs modern research in those fields, integrating a broad, comprehensive set of ideas.
So how are these fundamental theories developed, and why are they considered so well supported? Let's take a closer look at some of the data and research supporting the theory of natural selection to better see how a theory develops.
Comprehension Checkpoint
- The development of a scientific theory: Evolution and natural selection
The theory of evolution by natural selection is sometimes maligned as Charles Darwin 's speculation on the origin of modern life forms. However, evolutionary theory is not speculation. While Darwin is rightly credited with first articulating the theory of natural selection, his ideas built on more than a century of scientific research that came before him, and are supported by over a century and a half of research since.
- The Fixity Notion: Linnaeus

Figure 1: Cover of the 1760 edition of Systema Naturae .
Research about the origins and diversity of life proliferated in the 18th and 19th centuries. Carolus Linnaeus , a Swedish botanist and the father of modern taxonomy (see our module Taxonomy I for more information), was a devout Christian who believed in the concept of Fixity of Species , an idea based on the biblical story of creation. The Fixity of Species concept said that each species is based on an ideal form that has not changed over time. In the early stages of his career, Linnaeus traveled extensively and collected data on the structural similarities and differences between different species of plants. Noting that some very different plants had similar structures, he began to piece together his landmark work, Systema Naturae, in 1735 (Figure 1). In Systema , Linnaeus classified organisms into related groups based on similarities in their physical features. He developed a hierarchical classification system , even drawing relationships between seemingly disparate species (for example, humans, orangutans, and chimpanzees) based on the physical similarities that he observed between these organisms. Linnaeus did not explicitly discuss change in organisms or propose a reason for his hierarchy, but by grouping organisms based on physical characteristics, he suggested that species are related, unintentionally challenging the Fixity notion that each species is created in a unique, ideal form.
- The age of Earth: Leclerc and Hutton
Also in the early 1700s, Georges-Louis Leclerc, a French naturalist, and James Hutton , a Scottish geologist, began to develop new ideas about the age of the Earth. At the time, many people thought of the Earth as 6,000 years old, based on a strict interpretation of the events detailed in the Christian Old Testament by the influential Scottish Archbishop Ussher. By observing other planets and comets in the solar system , Leclerc hypothesized that Earth began as a hot, fiery ball of molten rock, mostly consisting of iron. Using the cooling rate of iron, Leclerc calculated that Earth must therefore be at least 70,000 years old in order to have reached its present temperature.
Hutton approached the same topic from a different perspective, gathering observations of the relationships between different rock formations and the rates of modern geological processes near his home in Scotland. He recognized that the relatively slow processes of erosion and sedimentation could not create all of the exposed rock layers in only a few thousand years (see our module The Rock Cycle ). Based on his extensive collection of data (just one of his many publications ran to 2,138 pages), Hutton suggested that the Earth was far older than human history – hundreds of millions of years old.
While we now know that both Leclerc and Hutton significantly underestimated the age of the Earth (by about 4 billion years), their work shattered long-held beliefs and opened a window into research on how life can change over these very long timescales.
- Fossil studies lead to the development of a theory of evolution: Cuvier
Figure 2: Illustration of an Indian elephant jaw and a mammoth jaw from Cuvier's 1796 paper.
With the age of Earth now extended by Leclerc and Hutton, more researchers began to turn their attention to studying past life. Fossils are the main way to study past life forms, and several key studies on fossils helped in the development of a theory of evolution . In 1795, Georges Cuvier began to work at the National Museum in Paris as a naturalist and anatomist. Through his work, Cuvier became interested in fossils found near Paris, which some claimed were the remains of the elephants that Hannibal rode over the Alps when he invaded Rome in 218 BCE . In studying both the fossils and living species , Cuvier documented different patterns in the dental structure and number of teeth between the fossils and modern elephants (Figure 2) (Horner, 1843). Based on these data , Cuvier hypothesized that the fossil remains were not left by Hannibal, but were from a distinct species of animal that once roamed through Europe and had gone extinct thousands of years earlier: the mammoth. The concept of species extinction had been discussed by a few individuals before Cuvier, but it was in direct opposition to the Fixity of Species concept – if every organism were based on a perfectly adapted, ideal form, how could any cease to exist? That would suggest it was no longer ideal.
While his work provided critical evidence of extinction , a key component of evolution , Cuvier was highly critical of the idea that species could change over time. As a result of his extensive studies of animal anatomy, Cuvier had developed a holistic view of organisms , stating that the
number, direction, and shape of the bones that compose each part of an animal's body are always in a necessary relation to all the other parts, in such a way that ... one can infer the whole from any one of them ...
In other words, Cuvier viewed each part of an organism as a unique, essential component of the whole organism. If one part were to change, he believed, the organism could not survive. His skepticism about the ability of organisms to change led him to criticize the whole idea of evolution , and his prominence in France as a scientist played a large role in discouraging the acceptance of the idea in the scientific community.
- Studies of invertebrates support a theory of change in species: Lamarck
Jean Baptiste Lamarck, a contemporary of Cuvier's at the National Museum in Paris, studied invertebrates like insects and worms. As Lamarck worked through the museum's large collection of invertebrates, he was impressed by the number and variety of organisms . He became convinced that organisms could, in fact, change through time, stating that
... time and favorable conditions are the two principal means which nature has employed in giving existence to all her productions. We know that for her time has no limit, and that consequently she always has it at her disposal.
This was a radical departure from both the fixity concept and Cuvier's ideas, and it built on the long timescale that geologists had recently established. Lamarck proposed that changes that occurred during an organism 's lifetime could be passed on to their offspring, suggesting, for example, that a body builder's muscles would be inherited by their children.
As it turned out, the mechanism by which Lamarck proposed that organisms change over time was wrong, and he is now often referred to disparagingly for his "inheritance of acquired characteristics" idea. Yet despite the fact that some of his ideas were discredited, Lamarck established a support for evolutionary theory that others would build on and improve.
- Rock layers as evidence for evolution: Smith
In the early 1800s, a British geologist and canal surveyor named William Smith added another component to the accumulating evidence for evolution . Smith observed that rock layers exposed in different parts of England bore similarities to one another: These layers (or strata) were arranged in a predictable order, and each layer contained distinct groups of fossils . From this series of observations , he developed a hypothesis that specific groups of animals followed one another in a definite sequence through Earth's history, and this sequence could be seen in the rock layers. Smith's hypothesis was based on his knowledge of geological principles , including the Law of Superposition.
The Law of Superposition states that sediments are deposited in a time sequence, with the oldest sediments deposited first, or at the bottom, and newer layers deposited on top. The concept was first expressed by the Persian scientist Avicenna in the 11th century, but was popularized by the Danish scientist Nicolas Steno in the 17th century. Note that the law does not state how sediments are deposited; it simply describes the relationship between the ages of deposited sediments.

Figure 3: Engraving from William Smith's 1815 monograph on identifying strata by fossils.
Smith backed up his hypothesis with extensive drawings of fossils uncovered during his research (Figure 3), thus allowing other scientists to confirm or dispute his findings. His hypothesis has, in fact, been confirmed by many other scientists and has come to be referred to as the Law of Faunal Succession. His work was critical to the formation of evolutionary theory as it not only confirmed Cuvier's work that organisms have gone extinct , but it also showed that the appearance of life does not date to the birth of the planet. Instead, the fossil record preserves a timeline of the appearance and disappearance of different organisms in the past, and in doing so offers evidence for change in organisms over time.
- The theory of evolution by natural selection: Darwin and Wallace
It was into this world that Charles Darwin entered: Linnaeus had developed a taxonomy of organisms based on their physical relationships, Leclerc and Hutton demonstrated that there was sufficient time in Earth's history for organisms to change, Cuvier showed that species of organisms have gone extinct , Lamarck proposed that organisms change over time, and Smith established a timeline of the appearance and disappearance of different organisms in the geological record .

Figure 4: Title page of the 1859 Murray edition of the Origin of Species by Charles Darwin.
Charles Darwin collected data during his work as a naturalist on the HMS Beagle starting in 1831. He took extensive notes on the geology of the places he visited; he made a major find of fossils of extinct animals in Patagonia and identified an extinct giant ground sloth named Megatherium . He experienced an earthquake in Chile that stranded beds of living mussels above water, where they would be preserved for years to come.
Perhaps most famously, he conducted extensive studies of animals on the Galápagos Islands, noting subtle differences in species of mockingbird, tortoise, and finch that were isolated on different islands with different environmental conditions. These subtle differences made the animals highly adapted to their environments .
This broad spectrum of data led Darwin to propose an idea about how organisms change "by means of natural selection" (Figure 4). But this idea was not based only on his work, it was also based on the accumulation of evidence and ideas of many others before him. Because his proposal encompassed and explained many different lines of evidence and previous work, they formed the basis of a new and robust scientific theory regarding change in organisms – the theory of evolution by natural selection .
Darwin's ideas were grounded in evidence and data so compelling that if he had not conceived them, someone else would have. In fact, someone else did. Between 1858 and 1859, Alfred Russel Wallace , a British naturalist, wrote a series of letters to Darwin that independently proposed natural selection as the means for evolutionary change. The letters were presented to the Linnean Society of London, a prominent scientific society at the time (see our module on Scientific Institutions and Societies ). This long chain of research highlights that theories are not just the work of one individual. At the same time, however, it often takes the insight and creativity of individuals to put together all of the pieces and propose a new theory . Both Darwin and Wallace were experienced naturalists who were familiar with the work of others. While all of the work leading up to 1830 contributed to the theory of evolution , Darwin's and Wallace's theory changed the way that future research was focused by presenting a comprehensive, well-substantiated set of ideas, thus becoming a fundamental theory of biological research.
- Expanding, testing, and refining scientific theories
- Genetics and evolution: Mendel and Dobzhansky
Since Darwin and Wallace first published their ideas, extensive research has tested and expanded the theory of evolution by natural selection . Darwin had no concept of genes or DNA or the mechanism by which characteristics were inherited within a species . A contemporary of Darwin's, the Austrian monk Gregor Mendel , first presented his own landmark study, Experiments in Plant Hybridization, in 1865 in which he provided the basic patterns of genetic inheritance , describing which characteristics (and evolutionary changes) can be passed on in organisms (see our Genetics I module for more information). Still, it wasn't until much later that a "gene" was defined as the heritable unit.
In 1937, the Ukrainian born geneticist Theodosius Dobzhansky published Genetics and the Origin of Species , a seminal work in which he described genes themselves and demonstrated that it is through mutations in genes that change occurs. The work defined evolution as "a change in the frequency of an allele within a gene pool" ( Dobzhansky, 1982 ). These studies and others in the field of genetics have added to Darwin's work, expanding the scope of the theory .
- Evolution under a microscope: Lenski
More recently, Dr. Richard Lenski, a scientist at Michigan State University, isolated a single Escherichia coli bacterium in 1989 as the first step of the longest running experimental test of evolutionary theory to date – a true test meant to replicate evolution and natural selection in the lab.
After the single microbe had multiplied, Lenski isolated the offspring into 12 different strains , each in their own glucose-supplied culture, predicting that the genetic make-up of each strain would change over time to become more adapted to their specific culture as predicted by evolutionary theory . These 12 lines have been nurtured for over 40,000 bacterial generations (luckily bacterial generations are much shorter than human generations) and exposed to different selective pressures such as heat , cold, antibiotics, and infection with other microorganisms. Lenski and colleagues have studied dozens of aspects of evolutionary theory with these genetically isolated populations . In 1999, they published a paper that demonstrated that random genetic mutations were common within the populations and highly diverse across different individual bacteria . However, "pivotal" mutations that are associated with beneficial changes in the group are shared by all descendants in a population and are much rarer than random mutations, as predicted by the theory of evolution by natural selection (Papadopoulos et al., 1999).
