

Assessing Research-Doctorate Programs: A Methodology Study (2003)
Chapter: appendix d: sample questionnaires.
Below is the uncorrected machine-read text of this chapter, intended to provide our own search engines and external engines with highly rich, chapter-representative searchable text of each book. Because it is UNCORRECTED material, please consider the following text as a useful but insufficient proxy for the authoritative book pages.
Appendix D Sample Questionnaires {These questionnaires are subject to further review and revision.) 1. Institutional Questionnaire 2. Program Questionnaire 3. Faculty Questionnaire 4. Student Questionnaires a. Questionnaire for Acimittecl-to-Cancliclacy Doctoral Students b. Questionnaire for Program Gracluates 105
106 Institutional Questionnaire To the institutional coordinator: This questionnaire is intended to collect data about university-provided resources that are available to all doctoral programs. Typically, the ideal respondent will be in the university's office of institutional research. Most of the questions apply to all programs. One, on laboratory space, applies only to the sciences (including some social sciences). In listing programs, please refer to the attached taxonomy and answer for those programs that are present at your institution. I. For the libraries at your institution: (Please enter the average over the past three years) a. What is the average size of your professional library staff in total FTEs? b. What is the average annual library budget? c. What is the average annual budget for acquisition of books? d. A, ~ What is the average annual budget for acquisition of: print journals electronic journals ? What is the average annual budget for microprint and electronic databases? 2. Is health care insurance available to graduate students uncler an institutional plan? Yes No a. If available, health care insurance is made available to: ~ Students only ~ Students end faculty b. If available, what is the level of institutional support? (Check all that apply) Institution covers premium costs for: Teaching assistants ~ Research assistants ~ All other full-time graduate students ~ Al] graduate students Institution covers partial premium costs for: Teaching assistants ~ Research assistants ~ All other full-time graduate students ~ All graduate students No institutional contribution for: ~ Teaching assistants ~ Research assistants ~ Other graduate students 3. Does the university provide childcare facilities that are available to graduate students? O Yes ~1 No a. If yes, is the cost subsidized by the institution? ~ Yes :] No b. If not, does the institution provide a listing of childcare providers to graduate students? O Yes ~ No 4. Is university-subsidized student housing available to doctoral students? :] Yes ~ No APPENDIX D
APPENDIX D If so, what is the percentage of the doctoral students who live in university-provided housing? 5. Are graduate students are unionized on your campus? ~ Yes ~ No If yes, ~ Some students ~ All students If yes, are teaching assistants unionized? ~ Yes ~ No If yes, ~ Some teaching assistants ~ All teaching assistants If yes, are research assistants unionized? ~ Yes ~ No If yes, ~ Some research assistants ~ All research assistants? 6. Which of the following apply to the doctoral program at the institutional level? a. The institution confers awards to honor graduate students for teaching and/or research. ~ Yes ~ No b. Awards are given to faculty for mentoring or other activities that promote scholarship of doctoral students. Yes ~ No c. The institution provides some form of travel support for doctoral students to attend professional meetings. ~ Yes ~ No d. There is an organized program at the institutional level to help doctoral students improve their teaching skills. ~ Yes ~ No e. The institution provides an office that assists doctoral students in learning about employment opportunities. ~ Yes ~ No 7. For the information displayed in the following table, please provide in a file sent by small to rdpilof~as~ed~ For the each doctoral program in science (including the social sciences) and engineering at your institution, what is the net assignable square feet (NASF) of research space dedicated to the program (exclude space that is used only for undergraduates)? Please use the same definitions for NASF and research space that are used in the NSF Survey of Scientific and Engineering Research Facilities. See "Taxonomy] for a list of the program iEelds in the study, and provide the information in the Emai! i ile for only those doctoral programs that are offered at your institution. 107
APPENDIX D Program #3 108 Program Research space NASF Shared space with other programs (Y/N) Program #1 Pro cram #2
APPENDIX D Background Information Program Questionnaire This information will enable the National Research Council to contact you if there are any questions about the data. It will also permit us to contact faculty for the purpose of administering a questionnaire to elicit reputational ratings and background! data ant! to contact students to obtain information about their perceptions of the practices and offerings ~ ~ ~ 1 of the doctoral program. Please note that in addition to the web questionnaire, we would like lists of faculty and previous employers to be sent to us via e-mail. Please indicate the doctoral program to which the following information applies 1. Please provide the name and e-mai! address of the program respondent who will serve as the primary contact with the graduate oro cram. Name: Title: E-mail address: Mailing Address: State Zip Cocle- If this is an interdisciplinary program, please list the departments affiliated with the program. For each individual identified in questions 2 and 3, please provide in a file sent by emai! to rdpilot~)nas.~du the information displayed in the table for the question. Program Faculty: For each faculty member or senior research fellow or associate who participates in your doctoral program by directing theses, serving on doctoral committees, or teaching graduate courses, please provide the following information. Name Rank Highest Gender Race/ US Citizen or Tenure E-mail l | Degree | (M or F) | Ethn city | Permanent | Status | Addres (Y/N) 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 = Faculty Employment History: For each faculty member listed in Question 2 who joined your program within the past five years, please provide the institution, company, or organization where he or she was employed immediately before joining your institution. pros
110 Name Prior employer Position at that employer 4. For the doctoral students in your program, please provide the number of students that fall into each of the following categories. a. Total number of students: b. Status: Full-time Part-time Unknown c. Gentler: Male Female Unknown d. Citizenship: U.S. Permanent Resilient Temporary Visa Unknown cI. Race/Ethnicity (if U.S. citizen or Permanent Residents) American Indian or Alaskan Native Asian or Pacific Islander Black White Hispanic Mexican American Puerto Rican Other Multiracial Unknown e. Percentage of doctoral students with master's degree Program Information 5. Does your program have a mission statement? If so, what is the mission statement? (50 words or less) ~ Yes :] No If there are particular areas of research emphasis in your doctoral program, please choose from the subfields in ETaxonomy]: APPENDIX D
APPENDIX D 6. How many Ph.D.s have been awarded in the program in each of the past five years? (Note: Years span from July ~ to June 30) 2001-02 2000-01 1999-00 1998-99 1997-98- 7. For each of the academic years listed in the following table, enter the number of students who entered the program in the year and the number who completed their degrees in 4, 6, or 8, years or are still in the program. (Note: Years span from July 1 to June 30) Entering Number Student of Academic Entering Year Cohort Doctoral Students 1992 1993 1993-1994 1994-1995 1995-1996 1996-1997 1997-1998 1998-1999 1999-2000 2000-2001 2001-2002 Number of Students admitted to candidacy by the end of the 4th year of enrollment Of those admitted to candidacy, number who complete within 4 years Of those admitted to candidacy, number who complete within 6 years Of those admitted to candidacy, number who complete within 8 years Of those admitted to candidacy, how many are still enrolled after 8 years? . I_ 7a. Averaged over the past three years, what percent of entering students withdrew from the program before completing two years of study? % 7b. Averaged over the past three years, what has been the median time to degree for those who completed the program? (Note: the median time is the number of years it takes half of the number of students from the same entering year who are admitted to candidacy to complete their degree.) 8. Is a master's degree required of students prior to admission to your program? ~ Yes ~ No 9. What proportion of your full-time first-year doctoral students receive full support throughout their first year (tuition and an adequate living allowance provided as stipend or salary in program related work (TA or RA)?
112 10. How many years of full financial support could students entering your doctoral program expect to receive from your institution or an external source? 1. Over the past five years approximately what fraction of the first-year students in your program received financial support either from your institution or from extramural grants or fellowships? Tuition only Tuition and stipend- Stipend only- 12. What proportion of currently enrolled doctoral students in your program (included in multiple categories if appropriate) are currently supported by: Externally funded fellowships: Externally funded traineeships: Externally funded research assistantships: University funded teaching assistantships: University funded research assistantships: University funded tuition waivers, fellowships, or stipends: 13. Averaged over the past three years, what are the average and minimum GRE scores for students accepted into the program? Average Verbal GRE: Minimum Verbal GRE: Average Quantitative GRE: Minimum Quantitative GRE: Do you require GRE subject scores for all students entering the program? ~ Yes ~ No 14. In each of the last three academic years, how many students did you accept into your doctoral program, and how many enrolled? 2000-2001 2001 -2002 2002-2003 Accepted Enrolled 15. What percentage of the doctoral students in your program have individually assigned workspaces for their exclusive use? TAs RAs All students 16. On average, how many courses per term is each graduate teaching assistant in the program expected to teach or assist a faculty member in teaching? With sole responsibility As an Assistant to a faculty member 17. Which of the following apply to your doctoral program? APPENDIX D
APPENDIX D a. The program confers awards to honor graduate students for teaching and/or research. ~ Yes ~1 No b. Awards are given to faculty for mentoring or other activities that promote scholarship of doctoral students. ~ Yes :] No The program provides some form of travel support for doctoral students to attend professional meetings. ~ Yes ~ No d. There is an organized program to help doctoral students improve their teaching skills. ~ Yes n No e. The program provides organized assistance to help doctoral students explore employment opportunities. Yes ~1 No 8. List up to 5 institutions with which your program normally competes for graduate students: Institution # 1 Institution #2- Institution #3 Institution #4 Institution #5 1 9. Does your program collect data about employment outcomes for your graduates? ~ Yes ~ No If yes, do you provide potential applicants with this information? ~ Yes ~ No 20. Please list those interdisciplinary centers in which doctoral students from your program participate (conduct research or teach). ~3
114 Faculty Questionnaire This questionnaire is part of the National Research Council's Pilot Test of the Assessment of Research Doctoral Programs. Your university has volunteered to participate in this pilot test to assist the National Research Council's study of the methodology used to assess doctoral programs. Further information about the methodology study may be found at www7.nationalacademies.org/resdoc/index.html You have been selected to receive this questionnaire because you are a member of the faculty who participates in the education of doctoral students at your university. This means that you either teach courses to doctoral students or supervise their dissertations. If this is not the case, please indicate that in question 1. The assessment of research doctoral programs is conducted approximately every ten years and consists of a reputational survey of doctoral programs and the collection of data about doctoral faculty and students in f~fty-seven areas of study. This questionnaire provides information that will assist the study in a number of ways: licit will help us construct a pool from which to select raters for the reputational survey; 2)it will provide us enough information about you that we can collect data on grants, citations, and publications from other sources; and Hit will permit a statistical description of the faculty in the graduate program or programs with which you are affiliated. Your answers will be treated as completely confidential by the National Research Council and will only be released as part of a statistical analysis. I. Program Identification a. Do you supervise dissertations, serve on doctoral committees, or teach graduate courses in a doctoral program? ~ Yes ~ No If your answer was "No", you do not need to complete the rest of the questionnaire. b. From the pulldown list, please choose the program of your primary affiliation/appointment tPull Down List of Res-Doc Programs] If you have difficulty locating your program on the list, please refer to the "Taxonomy] list with fields and subfields Please list all programs in which you supervise dissertations, serve on dissertation committees, or teach graduate courses and the average percentage of your time during the past year that you spent in all activities for each program with which you are associated. (Do not list programs where you are an outside reader.) Program Supervise dissertations Teach courses Serve on Percent of time spent in all (YIN) (YIN) dissertation activities for this program committees (YIN) ~ (total= IJ0%) ~ d. For the articles and books that you have published in the past five years, please list what fields you have published in Table 1. If you have a single publication that spans multiple fields, please indicate them and their fields in Table 2. APPENDIX D
APPENDIX D Table 1: Books and articles in a single field published in the past 3 years Field(see Taxonomy) ~ Articles ~ Books 1 1 ~ ' 1 1 1 Table 2: Books and articles in multiple fields published in the past 3 years Field (Enter all that apply) Articles Books II. Current Employment a. Department affiliation: b. Rank: ~ Instructor ~ Assistant Professor ~ Associate Professor ~ FullProfessor ~ Other c. Tenure status: ~ Tenure-track, not tenured Tenured ~ Non-tenure-track d. Year first employed at current institution: tIf employment was not continuous, please list year of most recent appointment at this institution.] Have you received an extramural grant or contract support in the past year? Yes ~ No f. Subfields of current research interest (refer to "Taxonomy] with subfields): Subfield # 1: Subfield #2: Subfield #3: g. Do you consider part of your research to be interdisciplinary? ~ Yes ~ No If so, what is the area of that research? h. Under what names or variants of your name have you published books or articles? III. Prior Experience What was your status prior to your current position? ~ Student ~ Postdoc ~ Faculty. ~ Other: Previous employer: Address: 115
116 IV. Educational Background City Title: Employment Sector: Industry (for profit) National laboratory State or local government Federal government agency International agency 4-year college or university 2-year college K- 12 school Hospital or clinic Foundation or nonprofit Military Other (specify: State/Country Zip Code- a. Highest degree earned: ~ Bachelor's ~ Master's ~ Ph.D. ~ Professional (M.D., J.D., D.V.M., for example) b. Institution that conferred highest degree: c. Field of highest degree: Other: d. Year of highest degree: tPulldown List] To what extent does the field of your current research, teaching, or professional activities differ from the field of your highest degree? ~ Very similar ~ Somewhat similar ~ Very different V. Demographic Information a. Date of birth: b. Gender: c. Citizenship Male Female U.S. Permanent Resident Temporary Visa (mmlddlyy) d. Race/Ethnicity (if U.S. citizen or permanent resident) American Indian or Alaskan Native Asian or Pacific Islander Black White APPENDIX D
APPENDIX D Hispanic (I Mexican American, ~ Puerto Rican, ~ Other) ~ Multiracial VI. Please provide your preferred e-mai! address (where you can be reached if there are questions.) Thank you for your time. ~7
118 Questionnaire for Admitted-to-Candidacy Doctoral Students This questionnaire is part of the National Research Council's Pilot Test of the Assessment of Research Doctoral Programs. Your university has volunteered to participate in this pilot test to assist the National Research Council's study of the methodology used to assess doctoral programs. One innovation we are considering is adding student responses about the educational processes of the program. We believe that students' input is important to improving the quality of the educational experience. Further information about the methodology study may be found at www7.nationalacademies.org/resdoc/index.htm! You have been selected to receive this questionnaire because you are a student who has completed over half of your doctoral program. If this is not the case, please indicate that in question 1. The assessment of research doctoral programs is conducted approximately every ten years and consists of a reputational survey of doctoral programs and the collection of data about doctoral faculty and students in fifty-four areas of study. This questionnaire will provide information that will assist the study in a number of ways: 1) it will provide a statistical description of students in your program; 2) it will provide information about practices in your program; and 3) it will help future students in the selection of graduate programs. Your answers will be treated as completely confidential by the National Research Council and will only be released as part of a statistical analysis. Individual answers will not be shared with faculty or administrators of your doctoral program except in aggregated form. Institution: Doctoral Program: Educational Program A. Year of enrollment in this doctoral program: B. Year you expect to receive your doctorate: C. Did you (or will you) receive a master's degree before this doctorate? ~ Yes ~ No D. Did you (or will you) receive a master's degree in your doctoral field as part of your training? ~ Yes ~ No Ifyes,didyouwritea master's thesis? ~ Yes ~ No E. During the course of your study for the Ph.D. will you also receive any of the following as part of a joint, concurrent, or combined degree program: Professional doctorate (e.g., MD, DDS, OD, JD)? ~ Yes Professional master's (e.g., MBA, MPA, MPH)? ~ Yes No ~ No F. During the course of your study for the Ph.D. will you also receive a certificate in another field? ~ Yes ~ No APPENDIX D
APPENDIX D G. What were your career goals at the time you entered graduate school? Check all that apply] U.S. Employment: Industry ~ Government ~ Nonprofit ~ University ~ 2-yr. college ~ 4-yr. college Other: Non-U.S. Employment: Industry ~ Government ~ Nonprofit ~ University 2-yr. college ~ 4-yr. college Other: ~ Unknown H. What are your current career plans? tcheck all that apply] U.S. Employment: Industry ~ Government ~ Nonprofit ~ University ~ 2-yr. college ~ 4-yr. college Other: Non-U.S. Employment: Industry ~ Government ~ Nonprofit ~ University 2-yr. college ~ 4-yr. college Other: ~ Unknown I. Of the following sources of support, which have been your primary sources during your doctoral studies? (Check the three largest) I. ~ Personal/family funds 2. ~ Research Assistant (RA) 3. ~ Teaching Assistant (TA) 4. ~ Training grant 5. ~ Fellowship 6. ~ Loans 7. ~ Concurrent employment related to your degree 8. ~ Concurrent employment unrelated to your degree 2. Program Characteristics A. Professional Development I. During your doctoral program have you received (or will you receive) instruction, practice or professional development training in: a. Oral communication and presentation skills: ~ Yes ~ No b. Writing proposals for funding: ~ Yes ~ No c. Preparing articles for publication: ~ Yes ~ No d. Working in collaborative groups: ~ Yes ~ No Conducting independent research/scholarship:~ Yes ~ No f. Project management ~ Yes ~ No g. Research / professional ethics ~ Yes ~ No h. Speaking to nonacademic audiences ~ Yes n No 119 Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
120 2. In your doctoral program did you have an opportunity to obtain teaching experience? Check the typets) of teaching experience you have had: a. mentoring a high school student b. mentoring an undergraduate student c. grading papers for undergraduate or graduate courses d. leading discussion sections of undergraduate or graduate courses e. leading laboratory sections of undergraduate or graduate courses f. lecturing in undergraduate or graduate courses g. tutoring undergraduates If you have had teaching experience, please answer the following, h. ~ received formal instruction in leaching. ~ Yes ~ No i. {received formal supervision end evaluation. ~ Yes ~ No j. ~ had opportunities to teach in a variety of academic environments. ~ Yes ~ No B. Program Environment 1. Does your program provide an annual or more frequent assessment of your progress? 2. Do you receive timely feedback on your research! 1 - - - - - _ Yes ~ No ~ Yes ~ No 3. Do you have access to career advice covering a variety of employment sectors? Yes ~ No ~ Yes ~ No a. If yes, are you encouraged to use it? 4. Do you have one or more faculty members at your institution that you consider mentors (i.e., individuals from whom you seek advice about your education, career development, and other matters of concern to you as a graduate student)? ~ Yes ~ No 5. How would you rate the quality of teaching by faculty in your program? ~ Excellent ~ Good ~ Fair ~ Poor 6. How would you rate the quality of your research experience? Excellent ~ Good ~ Fair ~ Poor 7. How would YOU rate the curriculum of your Ph.D. program? ~ Excellent ~ Good S. How would you rate the overall quality of your program _ ~ O ~ Fair ~ Poor ~ , , ~ ~ Excellent ~ Good ' ' ~ ~ ~ Lair ~ Poor 9. How would YOU rate the intellectual liveliness of your pro cram? ~ Excellent ~ Good 10. Considering the overall intellectual environment of your university, how much do you fee! you have benei ited from it? ~ A lot ~ Some APPENDIX D , - - ~ o n Fair n Poor ~ A little ~ Not at all
APPENDIX D C. Infrastructure I. Does your program give you access to: a. Your own personal work space b. Computer facilities Yes ~ No ~ Yes ~ No c. Other research facilities; if so, describe: 2. Does your program provide adequate space for interaction among students? C] Yes O No 3. Are the library resources available to you adequate to support your research and education? ~ Yes C] No D. Research productivity I. How many research presentations (including poster presentations) have you made at research conferences a. on your campus? b. at national or regional meetings? 2. How many research publications have you authored or co-authored during your cloctoral studies (include pieces accepted for publication but not yet published)? a. Refereed articles b. Book chapters c. Reviews d. Books or edited volumes 3. Background information A. Date of birth: (mm/~/yy) B. Gender: ~ Male n Female C. Citizenship U.S. Permanent Resident Temporary Visa D. Race/Ethnicity (if U.S. citizen) American Indian or Alaskan Native Asian or Pacific Islander Black White Hispanic Mexican American, ~ Puerto Rican, ~ Other) ~ Multiracial E. Dependent care responsibilities: 1. Number of children living with you: Age 6 or under Over age 6 3. Parents or other dependents ~ Yes ~ No 121
122 APPENDIX D G. Marital Status: Do you have a spouse or partner who lives with you? ~ Yes ~ No F. Level of Parents' Education: Mother Father High school diploma or less Some college/Bachelor's degree Advanced degree
APPENDIX D Five-Seven Years Post-Ph.D Questionnaire This questionnaire is part of the National Research Council's Pilot Test of the Assessment of Research Doctoral Programs. Your university has volunteered to participate in this pilot test to assist the National Research Council's study of the methodology used to assess doctoral programs. One innovation that we are considering is to add student responses to questions about the educational process of the program. Further information about the methodology study may be found at www7.nationalacademies. org/resdoc/index.html You have been selected to receive this questionnaire because you are a student who has received a Ph.D. from this program five to seven years ago. If this is not the case, please indicate that in question 1. ~ 4, , I, The assessment of research doctoral programs is conducted approximately every ten years and consists of a reputational survey of doctoral programs and the collection of data about doctoral faculty and students in fifty-four areas of study. This questionnaire provides information that will assist the study in a number of ways: 1) it will help us learn whether a high enough percentage of students respond so that we can add student observations to the larger study; 2) it will provide us enough information about practices in your program that we can compare the practices of graduate programs in your field at different universities; and 3) it will permit a statistical description of the f~rst-year students in the graduate program. Your answers will be treated as completely confidential by the National Research Council and will only be released as part of a statistical analysis. Individual answers will not be shared with faculty or administrators of your former doctoral program except in aggregated form. Educational Program a. Name of the program where you received your Ph.D. degree: b. Year of enrollment in the above Ph.D. program: c. Year you received your Ph.D.: d. Did you receive a master's degree at this institution before this Ph.D.? ~ Yes ~ No e. Were you enrolled as a full-time student throughout your Ph.D. program? ~ Yes ~ No f. Did you attend graduate school prior to enrollment in the above Ph.D. program? ~ Yes ~ No If so, what degrees or certificates, if any, do you hold? ~ Certificate ~ Master's ~ Doctoral ~ Professional g. What was your career goal when you completed your Ph.D.? U.S. Employment: Industry ~ Government ~ Nonprofit ~ University 2-yr. college ~ 4-yr. college Other: 123
124 Non-U.S. Employment: Industry ~ Government ~ Nonprofit ~ University 2-yr. college ~ 4-yr. college Other: ~ Unknown h. Have your career goals changed since you received your Ph.D.? ~ Yes ~ No i. During your Ph.D. program, were you supported by funds from outside the institution? ~ Yes ~ No (Check all that apply) Type: ~ Fellowship ~ Training Grant ~ Research Grant ~ Your employer ~ Other(Specify: ! J. Did you receive institutional support? ~ Yes ~ No (Check all that apply) Type: ~ Teaching Assistantship ~ Research Assistantship ~ Fellowship ~ Tuition scholarship or waiver only ~ Loan ~ None ~ Other(Specify: ! 2. Employment and Career Status a. First employer or place of postdoctoral study after Ph.D. completion: Name: Address: City State/Country Zip Code- Title: b. Employment Sector: Industry (for profit) National laboratory State or local government Federal government agency International agency University 4-year college 2-year college K-12 school Hospital or clinic Foundation or nonprofit Military Other (specify) APPENDIX D
APPENDIX D c. If you hold or have held a postdoctoral position or positions, how many , and at what institutions, companies or government agencies were they located? List chronologically starting with the most recent. Position # 1: Position#2: Position # 3: Position#4: Dates: Dates: Dates: Dates: d. Current employer: Name: Address: City State/Country Zip Code- Title: e. Current Employment Sector: Industry (for profit) National laboratory State or local government Federal government agency International agency University 4-year college 2-year college K-12 school Hospital or clinic Foundation or nonprofit Military ~ Other (specify) 3. Ph.D. Program Characteristics a. During your Ph.D. education, in which of the following areas was training PROVIDED, which skills or experiences have you USED since graduation, and which area do you wish you had learned MORE about? (check all that apply) 1) Teaching experiemce 2) Oral communication; presentation skills 3) Writing proposals for funding 4) Manuscript preparation Provided Provided Provided Provided Experience working in collaborative groups ~ Provided 6) Critical analysis 7) Locating and applying information 125 Used ~ More Used ~ More Used ~ More Used ~ More Provided Provided Used ~ More Used ~ More Used ~ More
26 8) Experience working with people of varied educational levels ~ Provided ~ Used ~ More 9) Experience working with people from diverse backgrounds ~ Provided ~ Used ~ More 10) Experience working in teams b. Research Productivity Provided ~ Used ~ More How many books or edited books have you published or are currently accepted for publication? 2) How many articles or book chapters have you published or are currently accepted for publication? 3) How many books or articles have you reviewed for publication? 4) How many reviews, enumerated in 3), have been or will be published? 5) How many refereed papers have you or a coauthor presented at professional conferences? How many awards have you received? (Respond to all categories.) a) For teaching: b) For research: From professional societies: From your institution or employer: 7) How many patents or licenses have you received? 8) How many grants have you received from your employer or institution? 9) How many grants have you received from extramural funding agencies? 4. Background Information a. Date of birth: b. Gender: c. Citizenship APPENDIX D Male Female U.S. Permanent Resident Temporary Visa (mmlddlyy)
APPENDIX D 127 d. Race/Ethnicity (ifU.S. citizen) American Indian or Alaskan Native Asian Pacific Islander Black White Hispanic (~ Mexican American, ~ Multiracial e. Martial Status ~ Married ~ Single f. Number of Children: Age 6 and under Over age 6 g. Level of Parents' Education: Less than high school High school diploma Some college Bachelor's degree Master's degree Professional degree Doctoral degree h. Is English your first language? Mother Yes ~ No Puerto Rican, ~ Other) Father
How should we assess and present information about the quality of research-doctorate programs? In recommending that the 1995 NRC rankings in Assessing the Quality of Research-Doctorate Programs: Continuity and Change be updated as soon as possible, this study presents an improved approach to doctoral program assessment which will be useful to administrators, faculty, and others with an interest in improving the education of Ph.D.s in the United States. It reviews the methodology of the 1995 NRC rankings and recommends changes, including the collection of new data about Ph.D. students, additional data about faculty, and new techniques to present data on the qualitative assessment of doctoral program reputation. It also recommends revision of the taxonomy of fields from that used in the 1995 rankings.
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.