- Punctuated equilibrium: Gould and Eldredge
While established scientific theories like evolution have a wealth of research and evidence supporting them, this does not mean that they cannot be refined as new information or new perspectives on existing data become available. For example, in 1972, biologist Stephen Jay Gould and paleontologist Niles Eldredge took a fresh look at the existing data regarding the timing by which evolutionary change takes place. Gould and Eldredge did not set out to challenge the theory of evolution; rather they used it as a guiding principle and asked more specific questions to add detail and nuance to the theory. This is true of all theories in science: they provide a framework for additional research. At the time, many biologists viewed evolution as occurring gradually, causing small incremental changes in organisms at a relatively steady rate. The idea is referred to as phyletic gradualism , and is rooted in the geological concept of uniformitarianism . After reexamining the available data, Gould and Eldredge came to a different explanation, suggesting that evolution consists of long periods of stability that are punctuated by occasional instances of dramatic change – a process they called punctuated equilibrium .
Like Darwin before them, their proposal is rooted in evidence and research on evolutionary change, and has been supported by multiple lines of evidence. In fact, punctuated equilibrium is now considered its own theory in evolutionary biology. Punctuated equilibrium is not as broad of a theory as natural selection . In science, some theories are broad and overarching of many concepts, such as the theory of evolution by natural selection; others focus on concepts at a smaller, or more targeted, scale such as punctuated equilibrium. And punctuated equilibrium does not challenge or weaken the concept of natural selection; rather, it represents a change in our understanding of the timing by which change occurs in organisms , and a theory within a theory. The theory of evolution by natural selection now includes both gradualism and punctuated equilibrium to describe the rate at which change proceeds.
- Hypotheses and laws: Other scientific concepts
One of the challenges in understanding scientific terms like theory is that there is not a precise definition even within the scientific community. Some scientists debate over whether certain proposals merit designation as a hypothesis or theory , and others mistakenly use the terms interchangeably. But there are differences in these terms. A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for an observable phenomenon. Hypotheses , just like theories , are based on observations from research . For example, LeClerc did not hypothesize that Earth had cooled from a molten ball of iron as a random guess; rather, he developed this hypothesis based on his observations of information from meteorites.
A scientist often proposes a hypothesis before research confirms it as a way of predicting the outcome of study to help better define the parameters of the research. LeClerc's hypothesis allowed him to use known parameters (the cooling rate of iron) to do additional work. A key component of a formal scientific hypothesis is that it is testable and falsifiable. For example, when Richard Lenski first isolated his 12 strains of bacteria , he likely hypothesized that random mutations would cause differences to appear within a period of time in the different strains of bacteria. But when a hypothesis is generated in science, a scientist will also make an alternative hypothesis , an explanation that explains a study if the data do not support the original hypothesis. If the different strains of bacteria in Lenski's work did not diverge over the indicated period of time, perhaps the rate of mutation was slower than first thought.
So you might ask, if theories are so well supported, do they eventually become laws? The answer is no – not because they aren't well-supported, but because theories and laws are two very different things. Laws describe phenomena, often mathematically. Theories, however, explain phenomena. For example, in 1687 Isaac Newton proposed a Theory of Gravitation, describing gravity as a force of attraction between two objects. As part of this theory, Newton developed a Law of Universal Gravitation that explains how this force operates. This law states that the force of gravity between two objects is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between those objects. Newton 's Law does not explain why this is true, but it describes how gravity functions (see our Gravity: Newtonian Relationships module for more detail). In 1916, Albert Einstein developed his theory of general relativity to explain the mechanism by which gravity has its effect. Einstein's work challenges Newton's theory, and has been found after extensive testing and research to more accurately describe the phenomenon of gravity. While Einstein's work has replaced Newton's as the dominant explanation of gravity in modern science, Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation is still used as it reasonably (and more simply) describes the force of gravity under many conditions. Similarly, the Law of Faunal Succession developed by William Smith does not explain why organisms follow each other in distinct, predictable ways in the rock layers, but it accurately describes the phenomenon.
Theories, hypotheses , and laws drive scientific progress
Theories, hypotheses , and laws are not simply important components of science, they drive scientific progress. For example, evolutionary biology now stands as a distinct field of science that focuses on the origins and descent of species . Geologists now rely on plate tectonics as a conceptual model and guiding theory when they are studying processes at work in Earth's crust . And physicists refer to atomic theory when they are predicting the existence of subatomic particles yet to be discovered. This does not mean that science is "finished," or that all of the important theories have been discovered already. Like evolution , progress in science happens both gradually and in short, dramatic bursts. Both types of progress are critical for creating a robust knowledge base with data as the foundation and scientific theories giving structure to that knowledge.
Table of Contents
- Theories, hypotheses, and laws drive scientific progress
Activate glossary term highlighting to easily identify key terms within the module. Once highlighted, you can click on these terms to view their definitions.
Activate NGSS annotations to easily identify NGSS standards within the module. Once highlighted, you can click on them to view these standards.

The Best PhD and Masters Consulting Company

Characteristics Of A Good Hypothesis
What exactly is a hypothesis.
A hypothesis is a conclusion reached after considering the evidence. This is the first step in any investigation, where the research questions are translated into a prediction. Variables, population, and the relationship between the variables are all included. A research hypothesis is a hypothesis that is tested to see if two or more variables have a relationship. Now let’s have a look at the characteristics of a good hypothesis.
Characteristics of
A good hypothesis has the following characteristics.
Ability To Predict
Closest to things that can be seen, testability, relevant to the issue, techniques that are applicable, new discoveries have been made as a result of this ., harmony & consistency.
- The similarity between the two phenomena.
- Observations from previous studies, current experiences, and feedback from rivals.
- Theories based on science.
- People’s thinking processes are influenced by general patterns.
- A straightforward hypothesis
- Complex Hypothesis
- Hypothesis with a certain direction
- Non-direction Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis
- Hypothesis of association and chance
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Scientific Methods
What is Hypothesis?
We have heard of many hypotheses which have led to great inventions in science. Assumptions that are made on the basis of some evidence are known as hypotheses. In this article, let us learn in detail about the hypothesis and the type of hypothesis with examples.
A hypothesis is an assumption that is made based on some evidence. This is the initial point of any investigation that translates the research questions into predictions. It includes components like variables, population and the relation between the variables. A research hypothesis is a hypothesis that is used to test the relationship between two or more variables.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Following are the characteristics of the hypothesis:
- The hypothesis should be clear and precise to consider it to be reliable.
- If the hypothesis is a relational hypothesis, then it should be stating the relationship between variables.
- The hypothesis must be specific and should have scope for conducting more tests.
- The way of explanation of the hypothesis must be very simple and it should also be understood that the simplicity of the hypothesis is not related to its significance.
Sources of Hypothesis
Following are the sources of hypothesis:
- The resemblance between the phenomenon.
- Observations from past studies, present-day experiences and from the competitors.
- Scientific theories.
- General patterns that influence the thinking process of people.
Types of Hypothesis
There are six forms of hypothesis and they are:
- Simple hypothesis
- Complex hypothesis
- Directional hypothesis
- Non-directional hypothesis
- Null hypothesis
- Associative and casual hypothesis
Simple Hypothesis
It shows a relationship between one dependent variable and a single independent variable. For example – If you eat more vegetables, you will lose weight faster. Here, eating more vegetables is an independent variable, while losing weight is the dependent variable.
Complex Hypothesis
It shows the relationship between two or more dependent variables and two or more independent variables. Eating more vegetables and fruits leads to weight loss, glowing skin, and reduces the risk of many diseases such as heart disease.
Directional Hypothesis
It shows how a researcher is intellectual and committed to a particular outcome. The relationship between the variables can also predict its nature. For example- children aged four years eating proper food over a five-year period are having higher IQ levels than children not having a proper meal. This shows the effect and direction of the effect.
Non-directional Hypothesis
It is used when there is no theory involved. It is a statement that a relationship exists between two variables, without predicting the exact nature (direction) of the relationship.
Null Hypothesis
It provides a statement which is contrary to the hypothesis. It’s a negative statement, and there is no relationship between independent and dependent variables. The symbol is denoted by “H O ”.
Associative and Causal Hypothesis
Associative hypothesis occurs when there is a change in one variable resulting in a change in the other variable. Whereas, the causal hypothesis proposes a cause and effect interaction between two or more variables.
Examples of Hypothesis
Following are the examples of hypotheses based on their types:
- Consumption of sugary drinks every day leads to obesity is an example of a simple hypothesis.
- All lilies have the same number of petals is an example of a null hypothesis.
- If a person gets 7 hours of sleep, then he will feel less fatigue than if he sleeps less. It is an example of a directional hypothesis.
Functions of Hypothesis
Following are the functions performed by the hypothesis:
- Hypothesis helps in making an observation and experiments possible.
- It becomes the start point for the investigation.
- Hypothesis helps in verifying the observations.
- It helps in directing the inquiries in the right direction.
How will Hypothesis help in the Scientific Method?
Researchers use hypotheses to put down their thoughts directing how the experiment would take place. Following are the steps that are involved in the scientific method:
- Formation of question
- Doing background research
- Creation of hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collection of data
- Result analysis
- Summarizing the experiment
- Communicating the results
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is hypothesis.
A hypothesis is an assumption made based on some evidence.
Give an example of simple hypothesis?
What are the types of hypothesis.
Types of hypothesis are:
- Associative and Casual hypothesis
State true or false: Hypothesis is the initial point of any investigation that translates the research questions into a prediction.
Define complex hypothesis..
A complex hypothesis shows the relationship between two or more dependent variables and two or more independent variables.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Physics related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

3.5: Developing A Hypothesis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 75017

- University of Missouri–St. Louis
Theories and Hypotheses
Before describing how to develop a hypothesis, it is important to distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis. A theory is a coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena. Although theories can take a variety of forms, one thing they have in common is that they go beyond the phenomena they explain by including variables, structures, processes, functions, or organizing principles that have not been observed directly. Consider, for example, Zajonc’s theory of social facilitation and social inhibition (1965). He pro- posed that being watched by others while performing a task creates a general state of physiological arousal, which increases the likelihood of the dominant (most likely) response. So for highly practiced tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make correct responses, but for relatively unpracticed tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make incorrect responses. Notice that this theory—which has come to be called drive theory—provides an explanation of both social facilitation and social inhibition that goes beyond the phenomena themselves by including concepts such as “arousal” and “dominant response,” along with processes such as the effect of arousal on the dominant response.
Outside of science, referring to an idea as a theory often implies that it is untested—perhaps no more than a wild guess. In science, however, the term theory has no such implication. A theory is simply an explanation or interpretation of a set of phenomena. It can be untested, but it can also be extensively tested, well supported, and accepted as an accurate description of the world by the scientific community. The theory of evolution by natural selection, for example, is a theory because it is an explanation of the diversity of life on earth—not because it is untested or unsupported by scientific research. On the contrary, the evidence for this theory is overwhelmingly positive and nearly all scientists accept its basic assumptions as accurate. Similarly, the “germ theory” of disease is a theory because it is an explanation of the origin of various diseases, not because there is any doubt that many diseases are caused by microorganisms that infect the body.
A hypothesis , on the other hand, is a specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate. It is an explanation that relies on just a few key concepts. Hypotheses are often specific predictions about what will happen in a particular study. They are developed by considering existing evidence and using reasoning to infer what will happen in the specific context of interest. Hypotheses are often but not always derived from theories. So a hypothesis is often a prediction based on a theory but some hypotheses are atheoretical and only after a set of observations has been made is a theory developed. This is because theories are broad in nature and explain larger bodies of data. So if our research question is really original then we may need to collect some data and make some observations before we can develop a broader theory.