Know the structure of a thesis and how to craft it
All-inclusive aid from topic selection, data analysis to questionnaire design
Give a fuelled-up start to your research journey & reach heights of excellency
The first document that showcases your future research endeavors
Phd academic writers, editors, peer reviewers, statisticians at your service
Support your research choices with literature-backed justifications
Introduce your PhD expedition with highest academic standards
Data collection tool that ensures appropriate and result-oriented findings
Give your incomplete manuscript the perfect academic finish
Format, layout, structure and content is all what makes a good thesis synopsis
A plethora of literary sources to add that extra edge to your research
RM is much more than research methods, read on to know more
Research aim/objective, prospective methodology & results to display your academic dexterity
Demographic information & research objective related set of questions to fetch the right data
- Questionnaire Development

Research-Specific Data Collection Tools
Designing a questionnaire for your PhD research is an important task which decides the fate of your research. Not only is the selection of type of questionnaire a tremendous task, but also creating appropriate questions, sections and subsections for the target audience entails a great deal of time (and knowledge). There are a list of questions that need to be answered before you can embark on the journey to designing that perfect questionnaire for data collection.
It requires a complete and thorough understanding of the attributes and framework necessary for an effective questionnaire development. In addition, one must possess in-depth knowledge about the topic and variables under study. For example, the researcher must decide and evaluate the research objectives. Then, identifying the measurements and questions by which you will collect data from respondents in the intended manner.
Some segregations to keep in mind
1. type of questionnaires.
2. Type of questions
3. sections.
The questionnaire must be in line with the objectives of research. Each question mentioned must refer to some objective. It should only contain relevant questions which must not hurt the sentiments of the target respondents in any way to avoid bias. A well-framed questionnaire can help answer the research questions appropriately and contribute towards a concrete discussions chapter for deriving at research-worthy conclusions.
Crafting an effective questionnaire for research
Questionnaire design is integral to correct data collection.
Identifying the purpose of questionnaire
The purpose is to generalise from a sample to the population so that speculation can be made about some characteristic, attitude, or behavior of this population.

Choosing a suitable type of questionnaire
The advantages of the different questionnaires to be kept in mind which will suit your research objectives. For this purpose, the researcher must decide whether the survey is longitudinal or cross-sectional, will the data be collected over a period or at one point in time only.

A form of data collection
Identify through which medium the questionnaire to be distributed and the data gathered, such as the mail, telephone, the internet, and personal interviews. Its rationale, costs, data availability, strengths and weakness must be kept under scrutiny.

Identifying the population
The size of the sample population, if the size can be determined, and the means of identifying individuals in the population are necessary.
Identification of variables
The variables need to be specified in an experiment so that it is evident to readers what groups are receiving the experimental treatment and what outcomes are being measured.
Ensure compliance to the checklist above to draft a well-researched and well-designed PhD questionnaire for your research. Also, you may find attached PhD questionnaire samples prepared by our experts useful for reference.

- Contact Us --> Contact Us
- You can also mail us at
- [email protected]
- or call us at
- 9845 629 207
Popular Links
- PhD Thesis Consultants
- PhD Research Methodology Writing
- Introduction Chapter Writing
- Questionnaire Designing
- Thesis Completion
- Thesis Synopsis Sample
- Literature Review Format
- Research Methodology Format
- Introduction Chapter Format
- Questionnaire Samples
Copyright © 2015-2024.All Rights Reserved.
Call us : 0091 80 4111 6961
Crafting Effective Questionnaires for PhD Research: A Step-by-Step Guide
- PhD Research
Do you know the major problems researchers can face if they don’t craft productive PhD research questionnaires ? They may be unable to replicate the research and are also unable to help the readers understand the answers of the research questions. And not only that, but crafting ineffective questionnaires for your PhD research, can lead to your entire research being a futile prospect. But the story takes a turn.
After extensive research, we have understood that there are basically 3 steps to craft effective questionnaires for your PhD research. In this blog, we are going to describe those 3 steps so that you not only craft effective questionnaires but also help others to craft Effective Questionnaires for your PhD research. So, let’s get started, shall we?
But wait 🤚!!! Do these three methods help you create good surveys for your PhD research? is the first query you ought to address to yourself. I mean, is there a crucial query you ought to have answered before diving into the subject? Please think through and then read the remaining blog.
Why is it necessary to design efficient questionnaires for PhD research? So you might not be able to create the ideal questionnaire for your PhD if you don’t know the reason. As a result, you could be asking, “What is the solution?” Please read the remaining posts on the blog to learn more about this.
Crafting effective questionnaires is crucial for PhD research for several reasons:
- Obtaining reliable and valid data : Effective questionnaires ensure that the data collected is reliable and valid, which is essential for making accurate conclusions and recommendations based on the research findings.
- Enhancing the credibility of the research : If a questionnaire is poorly constructed, it can undermine the credibility of the research and make it difficult to convince others of the findings.
- Improving response rates : An effective questionnaire is more likely to be completed by respondents, resulting in higher response rates and more representative data.
- Reducing bias : A well-crafted questionnaire reduces the potential for bias in the responses by ensuring that questions are clear, unbiased, and focused on the research objectives.
- Saving time and resources : By ensuring that the questionnaire is well-designed, researchers can save time and resources by collecting data that is directly relevant to the research question.
- Facilitating data analysis : An effective questionnaire can make data analysis easier and more accurate by ensuring that the questions are structured in a logical and consistent manner.
Hence, crafting an effective questionnaire is essential for obtaining reliable and valid data, enhancing the credibility of the research, improving response rates, reducing bias, saving time and resources, and facilitating data analysis. So, let’s jump into knowing the answers to these questions.
PhD research questionnaires development and validation

Before moving with this part, we have something important to discuss regarding the development of the PhD research questions. Can you guess what? It is as important as knowing the development process of PhD research questions.
Developing effective research questions is an essential step in the process of conducting a PhD research project. Here are some tips to help you develop effective PhD research questions:
- Start with a broad topic : Begin by identifying a broad topic area that you are interested in and that has not been extensively researched. The topic should be significant and relevant to your field of study.
- Review existing literature : Conduct a thorough review of existing literature to identify research gaps and potential areas of exploration.
- Narrow down your focus : Once you have identified a research gap, narrow down your focus by formulating research questions that are specific, focused, and clear. Avoid broad and vague questions that are difficult to answer.
- Make sure your research questions are feasible : Your research questions should be feasible and answerable within the timeframe and resources available for your PhD project.
- Test your questions : Share your research questions with your supervisor and peers to get feedback and refine them further.
- Make sure your research questions are original : Ensure that your research questions are original and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your field.
- Revise and refine : Continuously revise and refine your research questions throughout the PhD project as you gain more knowledge and insights.
Remember that developing effective PhD research questions is an iterative process and requires time, effort, and collaboration with your supervisor and peers.

Now, another question can come in our mind which is “why validation is needed for PhD research questionnaires?” It will help you decide whether to validate the questionnaires or not. So, let us know the answer to this question and then decide.
Validation is essential for PhD research questionnaires for several reasons:
- Ensuring reliability : Validation helps ensure that the questionnaire measures what it is intended to measure consistently across different participants and situations. This increases the validity of the data that is gathered.
- Minimizing measurement errors : Validation helps identify and minimize measurement errors that could lead to inaccurate data and potentially flawed research conclusions.
- Increasing validity : Validation helps ensure that the questionnaire is measuring the construct or concept it is intended to measure. This increases the validity of the data collected and the research conclusions.
- Enhancing credibility : A validated questionnaire enhances the credibility of the research and can make it easier to convince others of the research findings.
- Improving research quality : A validated questionnaire can lead to better quality research by ensuring that the data collected is relevant, reliable, and valid.
- Meeting ethical standards : Validating the questionnaire helps ensure that participants are not subjected to unnecessary or irrelevant questions, which is important for meeting ethical standards in research.
Hence, validation is needed for PhD research questionnaires to ensure reliability, minimize measurement errors, increase validity, enhance credibility, improve research quality, and meet ethical standards.
Validating a PhD research questionnaire involves several steps. Here are some key steps to consider:
- Develop a clear research question : The first step in validating a questionnaire is to develop a clear research question that the questionnaire is designed to answer.
- Determine the type of validity: There are different types of validity that a questionnaire can have, such as content validity, construct validity, criterion-related validity, and face validity. Determine which type(s) of validity are most relevant to your research.
- Develop the questionnaire: Develop the questionnaire based on the research question and the type(s) of validity being assessed. Ensure that the questions are clear, unbiased, and relevant to the research objectives.
- Conduct a pilot study : Administer the questionnaire to a small sample of participants (e.g., 10-15) to identify any problems with the questionnaire and assess the validity of the questions.
- Evaluate the questionnaire : Evaluate the questionnaire for content validity, construct validity, criterion-related validity, and face validity based on the data collected from the pilot study.
- Refine the questionnaire : Refine the questionnaire based on the feedback received during the pilot study and the validity assessment.
- Administer the questionnaire : Administer the final version of the questionnaire to the target population.
- Analyze the data : Analyze the data collected from the questionnaire to determine the reliability and validity of the questionnaire.
- Report the results : Report the results of the validity assessment in the research report, including the methods used to assess validity, the results of the assessment, and any limitations of the questionnaire.
Hence, validating a PhD research questionnaire involves developing a clear research question, determining the type(s) of validity to be assessed, developing the questionnaire, conducting a pilot study, evaluating the questionnaire, refining the questionnaire, administering the questionnaire, analyzing the data, and reporting the results.
Now, it’s time to go to the 2nd step which can help you a little more in crafting better questions in PhD research.
Types of validation of PhD research questionnaires

Now, it’s time to understand the different types of validation of the PhD research questionnaire. But again , the questioning will not end. Why do we need to know about different types of validation of PhD research questionnaires?
Knowing about different types of validation of PhD research questionnaires is important for several reasons:
- Ensuring the reliability and validity of data : Different types of validation can help ensure that the data collected from the questionnaire is reliable and valid, which is essential for making accurate conclusions and recommendations based on the research findings.
- Selecting the appropriate type of validation : Depending on the research question and the type of data being collected, different types of validation may be more appropriate. Knowing about different types of validation can help researchers select the most appropriate type(s) of validation for their research.
- Enhancing the credibility of the research : A well-validated questionnaire enhances the credibility of the research and can make it easier to convince others of the research findings.
- Improving research quality : Validating the questionnaire can lead to better quality research by ensuring that the data collected is relevant, reliable, and valid.
Now, I think there is no question left in this part except knowing the types of validation of PhD research questionnaires. If you have any questions in your mind, then you can comment below so that we can update the blog. So, let us jump into the answer to this question.
There are several types of validation of PhD research questionnaires. Some of the most typical varieties are listed below:
- Content validity : Content validity refers to the extent to which the questionnaire items adequately cover the intended content area. To assess content validity, researchers typically seek input from subject matter experts or use established guidelines or criteria to evaluate the relevance of the questionnaire items.
- Construct validity : Construct validity refers to the extent to which the questionnaire items measure the intended construct or concept. To assess construct validity, researchers may use statistical techniques, such as factor analysis or confirmatory factor analysis, to examine how well the questionnaire items align with the underlying construct.
- Criterion-related validity : Criterion-related validity refers to the extent to which the questionnaire items are related to an external criterion or standard that is known to be related to the construct of interest. To assess criterion-related validity, researchers may compare the questionnaire scores to scores on a standardized test or other measures of the same construct.
- Face validity : Face validity refers to the extent to which the questionnaire items appear to be relevant and appropriate to the participants. To assess face validity, researchers may ask participants to review the questionnaire and provide feedback on the clarity, relevance, and appropriateness of the items.
- Concurrent validity : Concurrent validity refers to the extent to which the questionnaire items correlate with an external criterion measured at the same time. For example, if a questionnaire is designed to measure depression, researchers may compare the questionnaire scores to scores on a depression scale administered at the same time.
- Predictive validity : Predictive validity refers to the extent to which the questionnaire items predict future behaviour or outcomes related to the construct of interest. For example, if a questionnaire is designed to measure job satisfaction, researchers may use the questionnaire scores to predict future job performance or turnover.
Hence, the most common types of validation of PhD research questionnaires include content validity, construct validity, criterion-related validity, face validity, concurrent validity, and predictive validity.
Principles and methods of PhD research questionnaires
We will divide this blog into two parts, in one part, we will describe the principles of PhD research questionnaires and in the next part, we will describe the methods of PhD research questionnaires. So, let us start the blog with the first part.
Understanding the principles of PhD research questionnaires is important because it enables a researcher to design effective and relevant questionnaires for their research. By following these principles, the researcher can ensure that the questions are clear, relevant, specific, feasible, original, testable, and significant, which will help them to gather accurate and useful data to answer their research questions.
Additionally, understanding the methods of designing and administering research questionnaires will help the researcher to avoid common pitfalls and mistakes in the process, such as asking biased or leading questions, administering the questionnaire to an inappropriate population, or failing to pilot test the questionnaire. Ultimately, a well-designed research questionnaire can be a valuable tool for gathering data in a PhD research project and can contribute to the development of new knowledge in the researcher’s field of study.
When formulating research questions for a PhD project, there are several principles that you should keep in mind:
- Clarity : Your research questions should be clear and concise so that readers can easily understand what you are investigating.
- Relevance : Your research questions should be relevant to your field of study and contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
- Specificity : Your research questions should be specific enough to guide your research and help you to focus on the key issues that you want to explore.
- Feasibility : Your research questions should be feasible to answer given the resources and time available for your PhD project.
- Originality : Your research questions should be original and innovative so that they contribute to the development of new knowledge in your field.
- Testability : Your research questions should be testable through empirical research methods so that you can gather data to support or refute your hypotheses.
- Significance : Your research questions should be significant in terms of their potential impact on your field of study, and should address important research gaps or unanswered questions.
By following these principles, you can develop research questions that will guide your PhD project and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in your field.
Now, it’s time to know the second part of this question which is the methods of PhD research questionnaires. It is the last step for us to craft better questionnaires for PhD research.
Research questionnaires can be a useful tool for gathering data in a PhD research project. When designing a research questionnaire, you should consider the following methods:
- Identify the research questions : The first step is to identify the research questions that you want to answer. Your questionnaire should be designed to collect data that will help you to answer these questions.
- Choose the appropriate type of questions : Decide on the type of questions you will use, such as open-ended or closed-ended questions. Closed-ended questions are usually easier to analyze and quantify, while open-ended questions can provide more in-depth and nuanced responses.
- Determine the format of the questionnaire : The questionnaire can be administered online or in person, and can be structured or unstructured. The format will depend on the nature of your research questions and the target population.
- Develop the questions : Develop clear and concise questions that are easy to understand and answer. Avoid using jargon or technical language that may be unfamiliar to your respondents.
- Pilot tests the questionnaire : Before administering the questionnaire to your target population, conduct a pilot test with a small group of people to identify any potential issues or misunderstandings.
- Administer the questionnaire : Once the questionnaire is finalized, administer it to your target population. You may need to provide instructions or assistance to ensure that respondents understand the questions and how to answer them.
- Analyze the data : After collecting the data, analyze it using statistical or qualitative methods, depending on the nature of the data and research questions.
By using these methods, you can develop an effective research questionnaire that will help you to collect data and answer your research questions.
But wait!!! It’s not over yet. I hope you are a research enthusiast who wants to know more about creating better PhD research questions . Also, if you want us to help you in this matter, you can definitely contact us with the given contact information on the website.
We haven’t answered one question in this blog. Can you guess the question? Then tell us in the comments.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request a Call Back
- Academic Writing
- Avoiding Rejection
- Data Analysis
- Data collection
- Dissertation
- Dissertation Defense Preparation
- Experimental Research
- Limitation and Delimitation
- Literature Review
- Manuscript Publication
- Quantitative Research
- Questionnaires
- Research Design
- Research Methodology
- Research Paper Writing
- Research Proposal
- Research Scholar
- Topic Selection
- Uncategorized
Recent Posts
- A Beginner’s Guide to Top 3 Best PhD Research Topics for 2024-25 thesis , Topic Selection January 16, 2024
- How to Write a Research Proposal and How NOT to in 2024 Research Proposal December 20, 2023
- 5 Unknown Differences Between Limitation and Delimitation Limitation and Delimitation November 21, 2023
- 3 Game-Changing Tips for PhD Thesis Writing in 2023-24 Citation , PhD Research , PhD Thesis November 3, 2023
- What to Do When PhD Dissertation Defense Preparation Derail? Dissertation Defense Preparation September 16, 2023
How to get published in SCI Indexed Journals