Theories and hypotheses always have this if-then relation- ship. “ If drive theory is correct, then cockroaches should run through a straight runway faster and through a branching runway more slowly when other cockroaches are present.” Although hypotheses are usually expressed as statements, they can always be rephrased as questions. “Do cockroaches run through a straight runway faster when other cockroaches are present?” Thus, deriving hypotheses from theories is an excellent way of generating interesting research questions.
But how do researchers derive hypotheses from theories? One way is to generate a research question using the techniques discussed in this chapter and then ask whether any theory implies an answer to that question. For example, you might wonder whether expressive writing about positive experiences improves health as much as expressive writing about traumatic experiences. Although this question is an interesting one on its own, you might then ask whether the habituation theory—the idea that expressive writing causes people to habituate to negative thoughts and feel- ings—implies an answer. In this case, it seems clear that if the habituation theory is correct, then expressive writing about positive experiences should not be effective because it would not cause people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings. A second way to derive hypotheses from theories is to focus on some component of the theory that has not yet been directly observed. For example, a researcher could focus on the process of habituation—perhaps hypothesizing that people should show fewer signs of emotional distress with each new writing session.
Among the very best hypotheses are those that distinguish between competing theories. For example, Norbert Schwarz and his colleagues considered two theories of how people make judgments about themselves, such as how assertive they are (Schwarz et al., 1991). Both theories held that such judgments are based on relevant examples that people bring to mind. However, one theory was that people base their judgments on the number of examples they bring to mind and the other was that people base their judgments on how easily they bring those examples to mind. To test these theories, the researchers asked people to recall either six times when they were assertive (which is easy for most people) or 12 times (which is difficult for most people). Then they asked them to judge their own assertiveness. Note that the number-of-examples theory implies that people who recalled 12 examples should judge themselves to be more assertive because they recalled more examples, but the ease-of-examples theory implies that participants who recalled six examples should judge themselves as more assertive because recalling the examples was easier. Thus the two theories made opposite predictions so that only one of the predictions could be confirmed. The surprising result was that participants who recalled fewer examples judged them- selves to be more assertive—providing particularly convincing evidence in favor of the ease-of-retrieval theory over the number-of-examples theory.
Theory Testing
The primary way that scientific researchers use theories is some- times called the hypothetico-deductive method (although this term is much more likely to be used by philosophers of science than by scientists themselves). Researchers begin with a set of phenomena and either construct a theory to explain or interpret the phenomena or choose an existing theory to work with. They then make a prediction about some new phenomenon that should be observed if the theory is correct. Again, this pre- diction is called a hypothesis. The researchers then conduct an empirical study to test the hypothesis. Finally, they reevaluate the theory in light of the new results and revise it if necessary. This process is usually conceptualized as a cycle because the researchers can then derive a new hypothesis from the revised theory, conduct a new empirical study to test the hypothesis, and so on. As Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) shows, this approach meshes nicely with the model of scientific research in psychology presented earlier in the textbook—creating a more detailed model of “theoretically motivated” or “theory-driven” research.
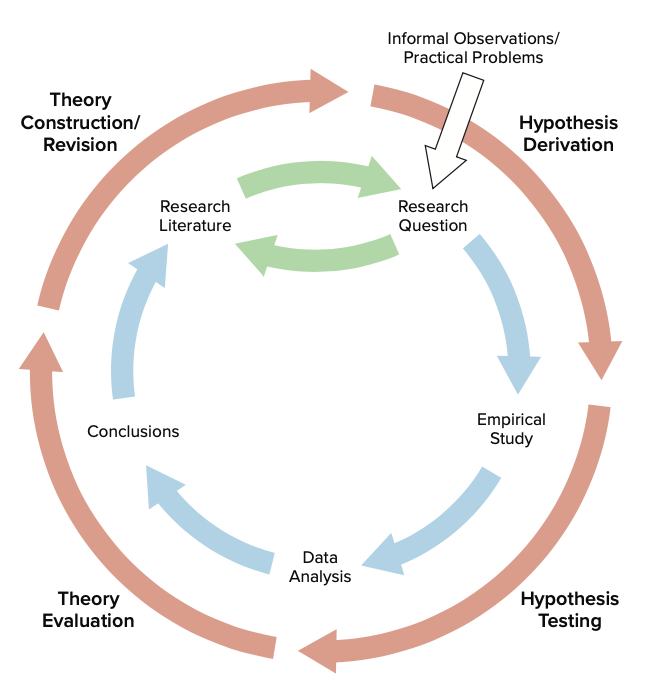
As an example, let us consider Zajonc’s research on social facilitation and inhibition. He started with a somewhat contradictory pattern of results from the research literature. He then constructed his drive theory, according to which being watched by others while performing a task causes physiological arousal, which increases an organism’s tendency to make the dominant response. This theory predicts social facilitation for well-learned tasks and social inhibition for poorly learned tasks. He now had a theory that organized previous results in a meaningful way—but he still needed to test it. He hypothesized that if his theory was correct, he should observe that the presence of others improves performance in a simple laboratory task but inhibits performance in a difficult version of the very same laboratory task. To test this hypothesis, one of the studies he conducted used cockroaches as subjects (Zajonc, Heingartner, & Herman, 1969). The cockroaches ran either down a straight runway (an easy task for a cockroach) or through a cross-shaped maze (a difficult task for a cock- roach) to escape into a dark chamber when a light was shined on them. They did this either while alone or in the presence of other cockroaches in clear plastic “audience boxes.” Zajonc found that cockroaches in the straight runway reached their goal more quickly in the presence of other cockroaches, but cockroaches in the cross-shaped maze reached their goal more slowly when they were in the presence of other cock- roaches. Thus he confirmed his hypothesis and provided support for his drive theory. (Zajonc also showed that drive theory existed in humans [Zajonc & Sales, 1966] in many other studies afterward).
Incorporating Theory into Your Research
When you write your research report or plan your presentation, be aware that there are two basic ways that researchers usually include theory. The first is to raise a research question, answer that question by conducting a new study, and then offer one or more theories (usually more) to explain or interpret the results. This format works well for applied research questions and for research questions that existing theories do not address. The second way is to describe one or more existing theories, derive a hypothesis from one of those theories, test the hypothesis in a new study, and finally reevaluate the theory. This format works well when there is an existing theory that addresses the research question—especially if the resulting hypothesis is surprising or conflicts with a hypothesis derived from a different theory.
To use theories in your research will not only give you guidance in coming up with experiment ideas and possible projects, but it lends legitimacy to your work. Psychologists have been interested in a variety of human behaviors and have developed many theories along the way. Using established theories will help you break new ground as a researcher, not limit you from developing your own ideas.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable . We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science, and it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false. Second, a good hypothesis must be logical . As described above, hypotheses are more than just a random guess. Hypotheses should be informed by previous theories or observations and logical reasoning. Typically, we begin with a broad and general theory and use deductive reasoning to generate a more specific hypothesis to test based on that theory. Occasionally, how- ever, when there is no theory to inform our hypothesis, we use inductive reasoning which involves using specific observations or research findings to form a more general hypothesis. Finally, the hypothesis should be positive . That is, the hypothesis should make a positive statement about the existence of a relationship or effect, rather than a statement that a relationship or effect does not exist. As scientists, we don’t set out to show that relationships do not exist or that effects do not occur so our hypotheses should not be worded in a way to suggest that an effect or relationship does not exist. The nature of science is to assume that something does not exist and then seek to find evidence to prove this wrong, to show that it really does exist. That may seem backward to you but that is the nature of the scientific method. The underlying reason for this is beyond the scope of this chapter but it has to do with statistical theory.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 26 November 2023
Impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution: evidence from China
- Yanfang Liu 1
Scientific Reports volume 13 , Article number: 20769 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
3653 Accesses
1 Citations
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Environmental sciences
- Environmental social sciences
The application of industrial robots is considered a significant factor affecting environmental pollution. Selecting industrial wastewater discharge, industrial SO 2 emissions and industrial soot emissions as the evaluation indicators of environmental pollution, this paper uses the panel data model and mediation effect model to empirically examine the impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution and its mechanisms. The conclusions are as follows: (1) Industrial robots can significantly reduce environmental pollution. (2) Industrial robots can reduce environmental pollution by improving the level of green technology innovation and optimizing the structure of employment skills. (3) With the increase in emissions of industrial wastewater, industrial SO 2 , and industrial dust, the impacts generated by industrial robots are exhibiting trends of a “W” shape, gradual intensification, and progressive weakening. (4) Regarding regional heterogeneity, industrial robots in the eastern region have the greatest negative impact on environmental pollution, followed by the central region, and the western region has the least negative impact on environmental pollution. Regarding time heterogeneity, the emission reduction effect of industrial robots after 2013 is greater than that before 2013. Based on the above conclusions, this paper suggests that the Chinese government and enterprises should increase investment in the robot industry. Using industrial robots to drive innovation in green technology and optimize employment skill structures, reducing environmental pollution.
Similar content being viewed by others

The impact of artificial intelligence on employment: the role of virtual agglomeration
Yang Shen & Xiuwu Zhang
The role of artificial intelligence in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals
Ricardo Vinuesa, Hossein Azizpour, … Francesco Fuso Nerini
Global energy use and carbon emissions from irrigated agriculture
Jingxiu Qin, Weili Duan, … Lorenzo Rosa
Introduction
Since the reform and opening up, China’s rapid economic growth has created a world-renowned “economic growth miracle” 1 . With the rapid economic growth, China’s environmental pollution problem is becoming more and more serious 2 . According to the “ Global Environmental Performance Index Report ” released by Yale University in the United States in 2022, China’s environmental performance index scores 28.4 points, ranking 160th out of 180 participating countries. The aggravation of environmental pollution not only affects residents’ health 3 , but also affects the efficiency of economic operation 4 . According to calculation of the General Administration of Environmental Protection, the World Bank and the Chinese Academy of Sciences, China’s annual losses caused by environmental pollution account for about 10% of GDP. Exploring the factors that affect environmental pollution and seeking ways to reduce environmental pollution are conducive to the development of economy within the scope of environment.
Industrial robots are machines that can be automatically controlled, repeatedly programmed, and multi-purpose 5 . They replace the low-skilled labor force engaged in procedural work 6 , reducing the raw materials required for manual operation. Industrial robots improve the clean technology level and energy efficiency of coal combustion, reducing pollutant emissions in front-end production. Industrial robots also monitor the energy consumption and sewage discharge in the production process in real time. The excessive discharge behavior of enterprises in the production process is regulated, reducing the emission of pollutants in the end treatment. Based on the selection and coding of literature (Appendix A ), this paper uses the meta-analysis method to compare the impacts of multiple factors such as economics, population, technology, and policy on environmental pollution. As shown in Table 1 , compared to other factors, industrial robots demonstrate greater advantages in reducing environmental pollution. There is a lack of research on the relationship between industrial robots and environmental pollution in China. With the advent of artificial intelligence era, China’s industrial robot industry has developed rapidly. According to data released by the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), from 1999 to 2019, China’s industrial robot ownership and installation shows an increasing trend year by year (Fig. 1 ). In 2013 and 2016, China’s industrial robot installation (36,560) and ownership (349,470) exceeds Japan for the first time, becoming the world’s largest country in terms of installation and ownership of industrial robots. Whether the application of industrial robots in China contributes to the reduction of environmental pollution? What is the mechanism of the impact of China’s industrial robots on environmental pollution? Researching this issue is crucial for filling the gaps in existing research and providing a reference for other countries to achieve emission reduction driven by robots.
Industrial robot installations in the world’s top five industrial robot markets from 1999 to 2019.
Based on the above analysis, this paper innovatively incorporates industrial robots and environmental pollution into a unified framework. Based on the panel data of 30 provinces in China from 2006 to 2019, this paper uses the ordinary panel model and mediating effect model to empirically test the impact of industrial robots on China’s environmental pollution and its transmission channels. The panel quantile model is used to empirically analyze the heterogeneous impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution under different environmental pollution levels.
Literature review
A large number of scholars have begun to study the problem of environmental pollution. Its research content mainly includes two aspects: The measurement of environmental pollution and its influencing factors. Regarding the measurement, some scholars have used SO 2 emissions 7 , industrial soot emissions 8 and PM2.5 concentration 9 and other single indicators to measure the degree of environmental pollution. The single indicator cannot fully and scientifically reflect the degree of environmental pollution. To make up for this defect, some scholars have included industrial SO 2 emissions, industrial wastewater discharge and industrial soot emissions into the environmental pollution evaluation system, and used the entropy method to measure environmental pollution level 10 . This method ignores the different characteristics and temporal and spatial trends of different pollutants, which makes the analysis one-sided. Regarding the influencing factors, economic factors such as economic development level 11 , foreign direct investment 12 and income 13 , population factors such as population size 14 and urbanization level 15 , energy consumption 16 all have an impact on environmental pollution. Specifically, economic development and technological innovation can effectively reduce environmental pollution 17 . The expansion of population size can aggravate environmental pollution. Income inequality can reduce environmental pollution, but higher income inequality may aggravate environmental pollution 18 . There are “pollution heaven hypothesis” and “pollution halo hypothesis” between foreign direct investment and environmental pollution 19 . Technological factors also have a non-negligible impact on environmental pollution 20 .
With continuous deepening of research, scholars have begun to focus on the impact of automation technology, especially industrial robot technology, on the environment. Ghobakhloo et al. 21 theoretically analyzed the impact of industrial robots on energy sustainability, contending that the application of industrial robots could foster sustainable development of energy. Using data from multiple countries, a few scholars have empirically analyzed the effect of industrial robots on environmental pollution (Table 2 ). Luan et al. 22 used panel data from 73 countries between 1993 and 2019 to empirically analyze the impact of industrial robots on air pollution, finding that the use of industrial robots intensifies environmental pollution. Using panel data from 66 countries from 1993 to 2018, Wang et al. 23 analyzed the impact of industrial robots on carbon intensity and found that industrial robots can reduce carbon intensity. On the basis of analyzing the overall impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution, some scholars conducted in-depth exploration of its mechanism. Based on data from 72 countries between 1993 and 2019, Chen et al. 5 explored the impact of industrial robots on the ecological footprint, discovering that industrial robots can reduce the ecological footprint through time saving effect, green employment effect and energy upgrading effect. Using panel data from 35 countries between 1993 and 2017, Li et al. 24 empirically examined the carbon emission reduction effect of industrial robots, finding that industrial robots can effectively reduce carbon emissions by increasing green total factor productivity and reducing energy intensity. Although the above studies have successfully estimated the overall impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution and its mechanisms, they have not fully considered the role of technological progress, labor structure and other factors in the relationship between the two. These studies all chose data from multiple countries as research samples and lack research on the relationship between industrial robots and environmental pollution in China, an emerging country.
The above literature provides inspiration for this study, but there are still shortcomings in the following aspects: Firstly, there is a lack of research on the relationship between industrial robots and environmental pollution in emerging countries. There are significant differences between emerging and developed countries in terms of institutional background and the degree of environmental pollution. As a representative emerging country, research on the relationship between industrial robots and environmental pollution in China can provide reliable references for other emerging countries. Secondly, theoretically, the study of the impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution is still in its initial stage. There are few studies that deeply explore its impact mechanism, and there is a lack of analysis of the role of technological progress and labor structure in the relationship between the two.
The innovations of this paper are as follows: (1) In terms of sample selection, this paper selects panel data from 30 provinces in China from 2006 to 2019 as research samples to explore the relationship between industrial robots and environmental pollution in China, providing references for other emerging countries to improve environmental quality using industrial robots. (2) In terms of theory, this paper is not limited to revealing the superficial relationship between industrial robots and environmental pollution. it starts from a new perspective and provides an in-depth analysis of how industrial robots affect environmental pollution through employment skill structure and green technology innovation. This not only enriches research in the fields of industrial robots and the environment, but is also of great significance in guiding the direction of industrial policy and technology research and development.
Theoretical analysis and hypothesis
Industrial robots and environmental pollution.
As shown in Fig. 2 , the impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution is mainly reflected in two aspects: Front-end production and end treatment. In front-end production, industrial robots enable artificial substitution effects 25 . Manual operation is replaced by machine operation, reducing the raw materials needed for manual operation. Through the specific program setting of industrial robots, clean energy is applied to industrial production 26 . The use of traditional fuels such as coal and oil is reduced. In terms of end treatment, the traditional pollutant concentration tester only measures a single type of pollutant. Its data cannot be obtained in time. It is easy to cause pollution incidents. Industrial robots can measure a variety of pollutants, and have the function of remote unmanned operation and warning. It reflects the pollution situation in time, reducing the probability of pollution incidents. The use of robots can upgrade sewage treatment equipment and improve the accuracy of pollution treatment, reducing pollutant emissions. Based on the above analysis, this paper proposes hypothesis 1.
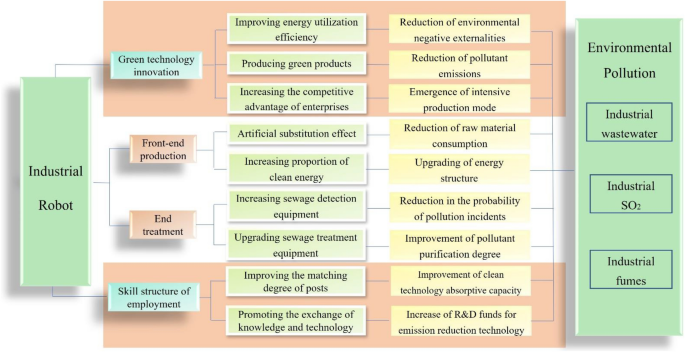
The impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution.
Hypothesis 1
The use of industrial robots can reduce environmental pollution.
Mediating effect of green technology innovation
Industrial robots can affect environmental pollution by promoting green technology innovation. The transmission path of “industrial robots-green technology innovation-environmental pollution” is formed. Industrial robots are the materialization of technological progress in the field of enterprise R&D. Its impact on green technology innovation is mainly manifested in the following two aspects: Firstly, industrial robots classify known knowledge, which helps enterprises to integrate internal and external knowledge 27 . The development of green technology innovation activities of enterprises is promoted. Secondly, enterprises can simulate existing green technologies through industrial robots. The shortcomings of green technology in each link are found. Based on this, enterprises can improve and perfect green technology in a targeted manner. Industrial robots can collect and organize data, which enables enterprises to predict production costs and raw material consumption. Excessive procurement by enterprises can occupy working capital. Inventory backlog leads to warehousing, logistics and other expenses, increasing storage costs 28 . Forecasting the consumption of raw materials allows enterprises to purchase precisely, preventing over-procurement and inventory backlog, thereby reducing the use of working capital and storage costs 29 . The production cost of enterprises is reduced. Enterprises have more funds for green technology research and development.
The continuous innovation of green technology is helpful to solve the problem of environmental pollution. Firstly, green technology innovation helps use resources better 30 , lowers dependence on old energy, and reduces environmental damage. Secondly, green technology innovation promotes the greening of enterprises in manufacturing, sales and after-sales 31 . The emission of pollutants in production process is reduced. Finally, green technology innovation improves the advantages of enterprises in market competition 32 . The production possibility curve expands outward, which encourages enterprises to carry out intensive production. Based on the above analysis, this paper proposes hypothesis 2.
Hypothesis 2
Industrial robots can reduce environmental pollution through green technology innovation.
Mediating effect of employment skill structure
Industrial robots can affect environmental pollution through employment skill structure. The transmission path of “industrial robots-employment skill structure-environmental pollution” is formed. Industrial robots have substitution effect and creation effect on the labor force, improving the employment skill structure. Regarding the substitution effect, enterprises use industrial robots to complete simple and repetitive tasks to improve production efficiency, which crowds out low-skilled labor 6 . Regarding the creation effect, industrial robots create a demand for new job roles that matches automation, such as robot engineers, data analysts, machine repairers, which increases the number of highly skilled labor 33 . The reduction of low-skilled labor and increase of high-skilled labor improve employment skill structure.
High-skilled labor is reflected in the level of education 34 . Its essence is to have a higher level of skills and environmental awareness, which is the key to reducing environmental pollution. Compared with low-skilled labor, high-skilled labor has stronger ability to acquire knowledge and understand skills, which improves the efficiency of cleaning equipment and promotes emission reduction. The interaction and communication between highly skilled labor is also crucial for emission reduction. The excessive wage gap between employees brings high communication costs, which hinders the exchange of knowledge and technology between different employees. The increase in the proportion of high-skilled labor can solve this problem and improve the production efficiency of enterprises 35 . The improvement of production efficiency enables more investment in emission reduction research, decreasing pollutant emissions. Based on the above analysis, this paper proposes hypothesis 3.
Hypothesis 3
Industrial robots can reduce environmental pollution by optimizing employment skills structure.
Model construction and variable selection
Model construction, panel data model.
The panel data model is a significant statistical method, first introduced by Mundlak 36 . Subsequently, numerous scholars have used this model to examine the baseline relationships between core explanatory variables and explained variables 37 . To test the impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution, this paper sets the following panel data model:
In formula ( 1 ), Y it is the explained variable, indicating the degree of environmental pollution in region i in year t . IR it is the core explanatory variable, indicating the installation density of industrial robots in region i in year t . X it is a series of control variables, including economic development level (GDP), urbanization level (URB), industrial structure (EC), government intervention (GOV) and environmental regulation (ER). \(\lambda i\) is the regional factor. \(\varphi t\) is the time factor. \(\varepsilon it\) is the disturbance term.
Mediating effect model
To test the transmission mechanism of industrial robots affecting environmental pollution, this paper sets the following mediating effect model:
In formula ( 2 ), M is the mediating variable, which mainly includes green technology innovation and employment skill structure. Formula ( 2 ) measures the impact of industrial robots on mediating variables. Formula ( 3 ) measures the impact of intermediary variables on environmental pollution. According to the principle of mediating effect 38 , the direct effect \(\theta 1\) , mediating effect \(\beta 1 \times \theta 2\) and total effect \(\alpha 1\) satisfy \(\alpha 1 = \theta 1 + \beta 1 \times \theta 2\) .
Panel quantile model
The panel quantile model was first proposed by Koenke and Bassett 39 . It is mainly used to analyze the impact of core explanatory variables on the explained variables under different quantiles 40 . To empirically test the heterogeneous impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution under different levels of environmental pollution, this paper sets the following panel quantile model:
In formula ( 4 ), \(\tau\) represents the quantile value. \(\gamma 1\) reflects the difference in the impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution at different quantiles. \(\gamma 2\) indicates the different effects of control variables at different quantiles.
Variable selection
Explained variable.
The explained variable is environmental pollution. Considering the timeliness and availability of data, this paper selects industrial wastewater discharge, industrial SO 2 emissions and industrial soot emissions as indicators of environmental pollution.
Explanatory variable
According to production theory, industrial robots can enhance production efficiency 41 . Efficient production implies reduced energy wastage, which in turn decreases the emission of pollutants. Industrial robots can upgrade pollution control equipment, heightening the precision in pollution treatment and reducing pollutant discharge. Referring to Acemoglu and Restrepo 25 , this paper selects the installation density of industrial robots as a measure. The specific formula is as follows:
In formula ( 5 ), Labor ji is the number of labor force in industry j in region i . IR jt is the stock of industrial robot use in industry j in the year t .