How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings
As a staple in data collection, questionnaires help uncover robust and reliable findings that can transform industries, shape policies, and revolutionize understanding. Whether you are exploring societal trends or delving into scientific phenomena, the effectiveness of your research questionnaire can make or break your findings.
In this article, we aim to understand the core purpose of questionnaires, exploring how they serve as essential tools for gathering systematic data, both qualitative and quantitative, from diverse respondents. Read on as we explore the key elements that make up a winning questionnaire, the art of framing questions which are both compelling and rigorous, and the careful balance between simplicity and depth.
Table of Contents
The Role of Questionnaires in Research
So, what is a questionnaire? A questionnaire is a structured set of questions designed to collect information, opinions, attitudes, or behaviors from respondents. It is one of the most commonly used data collection methods in research. Moreover, questionnaires can be used in various research fields, including social sciences, market research, healthcare, education, and psychology. Their adaptability makes them suitable for investigating diverse research questions.
Questionnaire and survey are two terms often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings in the context of research. A survey refers to the broader process of data collection that may involve various methods. A survey can encompass different data collection techniques, such as interviews , focus groups, observations, and yes, questionnaires.
Pros and Cons of Using Questionnaires in Research:
While questionnaires offer numerous advantages in research, they also come with some disadvantages that researchers must be aware of and address appropriately. Careful questionnaire design, validation, and consideration of potential biases can help mitigate these disadvantages and enhance the effectiveness of using questionnaires as a data collection method.

Structured vs Unstructured Questionnaires
Structured questionnaire:.
A structured questionnaire consists of questions with predefined response options. Respondents are presented with a fixed set of choices and are required to select from those options. The questions in a structured questionnaire are designed to elicit specific and quantifiable responses. Structured questionnaires are particularly useful for collecting quantitative data and are often employed in surveys and studies where standardized and comparable data are necessary.
Advantages of Structured Questionnaires:
- Easy to analyze and interpret: The fixed response options facilitate straightforward data analysis and comparison across respondents.
- Efficient for large-scale data collection: Structured questionnaires are time-efficient, allowing researchers to collect data from a large number of respondents.
- Reduces response bias: The predefined response options minimize potential response bias and maintain consistency in data collection.
Limitations of Structured Questionnaires:
- Lack of depth: Structured questionnaires may not capture in-depth insights or nuances as respondents are limited to pre-defined response choices. Hence, they may not reveal the reasons behind respondents’ choices, limiting the understanding of their perspectives.
- Limited flexibility: The fixed response options may not cover all potential responses, therefore, potentially restricting respondents’ answers.
Unstructured Questionnaire:
An unstructured questionnaire consists of questions that allow respondents to provide detailed and unrestricted responses. Unlike structured questionnaires, there are no predefined response options, giving respondents the freedom to express their thoughts in their own words. Furthermore, unstructured questionnaires are valuable for collecting qualitative data and obtaining in-depth insights into respondents’ experiences, opinions, or feelings.
Advantages of Unstructured Questionnaires:
- Rich qualitative data: Unstructured questionnaires yield detailed and comprehensive qualitative data, providing valuable and novel insights into respondents’ perspectives.
- Flexibility in responses: Respondents have the freedom to express themselves in their own words. Hence, allowing for a wide range of responses.
Limitations of Unstructured Questionnaires:
- Time-consuming analysis: Analyzing open-ended responses can be time-consuming, since, each response requires careful reading and interpretation.
- Subjectivity in interpretation: The analysis of open-ended responses may be subjective, as researchers interpret and categorize responses based on their judgment.
- May require smaller sample size: Due to the depth of responses, researchers may need a smaller sample size for comprehensive analysis, making generalizations more challenging.
Types of Questions in a Questionnaire
In a questionnaire, researchers typically use the following most common types of questions to gather a variety of information from respondents:
1. Open-Ended Questions:
These questions allow respondents to provide detailed and unrestricted responses in their own words. Open-ended questions are valuable for gathering qualitative data and in-depth insights.
Example: What suggestions do you have for improving our product?
2. Multiple-Choice Questions
Respondents choose one answer from a list of provided options. This type of question is suitable for gathering categorical data or preferences.
Example: Which of the following social media/academic networking platforms do you use to promote your research?
- ResearchGate
- Academia.edu
3. Dichotomous Questions
Respondents choose between two options, typically “yes” or “no”, “true” or “false”, or “agree” or “disagree”.
Example: Have you ever published in open access journals before?
4. Scaling Questions
These questions, also known as rating scale questions, use a predefined scale that allows respondents to rate or rank their level of agreement, satisfaction, importance, or other subjective assessments. These scales help researchers quantify subjective data and make comparisons across respondents.
There are several types of scaling techniques used in scaling questions:
i. Likert Scale:
The Likert scale is one of the most common scaling techniques. It presents respondents with a series of statements and asks them to rate their level of agreement or disagreement using a range of options, typically from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree”.For example: Please indicate your level of agreement with the statement: “The content presented in the webinar was relevant and aligned with the advertised topic.”
- Strongly Agree
- Strongly Disagree
ii. Semantic Differential Scale:
The semantic differential scale measures respondents’ perceptions or attitudes towards an item using opposite adjectives or bipolar words. Respondents rate the item on a scale between the two opposites. For example:
- Easy —— Difficult
- Satisfied —— Unsatisfied
- Very likely —— Very unlikely
iii. Numerical Rating Scale:
This scale requires respondents to provide a numerical rating on a predefined scale. It can be a simple 1 to 5 or 1 to 10 scale, where higher numbers indicate higher agreement, satisfaction, or importance.
iv. Ranking Questions:
Respondents rank items in order of preference or importance. Ranking questions help identify preferences or priorities.
Example: Please rank the following features of our app in order of importance (1 = Most Important, 5 = Least Important):
- User Interface
- Functionality
- Customer Support
By using a mix of question types, researchers can gather both quantitative and qualitative data, providing a comprehensive understanding of the research topic and enabling meaningful analysis and interpretation of the results. The choice of question types depends on the research objectives , the desired depth of information, and the data analysis requirements.
Methods of Administering Questionnaires
There are several methods for administering questionnaires, and the choice of method depends on factors such as the target population, research objectives , convenience, and resources available. Here are some common methods of administering questionnaires:

Each method has its advantages and limitations. Online surveys offer convenience and a large reach, but they may be limited to individuals with internet access. Face-to-face interviews allow for in-depth responses but can be time-consuming and costly. Telephone surveys have broad reach but may be limited by declining response rates. Researchers should choose the method that best suits their research objectives, target population, and available resources to ensure successful data collection.
How to Design a Questionnaire
Designing a good questionnaire is crucial for gathering accurate and meaningful data that aligns with your research objectives. Here are essential steps and tips to create a well-designed questionnaire:
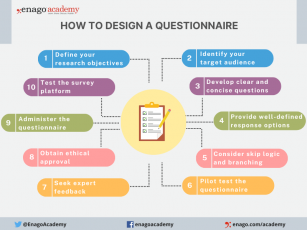
1. Define Your Research Objectives : Clearly outline the purpose and specific information you aim to gather through the questionnaire.
2. Identify Your Target Audience : Understand respondents’ characteristics and tailor the questionnaire accordingly.
3. Develop the Questions :
- Write Clear and Concise Questions
- Avoid Leading or Biasing Questions
- Sequence Questions Logically
- Group Related Questions
- Include Demographic Questions
4. Provide Well-defined Response Options : Offer exhaustive response choices for closed-ended questions.
5. Consider Skip Logic and Branching : Customize the questionnaire based on previous answers.
6. Pilot Test the Questionnaire : Identify and address issues through a pilot study .
7. Seek Expert Feedback : Validate the questionnaire with subject matter experts.
8. Obtain Ethical Approval : Comply with ethical guidelines , obtain consent, and ensure confidentiality before administering the questionnaire.
9. Administer the Questionnaire : Choose the right mode and provide clear instructions.
10. Test the Survey Platform : Ensure compatibility and usability for online surveys.
By following these steps and paying attention to questionnaire design principles, you can create a well-structured and effective questionnaire that gathers reliable data and helps you achieve your research objectives.
Characteristics of a Good Questionnaire
A good questionnaire possesses several essential elements that contribute to its effectiveness. Furthermore, these characteristics ensure that the questionnaire is well-designed, easy to understand, and capable of providing valuable insights. Here are some key characteristics of a good questionnaire:
1. Clarity and Simplicity : Questions should be clear, concise, and unambiguous. Avoid using complex language or technical terms that may confuse respondents. Simple and straightforward questions ensure that respondents interpret them consistently.
2. Relevance and Focus : Each question should directly relate to the research objectives and contribute to answering the research questions. Consequently, avoid including extraneous or irrelevant questions that could lead to data clutter.
3. Mix of Question Types : Utilize a mix of question types, including open-ended, Likert scale, and multiple-choice questions. This variety allows for both qualitative and quantitative data collections .
4. Validity and Reliability : Ensure the questionnaire measures what it intends to measure (validity) and produces consistent results upon repeated administration (reliability). Validation should be conducted through expert review and previous research.
5. Appropriate Length : Keep the questionnaire’s length appropriate and manageable to avoid respondent fatigue or dropouts. Long questionnaires may result in incomplete or rushed responses.
6. Clear Instructions : Include clear instructions at the beginning of the questionnaire to guide respondents on how to complete it. Explain any technical terms, formats, or concepts if necessary.
7. User-Friendly Format : Design the questionnaire to be visually appealing and user-friendly. Use consistent formatting, adequate spacing, and a logical page layout.
8. Data Validation and Cleaning : Incorporate validation checks to ensure data accuracy and reliability. Consider mechanisms to detect and correct inconsistent or missing responses during data cleaning.
By incorporating these characteristics, researchers can create a questionnaire that maximizes data quality, minimizes response bias, and provides valuable insights for their research.
In the pursuit of advancing research and gaining meaningful insights, investing time and effort into designing effective questionnaires is a crucial step. A well-designed questionnaire is more than a mere set of questions; it is a masterpiece of precision and ingenuity. Each question plays a vital role in shaping the narrative of our research, guiding us through the labyrinth of data to meaningful conclusions. Indeed, a well-designed questionnaire serves as a powerful tool for unlocking valuable insights and generating robust findings that impact society positively.
Have you ever designed a research questionnaire? Reflect on your experience and share your insights with researchers globally through Enago Academy’s Open Blogging Platform . Join our diverse community of 1000K+ researchers and authors to exchange ideas, strategies, and best practices, and together, let’s shape the future of data collection and maximize the impact of questionnaires in the ever-evolving landscape of research.
Frequently Asked Questions
A research questionnaire is a structured tool used to gather data from participants in a systematic manner. It consists of a series of carefully crafted questions designed to collect specific information related to a research study.
Questionnaires play a pivotal role in both quantitative and qualitative research, enabling researchers to collect insights, opinions, attitudes, or behaviors from respondents. This aids in hypothesis testing, understanding, and informed decision-making, ensuring consistency, efficiency, and facilitating comparisons.
Questionnaires are a versatile tool employed in various research designs to gather data efficiently and comprehensively. They find extensive use in both quantitative and qualitative research methodologies, making them a fundamental component of research across disciplines. Some research designs that commonly utilize questionnaires include: a) Cross-Sectional Studies b) Longitudinal Studies c) Descriptive Research d) Correlational Studies e) Causal-Comparative Studies f) Experimental Research g) Survey Research h) Case Studies i) Exploratory Research
A survey is a comprehensive data collection method that can include various techniques like interviews and observations. A questionnaire is a specific set of structured questions within a survey designed to gather standardized responses. While a survey is a broader approach, a questionnaire is a focused tool for collecting specific data.
The choice of questionnaire type depends on the research objectives, the type of data required, and the preferences of respondents. Some common types include: • Structured Questionnaires: These questionnaires consist of predefined, closed-ended questions with fixed response options. They are easy to analyze and suitable for quantitative research. • Semi-Structured Questionnaires: These questionnaires combine closed-ended questions with open-ended ones. They offer more flexibility for respondents to provide detailed explanations. • Unstructured Questionnaires: These questionnaires contain open-ended questions only, allowing respondents to express their thoughts and opinions freely. They are commonly used in qualitative research.
Following these steps ensures effective questionnaire administration for reliable data collection: • Choose a Method: Decide on online, face-to-face, mail, or phone administration. • Online Surveys: Use platforms like SurveyMonkey • Pilot Test: Test on a small group before full deployment • Clear Instructions: Provide concise guidelines • Follow-Up: Send reminders if needed
Thank you, Riya. This is quite helpful. As discussed, response bias is one of the disadvantages in the use of questionnaires. One way to help limit this can be to use scenario based questions. These type of questions may help the respondents to be more reflective and active in the process.
Thank you, Dear Riya. This is quite helpful.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Industry News
- Trending Now
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…

Science under Surveillance: Journals adopt advanced AI to uncover image manipulation
Journals are increasingly turning to cutting-edge AI tools to uncover deceitful images published in manuscripts.…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
Imperial College London Imperial College London
Latest news.

New synthesis platform allows for rapid cancer drug synthesis and testing

Imperial celebrates its international scholars and continues to grow programmes

Enterprise Lab and The Greenhouse highly ranked in FT list of top startup hubs
- Research groups
For PhD students - how to formulate a research question
Different students enter the PhD program with different backgrounds. Some students take research-oriented modules (courses in US) at undergraduate level. Some other do a research masters before doing a PhD. However, the kind of research questions we address in a PhD are very new and requires a long period of deeper investigation. Therefore, it is important to know how to find a good question that gets you excited.
Direct encounter : Usually, a good question comes from an experience. In my case, I experienced how hard it is to derive the dynamics of a robot with high degrees of freedom (DoF). I actually tried to manually derive dynamics of a 4-DoF manipulator called Mark-II from Yasakawa Corporation, and then ran a Mathematica program to do a symbolic derivation for a 7-DoF robot manipulator called PA-10. I experienced how long the equations grew and thought how the brain might be dealing with a body of about 37 DoFs for model based predictive control. This direct encounter with the problem is very important, because it gives you a cause to work towards.
Look around : After finding a problem worthy of addressing, look around to see how others have approached to solve it. This is where you will see different schools of thought. Be careful. There are glaring band-waggons out there. It is so tempting to get in one of them. Don’t blindly follow them unless you have a good reason. Usually following is tiring. Think carefully trying out simple derivations and doing simulations or even doing simple physical experiments to see what kind of approaches get you excited. Some approaches appear very exciting, but direct usage will prove to be not so effective. At this point, it is very important to consult your supervisor. The supervisor may have a favorite approach. Most experienced supervisors are open for change and a good reasoned discussion will help you to benefit from their experience to polish up your research question and the method you want to address it. You should always check if there are quantifiable methods to address your research question. For instance, if you want to test whether there is a particular class of mechanisms available to minimise the size of collision force when a robot is dropped from a height, you should think about testing methods, candidate mechanisms, and the range of design paramaters to assess the scope of analysis. Sometimes, your laboratory may not have the full capacity to help you. This is where you can look for collaborations. Try to reach this level of planning logistics within the first 4-6 months in your PhD.
First experiment is important : Once you know your cause for the PhD and once the approach and collaborations are established, break your approach down to smaller steps. Don’t worry too much about how the last experiment will be done. Worry about your first experiment. Distill out a refined research question that needs a novel answer that you can reach in about 6 months. This is important to boost confidence. Temptations will be high to find the ultimate answer to bring your field to a conclusion, but even in that case, it is important to make a first firm step. In this first step, master the tools and techniques involved in your field. In my lab, students take this time to master robot design and fabrication skills, coding skills, data analysis skills, and cool math you can use to solve difficult problems. Develop the habit of reading at least one paper a week that empowers you with powerful tools to solve problems.
Documentation : It is important to develop the habit of keeping things in a well sorted file structure. Open a folder for each project. Have sub-folders for data, reports, codes, papers you read (using a repository like Madeley is also great), designs, and other resources. This is going to save time when you write a paper at some point. Now you have cloud resources like Box and Onedrive. Back up everything securely.
Writing the first paper : If everything works out, after about one year into the PhD, you will have some new results worthy of publishing. Sometimes, the first attempt doesn’t work out. But all failed attempts teach us lessons. Don’t get discouraged if the first experiment doesn’t work out. Develop the resilience to come back with a different approach or to formulate the question in a different way. Then when you write the first paper, you will have comparative results. The importance of reading papers at least one per week is that in 6 months, you would have read at least 25 papers. This is enough to write your first paper. Start writing why the question you addressed is new and important, and back it up with papers you read. Write down your methods very clearly keeping in mind that somebody should be able to read your paper and be able to replicate it for independent verification. Results and interpretations need to be as sharp and consistent as possible. Plan to go through several rounds of revisions with your supervisor and lab mates before any submission deadlines. I ask my PhD students to have the paper in a reasonable level for revision at least one month before the deadline. Have this as a ballpark period for revision in your first paper. This is the time where you develop the skills of articulating a concept clearly, present it to an audience, receive criticisms, and develop good habits of critical reflection.
Completing the cycle : You will of course get review feedback. Some suggestions I have given in this note can be useful to go the rest of the journey. Once you get your first paper published, you will have your next research questions coming up easily. The advantage of taking an approach you are passionate about to serve the cause you selected is that it will naturally line up the next set of questions and methods you should be pursuing. My advise is to go through this full cycle of raising a question to publishing results at least 3 times during your PhD. It will give you a seasoned experience of the art of formulating good research questions.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Perspect Clin Res
- v.14(3); Jul-Sep 2023
- PMC10405529
Designing and validating a research questionnaire - Part 1
Priya ranganathan.
Department of Anaesthesiology, Tata Memorial Centre, Homi Bhabha National Institute, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
Carlo Caduff
1 Department of Global Health and Social Medicine, King’s College London, London, United Kingdom
Questionnaires are often used as part of research studies to collect data from participants. However, the information obtained through a questionnaire is dependent on how it has been designed, used, and validated. In this article, we look at the types of research questionnaires, their applications and limitations, and how a new questionnaire is developed.
INTRODUCTION
In research studies, questionnaires are commonly used as data collection tools, either as the only source of information or in combination with other techniques in mixed-method studies. However, the quality and accuracy of data collected using a questionnaire depend on how it is designed, used, and validated. In this two-part series, we discuss how to design (part 1) and how to use and validate (part 2) a research questionnaire. It is important to emphasize that questionnaires seek to gather information from other people and therefore entail a social relationship between those who are doing the research and those who are being researched. This social relationship comes with an obligation to learn from others , an obligation that goes beyond the purely instrumental rationality of gathering data. In that sense, we underscore that any research method is not simply a tool but a situation, a relationship, a negotiation, and an encounter. This points to both ethical questions (what is the relationship between the researcher and the researched?) and epistemological ones (what are the conditions under which we can know something?).
At the start of any kind of research project, it is crucial to select the right methodological approach. What is the research question, what is the research object, and what can a questionnaire realistically achieve? Not every research question and not every research object are suitable to the questionnaire as a method. Questionnaires can only provide certain kinds of empirical evidence and it is thus important to be aware of the limitations that are inherent in any kind of methodology.
WHAT IS A RESEARCH QUESTIONNAIRE?
A research questionnaire can be defined as a data collection tool consisting of a series of questions or items that are used to collect information from respondents and thus learn about their knowledge, opinions, attitudes, beliefs, and behavior and informed by a positivist philosophy of the natural sciences that consider methods mainly as a set of rules for the production of knowledge; questionnaires are frequently used instrumentally as a standardized and standardizing tool to ask a set of questions to participants. Outside of such a positivist philosophy, questionnaires can be seen as an encounter between the researcher and the researched, where knowledge is not simply gathered but negotiated through a distinct form of communication that is the questionnaire.
STRENGTHS AND LIMITATIONS OF QUESTIONNAIRES
A questionnaire may not always be the most appropriate way of engaging with research participants and generating knowledge that is needed for a research study. Questionnaires have advantages that have made them very popular, especially in quantitative studies driven by a positivist philosophy: they are a low-cost method for the rapid collection of large amounts of data, even from a wide sample. They are practical, can be standardized, and allow comparison between groups and locations. However, it is important to remember that a questionnaire only captures the information that the method itself (as the structured relationship between the researcher and the researched) allows for and that the respondents are willing to provide. For example, a questionnaire on diet captures what the respondents say they eat and not what they are eating. The problem of social desirability emerges precisely because the research process itself involves a social relationship. This means that respondents may often provide socially acceptable and idealized answers, particularly in relation to sensitive questions, for example, alcohol consumption, drug use, and sexual practices. Questionnaires are most useful for studies investigating knowledge, beliefs, values, self-understandings, and self-perceptions that reflect broader social, cultural, and political norms that may well diverge from actual practices.
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONNAIRES
Research questionnaires may be classified in several ways:
Depending on mode of administration
Research questionnaires may be self-administered (by the research participant) or researcher administered. Self-administered (also known as self-reported or self-completed) questionnaires are designed to be completed by respondents without assistance from a researcher. Self-reported questionnaires may be administered to participants directly during hospital or clinic visits, mailed through the post or E-mail, or accessed through websites. This technique allows respondents to answer at their own pace and simplifies research costs and logistics. The anonymity offered by self-reporting may facilitate more accurate answers. However, the disadvantages are that there may be misinterpretations of questions and low response rates. Significantly, relevant context information is missing to make sense of the answers provided. Researcher-reported (or interviewer-reported) questionnaires may be administered face-to-face or through remote techniques such as telephone or videoconference and are associated with higher response rates. They allow the researcher to have a better understanding of how the data are collected and how answers are negotiated, but are more resource intensive and require more training from the researchers.
The choice between self-administered and researcher-administered questionnaires depends on various factors such as the characteristics of the target audience (e.g., literacy and comprehension level and ability to use technology), costs involved, and the need for confidentiality/privacy.
Depending on the format of the questions
Research questionnaires can have structured or semi-structured formats. Semi-structured questionnaires allow respondents to answer more freely and on their terms, with no restrictions on their responses. They allow for unusual or surprising responses and are useful to explore and discover a range of answers to determine common themes. Typically, the analysis of responses to open-ended questions is more complex and requires coding and analysis. In contrast, structured questionnaires provide a predefined set of responses for the participant to choose from. The use of standard items makes the questionnaire easier to complete and allows quick aggregation, quantification, and analysis of the data. However, structured questionnaires can be restrictive if the scope of responses is limited and may miss potential answers. They also may suggest answers that respondents may not have considered before. Respondents may be forced to fit their answers into the predetermined format and may not be able to express personal views and say what they really want to say or think. In general, this type of questionnaire can turn the research process into a mechanical, anonymous survey with little incentive for participants to feel engaged, understood, and taken seriously.
STRUCTURED QUESTIONS: FORMATS
Some examples of close-ended questions include:
e.g., Please indicate your marital status:
- Prefer not to say.
e.g., Describe your areas of work (circle or tick all that apply):
- Clinical service
- Administration
- Strongly agree
- Strongly disagree.
- Numerical scales: Please rate your current pain on a scale of 1–10 where 1 is no pain and 10 is the worst imaginable pain
- Symbolic scales: For example, the Wong-Baker FACES scale to rate pain in older children
- Ranking: Rank the following cities as per the quality of public health care, where 1 is the best and 5 is the worst.
A matrix questionnaire consists of a series of rows with items to be answered with a series of columns providing the same answer options. This is an efficient way of getting the respondent to provide answers to multiple questions. The EORTC QLQ-C30 is an example of a matrix questionnaire.[ 1 ]
For a more detailed review of the types of research questions, readers are referred to a paper by Boynton and Greenhalgh.[ 2 ]
USING PRE-EXISTING QUESTIONNAIRES VERSUS DEVELOPING A NEW QUESTIONNAIRE
Before developing a questionnaire for a research study, a researcher can check whether there are any preexisting-validated questionnaires that might be adapted and used for the study. The use of validated questionnaires saves time and resources needed to design a new questionnaire and allows comparability between studies.
However, certain aspects need to be kept in mind: is the population/context/purpose for which the original questionnaire was designed similar to the new study? Is cross-cultural adaptation required? Are there any permission needed to use the questionnaire? In many situations, the development of a new questionnaire may be more appropriate given that any research project entails both methodological and epistemological questions: what is the object of knowledge and what are the conditions under which it can be known? It is important to understand that the standardizing nature of questionnaires contributes to the standardization of objects of knowledge. Thus, the seeming similarity in the object of study across diverse locations may be an artifact of the method. Whatever method one uses, it will always operate as the ground on which the object of study is known.
DESIGNING A NEW RESEARCH QUESTIONNAIRE
Once the researcher has decided to design a new questionnaire, several steps should be considered:
Gathering content
It creates a conceptual framework to identify all relevant areas for which the questionnaire will be used to collect information. This may require a scoping review of the published literature, appraising other questionnaires on similar topics, or the use of focus groups to identify common themes.
Create a list of questions
Questions need to be carefully formulated with attention to language and wording to avoid ambiguity and misinterpretation. Table 1 lists a few examples of poorlyworded questions that could have been phrased in a more appropriate manner. Other important aspects to be noted are:
Examples of poorly phrased questions in a research questionnaire
- Provide a brief introduction to the research study along with instructions on how to complete the questionnaire
- Allow respondents to indicate levels of intensity in their replies, so that they are not forced into “yes” or “no” answers where intensity of feeling may be more appropriate
- Collect specific and detailed data wherever possible – this can be coded into categories. For example, age can be captured in years and later classified as <18 years, 18–45 years, 46 years, and above. The reverse is not possible
- Avoid technical terms, slang, and abbreviations. Tailor the reading level to the expected education level of respondents
- The format of the questionnaire should be attractive with different sections for various subtopics. The font should be large and easy to read, especially if the questionnaire is targeted at the elderly
- Question sequence: questions should be arranged from general to specific, from easy to difficult, from facts to opinions, and sensitive topics should be introduced later in the questionnaire.[ 3 ] Usually, demographic details are captured initially followed by questions on other aspects
- Use contingency questions: these are questions which need to be answered only by a subgroup of the respondents who provide a particular answer to a previous question. This ensures that participants only respond to relevant sections of the questionnaire, for example, Do you smoke? If yes, then how long have you been smoking? If not, then please go to the next section.
TESTING A QUESTIONNAIRE
A questionnaire needs to be valid and reliable, and therefore, any new questionnaire needs to be pilot tested in a small sample of respondents who are representative of the larger population. In addition to validity and reliability, pilot testing provides information on the time taken to complete the questionnaire and whether any questions are confusing or misleading and need to be rephrased. Validity indicates that the questionnaire measures what it claims to measure – this means taking into consideration the limitations that come with any questionnaire-based study. Reliability means that the questionnaire yields consistent responses when administered repeatedly even by different researchers, and any variations in the results are due to actual differences between participants and not because of problems with the interpretation of the questions or their responses. In the next article in this series, we will discuss methods to determine the reliability and validity of a questionnaire.

Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
- Utility Menu
Harvard University Program on Survey Research
- Questionnaire Design Tip Sheet
This PSR Tip Sheet provides some basic tips about how to write good survey questions and design a good survey questionnaire.
PSR Resources
- Managing and Manipulating Survey Data: A Beginners Guide
- Finding and Hiring Survey Contractors
- How to Frame and Explain the Survey Data Used in a Thesis
- Overview of Cognitive Testing and Questionnaire Evaluation
- Sampling, Coverage, and Nonresponse Tip Sheet
- Introduction to Surveys for Honors Thesis Writers
- PSR Introduction to the Survey Process
- Related Centers/Programs at Harvard
- General Survey Reference
- Institutional Review Boards
- Select Funding Opportunities
- Survey Analysis Software
- Professional Standards
- Professional Organizations
- Major Public Polls
- Survey Data Collections
- Major Longitudinal Surveys
- Other Links

Dissertation Questionnaire

A dissertation is a document usually a requirement for a doctoral degree especially in the field of philosophy. This long essay discusses a particular subject matter uses questionnaires and other sources of data and is used to validate its content. The questionnaire’s importance is evident in the processes of data gathering as it can make the dissertation factual, effective and usable.
Having a well-curated and formatted document to follow when making a dissertation can be very beneficial to an individual who is currently immersed in the data gathering stage of the specific research study. We have gathered downloadable samples and templates of questionnaires so it will be easier for you to curate your own.
Dissertation Timeline Gantt Chart Template

Size: 55 KB
Dissertation Research Gantt Chart Template

Size: 43 KB
Dissertation Project Gantt Chart Template

Size: 41 KB
Dissertation Plan Gantt Chart Template
Size: 51 KB
Dissertation Research Questionnaire

Size: 18 KB
Dissertation Proposal Questionnaire

Size: 131 KB
Sample Dissertation Questionnaire

Size: 10 KB
What Is a Dissertation Questionnaire?
A dissertation questionnaire can be defined as follows:
- It is a document used in the processes of data gathering.
- Questionnaires in PDF used for a dissertation contain questions that can help assess the current condition of the community which is the subject of study within the dissertation.
- It specifies the questions that are needed to be answered to assure that there is a basis in terms of the results that will be presented in a dissertation.
How to Write a Dissertation Questionnaire
Writing an efficient and comprehensive dissertation questionnaire can greatly affect the entire dissertation. You can make one by following these steps:
- Be specific with the kind of dissertation that you are creating and align the purposes of the dissertation questionnaire that you need to make to your study.
- List down the information needed from the community who will provide the answers to your questions.
- Open a software where you can create a questionnaire template. You may also download survey questionnaire examples and templates to have a faster time in formatting the document.
- The purpose of the dissertation questionnaire.
- The guidelines and instructions in answering the dissertation questions.
- The name of the person to who will use the questionnaire results to his/her dissertation.
- The institution to whom the dissertation will be passed.
- List down the questions based on your needs.
Undergraduate Dissertation Questionnaire

Size: 12 KB
Project Management Dissertation

Size: 54 KB
Guidelines for Writing a Dissertation Questionnaire
There are no strict rules in writing a dissertation questionnaire. However, there are some tips that can help you to create a dissertation questionnaire that is relevant to the study that you are currently doing. Some guidelines:
- Make sure that you are well aware of the data that is needed in your dissertation so you can properly curate questions that can supply your information needs.
- It will be best to use a dissertation questionnaire format that is organized, easy to understand, and properly structured. This will help the people who will answer the dissertation questionnaire quickly know how they can provide the items that you would like to know.
- Always make sure that your instructions in answering the questions are precise and directly stated.
- You may look at questionnaires in Word for comparisons. Doing this will help you assess whether there are still areas of improvement that you may tap with the content and format of the dissertation questionnaire that you have created.
Keeping this guidelines in mind and implementing them accordingly will allow you to create a dissertation questionnaire that is beneficial to the processes that you need to have an outstanding dissertation.

Questionnaire Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a fun quiz to find out which historical figure you're most like in your study habits
Design a survey to discover students' favorite school subjects and why they love them.
Masters Compare - Find your perfect masters course.

- Studying a Postgraduate degree
Your postgraduate student guide to using a research questionnaire for your dissertation
Share this article.
- Facebook Sharer
- Twitter Sharer
- LinkedIn Sharer

Explore other topics
- Funding a Postgraduate course
- Living as a Postgraduate student
- Popular masters degree subjects
- Student Wellbeing
- Finding a PhD or Masters Course
Think Postgrad
Frequently asked questions.
There are a few key steps in creating a dissertation for use in your thesis. Firstly, you should think about the topic you are studying and who you need to respond to your questionnaire. You then need to think about how you can deliver the questions, this can be in the form of in-person interviews or emails. You can begin to formulate your questions and format.
Visit the Studying for a PhD section for more information and advice.
Prof Martyn Denscombe, author of “ The Good Research Guide, 6th edition ”, gives expert advice on using a questionnaire survey for your postgraduate dissertation.
Questionnaire surveys are a well-established way of collecting data. They can be used with relatively small-scale research projects, and research questionnaires can be designed and delivered quite quickly and cheaply. It is not surprising, therefore, that when it comes to conducting research for a master’s dissertation, questionnaire surveys feature prominently as the research method of choice.
Occasionally such thesis surveys will be sent out by post, and sometimes the questionnaires will be distributed by hand. But the popularity of questionnaire surveys in the context of master’s dissertations is principally due to the benefits of using online web-based questionnaires. There are two main aspects to this.
First, the software for producing and delivering web questionnaires, with their features such as drop-down menus and tick-box answers, is user-friendly and inexpensive.
Second, online surveys make it possible to contact people across the globe without travelling anywhere which, given the time and resource constraints faced when producing a dissertation, makes online surveys all the more enticing. (And, for the more adventurous students, there are also developing possibilities for the use of social media such as Facebook and SMS texts for contacting people to participate in the survey.)
In the context of a master’s dissertation, however, the quality of the survey data is a vital issue. The grade for the dissertation will depend on being able to defend the use of the data from the survey as the basis for advanced, master’s level academic enquiry. Which means it is not good enough to simply rely on getting 100 or so people to complete your questionnaire. Students are expected to be aware of the pros and cons of questionnaire surveys and to be able to justify the value of the data they have collected in the face of probing questions such as:
- Who are the respondents and how they were selected?
- How representative are the respondents of the whole group being studied?
- What response rate was achieved by the survey?
- Are the questions suitable in relation to the topic and the particular respondents?
- What likelihood is there that respondents gave honest answers to the questions?
This is where The Good Research Guide, 6th edition becomes so valuable.
It not only identifies the key points that need to be addressed in order to conduct a competent questionnaire survey, it gets right to the heart of the matter with plenty of practical guidance on how to deal with the issues. In a straightforward style, using plain language, this bestselling book covers a range of alternative strategies and methods for conducting small-scale social research projects and outlines some of the main ways in which the data can be analysed.
Read Prof Martyn Denscombe’s advice on using a Case Study for your postgraduate dissertation
- Advertisers
- Cookie Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Sorry! You need to sign up
Sign up to Postgraduate Studentships
Sign up to compare masters
Opportunity added!
Thanks for making your selection. Click below to view your list.
Course Added
Thanks for making your selection. Click below to view your comparisons.

Think Postgrad Ltd 2008-2024 Website By Parachute
Research Proposal Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template
If you’re getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.
Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .
How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Dean's Message
- Mission Statement
- Diversity At VUSN
- Our History
- Faculty Fellows & Honors
- Accreditation
- Privacy Policy
- Academic Programs
- Master of Science in Nursing
- Master of Nursing
- Doctor of Nursing Practice
- PhD in Nursing Science
- Post-Master's Certificate
- Postdoctoral Program
- Special (Non-Degree) Students
- Admissions Information
- Admissions Requirements
- MSN Admissions
- MN Admissions
- DNP Admissions
- PhD Admissions
- Post-Master's Certificates
- Postdoctoral Admissions
- Center for Research Development and Scholarship (CRDS)
- Signature Areas
- CRDS Behavorial Labs
- Research Resources
- Faculty Scholarship Program
- Research Faculty
- Preparing For Practice
- Faculty Practice Network
- Credentialing Process
- Faculty Practice History
- Vanderbilt Nurse-Midwifery Faculty Practice
- What is Advanced Practice Nursing?
- Preceptor Resources
- The Vanderbilt Advantage
- Making A Difference
- Informatics
- Global Health
- Organizations
- Veterans/Military
Examples of Research Questions
Phd in nursing science program, examples of broad clinical research questions include:.
- Does the administration of pain medication at time of surgical incision reduce the need for pain medication twenty-four hours after surgery?
- What maternal factors are associated with obesity in toddlers?
- What elements of a peer support intervention prevent suicide in high school females?
- What is the most accurate and comprehensive way to determine men’s experience of physical assault?
- Is yoga as effective as traditional physical therapy in reducing lymphedema in patients who have had head and neck cancer treatment?
- In the third stage of labor, what is the effect of cord cutting within the first three minutes on placenta separation?
- Do teenagers with Type 1 diabetes who receive phone tweet reminders maintain lower blood sugars than those who do not?
- Do the elderly diagnosed with dementia experience pain?
- How can siblings’ risk of depression be predicted after the death of a child?
- How can cachexia be prevented in cancer patients receiving aggressive protocols involving radiation and chemotherapy?
Examples of some general health services research questions are:
- Does the organization of renal transplant nurse coordinators’ responsibilities influence live donor rates?
- What activities of nurse managers are associated with nurse turnover? 30 day readmission rates?
- What effect does the Nurse Faculty Loan program have on the nurse researcher workforce? What effect would a 20% decrease in funds have?
- How do psychiatric hospital unit designs influence the incidence of patients’ aggression?
- What are Native American patient preferences regarding the timing, location and costs for weight management counseling and how will meeting these preferences influence participation?
- What predicts registered nurse retention in the US Army?
- How, if at all, are the timing and location of suicide prevention appointments linked to veterans‘ suicide rates?
- What predicts the sustainability of quality improvement programs in operating rooms?
- Do integrated computerized nursing records across points of care improve patient outcomes?
- How many nurse practitioners will the US need in 2020?
PhD Resources
- REQUEST INFO
- CAREER SERVICES
- PRIVACY POLICY
- VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY
- VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER
DISTINCTIONS