Mediating variable
Green technology innovation. Industrial robots can increase the demand for highly-skilled labor 42 , subsequently influencing green technology innovation. Compared to ordinary labor, highly-skilled labor possesses a richer knowledge base and technological learning capability, improving the level of green technology innovation. Green technology innovation can improve energy efficiency 43 , reducing pollution generated by energy consumption. The measurement methods of green technology innovation mainly include three kinds: The first method is to use simple technology invention patents as measurement indicators. Some of technical invention patents are not applied to the production process of enterprise, they cannot fully reflect the level of technological innovation. The second method is to use green product innovation and green process innovation as measurement indicators. The third method is to use the number of green patent applications or authorizations as a measure 44 . This paper selects the number of green patent applications as a measure of green technology innovation.
Employment skill structure. The use of industrial robots reduces the demand for labor performing simple repetitive tasks and increases the need for engineers, technicians, and other specialized skilled personnel, improving the employment skill structure 45 . Compared to ordinary workers, highly-skilled laborers typically have a stronger environmental awareness 46 . Such environmental consciousness may influence corporate decisions, prompting companies to adopt eco-friendly production methods, thus reducing environmental pollution. There are two main methods to measure the structure of employment skills: One is to use the proportion of employees with college degree or above in the total number of employees as a measure. The other is to use the proportion of researchers as a measure. The educational level can better reflect the skill differences of workers. This paper uses the first method to measure the employment skill structure.
Control variable
Economic development level. According to the EKC hypothesis 47 , in the initial stage of economic development, economic development mainly depends on input of production factors, which aggravates environmental pollution. With the continuous development of economy, people begin to put forward higher requirements for environmental quality. The government also begins to adopt more stringent policies to control environmental pollution, which can reduce the level of environmental pollution. According to Liu and Lin 48 , This paper uses per capita GDP to measure economic development level.
Urbanization level. The improvement of urbanization level has both positive and negative effects on pollution. Urbanization can improve the agglomeration effect of cities. The improvement of agglomeration effect can not only promote the sharing of public resources such as infrastructure, health care, but also facilitate the centralized treatment of pollution. The efficiency of environmental governance is improved 49 . The acceleration of urbanization can increase the demand for housing, home appliances and private cars, which increases pollutant emissions 50 . This paper uses the proportion of urban population to total population to measure the level of urbanization.
Industrial structure. Industrial structure is one of the key factors that determine the quality of a country’s environmental conditions 51 . The increase in the proportion of capital and technology-intensive industries can effectively improve resource utilization efficiency and improve resource waste 52 . This paper selects the ratio of the added value of the tertiary industry to the secondary industry to measure industrial structure.
Government intervention. Government intervention mainly affects environmental pollution from the following two aspects: Firstly, the government can give high-tech, energy-saving and consumption-reducing enterprises relevant preferential policies, which promotes the development of emission reduction technologies for these enterprises 53 . Secondly, the government strengthens environmental regulation by increasing investment in environmental law enforcement funds, thus forcing enterprises to save energy and reduce emissions 54 . This paper selects the proportion of government expenditure in GDP to measure government intervention.
Environmental regulation. The investment in environmental pollution control is conducive to the development of clean and environmental protection technology, optimizing the process flow and improving the green production efficiency of enterprises 55 . Pollutant emissions are reduced. This paper selects the proportion of investment in pollution control to GDP to measure environmental regulation.
Data sources and descriptive statistics
This paper selects the panel data of 30 provinces in China from 2006 to 2019 as the research sample. Among them, the installation data of industrial robots are derived from International Federation of Robotics (IFR). The data of labor force and employees with college degree or above are from China Labor Statistics Yearbook . Other data are from the China Statistical Yearbook . The descriptive statistics of variables are shown in Table 3 . Considering the breadth of application and the reliability of analysis capabilities, this paper uses Stata 16 for regression analysis.
Results analysis
Spatial and temporal characteristics of environmental pollution and industrial robots in china, environmental pollution.
Figure 3 a shows the overall trend of average industrial wastewater discharge in China from 2006 to 2019. From 2006 to 2019, the discharge of industrial wastewater shows a fluctuating downward trend, mainly due to the improvement of wastewater treatment facilities and the improvement of treatment capacity. Figure 3 b shows the changing trend of average industrial wastewater discharge in 30 provinces of China from 2006 to 2019. Industrial wastewater discharge in most provinces has declined. There are also some provinces such as Fujian, Guizhou and Qinghai, which have increased industrial wastewater discharge. Their emission reduction task is very arduous.
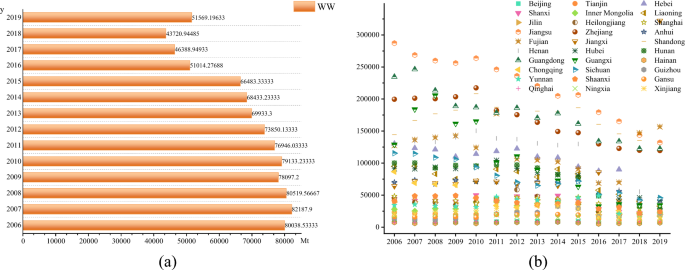
Industrial wastewater discharge from 2006 to 2019.
Figure 4 a shows the overall trend of average industrial SO 2 emissions in China from 2006 to 2019. From 2006 to 2019, industrial SO 2 emissions shows a fluctuating downward trend, indicating that air pollution control and supervision are effective. Figure 4 b shows the trend of average industrial SO 2 emissions in 30 provinces of China from 2006 to 2019. Similar to industrial wastewater, industrial SO 2 emissions decrease in most provinces.
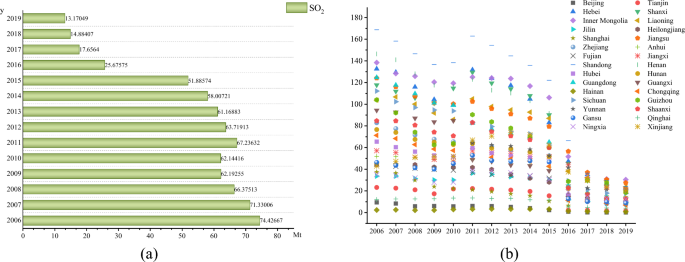
Industrial SO 2 emissions from 2006 to 2019.
Figure 5 a shows the overall trend of average industrial soot emissions in China from 2006 to 2019. Different from industrial wastewater and industrial SO 2 , the emission of industrial soot is increasing year by year. From the perspective of governance investment structure, compared with industrial wastewater and industrial SO 2 , the investment proportion of industrial soot is low. From the perspective of source, industrial soot mainly comes from urban operation, industrial manufacturing and so on. The acceleration of urbanization and the expansion of manufacturing scale have led to an increase in industrial soot emissions. Figure 5 b shows the trend of industrial soot emissions in 30 provinces in China from 2006 to 2019. The industrial soot emissions in most provinces have increased.
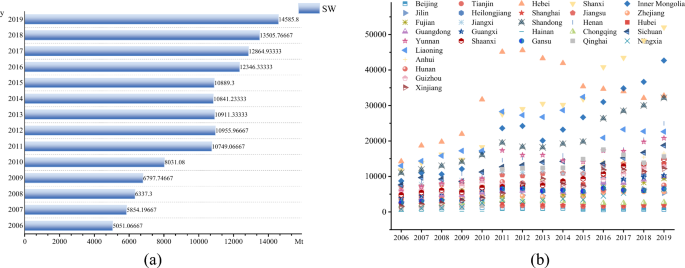
Industrial soot emissions from 2006 to 2019.
Figure 6 shows the spatial distribution characteristics of industrial wastewater, industrial SO 2 and industrial soot emissions. The three types of pollutant emissions in the central region are the largest, followed by the eastern region, and the three types of pollutant emissions in the western region are the smallest. Due to resource conditions and geographical location, the central region is mainly dominated by heavy industry. The extensive development model of high input and consumption makes its pollutant emissions higher than the eastern and western regions. The eastern region is mainly capital-intensive and technology-intensive industries, which makes its pollutant emissions lower than the central region. Although the leading industry in the western region is heavy industry, its factory production and transportation scale are not large, which produces less pollutants.
Spatial distribution characteristics of industrial wastewater, industrial SO 2 and industrial soot.
Industrial robots
Figure 7 a shows the overall trend of installation density of industrial robots in China from 2006 to 2019. From 2006 to 2019, the installation density of industrial robots in China shows an increasing trend year by year. The increase of labor cost and the decrease of industrial robot cost make enterprises use more industrial robots, which has a substitution effect on labor force. The installation density of industrial robots is increased. Figure 7 b shows the trend of installation density of industrial robots in 30 provinces of China from 2006 to 2019. The installation density of industrial robots in most provinces has increased. Among them, the installation density of industrial robots in Guangdong Province has the largest growth rate. The installation density of industrial robots in Heilongjiang Province has the smallest growth rate.
Installation density of industrial robots from 2006 to 2019.
Figure 8 shows the spatial distribution characteristics of installation density of industrial robots. The installation density of industrial robots in the eastern region is the largest, followed by the central region, and the installation density of industrial robots in the western region is the smallest. The eastern region is economically developed and attracts lots of talents to gather here, which provides talent support for the development of industrial robots. Advanced technology also leads to the rapid development of industrial robots in the eastern region. The economy of western region is backward, which inhibits the development of industrial robots.
Spatial distribution characteristics of industrial robots.
Benchmark regression results
Table 4 reports the estimation results of the ordinary panel model. Among them, the F test and LM test show that the mixed OLS model should not be used. The Hausman test shows that the fixed effect model should be selected in the fixed effect model and random effect model. This paper selects the estimation results of the fixed effect model to explain.
Regarding the core explanatory variable, industrial robots have a significant negative impact on the emissions of industrial wastewater, industrial SO 2 and industrial soot. Specifically, industrial robots have the greatest negative impact on industrial soot emissions, with a coefficient of -0.277 and passing the 1% significance level. The negative impact of industrial robots on industrial wastewater discharge is second, with an estimated coefficient of -0.242, which also passes the 1% significance level. The negative impact of industrial robots on industrial SO 2 emissions is the smallest, with an estimated coefficient of -0.0875 and passing the 10% significant level. Compared with industrial wastewater and SO 2 , industrial robots have some unique advantages in reducing industrial soot emissions. Firstly, in terms of emission sources, industrial soot emissions mainly come from physical processes such as cutting. These processes can be significantly improved through precise control of industrial robots. Industrial SO 2 comes from the combustion process. Industrial wastewater originates from various industrial processes. It is difficult for industrial robots to directly control these processes. Secondly, in terms of source control and terminal treatment, industrial robots can reduce excessive processing and waste of raw materials, thereby controlling industrial soot emissions at the source. For industrial SO 2 and industrial wastewater, industrial robots mainly play a role in terminal treatment. Since the terminal treatment of industrial SO 2 and industrial wastewater often involves complex chemical treatment processes, it is difficult for industrial robot technology to fully participate in these processes. This makes the impact of industrial robots in the field of industrial SO 2 and industrial wastewater more limited than that in the field of industrial soot.
Regarding the control variables, the level of economic development has a significant inhibitory effect on industrial SO 2 emissions. The higher the level of economic development, the stronger the residents’ awareness of environmental protection, which constrains the pollution behavior of enterprises. The government also adopts strict policies to control pollutant emissions. The impact of urbanization level on the discharge of industrial wastewater, industrial SO 2 and industrial soot is significantly negative. The improvement of urbanization level can improve the efficiency of resource sharing and the centralized treatment of pollutants, reducing environmental pollution. The industrial structure significantly reduces industrial SO 2 and industrial soot emissions. The upgrading of industrial structure not only reduces the demand for energy, but also improves the efficiency of resource utilization. The degree of government intervention only significantly reduces the discharge of industrial wastewater. The possible reason is that to promote economic development, the government invests more money in high-yield areas, which crowds out investment in the environmental field. Similar to the degree of government intervention, environmental regulation has a negative impact on industrial wastewater discharge. The government’s environmental governance investment has not given some support to the enterprise’s clean technology research, which makes the pollution control investment not produce good emission reduction effect.