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Survey Research | Definition, Examples & Methods
Survey Research | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on August 20, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Survey research means collecting information about a group of people by asking them questions and analyzing the results. To conduct an effective survey, follow these six steps:
- Determine who will participate in the survey
- Decide the type of survey (mail, online, or in-person)
- Design the survey questions and layout
- Distribute the survey
- Analyze the responses
- Write up the results
Surveys are a flexible method of data collection that can be used in many different types of research .
Table of contents
What are surveys used for, step 1: define the population and sample, step 2: decide on the type of survey, step 3: design the survey questions, step 4: distribute the survey and collect responses, step 5: analyze the survey results, step 6: write up the survey results, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about surveys.
Surveys are used as a method of gathering data in many different fields. They are a good choice when you want to find out about the characteristics, preferences, opinions, or beliefs of a group of people.
Common uses of survey research include:
- Social research : investigating the experiences and characteristics of different social groups
- Market research : finding out what customers think about products, services, and companies
- Health research : collecting data from patients about symptoms and treatments
- Politics : measuring public opinion about parties and policies
- Psychology : researching personality traits, preferences and behaviours
Surveys can be used in both cross-sectional studies , where you collect data just once, and in longitudinal studies , where you survey the same sample several times over an extended period.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Before you start conducting survey research, you should already have a clear research question that defines what you want to find out. Based on this question, you need to determine exactly who you will target to participate in the survey.
Populations
The target population is the specific group of people that you want to find out about. This group can be very broad or relatively narrow. For example:
- The population of Brazil
- US college students
- Second-generation immigrants in the Netherlands
- Customers of a specific company aged 18-24
- British transgender women over the age of 50
Your survey should aim to produce results that can be generalized to the whole population. That means you need to carefully define exactly who you want to draw conclusions about.
Several common research biases can arise if your survey is not generalizable, particularly sampling bias and selection bias . The presence of these biases have serious repercussions for the validity of your results.
It’s rarely possible to survey the entire population of your research – it would be very difficult to get a response from every person in Brazil or every college student in the US. Instead, you will usually survey a sample from the population.
The sample size depends on how big the population is. You can use an online sample calculator to work out how many responses you need.
There are many sampling methods that allow you to generalize to broad populations. In general, though, the sample should aim to be representative of the population as a whole. The larger and more representative your sample, the more valid your conclusions. Again, beware of various types of sampling bias as you design your sample, particularly self-selection bias , nonresponse bias , undercoverage bias , and survivorship bias .
There are two main types of survey:
- A questionnaire , where a list of questions is distributed by mail, online or in person, and respondents fill it out themselves.
- An interview , where the researcher asks a set of questions by phone or in person and records the responses.
Which type you choose depends on the sample size and location, as well as the focus of the research.
Questionnaires
Sending out a paper survey by mail is a common method of gathering demographic information (for example, in a government census of the population).
- You can easily access a large sample.
- You have some control over who is included in the sample (e.g. residents of a specific region).
- The response rate is often low, and at risk for biases like self-selection bias .
Online surveys are a popular choice for students doing dissertation research , due to the low cost and flexibility of this method. There are many online tools available for constructing surveys, such as SurveyMonkey and Google Forms .
- You can quickly access a large sample without constraints on time or location.
- The data is easy to process and analyze.
- The anonymity and accessibility of online surveys mean you have less control over who responds, which can lead to biases like self-selection bias .
If your research focuses on a specific location, you can distribute a written questionnaire to be completed by respondents on the spot. For example, you could approach the customers of a shopping mall or ask all students to complete a questionnaire at the end of a class.
- You can screen respondents to make sure only people in the target population are included in the sample.
- You can collect time- and location-specific data (e.g. the opinions of a store’s weekday customers).
- The sample size will be smaller, so this method is less suitable for collecting data on broad populations and is at risk for sampling bias .
Oral interviews are a useful method for smaller sample sizes. They allow you to gather more in-depth information on people’s opinions and preferences. You can conduct interviews by phone or in person.
- You have personal contact with respondents, so you know exactly who will be included in the sample in advance.
- You can clarify questions and ask for follow-up information when necessary.
- The lack of anonymity may cause respondents to answer less honestly, and there is more risk of researcher bias.
Like questionnaires, interviews can be used to collect quantitative data: the researcher records each response as a category or rating and statistically analyzes the results. But they are more commonly used to collect qualitative data : the interviewees’ full responses are transcribed and analyzed individually to gain a richer understanding of their opinions and feelings.
Next, you need to decide which questions you will ask and how you will ask them. It’s important to consider:
- The type of questions
- The content of the questions
- The phrasing of the questions
- The ordering and layout of the survey
Open-ended vs closed-ended questions
There are two main forms of survey questions: open-ended and closed-ended. Many surveys use a combination of both.
Closed-ended questions give the respondent a predetermined set of answers to choose from. A closed-ended question can include:
- A binary answer (e.g. yes/no or agree/disagree )
- A scale (e.g. a Likert scale with five points ranging from strongly agree to strongly disagree )
- A list of options with a single answer possible (e.g. age categories)
- A list of options with multiple answers possible (e.g. leisure interests)
Closed-ended questions are best for quantitative research . They provide you with numerical data that can be statistically analyzed to find patterns, trends, and correlations .
Open-ended questions are best for qualitative research. This type of question has no predetermined answers to choose from. Instead, the respondent answers in their own words.
Open questions are most common in interviews, but you can also use them in questionnaires. They are often useful as follow-up questions to ask for more detailed explanations of responses to the closed questions.
The content of the survey questions
To ensure the validity and reliability of your results, you need to carefully consider each question in the survey. All questions should be narrowly focused with enough context for the respondent to answer accurately. Avoid questions that are not directly relevant to the survey’s purpose.
When constructing closed-ended questions, ensure that the options cover all possibilities. If you include a list of options that isn’t exhaustive, you can add an “other” field.
Phrasing the survey questions
In terms of language, the survey questions should be as clear and precise as possible. Tailor the questions to your target population, keeping in mind their level of knowledge of the topic. Avoid jargon or industry-specific terminology.
Survey questions are at risk for biases like social desirability bias , the Hawthorne effect , or demand characteristics . It’s critical to use language that respondents will easily understand, and avoid words with vague or ambiguous meanings. Make sure your questions are phrased neutrally, with no indication that you’d prefer a particular answer or emotion.
Ordering the survey questions
The questions should be arranged in a logical order. Start with easy, non-sensitive, closed-ended questions that will encourage the respondent to continue.
If the survey covers several different topics or themes, group together related questions. You can divide a questionnaire into sections to help respondents understand what is being asked in each part.
If a question refers back to or depends on the answer to a previous question, they should be placed directly next to one another.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Before you start, create a clear plan for where, when, how, and with whom you will conduct the survey. Determine in advance how many responses you require and how you will gain access to the sample.
When you are satisfied that you have created a strong research design suitable for answering your research questions, you can conduct the survey through your method of choice – by mail, online, or in person.
There are many methods of analyzing the results of your survey. First you have to process the data, usually with the help of a computer program to sort all the responses. You should also clean the data by removing incomplete or incorrectly completed responses.
If you asked open-ended questions, you will have to code the responses by assigning labels to each response and organizing them into categories or themes. You can also use more qualitative methods, such as thematic analysis , which is especially suitable for analyzing interviews.
Statistical analysis is usually conducted using programs like SPSS or Stata. The same set of survey data can be subject to many analyses.
Finally, when you have collected and analyzed all the necessary data, you will write it up as part of your thesis, dissertation , or research paper .
In the methodology section, you describe exactly how you conducted the survey. You should explain the types of questions you used, the sampling method, when and where the survey took place, and the response rate. You can include the full questionnaire as an appendix and refer to it in the text if relevant.
Then introduce the analysis by describing how you prepared the data and the statistical methods you used to analyze it. In the results section, you summarize the key results from your analysis.
In the discussion and conclusion , you give your explanations and interpretations of these results, answer your research question, and reflect on the implications and limitations of the research.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Student’s t -distribution
- Normal distribution
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Data cleansing
- Reproducibility vs Replicability
- Peer review
- Prospective cohort study
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Placebo effect
- Hawthorne effect
- Hindsight bias
- Affect heuristic
- Social desirability bias
A questionnaire is a data collection tool or instrument, while a survey is an overarching research method that involves collecting and analyzing data from people using questionnaires.
A Likert scale is a rating scale that quantitatively assesses opinions, attitudes, or behaviors. It is made up of 4 or more questions that measure a single attitude or trait when response scores are combined.
To use a Likert scale in a survey , you present participants with Likert-type questions or statements, and a continuum of items, usually with 5 or 7 possible responses, to capture their degree of agreement.
Individual Likert-type questions are generally considered ordinal data , because the items have clear rank order, but don’t have an even distribution.
Overall Likert scale scores are sometimes treated as interval data. These scores are considered to have directionality and even spacing between them.
The type of data determines what statistical tests you should use to analyze your data.
The priorities of a research design can vary depending on the field, but you usually have to specify:
- Your research questions and/or hypotheses
- Your overall approach (e.g., qualitative or quantitative )
- The type of design you’re using (e.g., a survey , experiment , or case study )
- Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects
- Your data collection methods (e.g., questionnaires , observations)
- Your data collection procedures (e.g., operationalization , timing and data management)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical tests or thematic analysis )
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, June 22). Survey Research | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved March 30, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/survey-research/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, questionnaire design | methods, question types & examples, what is a likert scale | guide & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Develop a Questionnaire for Research
Last Updated: December 4, 2022 Fact Checked
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 24 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time. There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 586,513 times. Learn more...
A questionnaire is a technique for collecting data in which a respondent provides answers to a series of questions. [1] X Research source To develop a questionnaire that will collect the data you want takes effort and time. However, by taking a step-by-step approach to questionnaire development, you can come up with an effective means to collect data that will answer your unique research question.
Designing Your Questionnaire

- Come up with a research question. It can be one question or several, but this should be the focal point of your questionnaire.
- Develop one or several hypotheses that you want to test. The questions that you include on your questionnaire should be aimed at systematically testing these hypotheses.

- Dichotomous question: this is a question that will generally be a “yes/no” question, but may also be an “agree/disagree” question. It is the quickest and simplest question to analyze, but is not a highly sensitive measure.
- Open-ended questions: these questions allow the respondent to respond in their own words. They can be useful for gaining insight into the feelings of the respondent, but can be a challenge when it comes to analysis of data. It is recommended to use open-ended questions to address the issue of “why.” [2] X Research source
- Multiple choice questions: these questions consist of three or more mutually-exclusive categories and ask for a single answer or several answers. [3] X Research source Multiple choice questions allow for easy analysis of results, but may not give the respondent the answer they want.
- Rank-order (or ordinal) scale questions: this type of question asks your respondent to rank items or choose items in a particular order from a set. For example, it might ask your respondents to order five things from least to most important. These types of questions forces discrimination among alternatives, but does not address the issue of why the respondent made these discriminations. [4] X Research source
- Rating scale questions: these questions allow the respondent to assess a particular issue based on a given dimension. You can provide a scale that gives an equal number of positive and negative choices, for example, ranging from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree.” [5] X Research source These questions are very flexible, but also do not answer the question “why.”

- Write questions that are succinct and simple. You should not be writing complex statements or using technical jargon, as it will only confuse your respondents and lead to incorrect responses.
- Ask only one question at a time. This will help avoid confusion
- Asking questions such as these usually require you to anonymize or encrypt the demographic data you collect.
- Determine if you will include an answer such as “I don’t know” or “Not applicable to me.” While these can give your respondents a way of not answering certain questions, providing these options can also lead to missing data, which can be problematic during data analysis.
- Put the most important questions at the beginning of your questionnaire. [7] X Research source This can help you gather important data even if you sense that your respondents may be becoming distracted by the end of the questionnaire.

- Only include questions that are directly useful to your research question. [9] X Trustworthy Source Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations Specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for leading international efforts to end world hunger and improve nutrition Go to source A questionnaire is not an opportunity to collect all kinds of information about your respondents.
- Avoid asking redundant questions. This will frustrate those who are taking your questionnaire.

- Consider if you want your questionnaire to collect information from both men and women. Some studies will only survey one sex.
- Consider including a range of ages in your target demographic. For example, you can consider young adult to be 18-29 years old, adults to be 30-54 years old, and mature adults to be 55+. Providing the an age range will help you get more respondents than limiting yourself to a specific age.
- Consider what else would make a person a target for your questionnaire. Do they need to drive a car? Do they need to have health insurance? Do they need to have a child under 3? Make sure you are very clear about this before you distribute your questionnaire.

- Consider an anonymous questionnaire. You may not want to ask for names on your questionnaire. This is one step you can take to prevent privacy, however it is often possible to figure out a respondent’s identity using other demographic information (such as age, physical features, or zipcode).
- Consider de-identifying the identity of your respondents. Give each questionnaire (and thus, each respondent) a unique number or word, and only refer to them using that new identifier. Shred any personal information that can be used to determine identity.
- Remember that you do not need to collect much demographic information to be able to identify someone. People may be wary to provide this information, so you may get more respondents by asking less demographic questions (if it is possible for your questionnaire).
- Make sure you destroy all identifying information after your study is complete.
Writing your questionnaire

- My name is Jack Smith and I am one of the creators of this questionnaire. I am part of the Department of Psychology at the University of Michigan, where I am focusing in developing cognition in infants.
- I’m Kelly Smith, a 3rd year undergraduate student at the University of New Mexico. This questionnaire is part of my final exam in statistics.
- My name is Steve Johnson, and I’m a marketing analyst for The Best Company. I’ve been working on questionnaire development to determine attitudes surrounding drug use in Canada for several years.

- I am collecting data regarding the attitudes surrounding gun control. This information is being collected for my Anthropology 101 class at the University of Maryland.
- This questionnaire will ask you 15 questions about your eating and exercise habits. We are attempting to make a correlation between healthy eating, frequency of exercise, and incidence of cancer in mature adults.
- This questionnaire will ask you about your recent experiences with international air travel. There will be three sections of questions that will ask you to recount your recent trips and your feelings surrounding these trips, as well as your travel plans for the future. We are looking to understand how a person’s feelings surrounding air travel impact their future plans.

- Beware that if you are collecting information for a university or for publication, you may need to check in with your institution’s Institutional Review Board (IRB) for permission before beginning. Most research universities have a dedicated IRB staff, and their information can usually be found on the school’s website.
- Remember that transparency is best. It is important to be honest about what will happen with the data you collect.
- Include an informed consent for if necessary. Note that you cannot guarantee confidentiality, but you will make all reasonable attempts to ensure that you protect their information. [12] X Research source

- Time yourself taking the survey. Then consider that it will take some people longer than you, and some people less time than you.
- Provide a time range instead of a specific time. For example, it’s better to say that a survey will take between 15 and 30 minutes than to say it will take 15 minutes and have some respondents quit halfway through.
- Use this as a reason to keep your survey concise! You will feel much better asking people to take a 20 minute survey than you will asking them to take a 3 hour one.

- Incentives can attract the wrong kind of respondent. You don’t want to incorporate responses from people who rush through your questionnaire just to get the reward at the end. This is a danger of offering an incentive. [13] X Research source
- Incentives can encourage people to respond to your survey who might not have responded without a reward. This is a situation in which incentives can help you reach your target number of respondents. [14] X Research source
- Consider the strategy used by SurveyMonkey. Instead of directly paying respondents to take their surveys, they offer 50 cents to the charity of their choice when a respondent fills out a survey. They feel that this lessens the chances that a respondent will fill out a questionnaire out of pure self-interest. [15] X Research source
- Consider entering each respondent in to a drawing for a prize if they complete the questionnaire. You can offer a 25$ gift card to a restaurant, or a new iPod, or a ticket to a movie. This makes it less tempting just to respond to your questionnaire for the incentive alone, but still offers the chance of a pleasant reward.

- Always proof read. Check for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors.
- Include a title. This is a good way for your respondents to understand the focus of the survey as quickly as possible.
- Thank your respondents. Thank them for taking the time and effort to complete your survey.
Distributing Your Questionnaire

- Was the questionnaire easy to understand? Were there any questions that confused you?
- Was the questionnaire easy to access? (Especially important if your questionnaire is online).
- Do you feel the questionnaire was worth your time?
- Were you comfortable answering the questions asked?
- Are there any improvements you would make to the questionnaire?