Mediation effect regression results
Green technology innovation.
Table 5 reports the results of intermediary effect model when green technology innovation is used as an intermediary variable. Industrial robots can have a positive impact on green technology innovation. For every 1% increase in the installation density of industrial robots, the level of green technology innovation increases by 0.722%. After adding the green technology innovation, the estimated coefficient of industrial robots has decreased, which shows that the intermediary variable is effective.
In the impact of industrial robots on industrial wastewater discharge, the mediating effect of green technology innovation accounts for 8.17% of the total effect. In the impact of industrial robots on industrial SO 2 emissions, the mediating effect of green technology innovation accounts for 11.8% of the total effect. In the impact of industrial robots on industrial soot emissions, the mediating effect of green technology innovation accounts for 3.72% of the total effect.
Employment skill structure
Table 6 reports the results of intermediary effect model when the employment skill structure is used as an intermediary variable. Industrial robots have a positive impact on the employment skill structure. For every 1% increase in the installation density of industrial robots, the employment skill structure is improved by 0.0837%. Similar to green technology innovation, the intermediary variable of employment skill structure is also effective.
In the impact of industrial robots on industrial wastewater discharge, the mediating effect of employment skill structure accounts for 6.67% of the total effect. In the impact of industrial robots on industrial SO 2 emissions, the mediating effect of employment skill structure accounts for 20.66% of the total effect. In the impact of industrial robots on industrial soot emissions, the mediating effect of employment skill structure accounts for 15.53% of the total effect.
Robustness test and endogeneity problem
Robustness test.
To ensure the robustness of the regression results, this paper tests the robustness by replacing core explanatory variables, shrinking tail and replacing sample. Regarding the replacement of core explanatory variables, in the benchmark regression, the installation density of industrial robots is measured by the stock of industrial robots. Replacing the industrial robot stock with the industrial robot installation quantity, this paper re-measures the industrial robot installation density. Regarding the tail reduction processing, this paper reduces the extreme outliers of all variables in the upper and lower 1% to eliminate the influence of extreme outliers. Regarding the replacement of samples, this paper removes the four municipalities from the sample. The estimation results are shown in Table 7 . Industrial robots still have a significant negative impact on environmental pollution, which confirms the robustness of benchmark regression results.
Endogeneity problem
Logically speaking, although the use of industrial robots can reduce environmental pollution, there may be reverse causality. Enterprises may increase the use of industrial robots to meet emission reduction standards, which increases the use of industrial robots in a region. Due to the existence of reverse causality, there is an endogenous problem that cannot be ignored between industrial robots and environmental pollution.
To solve the impact of endogenous problems on the estimation results, this paper uses the instrumental variable method to estimate. According to the selection criteria of instrumental variables, this paper selects the installation density of industrial robots in the United States as the instrumental variable. The trend of the installation density of industrial robots in the United States during the sample period is similar to that of China, which is consistent with the correlation characteristics of instrumental variables. The application of industrial robots in the United States is rarely affected by China’s economic and social factors, and cannot affect China’s environmental pollution, which is in line with the exogenous characteristics of instrumental variables.
Table 8 reports the estimation results of instrumental variable method. Among them, the column (1) is listed as the first stage regression result. The estimated coefficient of instrumental variable is significantly positive, which is consistent with the correlation. Column (2), column (3) and column (4) of Table 8 are the second stage regression results of industrial wastewater, industrial SO 2 and industrial soot emissions as explanatory variables. The estimated coefficients of industrial robots are significantly negative, which again verifies the hypothesis that industrial robots can reduce environmental pollution. Compared with Table 4 , the absolute value of estimated coefficient of industrial robots is reduced, which indicates that the endogenous problems caused by industrial robots overestimate the emission reduction effect of industrial robots. The test results prove the validity of the instrumental variables.
Panel quantile regression results
Traditional panel data models might obscure the differential impacts of industrial robots at specific pollution levels. To address this issue, this paper uses a panel quantile regression model to empirically analyze the effects of industrial robots across different environmental pollution levels.
Table 9 shows that industrial robots have a negative impact on industrial wastewater discharge. With the increase of the quantile of industrial wastewater discharge, the regression coefficient of industrial robots shows a W-shaped change. Specifically, when the industrial wastewater discharge is in the 0.1 quantile, the regression coefficient of industrial robot is − 0.229, and it passes the 1% significant level. When the industrial wastewater discharge is in the 0.25 quantile, the impact of industrial robots on industrial wastewater discharge is gradually enhanced. Its regression coefficient decreases from − 0.229 to − 0.256. When the industrial wastewater discharge is in the 0.5 quantile, the regression coefficient of industrial robot increases from − 0.256 to − 0.152. When the industrial wastewater discharge is at the 0.75 quantile, the regression coefficient of industrial robot decreases from − 0.152 to − 0.211. When the industrial wastewater discharge is in the 0.9 quantile, the regression coefficient of industrial robot increases from − 0.211 to − 0.188. For every 1% increase in the installation density of industrial robots, the discharge of industrial wastewater is reduced by 0.188%.
When industrial wastewater discharge is at a low percentile, the use of industrial robots can replace traditional production methods, reducing energy waste and wastewater discharge. As industrial wastewater discharge increases, the production process becomes more complex. Industrial robots may be involved in high-pollution, high-emission productions, diminishing the robots’ emission-reducing effects. When industrial wastewater discharge reaches high levels, pressured enterprises seek environmentally friendly production methods and use eco-friendly industrial robots to reduce wastewater discharge. As wastewater discharge continues to rise, enterprises tend to prioritize production efficiency over emission control, weakening the negative impact of industrial robots on wastewater discharge. When wastewater discharge is at a high percentile, enterprises should balance production efficiency and environmental protection needs, by introducing eco-friendly industrial robots to reduce wastewater discharge.
Table 10 shows that with the increase of industrial SO 2 emission quantile level, the negative impact of industrial robots on industrial SO 2 emissions gradually increases. Specifically, when industrial SO 2 emissions are below 0.5 quantile, the impact of industrial robots on industrial SO 2 emissions is not significant. When the industrial SO 2 emissions are above 0.5 quantile, the negative impact of industrial robots on industrial SO 2 emissions gradually appears.
When industrial SO 2 emissions are at a low percentile, the application of industrial robots primarily aims to enhance production efficiency, not to reduce SO 2 emissions. Enterprises should invest in the development of eco-friendly industrial robots, ensuring they are readily available for deployment when a reduction in industrial SO 2 emissions is necessary. As industrial SO 2 emissions continue to rise, both the government and the public pay increasing attention to the issue of SO 2 emissions. To meet stringent environmental standards, enterprises begin to use industrial robots to optimize the production process, reduce reliance on sulfur fuels, and consequently decrease SO 2 emissions. Enterprises should regularly evaluate the emission reduction effectiveness of industrial robots, using the assessment data to upgrade and modify the robots’ emission reduction technologies.
Table 11 shows that with the increase of industrial soot emissions quantile level, the negative impact of industrial robots on industrial soot emissions gradually weakens. Specifically, when industrial soot emissions are below 0.75 quantile, industrial robots have a significant negative impact on industrial soot emissions. This negative effect decreases with the increase of industrial soot emissions. When the industrial soot emissions are above 0.75 quantile, the negative impact of industrial robots on industrial soot emissions gradually disappears.
When industrial soot emissions are at a low percentile, they come from a few sources easily managed by industrial robots. As industrial soot emissions increase, the sources become more diverse and complex, making it harder for industrial robots to control. Even with growing environmental awareness, it may take time to effectively use robots in high-emission production processes and control industrial soot emissions. Enterprises should focus on researching how to better integrate industrial robot technology with production processes that have high soot emission levels. The government should provide financial and technical support to enterprises, assisting them in using industrial robots more effectively for emission reduction.
Figure 9 intuitively reflects the trend of the regression coefficient of industrial robots with the changes of industrial wastewater, industrial SO 2 and industrial soot emissions. Figure 9 a shows that with the increase of industrial wastewater discharge, the regression coefficient of industrial robots shows a W-shaped trend. Figure 9 b shows that with the increase of industrial SO 2 emissions, the regression coefficient of industrial robots gradually decreases. The negative impact of industrial robots on industrial SO 2 emissions is gradually increasing. Figure 9 c shows that with the increase of industrial soot emissions, the regression coefficient of industrial robots shows a gradual increasing trend. The negative impact of industrial robots on industrial soot emissions has gradually weakened. Figure 9 a, b and c confirm the estimation results of Tables 9 , 10 and 11 .
Change of quantile regression coefficient.
Heterogeneity analysis
Regional heterogeneity.
This paper divides China into three regions: Eastern, central and western regions according to geographical location. The estimated results are shown in Table 12 . The industrial robots in eastern region have the greatest negative impact on three pollutants, followed by central region, and the industrial robots in western region have the least negative impact on three pollutants. The use of industrial robots in eastern region far exceeds that in central and western regions. The eastern region is far more than central and western regions in terms of human capital, technological innovation and financial support. Compared with central and western regions, the artificial substitution effect, upgrading of sewage treatment equipment and improvement of energy utilization efficiency brought by industrial robots in eastern region are more obvious.
Time heterogeneity
The development of industrial robots is closely related to policy support 56 . In 2013, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued the “ Guiding Opinions on Promoting the Development of Industrial Robot Industry ”. This document proposes: By 2020, 3 to 5 internationally competitive leading enterprises and 8 to 10 supporting industrial clusters are cultivated. In terms of high-end robots, domestic robots account for about 45% of the market share, which provides policy support for the development of industrial robots. Based on this, this paper divides the total sample into two periods: 2006–2012 and 2013–2019, and analyzes the heterogeneous impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution in different periods. The estimation results are shown in Table 13 . Compared with 2006–2012, the emission reduction effect of industrial robots during 2013–2019 is greater.
The use of industrial robots can effectively reduce environmental pollution, which is consistent with hypothesis 1. This is contrary to the findings of Luan et al. 22 , who believed that the use of industrial robots would exacerbate air pollution. The inconsistency in research conclusions may be due to differences in research focus, sample size, and maturity of industrial robot technology. In terms of research focus, this paper mainly focuses on the role of industrial robots in reducing pollutant emissions during industrial production processes. Their research focuses more on the energy consumption caused by the production and use of industrial robots, which could aggravate environmental pollution. In terms of sample size, the sample size of this paper is 30 provinces in China from 2006 to 2019. These regions share consistency in economic development, industrial policies and environmental regulations. Their sample size is 74 countries from 1993 to 2019. These countries cover different geographical, economic and industrial development stages, affecting the combined effect of robots on environmental pollution. In terms of the maturity of industrial robots, the maturity of industrial robot technology has undergone tremendous changes from 1993 to 2019. In the early stages, industrial robot technology was immature, which might cause environmental pollution. In recent years, industrial robot technology has gradually matured, and its operating characteristics have become environmentally friendly. Their impact on environmental pollution has gradually improved. This paper mainly conducts research on the mature stage of industrial robot technology. Their research covers the transition period from immature to mature industrial robot technology. The primary reason that the use of industrial robots can reduce environmental pollution is: The use of industrial robots has a substitution effect on labor force, which reduces the raw materials needed for manual operation. For example, in the industrial spraying of manufacturing industry, the spraying robot can improve the spraying quality and material utilization rate, thereby reducing the waste of raw materials by manual operation. Zhang et al. 57 argued that energy consumption has been the primary source of environmental pollution. Coal is the main energy in China, and the proportion of clean energy is low 58 . In 2022, clean energy such as natural gas, hydropower, wind power and solar power in China accounts for only 25.9% of the total energy consumption, which can cause serious environmental pollution problems. Industrial robots can promote the use of clean energy in industrial production and the upgrading of energy structure 24 . The reduction of raw materials and the upgrading of energy structure can control pollutant emissions in front-end production. On September 1, 2021, the World Economic Forum (WEF) released the report “ Using Artificial Intelligence to Accelerate Energy Transformation ”. The report points out that industrial robots can upgrade pollution monitoring equipment and sewage equipment, which reduces pollutant emissions in end-of-pipe treatment. Ye et al. 59 also share the same viewpoint.
The use of industrial robots can reduce environmental pollution through green technology innovation, which is consistent with hypothesis 2. Industrial robots promote the integration of knowledge, which helps enterprises to carry out green technology innovation activities. Meanwhile, Jung et al. 60 suggested that industrial robots can lower production costs for companies, allowing them to invest in green technology research. The level of green technology innovation is improved. Green technology innovation reduces environmental pollution through the following three aspects: Firstly, the improvement of energy utilization efficiency. China’s utilization efficiency of traditional energy sources such as coal is not high. The report of “ 2013-Global Energy Industry Efficiency Research ” points out that China’s energy utilization rate is only ranked 74th in the world in 2013. Low energy efficiency brings serious environmental pollution problems 61 . Du et al. 62 found that the innovation of green technologies, such as clean coal, can enhance energy efficiency and decrease environmental pollution. Secondly, the production of green products. Green technology innovation accelerates the green and recyclable process of production, thereby reducing the pollutants generated in production process. Thirdly, the improvement of enterprise competitive advantage. Green technology innovation can enable enterprises to gain greater competitive advantage in green development 63 . The supply of environmentally friendly products increases, which not only meets the green consumption needs of consumers, but also reduces the emission of pollutants.
Industrial robots can reduce environmental pollution by optimizing the structure of employment skills, which is consistent with hypothesis 3. Autor et al. 64 contended that industrial robots would replace conventional manual labor positions, reducing the demand for low-skilled labor. Industrial robots represent the development of numerical intelligence. With the continuous development of digital intelligence, the demand for high-skilled labor in enterprises has increased. Koch et al. 65 demonstrated that the use of industrial robots in Spanish manufacturing firms leads to an increase in the number of skilled workers. In February 2020, the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security, the State Administration of Market Supervision and the National Bureau of Statistics jointly issues 16 new professions such as intelligent manufacturing engineering and technical personnel, industrial Internet engineering and technical personnel, and virtual reality engineering and technical personnel to the society. These new occupations increase the demand for highly skilled labor. The reduction of low-skilled labor and increase of high-skilled labor optimize the structure of employment skills. The optimization of employment skill structure narrows the wage gap between employees, reducing the communication cost of employees. Employees learn and exchange technology with each other, which not only improves the absorption capacity of clean technology. It also improves the production efficiency of enterprises and increases corporate profits, so that enterprises can use more funds for clean technology research and development, thereby reducing environmental pollution.
Conclusions and policy recommendations
Based on the panel data of 30 provinces in China from 2006 to 2019, this paper uses the panel data model and mediating effect model to empirically test the impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution and its transmission mechanism. This paper uses panel quantile model, regional samples and time samples to further analyze the heterogeneous impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution. The conclusions are as follows: (1) Industrial robots can significantly reduce environmental pollution. For every 1% increase in industrial robots, the emissions of industrial wastewater, industrial SO 2 , and industrial dust and smoke decrease by − 0.242%, − 0.0875%, and − 0.277%. This finding is contrary to that of Luan et al. 22 , who argued that the use of industrial robots exacerbates air pollution. The results of this paper provide a contrasting perspective, highlighting the potential value of industrial robots in mitigating environmental pollution. (2) Industrial robots can reduce environmental pollution by improving green technology innovation level and optimizing employment skills structure. In the impact of industrial robots on industrial wastewater discharge, the mediating effect of green technology innovation accounts for 8.17% of total effect. The mediating effect of employment skill structure accounts for 6.67% of total effect. In the impact of industrial robots on industrial SO 2 emissions, the mediating effect of green technology innovation accounts for 11.8% of total effect. The mediating effect of employment skill structure accounts for 20.66% of total effect. In the impact of industrial robots on industrial soot emissions, the mediating effect of green technology innovation accounts for 3.72% of total effect. The mediating effect of employment skill structure accounts for 15.53% of total effect. While Obobisa et al. 66 and Zhang et al. 67 highlighted the role of green technological innovation in addressing environmental pollution. Chiacchio et al. 68 and Dekle 69 focused on the effects of industrial robots on employment. The mediating impact of technology and employment in the context of robots affecting pollution hasn’t been addressed. Our research provides the first in-depth exploration of this crucial intersection. (3) Under different environmental pollution levels, the impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution is different. Among them, with the increase of industrial wastewater discharge, the impact of industrial robots on industrial wastewater discharge shows a “W-shaped” change. With the increase of industrial SO 2 emissions, the negative impact of industrial robots on industrial SO 2 emissions is gradually increasing. On the contrary, with the increase of industrial soot emissions, the negative impact of industrial robots on industrial soot emissions gradually weakens. (4) Industrial robots in different regions and different periods have heterogeneous effects on environmental pollution. Regarding regional heterogeneity, industrial robots in eastern region have the greatest negative impact on environmental pollution, followed by central region, and western region has the least negative impact on environmental pollution. Regarding time heterogeneity, the negative impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution in 2013–2019 is greater than that in 2006–2012. Chen et al. 5 and Li et al. 24 both examined the overarching impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution. They did not consider the varying effects of robots on pollution across different regions and time periods. Breaking away from the limitations of previous holistic approaches, our study offers scholars a deeper understanding of the diverse environmental effects of industrial robots.
According to the above research conclusions, this paper believes that the government and enterprises can promote emission reduction through industrial robots from the following aspects.
Increase the scale of investment in robot industry and promote the development of robot industry. China’s industrial robot ownership ranks first in the world. Its industrial robot installation density is lower than that of developed countries such as the United States, Japan and South Korea. The Chinese government should give some financial support to robot industry and promote the development of robot industry, so as to effectively reduce environmental pollution. The R&D investment of industrial robots should be increased so that they can play a full role in reducing raw material consumption, improving energy efficiency and sewage treatment capacity.
Give full play to the role of industrial robots in promoting green technology innovation. Industrial robots can reduce environmental pollution through green technology innovation. The role of industrial robots in innovation should be highly valued. The advantages of knowledge integration and data processing of industrial robots should be fully utilized. Meanwhile, the government should support high-polluting enterprises that do not have industrial robots from the aspects of capital, talents and technology, so as to open up the channels for these enterprises to develop and improve clean technology by using industrial robots.
Give full play to the role of industrial robots in optimizing employment skills structure. The use of industrial robots can create jobs with higher skill requirements and increase the demand for highly skilled talents. China is relatively short of talents in the field of emerging technologies. The education department should actively build disciplines related to industrial robots to provide talent support for high-skilled positions. Enterprises can also improve the skill level of the existing labor force through on-the-job training and job competition.
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from Yanfang Liu on reasonable request.
Liu, Y. & Dong, F. How technological innovation impacts urban green economy efficiency in emerging economies: A case study of 278 Chinese cities. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 169 , 105534 (2021).
Article Google Scholar
Wang, Y. & Chen, X. Natural resource endowment and ecological efficiency in China: Revisiting resource curse in the context of ecological efficiency. Resour. Policy 66 , 101610 (2020).
Kampa, M. & Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 151 , 362–367 (2008).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Feng, Y., Chen, H., Chen, Z., Wang, Y. & Wei, W. Has environmental information disclosure eased the economic inhibition of air pollution?. J. Clean. Prod. 284 , 125412 (2021).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Chen, Y., Cheng, L. & Lee, C.-C. How does the use of industrial robots affect the ecological footprint? International evidence. Ecol. Econ. 198 , 107483 (2022).
Krenz, A., Prettner, K. & Strulik, H. Robots, reshoring, and the lot of low-skilled workers. Eur. Econ. Rev. 136 , 103744 (2021).
Xu, C., Zhao, W., Zhang, M. & Cheng, B. Pollution haven or halo? The role of the energy transition in the impact of FDI on SO 2 emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 763 , 143002 (2021).
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Yuan, H. et al. Influences and transmission mechanisms of financial agglomeration on environmental pollution. J. Environ. Manag. 303 , 114136 (2022).
Liu, G., Dong, X., Kong, Z. & Dong, K. Does national air quality monitoring reduce local air pollution? The case of PM 2.5 for China. J. Environ. Manag. 296 , 113232 (2021).
Ren, S., Hao, Y. & Wu, H. Digitalization and environment governance: Does internet development reduce environmental pollution?. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 66 , 1533–1562 (2023).
Zhao, J., Zhao, Z. & Zhang, H. The impact of growth, energy and financial development on environmental pollution in China: New evidence from a spatial econometric analysis. Energy Econ. 93 , 104506 (2021).
Wang, H. & Liu, H. Foreign direct investment, environmental regulation, and environmental pollution: An empirical study based on threshold effects for different Chinese regions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26 , 5394–5409 (2019).
Albulescu, C. T., Tiwari, A. K., Yoon, S.-M. & Kang, S. H. FDI, income, and environmental pollution in Latin America: Replication and extension using panel quantiles regression analysis. Energy Economics 84 , 104504 (2019).
Li, K., Fang, L. & He, L. How population and energy price affect China’s environmental pollution?. Energy Policy 129 , 386–396 (2019).
Liang, L., Wang, Z. & Li, J. The effect of urbanization on environmental pollution in rapidly developing urban agglomerations. J. Clean. Prod. 237 , 117649 (2019).
Sharma, R., Shahbaz, M., Kautish, P. & Vo, X. V. Does energy consumption reinforce environmental pollution? Evidence from emerging Asian economies. J. Environ. Manag. 297 , 113272 (2021).
Chen, F., Wang, M. & Pu, Z. The impact of technological innovation on air pollution: Firm-level evidence from China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 177 , 121521 (2022).
Hao, Y., Chen, H. & Zhang, Q. Will income inequality affect environmental quality? Analysis based on China’s provincial panel data. Ecol. Ind. 67 , 533–542 (2016).
Liu, Q., Wang, S., Zhang, W., Zhan, D. & Li, J. Does foreign direct investment affect environmental pollution in China’s cities? A spatial econometric perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 613 , 521–529 (2018).
Article ADS PubMed Google Scholar
Mughal, N. et al. The role of technological innovation in environmental pollution, energy consumption and sustainable economic growth: Evidence from South Asian economies. Energy Strat. Rev. 39 , 100745 (2022).
Ghobakhloo, M. & Fathi, M. Industry 4.0 and opportunities for energy sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 295 , 126427 (2021).
Luan, F., Yang, X., Chen, Y. & Regis, P. J. Industrial robots and air environment: A moderated mediation model of population density and energy consumption. Sustain. Prod. Consump. 30 , 870–888 (2022).
Wang, Q., Li, Y. & Li, R. Do industrial robots reduce carbon intensity? The role of natural resource rents and corruption control. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29760-7 (2023).
Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Pan, A., Han, M. & Veglianti, E. Carbon emission reduction effects of industrial robot applications: Heterogeneity characteristics and influencing mechanisms. Technol. Soc. 70 , 102034 (2022).
Acemoglu, D. & Restrepo, P. Robots and jobs: Evidence from US labor markets. J. Polit. Econ. 128 , 2188–2244 (2020).