- Use an online site, such as SurveyMonkey.com. This site allows you to write your own questionnaire with their survey builder, and provides additional options such as the option to buy a target audience and use their analytics to analyze your data. [19] X Research source
- Consider using the mail. If you mail your survey, always make sure you include a self-addressed stamped envelope so that the respondent can easily mail their responses back. Make sure that your questionnaire will fit inside a standard business envelope.
- Conduct face-to-face interviews. This can be a good way to ensure that you are reaching your target demographic and can reduce missing information in your questionnaires, as it is more difficult for a respondent to avoid answering a question when you ask it directly.
- Try using the telephone. While this can be a more time-effective way to collect your data, it can be difficult to get people to respond to telephone questionnaires.

- Make your deadline reasonable. Giving respondents up to 2 weeks to answer should be more than sufficient. Anything longer and you risk your respondents forgetting about your questionnaire.
- Consider providing a reminder. A week before the deadline is a good time to provide a gentle reminder about returning the questionnaire. Include a replacement of the questionnaire in case it has been misplaced by your respondent. [20] X Research source
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.questionpro.com/blog/what-is-a-questionnaire/
- ↑ https://www.hotjar.com/blog/open-ended-questions/
- ↑ https://www.questionpro.com/a/showArticle.do?articleID=survey-questions
- ↑ https://surveysparrow.com/blog/ranking-questions-examples/
- ↑ https://www.lumoa.me/blog/rating-scale/
- ↑ http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project_ideas/Soc_survey.shtml
- ↑ http://www.monash.edu.au/lls/hdr/design/2.4.3.html
- ↑ http://www.fao.org/docrep/W3241E/w3241e05.htm
- ↑ http://managementhelp.org/businessresearch/questionaires.htm
- ↑ https://www.surveymonkey.com/mp/survey-rewards/
- ↑ http://www.ideafit.com/fitness-library/how-to-develop-a-questionnaire
- ↑ https://www.surveymonkey.com/mp/take-a-tour/?ut_source=header
About This Article
To develop a questionnaire for research, identify the main objective of your research to act as the focal point for the questionnaire. Then, choose the type of questions that you want to include, and come up with succinct, straightforward questions to gather the information that you need to answer your questions. Keep your questionnaire as short as possible, and identify a target demographic who you would like to answer the questions. Remember to make the questionnaires as anonymous as possible to protect the integrity of the person answering the questions! For tips on writing out your questions and distributing the questionnaire, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Abdul Bari Khan
Nov 11, 2020
Did this article help you?

Jul 25, 2023
Iman Ilhusadi
Nov 26, 2016
Jaydeepa Das
Aug 21, 2018
Atefeh Abdollahi
Jan 3, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 12 March 2024
Bring PhD assessment into the twenty-first century
You have full access to this article via your institution.

Innovation in PhD education has not reached how doctoral degrees are assessed. Credit: Dan Dunkley/Science Photo Library
Research and teaching in today’s universities are unrecognizable compared with what they were in the early nineteenth century, when Germany and later France gave the world the modern research doctorate. And yet significant aspects of the process of acquiring and assessing a doctorate have remained remarkably constant. A minimum of three years of independent study mentored by a single individual culminates in the production of the doctoral thesis — often a magisterial, book-length piece of work that is assessed in an oral examination by a few senior academic researchers. In an age in which there is much research-informed innovation in teaching and learning, the assessment of the doctoral thesis represents a curious throwback that is seemingly impervious to meaningful reform.
But reform is needed. Some doctoral candidates perceive the current assessment system to lack transparency, and examiners report concerns of falling standards ( G. Houston A Study of the PhD Examination: Process, Attributes and Outcomes . PhD thesis, Oxford Univ.; 2018 ). Making the qualification more structured would help — and, equally importantly, would bring the assessment of PhD education in line with education across the board. PhD candidates with experience of modern assessment methods will become better researchers, wherever they work. Indeed, most will not be working in universities: the majority of PhD holders find employment outside academia.

Collection: Career resources for PhD students
It’s not that PhD training is completely stuck in the nineteenth century. Today’s doctoral candidates can choose from a range of pathways. Professional doctorates, often used in engineering, are jointly supervised by an employer and an academic, and are aimed at solving industry-based problems. Another innovation is PhD by publication, in which, instead of a final thesis on one or more research questions, the criterion for an award is a minimum number of papers published or accepted for publication. In some countries, doctoral students are increasingly being trained in cohorts, with the aim of providing a less isolating experience than that offered by the conventional supervisor–student relationship. PhD candidates are also encouraged to acquire transferable skills — for example, in data analysis, public engagement, project management or business, economics and finance. The value of such training would be even greater if these skills were to be formally assessed alongside a dissertation rather than seen as optional.
And yet, most PhDs are still assessed after the production of a final dissertation, according to a format that, at its core, has not changed for at least half a century, as speakers and delegates noted at an event in London last month on PhD assessment, organized by the Society for Research in Higher Educatio n. Innovations in assessment that are common at other levels of education are struggling to find their way into the conventional doctoral programme.
Take the concept of learning objectives. Intended to aid consistency, fairness and transparency, learning objectives are a summary of what a student is expected to know and how they will be assessed, and are given at the start of a course of study. Part of the ambition is also to help tutors to keep track of their students’ learning and take remedial action before it is too late.

PhD training is no longer fit for purpose — it needs reform now
Formative assessment is another practice that has yet to find its way into PhD assessment consistently. Here, a tutor evaluates a student’s progress at the mid-point of a course and gives feedback or guidance on what students need to do to improve ahead of their final, or summative, assessment. It is not that these methods are absent from modern PhDs; a conscientious supervisor will not leave candidates to sink or swim until the last day. But at many institutions, such approaches are not required of PhD supervisors.
Part of the difficulty is that PhD training is carried out in research departments by people who do not need to have teaching qualifications or awareness of innovations based on education research. Supervisors shouldn’t just be experts in their field, they should also know how best to convey that subject knowledge — along with knowledge of research methods — to their students.
It is probably not possible for universities to require all doctoral supervisors to have teaching qualifications. But there are smaller changes that can be made. At a minimum, doctoral supervisors should take the time to engage with the research that exists in the field of PhD education, and how it can apply to their interactions with students.
There can be no one-size-fits-all solution to improving how a PhD is assessed, because different subjects often have bespoke needs and practices ( P. Denicolo Qual. Assur. Educ. 11 , 84–91; 2003 ). But supervisors and representatives of individual subject communities must continue to discuss what is most appropriate for their disciplines.
All things considered, there is benefit to adopting a more structured approach to PhD assessment. It is high time that PhD education caught up with changes that are now mainstream at most other levels of education. That must start with a closer partnership between education researchers, PhD supervisors and organizers of doctoral-training programmes in universities. This partnership will benefit everyone — PhD supervisors and doctoral students coming into the research workforce, whether in universities or elsewhere.
Education and training in research has entered many secondary schools, along with undergraduate teaching, which is a good thing. In the spirit of mutual learning, research doctoral supervisors, too, will benefit by going back to school.
Nature 627 , 244 (2024)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-00718-0
Reprints and permissions
Related Articles

- Scientific community

How scientists are making the most of Reddit
Career Feature 01 APR 24

Overcoming low vision to prove my abilities under pressure
Career Q&A 28 MAR 24

How a spreadsheet helped me to land my dream job
Career Column 28 MAR 24
Cuts to postgraduate funding threaten Brazilian science — again
Correspondence 26 MAR 24
Don’t underestimate the rising threat of groundwater to coastal cities

‘Exhausted and insulted’: how harsh visa-application policies are hobbling global research
World View 26 MAR 24
Supervisory Bioinformatics Specialist, CTG Program Head
National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Library of Medicine (NLM) National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Information Engineering...
Washington D.C. (US)
National Library of Medicine, National Center for Biotechnology Information
Postdoc Research Associates in Single Cell Multi-Omics Analysis and Molecular Biology
The Cao Lab at UT Dallas is seeking for two highly motivated postdocs in Single Cell Multi-Omics Analysis and Molecular Biology to join us.
Dallas, Texas (US)
the Department of Bioengineering, UT Dallas
Expression of Interest – Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions – Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024 (MSCA-PF)
Academic institutions in Brittany are looking for excellent postdoctoral researchers willing to apply for a Marie S. Curie Postdoctoral Fellowship.
France (FR)
Plateforme projets européens (2PE) -Bretagne
Tenure-track Assistant Professor in Ecological and Evolutionary Modeling
Tenure-track Assistant Professor in Ecosystem Ecology linked to IceLab’s Center for modeling adaptive mechanisms in living systems under stress
Umeå, Sweden
Umeå University
Faculty Positions in Westlake University
Founded in 2018, Westlake University is a new type of non-profit research-oriented university in Hangzhou, China, supported by public a...
Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Westlake University
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To the institutional coordinator: This questionnaire is intended to collect data about university-provided resources that are available to all doctoral programs. Typically, the ideal respondent will be in the university's office of institutional research. Most of the questions apply to all programs. One, on laboratory space, applies only to the ...
118 Questionnaire for Admitted-to-Candidacy Doctoral Students This questionnaire is part of the National Research Council's Pilot Test of the Assessment of Research Doctoral Programs. Your university has volunteered to participate in this pilot test to assist the National Research Council's study of the methodology used to assess doctoral programs.
1. Type of Questionnaires. 2. Type of questions. 3. Sections. The questionnaire must be in line with the objectives of research. Each question mentioned must refer to some objective. It should only contain relevant questions which must not hurt the sentiments of the target respondents in any way to avoid bias.
Crafting effective questionnaires is crucial for PhD research for several reasons: Obtaining reliable and valid data: Effective questionnaires ensure that the data collected is reliable and valid, which is essential for making accurate conclusions and recommendations based on the research findings. Enhancing the credibility of the research: If ...
Questionnaires vs. surveys. A survey is a research method where you collect and analyze data from a group of people. A questionnaire is a specific tool or instrument for collecting the data.. Designing a questionnaire means creating valid and reliable questions that address your research objectives, placing them in a useful order, and selecting an appropriate method for administration.
A questionnaire is an important instrument in a research study to help the researcher collect relevant data regarding the research topic. It is significant to ensure that the design of the ...
Research Aims: Examples. True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording "this research aims to…", "this research seeks to…", and so on. For example: "This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.". "This study sets out to assess the interaction between student ...
10. Test the Survey Platform: Ensure compatibility and usability for online surveys. By following these steps and paying attention to questionnaire design principles, you can create a well-structured and effective questionnaire that gathers reliable data and helps you achieve your research objectives.
Designing a Questionnaire for a Research Paper: A Comprehensive Guide to Design and Develop an Effective Questionnaire . Hamed Taherdoost . University Canada West, Vancouver, Canada . E-mail: [email protected] . Abstract - A questionnaire is an important instrument in a research study to help the researcher collect relevant data
Work on developing different section for the questionnaire then in each section you can frame the related question. Try to add different types of questions such as rating scale, multiple choices ...
Different students enter the PhD program with different backgrounds. Some students take research-oriented modules (courses in US) at undergraduate level. Some other do a research masters before doing a PhD. However, the kind of research questions we address in a PhD are very new and requires a long period of deeper investigation.
However, the quality and accuracy of data collected using a questionnaire depend on how it is designed, used, and validated. In this two-part series, we discuss how to design (part 1) and how to use and validate (part 2) a research questionnaire. It is important to emphasize that questionnaires seek to gather information from other people and ...
Guides to Survey Research. Managing and Manipulating Survey Data: A Beginners Guide; Finding and Hiring Survey Contractors; How to Frame and Explain the Survey Data Used in a Thesis; Overview of Cognitive Testing and Questionnaire Evaluation; Questionnaire Design Tip Sheet; Sampling, Coverage, and Nonresponse Tip Sheet; PSR Survey Toolbox
Dissertation Questionnaire. A dissertation is a document usually a requirement for a doctoral degree especially in the field of philosophy. This long essay discusses a particular subject matter uses questionnaires and other sources of data and is used to validate its content. The questionnaire's importance is evident in the processes of data gathering as it can make the dissertation factual ...
The design and use of questionnaires are important aspects of. educational research (Newby, 2013, Cohen et al., 2017). By. following key considerations about the design and. operationalization of ...
Model Exams and Sample Exam Questions: PhD Qualifying Examinations . 1 This Guide In this guide, there are a number of models of different qualifying exams and samples of some more questions from the different areas of specialization. This is meant as a reference for some of the different ways the ... Research/Methodology, (2) Ethics, (3)
Prof Martyn Denscombe, author of "The Good Research Guide, 6th edition", gives expert advice on using a questionnaire survey for your postgraduate dissertation. Questionnaire surveys are a well-established way of collecting data. They can be used with relatively small-scale research projects, and research questionnaires can be designed and delivered quite quickly and cheaply.
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level project, and one for a PhD-level ...
Examples of some general health services research questions are: Does the organization of renal transplant nurse coordinators' responsibilities influence live donor rates? What activities of nurse managers are associated with nurse turnover? 30 day readmission rates? What effect does the Nurse Faculty Loan program have on the nurse researcher ...
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
Survey research means collecting information about a group of people by asking them questions and analyzing the results. To conduct an effective survey, follow these six steps: Determine who will participate in the survey. Decide the type of survey (mail, online, or in-person) Design the survey questions and layout.
Come up with a research question. It can be one question or several, but this should be the focal point of your questionnaire. Develop one or several hypotheses that you want to test. The questions that you include on your questionnaire should be aimed at systematically testing these hypotheses. 2.
November 2013. Kevin Daniel André Carillo. Download. PDF | On Nov 12, 2013, Kevin Daniel André Carillo published PhD - Final survey questionnaire | Find, read and cite all the research you need ...
Another innovation is PhD by publication, in which, instead of a final thesis on one or more research questions, the criterion for an award is a minimum number of papers published or accepted for ...