Liu, J., Liu, L., Qian, Y. & Song, S. The effect of artificial intelligence on carbon intensity: Evidence from China’s industrial sector. Socio Econ. Plan. Sci. 83 , 101002 (2022).
Lee, C.-C., Qin, S. & Li, Y. Does industrial robot application promote green technology innovation in the manufacturing industry?. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 183 , 121893 (2022).
Riza, M., Purba, H. H. & Mukhlisin,. The implementation of economic order quantity for reducing inventory cost. Res. Logist. Prod. 8 , 207–216 (2018).
Google Scholar
Tang, Z. & Ge, Y. CNN model optimization and intelligent balance model for material demand forecast. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 13 , 978–986 (2022).
Wang, Q. & Ren, S. Evaluation of green technology innovation efficiency in a regional context: A dynamic network slacks-based measuring approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 182 , 121836 (2022).
Chang, K., Liu, L., Luo, D. & Xing, K. The impact of green technology innovation on carbon dioxide emissions: The role of local environmental regulations. J. Environ. Manag. 340 , 117990 (2023).
Tu, Y. & Wu, W. How does green innovation improve enterprises’ competitive advantage? The role of organizational learning. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 26 , 504–516 (2021).
Dauth, W., Findeisen, S., Südekum, J. & Woessner, N. German robots-the impact of industrial robots on workers (2017).
Berger, N. & Fisher, P. A well-educated workforce is key to state prosperity. Economic Policy Institute 22 , 1–14 (2013).
Bourke, J. & Roper, S. AMT adoption and innovation: An investigation of dynamic and complementary effects. Technovation 55 , 42–55 (2016).
Mundlak, Y. On the pooling of time series and cross section data. Econometrica J. Econom. Soc. 46 , 69–85 (1978).
Article MathSciNet MATH Google Scholar
Sun, B., Li, J., Zhong, S. & Liang, T. Impact of digital finance on energy-based carbon intensity: Evidence from mediating effects perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 327 , 116832 (2023).
MacKinnon, D. P., Warsi, G. & Dwyer, J. H. A simulation study of mediated effect measures. Multivar. Behav. Res. 30 , 41–62 (1995).
Koenker, R. & Bassett, G. Jr. Regression quantiles. Econometrica J. Econom. Soc. 23 , 33–50 (1978).
Akram, R., Chen, F., Khalid, F., Ye, Z. & Majeed, M. T. Heterogeneous effects of energy efficiency and renewable energy on carbon emissions: Evidence from developing countries. J. Clean. Prod. 247 , 119122 (2020).
Pham, A.-D. & Ahn, H.-J. Rigid precision reducers for machining industrial robots. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 22 , 1469–1486 (2021).
Du, L. & Lin, W. Does the application of industrial robots overcome the Solow paradox? Evidence from China. Technol. Soc. 68 , 101932 (2022).
Sun, H., Edziah, B. K., Sun, C. & Kporsu, A. K. Institutional quality, green innovation and energy efficiency. Energy Policy 135 , 111002 (2019).
Wang, X., Su, Z. & Mao, J. How does haze pollution affect green technology innovation? A tale of the government economic and environmental target constraints. J. Environ. Manag. 334 , 117473 (2023).
Tang, C., Huang, K. & Liu, Q. Robots and skill-biased development in employment structure: Evidence from China. Econ. Lett. 205 , 109960 (2021).
Cicatiello, L., Ercolano, S., Gaeta, G. L. & Pinto, M. Willingness to pay for environmental protection and the importance of pollutant industries in the regional economy. Evidence from Italy. Ecol. Econ. 177 , 106774 (2020).
Xie, Q., Xu, X. & Liu, X. Is there an EKC between economic growth and smog pollution in China? New evidence from semiparametric spatial autoregressive models. J. Clean. Prod. 220 , 873–883 (2019).
Liu, K. & Lin, B. Research on influencing factors of environmental pollution in China: A spatial econometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 206 , 356–364 (2019).
Wang, Y. & Wang, J. Does industrial agglomeration facilitate environmental performance: New evidence from urban China?. J. Environ. Manag. 248 , 109244 (2019).
Cheng, Z. & Hu, X. The effects of urbanization and urban sprawl on CO 2 emissions in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 25 , 1792–1808 (2023).
Hu, W., Tian, J. & Chen, L. An industrial structure adjustment model to facilitate high-quality development of an eco-industrial park. Sci. Total Environ. 766 , 142502 (2021).
Hao, Y. et al. Reexamining the relationships among urbanization, industrial structure, and environmental pollution in China—New evidence using the dynamic threshold panel model. Energy Rep. 6 , 28–39 (2020).
Guo, Y., Xia, X., Zhang, S. & Zhang, D. Environmental regulation, government R&D funding and green technology innovation: Evidence from China provincial data. Sustainability 10 , 940 (2018).
Ouyang, X., Li, Q. & Du, K. How does environmental regulation promote technological innovations in the industrial sector? Evidence from Chinese provincial panel data. Energy Policy 139 , 111310 (2020).
Zhang, W. & Li, G. Environmental decentralization, environmental protection investment, and green technology innovation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09849-z (2020).
Cheng, H., Jia, R., Li, D. & Li, H. The rise of robots in China. J. Econ. Perspect. 33 , 71–88 (2019).
Zhang, X. et al. Evaluating the relationships among economic growth, energy consumption, air emissions and air environmental protection investment in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 18 , 259–270 (2013).
Jia, Z. & Lin, B. How to achieve the first step of the carbon-neutrality 2060 target in China: The coal substitution perspective. Energy 233 , 121179 (2021).
Ye, Z. et al. Tackling environmental challenges in pollution controls using artificial intelligence: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 699 , 134279 (2020).
Jung, J. H. & Lim, D.-G. Industrial robots, employment growth, and labor cost: A simultaneous equation analysis. Technol. Forecas. Soc. Change 159 , 120202 (2020).
Liu, H., Zhang, Z., Zhang, T. & Wang, L. Revisiting China’s provincial energy efficiency and its influencing factors. Energy 208 , 118361 (2020).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Du, K. & Li, J. Towards a green world: How do green technology innovations affect total-factor carbon productivity. Energy Policy 131 , 240–250 (2019).
Li, G., Wang, X., Su, S. & Su, Y. How green technological innovation ability influences enterprise competitiveness. Technol. Soc. 59 , 101136 (2019).
Autor, D. H., Levy, F. & Murnane, R. J. The skill content of recent technological change: An empirical exploration. Q. J. Econ. 118 , 1279–1333 (2003).
Article MATH Google Scholar
Koch, M., Manuylov, I. & Smolka, M. Robots and firms. Econ. J. 131 , 2553–2584 (2021).
Obobisa, E. S., Chen, H. & Mensah, I. A. The impact of green technological innovation and institutional quality on CO 2 emissions in African countries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 180 , 121670 (2022).
Zhang, M. & Liu, Y. Influence of digital finance and green technology innovation on China’s carbon emission efficiency: Empirical analysis based on spatial metrology. Sci. Total Environ. 838 , 156463 (2022).
Chiacchio, F., Petropoulos, G. & Pichler, D. The impact of industrial robots on EU employment and wages: A local labour market approach (Bruegel working paper, 2018).
Dekle, R. Robots and industrial labor: Evidence from Japan. J. Jpn. Int. Econ. 58 , 101108 (2020).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Harbin Vocational College of Science and Technology, Harbin, 150300, Heilongjiang, People’s Republic of China
Yanfang Liu
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Y.L.: Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, Methodology, Software. I have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yanfang Liu .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Liu, Y. Impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution: evidence from China. Sci Rep 13 , 20769 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-47380-6
Download citation
Received : 24 July 2023
Accepted : 13 November 2023
Published : 26 November 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-47380-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Anthropocene newsletter — what matters in anthropocene research, free to your inbox weekly.

COMMENTS
hypothesis. science. scientific hypothesis, an idea that proposes a tentative explanation about a phenomenon or a narrow set of phenomena observed in the natural world. The two primary features of a scientific hypothesis are falsifiability and testability, which are reflected in an "If…then" statement summarizing the idea and in the ...
A snapshot analysis of citation activity of hypothesis articles may reveal interest of the global scientific community towards their implications across various disciplines and countries. As a prime example, Strachan's hygiene hypothesis, published in 1989,10 is still attracting numerous citations on Scopus, the largest bibliographic database ...
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
A scientific hypothesis is a tentative, testable explanation for a phenomenon in the natural world. It's the initial building block in the scientific method.Many describe it as an "educated guess ...
7. Statistical hypothesis. The point of a statistical hypothesis is to test an already existing hypothesis by studying a population sample. Hypothesis like "44% of the Indian population belong in the age group of 22-27." leverage evidence to prove or disprove a particular statement. Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis. There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable. We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you'll recall Popper's falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm ...
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes - specificity, clarity and testability. Let's take a look at these more closely.
A hypothesis is a supposition or tentative explanation for (a group of) phenomena, (a set of) facts, or a scientific inquiry that may be tested, verified or answered by further investigation or methodological experiment. It is like a scientific guess. It's an idea or prediction that scientists make before they do experiments.
A scientific hypothesis should have a sound basis on previously published literature as well as the scientist's observations. Randomly generated (a priori) hypotheses are unlikely to be proven. A thorough literature search should form the basis of a hypothesis based on published evidence.7.
The scientific method. At the core of biology and other sciences lies a problem-solving approach called the scientific method. The scientific method has five basic steps, plus one feedback step: Make an observation. Ask a question. Form a hypothesis, or testable explanation. Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
Definition: Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation. Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments ...
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for an observation. The definition depends on the subject. In science, a hypothesis is part of the scientific method. It is a prediction or explanation that is tested by an experiment. Observations and experiments may disprove a scientific hypothesis, but can never entirely prove one.
A hypothesis is an educated guess or prediction of what will happen. In science, a hypothesis proposes a relationship between factors called variables. A good hypothesis relates an independent variable and a dependent variable. The effect on the dependent variable depends on or is determined by what happens when you change the independent variable.
There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable. We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you'll recall Popper's falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false.
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good ...
FAQs: Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis. In the realm of scientific research, a hypothesis plays a crucial role in formulating and testing ideas. A good hypothesis serves as the foundation for an experiment or study, guiding the researcher towards meaningful results. In this FAQ-style subsection, we'll explore the characteristics of a good ...
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis. There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable. We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you'll recall Popper's falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm ...
Hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a study. Hypotheses are drawn from theories and research questions or from direct observations. In fact, a research problem can be formulated as a hypothesis. To test the hypothesis we need to formulate it in terms that can actually be analysed with statistical tools.
A scientific hypothesis is an inferred explanation of an observation or research finding; while more exploratory in nature than a theory, it is based on existing scientific knowledge. ... but by grouping organisms based on physical characteristics, he suggested that species are related, unintentionally challenging the Fixity notion that each ...
"A hypothesis would be simple if a researcher has more insight towards the problem," P.V. Young states. W-ocean said, "A theory should be as sharp as a razor's blade". As a result, a good hypothesis must be straightforward and devoid of complication. Clarity A hypothesis must have a coherent conceptual foundation.
Following are the characteristics of the hypothesis: The hypothesis should be clear and precise to consider it to be reliable. If the hypothesis is a relational hypothesis, then it should be stating the relationship between variables. The hypothesis must be specific and should have scope for conducting more tests.
A hypothesis is a prediction of what you expect the dependent variable to be. In good science, the hypothesis is advanced before the data are gathered (or at least before they are examined). A hypothesis does not attempt to explain data, that is the role of theory. Hypotheses are tested by surveys & experiments which is quantitative research.
There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable. We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science, and it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false. Second, a good hypothesis must be logical.
This method ignores the different characteristics and temporal and spatial trends of different pollutants, which makes the analysis one-sided. ... There are "pollution heaven hypothesis" and ...